59 Great and Popular Scientists
Since ancient times, we have heard the mention of scholars in the fields of art, literature etc. With the passage of time, man changed his imagination and curiosity into reality in other areas as well. In the modern era, science has been considered as the basis of development, so we should keep this in mind and remember those scientists who made such important discoveries.
Many geniuses, innovators, and scientists have walked on this earth. Inventions by them changed the world in a big way. Their contributions to the field of science are immense. Most of these scientists are well-known all over the world. The many years of great hard work that these scientists have put in is simply incredible. Here’s the list of great and popular non-Indian scientists. The development of scientific thought in the modern world can be attributed to these great minds. They brought about an unparalleled change in global scientific thought. Their creativity and mental aptitude essentially shaped the way we live now. Their work is still used by universities and research scholars giving way to modern scientific thinking. The amazing works of these scientists are reflected even today in fields like nuclear science, biotechnology, biological science, digital media, energy, cloud computing, and even Artificial Intelligence. Their thoughts still have the power to almost entirely reshape the way we live. Come, in this list of today, we look at the great scientists around the world whose discoveries brought humanity and science to new peaks –
Note: Indian Scientists are not added to this list. We have made a separate list for them. You can see here: Modern Indian Scientists | Ancient Indian Scientists
Thomas Edison
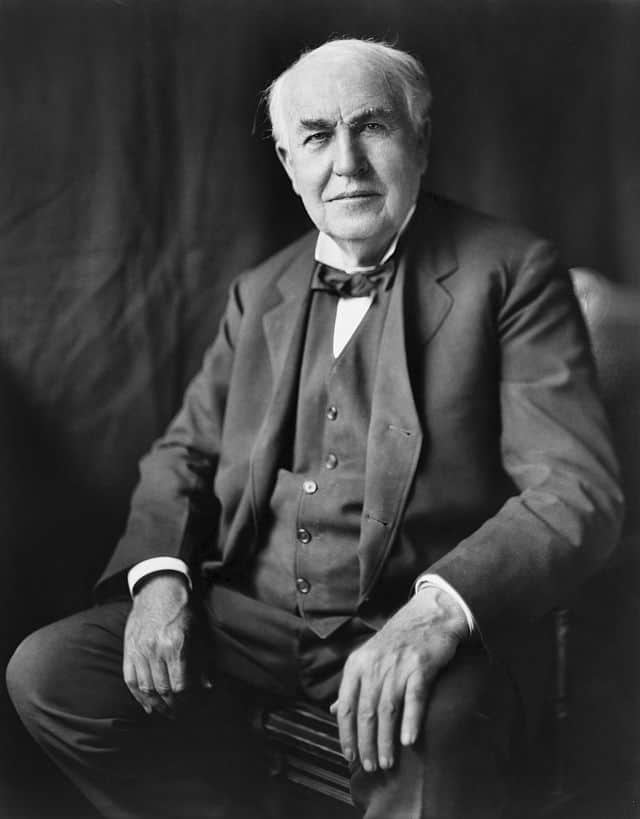

Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847 – October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman who has been described as America’s greatest inventor. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, which include the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and early versions of the electric light bulb, have had a widespread impact on the modern industrialized world. He was one of the first inventors to apply the principles of organized science and teamwork to the process of invention, working with many researchers and employees. He established the first industrial research laboratory.Edison was raised in the American Midwest; early in his career he worked as a telegraph operator, which inspired some of his earliest inventions. In 1876, he established his first laboratory facility in Menlo Park, New Jersey, where many of his early inventions were developed. He later established a botanic laboratory in Fort Myers, Florida in collaboration with businessmen Henry Ford and Harvey S. Firestone, and a laboratory in West Orange, New Jersey that featured the world’s first film studio, the Black Maria. He was a prolific inventor, holding 1,093 US patents in his name, as well as patents in other countries. Edison married twice and fathered six children. He died in 1931 of complications of diabetes.
Read More About Thomas Edison / Source
Albert Einstein
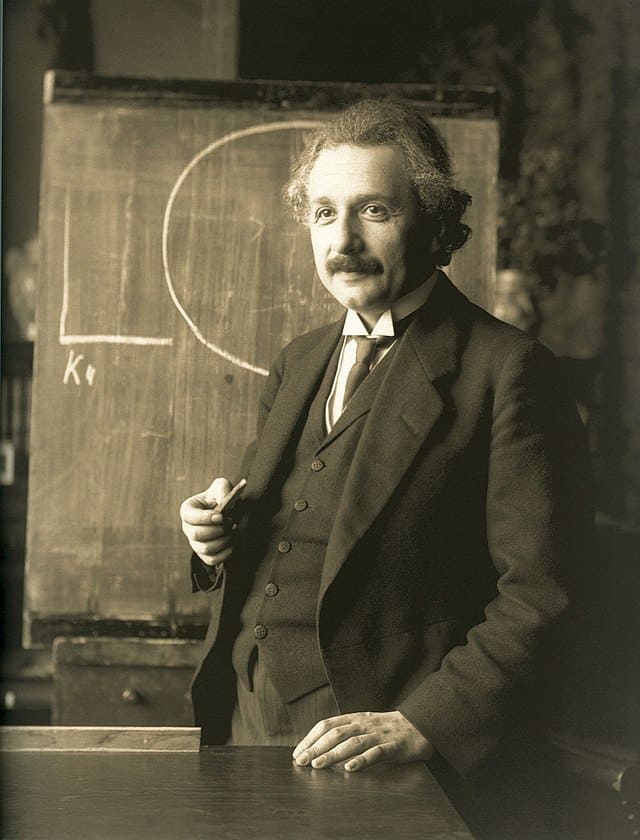
Albert Einstein (14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics). His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He is best known to the general public for his mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which has been dubbed “the world’s most famous equation”. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics “for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect”, a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory.
The son of a salesman who later operated an electrochemical factory, Einstein was born in the German Empire, but moved to Switzerland in 1895, forsaking his German citizenship the following year. Specializing in physics and mathematics, he received his academic teaching diploma from the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zürich in 1900. The following year, he acquired Swiss citizenship, which he kept for his entire life. After initially struggling to find work, from 1902 to 1909 he was employed as a patent examiner at the Swiss Patent Office in Bern.
Near the beginning of his career, Einstein thought that the laws of classical mechanics could no longer be reconciled with those of the electromagnetic field. This led him to develop his special theory of relativity during his time as a patent clerk. In 1905, called his annus mirabilis (‘miracle year’), he published four groundbreaking papers which attracted the attention of the academic world; the first paper outlined the theory of the photoelectric effect, the second explained Brownian motion, the third introduced special relativity, and the fourth mass–energy equivalence. That year, at the age of 26, he was awarded a PhD by the University of Zurich.
Although initially treated with skepticism from many in the scientific community, Einstein’s works gradually came to be recognised as significant advancements. He was invited to teach theoretical physics at the University of Bern in 1908 and the following year moved to the University of Zurich, then in 1911 to Charles University in Prague before returning to ETH (the newly renamed Federal Polytechnic School) in Zürich in 1912. In 1914, he was elected to the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin, where he remained for 19 years. Soon after publishing his work on special relativity, Einstein began working to extend the theory to gravitational fields; he then published a paper on general relativity in 1916, introducing his theory of gravitation. He continued to deal with problems of statistical mechanics and quantum theory, which led to his explanations of particle theory and the motion of molecules. He also investigated the thermal properties of light and the quantum theory of radiation, the basis of the laser, which laid the foundation of the photon theory of light. In 1917, he applied the general theory of relativity to model the structure of the universe.In 1933, while Einstein was visiting the United States, Adolf Hitler came to power. Because of his Jewish background, Einstein did not return to Germany. He settled in the United States and became an American citizen in 1940. On the eve of World War II, he endorsed a letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt alerting him to the potential German nuclear weapons program and recommending that the US begin similar research. Einstein supported the Allies, but generally denounced the idea of nuclear weapons.
Einstein was affiliated with the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, until his death in 1955. He published more than 300 scientific papers and more than 150 non-scientific works. His intellectual achievements and originality have made the word “Einstein” synonymous with “genius”. Eugene Wigner compared him to his contemporaries, writing that “Einstein’s understanding was deeper even than Jancsi von Neumann’s. His mind was both more penetrating and more original than von Neumann’s.”
Read More About Albert Einstein / Source
Nikola Tesla
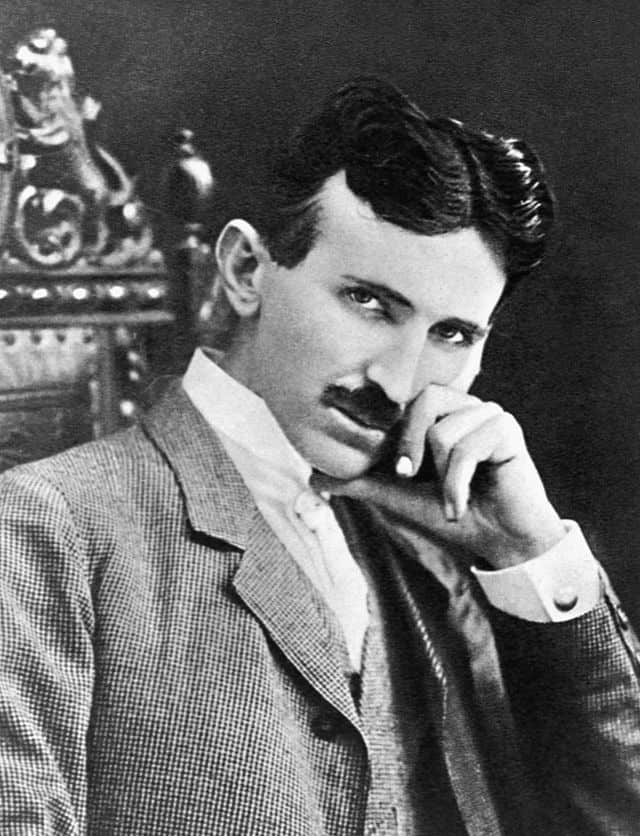

Nikola Tesla (10 July 1856 – 7 January 1943) was a Serbian-American inventor, electrical engineer, mechanical engineer, and futurist best known for his contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.Born and raised in the Austrian Empire, Tesla studied engineering and physics in the 1870s without receiving a degree, gaining practical experience in the early 1880s working in telephony and at Continental Edison in the new electric power industry. In 1884 he emigrated to the United States, where he became a naturalized citizen. He worked for a short time at the Edison Machine Works in New York City before he struck out on his own. With the help of partners to finance and market his ideas, Tesla set up laboratories and companies in New York to develop a range of electrical and mechanical devices. His alternating current (AC) induction motor and related polyphase AC patents, licensed by Westinghouse Electric in 1888, earned him a considerable amount of money and became the cornerstone of the polyphase system which that company eventually marketed.
Attempting to develop inventions he could patent and market, Tesla conducted a range of experiments with mechanical oscillators/generators, electrical discharge tubes, and early X-ray imaging. He also built a wireless-controlled boat, one of the first-ever exhibited. Tesla became well known as an inventor and demonstrated his achievements to celebrities and wealthy patrons at his lab, and was noted for his showmanship at public lectures. Throughout the 1890s, Tesla pursued his ideas for wireless lighting and worldwide wireless electric power distribution in his high-voltage, high-frequency power experiments in New York and Colorado Springs. In 1893, he made pronouncements on the possibility of wireless communication with his devices. Tesla tried to put these ideas to practical use in his unfinished Wardenclyffe Tower project, an intercontinental wireless communication and power transmitter but ran out of funding before he could complete it.After Wardenclyffe, Tesla experimented with a series of inventions in the 1910s and 1920s with varying degrees of success. Having spent most of his money, Tesla lived in a series of New York hotels, leaving behind unpaid bills. He died in New York City in January 1943. Tesla’s work fell into relative obscurity following his death, until 1960, when the General Conference on Weights and Measures named the SI unit of magnetic flux density the tesla in his honor. There has been a resurgence in popular interest in Tesla since the 1990s.
Read More About Nikola Tesla / Source
Alexander Graham Bell

Alexander Graham Bell ( March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was a Scottish-born inventor, scientist, and engineer who is credited with inventing and patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885.Bell’s father, grandfather, and brother had all been associated with work on elocution and speech and both his mother and wife were deaf, profoundly influencing Bell’s life’s work. His research on hearing and speech further led him to experiment with hearing devices which eventually culminated in Bell being awarded the first U.S. patent for the telephone, on March 7, 1876. Bell considered his invention an intrusion on his real work as a scientist and refused to have a telephone in his study.Many other inventions marked Bell’s later life, including groundbreaking work in optical telecommunications, hydrofoils, and aeronautics. Although Bell was not one of the 33 founders of the National Geographic Society, he had a strong influence on the magazine while serving as the second president from January 7, 1898, until 1903.Beyond his scientific work, Bell was an advocate of compulsory sterilization and served as chairman or president of several eugenics organizations.
Read More About Alexander Graham Bell / Source
Stephen Hawking

Stephen William Hawking (8 January 1942 – 14 March 2018) was an English theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author who was director of research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at the University of Cambridge at the time of his death. He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge between 1979 and 2009.
Hawking was born in Oxford into a family of doctors. Hawking began his university education at University College, Oxford in October 1959 at the age of 17, where he received a first-class BA (Hons.) degree in physics. He began his graduate work at Trinity Hall, Cambridge in October 1962, where he obtained his PhD degree in applied mathematics and theoretical physics, specialising in general relativity and cosmology in March 1966. During this period—in 1963—Hawking was diagnosed with an early-onset slow-progressing form of motor neurone disease (also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or Lou Gehrig’s disease) that gradually paralysed him over the decades. After the loss of his speech, he was able to communicate through a speech-generating device—initially through use of a handheld switch, and eventually by using a single cheek muscle.
Hawking’s scientific works included a collaboration with Roger Penrose on gravitational singularity theorems in the framework of general relativity and the theoretical prediction that black holes emit radiation, often called Hawking radiation. Initially, Hawking radiation was controversial. By the late 1970s and following the publication of further research, the discovery was widely accepted as a significant breakthrough in theoretical physics. Hawking was the first to set out a theory of cosmology explained by a union of the general theory of relativity and quantum mechanics. He was a vigorous supporter of the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics.Hawking achieved commercial success with several works of popular science in which he discussed his theories and cosmology in general. His book A Brief History of Time appeared on the Sunday Times bestseller list for a record-breaking 237 weeks. Hawking was a Fellow of the Royal Society, a lifetime member of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, and a recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the highest civilian award in the United States. In 2002, Hawking was ranked number 25 in the BBC’s poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. He died on 14 March 2018 at the age of 76, after living with motor neurone disease for more than 50 years.
Read More About Stephen Hawking / Source
Leonardo da Vinci
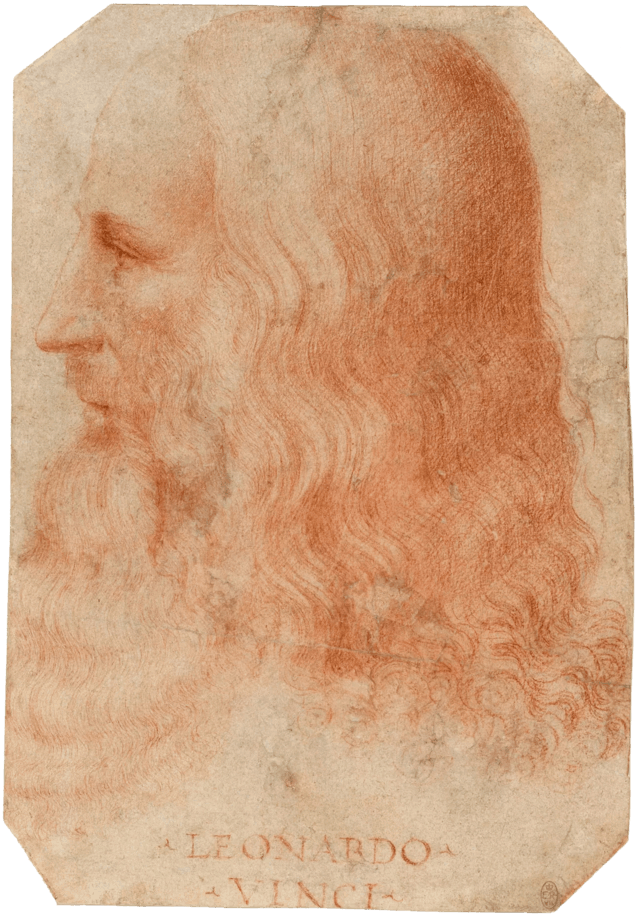

Leonardo da Vinci ( 14/15 April 1452 – 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who is widely considered one of the most diversely talented individuals ever to have lived. While his fame initially rested on his achievements as a painter, he also became known for his notebooks, in which he made drawings and notes on science and invention; these involve a variety of subjects including anatomy, astronomy, botany, cartography, painting, and palaeontology. Leonardo’s genius epitomized the Renaissance humanist idea, and his collective works compose a contribution to later generations of artists rivalled only by that of his contemporary Michelangelo.Properly named Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci, Leonardo was born out of wedlock to a notary, Piero da Vinci, and a peasant woman, Caterina, in Vinci, in the region of Florence, Italy. Leonardo was educated in the studio of the renowned Italian painter Andrea del Verrocchio. Much of his earlier working life was spent in the service of Ludovico il Moro in Milan, and he later worked in Rome, Bologna and Venice. He spent his last three years in France, where he died in 1519.
Although he had no formal academic training, many historians and scholars regard Leonardo as the prime exemplar of the “Renaissance Man” or “Universal Genius”, an individual of “unquenchable curiosity” and “feverishly inventive imagination.” According to art historian Helen Gardner, the scope and depth of his interests were without precedent in recorded history, and “his mind and personality seem to us superhuman, while the man himself mysterious and remote.” Scholars interpret his view of the world as being based in logic, though the empirical methods he used were unorthodox for his time.Leonardo is widely considered one of the greatest painters of all time. Mona Lisa is the most famous of his works and the most famous portrait ever made. The Last Supper is the most reproduced religious painting of all time and his Vitruvian Man drawing is also regarded as a cultural icon. In 2017, Salvator Mundi was sold at auction for $450.3 million, setting a new record for most expensive painting ever sold at public auction.Leonardo is revered for his technological ingenuity. He conceptualized flying machines, a type of armoured fighting vehicle, concentrated solar power, an adding machine, and the double hull. Relatively few of his designs were constructed or even feasible during his lifetime, as the modern scientific approaches to metallurgy and engineering were only in their infancy during the Renaissance. Some of his smaller inventions, however, entered the world of manufacturing unheralded, such as an automated bobbin winder and a machine for testing the tensile strength of wire. He is also sometimes credited with the inventions of the parachute, helicopter, and tank. He made substantial discoveries in anatomy, civil engineering, geology, optics, and hydrodynamics, but he did not publish his findings and they had little to no direct influence on subsequent science.
Read More About Leonardo da Vinci / Source
Isaac Newton

Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, theologian, and author (described in his own day as a “natural philosopher”) who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing the infinitesimal calculus.
In Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to prove Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System’s heliocentricity. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton’s inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems.
Newton built the first practical reflecting telescope and developed a sophisticated theory of colour based on the observation that a prism separates white light into the colours of the visible spectrum. His work on light was collected in his highly influential book Opticks, published in 1704. He also formulated an empirical law of cooling, made the first theoretical calculation of the speed of sound, and introduced the notion of a Newtonian fluid. In addition to his work on calculus, as a mathematician Newton contributed to the study of power series, generalised the binomial theorem to non-integer exponents, developed a method for approximating the roots of a function, and classified most of the cubic plane curves.
Newton was a fellow of Trinity College and the second Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge. He was a devout but unorthodox Christian who privately rejected the doctrine of the Trinity. Unusually for a member of the Cambridge faculty of the day, he refused to take holy orders in the Church of England. Beyond his work on the mathematical sciences, Newton dedicated much of his time to the study of alchemy and biblical chronology, but most of his work in those areas remained unpublished until long after his death. Politically and personally tied to the Whig party, Newton served two brief terms as Member of Parliament for the University of Cambridge, in 1689–90 and 1701–02. He was knighted by Queen Anne in 1705 and spent the last three decades of his life in London, serving as Warden (1696–1699) and Master (1699–1727) of the Royal Mint, as well as president of the Royal Society (1703–1727).
Read More About Isaac Newton / Source
Humphry Davy
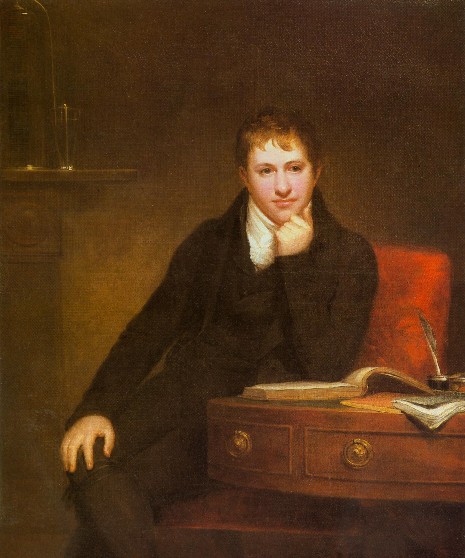

Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 1778 – 29 May 1829) was a Cornish chemist and inventor, who is best remembered today for isolating, by using electricity, a series of elements for the first time: potassium and sodium in 1807 and calcium, strontium, barium, magnesium and boron the following year, as well as discovering the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine. Davy also studied the forces involved in these separations, inventing the new field of electrochemistry.
In 1799, he experimented with nitrous oxide and was astonished at how it made him laugh, so he nicknamed it “laughing gas” and wrote about its potential anaesthetic properties in relieving pain during surgery. He also invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp.
Davy was a baronet, President of the Royal Society (PRS), Member of the Royal Irish Academy (MRIA), and Fellow of the Geological Society (FGS). Berzelius called Davy’s 1806 Bakerian Lecture On Some Chemical Agencies of Electricity “one of the best memoirs which has ever enriched the theory of chemistry.”
Read More About Humphry Davy / Source
Louis Pasteur
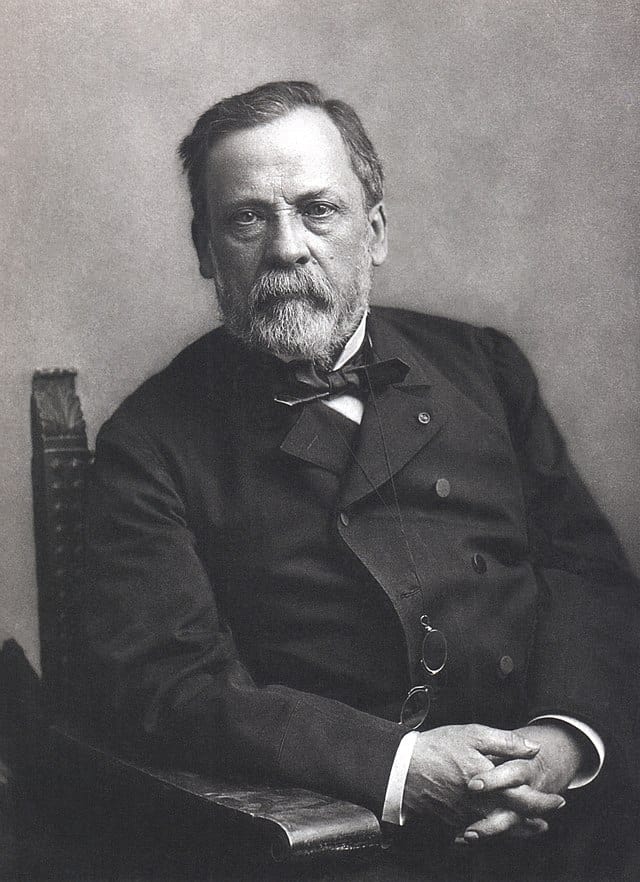

Louis Pasteur ( December 27, 1822 – September 28, 1895) was a French biologist, microbiologist, and chemist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization. He is remembered for his remarkable breakthroughs in the causes and prevention of diseases, and his discoveries have saved many lives ever since. He reduced mortality from puerperal fever and created the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax.
His medical discoveries provided direct support for the germ theory of disease and its application in clinical medicine. He is best known to the general public for his invention of the technique of treating milk and wine to stop bacterial contamination, a process now called pasteurization. He is regarded as one of the three main founders of bacteriology, together with Ferdinand Cohn and Robert Koch, and is popularly known as the “father of microbiology”.Pasteur was responsible for disproving the doctrine of spontaneous generation. He performed experiments that showed that, without contamination, microorganisms could not develop. Under the auspices of the French Academy of Sciences, he demonstrated that in sterilized and sealed flasks, nothing ever developed; and, conversely, in sterilized but open flasks, microorganisms could grow. Although Pasteur was not the first to propose the germ theory, his experiments indicated its correctness and convinced most of Europe that it was true.
Today, he is often regarded as one of the fathers of germ theory. Pasteur made significant discoveries in chemistry, most notably on the molecular basis for the asymmetry of certain crystals and racemization. Early in his career, his investigation of tartaric acid resulted in the first resolution of what is now called optical isomers. His work led the way to the current understanding of a fundamental principle in the structure of organic compounds.
He was the director of the Pasteur Institute, established in 1887, until his death, and his body was interred in a vault beneath the institute. Although Pasteur made groundbreaking experiments, his reputation became associated with various controversies. Historical reassessment of his notebook revealed that he practiced deception to overcome his rivals.
Read More About Louis Pasteur / Source
Galileo Galilei
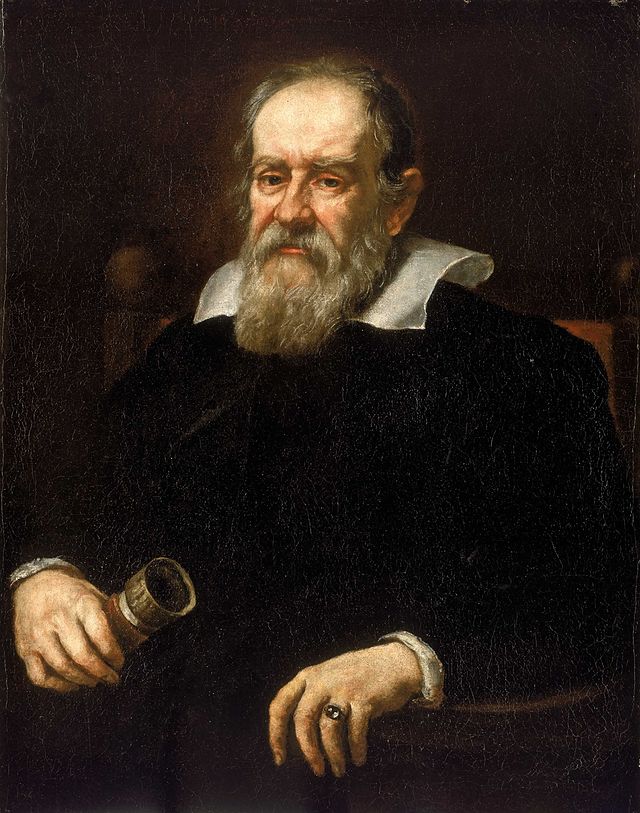

Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de’ Galilei ( 15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath, from Pisa. Galileo has been called the “father of observational astronomy”, the “father of modern physics”, the “father of the scientific method”, and the “father of modern science”.Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of pendulums and “hydrostatic balances”. He invented the thermoscope and various military compasses, and used the telescope for scientific observations of celestial objects. His contributions to observational astronomy include the telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, the observation of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, the observation of Saturn’s rings, and the analysis of sunspots.
Galileo’s championing of heliocentrism and Copernicanism met with opposition from within the Catholic Church and from some astronomers. The matter was investigated by the Roman Inquisition in 1615, which concluded that heliocentrism was “foolish and absurd in philosophy, and formally heretical since it explicitly contradicts in many places the sense of Holy Scripture”.Galileo later defended his views in Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems (1632), which appeared to attack Pope Urban VIII and thus alienated both the Pope and the Jesuits, who had both supported Galileo up until this point. He was tried by the Inquisition, found “vehemently suspect of heresy”, and forced to recant. He spent the rest of his life under house arrest. During this time, he wrote Two New Sciences (1638), primarily concerning kinematics and the strength of materials, summarizing work he had done some forty years earlier.
Read More About Galileo Galilei / Source
Archimedes
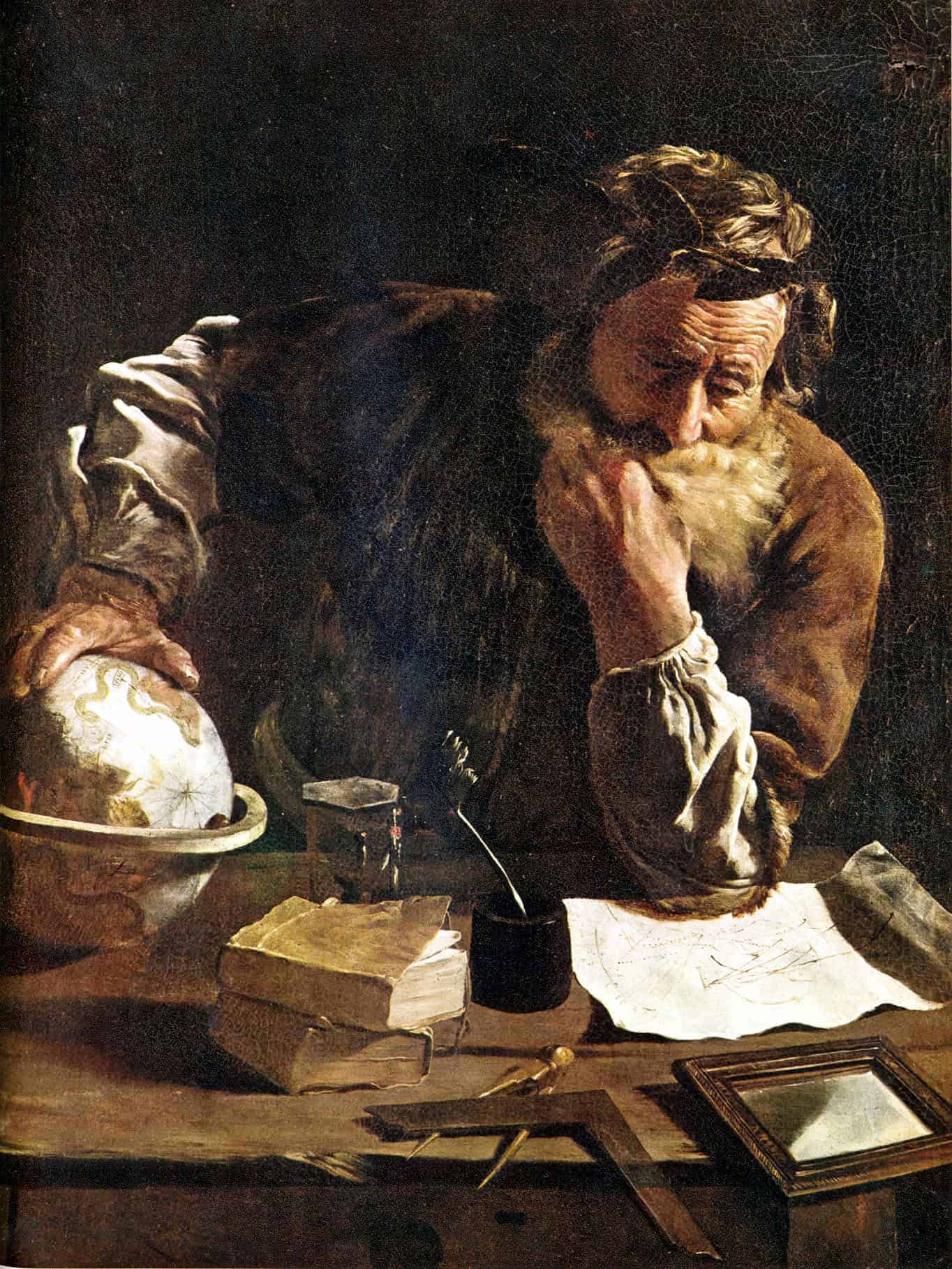

Archimedes of Syracuse ( c. 287 – c. 212 BC) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Considered to be the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time, Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying concepts of infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems, including: the area of a circle; the surface area and volume of a sphere; area of an ellipse; the area under a parabola; the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution; the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution; and the area of a spiral.His other mathematical achievements include deriving an accurate approximation of pi; defining and investigating the spiral that now bears his name; and creating a system using exponentiation for expressing very large numbers. He was also one of the first to apply mathematics to physical phenomena, founding hydrostatics and statics, including an explanation of the principle of the lever. He is credited with designing innovative machines, such as his screw pump, compound pulleys, and defensive war machines to protect his native Syracuse from invasion.
Read More About Archimedes / Source
Nicolaus Copernicus
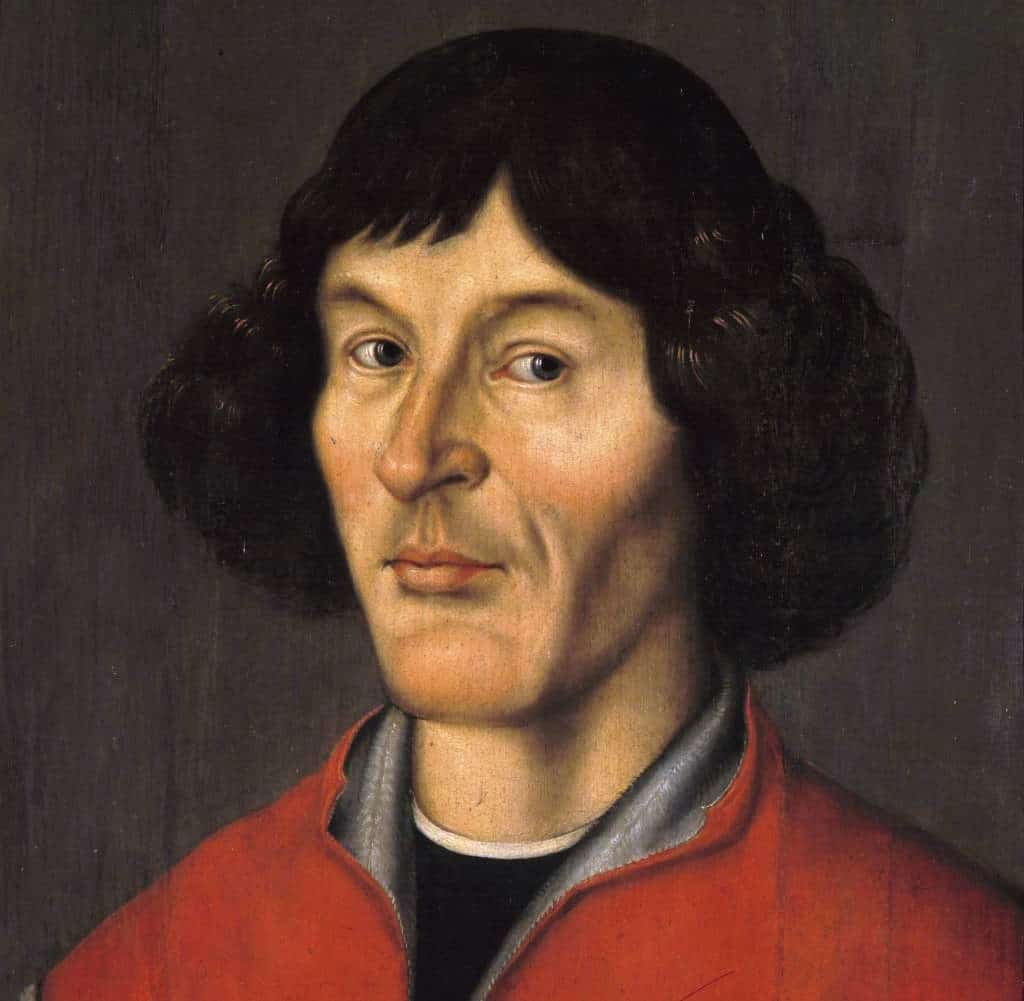

Nicolaus Copernicus ( 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance-era mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center. In all likelihood, Copernicus developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier.
Read More About Nicolaus Copernicus / Source
Marie Curie
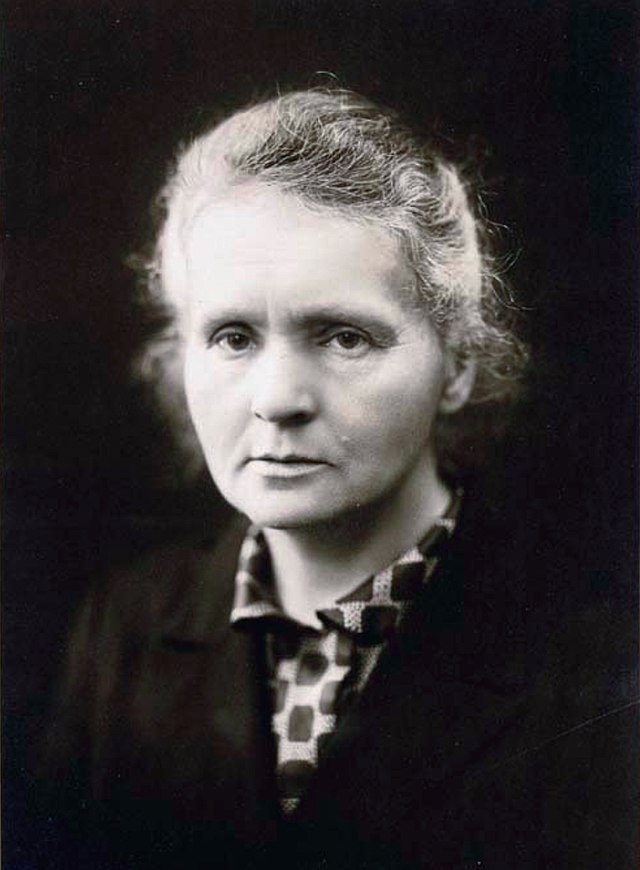

Marie Skłodowska Curie, born Maria Salomea Skłodowska (7 November 1867 – 4 July 1934), was a Polish and naturalized-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity.
As the first of the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes, she was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, the first person and the only woman to win the Nobel Prize twice, and the only person to win the Nobel Prize in two scientific fields. She was also the first woman to become a professor at the University of Paris.She was born in Warsaw, in what was then the Kingdom of Poland, part of the Russian Empire. She studied at Warsaw’s clandestine Flying University and began her practical scientific training in Warsaw. In 1891, aged 24, she followed her elder sister Bronisława to study in Paris, where she earned her higher degrees and conducted her subsequent scientific work.
She shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics with her husband Pierre Curie and physicist Henri Becquerel, for their pioneering work developing the theory of “radioactivity” (a term she coined). Using techniques she invented for isolating radioactive isotopes, she won the 1911 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of two elements, polonium and radium.
Under her direction, the world’s first studies were conducted into the treatment of neoplasms using radioactive isotopes. She founded the Curie Institutes in Paris and in Warsaw, which remain major centres of medical research today. During World War I she developed mobile radiography units to provide X-ray services to field hospitals.
While a French citizen, Marie Skłodowska Curie, who used both surnames, never lost her sense of Polish identity. She taught her daughters the Polish language and took them on visits to Poland. She named the first chemical element she discovered polonium, after her native country.Marie Curie died in 1934, aged 66, at the Sancellemoz sanatorium in Passy (Haute-Savoie), France, of aplastic anaemia from exposure to radiation in the course of her scientific research and in the course of her radiological work at field hospitals during World War I. In 1995, she became the first woman to be entombed on her own merits in the Panthéon in Paris.
Read More About Marie Curie / Source
J. J. Thomson
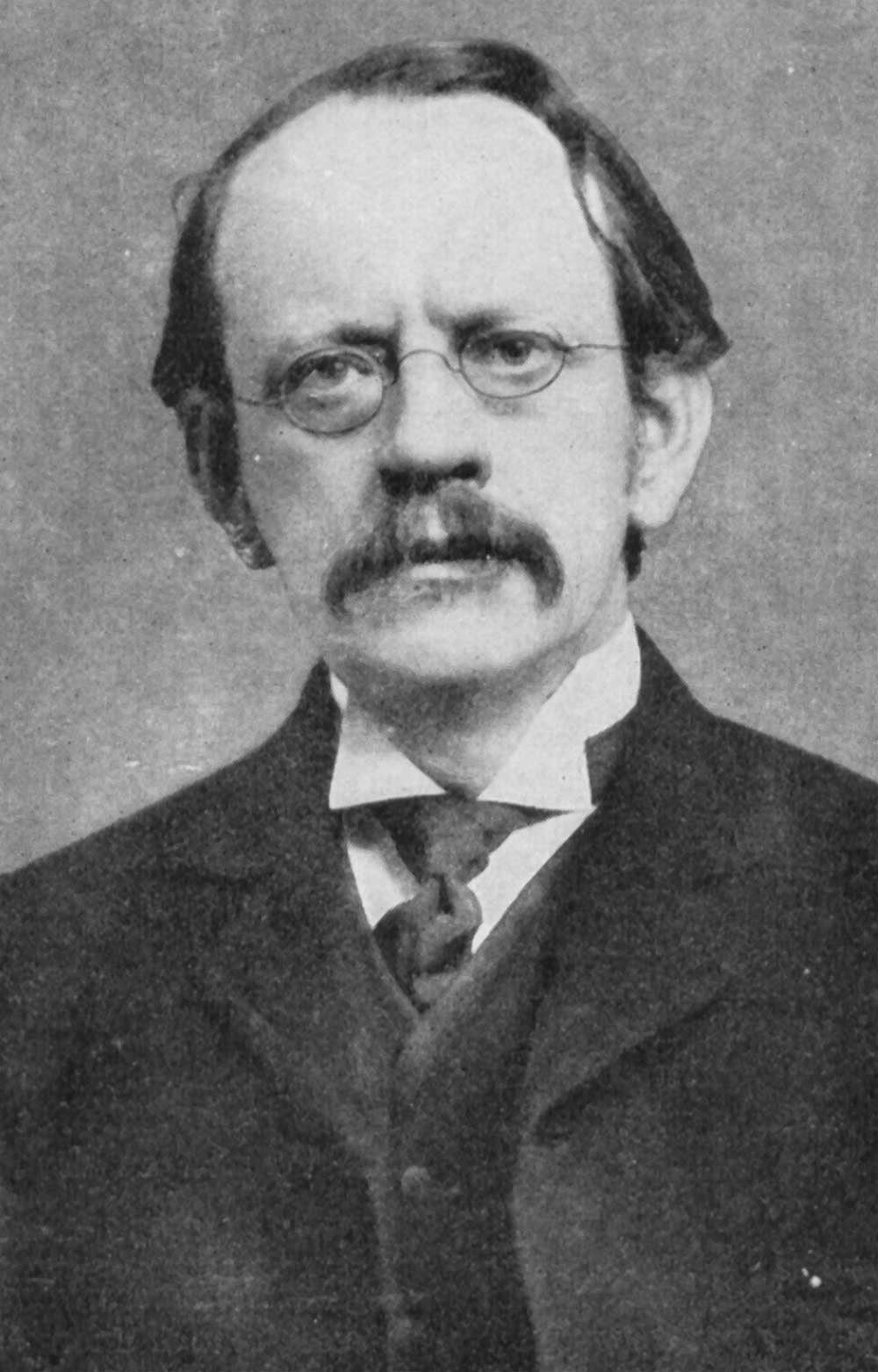

Sir Joseph John Thomson (18 December 1856 – 30 August 1940) was a British physicist and Nobel Laureate in Physics, credited with the discovery of the electron, the first subatomic particle to be discovered.
In 1897, Thomson showed that cathode rays were composed of previously unknown negatively charged particles (now called electrons), which he calculated must have bodies much smaller than atoms and a very large charge-to-mass ratio. Thomson is also credited with finding the first evidence for isotopes of a stable (non-radioactive) element in 1913, as part of his exploration into the composition of canal rays (positive ions). His experiments to determine the nature of positively charged particles, with Francis William Aston, were the first use of mass spectrometry and led to the development of the mass spectrograph.Thomson was awarded the 1906 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the conduction of electricity in gases.
Read More About J. J. Thomson / Source
Robert Hooke

Robert Hooke FRS (28 July [O.S. 18 July] 1635 – 3 March 1703) was an English scientist and architect, a polymath, recently called “England’s Leonardo”, who, using a microscope, was the first to visualize a microorganism. An impoverished scientific inquirer in young adulthood, he found wealth and esteem by performing over half of the architectural surveys after London’s great fire of 1666. Hooke was also a member of the Royal Society and since 1662 was its curator of experiments. Hooke was also Professor of Geometry at Gresham College.
As an assistant to physical scientist Robert Boyle, Hooke built the vacuum pumps used in Boyle’s experiments on gas law, and himself conducted experiments. In 1673, Hooke built the earliest Gregorian telescope, and then he observed the rotations of the planets Mars and Jupiter. Hooke’s 1665 book Micrographia spurred microscopic investigations. Thus observing microscopic fossils, Hooke endorsed biological evolution. Investigating in optics, specifically light refraction, he inferred a wave theory of light. And his is the first recorded hypothesis of heat expanding matter, air’s composition by small particles at larger distances, and heat as energy.
Read More About Robert Hooke / Source
Gregor Mendel
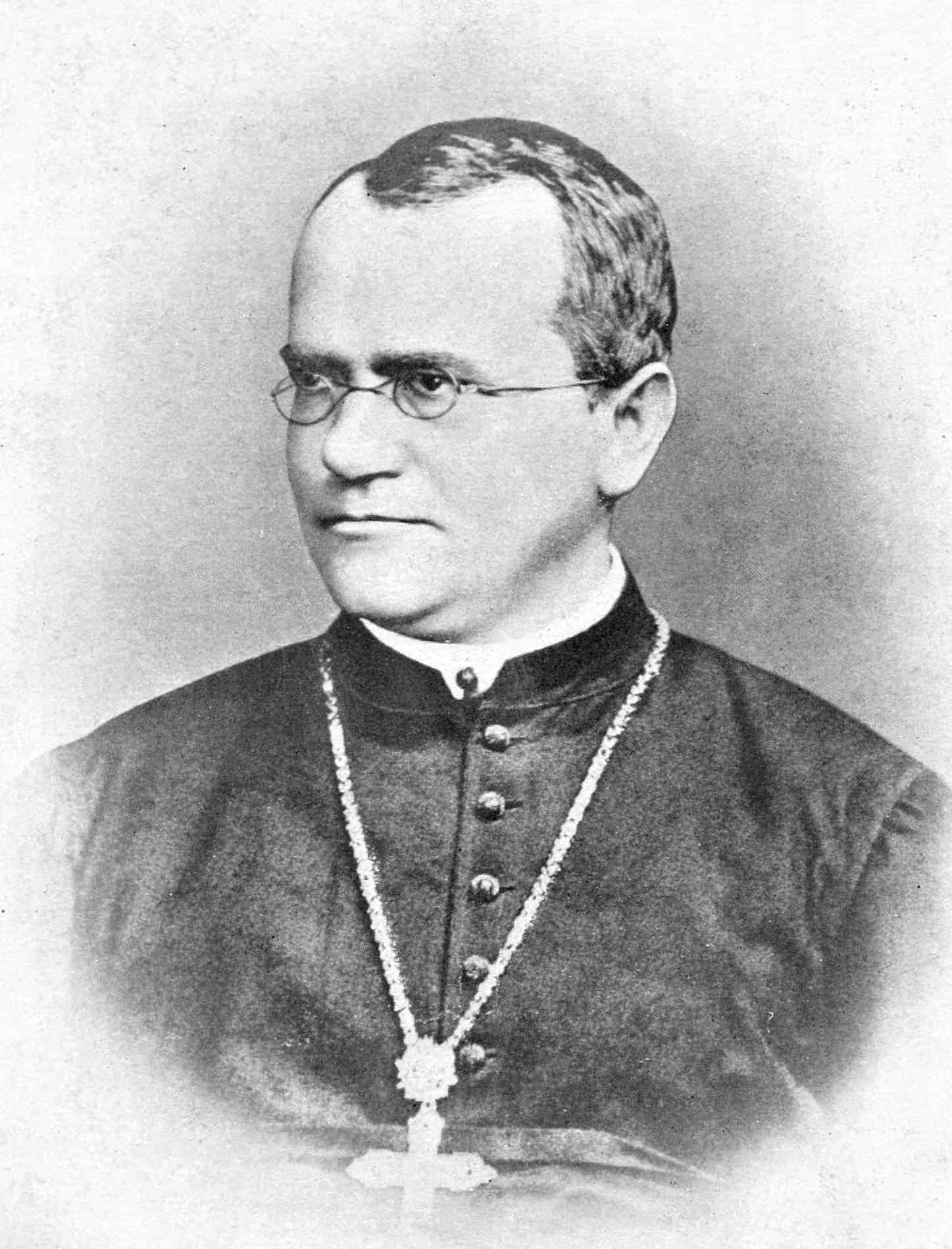

Gregor Johann Mendel ( 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was a scientist, meteorologist, mathematician, biologist, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas’ Abbey in Brno, Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel was born in a German-speaking family in the Silesian part of the Austrian Empire (today’s Czech Republic) and gained posthumous recognition as the founder of the modern science of genetics. Though farmers had known for millennia that crossbreeding of animals and plants could favor certain desirable traits, Mendel’s pea plant experiments conducted between 1856 and 1863 established many of the rules of heredity, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance.Mendel worked with seven characteristics of pea plants: plant height, pod shape and color, seed shape and color, and flower position and color. Taking seed color as an example, Mendel showed that when a true-breeding yellow pea and a true-breeding green pea were cross-bred their offspring always produced yellow seeds. However, in the next generation, the green peas reappeared at a ratio of 1 green to 3 yellow. To explain this phenomenon, Mendel coined the terms “recessive” and “dominant” in reference to certain traits. In the preceding example, the green trait, which seems to have vanished in the first filial generation, is recessive and the yellow is dominant. He published his work in 1866, demonstrating the actions of invisible “factors”—now called genes—in predictably determining the traits of an organism.
Read More About Gregor Mendel / Source
Alexander Fleming

Sir Alexander Fleming (6 August 1881 – 11 March 1955) was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the enzyme lysozyme and the world’s first broadly effective antibiotic substance which he named penicillin. He discovered lysozyme from his nasal discharge in 1922, and along with it a bacterium he named Micrococcus Lysodeikticus, later renamed Micrococcus luteus. His discovery of what is later named benzylpenicillin (or penicillin G) from the mould Penicillium rubens in 1928, is described as the “single greatest victory ever achieved over disease.” For this discovery he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.Fleming was knighted for his scientific achievements in 1944. In 1999, he was named in Time magazine’s list of the 100 Most Important People of the 20th century. In 2002, he was chosen in the BBC’s television poll for determining the 100 Greatest Britons, and in 2009, he was also voted third “greatest Scot” in an opinion poll conducted by STV, behind only Robert Burns and William Wallace.
Read More About Alexander Fleming / Source
Edwin Hubble

Edwin Powell Hubble (November 20, 1889 – September 28, 1953) was an American astronomer. He played a crucial role in establishing the fields of extragalactic astronomy and observational cosmology.Hubble proved that many objects previously thought to be clouds of dust and gas and classified as “nebulae” were actually galaxies beyond the Milky Way. He used the strong direct relationship between a classical Cepheid variable’s luminosity and pulsation period (discovered in 1908 by Henrietta Swan Leavitt) for scaling galactic and extragalactic distances.Hubble provided evidence that the recessional velocity of a galaxy increases with its distance from the Earth, a property now known as “Hubble’s law”, despite the fact that it had been both proposed and demonstrated observationally two years earlier by Georges Lemaître. The Hubble–Lemaître law implies that the universe is expanding. A decade before, the American astronomer Vesto Slipher had provided the first evidence that the light from many of these nebulae was strongly red-shifted, indicative of high recession velocities.Hubble’s name is most widely recognized for the Hubble Space Telescope, which was named in his honor, with a model prominently displayed in his hometown of Marshfield, Missouri.
Read More About Edwin Hubble / Source
Amedeo Avogadro
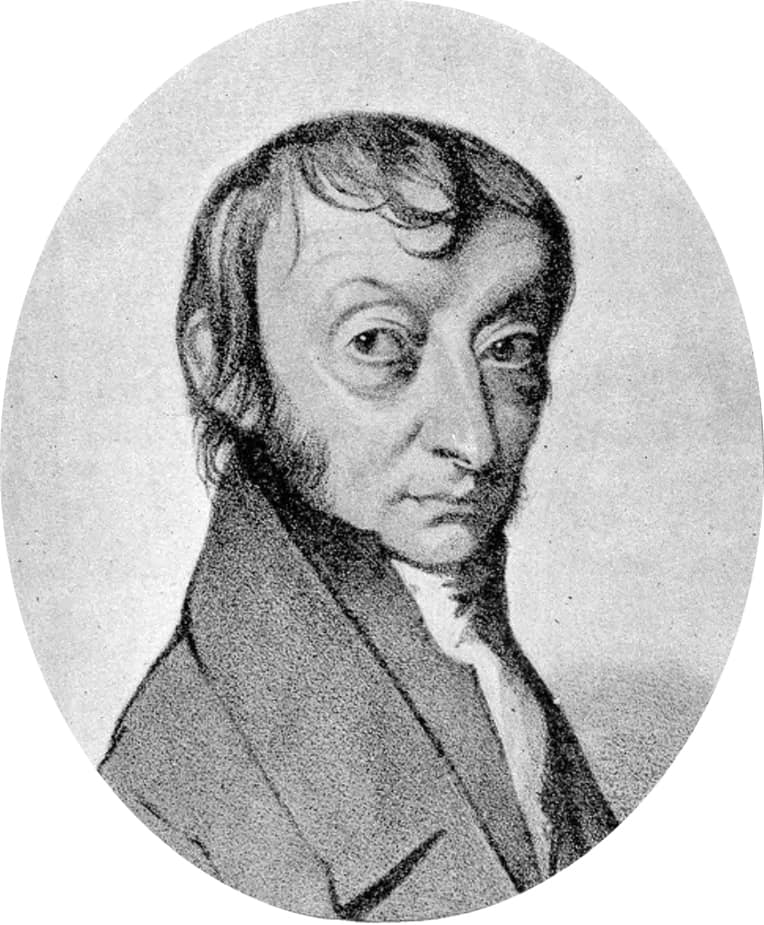

Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto ( 9 August 1776 – 9 July 1856) was an Italian scientist, most noted for his contribution to molecular theory now known as Avogadro’s law, which states that equal volumes of gases under the same conditions of temperature and pressure will contain equal numbers of molecules. In tribute to him, the number of elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions or other particles) in 1 mole of a substance, 6.02214076×1023, is known as the Avogadro constant, one of the seven SI base units and represented by NA.
Read More About Amedeo Avogadro / Source
Carl Sagan

Carl Edward Sagan (; November 9, 1934 – December 20, 1996) was an American astronomer, planetary scientist, cosmologist, astrophysicist, astrobiologist, author, poet, and science communicator. His best known scientific contribution is research on extraterrestrial life, including experimental demonstration of the production of amino acids from basic chemicals by radiation. Sagan assembled the first physical messages sent into space: the Pioneer plaque and the Voyager Golden Record, universal messages that could potentially be understood by any extraterrestrial intelligence that might find them. Sagan argued the now-accepted hypothesis that the high surface temperatures of Venus can be attributed to and calculated using the greenhouse effect.Initially an associate professor at Harvard and later at Cornell, from 1976 to his death, he was the David Duncan Professor of Astronomy and Space Sciences at the latter. Sagan published more than 600 scientific papers and articles and was author, co-author or editor of more than 20 books. He wrote many popular science books, such as The Dragons of Eden, Broca’s Brain and Pale Blue Dot, and narrated and co-wrote the award-winning 1980 television series Cosmos: A Personal Voyage. The most widely watched series in the history of American public television, Cosmos has been seen by at least 500 million people across 60 different countries.
Read More About Carl Sagan / Source
John Dalton
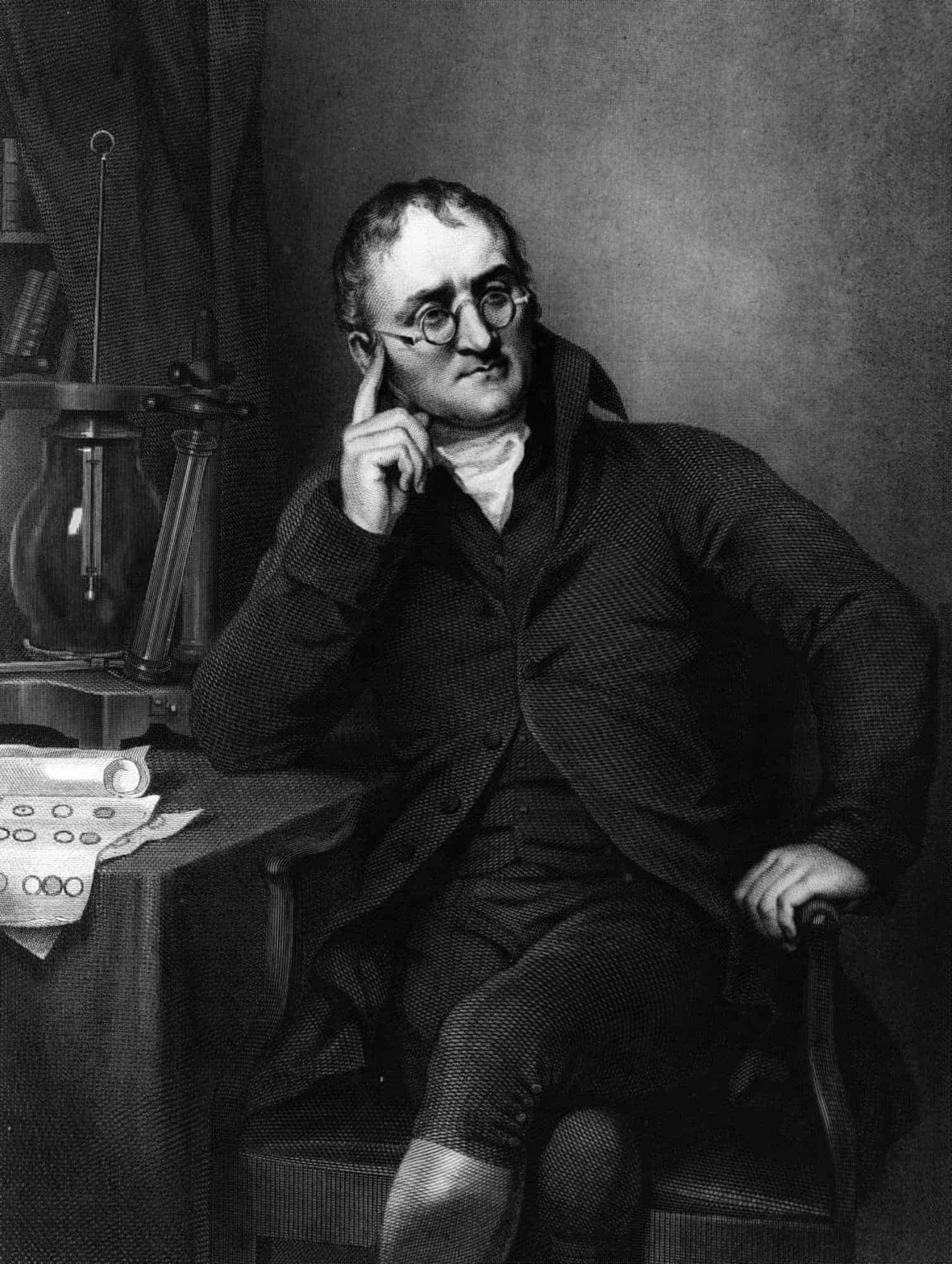

John Dalton FRS ( 6 September 1766 – 27 July 1844) was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist. He is best known for introducing the atomic theory into chemistry, and for his research into colour blindness, sometimes referred to as Daltonism in his honour. Dalton was the first scientist to use the term atom for the smallest particle of matter, which originated from Greek word ‘atomos’ meaning cannot be divided further.
Read More About John Dalton / Source
James Clerk Maxwell

James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish scientist in the field of mathematical physics. His most notable achievement was to formulate the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, bringing together for the first time electricity, magnetism, and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell’s equations for electromagnetism have been called the “second great unification in physics” where the first one had been realised by Isaac Newton.
With the publication of “A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field” in 1865, Maxwell demonstrated that electric and magnetic fields travel through space as waves moving at the speed of light. He proposed that light is an undulation in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. The unification of light and electrical phenomena led his prediction of the existence of radio waves. Maxwell is also regarded as a founder of the modern field of electrical engineering.He helped develop the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution, a statistical means of describing aspects of the kinetic theory of gases. He is also known for presenting the first durable colour photograph in 1861 and for his foundational work on analysing the rigidity of rod-and-joint frameworks (trusses) like those in many bridges.
Read More About James Clerk Maxwell / Source
Benjamin Franklin

Benjamin Franklin (January 17, 1706 [O.S. January 6, 1705] – April 17, 1790) was a British American polymath and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. Franklin was a leading writer, printer, political philosopher, politician, Freemason, postmaster, scientist, inventor, humorist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his discoveries and theories regarding electricity. As an inventor, he is known for the lightning rod, bifocals, and the Franklin stove, among other inventions. He founded many civic organizations, including the Library Company, Philadelphia’s first fire department, and the University of Pennsylvania.Franklin earned the title of “The First American” for his early and indefatigable campaigning for colonial unity, initially as an author and spokesman in London for several colonies. As the first United States ambassador to France, he exemplified the emerging American nation. Franklin was foundational in defining the American ethos as a marriage of the practical values of thrift, hard work, education, community spirit, self-governing institutions, and opposition to authoritarianism both political and religious, with the scientific and tolerant values of the Enlightenment. In the words of historian Henry Steele Commager, “In a Franklin could be merged the virtues of Puritanism without its defects, the illumination of the Enlightenment without its heat.” To Walter Isaacson, this makes Franklin “the most accomplished American of his age and the most influential in inventing the type of society America would become.”Franklin became a successful newspaper editor and printer in Philadelphia, the leading city in the colonies, publishing the Pennsylvania Gazette at the age of 23. He became wealthy publishing this and Poor Richard’s Almanack, which he authored under the pseudonym “Richard Saunders”. After 1767, he was associated with the Pennsylvania Chronicle, a newspaper that was known for its revolutionary sentiments and criticisms of the policies of the British Parliament and the Crown.
He pioneered and was the first president of Academy and College of Philadelphia which opened in 1751 and later became the University of Pennsylvania. He organized and was the first secretary of the American Philosophical Society and was elected president in 1769. Franklin became a national hero in America as an agent for several colonies when he spearheaded an effort in London to have the Parliament of Great Britain repeal the unpopular Stamp Act. An accomplished diplomat, he was widely admired among the French as American minister to Paris and was a major figure in the development of positive Franco–American relations. His efforts proved vital for the American Revolution in securing shipments of crucial munitions from France.
He was promoted to deputy postmaster-general for the British colonies on August 10, 1753, having been Philadelphia postmaster for many years, and this enabled him to set up the first national communications network. During the revolution, he became the first United States postmaster general. He was active in community affairs and colonial and state politics, as well as national and international affairs. From 1785 to 1788, he served as governor of Pennsylvania. He initially owned and dealt in slaves but, by the late 1750s, he began arguing against slavery, became an abolitionist, and promoted education and the integration of blacks in American Society.
His life and legacy of scientific and political achievement, and his status as one of America’s most influential Founding Fathers, have seen Franklin honored more than two centuries after his death on the fifty-cent piece, the $100 bill, warships, and the names of many towns, counties, educational institutions, and corporations, as well as numerous cultural references.
Read More About Benjamin Franklin / Source
William Harvey
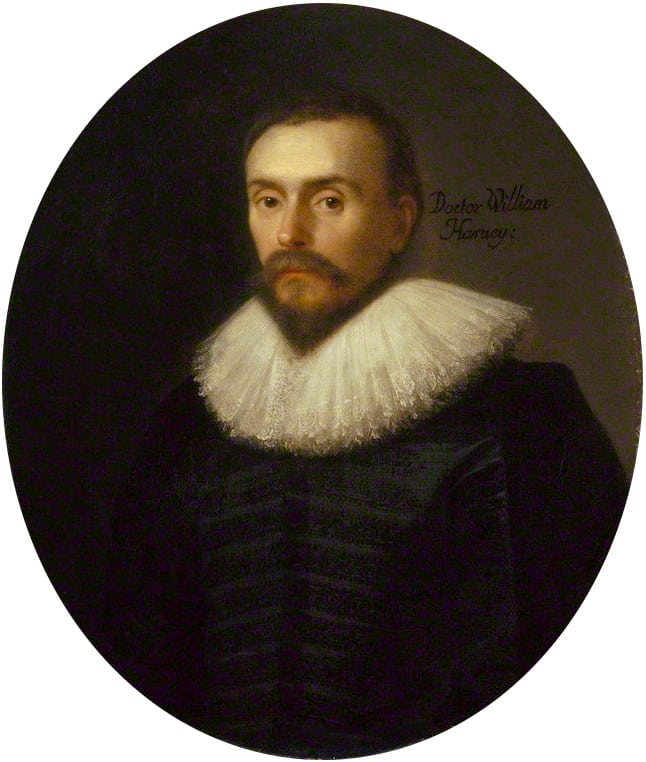

William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the brain and the rest of the body by the heart, though earlier writers, such as Realdo Colombo, Michael Servetus, and Jacques Dubois, had provided precursors of the theory.
Read More About William Harvey / Source
Charles H. Townes
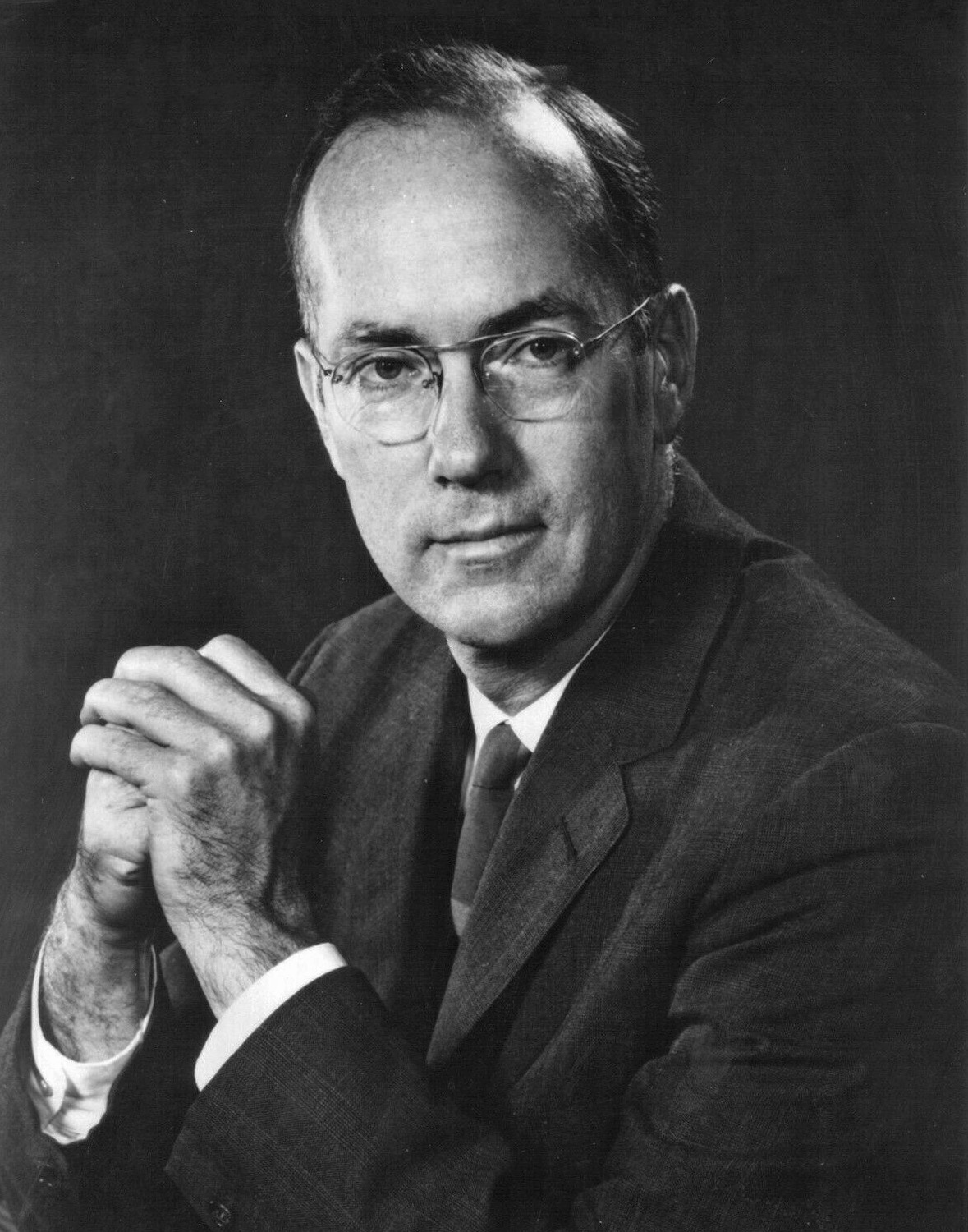

Charles Hard Townes (July 28, 1915 – January 27, 2015) was an American physicist. Townes worked on the theory and application of the maser, for which he obtained the fundamental patent, and other work in quantum electronics associated with both maser and laser devices. He shared the 1964 Nobel Prize in Physics with Nikolay Basov and Alexander Prokhorov. Townes was an adviser to the United States Government, meeting every US President from Harry Truman (1945) to Bill Clinton (1999).
He directed the US government Science and Technology Advisory Committee for the Apollo lunar landing program. After becoming a professor of the University of California at Berkeley in 1967, he began an astrophysical program that produced several important discoveries, for example, the black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Townes was religious and believed that science and religion are converging to provide a greater understanding of the nature and purpose of the universe.
Read More About Charles H. Townes / Source
Richard Feynman

Richard Phillips Feynman ( May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist, known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, as well as his work in particle physics for which he proposed the parton model. For contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 jointly with Julian Schwinger and Shin’ichirō Tomonaga.
Feynman developed a widely used pictorial representation scheme for the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles, which later became known as Feynman diagrams. During his lifetime, Feynman became one of the best-known scientists in the world. In a 1999 poll of 130 leading physicists worldwide by the British journal Physics World, he was ranked as one of the ten greatest physicists of all time.He assisted in the development of the atomic bomb during World War II and became known to a wide public in the 1980s as a member of the Rogers Commission, the panel that investigated the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster. Along with his work in theoretical physics, Feynman has been credited with pioneering the field of quantum computing and introducing the concept of nanotechnology. He held the Richard C.
Read More About Richard Feynman / Source
George Washington Carver
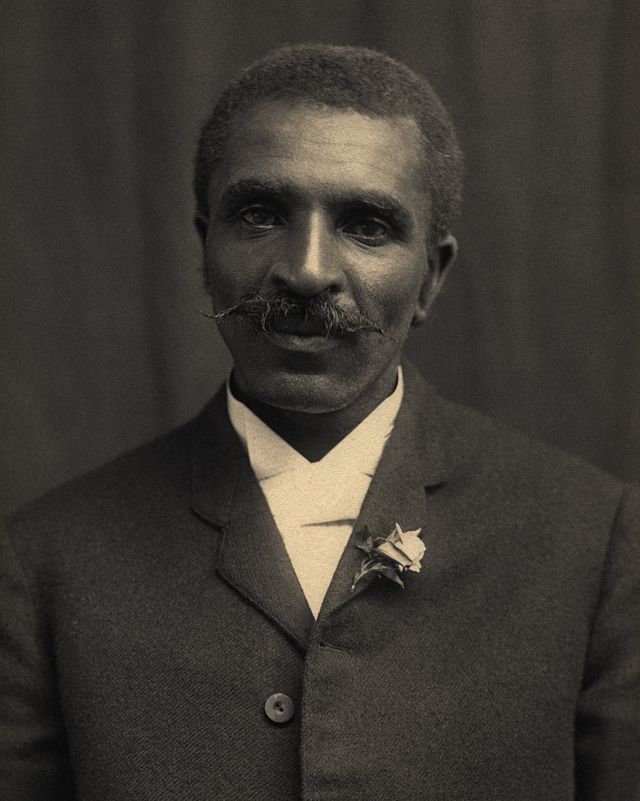

George Washington Carver (1860s – January 5, 1943) was an American agricultural scientist and inventor who promoted alternative crops to cotton and methods to prevent soil depletion. He was the most prominent black scientist of the early 20th century.
While a professor at Tuskegee Institute, Carver developed techniques to improve soils depleted by repeated plantings of cotton. He wanted poor farmers to grow other crops, such as peanuts and sweet potatoes, as a source of their own food and to improve their quality of life. The most popular of his 44 practical bulletins for farmers contained 105 food recipes using peanuts. Although he spent years developing and promoting numerous products made from peanuts, none became commercially successful.Apart from his work to improve the lives of farmers, Carver was also a leader in promoting environmentalism. He received numerous honors for his work, including the Spingarn Medal of the NAACP. In an era of high racial polarization, his fame reached beyond the black community. He was widely recognized and praised in the white community for his many achievements and talents. In 1941, Time magazine dubbed Carver a “Black Leonardo”.Color film of Carver shot in 1937 at the Tuskegee Institute by African American surgeon Allen Alexander was added to the National Film Registry of the Library of Congress in 2019. The 12 minutes of footage includes Carver in his apartment, office and laboratory, as well as images of him tending flowers and displaying his paintings. The film was digitized by The National Archives as part of its multi-year effort to preserve and make available the historically significant film collections of the National Park Service. It can be seen on the US National Film Archives YouTube channel.
Read More About George Washington Carver / Source
Niels Bohr
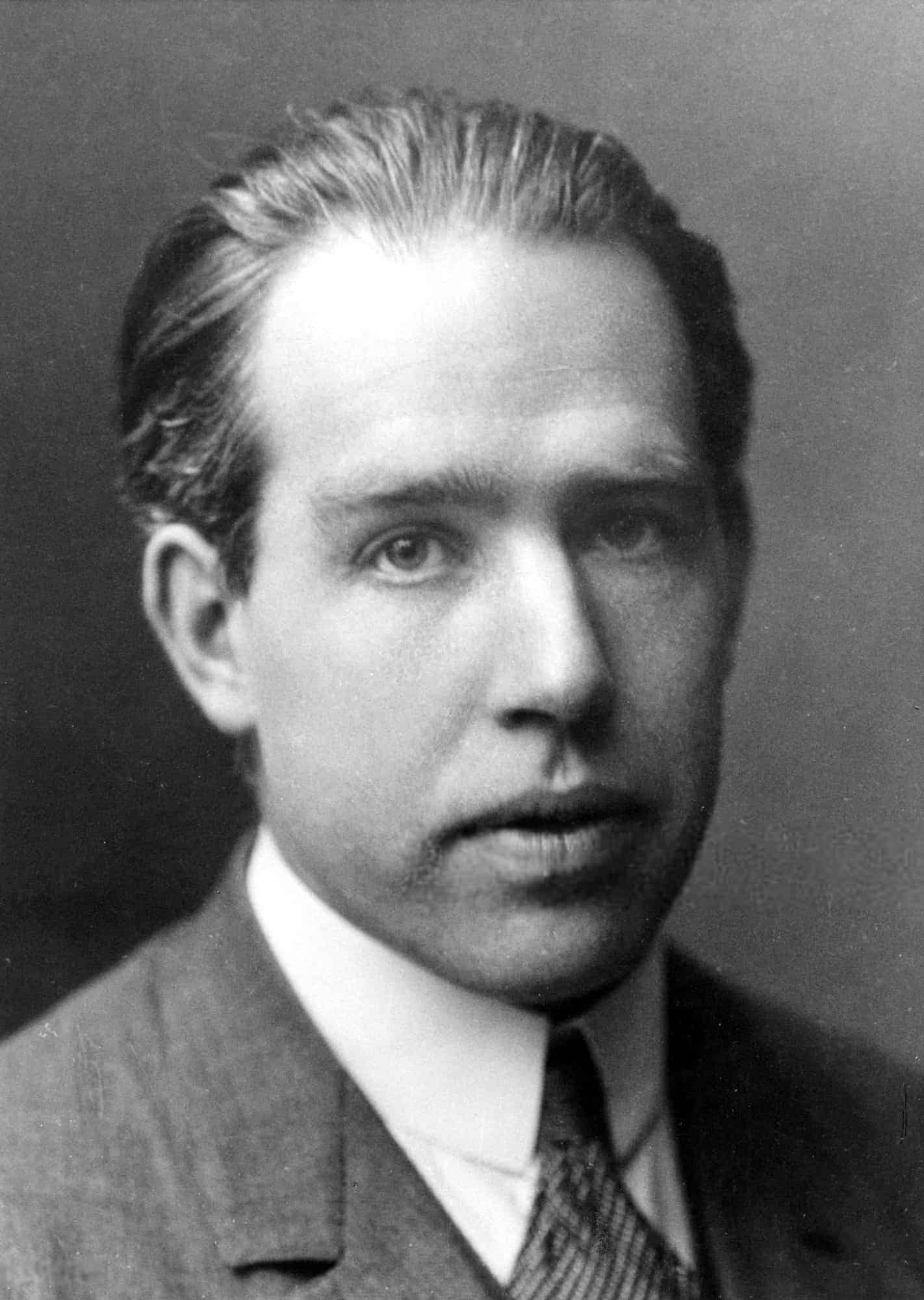

Niels Henrik David Bohr ( 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research.
Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr’s thinking in both science and philosophy.
Bohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Copenhagen, now known as the Niels Bohr Institute, which opened in 1920. Bohr mentored and collaborated with physicists including Hans Kramers, Oskar Klein, George de Hevesy, and Werner Heisenberg. He predicted the existence of a new zirconium-like element, which was named hafnium, after the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Later, the element bohrium was named after him.
Read More About Niels Bohr / Source
John Bardeen

John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American physicist. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Brattain for the invention of the transistor; and again in 1972 with Leon N Cooper and John Robert Schrieffer for a fundamental theory of conventional superconductivity known as the BCS theory.The transistor revolutionized the electronics industry, making possible the development of almost every modern electronic device, from telephones to computers, and ushering in the Information Age. Bardeen’s developments in superconductivity—for which he was awarded his second Nobel Prize—are used in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and medical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Born and raised in Wisconsin, Bardeen received a PhD in physics from Princeton University. After serving in World War II, he was a researcher at Bell Labs, and a professor at the University of Illinois. In 1990, Bardeen appeared on Life magazine’s list of “100 Most Influential Americans of the Century.”
Read More About John Bardeen / Source
Johannes Kepler
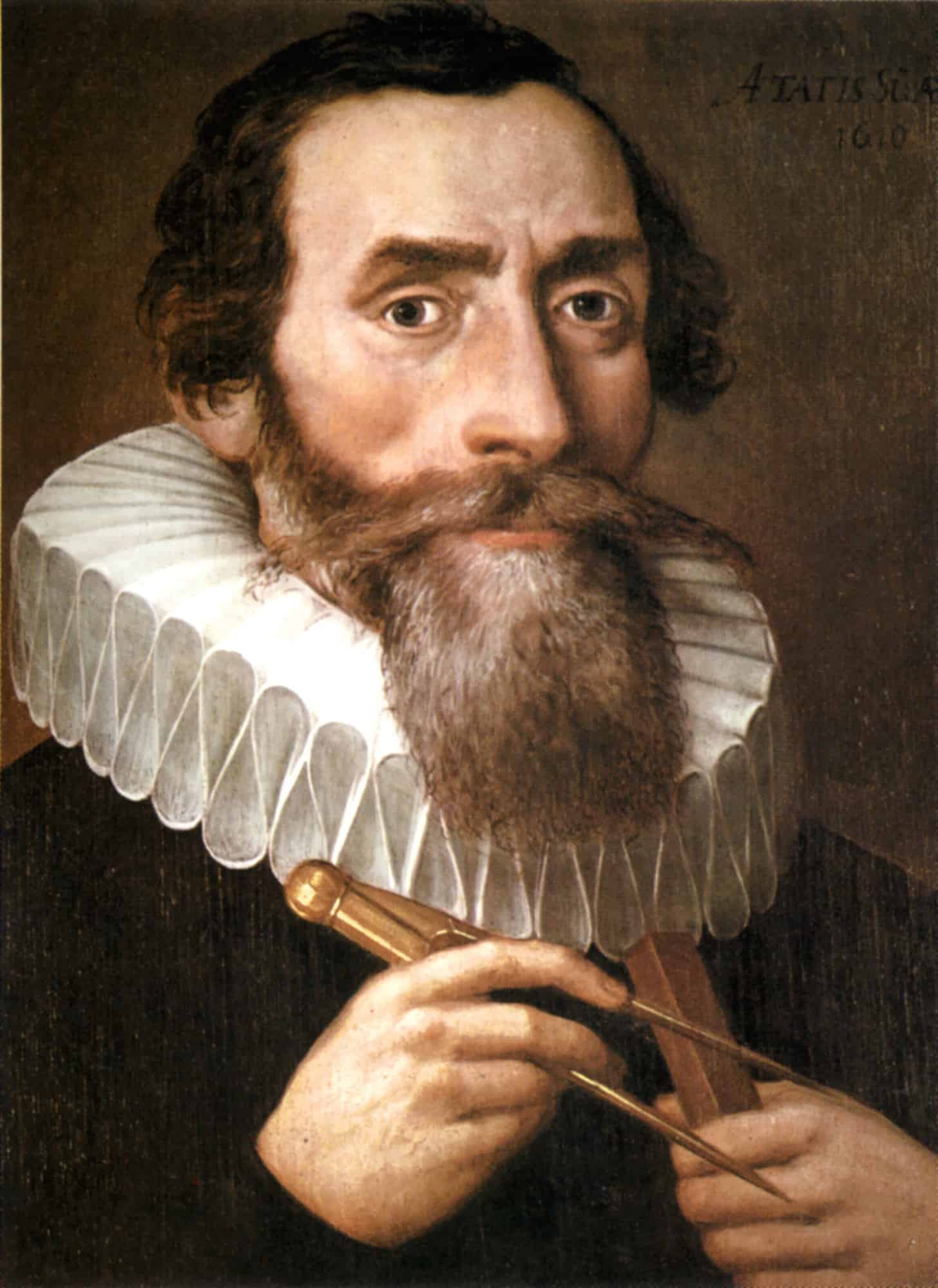

Johannes Kepler ( 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer. He is a key figure in the 17th-century scientific revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae. These works also provided one of the foundations for Newton’s theory of universal gravitation.
Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Later he became an assistant to the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He also taught mathematics in Linz, and was an adviser to General Wallenstein. Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, invented an improved version of the refracting (or Keplerian) telescope, and was mentioned in the telescopic discoveries of his contemporary Galileo Galilei. He was a corresponding member of the Accademia dei Lincei in Rome.
Read More About Johannes Kepler / Source
Michael Faraday
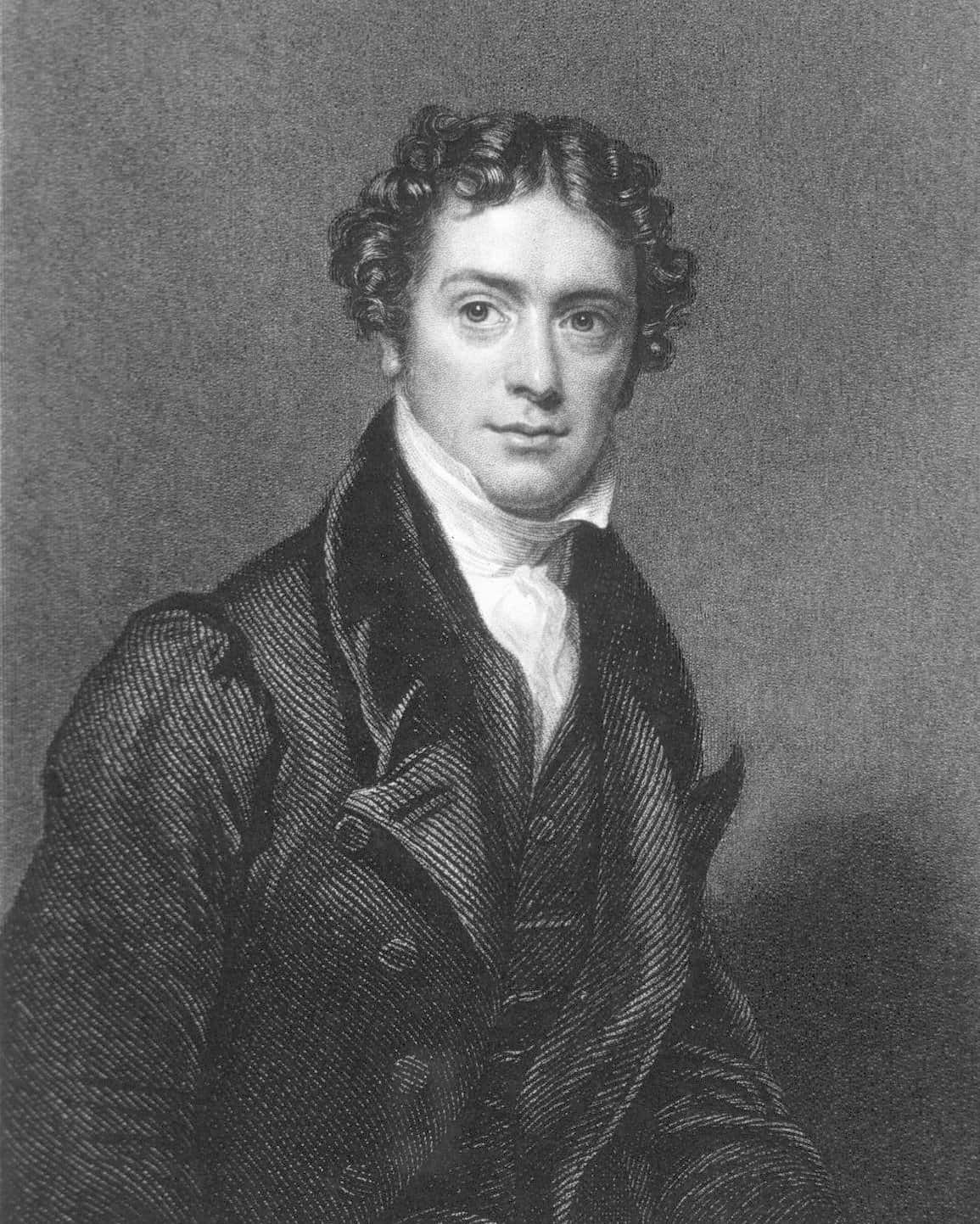

Michael Faraday ( 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis.
Although Faraday received little formal education, he was one of the most influential scientists in history. It was by his research on the magnetic field around a conductor carrying a direct current that Faraday established the basis for the concept of the electromagnetic field in physics. Faraday also established that magnetism could affect rays of light and that there was an underlying relationship between the two phenomena. He similarly discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction and diamagnetism, and the laws of electrolysis. His inventions of electromagnetic rotary devices formed the foundation of electric motor technology, and it was largely due to his efforts that electricity became practical for use in technology.As a chemist, Faraday discovered benzene, investigated the clathrate hydrate of chlorine, invented an early form of the Bunsen burner and the system of oxidation numbers, and popularised terminology such as “anode”, “cathode”, “electrode” and “ion”. Faraday ultimately became the first and foremost Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution, a lifetime position.
Read More About Michael Faraday / Source
E. O. Wilson
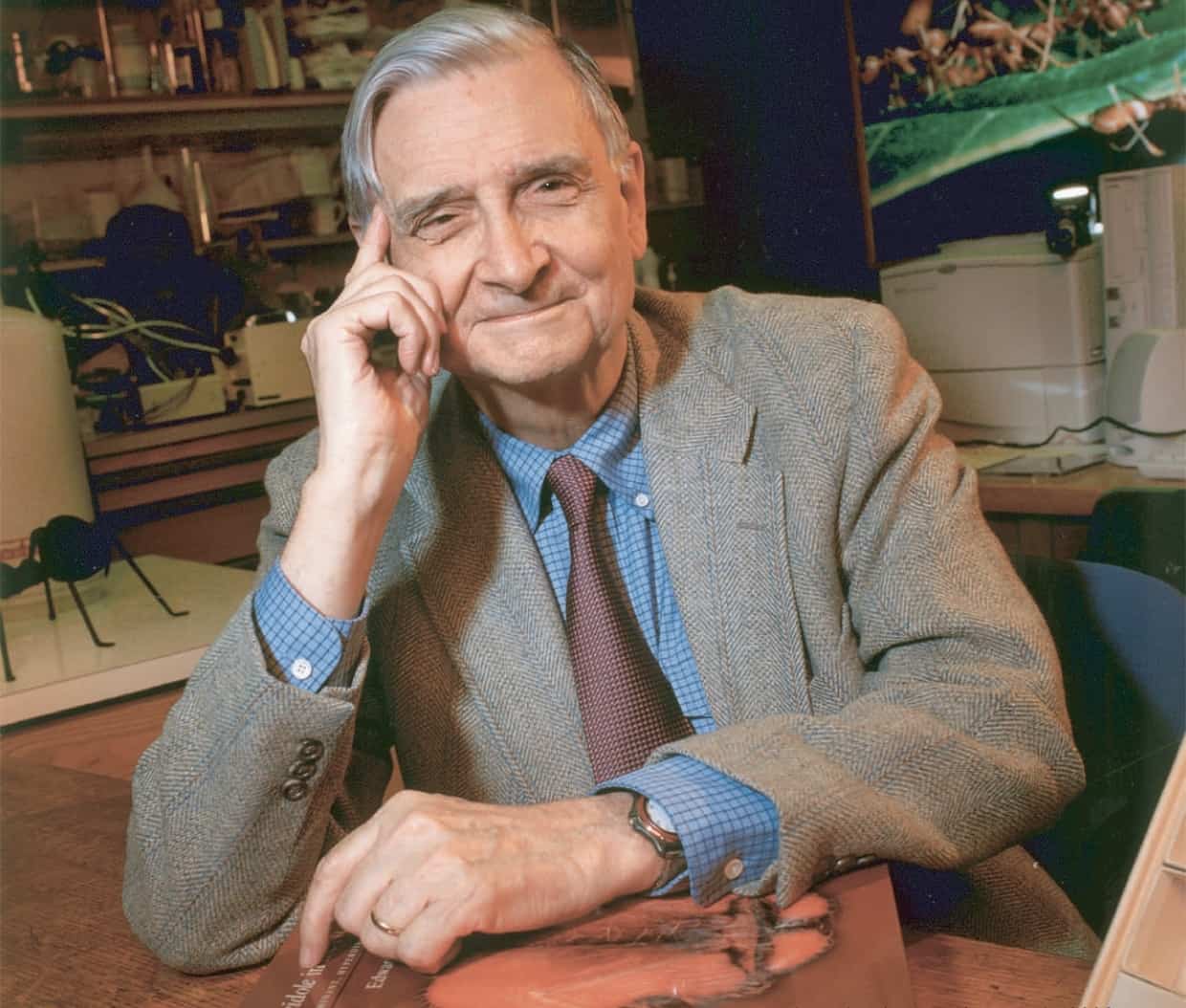

Edward Osborne Wilson (born June 10, 1929), usually cited as E. O. Wilson, is an American biologist, naturalist, and writer. His biological specialty is myrmecology, the study of ants, on which he has been called the world’s leading expert.Wilson has been called “the father of sociobiology” and “the father of biodiversity” for his environmental advocacy, and his secular-humanist and deist ideas pertaining to religious and ethical matters. Among his greatest contributions to ecological theory is the theory of island biogeography, which he developed in collaboration with the mathematical ecologist Robert MacArthur. This theory served as the foundation of the field of conservation area design, as well as the unified neutral theory of biodiversity of Stephen Hubbell.
Wilson is the Pellegrino University Research Professor, Emeritus in Entomology for the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology at Harvard University, a lecturer at Duke University, and a Fellow of the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry. He is a Humanist Laureate of the International Academy of Humanism. He is a two-time winner of the Pulitzer Prize for General Nonfiction (for On Human Nature in 1979, and The Ants in 1991) and a New York Times bestselling author for The Social Conquest of Earth, Letters to a Young Scientist, and The Meaning of Human Existence.
Read More About E. O. Wilson / Source
Avicenna
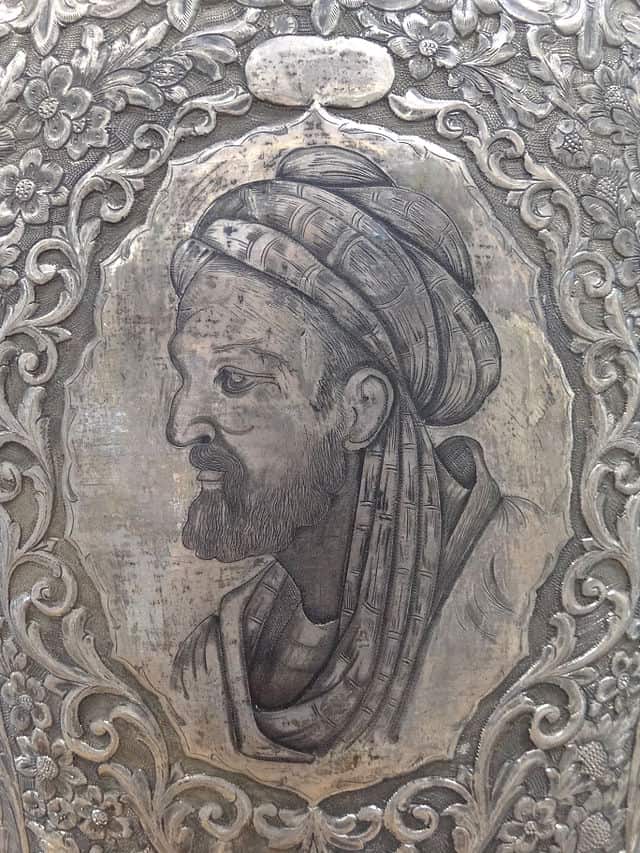

Ibn Sina, also known as Abu Ali Sina, Pur Sina, and often known in the West as Avicenna (c. 980 – June 1037), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, thinkers and writers of the Islamic Golden Age, and the father of early modern medicine. Sajjad H. Rizvi has called Avicenna “arguably the most influential philosopher of the pre-modern era”. He was a Muslim Peripatetic philosopher influenced by Aristotelian philosophy. Of the 450 works he is believed to have written, around 240 have survived, including 150 on philosophy and 40 on medicine.His most famous works are The Book of Healing, a philosophical and scientific encyclopedia, and The Canon of Medicine, a medical encyclopedia which became a standard medical text at many medieval universities and remained in use as late as 1650.Besides philosophy and medicine, Avicenna’s corpus includes writings on astronomy, alchemy, geography and geology, psychology, Islamic theology, logic, mathematics, physics and works of poetry.
Read More About Avicenna / Source
Carl Linnaeus
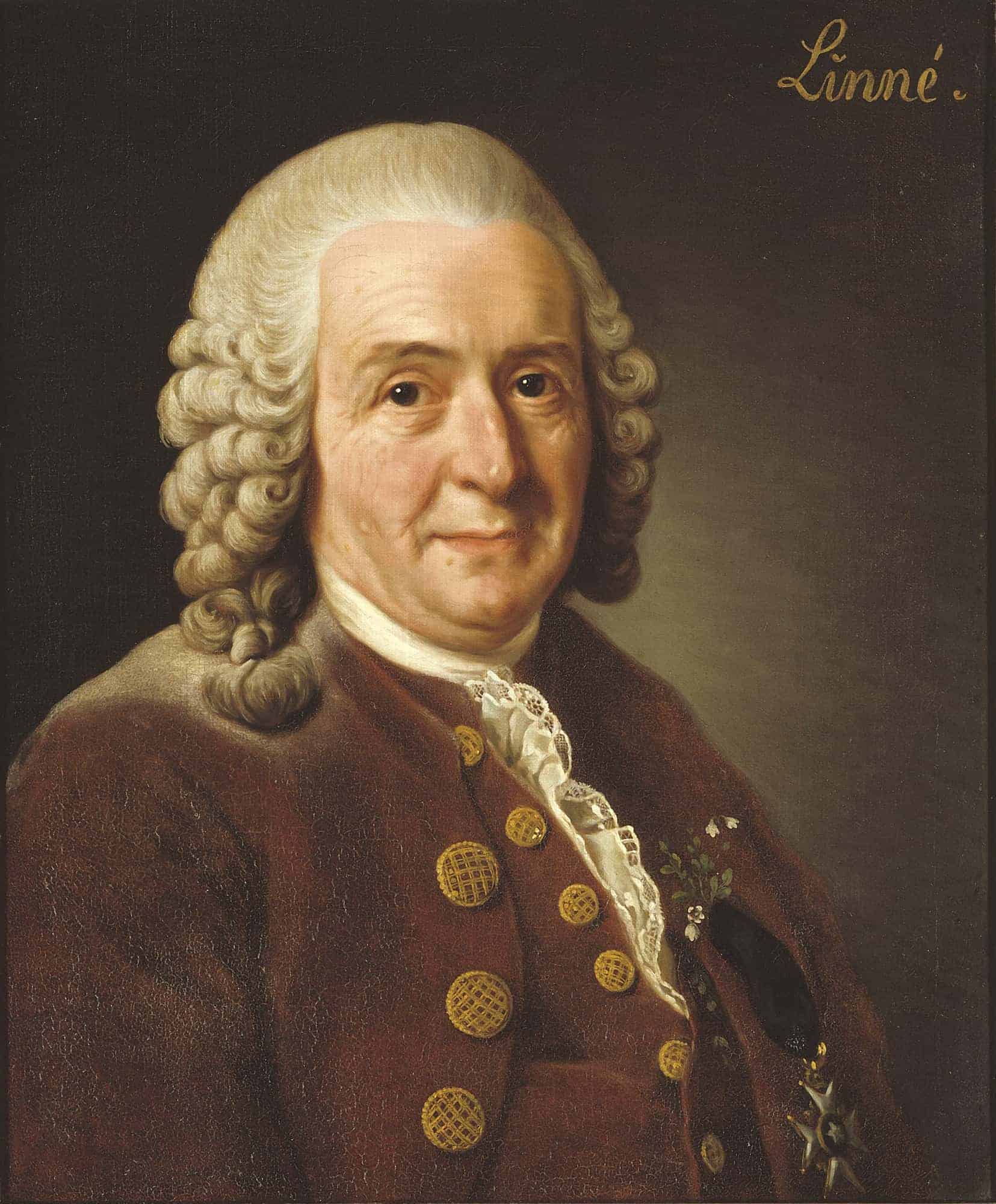

Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement as Carl von Linné, was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the “father of modern taxonomy”. Many of his writings were in Latin, and his name is rendered in Latin as Carolus Linnæus (after 1761 Carolus a Linné).
Linnaeus was born in the countryside of Småland in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his Systema Naturae in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect and classify animals, plants, and minerals, while publishing several volumes. He was one of the most acclaimed scientists in Europe at the time of his death.
Read More About Carl Linnaeus / Source
Dmitri Mendeleev
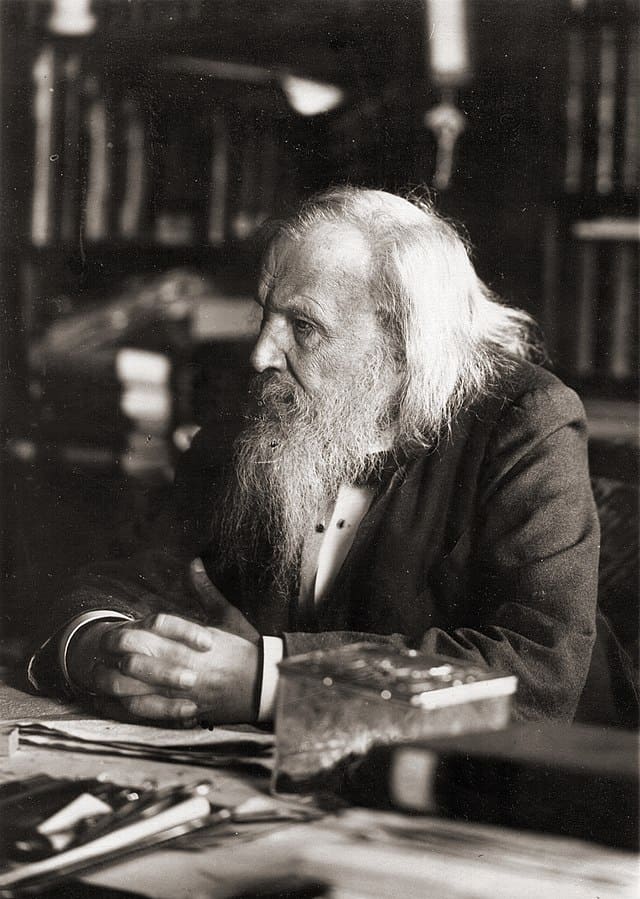

Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev [(often romanized as Mendeleyev or Mendeleef) (8 February 1834 – 2 February 1907)] was a Russian chemist and inventor. He is best remembered for formulating the Periodic Law and creating a farsighted version of the periodic table of elements. He used the Periodic Law not only to correct the then-accepted properties of some known elements, such as the valence and atomic weight of uranium, but also to predict the properties of eight elements that were yet to be discovered.
Read More About Dmitri Mendeleev / Source
Paul Dirac
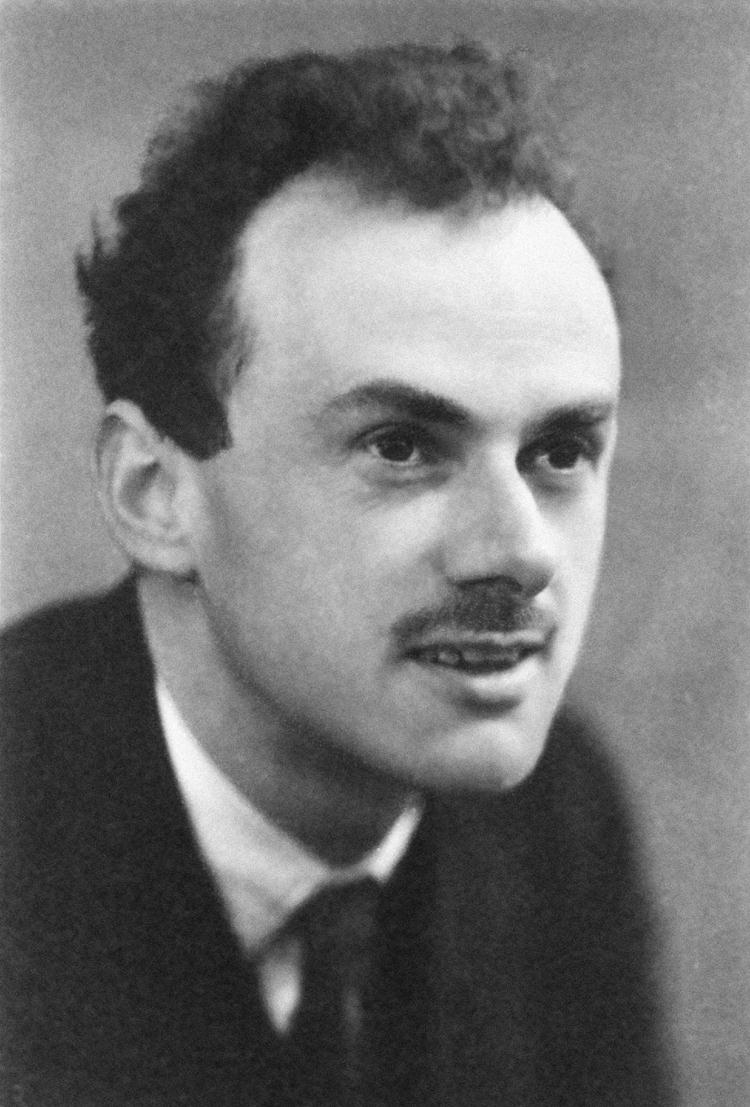
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac (; 8 August 1902 – 20 October 1984) was an English theoretical physicist who is regarded as one of the most significant physicists of the 20th century.Dirac made fundamental contributions to the early development of both quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics. Among other discoveries, he formulated the Dirac equation which describes the behaviour of fermions and predicted the existence of antimatter. Dirac shared the 1933 Nobel Prize in Physics with Erwin Schrödinger “for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory”. He also made significant contributions to the reconciliation of general relativity with quantum mechanics.
Dirac was regarded by his friends and colleagues as unusual in character. In a 1926 letter to Paul Ehrenfest, Albert Einstein wrote of Dirac, “I have trouble with Dirac. This balancing on the dizzying path between genius and madness is awful.” In another letter he wrote, “I don’t understand Dirac at all (Compton effect).”He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge, was a member of the Center for Theoretical Studies, University of Miami, and spent the last decade of his life at Florida State University.
Read More About Paul Dirac / Source
Enrico Fermi
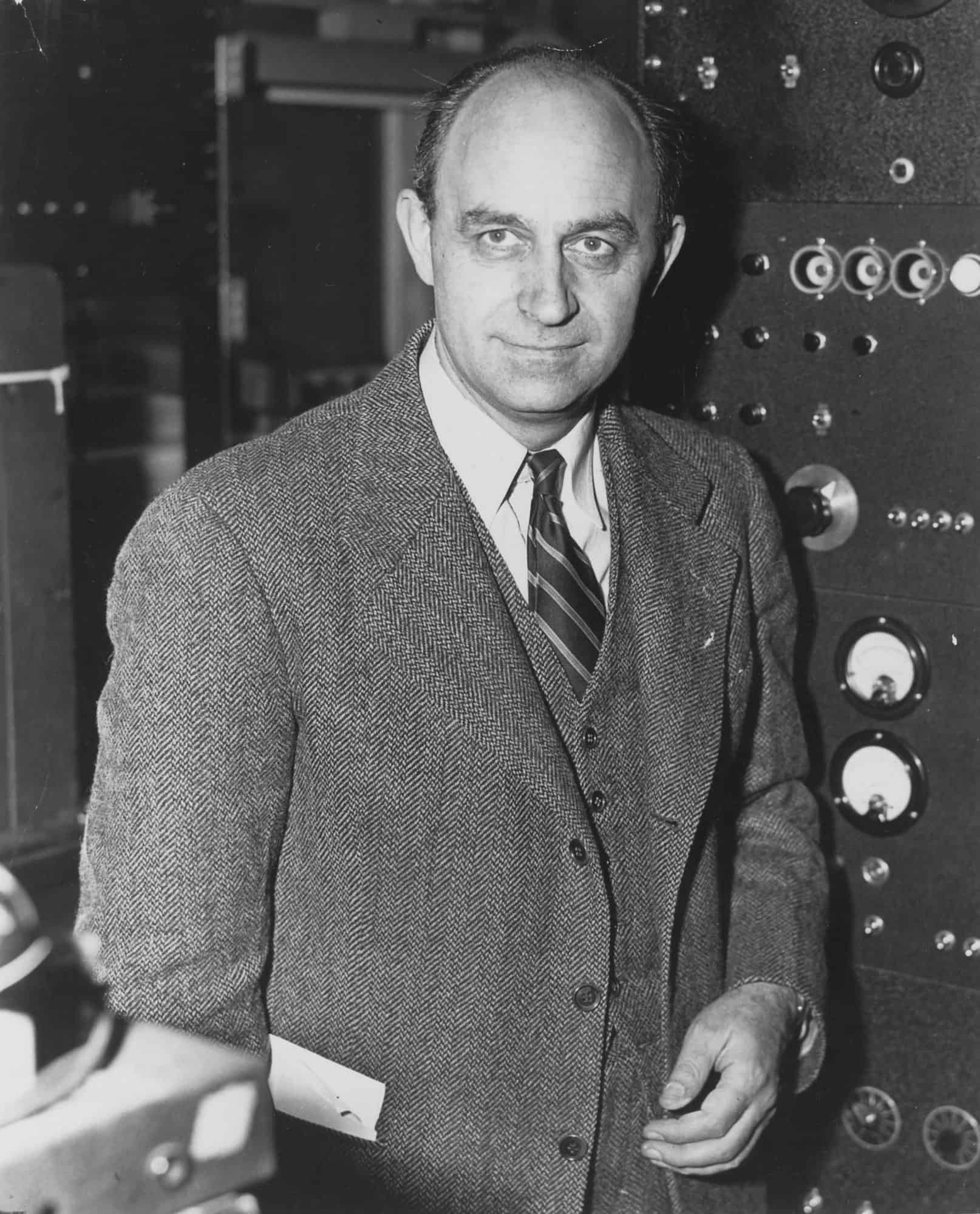

Enrico Fermi ( 29 September 1901 – 28 November 1954) was an Italian (later naturalized American) physicist and the creator of the world’s first nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1. He has been called the “architect of the nuclear age” and the “architect of the atomic bomb”. He was one of very few physicists to excel in both theoretical physics and experimental physics. Fermi was awarded the 1938 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on induced radioactivity by neutron bombardment and for the discovery of transuranium elements. With his colleagues, Fermi filed several patents related to the use of nuclear power, all of which were taken over by the US government. He made significant contributions to the development of statistical mechanics, quantum theory, and nuclear and particle physics.
Fermi’s first major contribution involved the field of statistical mechanics. After Wolfgang Pauli formulated his exclusion principle in 1925, Fermi followed with a paper in which he applied the principle to an ideal gas, employing a statistical formulation now known as Fermi–Dirac statistics. Today, particles that obey the exclusion principle are called “fermions”.
Read More About Enrico Fermi / Source
Ernest Rutherford
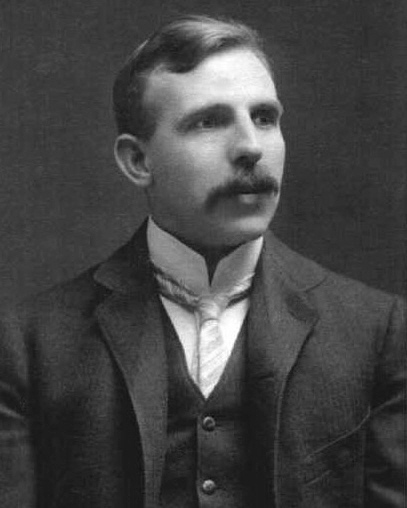

Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, (30 August 1871 – 19 October 1937) was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics. Encyclopædia Britannica considers him to be the greatest experimentalist since Michael Faraday (1791–1867). Like all New Zealanders at this time, he was a British subject, and spent much of his career in the United Kingdom.
In early work, Rutherford discovered the concept of radioactive half-life, the radioactive element radon, and differentiated and named alpha and beta radiation. This work was performed at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is the basis for the Nobel Prize in Chemistry he was awarded in 1908 “for his investigations into the disintegration of the elements, and the chemistry of radioactive substances”, for which he was the first Canadian and Oceanian Nobel laureate.
Read More About Ernest Rutherford / Source
Barbara McClintock
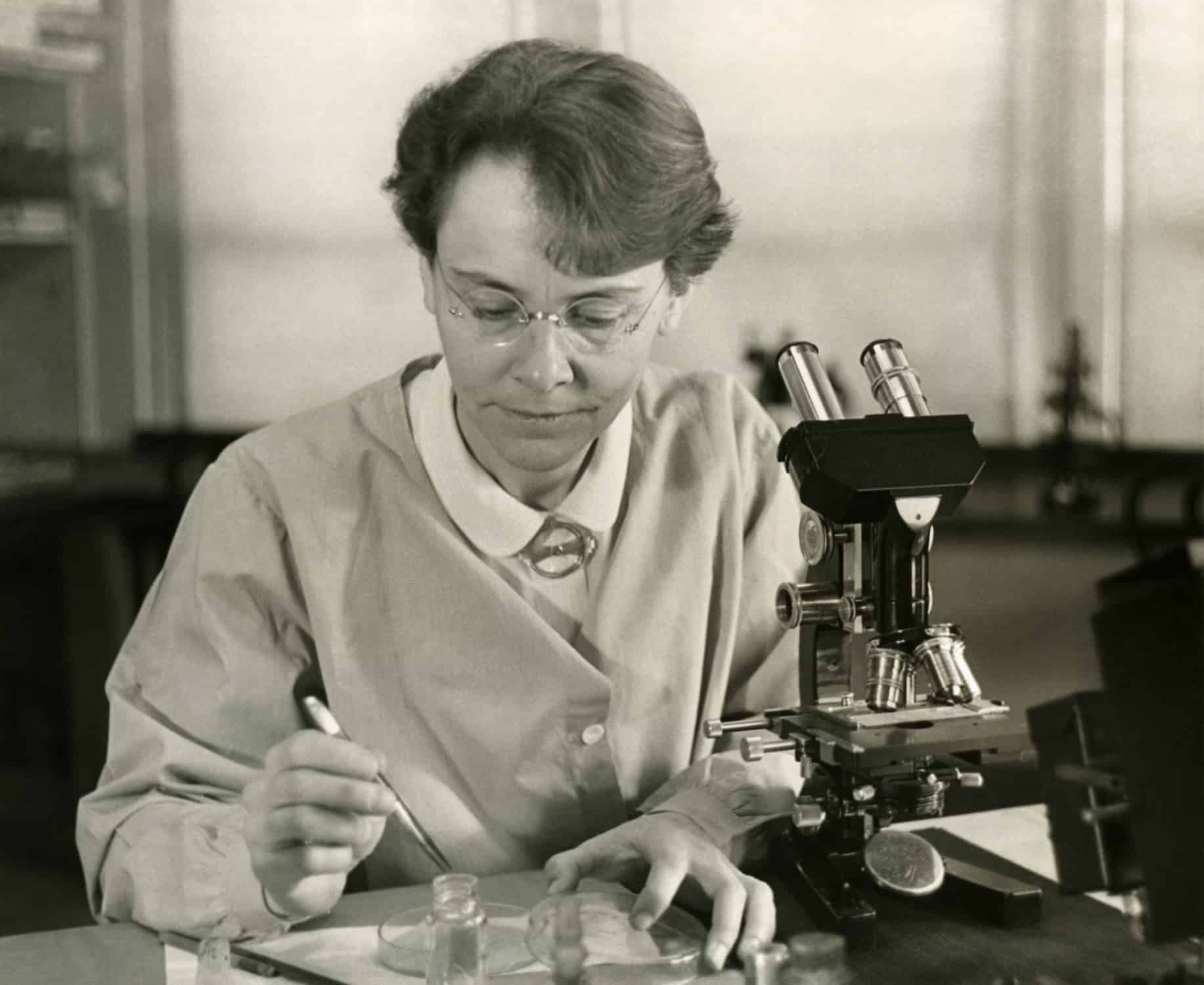

Barbara McClintock (June 16, 1902 – September 2, 1992) was an American scientist and cytogeneticist who was awarded the 1983 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. McClintock received her PhD in botany from Cornell University in 1927. There she started her career as the leader in the development of maize cytogenetics, the focus of her research for the rest of her life. From the late 1920s, McClintock studied chromosomes and how they change during reproduction in maize. She developed the technique for visualizing maize chromosomes and used microscopic analysis to demonstrate many fundamental genetic ideas. One of those ideas was the notion of genetic recombination by crossing-over during meiosis—a mechanism by which chromosomes exchange information. She produced the first genetic map for maize, linking regions of the chromosome to physical traits. She demonstrated the role of the telomere and centromere, regions of the chromosome that are important in the conservation of genetic information. She was recognized as among the best in the field, awarded prestigious fellowships, and elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 1944.
During the 1940s and 1950s, McClintock discovered transposition and used it to demonstrate that genes are responsible for turning physical characteristics on and off. She developed theories to explain the suppression and expression of genetic information from one generation of maize plants to the next. Due to skepticism of her research and its implications, she stopped publishing her data in 1953.
Read More About Barbara McClintock / Source
Otto Hahn
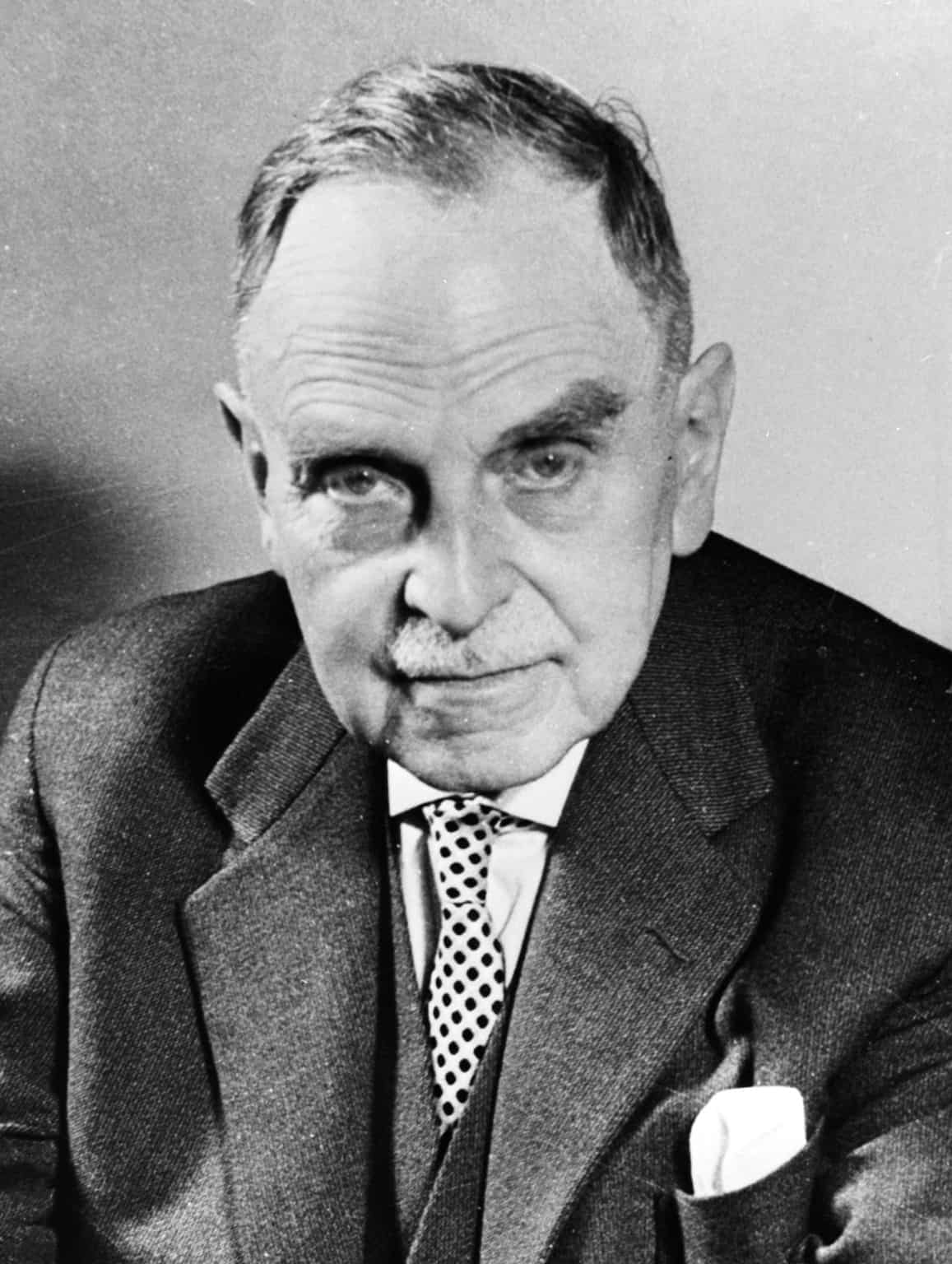

Otto Hahn (pronounced [ˈɔto ˈhaːn] (listen); 8 March 1879 – 28 July 1968) was a German chemist, and a pioneer in the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry. Hahn is referred to as the father of nuclear chemistry. Hahn and Lise Meitner discovered radioactive isotopes of radium, thorium, protactinium and uranium. He also discovered the phenomena of radioactive recoil and nuclear isomerism, and pioneered rubidium–strontium dating. In 1938, Hahn, Lise Meitner and Fritz Strassmann discovered nuclear fission, for which Hahn received the 1944 Nobel Prize for Chemistry. Nuclear fission was the basis for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.
A graduate of the University of Marburg, Hahn studied under Sir William Ramsay at University College London, and at McGill University in Montreal under Ernest Rutherford, where he discovered several new radioactive isotopes. He returned to Germany in 1906, and Emil Fischer placed a former woodworking shop in the basement of the Chemical Institute at the University of Berlin at his disposal to use as a laboratory. Hahn completed his habilitation in the spring of 1907, and became a Privatdozent. In 1912, he became head of the Radioactivity Department of the newly founded Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Chemistry.
Read More About Otto Hahn / Source
Robert Koch
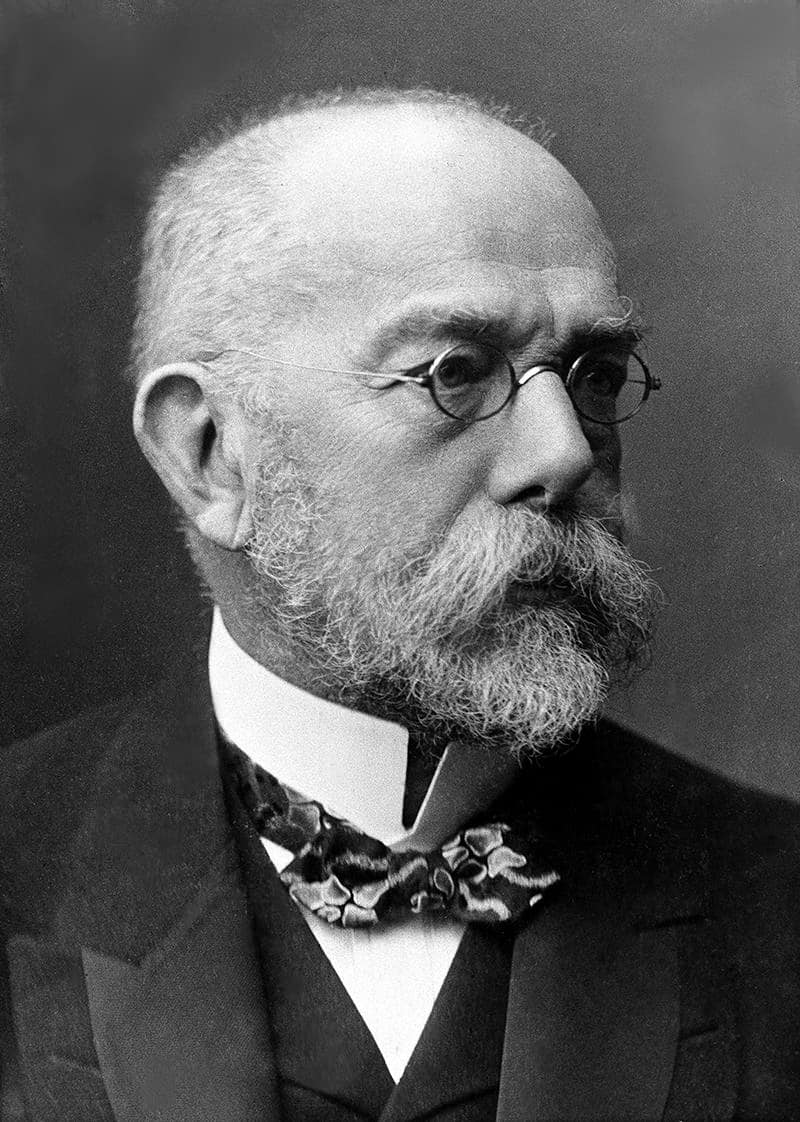

Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch (English: ; German: [ˈʁoː.bɛʁt kɔx] (listen); 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As one of the main founders of modern bacteriology, he identified the specific causative agents of tuberculosis, cholera, and anthrax and also gave experimental support for the concept of infectious disease, which included experiments on humans and animals. Koch created and improved laboratory technologies and techniques in the field of microbiology, and made key discoveries in public health. His research led to the creation of Koch’s postulates, a series of four generalized principles linking specific microorganisms to specific diseases that proved influential on subsequent epidemiological principles such as the Bradford Hill criteria. For his research on tuberculosis, Koch received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1905. The Robert Koch Institute is named in his honour.
Read More About Robert Koch / Source
Antoine Henri Becquerel

Antoine Henri Becquerel (15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French engineer, physicist, Nobel laureate, and the first person to discover evidence of radioactivity. For work in this field he, along with Marie Skłodowska-Curie (Marie Curie) and Pierre Curie, received the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics. The SI unit for radioactivity, the becquerel (Bq), is named after him.
Read More About Antoine Henri Becquerel / Source
Charles Darwin
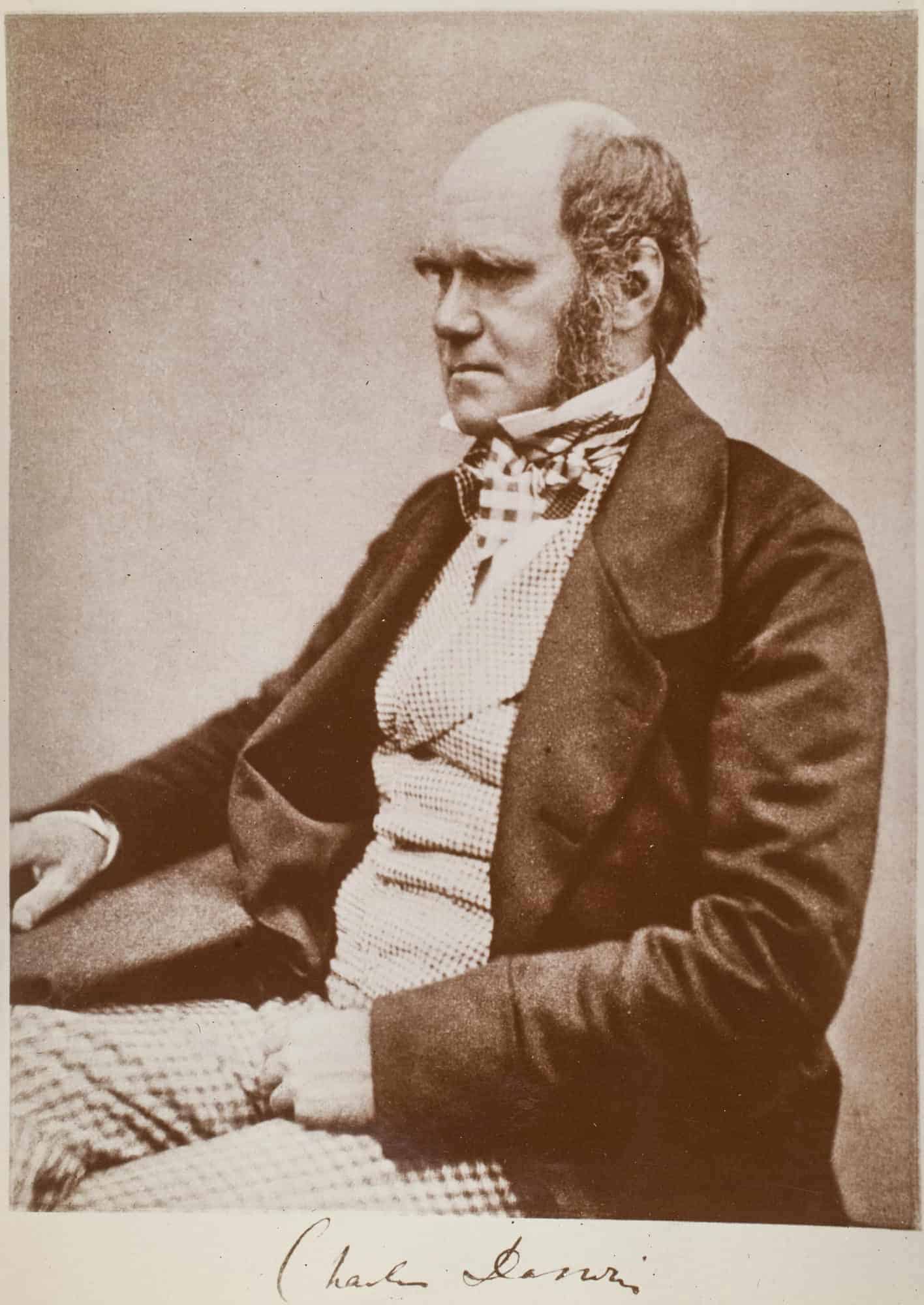

Charles Robert Darwin ( 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, best known for his contributions to the science of evolution. His proposition that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestors is now widely accepted, and considered a foundational concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history, and he was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.Darwin published his theory of evolution with compelling evidence in his 1859 book On the Origin of Species. By the 1870s, the scientific community and a majority of the educated public had accepted evolution as a fact. However, many favoured competing explanations which gave only a minor role to natural selection, and it was not until the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis from the 1930s to the 1950s that a broad consensus developed in which natural selection was the basic mechanism of evolution.
Read More About Charles Darwin / Source
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz

Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz ( 1 July 1646 [O.S. 21 June] – 14 November 1716) was a prominent German polymath and one of the most important logicians, mathematicians and natural philosophers of the Enlightenment. As a representative of the seventeenth-century tradition of rationalism, Leibniz developed, as his most prominent accomplishment, the ideas of differential and integral calculus, independently of Isaac Newton’s contemporaneous developments. Mathematical works have consistently favored Leibniz’s notation as the conventional expression of calculus. It was only in the 20th century that Leibniz’s law of continuity and transcendental law of homogeneity found mathematical implementation (by means of non-standard analysis). He became one of the most prolific inventors in the field of mechanical calculators. While working on adding automatic multiplication and division to Pascal’s calculator, he was the first to describe a pinwheel calculator in 1685 and invented the Leibniz wheel, used in the arithmometer, the first mass-produced mechanical calculator. He also refined the binary number system, which is the foundation of nearly all digital (electronic, solid-state, discrete logic) computers, including the Von Neumann machine, which is the standard design paradigm, or “computer architecture”, followed from the second half of the 20th century, and into the 21st.
Read More About Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz / Source
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
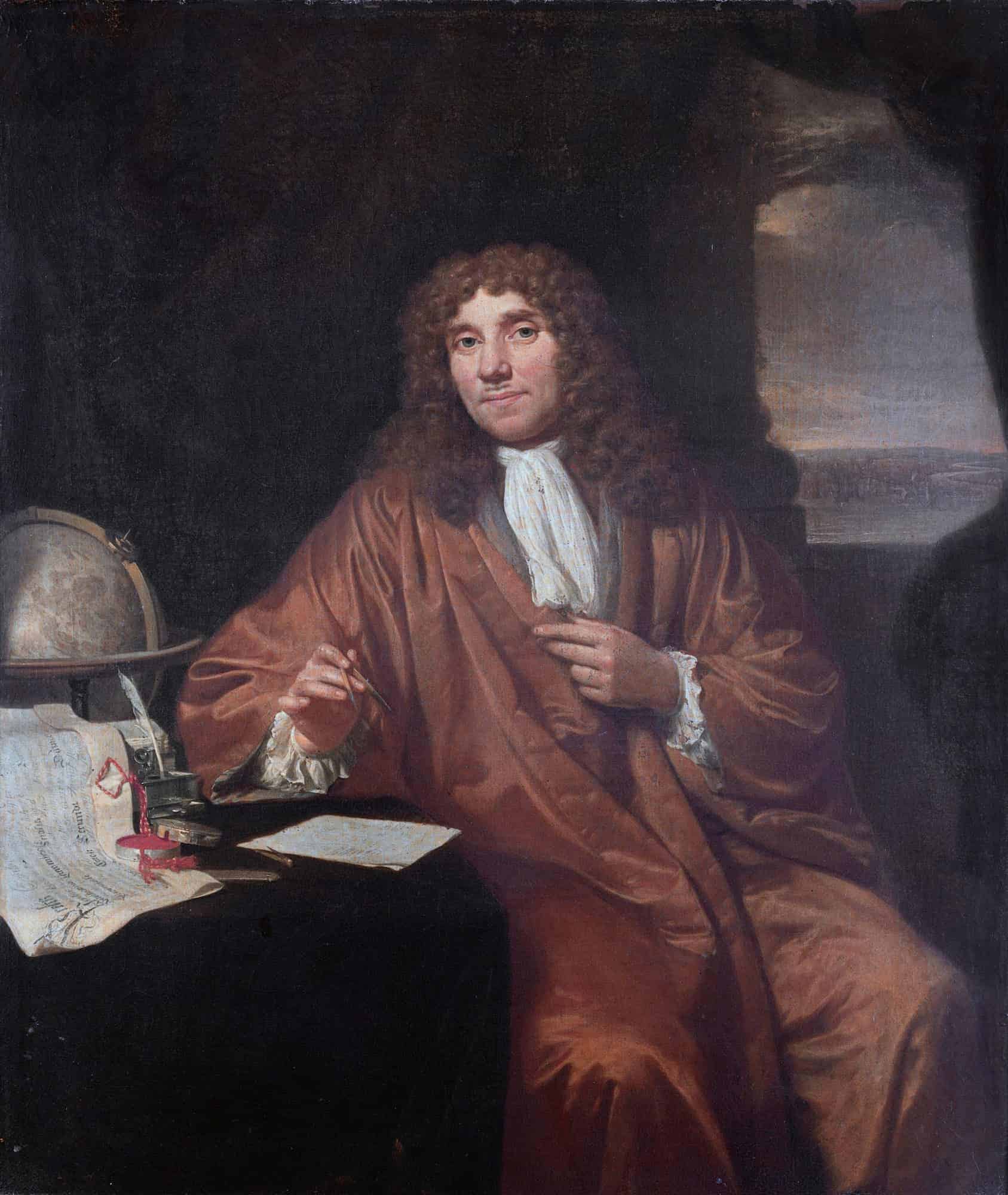

Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch businessman and scientist in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as “the Father of Microbiology”, and one of the first microscopists and microbiologists. Van Leeuwenhoek is best known for his pioneering work in microscopy and for his contributions toward the establishment of microbiology as a scientific discipline.
Raised in Delft, Dutch Republic, van Leeuwenhoek worked as a draper in his youth and founded his own shop in 1654. He became well recognized in municipal politics and developed an interest in lensmaking. In the 1670s, he started to explore microbial life with his microscope. This was one of the notable achievements of the Golden Age of Dutch exploration and discovery (c. 1590s–1720s).
Read More About Antonie van Leeuwenhoek / Source
Lise Meitner
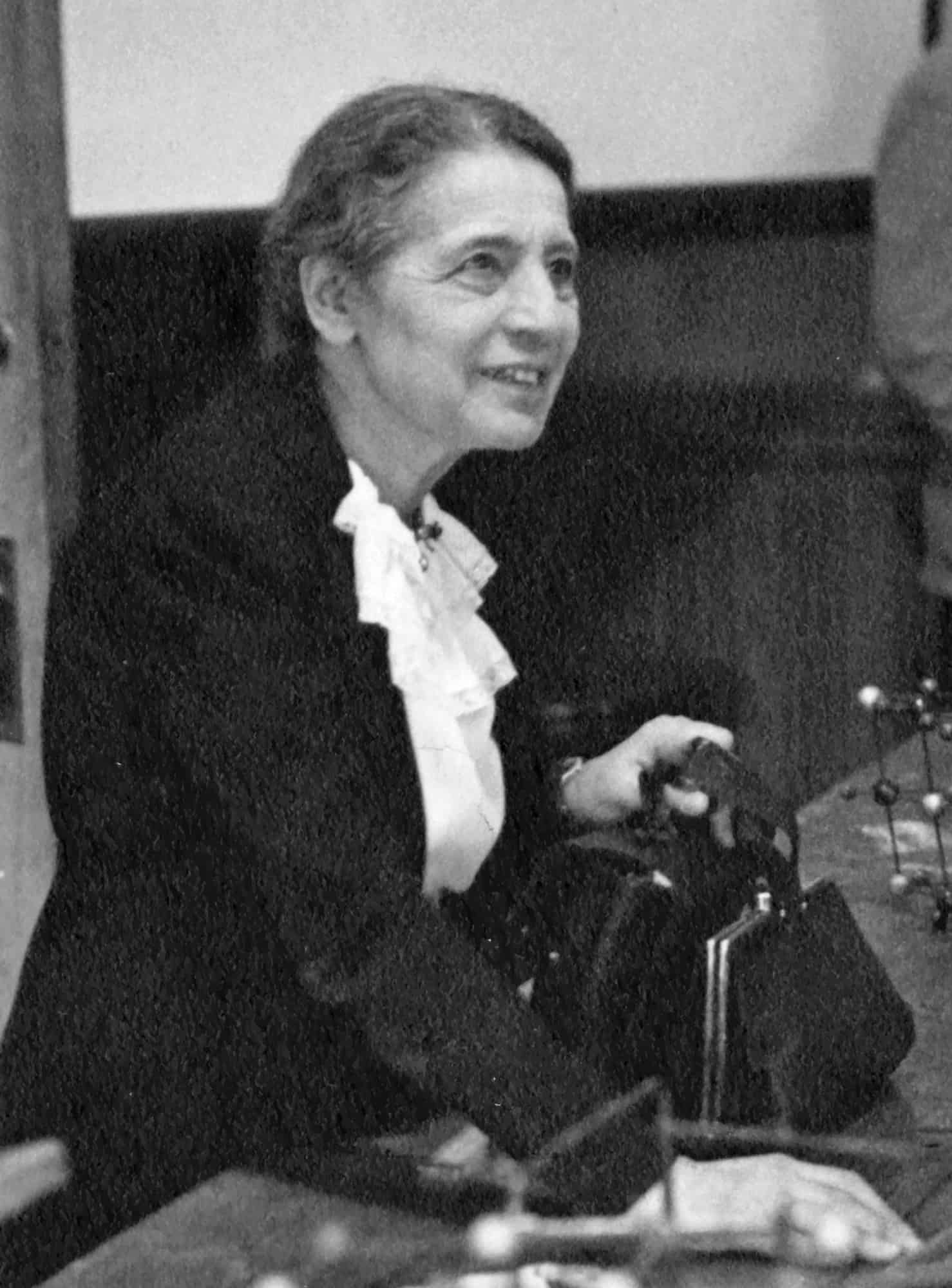

Lise Meitner ( 7 November 1878 – 27 October 1968) was an Austrian-Swedish physicist who contributed to the discoveries of the element protactinium and nuclear fission. While working at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute on radioactivity, she discovered the radioactive isotope protactinium-231 in 1917. In 1938, Meitner and nephew-physicist Otto Robert Frisch discovered nuclear fission. She was praised by Albert Einstein as the “German Marie Curie”.Completing her doctoral research in 1905, Meitner became the first woman from the University of Vienna and second in the world to earn a doctorate in physics. She spent most of her scientific career in Berlin, Germany, where she was a physics professor and a department head at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute; she was the first woman to become a full professor of physics in Germany. She lost these positions in the 1930s because of the anti-Jewish Nuremberg Laws of Nazi Germany, and in 1938 she fled to Sweden, where she lived for many years, ultimately becoming a Swedish citizen.
Read More About Lise Meitner / Source
Maurice Wilkins
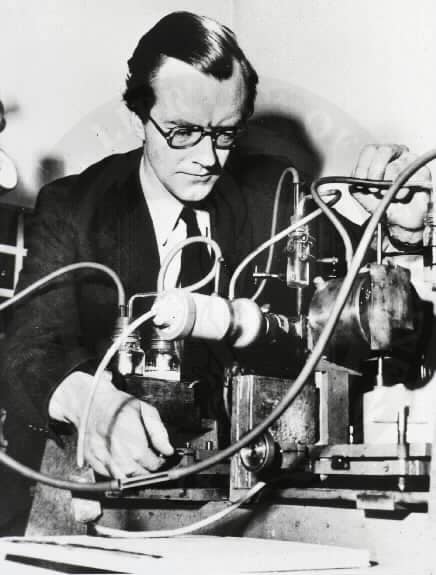
Maurice Hugh Frederick Wilkins CBE FRS (15 December 1916 – 5 October 2004) was a New Zealand-born British biophysicist and Nobel laureate whose research spanned multiple areas of physics and biophysics, contributing to the scientific understanding of phosphorescence, isotope separation, optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction, and to the development of radar. He is best known for his work at King’s College London on the structure of DNA.
Read More About Maurice Wilkins / Source
Alessandro Volta

Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (18 February 1745 – 5 March 1827) was an Italian physicist, chemist, and pioneer of electricity and power who is credited as the inventor of the electric battery and the discoverer of methane. He invented the Voltaic pile in 1799, and reported the results of his experiments in 1800 in a two-part letter to the President of the Royal Society. With this invention Volta proved that electricity could be generated chemically and debunked the prevalent theory that electricity was generated solely by living beings. Volta’s invention sparked a great amount of scientific excitement and led others to conduct similar experiments which eventually led to the development of the field of electrochemistry.Volta also drew admiration from Napoleon Bonaparte for his invention, and was invited to the Institute of France to demonstrate his invention to the members of the Institute. Volta enjoyed a certain amount of closeness with the emperor throughout his life and he was conferred numerous honours by him. Volta held the chair of experimental physics at the University of Pavia for nearly 40 years and was widely idolised by his students.Despite his professional success, Volta tended to be a person inclined towards domestic life and this was more apparent in his later years.
Read More About Alessandro Volta / Source
Craig Venter
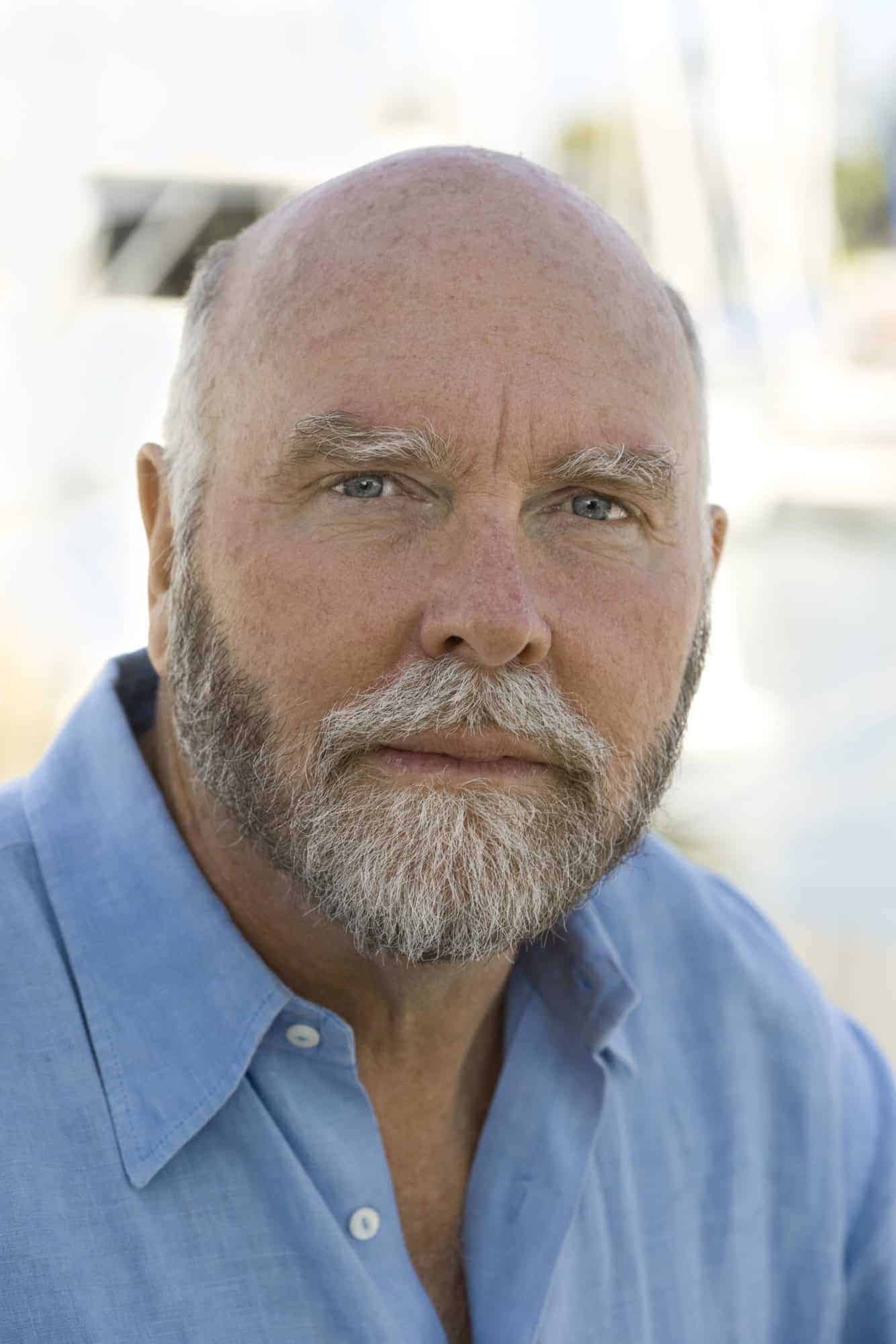

John Craig Venter (born October 14, 1946) is an American biotechnologist and businessman. He is known for leading the first draft sequence of the human genome and assembled the first team to transfect a cell with a synthetic chromosome. Venter founded Celera Genomics, The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) and the J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI), where he currently serves as CEO. He was the co-founder of Human Longevity Inc. and Synthetic Genomics. He was listed on Time magazine’s 2007 and 2008 Time 100 list of the most influential people in the world. In 2010, the British magazine New Statesman listed Craig Venter at 14th in the list of “The World’s 50 Most Influential Figures 2010”. In 2012, Venter was honored with Dan David Prize for his contribution to genome research. He is a member of the USA Science and Engineering Festival’s Advisory Board.
Read More About Craig Venter / Source
Stephen Jay Gould

Stephen Jay Gould ( September 10, 1941 – May 20, 2002) was an American paleontologist, evolutionary biologist, and historian of science. He was one of the most influential and widely read authors of popular science of his generation. Gould spent most of his career teaching at Harvard University and working at the American Museum of Natural History in New York. In 1996, Gould was hired as the Vincent Astor Visiting Research Professor of Biology at New York University, where he divided his time teaching there and at Harvard.
Gould’s most significant contribution to evolutionary biology was the theory of punctuated equilibrium developed with Niles Eldredge in 1972. The theory proposes that most evolution is characterized by long periods of evolutionary stability, infrequently punctuated by swift periods of branching speciation. The theory was contrasted against phyletic gradualism, the popular idea that evolutionary change is marked by a pattern of smooth and continuous change in the fossil record.Most of Gould’s empirical research was based on the land snail genera Poecilozonites and Cerion. He also made important contributions to evolutionary developmental biology, receiving broad professional recognition for his book Ontogeny and Phylogeny. In evolutionary theory he opposed strict selectionism, sociobiology as applied to humans, and evolutionary psychology.
Read More About Stephen Jay Gould / Source
Rachel Carson
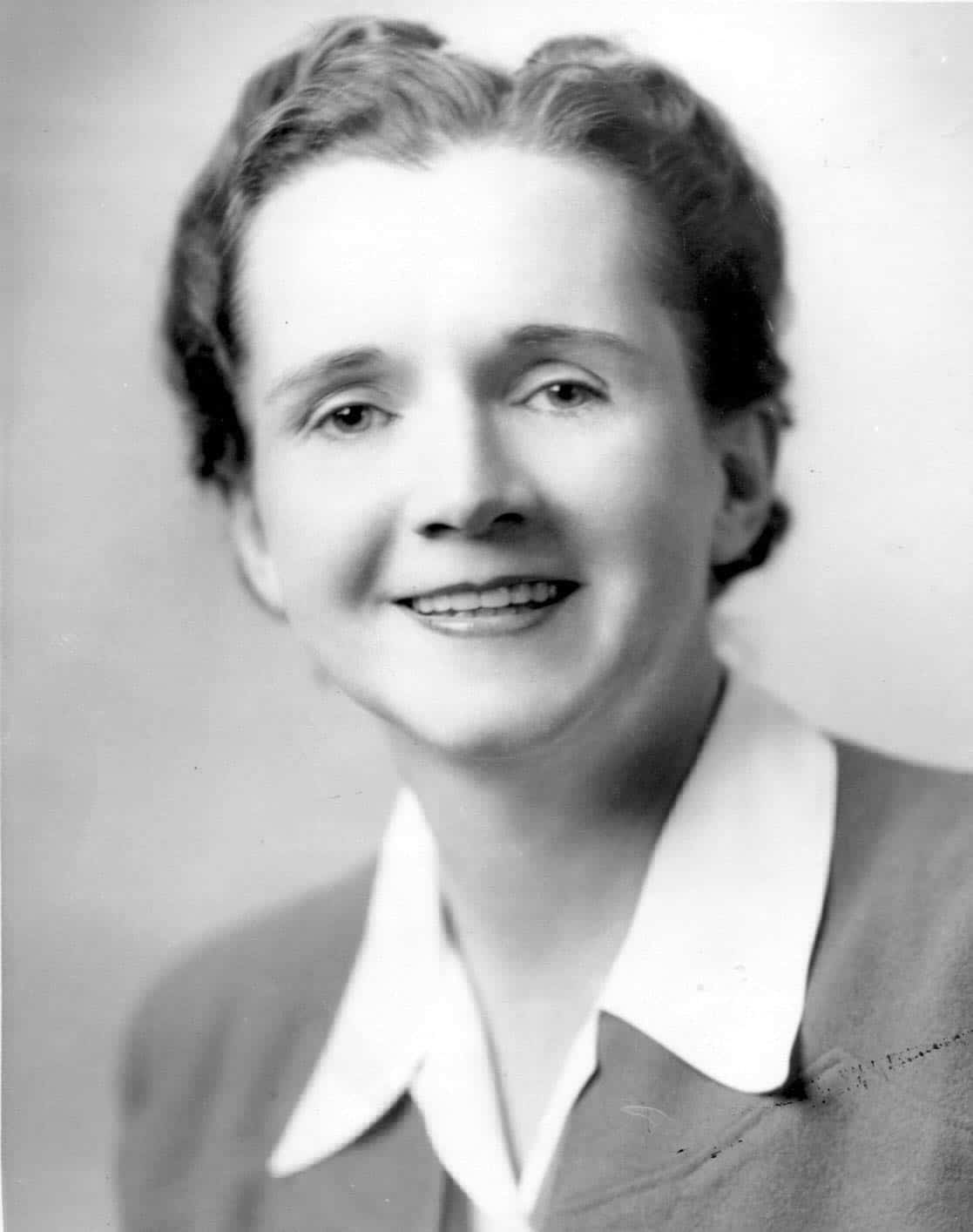

Rachel Louise Carson (May 27, 1907 – April 14, 1964) was an American marine biologist, author, and conservationist whose book Silent Spring and other writings are credited with advancing the global environmental movement.
Carson began her career as an aquatic biologist in the U.S. Bureau of Fisheries, and became a full-time nature writer in the 1950s. Her widely praised 1951 bestseller The Sea Around Us won her a U.S. National Book Award, recognition as a gifted writer, and financial security. Her next book, The Edge of the Sea, and the reissued version of her first book, Under the Sea Wind, were also bestsellers. This sea trilogy explores the whole of ocean life from the shores to the depths.
Late in the 1950s, Carson turned her attention to conservation, especially some problems that she believed were caused by synthetic pesticides. The result was the book Silent Spring (1962), which brought environmental concerns to an unprecedented share of the American people. Although Silent Spring was met with fierce opposition by chemical companies, it spurred a reversal in national pesticide policy, which led to a nationwide ban on DDT and other pesticides. It also inspired a grassroots environmental movement that led to the creation of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Carson was posthumously awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by President Jimmy Carter.
Read More About Rachel Carson / Source
Linus Pauling
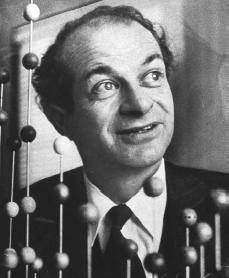
Linus Carl Pauling ( February 28, 1901 – August 19, 1994) was an American chemist, biochemist, chemical engineer, peace activist, author, and educator. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. New Scientist called him one of the 20 greatest scientists of all time, and as of 2000, he was rated the 16th most important scientist in history. For his scientific work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. For his peace activism, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962. He is one of four individuals to have won more than one Nobel Prize (the others being Marie Curie, John Bardeen and Frederick Sanger). Of these, he is the only person to have been awarded two unshared Nobel Prizes, and one of two people to be awarded Nobel Prizes in different fields, the other being Marie Curie. He was married to the American human rights activist Ava Helen Pauling.
Pauling was one of the founders of the fields of quantum chemistry and molecular biology. His contributions to the theory of the chemical bond include the concept of orbital hybridisation and the first accurate scale of electronegativities of the elements.
Read More About Linus Pauling / Source
Max Planck
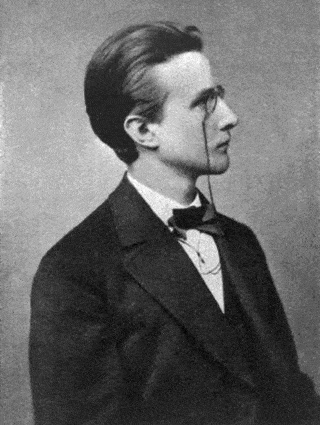
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck, ForMemRS ( 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.Planck made many contributions to theoretical physics, but his fame as a physicist rests primarily on his role as the originator of quantum theory, which revolutionized human understanding of atomic and subatomic processes. In 1948, the German scientific institution Kaiser Wilhelm Society (of which Planck was twice president) was renamed Max Planck Society (MPS). The MPS now includes 83 institutions representing a wide range of scientific directions.
Read More About Max Planck / Source
Blaise Pascal
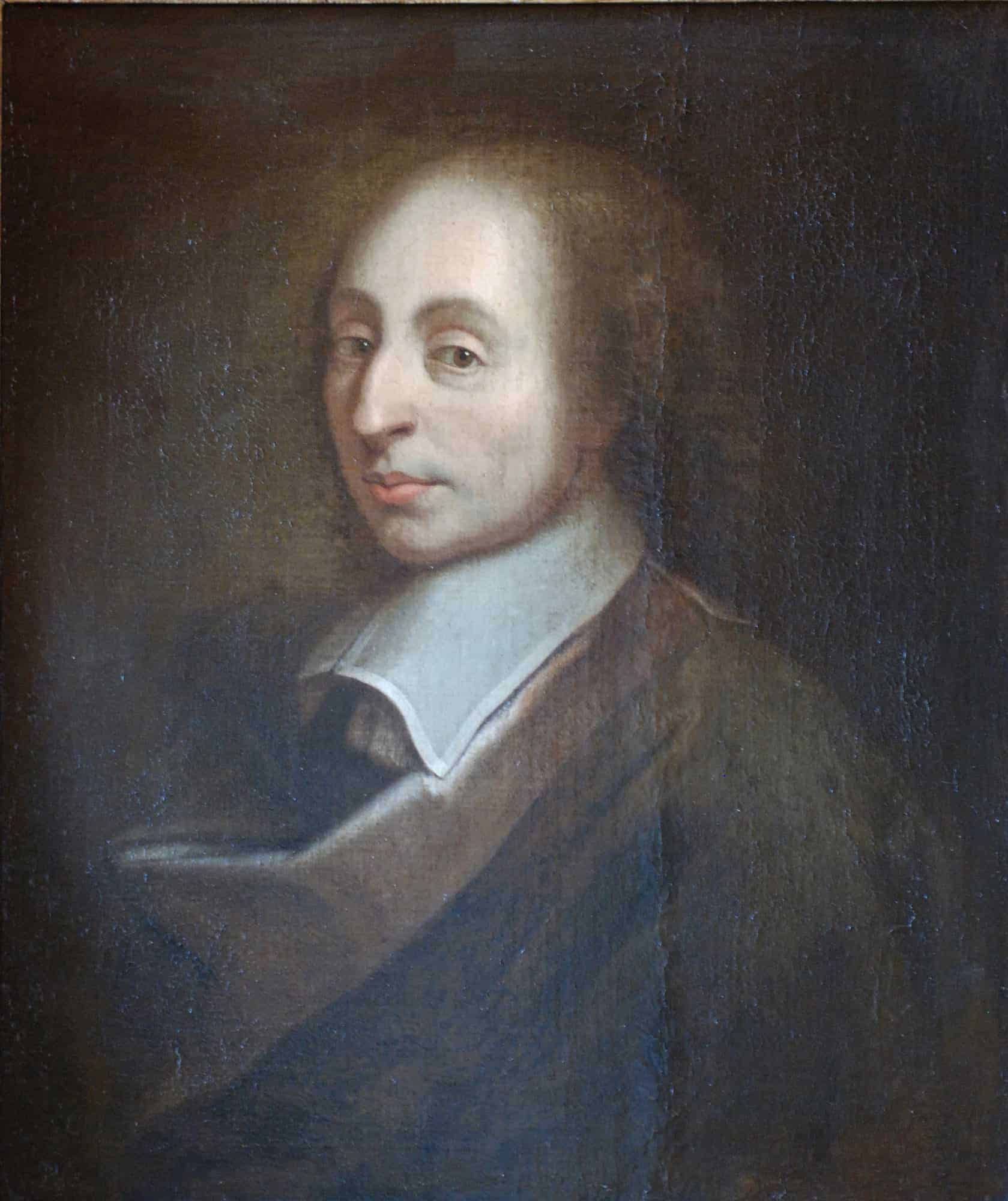

Blaise Pascal ( 19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, writer and Catholic theologian.
He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pascal’s earliest mathematical work was on the conics sections; he wrote a significant treatise on the subject of projective geometry at the age of 16. He later corresponded with Pierre de Fermat on probability theory, strongly influencing the development of modern economics and social science. In 1642, while still a teenager, he started some pioneering work on calculating machines (called Pascal’s calculators and later Pascalines), establishing him as one of the first two inventors of the mechanical calculator.He also worked in the natural and applied sciences, where he made important contributions to the study of fluids, and clarified the concepts of pressure and vacuum by generalising the work of Evangelista Torricelli. Following Galileo Galilei and Torricelli, in 1647, he rebutted Aristotle’s followers who insisted that nature abhors a vacuum. Pascal’s results caused many disputes before being accepted. Pascal also wrote in defense of the scientific method.
Read More About Blaise Pascal / Source
Tim Berners-Lee

Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web. He is a Professorial Fellow of Computer Science at the University of Oxford and a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on 12 March 1989, then implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and server via the Internet in mid-November.Berners-Lee is the director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) which oversees the continued development of the Web. He is also the founder of the World Wide Web Foundation and is a senior researcher and holder of the 3Com founders chair at the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). He is a director of the Web Science Research Initiative (WSRI) and a member of the advisory board of the MIT Center for Collective Intelligence. In 2011, he was named as a member of the board of trustees of the Ford Foundation. He is a founder and president of the Open Data Institute and is currently an advisor at social network MeWe.
Read More About Tim Berners-Lee / Source
James Watson

James Dewey Watson KBE (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and Maurice Wilkins were awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine “for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material”. In subsequent years, it has been recognized that Watson and his colleagues did not properly attribute colleague Rosalind Franklin for her contributions to the discovery of the double helix structure.Watson earned degrees at the University of Chicago (BS, 1947) and Indiana University (PhD, 1950). Following a post-doctoral year at the University of Copenhagen with Herman Kalckar and Ole Maaløe, Watson worked at the University of Cambridge’s Cavendish Laboratory in England, where he first met his future collaborator Francis Crick. From 1956 to 1976, Watson was on the faculty of the Harvard University Biology Department, promoting research in molecular biology.
Read More About James Watson / Source
John von Neumann

John von Neumann ( December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. Von Neumann was generally regarded as the foremost mathematician of his time and said to be “the last representative of the great mathematicians”. He integrated pure and applied sciences.
Read More About John von Neumann / Source
Werner Heisenberg

Werner Karl Heisenberg ( 5 December 1901 – 1 February 1976) was a German theoretical physicist and one of the key pioneers of quantum mechanics. He published his work in 1925 in a breakthrough paper. In the subsequent series of papers with Max Born and Pascual Jordan, during the same year, this matrix formulation of quantum mechanics was substantially elaborated. He is known for the uncertainty principle, which he published in 1927. Heisenberg was awarded the 1932 Nobel Prize in Physics “for the creation of quantum mechanics”.Heisenberg also made important contributions to the theories of the hydrodynamics of turbulent flows, the atomic nucleus, ferromagnetism, cosmic rays, and subatomic particles. He was a principal scientist in the German nuclear weapons program during World War II. He was also instrumental in planning the first West German nuclear reactor at Karlsruhe, together with a research reactor in Munich, in 1957.
Read More About Werner Heisenberg / Source
Lord (William Thomson) Kelvin

William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 1824 – 17 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important work in the mathematical analysis of electricity and formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and did much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its modern form. He received the Royal Society’s Copley Medal in 1883, was its President 1890–1895, and in 1892 was the first British scientist to be elevated to the House of Lords.Absolute temperatures are stated in units of kelvin in his honour. While the existence of a lower limit to temperature (absolute zero) was known prior to his work, Kelvin is known for determining its correct value as approximately −273.15 degrees Celsius or −459.67 degrees Fahrenheit. The Joule–Thomson effect is also named in his honour.
He worked closely with mathematics professor Hugh Blackburn in his work. He also had a career as an electric telegraph engineer and inventor, which propelled him into the public eye and ensured his wealth, fame and honour. For his work on the transatlantic telegraph project he was knighted in 1866 by Queen Victoria, becoming Sir William Thomson. He had extensive maritime interests and was most noted for his work on the mariner’s compass, which previously had limited reliability.
He was ennobled in 1892 in recognition of his achievements in thermodynamics, and of his opposition to Irish Home Rule, becoming Baron Kelvin, of Largs in the County of Ayr. The title refers to the River Kelvin, which flows near his laboratory at the University of Glasgow’s Gilmorehill home at Hillhead. Despite offers of elevated posts from several world-renowned universities, Kelvin refused to leave Glasgow, remaining until his eventual retirement from that post in 1899. Active in industrial research and development, he was recruited around 1899 by George Eastman to serve as vice-chairman of the board of the British company Kodak Limited, affiliated with Eastman Kodak. In 1904 he became Chancellor of the University of Glasgow.His home was the red sandstone mansion Netherhall, in Largs, which he built in the 1870s and where he died. The Hunterian Museum at the University of Glasgow has a permanent exhibition on the work of Kelvin including many of his original papers, instruments, and other artefacts, such as his smoking pipe.
Read More About Lord (William Thomson) Kelvin / Source





