32 Most Popular Sports in the World
Sport is a competitive activity governed by many rules and regulations. Sports are commonly called activities where the physical ability of the competitor is the sole or primary determinant of the outcome of the game. Sports are generally defined as an organized, competitive and trained physical activity, with commitment and fairness.
Industrialization has also led to increased leisure time for citizens of developed and developing countries, allowing citizens to participate in sporting events and reach the grounds as spectators, participate and participate more in athletic activities. These trends continued with the proliferation of mass media and global media.Professionalism prevailed, leading to an increase in the popularity of sports, as sports fans began to enjoy the game of professional players through radio, television and the Internet. Apart from this, the custom of enjoying amateur participation in exercise and sports also increased.
Despite being a form of entertainment for the game participants, many games are played in front of the audience. Most professional sports are played under some kind of ‘theater’, a stadium, grounds, golf course, race track, or open road for general public viewing. Often there is a provision of tickets for them.
The game now also attracts large TV viewers or radio listeners, as rival broadcasters bid large sums for ‘rights’ broadcasting certain sports. The Football World Cup attracts millions of TV viewers worldwide, such as the 2006 finals alone attracted 700 million viewers worldwide. NFL championship game in USA Super Bowl- became one of the most watched television broadcasts of the year. Super Bowl Sunday, in a way, becomes a national holiday in the US, with viewership so high that in 2007 it received $ 2.6 million in ads for every 30-second slot.
So today we will tell you about some popular games for which people around the world are crazy –
Cricket
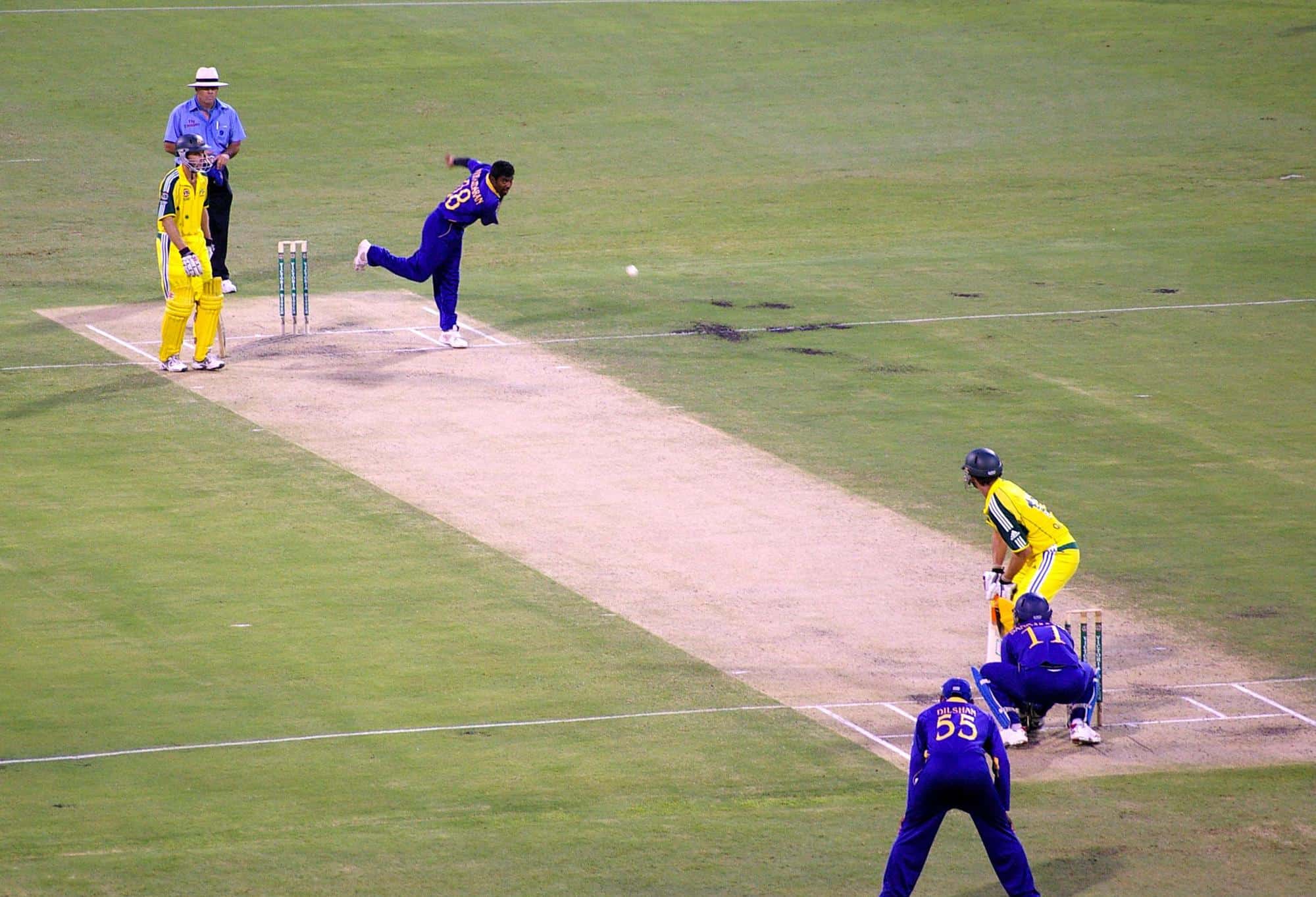

Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a 22-yard (20-metre) pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striking the ball bowled at the wicket with the bat (and running between the wickets), while the bowling and fielding side tries to prevent this (by preventing the ball from leaving the field, and getting the ball to either wicket) and dismiss each batter (so they are “out”). Means of dismissal include being bowled, when the ball hits the stumps and dislodges the bails, and by the fielding side either catching the ball after it is hit by the bat, but before it hits the ground, or hitting a wicket with the ball before a batter can cross the crease in front of the wicket. When ten batters have been dismissed, the innings ends and the teams swap roles. The game is adjudicated by two umpires, aided by a third umpire and match referee in international matches. They communicate with two off-field scorers who record the match’s statistical information.
Forms of cricket range from Twenty20, with each team batting for a single innings of 20 overs, to Test matches played over five days. Traditionally cricketers play in all-white kit, but in limited overs cricket they wear club or team colours. In addition to the basic kit, some players wear protective gear to prevent injury caused by the ball, which is a hard, solid spheroid made of compressed leather with a slightly raised sewn seam enclosing a cork core layered with tightly wound string.
The earliest reference to cricket is in South East England in the mid-16th century. It spread globally with the expansion of the British Empire, with the first international matches in the second half of the 19th century. The game’s governing body is the International Cricket Council (ICC), which has over 100 members, twelve of which are full members who play Test matches. The game’s rules, the Laws of Cricket, are maintained by Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) in London. The sport is followed primarily in the Indian subcontinent, Australasia, the United Kingdom, southern Africa and the West Indies. Women’s cricket, which is organised and played separately, has also achieved international standard. The most successful side playing international cricket is Australia, which has won seven One Day International trophies, including five World Cups, more than any other country and has been the top-rated Test side more than any other country.
Read More About Cricket / Source
Football (Soccer)
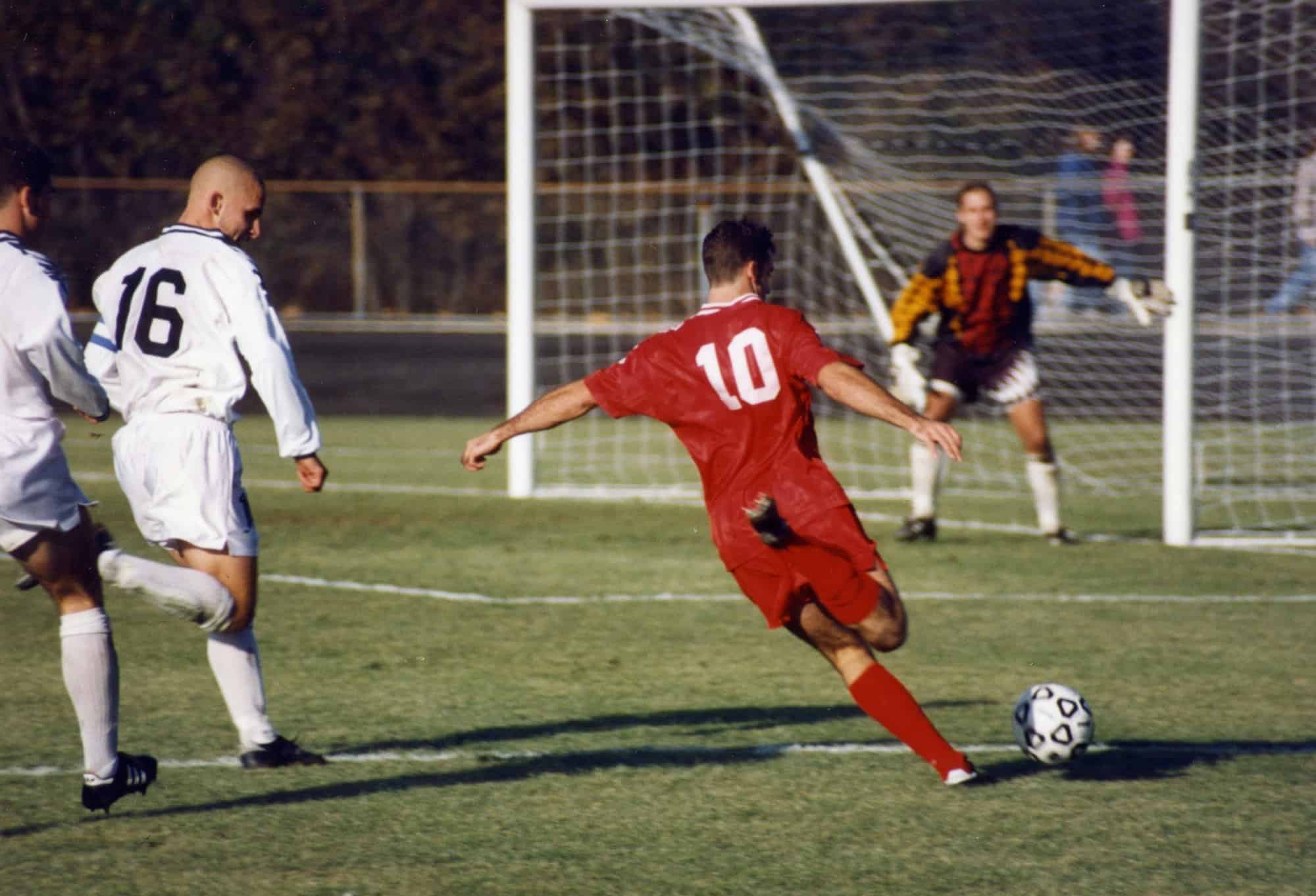

Association football, more commonly known as football (especially in countries where association football is the only popular code of football) or soccer (originally also spelled foot-ball), is a team sport played with a spherical ball between two teams of 11 players. It is played by approximately 250 million players in over 200 countries and dependencies, making it the world’s most popular sport. The game is played on a rectangular field called a pitch with a goal at each end. The object of the game is to outscore the opposition by moving the ball beyond the goal line into the opposing goal. The team with the higher number of goals wins the game.
Football is played in accordance with a set of rules known as the Laws of the Game. The ball is 68–70 cm (27–28 in) in circumference and known as the football. The two teams each compete to get the ball into the other team’s goal (between the posts and under the bar), thereby scoring a goal. The team that has scored more goals at the end of the game is the winner; if both teams have scored an equal number of goals then the game is a draw. Each team is led by a captain who has only one official responsibility as mandated by the Laws of the Game: to represent their team in the coin toss prior to kick-off or penalty kicks.Players are not allowed to touch the ball with hands or arms while it is in play, except for the goalkeepers within the penalty area. Other players mainly use their feet to strike or pass the ball, but may also use any other part of their body except the hands and the arms. The team that scores most goals by the end of the match wins. If the score is level at the end of the game, either a draw is declared or the game goes into extra time or a penalty shootout depending on the format of the competition.
Football is governed internationally by the International Federation of Association Football (FIFA; French: Fédération Internationale de Football Association), which organises World Cups for both men and women every four years. The FIFA World Cup has taken place every four years since 1930 with the exception of 1942 and 1946 tournaments, which were cancelled due to World War II. Approximately 190–200 national teams compete in qualifying tournaments within the scope of continental confederations for a place in the finals. The finals tournament, which is held every four years, involves 32 national teams competing over a four-week period. It is the most prestigious football tournament in the world as well as the most widely viewed and followed sporting event in the world, exceeding the Olympic Games.
The most prestigious competition in club football is the UEFA Champions League which attracts an extensive television audience throughout the world. The final of the tournament has been, in recent years, the most-watched annual sporting event in the world. The top five European leagues are the Premier League (England), La Liga (Spain), Bundesliga (Germany), Serie A (Italy), and Ligue 1 (France). Attracting most of the world’s best players, each of the leagues has a total wage cost in excess of £600 million/€763 million/US$1.185 billion.Football is one of a family of football codes, which emerged from various ball games played worldwide since antiquity. The modern game traces its origins to 1863 when the Laws of the Game were originally codified in England by The Football Association.
Read More About Football (Soccer) / Source
Field hockey
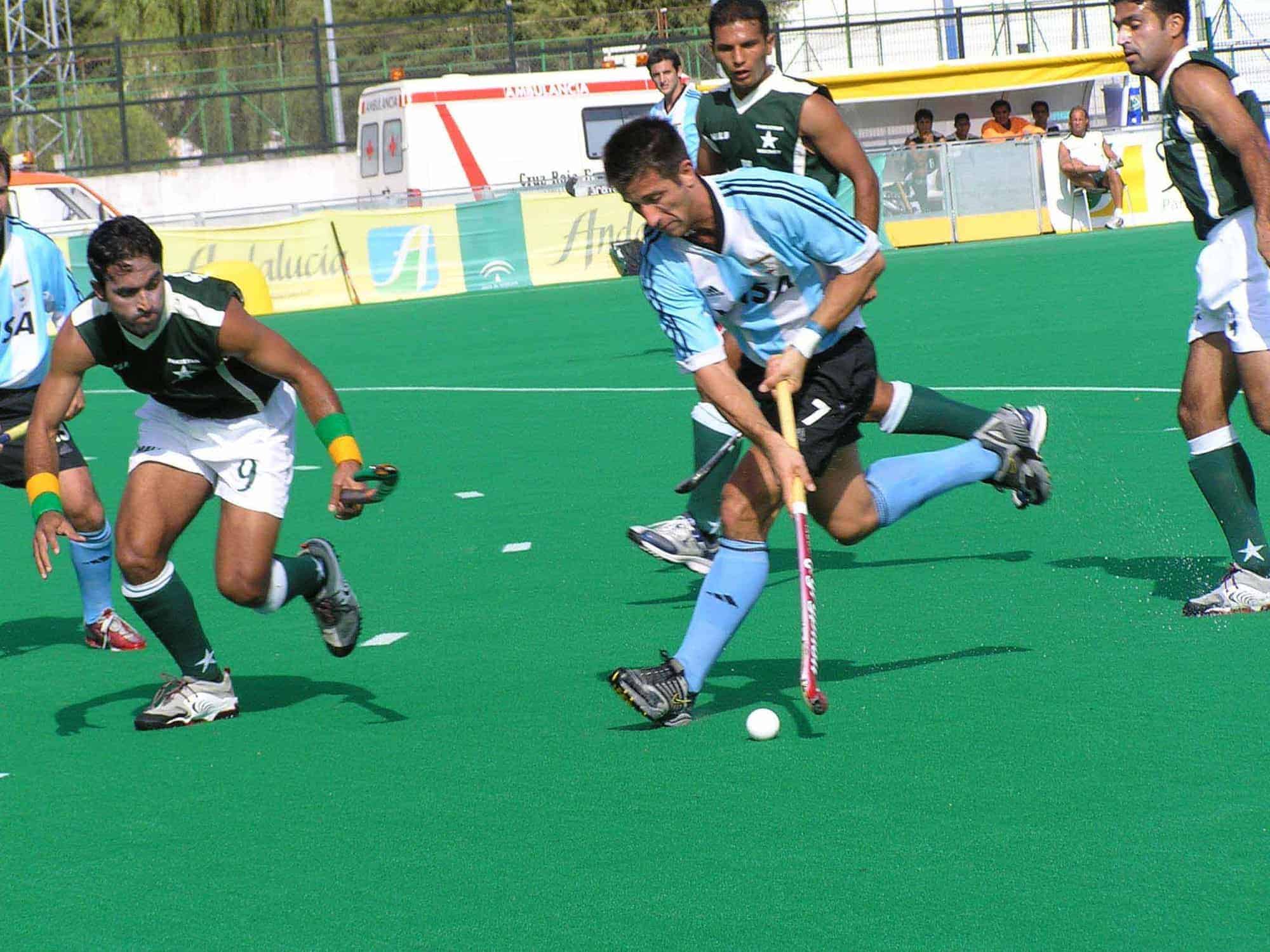

Field hockey is a widely played team sport of the hockey family. The game can be played on grass, watered turf, artificial turf or synthetic field, as well as an indoor boarded surface. Each team plays with ten field players and a goalkeeper. Players use sticks made of wood, carbon fibre, fibre glass, or a combination of carbon fibre and fibre glass in different quantities, to hit a round, hard, plastic hockey ball. The length of the hockey stick is based on the player’s individual height: the top of the stick usually comes to the players hip, and taller players typically have longer sticks. The sticks have a round side and a flat side, and only the flat face of the stick is allowed to be used. Use of the other side results in a foul. Goalies often have a different design of stick, although they can also use an ordinary field hockey stick. The specific goal-keeping sticks have another curve at the end of the stick, which is to give it more surface area to block the ball. The uniform consists of shin guards, shoes, shorts or a skirt, a mouthguard and a jersey.
The game is played globally, particularly in parts of Western Europe, South Asia, Southern Africa, Australia, New Zealand, Argentina, and parts of the United States, primarily New England and the Mid-Atlantic states.Known simply as “hockey” in most territories, the term “field hockey” is used primarily in Canada and the United States where ice hockey is more popular. In Sweden, the term landhockey is used, and to some degree in Norway, where the game is governed by the Norges Bandyforbund.During play, goal keepers are the only players allowed to touch the ball with any part of their body, while field players can only play the ball with the flat side of their stick. A player’s hand is considered part of the stick if holding the stick. If the ball is touched with the rounded part of the stick, it will result in a penalty. Goal keepers also cannot play the ball with the back of their stick.
The team that scores the most goals by the end of the match wins. If the score is tied at the end of the game, either a draw is declared or the game goes into extra time, or there is a penalty shoot-out, depending on the format of the competition. There are many variations to overtime play that depend on the league or tournament rules. In American college play, a seven-aside overtime period consists of a 10-minute golden goal period with seven players for each team. If a tie still remains, the game enters a one-on-one competition where each team chooses five players to dribble from the 25-yard (23 m) line down to the circle against the opposing goalie. The player has eight seconds to score against the goalie while keeping the ball in bounds. The game ends after a goal is scored, the ball goes out of bounds, a foul is committed (ending in either a penalty stroke or flick or the end of the one-on-one) or time expires. If the tie still persists, more rounds are played until one team has scored.
The governing body of field hockey is the International Hockey Federation (FIH), called the Fédération Internationale de Hockey in French, with men and women being represented internationally in competitions including the Olympic Games, World Cup, World League, Champions Trophy and Junior World Cup, with many countries running extensive junior, senior, and masters club competitions. The FIH is also responsible for organizing the Hockey Rules Board and developing the rules of the game.
A popular variant of field hockey is indoor field hockey, which differs in a number of respects while embodying the primary principles of hockey. Indoor hockey is a 5-a-side variant, using a field which is reduced to approximately 40 m × 20 m (131 ft × 66 ft). Although many of the rules remain the same, including obstruction and feet, there are several key variations: players may not raise the ball unless shooting at goal, players may not hit the ball, instead using pushes to transfer it, and the sidelines are replaced with solid barriers, from which the ball will rebound and remain in play. In addition, the regulation guidelines for the indoor field hockey stick require a slightly thinner, lighter stick than an outdoor one.
Read More About Field hockey / Source
Volleyball
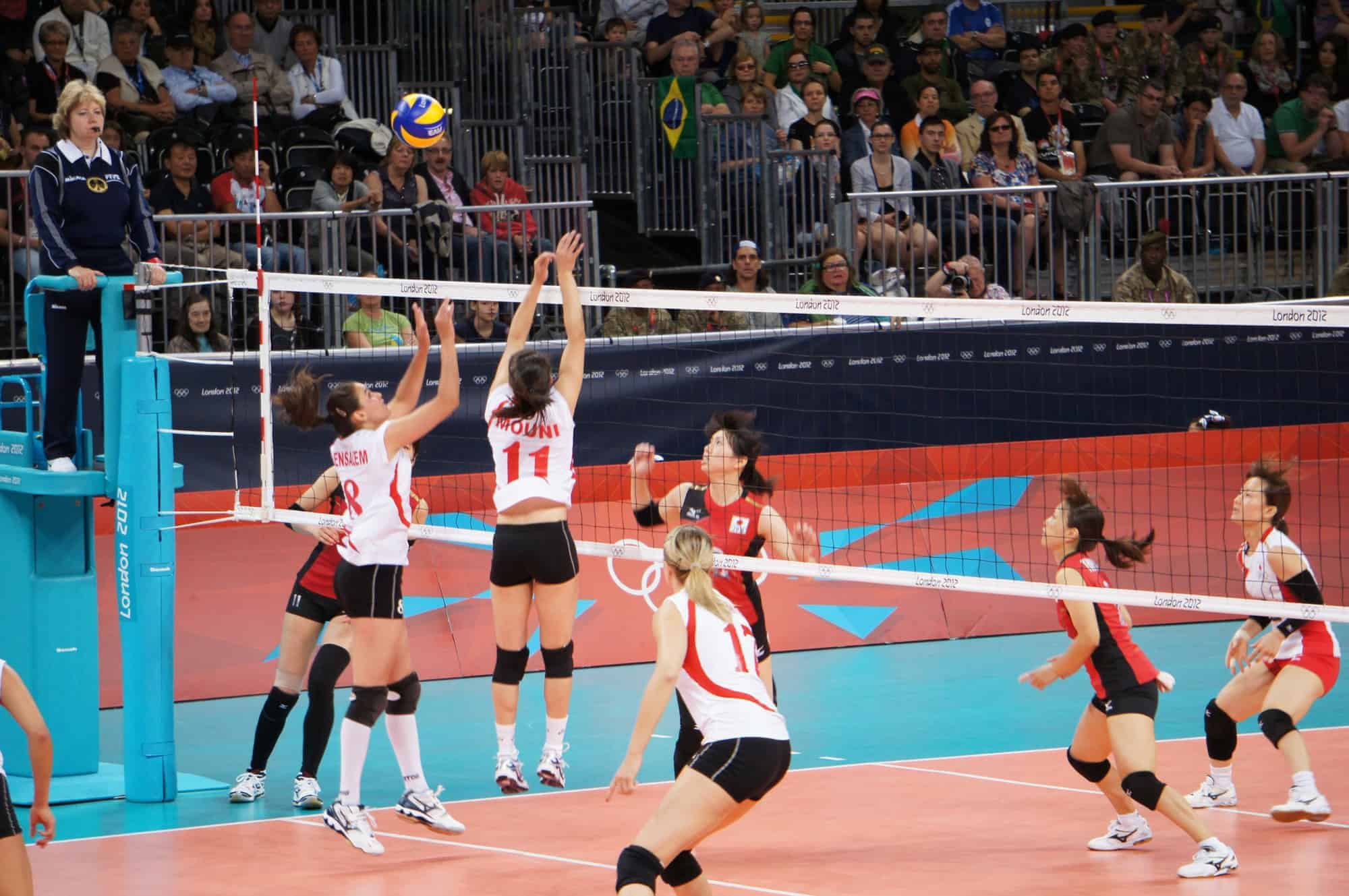

Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team’s court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Summer Olympic Games since Tokyo 1964.
The complete set of rules is extensive, but play essentially proceeds as follows: a player on one of the teams begins a ‘rally’ by serving the ball (tossing or releasing it and then hitting it with a hand or arm), from behind the back boundary line of the court, over the net, and into the receiving team’s court. The receiving team must not let the ball be grounded within their court. The team may touch the ball up to 3 times, but individual players may not touch the ball twice consecutively. Typically, the first two touches are used to set up for an attack, an attempt to direct the ball back over the net in such a way that the serving team is unable to prevent it from being grounded in their court.
The rally continues, with each team allowed as many as three consecutive touches, until either (1): a team makes a kill, grounding the ball on the opponent’s court and winning the rally; or (2): a team commits a fault and loses the rally. The team that wins the rally is awarded a point and serves the ball to start the next rally. A few of the most common faults include:
causing the ball to touch the ground or floor outside the opponents’ court or without first passing over the net;
catching and throwing the ball;
double hit: two consecutive contacts with the ball made by the same player;
four consecutive contacts with the ball made by the same team;
net foul: touching the net during play;
foot fault: the foot crosses over the boundary line when serving.The ball is usually played with the hands or arms, but players can legally strike or push (short contact) the ball with any part of the body.
A number of consistent techniques have evolved in volleyball, including spiking and blocking (because these plays are made above the top of the net, the vertical jump is an athletic skill emphasized in the sport) as well as passing, setting, and specialized player positions and offensive and defensive structures.
Read More About Volleyball / Source
Tennis
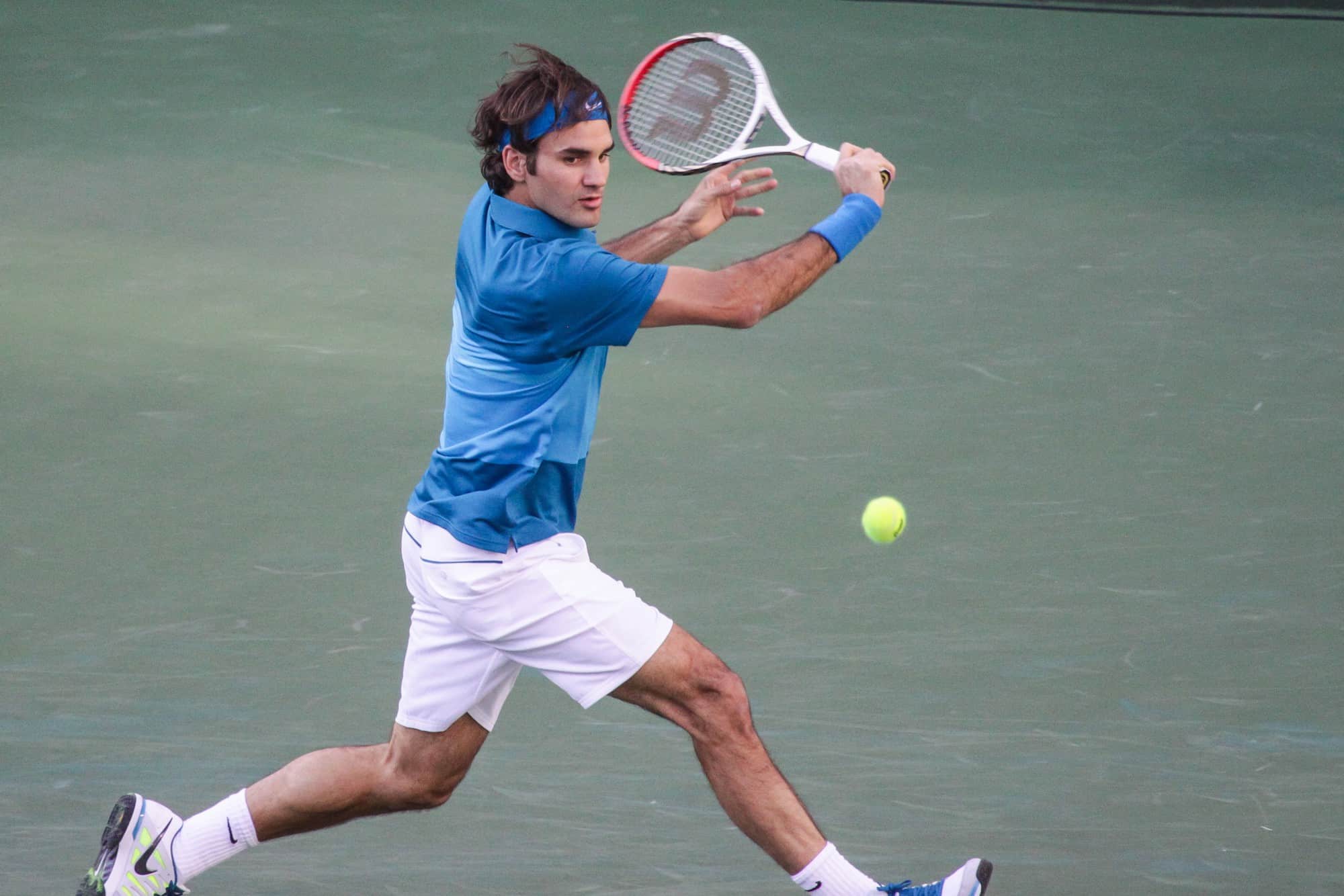

Tennis is a racket sport that can be played individually against a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball covered with felt over or around a net and into the opponent’s court. The object of the game is to maneuver the ball in such a way that the opponent is not able to play a valid return. The player who is unable to return the ball will not gain a point, while the opposite player will.
Tennis is an Olympic sport and is played at all levels of society and at all ages. The sport can be played by anyone who can hold a racket, including wheelchair users. The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the late 19th century as lawn tennis. It had close connections both to various field (lawn) games such as croquet and bowls as well as to the older racket sport today called real tennis. During most of the 19th century, in fact, the term tennis referred to real tennis, not lawn tennis.
The rules of modern tennis have changed little since the 1890s. Two exceptions are that from 1908 to 1961 the server had to keep one foot on the ground at all times, and the adoption of the tiebreak in the 1970s. A recent addition to professional tennis has been the adoption of electronic review technology coupled with a point-challenge system, which allows a player to contest the line call of a point, a system known as Hawk-Eye.
Tennis is played by millions of recreational players and is also a popular worldwide spectator sport. The four Grand Slam tournaments (also referred to as the Majors) are especially popular: the Australian Open played on hard courts, the French Open played on red clay courts, Wimbledon played on grass courts, and the US Open also played on hard courts.
Read More About Tennis / Source
Basketball
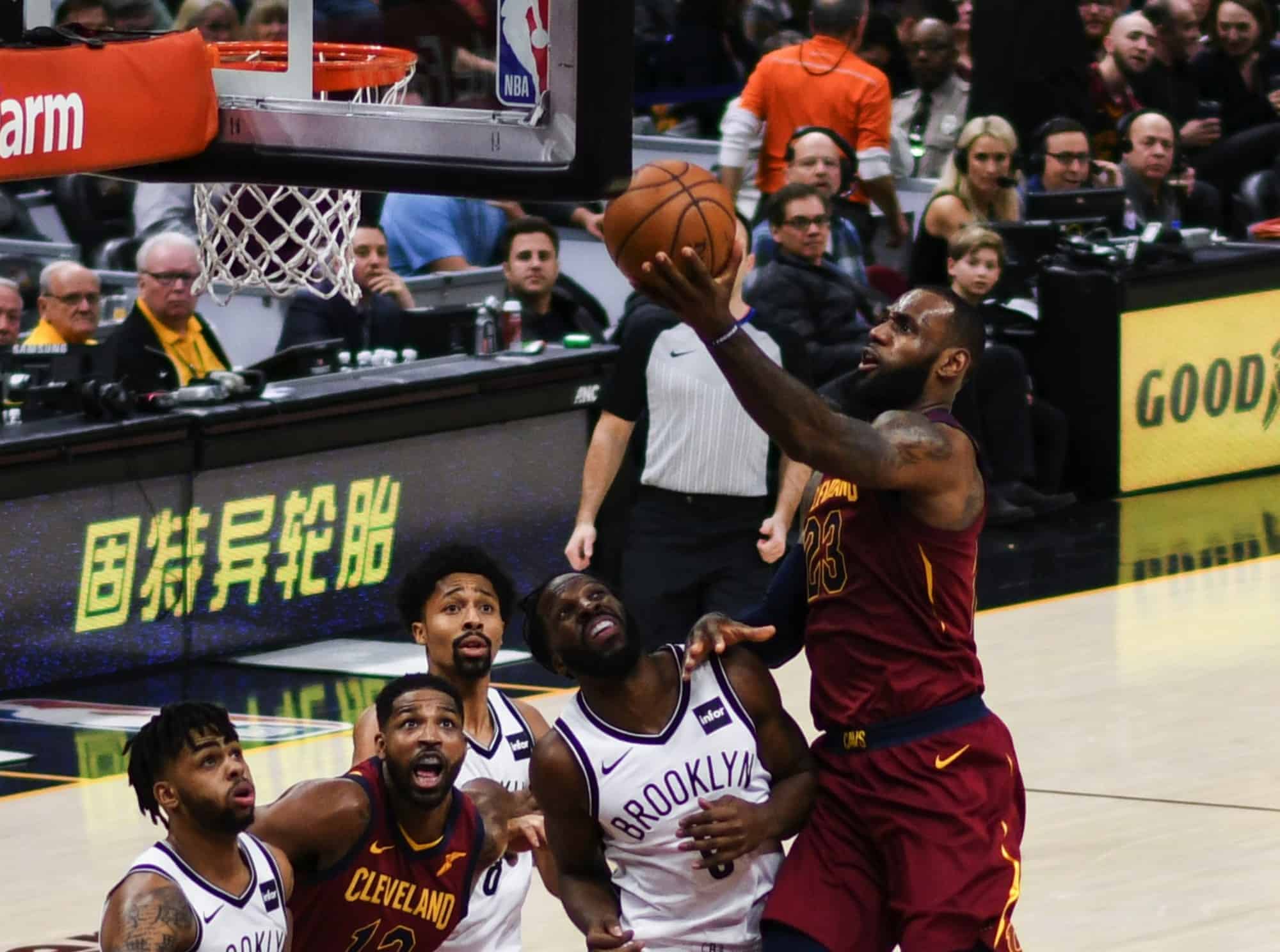

Basketball, colloquially referred to as hoops, is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately 9.4 inches (24 cm) in diameter) through the defender’s hoop (a basket 18 inches (46 cm) in diameter mounted 10 feet (3.048 m) high to a backboard at each end of the court) while preventing the opposing team from shooting through their own hoop. A field goal is worth two points, unless made from behind the three-point line, when it is worth three. After a foul, timed play stops and the player fouled or designated to shoot a technical foul is given one, two or three one-point free throws. The team with the most points at the end of the game wins, but if regulation play expires with the score tied, an additional period of play (overtime) is mandated.
Players advance the ball by bouncing it while walking or running (dribbling) or by passing it to a teammate, both of which require considerable skill. On offense, players may use a variety of shots—the lay-up, the jump shot, or a dunk; on defense, they may steal the ball from a dribbler, intercept passes, or block shots; either offense or defense may collect a rebound, that is, a missed shot that bounces from rim or backboard. It is a violation to lift or drag one’s pivot foot without dribbling the ball, to carry it, or to hold the ball with both hands then resume dribbling.
The five players on each side fall into five playing positions. The tallest player is usually the center, the second-tallest and strongest is the power forward, a slightly shorter but more agile player is the small forward, and the shortest players or the best ball handlers are the shooting guard and the point guard, who implements the coach’s game plan by managing the execution of offensive and defensive plays (player positioning). Informally, players may play three-on-three, two-on-two, and one-on-one.
Invented in 1891 by Canadian-American gym teacher James Naismith in Springfield, Massachusetts, United States, basketball has evolved to become one of the world’s most popular and widely viewed sports. The National Basketball Association (NBA) is the most significant professional basketball league in the world in terms of popularity, salaries, talent, and level of competition. Outside North America, the top clubs from national leagues qualify to continental championships such as the EuroLeague and the Basketball Champions League Americas. The FIBA Basketball World Cup and Men’s Olympic Basketball Tournament are the major international events of the sport and attract top national teams from around the world. Each continent hosts regional competitions for national teams, like EuroBasket and FIBA AmeriCup.
The FIBA Women’s Basketball World Cup and Women’s Olympic Basketball Tournament feature top national teams from continental championships. The main North American league is the WNBA (NCAA Women’s Division I Basketball Championship is also popular), whereas strongest European clubs participate in the EuroLeague Women.
Read More About Basketball / Source
Table Tennis
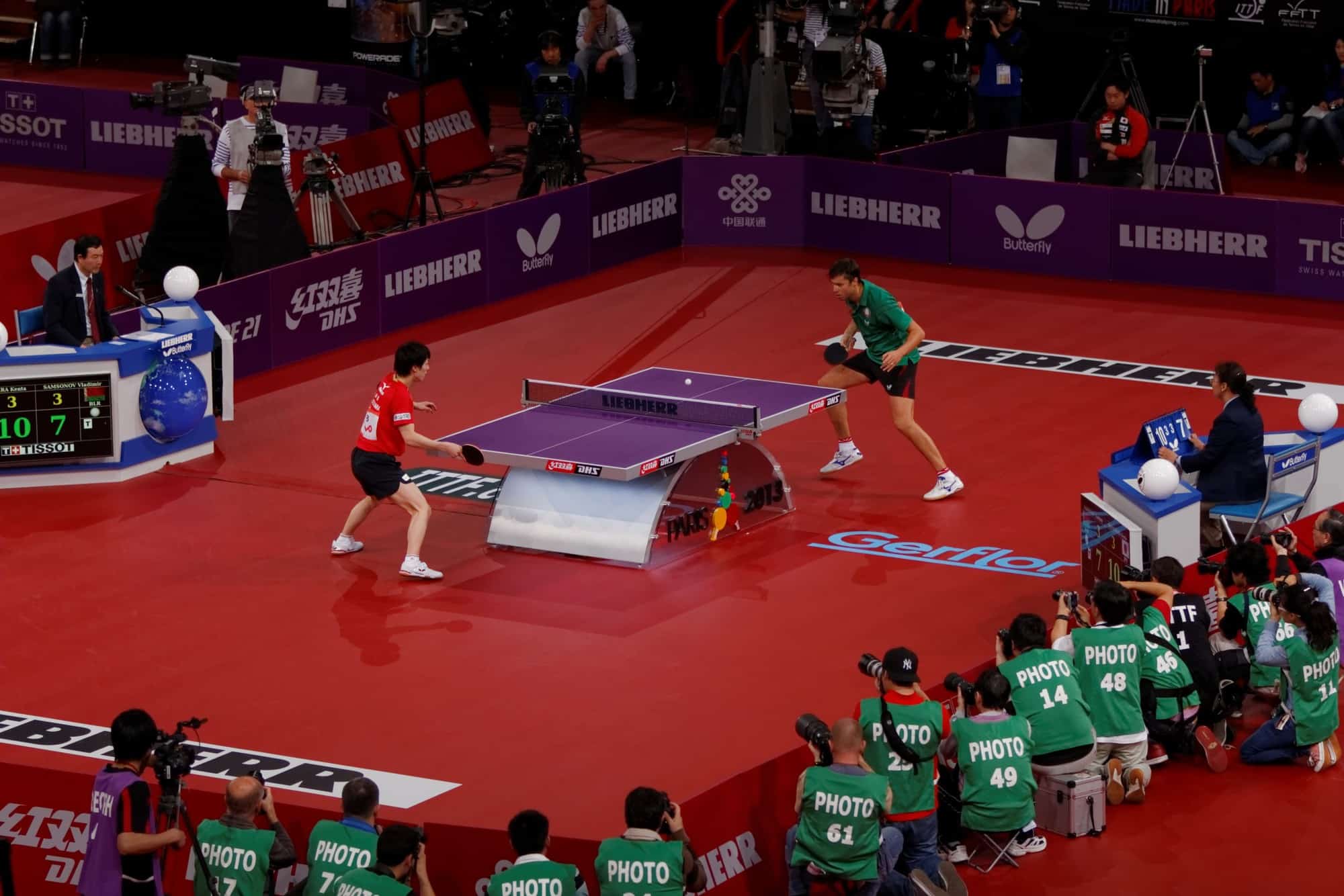

Table tennis, also known as ping-pong and whiff-whaff, is a sport in which two or four players hit a lightweight ball, also known as the ping-pong ball, back and forth across a table using small rackets. The game takes place on a hard table divided by a net. Except for the initial serve, the rules are generally as follows: players must allow a ball played toward them to bounce one time on their side of the table, and must return it so that it bounces on the opposite side at least once. A point is scored when a player fails to return the ball within the rules. Play is fast and demands quick reactions. Spinning the ball alters its trajectory and limits an opponent’s options, giving the hitter a great advantage.
Table tennis is governed by the worldwide organization International Table Tennis Federation (ITTF), founded in 1926. ITTF currently includes 226 member associations. The table tennis official rules are specified in the ITTF handbook. Table tennis has been an Olympic sport since 1988, with several event categories. From 1988 until 2004, these were men’s singles, women’s singles, men’s doubles and women’s doubles. Since 2008, a team event has been played instead of the doubles.
Read More About Table Tennis / Source
Baseball
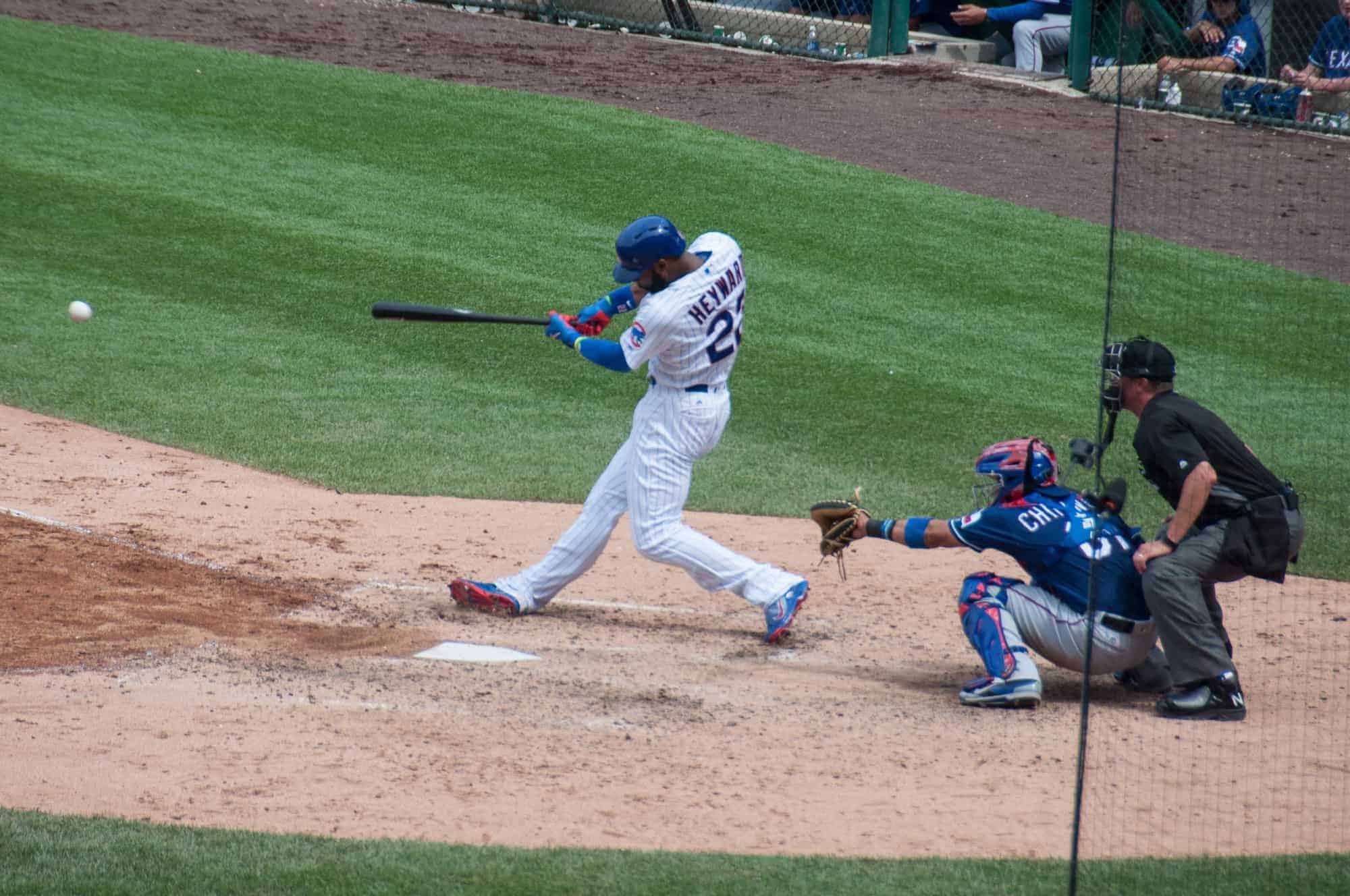

Baseball is a bat-and-ball game played between two opposing teams who take turns batting and fielding. The game proceeds when a player on the fielding team, called the pitcher, throws a ball which a player on the batting team tries to hit with a bat. The objective of the offensive team (batting team) is to hit the ball into the field of play, allowing its players to run the bases, having them advance counter-clockwise around four bases to score what are called “runs”. The objective of the defensive team (fielding team) is to prevent batters from becoming runners, and to prevent runners’ advance around the bases. A run is scored when a runner legally advances around the bases in order and touches home plate (the place where the player started as a batter). The team that scores the most runs by the end of the game is the winner.
The first objective of the batting team is to have a player reach first base safely. A player on the batting team who reaches first base without being called “out” can attempt to advance to subsequent bases as a runner, either immediately or during teammates’ turns batting. The fielding team tries to prevent runs by getting batters or runners “out”, which forces them out of the field of play. Both the pitcher and fielders have methods of getting the batting team’s players out. The opposing teams switch back and forth between batting and fielding; the batting team’s turn to bat is over once the fielding team records three outs. One turn batting for each team constitutes an inning. A game is usually composed of nine innings, and the team with the greater number of runs at the end of the game wins. If scores are tied at the end of nine innings, extra innings are usually played. Baseball has no game clock, although most games end in the ninth inning.
Baseball evolved from older bat-and-ball games already being played in England by the mid-18th century. This game was brought by immigrants to North America, where the modern version developed. By the late 19th century, baseball was widely recognized as the national sport of the United States. Baseball is popular in North America and parts of Central and South America, the Caribbean, and East Asia, particularly in Japan, South Korea and Taiwan.
In the United States and Canada, professional Major League Baseball (MLB) teams are divided into the National League (NL) and American League (AL), each with three divisions: East, West, and Central. The MLB champion is determined by playoffs that culminate in the World Series. The top level of play is similarly split in Japan between the Central and Pacific Leagues and in Cuba between the West League and East League. The World Baseball Classic, organized by the World Baseball Softball Confederation, is the major international competition of the sport and attracts the top national teams from around the world.
Read More About Baseball / Source
Formula One
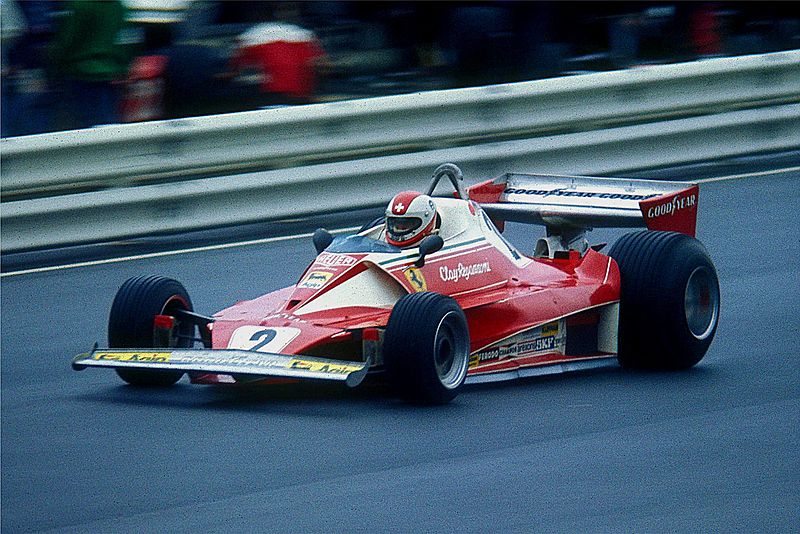

Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international auto racing for single-seater racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile (FIA). The series is owned by Liberty Media, an American mass media company controlled by its founder and chairman John C. Malone, through its wholly owned subsidiary, the Formula One Group. The World Drivers’ Championship, which became the FIA Formula One World Championship in 1981, has been one of the premier forms of racing around the world since its inaugural season in 1950. The word “formula” in the name refers to the set of rules to which all participants’ cars must conform. A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as Grands Prix (French for ”grand prizes’ or ‘great prizes”), which take place worldwide on purpose-built circuits and on closed public roads.
The results of each race are evaluated using a points system to determine two annual World Championships: one for drivers, the other for constructors. Drivers must hold valid Super Licences, the highest class of racing licence issued by the FIA. The races must run on tracks graded “1” (formerly “A”), the highest grade-rating issued by the FIA. Most events occur in rural locations on purpose-built tracks, but several events take place on city streets.
Formula One cars are the fastest regulated road-course racing cars in the world, owing to very high cornering speeds achieved through the generation of large amounts of aerodynamic downforce. The cars underwent major changes in 2017, allowing wider front and rear wings, and wider tyres, resulting in peak cornering forces near 6.5 lateral g and top speeds of up to approximately 350 km/h (215 mph). As of 2019 the hybrid engines are limited in performance to a maximum of 15,000 rpm; the cars are very dependent on electronics and aerodynamics, suspension and tyres. Traction control and other driving aids have been banned since 2008.While Europe is the sport’s traditional base, the championship operates globally, with 11 of the 21 races in the 2019 season taking place outside Europe. With the annual cost of running a mid-tier team—designing, building, and maintaining cars, pay, transport—being US$120 million, its financial and political battles are widely reported. Its high profile and popularity have created a major merchandising environment, which has resulted in large investments from sponsors and budgets (in the hundreds of millions for the constructors). On 23 January 2017 Liberty Media confirmed the completion of the acquisition of Delta Topco, the company that controls Formula One, from private-equity firm CVC Capital Partners for $8 billion.In August 2020, a new Concorde Agreement was signed by all 10 F1 teams committing them to the sport until 2025, including a $145m budget cap for car development to support equal competition and sustainable development in the future.
Read More About Formula One / Source
Rugby Union
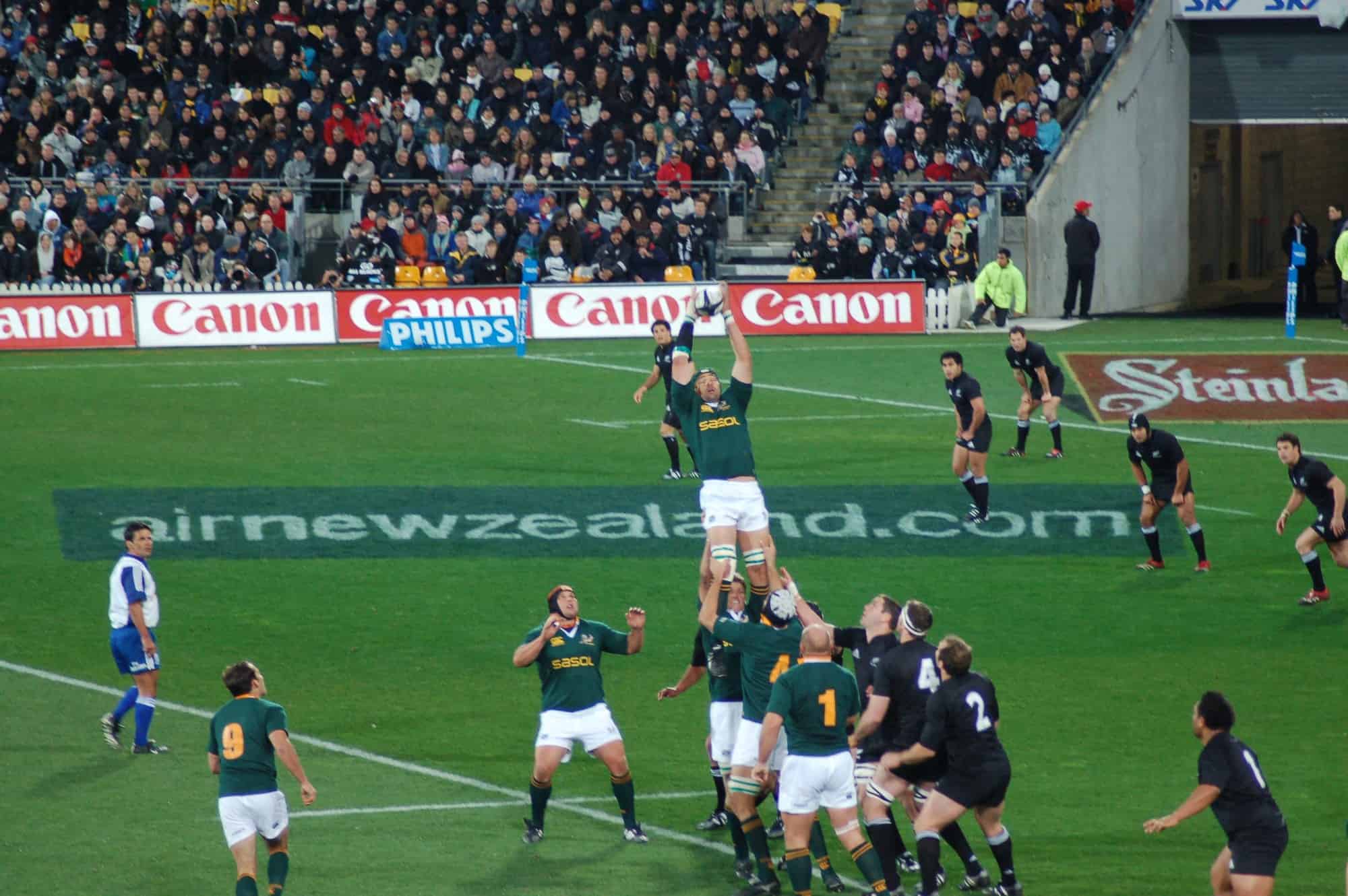

Rugby union, widely known simply as rugby, is a full-contact team sport that originated in England in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In its most common form, a game is played between two teams of 15 players each, using an oval-shaped ball on a rectangular field called a pitch. The field has H-shaped goalposts at both ends.
Rugby union is a popular sport around the world, played by male and female players of all ages. In 2014, there were more than 6 million people playing worldwide, of whom 2.36 million were registered players. World Rugby, previously called the International Rugby Football Board (IRFB) and the International Rugby Board (IRB), has been the governing body for rugby union since 1886, and currently has 101 countries as full members and 18 associate members.
In 1845, the first laws were written by pupils at Rugby School; other significant events in the early development of rugby include the decision by Blackheath F.C. to leave the Football Association in 1863 and, in 1895, the split between rugby union and rugby league. Historically rugby union was an amateur sport, but in 1995 formal restrictions on payments to players were removed, making the game openly professional at the highest level for the first time.Rugby union spread from the Home Nations of Great Britain and Ireland, with other early exponents of the sport including Australia, New Zealand, South Africa and France. The sport is followed primarily in the British Isles, France, Australasia, Southern Africa, Argentina and to a lesser extent Italy, Uruguay, Canada and Japan, its growth occurring during the expansion of the British Empire and through French proponents (Rugby Europe) in Europe. Countries that have adopted rugby union as their de facto national sport include Fiji, Georgia, Madagascar, New Zealand, Samoa, Tonga and Wales.
International matches have taken place since 1871 when the first game was played between Scotland and England at Raeburn Place in Edinburgh. The Rugby World Cup, first held in 1987, is contested every four years. The Six Nations Championship in Europe and The Rugby Championship in the Southern Hemisphere are other major international competitions that are held annually.
National club and provincial competitions include the Premiership in England, the Top 14 in France, the Mitre 10 Cup in New Zealand, the Top League in Japan, the Currie Cup in South Africa and the National Rugby Championship in Australia. Other transnational club competitions include the European Rugby Champions Cup, the Pro14 in Europe and South Africa, and Super Rugby and Global Rapid Rugby in the Southern Hemisphere.
Read More About Rugby Union / Source
Sport of athletics
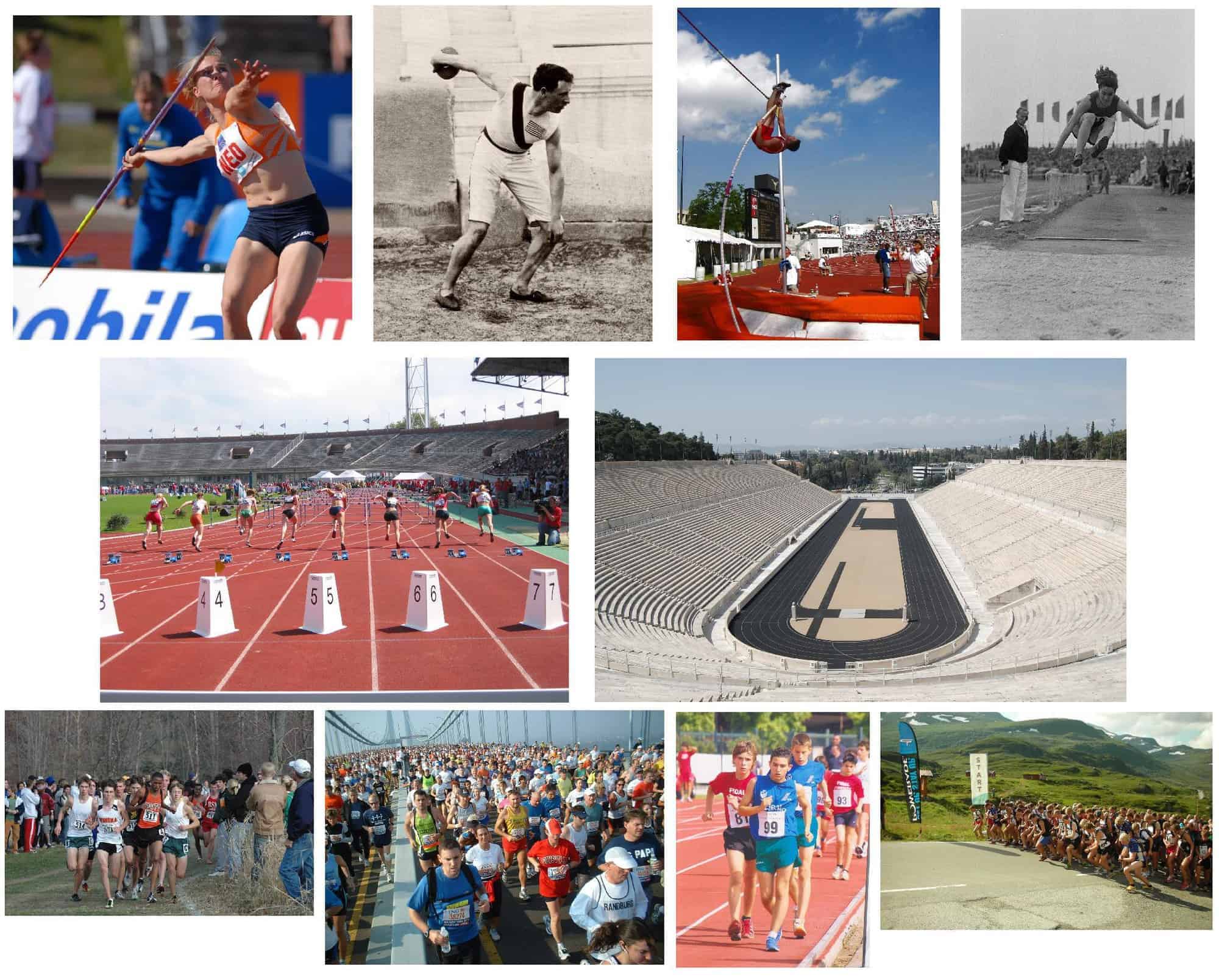

Athletics is a group of sporting events that involves competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking. The most common types of athletics competitions are track and field, road running, cross country running, and racewalking.
The results of racing events are decided by finishing position (or time, where measured), while the jumps and throws are won by the athlete that achieves the highest or furthest measurement from a series of attempts. The simplicity of the competitions, and the lack of a need for expensive equipment, makes athletics one of the most common types of sports in the world. Athletics is mostly an individual sport, with the exception of relay races and competitions which combine athletes’ performances for a team score, such as cross country.
Organized athletics are traced back to the Ancient Olympic Games from 776 BC. The rules and format of the modern events in athletics were defined in Western Europe and North America in the 19th and early 20th century, and were then spread to other parts of the world. Most modern top level meetings are held under the auspices of World Athletics, the global governing body for the sport of athletics, or its member continental and national federations.
The athletics meeting forms the backbone of the Summer Olympics. The foremost international athletics meeting is the World Athletics Championships, which incorporates track and field, marathon running and race walking. Other top level competitions in athletics include the World Athletics Cross Country Championships and the World Half Marathon Championships. Athletes with a physical disability compete at the Summer Paralympics and the World Para Athletics Championships.
The word athletics is derived from the Ancient Greek ἀθλητής (athlētēs, “combatant in public games”) from ἆθλον (athlon, “prize”) or ἆθλος (athlos, “competition”). Initially, the term described athletic contests in general – i.e. sporting competition based primarily on human physical feats. In the 19th century, the term athletics acquired a more narrow definition in Europe and came to describe sports involving competitive running, walking, jumping and throwing. This definition continues to be prominent in the United Kingdom and the former British Empire. Related words in Germanic and Romance languages also have a similar meaning.
In much of North America, athletics is synonymous with sports in general, maintaining the historical usage of the term. The word “athletics” is rarely used to refer to the sport of athletics in this region. Track and field is preferred, and is used in the United States and Canada to refer to athletics events, including racewalking and marathon running (although cross country running is typically considered a separate sport).
Read More About Sport of athletics / Source
Golf
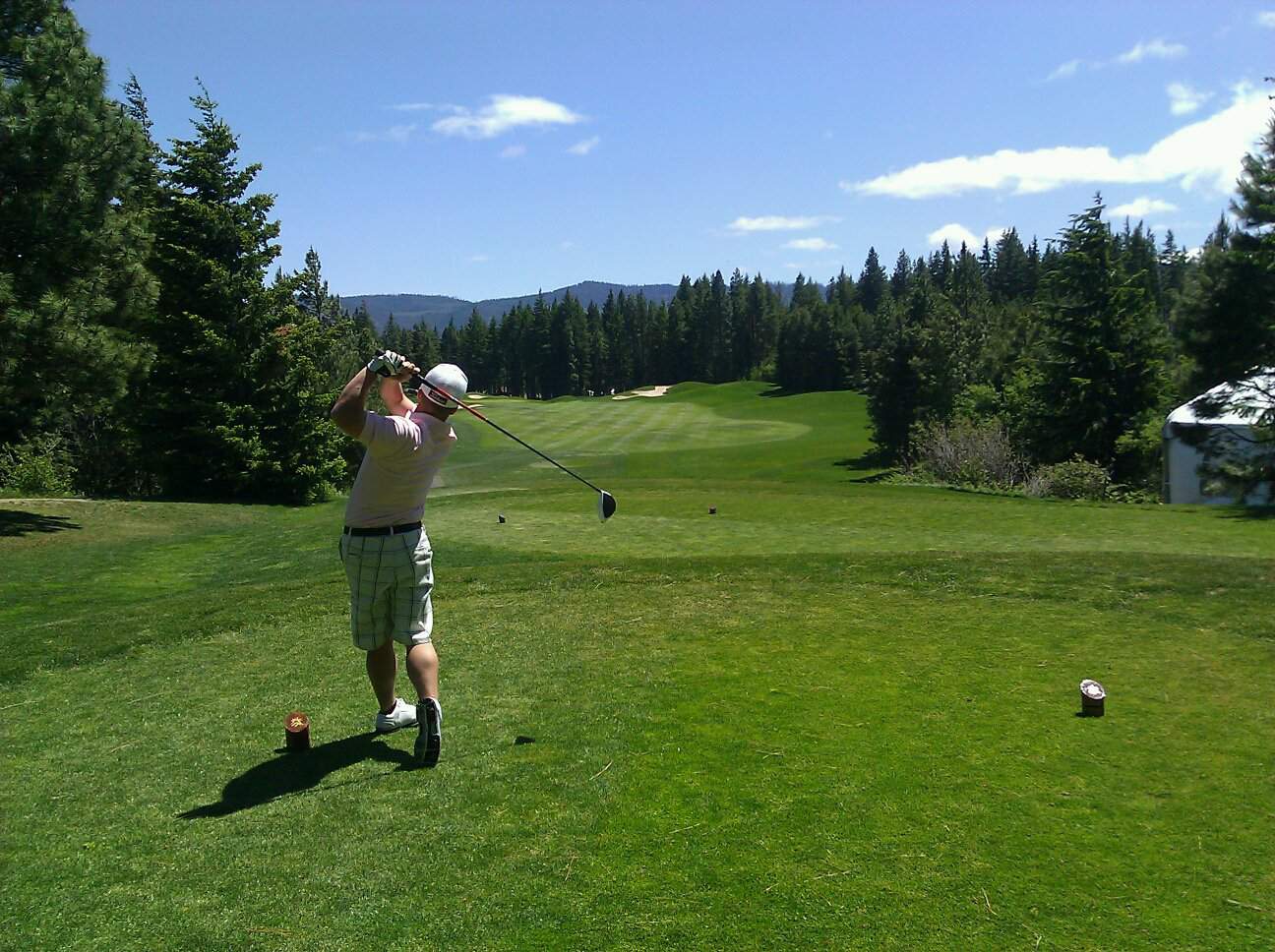

Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not utilize a standardized playing area, and coping with the varied terrains encountered on different courses is a key part of the game. The game at the usual level is played on a course with an arranged progression of 18 holes, though recreational courses can be smaller, often having nine holes. Each hole on the course must contain a teeing ground to start from, and a putting green containing the actual hole or cup 4 1⁄4 inches (11 cm) in diameter. There are other standard forms of terrain in between, such as the fairway, rough (long grass), bunkers (or “sand traps”), and various hazards (water, rocks) but each hole on a course is unique in its specific layout and arrangement.
Golf is played for the lowest number of strokes by an individual, known as stroke play, or the lowest score on the most individual holes in a complete round by an individual or team, known as match play. Stroke play is the most commonly seen format at all levels, but most especially at the elite level.
The modern game of golf originated in 15th century Scotland. The 18-hole round was created at the Old Course at St Andrews in 1764. Golf’s first major, and the world’s oldest tournament in existence, is The Open Championship, also known as the British Open, which was first played in 1860 in Ayrshire, Scotland. This is one of the four major championships in men’s professional golf, the other three being played in the United States: The Masters, the U.S. Open, and the PGA Championship.
Boxing
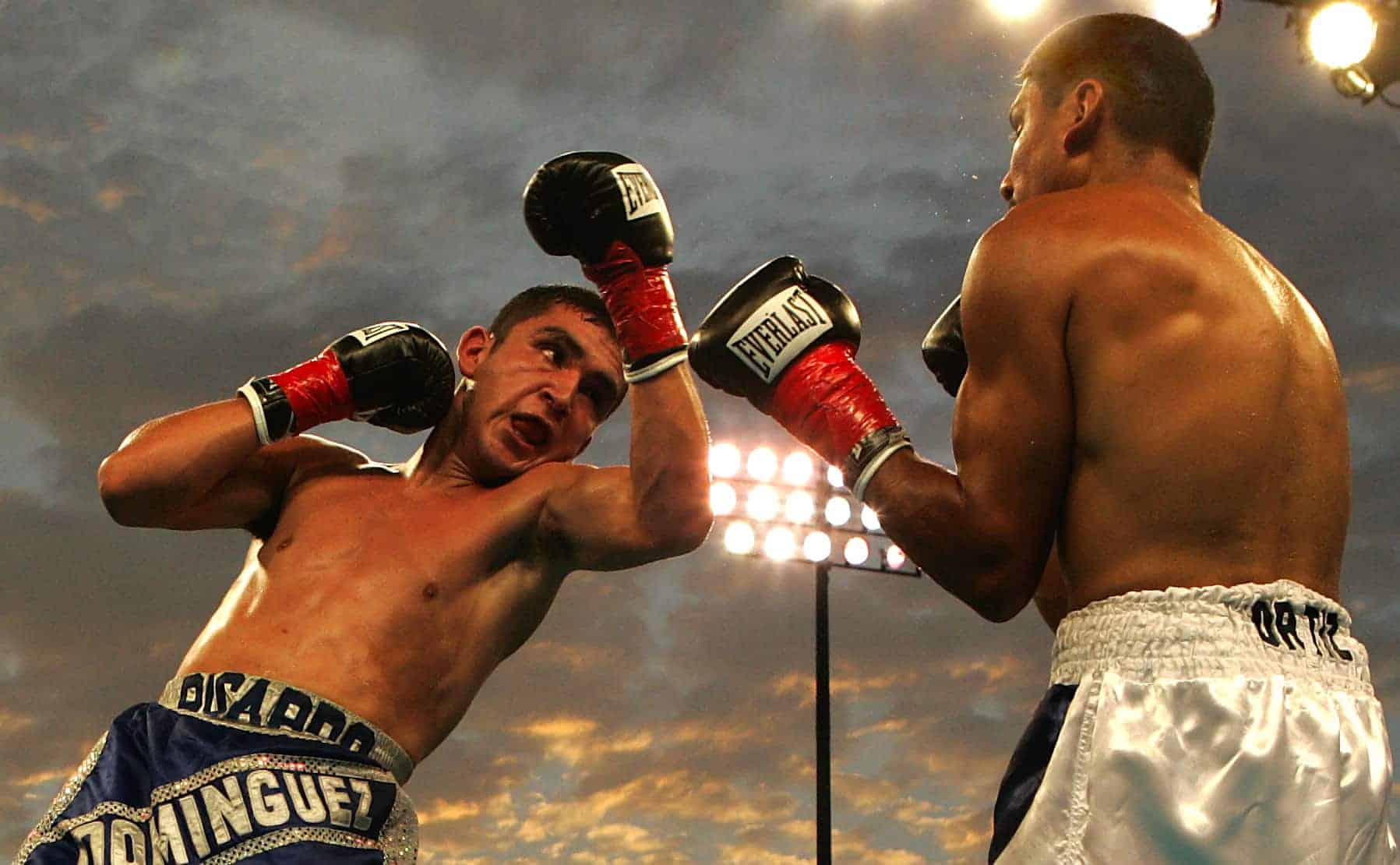

Boxing is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves, throw punches at each other for a predetermined amount of time in a boxing ring.
Amateur boxing is both an Olympic and Commonwealth Games sport and is a standard fixture in most international games—it also has its own World Championships. Boxing is overseen by a referee over a series of one-to-three-minute intervals called rounds.
A winner can be resolved before the completion of the rounds when a referee deems an opponent incapable of continuing, disqualification of an opponent, or resignation of an opponent. When the fight reaches the end of its final round with both opponents still standing, the judges’ scorecards determine the victor. In the event that both fighters gain equal scores from the judges, professional bouts are considered a draw. In Olympic boxing, because a winner must be declared, judges award the contest to one fighter on technical criteria.
While humans have fought in hand-to-hand combat since the dawn of human history, the earliest evidence of fist-fighting sporting contests date back to the ancient Near East in the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC. The earliest evidence of boxing rules date back to Ancient Greece, where boxing was established as an Olympic game in 688 BC. Boxing evolved from 16th- and 18th-century prizefights, largely in Great Britain, to the forerunner of modern boxing in the mid-19th century with the 1867 introduction of the Marquess of Queensberry Rules.
Read More About Boxing / Source
Athletics - Track and field

Track and field (Athletics) is a sport which includes athletic contests established on the skills of running, jumping, and throwing. The name is derived from where the sport takes place, a running track and a grass field for the throwing and some of the jumping events. Track and field is categorized under the umbrella sport of athletics, which also includes road running, cross country running, and racewalking.
The foot racing events, which include sprints, middle- and long-distance events, racewalking and hurdling, are won by the athlete who completes it in the least time. The jumping and throwing events are won by those who achieve the greatest distance or height. Regular jumping events include long jump, triple jump, high jump and pole vault, while the most common throwing events are shot put, javelin, discus and hammer. There are also “combined events” or “multi events”, such as the pentathlon consisting of five events, heptathlon consisting of seven events, and decathlon consisting of ten events. In these, athletes participate in a combination of track and field events. Most track and field events are individual sports with a single victor; the most prominent team events are relay races, which typically feature teams of four. Events are almost exclusively divided by gender, although both the men’s and women’s competitions are usually held at the same venue. If a race has too many people to run all at once, preliminary heats will be run to narrow down the field of participants.
Track and field is one of the oldest sports. In ancient times, it was an event held in conjunction with festivals and sports meets such as the Ancient Olympic Games in Greece. In modern times, the two most prestigious international track and field competitions are the athletics competition at the Olympic Games and the World Athletics Championships. World Athletics, formerly known as the International Association of Athletics Federations is the international governing body for the sport of athletics.
Records are kept of the best performances in specific events, at world and national levels, right down to a personal level. However, if athletes are deemed to have violated the event’s rules or regulations, they are disqualified from the competition and their marks are erased.
In the United States, the term track and field may refer to other athletics events, such as cross country, the marathon and road running, rather than strictly track-based events.
Read More About Athletics - Track and field / Source
Mixed Martial Arts (MMA)
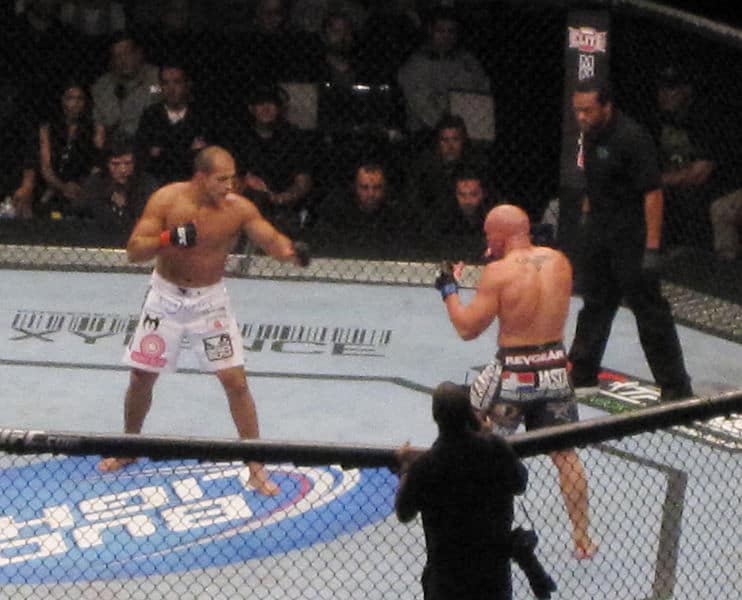

Mixed martial arts (MMA) sometimes referred to as cage fighting, is a full-contact combat sport based on striking, grappling and ground fighting, incorporating techniques from various combat sports and martial arts from around the world. The first documented use of the term mixed martial arts was in a review of UFC 1 by television critic Howard Rosenberg in 1993. The question of who actually coined the term is subject to debate.During the early 20th century, various interstylistic contests took place throughout Japan and in the countries of the Four Asian Tigers. In Brazil, there was the sport of Vale Tudo, in which fighters from various styles fought with little to no rules. The Gracie family was known to promote Vale Tudo matches as a way to promote their own Brazilian jiu-jitsu style. An early high-profile mixed martial arts bout was fought in 1951, between the judoka Masahiko Kimura and Brazilian jiu-jitsu founder Hélio Gracie in Brazil. In the West, the concept of combining elements of multiple martial arts was popularized by Bruce Lee’s Jeet Kune Do during the late 1960s to early 1970s. A precursor to modern MMA was the 1976 Muhammad Ali vs. Antonio Inoki bout, fought between boxer Muhammad Ali and wrestler Antonio Inoki in Japan, where it later inspired the foundation of Pancrase in 1993 and Pride Fighting Championships in 1997.
In 1980, CV Productions, Inc. created the first regulated MMA league in the United States, called Tough Guy Contest, which was later renamed Battle of the Superfighters. The company sanctioned ten tournaments in Pennsylvania. However, in 1983 the Pennsylvania State Senate passed a bill prohibiting the sport. In 1993, the Gracie family brought Brazilian jiu-jitsu, developed in Brazil from the 1920s, to the United States by founding the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) MMA promotion company in 1993. The company held an event with almost no rules, mostly due to the influence of Art Davie and Rorion Gracie attempting to replicate Vale Tudo fights that existed in Brazil and would later implement a different set of rules (example: eliminating kicking a grounded opponent), which differed from other leagues which were more in favour of realistic fights.
Originally promoted as a competition to find the most effective martial arts for real unarmed combat, competitors from different fighting styles were pitted against one another in contests with relatively few rules. Later, individual fighters incorporated multiple martial arts into their style. MMA promoters were pressured to adopt additional rules to increase competitors’ safety, to comply with sport regulations and to broaden mainstream acceptance of the sport. Following these changes, the sport has seen increased popularity with a pay-per-view business that rivals boxing and professional wrestling.
Read More About Mixed Martial Arts (MMA) / Source
American Football
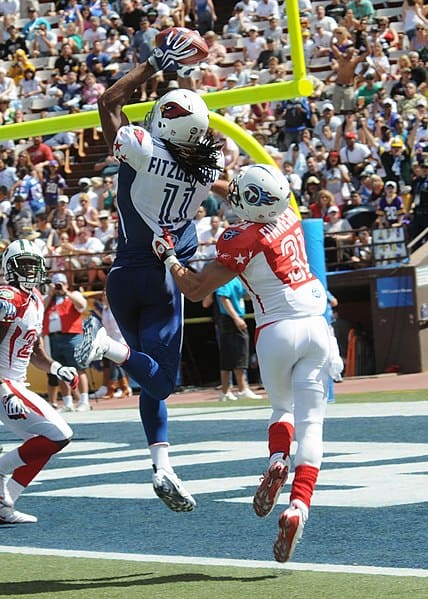

American football, referred to as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team with possession of the oval-shaped football, attempts to advance down the field by running with the ball or passing it, while the defense, the team without possession of the ball, aims to stop the offense’s advance and to take control of the ball for themselves. The offense must advance at least ten yards in four downs or plays; if they fail, they turn over the football to the defense, but if they succeed, they are given a new set of four downs to continue the drive. Points are scored primarily by advancing the ball into the opposing team’s end zone for a touchdown or kicking the ball through the opponent’s goalposts for a field goal. The team with the most points at the end of a game wins.
American football evolved in the United States, originating from the sports of soccer and rugby. The first American football match was played on November 6, 1869, between two college teams, Rutgers and Princeton, using rules based on the rules of soccer at the time. A set of rule changes drawn up from 1880 onward by Walter Camp, the “Father of American Football”, established the snap, the line of scrimmage, eleven-player teams, and the concept of downs. Later rule changes legalized the forward pass, created the neutral zone and specified the size and shape of the football. The sport is closely related to Canadian football, which evolved in parallel with and at the same time as the American game (although their rules were developed independently from that of Camp’s). Most of the features that distinguish American football from rugby and soccer are also present in Canadian football. The two sports are considered the primary variants of gridiron football.
American football is the most popular sport in the United States. The most popular forms of the game are professional and college football, with the other major levels being high school and youth football. As of 2012, nearly 1.1 million high school athletes and 70,000 college athletes play the sport in the United States annually. The National Football League, the most popular American football league, has the highest average attendance of any professional sports league in the world. Its championship game, the Super Bowl, ranks among the most-watched club sporting events in the world. The league has an annual revenue of around US$13 billion. Other professional leagues exist worldwide, but the sport does not have the international popularity of other American sports like baseball or basketball.
Read More About American Football / Source
Ice hockey
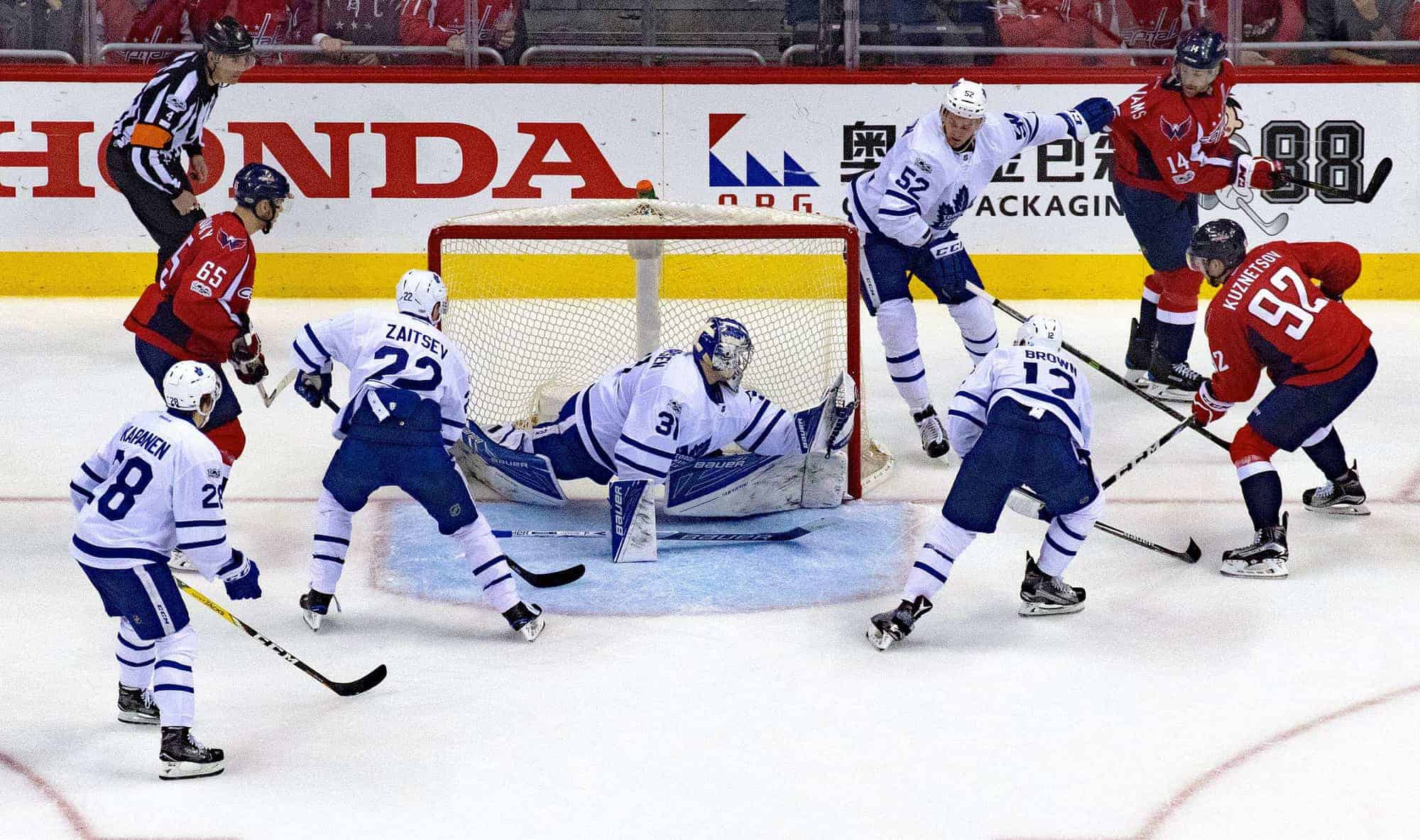

Ice hockey is a contact team sport played on ice, usually in a rink, in which two teams of skaters use their sticks to shoot a vulcanized rubber puck into their opponent’s net to score goals. The sport is known to be fast-paced and physical, with teams usually fielding six players at a time: one goaltender, and five players who skate the span of the ice trying to control the puck and score goals against the opposing team.
Ice hockey is most popular in Canada, central and eastern Europe, the Nordic countries, Russia, and the United States. Ice hockey is the official national winter sport of Canada. In addition, ice hockey is the most popular winter sport in Belarus, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Finland, Latvia, Russia, Slovakia, Sweden, and Switzerland. North America’s National Hockey League (NHL) is the highest level for men’s ice hockey and the strongest professional ice hockey league in the world. The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) is the highest league in Russia and much of Eastern Europe. The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) is the formal governing body for international ice hockey, with the IIHF managing international tournaments and maintaining the IIHF World Ranking. Worldwide, there are ice hockey federations in 76 countries.In Canada, the United States, Nordic countries, and some other European countries the sport is known simply as hockey; the name “ice hockey” is used in places where “hockey” more often refers to field hockey, such as countries in South America, Asia, Africa, Australasia, and some European countries including the United Kingdom, Ireland and the Netherlands.Ice hockey is believed to have evolved from simple stick and ball games played in the 18th and 19th centuries in the United Kingdom and elsewhere. These games were brought to North America and several similar winter games using informal rules were developed, such as shinny and ice polo. The contemporary sport of ice hockey was developed in Canada, most notably in Montreal, where the first indoor hockey game was played on March 3, 1875. Some characteristics of that game, such as the length of the ice rink and the use of a puck, have been retained to this day. Amateur ice hockey leagues began in the 1880s, and professional ice hockey originated around 1900. The Stanley Cup, emblematic of ice hockey club supremacy, was first awarded in 1893 to recognize the Canadian amateur champion and later became the championship trophy of the NHL. In the early 1900s, the Canadian rules were adopted by the Ligue Internationale de Hockey Sur Glace, the precursor of the IIHF and the sport was played for the first time at the Olympics during the 1920 Summer Olympics. Despite women having played since the beginnings of the game, women’s hockey was not professionally organised until much later, the first IIHF Women’s World Championship being held in 1990 and the being introduced into the Olympics in 1998.
In international competitions, the national teams of six countries (the Big Six) predominate: Canada, Czech Republic, Finland, Russia, Sweden and the United States. Of the 69 medals awarded all-time in men’s competition at the Olympics, only seven medals were not awarded to one of those countries (or two of their precursors, the Soviet Union for Russia, and Czechoslovakia for the Czech Republic). In the annual Ice Hockey World Championships, 177 of 201 medals have been awarded to the six nations. Teams outside the Big Six have won only five medals in either competition since 1953. The World Cup of Hockey is organized by the National Hockey League and the National Hockey League Players’ Association (NHLPA), unlike the annual World Championships and quadrennial Olympic tournament, both run by the International Ice Hockey Federation. World Cup games are played under NHL rules and not those of the IIHF, and the tournament occurs prior to the NHL pre-season, allowing for all NHL players to be available, unlike the World Championships, which overlaps with the NHL’s Stanley Cup playoffs. Furthermore, all 12 Women’s Olympic and 36 IIHF World Women’s Championship medals were awarded to one of the Big Six. The Canadian national team or the United States national team have between them won every gold medal of either series.
Read More About Ice hockey / Source
Grand Prix Motorcycle Racing (Moto GP)
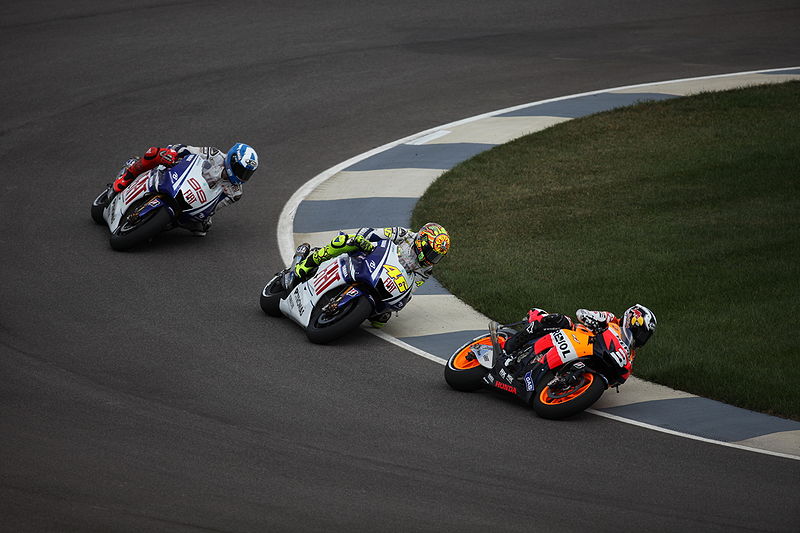

Grand Prix motorcycle racing is the premier class of motorcycle road racing events held on road circuits sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme (FIM). Independent motorcycle racing events have been held since the start of the twentieth century and large national events were often given the title Grand Prix. The foundation of the Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme as the international governing body for motorcycle sport in 1949 provided the opportunity to coordinate rules and regulations in order that selected events could count towards official World Championships. It is the oldest established motorsport world championship.Grand Prix motorcycles are purpose-built racing machines that are unavailable for purchase by the general public and unable to be ridden legally on public roads. This contrasts with the various production-based categories of racing, such as the Superbike World Championship and the Isle of Man TT Races that feature modified versions of road-going motorcycles available to the public. The current top division is known as MotoGP since 2002 when the four-stroke era began. Prior to that, the largest class was 500cc, both of which form a historical continuum as the official World Championship, although all classes have official status.
The championship is currently divided into four classes: the eponymous MotoGP, Moto2, Moto3 and MotoE. The first three classes use four-stroke engines, while the MotoE class (new in 2019) uses electric motorcycles. The 2019 MotoGP season comprises 19 Grands Prix, with 12 held in Europe, three in Asia, two in the Americas, and one each in Australia and the Middle East.
The most successful rider in Grand Prix history is Giacomo Agostini with 15 titles and 122 race wins. In the top-flight series, Agostini holds the title record with eight, followed by active riders Valentino Rossi with seven and Marc Márquez with six. As of 2019, Rossi holds the record for most top-flight race wins with 89.
Read More About Grand Prix Motorcycle Racing (Moto GP) / Source
Badminton
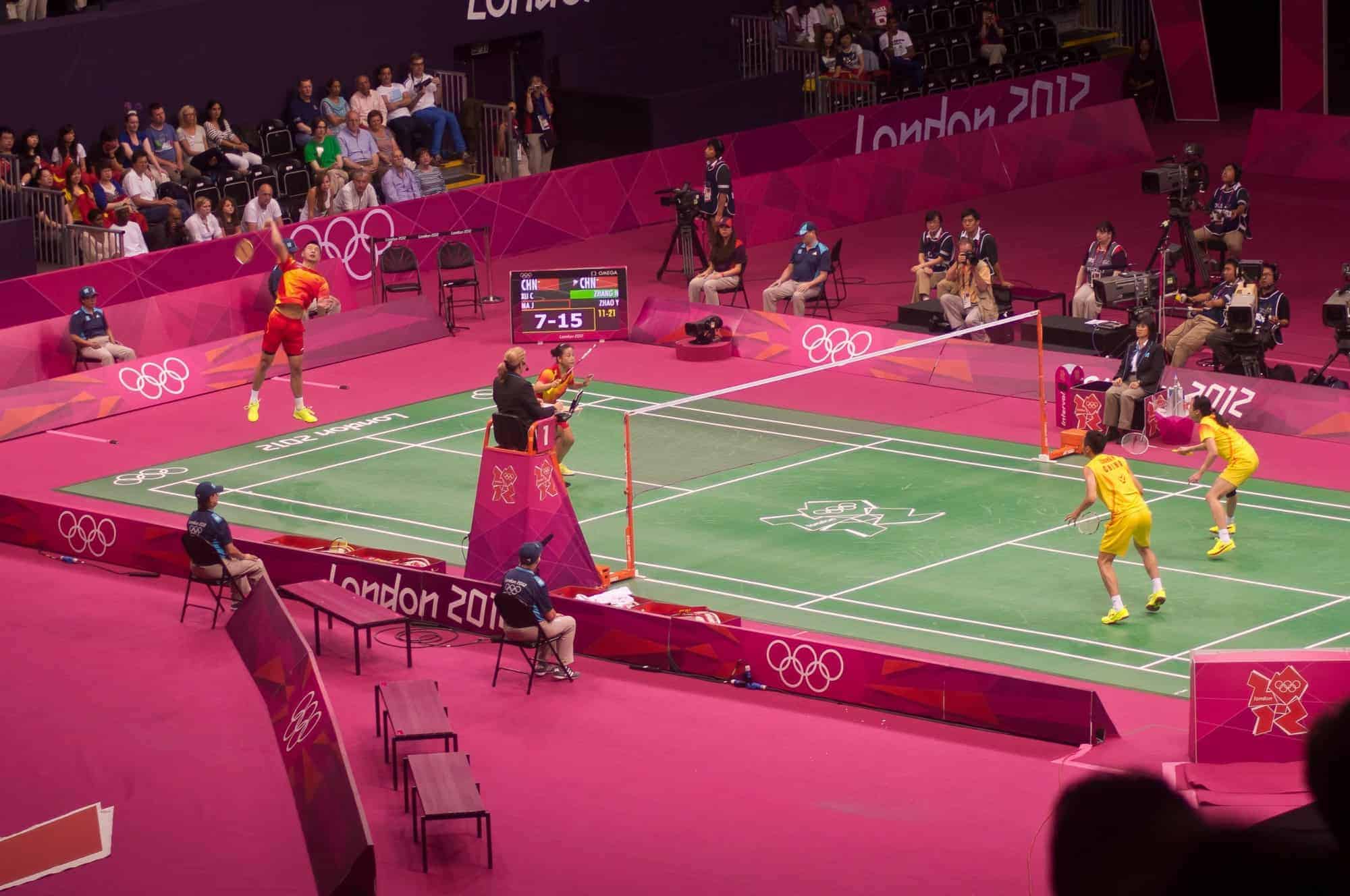

Badminton is a racquet sport played using racquets to hit a shuttlecock across a net. Although it may be played with larger teams, the most common forms of the game are “singles” (with one player per side) and “doubles” (with two players per side). Badminton is often played as a casual outdoor activity in a yard or on a beach; formal games are played on a rectangular indoor court. Points are scored by striking the shuttlecock with the racquet and landing it within the opposing side’s half of the court.
Each side may only strike the shuttlecock once before it passes over the net. Play ends once the shuttlecock has struck the floor or if a fault has been called by the umpire, service judge, or (in their absence) the opposing side.The shuttlecock is a feathered or (in informal matches) plastic projectile which flies differently from the balls used in many other sports. In particular, the feathers create much higher drag, causing the shuttlecock to decelerate more rapidly. Shuttlecocks also have a high top speed compared to the balls in other racquet sports. The flight of the shuttlecock gives the sport its distinctive nature.
The game developed in British India from the earlier game of battledore and shuttlecock. European play came to be dominated by Denmark but the game has become very popular in Asia, with recent competitions dominated by China. Since 1992, badminton has been a Summer Olympic sport with four events: men’s singles, women’s singles, men’s doubles, and women’s doubles, with mixed doubles added four years later. At high levels of play, the sport demands excellent fitness: players require aerobic stamina, agility, strength, speed, and precision. It is also a technical sport, requiring good motor coordination and the development of sophisticated racquet movements.
Read More About Badminton / Source
Cycling
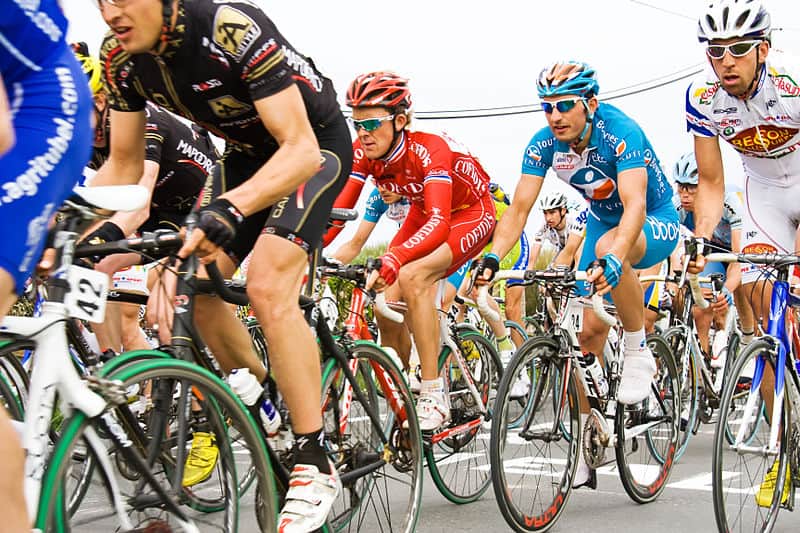

Cycle sport is competitive physical activity using bicycles. There are several categories of bicycle racing including road bicycle racing, time trialling, cyclo-cross, mountain bike racing, track cycling, BMX, and cycle speedway. Non-racing cycling sports include artistic cycling, cycle polo, freestyle BMX and mountain bike trials. The Union Cycliste Internationale (UCI) is the world governing body for cycling and international competitive cycling events. The International Human Powered Vehicle Association is the governing body for human-powered vehicles that imposes far fewer restrictions on their design than does the UCI. The UltraMarathon Cycling Association is the governing body for many ultra-distance cycling races.
Bicycle racing is recognised as an Olympic sport. Bicycle races are popular all over the world, especially in Europe. The countries most devoted to bicycle racing include Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain and Switzerland. Other countries with international standing include Australia, Luxembourg, United Kingdom, United States and Colombia.
Read More About Cycling / Source
Gymnastics
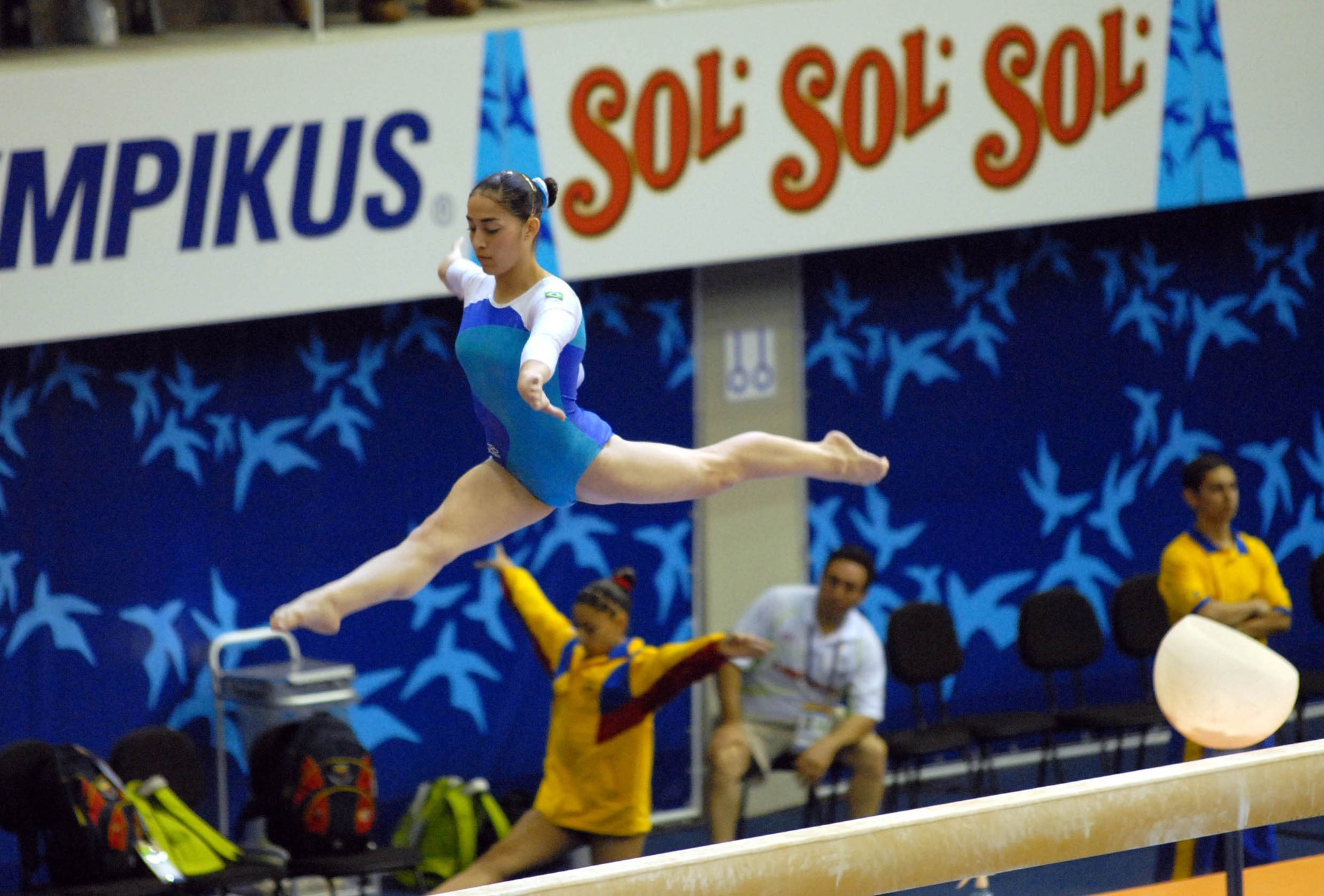

Gymnastics is a sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, shoulders, back, chest, and abdominal muscle groups. Gymnastics evolved from exercises used by the ancient Greeks that included skills for mounting and dismounting a horse and from circus performance skills.
The most common form of competitive gymnastics is artistic gymnastics, which consists of for women (WAG), the events floor, vault, uneven bars, and beam. For men (MAG), it consists of the events floor, vault, rings, pommel horse, parallel bars, and horizontal bar. The governing body for gymnastics through out the world is the Fédération Internationale de Gymnastique (FIG). Eight sports are governed by the FIG, which include Gymnastics for All, Men’s and Women’s Artistic Gymnastics, Rhythmic Gymnastics, Trampoline (including Double Mini-trampoline), Tumbling, acrobatic, aerobic and Parkour. Disciplines not currently recognized by FIG include wheel gymnastics, aesthetic group gymnastics, men’s rhythmic gymnastics, TeamGym, and mallakhamba.
Participants in gymnastics-related sports can include young children, recreational-level athletes, and competitive athletes at varying levels of skill, including world-class athletes.
Read More About Gymnastics / Source
Wrestling
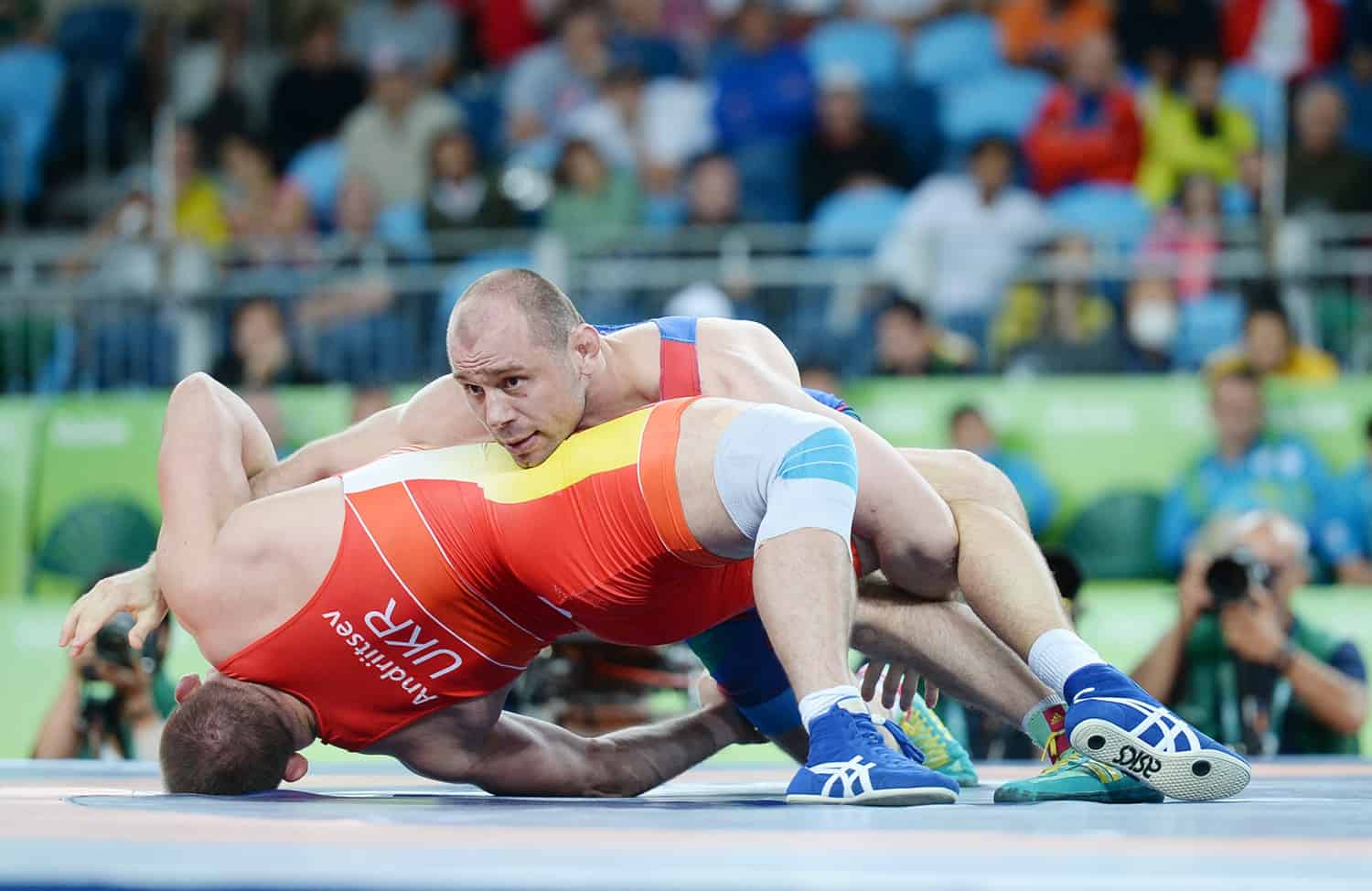

Wrestling is a combat sport involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. The sport can either be genuinely competitive or sportive entertainment (see professional wrestling). Wrestling comes in different types such as folkstyle, freestyle, Greco-Roman, catch, submission, judo, sambo and others. A wrestling bout is a physical competition, between two (occasionally more) competitors or sparring partners, who attempt to gain and maintain a superior position. There are a wide range of styles with varying rules with both traditional historic and modern styles. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into other martial arts as well as military hand-to-hand combat systems.
The term wrestling is attested in late Old English, as wræstlunge (glossing palestram).
Read More About Wrestling / Source
Swimming
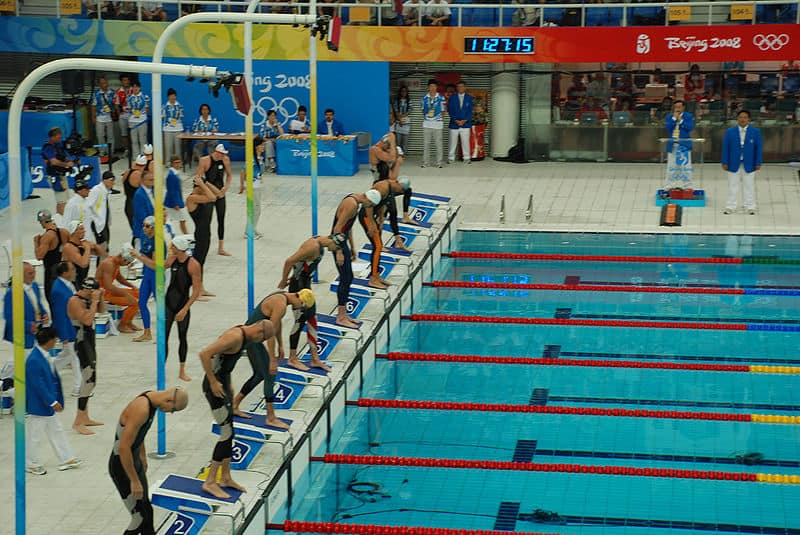

Swimming is an individual or team racing sport that requires the use of one’s entire body to move through water. The sport takes place in pools or open water (e.g., in a sea or lake). Competitive swimming is one of the most popular Olympic sports, with varied distance events in butterfly, backstroke, breaststroke, freestyle, and individual medley. In addition to these individual events, four swimmers can take part in either a freestyle or medley relay. A medley relay consists of four swimmers who will each swim a different stroke, ordered as backstroke, breaststroke, butterfly and freestyle.Swimming each stroke requires a set of specific techniques; in competition, there are distinct regulations concerning the acceptable form for each individual stroke. There are also regulations on what types of swimsuits, caps, jewelry and injury tape that are allowed at competitions. Although it is possible for competitive swimmers to incur several injuries from the sport, such as tendinitis in the shoulders or knees, there are also multiple health benefits associated with the sport.
Read More About Swimming / Source
Kabaddi
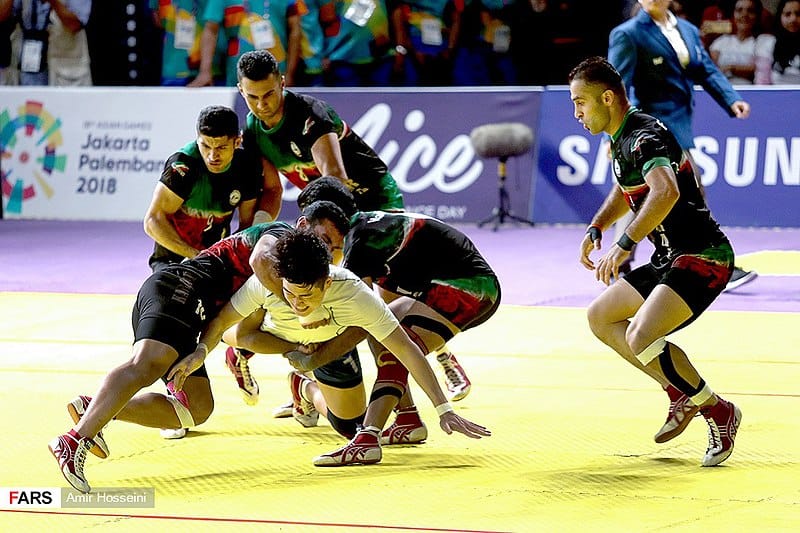

Kabaddi is a contact team sport. Played between two teams of seven players, the objective of the game is for a single player on offence, referred to as a “raider”, to run into the opposing team’s half of a court, tag out as many of their defenders as possible, and return to their own half of the court, all without being tackled by the defenders, and in a single breath. Points are scored for each player tagged by the raider, while the opposing team earns a point for stopping the raider. Players are taken out of the game if they are tagged or tackled, but are brought back in for each point scored by their team from a tag or tackle.
It is popular in the Indian subcontinent and other surrounding Asian countries. Although accounts of kabaddi appear in the histories of ancient India, the game was popularised as a competitive sport in the 20th century. It is the national sport of Bangladesh. It is the state game of the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh.There are two major disciplines of kabaddi: “Punjabi kabaddi”, also referred to as “circle style”, comprises traditional forms of the sport that are played on a circular field outdoors, while the “standard style”, played on a rectangular court indoors, is the discipline played in major professional leagues and international competitions such as the Asian Games.
The game is known by numerous names in different parts of South Asia, such as: kabaddi or chedugudu in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana; kabaddi in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Kerala; kabadi or ha-du-du in Bangladesh; bhavatik in Maldives, kauddi or kabaddi in the Punjab region; hu-tu-tu in Western India, hu-do-do in Eastern India; chadakudu in South India; kapardi in Nepal; and kabadi or sadugudu in Tamil Nadu.
Read More About Kabaddi / Source
Skiing
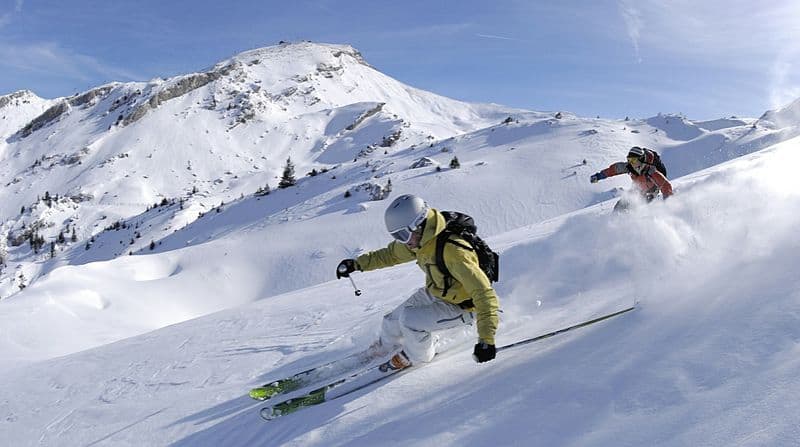

Skiing is a means of transport using skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), and the International Ski Federation (FIS).
Read More About Skiing / Source
Horse Racing
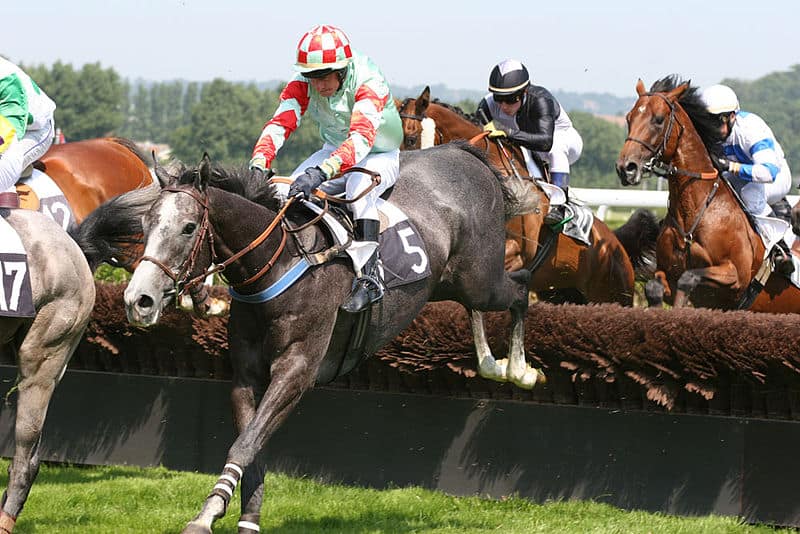

Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance, for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic premise – to identify which of two or more horses is the fastest over a set course or distance – has been unchanged since at least classical antiquity.Horse races vary widely in format and many countries have developed their own particular traditions around the sport. Variations include restricting races to particular breeds, running over obstacles (cross-country), running over different distances (typically a mile, mile and a quarter, mile and an 8th, mile and a 16th), running on different track surfaces and running in different gaits.
While horses are sometimes raced purely for sport, a major part of horse racing’s interest and economic importance is in the gambling associated with it, an activity that in 2008 generated a worldwide market worth around US$115 billion. Many people use a handicapper which is one who assigns weights for a handicap race and makes selections based on past performances.
Read More About Horse Racing / Source
Snooker
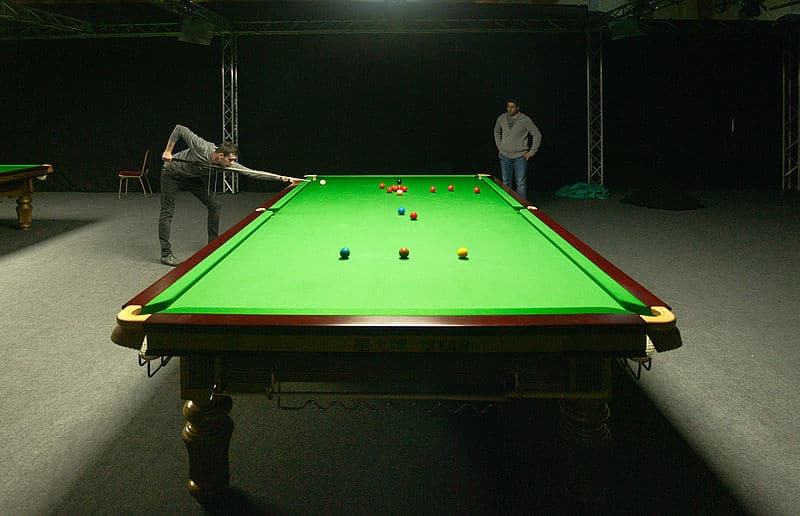

Snooker is a cue sport that originated among British Army officers stationed in India in the second half of the 19th century. It is played on a rectangular table covered with a green cloth (or “baize”), with pockets at each of the four corners and in the middle of each long side. Using a cue stick and 21 coloured balls, players must strike the white ball (or “cue ball”) to pot or pocket the remaining balls in the correct sequence, accumulating points for each pot. An individual game (or frame) is won by the player scoring the most points. A match is won when a player wins a predetermined number of frames.
Snooker gained its identity in 1875 when army officer Sir Neville Chamberlain (1856–1944), stationed in Ootacamund, Madras, devised a set of rules that combined pyramid and black pool. The word snooker was a long-used military term for inexperienced or first-year personnel. The game grew in popularity in the United Kingdom, and the Billiards Association and Control Club was formed in 1919. It is now governed by the World Professional Billiards and Snooker Association (WPBSA).
The World Snooker Championship has taken place since 1927. Joe Davis, a key figure and pioneer in the early growth of the sport, won the championship 15 straight times between 1927 and 1946. The “modern era” began in 1969 after the broadcaster BBC commissioned the snooker television show Pot Black and later began to air the World Championship in 1978. Key figures in the game were Ray Reardon in the 1970s, Steve Davis in the 1980s, and Stephen Hendry in the 1990s, each winning six or more World championships. Since 2000, Ronnie O’Sullivan has won the most world titles, with six. Top professional players now compete regularly around the world and earn millions of pounds on the World Snooker Tour, which features players from across the world.
Read More About Snooker / Source
Shooting
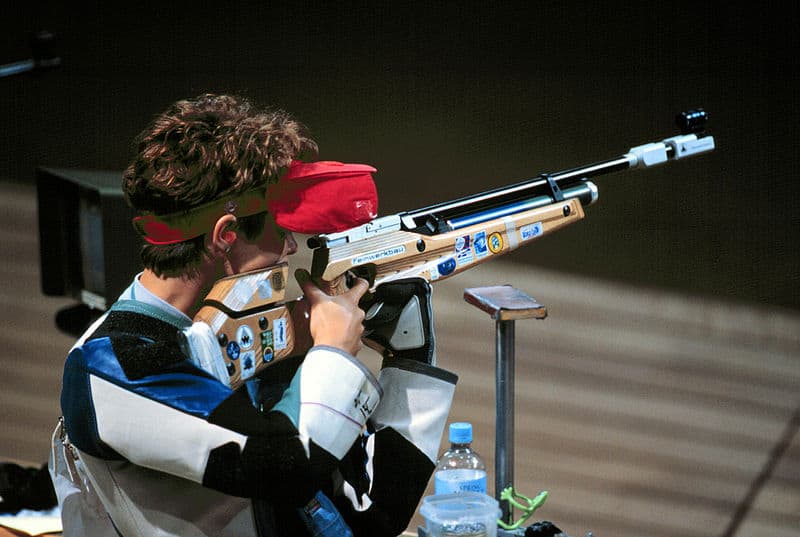

Shooting sports is a collective group of competitive and recreational sporting activities involving proficiency tests of accuracy, precision and speed in shooting — the art of using various types of ranged firearms, mainly referring to man-portable guns (firearms and airguns, in forms such as handguns, rifles and shotguns) and bows/crossbows.Different disciplines of shooting sports can be categorized by equipment, shooting distances, targets, time limits and degrees of athleticism involved. Shooting sports may involve both team and individual competition, and team performance is usually assessed by summing the scores of the individual team members. Due to the noise of shooting and the high (and often lethal) impact energy of the projectiles, shooting sports are typically conducted at either designated permanent shooting ranges or temporary shooting fields in the area away from settlements.
Read More About Shooting / Source
Handball
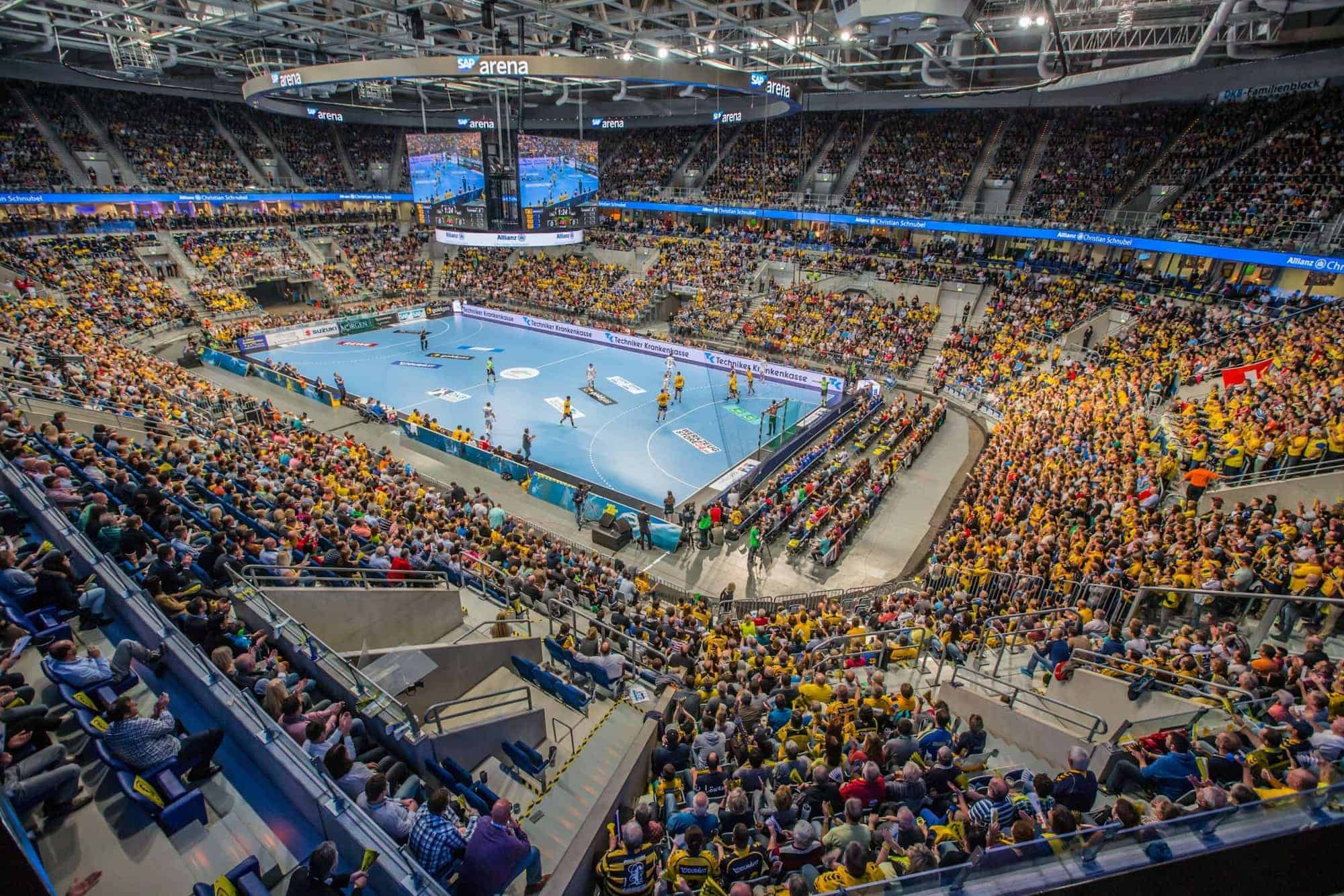

Handball (also known as team handball, European handball or Olympic handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of throwing it into the goal of the other team. A standard match consists of two periods of 30 minutes, and the team that scores more goals wins.
Modern handball is played on a court of 40 by 20 metres (131 by 66 ft), with a goal in the middle of each end. The goals are surrounded by a 6-meter (20 ft) zone where only the defending goalkeeper is allowed; goals must be scored by throwing the ball from outside the zone or while “diving” into it. The sport is usually played indoors, but outdoor variants exist in the forms of field handball, Czech handball (which were more common in the past) and beach handball. The game is fast and high-scoring: professional teams now typically score between 20 and 35 goals each, though lower scores were not uncommon until a few decades ago. Players may score hat tricks. Body contact is permitted for the defenders trying to stop the attackers from approaching the goal. No protective equipment is mandated, but players may wear soft protective bands, pads and mouth guards.The game was codified at the end of the 19th century in Denmark. The modern set of rules was published on 29 October 1917 in Berlin, which is seen as the date of birth of the sport, and had several revisions since. The first official handball match was played in the same year in Germany. The first international games were played under these rules for men in 1925 and for women in 1930. Men’s handball was first played at the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin as outdoors, and the next time at the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich as indoors, and has been an Olympic sport since. Women’s team handball was added at the 1976 Summer Olympics.
The International Handball Federation was formed in 1946 and, as of 2016, has 197 member federations. The sport is most popular in Europe, and European countries have won all medals but one in the men’s world championships since 1938. In the women’s world championships, only two non-European countries have won the title: South Korea and Brazil. The game also enjoys popularity in East Asia, North Africa and parts of South America.
Read More About Handball / Source
Chess
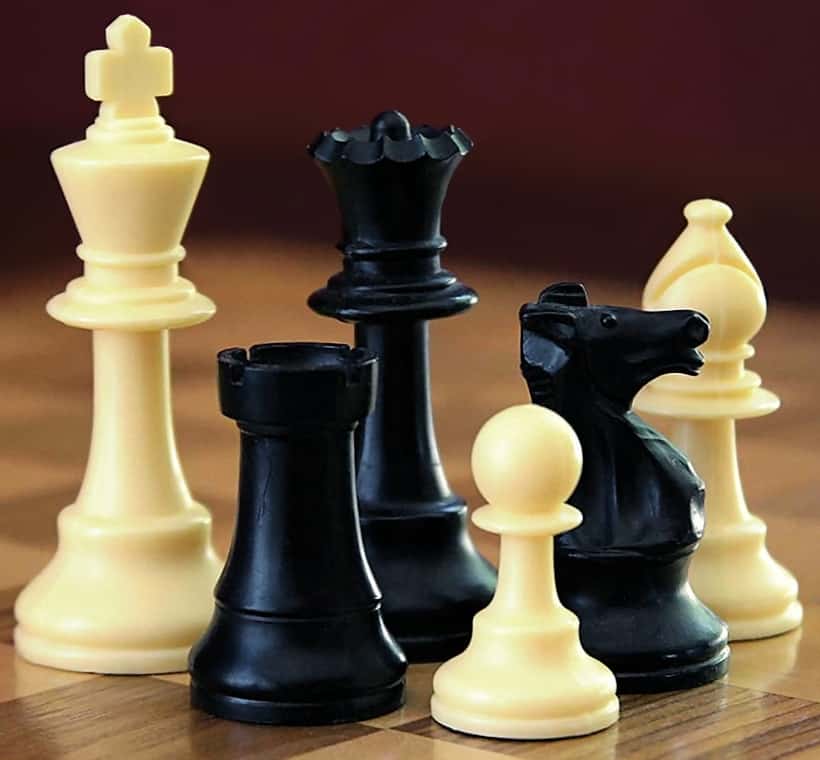

Chess is a board game played between two players. It is sometimes called Western chess or international chess to distinguish it from related games such as xiangqi and shogi. The current form of the game emerged in Southern Europe during the second half of the 15th century after evolving from chaturanga, a similar but much older game of Indian origin. Today, chess is one of the world’s most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide.
Chess is an abstract strategy game and involves no hidden information. It is played on a square chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player (one controlling the white pieces, the other controlling the black pieces) controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, two bishops, two knights, and eight pawns. The object of the game is to checkmate the opponent’s king, whereby the king is under immediate attack (in “check”) and there is no way for it to escape. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw.
Organized chess arose in the 19th century. Chess competition today is governed internationally by FIDE (International Chess Federation). The first universally recognized World Chess Champion, Wilhelm Steinitz, claimed his title in 1886; Magnus Carlsen is the current World Champion. A huge body of chess theory has developed since the game’s inception. Aspects of art are found in chess composition; and chess in its turn influenced Western culture and art and has connections with other fields such as mathematics, computer science, and psychology.
One of the goals of early computer scientists was to create a chess-playing machine. In 1997, Deep Blue became the first computer to beat the reigning World Champion in a match when it defeated Garry Kasparov. Today’s chess engines are significantly stronger than the best human players, and have deeply influenced the development of chess theory.
Read More About Chess / Source
Hurling
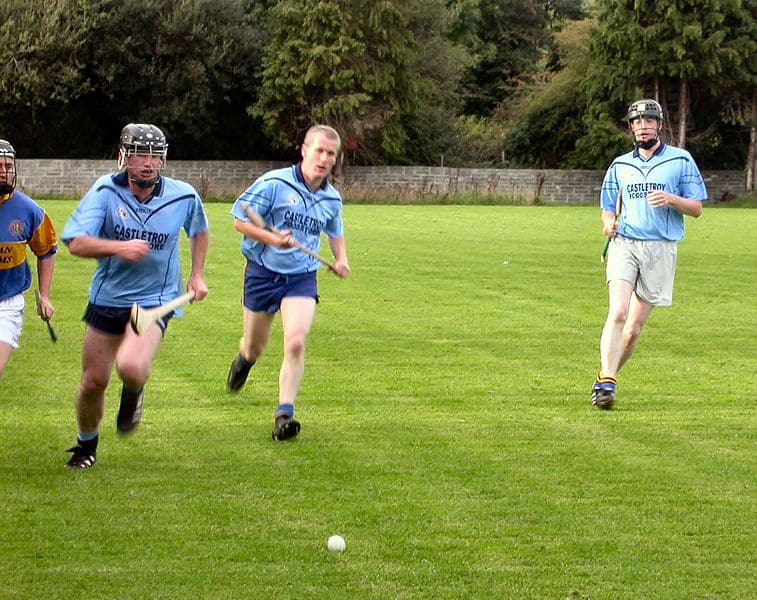

Hurling (Irish: iománaíocht, iomáint) is an outdoor team game of ancient Gaelic Irish origin, played by men. One of Ireland’s native Gaelic games, it shares a number of features with Gaelic football, such as the field and goals, the number of players, and much terminology. There is a similar game for women called camogie (camógaíocht). It shares a common Gaelic root with the sport of shinty (camanachd), which is played predominantly in Scotland.
The objective of the game is for players to use a wooden (ash) stick called a hurley (in Irish a camán, pronounced or ) to hit a small ball called a sliotar between the opponents’ goalposts either over the crossbar for one point, or under the crossbar into a net guarded by a goalkeeper for three points. The sliotar can be caught in the hand and carried for not more than four steps, struck in the air, or struck on the ground with the hurley. It can be kicked, or slapped with an open hand (the hand pass) for short-range passing. A player who wants to carry the ball for more than four steps has to bounce or balance the sliotar on the end of the stick, and the ball can only be handled twice while in the player’s possession.
Provided that a player has at least one foot on the ground, a player may make a shoulder to shoulder charge on an opponent who is in possession of the ball or is playing the ball or when both players are moving in the direction of the ball to play it.
No protective padding is worn by players. A plastic protective helmet with a faceguard is mandatory for all age groups, including senior level, as of 2010. The game has been described as “a bastion of humility”, with player names absent from jerseys and a player’s number decided by his position on the field.Hurling is administered by the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA). It is played throughout the world, and is popular among members of the Irish diaspora in North America, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Argentina, and South Korea. In many parts of Ireland, however, hurling is a fixture of life. It has featured regularly in art forms such as film, music and literature. The final of the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship was listed in second place by CNN in its “10 sporting events you have to see live”, after the Olympic Games and ahead of both the FIFA World Cup and UEFA European Football Championship. After covering the 1959 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final between Kilkenny and Waterford for BBC Television, English commentator Kenneth Wolstenholme was moved to describe hurling as his second favourite sport in the world after his first love, football. Alex Ferguson used footage of an All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship final in an attempt to motivate his players during his time as manager of Premier League football club Manchester United; the players winced at the standard of physicality and intensity in which the hurlers were engaged. In 2007, Forbes magazine described the media attention and population multiplication of Thurles town ahead of one of the game’s annual provincial hurling finals as being “the rough equivalent of 30 million Americans watching a regional lacrosse game”.UNESCO lists hurling as an element of Intangible cultural heritage.
Read More About Hurling / Source
Bowling
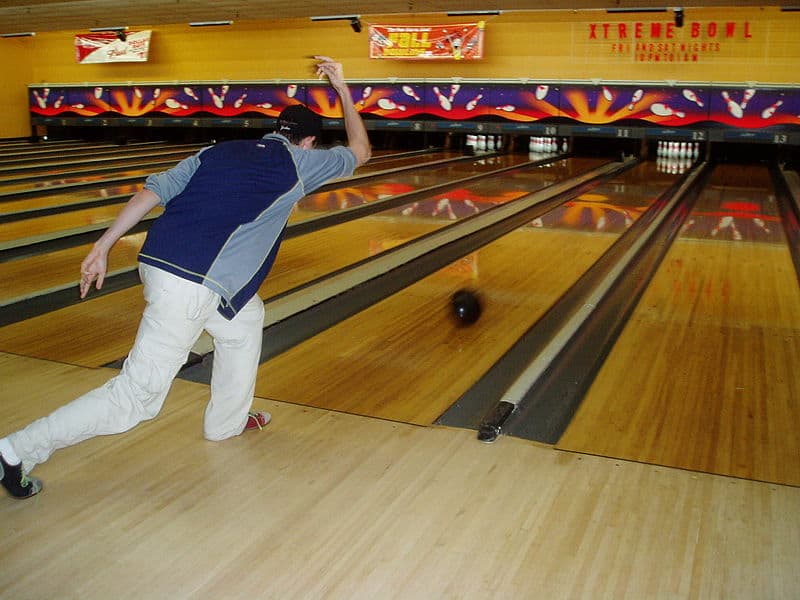

Bowling is a target sport and recreational activity in which a player rolls a ball toward pins (in pin bowling) or another target (in target bowling). The term bowling usually refers to ten-pin bowling, though in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth countries bowling could also refer to lawn bowls.
In pin bowling, the goal is to knock over pins on a long playing surface known as a lane. A strike is achieved when all the pins are knocked down on the first roll, and a spare is achieved if all the pins are knocked over on a second roll.
Lanes have a wood or synthetic surface onto which protective lubricating oil is applied in different specified oil patterns that vary ball path trajectories and characteristics. Common types of pin bowling include ten-pin, candlepin, duckpin, nine-pin, five-pin and kegel. The historical game skittles is the forerunner of modern pin bowling.
In target bowling, the aim is usually to get the ball as close to a mark as possible. The surface in target bowling may be grass, gravel, or synthetic. Lawn bowls, bocce, carpet bowls, pétanque, and boules may have both indoor and outdoor varieties.
Bowling is played by 100 million people in more than 90 countries (including 70 million in the United States alone), and is the subject of video games.
Read More About Bowling / Source