100 Most Spoken Languages in the World
Currently, more or less 7,000 languages are spoken all over the world. Some languages are spoken by millions in a vast region while some are popular in a tiny area. But the purpose of all these languages is the same which is- conveying one’s feelings and give a message. Moreover, each country has its own official language. It helps people in communicating with each other in a coherent and consistent way. And any official language is spoken by a majority of people in any country. Here, we have created a list of the most spoken languages in the world. Determining it obviously is a daunting task since the horizon of this knowledge is quite vast. But still, these are rough estimates by studying which you can have a clarity about the popularity of any language. These languages connect people in a single thread and solve critical problems.
The list is based on the languages with most native speakers.
Hindi

Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of Northern India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with the English language. It is an official language in 9 States and 3 Union Territories and an additional official language in 3 other States. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.
Read More About Hindi / Source
Mandarin Chinese

Mandarin is a group of Sinitic (Chinese) languages spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese. Because Mandarin originated in North China and most Mandarin languages and dialects are found in the north, the group is sometimes referred to as Northern Chinese (北方话, běifānghuà, ‘northern speech’). Many varieties of Mandarin, such as those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze (including the old capital Nanjing), are not mutually intelligible or are only partially intelligible with the standard language. Nevertheless, Mandarin is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly a billion).
Read More About Mandarin Chinese / Source
Spanish language
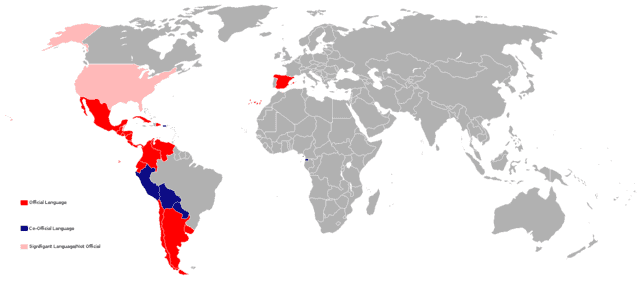
Spanish is a Romance language that originated in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a global language with nearly 500 million native speakers, mainly in Spain and the Americas. It is the world’s second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese, and the world’s fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindi.
Read More About Spanish language / Source
English language

English is a West Germanic language first spoken in early medieval England, which has eventually become the leading language of international discourse in the 21st century. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name, England. Both names derive from Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea. English is most closely related to Frisian and Low Saxon, while its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages, particularly Old Norse (a North Germanic language), as well as Latin and French.
Read More About English language / Source
Arabic

Arabic is a Semitic language that first emerged in the 1st to 4th centuries CE. It is now the lingua franca of the Arab world. It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living in the Arabian Peninsula bounded by eastern Egypt in the west, Mesopotamia in the east, and the Anti-Lebanon mountains and Northern Syria in the north, as perceived by ancient Greek geographers The ISO assigns language codes to thirty varieties of Arabic, including its standard form, Modern Standard Arabic, also referred to as Literary Arabic, which is modernized Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā (اَلعَرَبِيَّةُ ٱلْفُصْحَىٰ “the eloquent Arabic”) or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ). Modern Standard Arabic is an official language of 26 states and 1 disputed territory, the third most after English and French.
Read More About Arabic / Source
Japanese language

Japanese is an East Asian language spoken by about 128 million people, primarily in Japan, where it is the national language. It is a member of the Japonic (or Japanese-Ryukyuan) language family, and its relation to other languages, such as Korean, is debated. Japonic languages have been grouped with other language families such as Ainu, Austroasiatic, and the now-discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals has gained widespread acceptance.
Read More About Japanese language / Source
Portuguese language
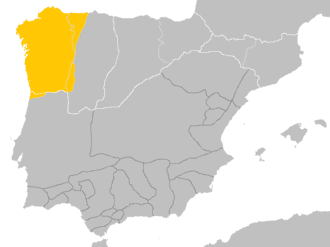
Portuguese is a Romance language originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is the sole official language of Portugal, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde, São Tomé and Príncipe, and Brazil, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as “Lusophone” (lusófono). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese and Portuguese creole speakers are also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology and its lexicon.
Read More About Portuguese language / Source
Urdu

Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the official national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. In India, Urdu is an Eighth Schedule language whose status, function, and cultural heritage is recognized by the Constitution of India; it has some form of official status in several Indian states. In Nepal, Urdu is a registered regional dialect. Urdu has been described as a Persianised standard register of the Hindustani language. Urdu and Hindi share a common Indo-Aryan vocabulary base and very similar phonology and syntax, making them mutually intelligible in colloquial speech.
Wu Chinese
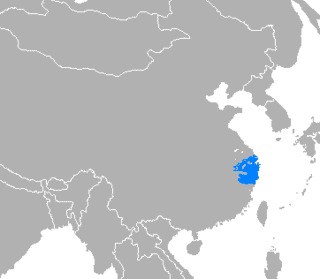
Wu is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages spoken primarily in Shanghai, Zhejiang Province, the southern half of Jiangsu Province and surrounding areas. Major Wu varieties include those of Shanghai, Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Shaoxing, Wenzhou, Jinhua and Yongkang. Wu speakers, such as Chiang Kai-shek, Lu Xun and Cai Yuanpei, occupied positions of great importance in modern Chinese culture and politics.
Read More About Wu Chinese / Source
Korean language

Korean is an East Asian language spoken by about 77 million people. It is the official and national language of both Koreas: North Korea and South Korea, with different standardized official forms used in each country. It is a recognised minority language in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture and Changbai Korean Autonomous County of Jilin Province, China. It is also spoken in parts of Sakhalin, Russia and Central Asia.
Read More About Korean language / Source
Russian language
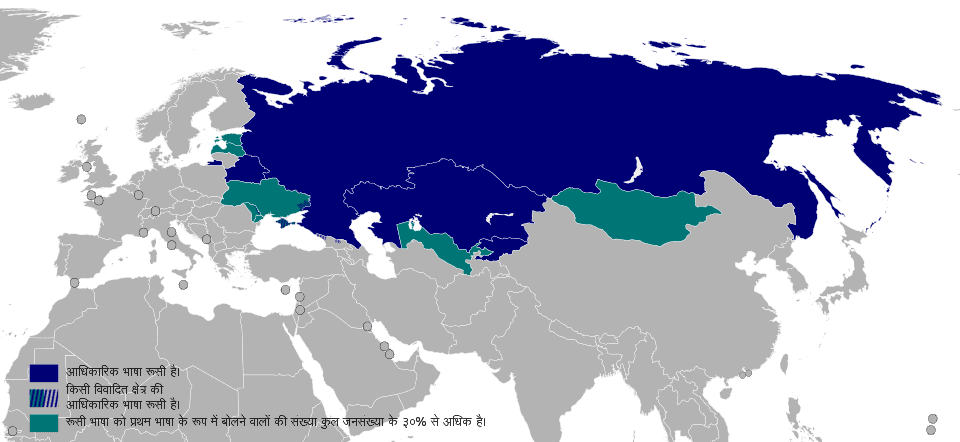
Russian (русский язык, tr. russkiy yazyk) is an East Slavic language native to the Russians in Eastern Europe. It is an official language in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely throughout the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. Russian belongs to the family of Indo-European languages, one of the four living members of the East Slavic languages alongside, and part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch.
Read More About Russian language / Source
Telugu language
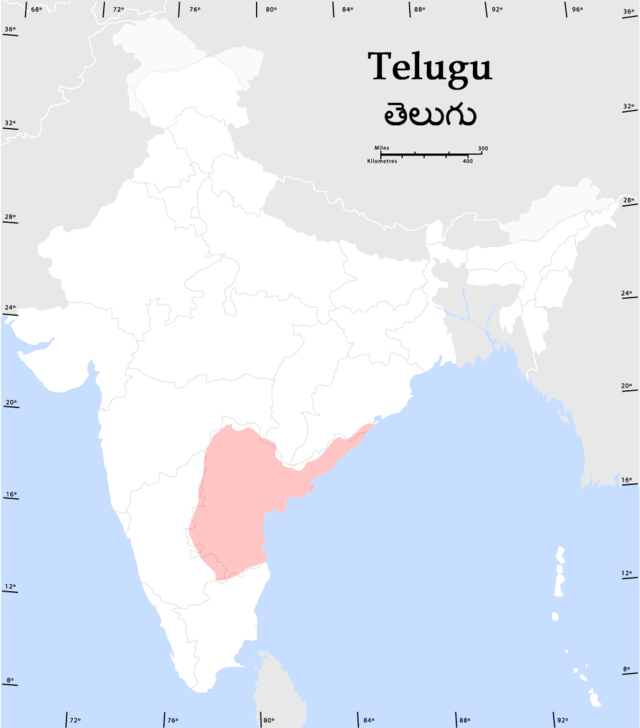
Telugu is a Dravidian language spoken by Telugu people predominantly living in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. It stands alongside Hindi and Bengali as one of the few languages with primary official language status in more than one Indian state. Telugu is also a linguistic minority in the states of Odisha, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Punjab, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is one of six languages designated a classical language of India by the country’s government.
Read More About Telugu language / Source
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken predominantly by around 83 million Marathi people of Maharashtra, India. It is the official language and co-official language in the Maharashtra and Goa states of Western India, respectively and is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. With 83 million speakers as 2011, Marathi ranks 10th in the list of most spoken languages in the world. Marathi has the third largest number of native speakers in India, after Hindi and Bengali. The language has some of the oldest literature of all modern Indian languages, dating from around 600 AD. The major dialects of Marathi are Standard Marathi and the Varhadi dialect. Koli, Agri and Malvani Konkani have been heavily influenced by Marathi varieties.
Read More About Marathi language / Source
Pashto

Pashto, sometimes spelled Pukhto or Pakhto, is an Eastern Iranian language of the Indo-European family. It is known in Persian literature as Afghani . The language is natively spoken by Pashtuns (also called Pukhtuns/Pakhtuns; historically known as ethnic Afghans), an ethnic group of Afghanistan and Pakistan. Pashto comprises, along with Dari (alternatively known as ‘Afghan Persian’), the two languages of Afghanistan with official status. Pashto is also the second-largest regional language in Pakistan, mainly spoken in the northwestern province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and the northern districts of the Balochistan province. Likewise, it is the primary language of the Pashtun diaspora around the world; the total number of Pashto-speakers is thought to be at least 40 million, although some estimates place it as high as 60 million.
Read More About Pashto / Source
Bengali language
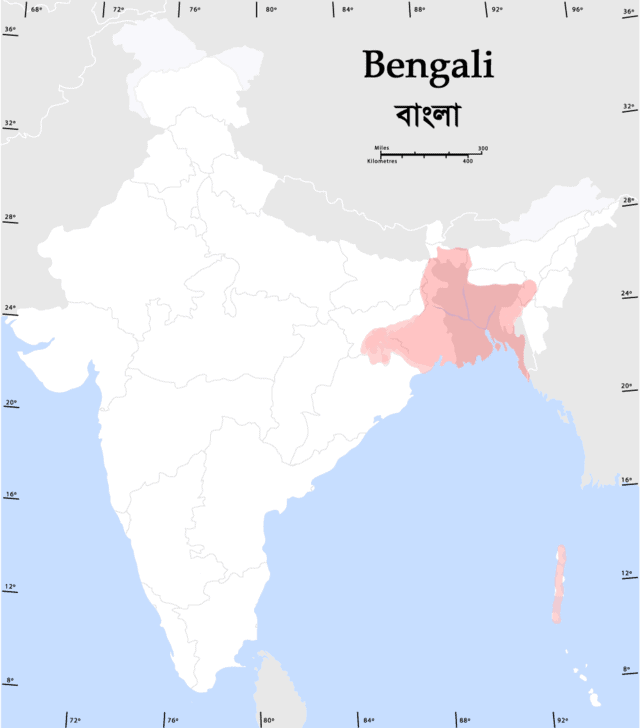
Bengali, also known by its endonym Bangla, is an Indo-Aryan language and the lingua franca of the Bengal region of Indian subcontinent. It is the most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second most widely spoken of the 22 scheduled languages of India, after Hindi. With approximately 228 million native speakers and another 37 million as second language speakers, Bengali is the fifth most-spoken native language and the seventh most spoken language by total number of speakers in the world.
Read More About Bengali language / Source
German language
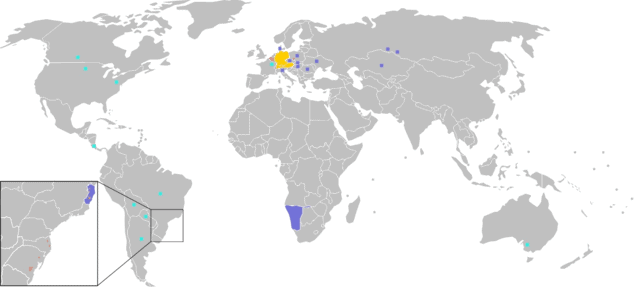
The German language is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg, Belgium and parts of southwestern Poland, as well as a national language in Namibia. German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German (Low Saxon), Luxembourgish, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish, although these belong to the North Germanic group. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language after English.
Read More About German language / Source
Malay language
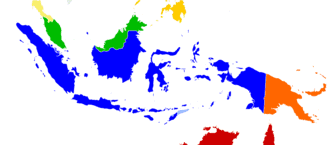
Malay is an Austronesian language officially spoken in Indonesia, Brunei, Malaysia and Singapore and unofficially spoken in East Timor and parts of Thailand. A language of the Malays, it is spoken by 290 million people (around 260 million as Indonesian) across the Malay World.
Read More About Malay language / Source
French language
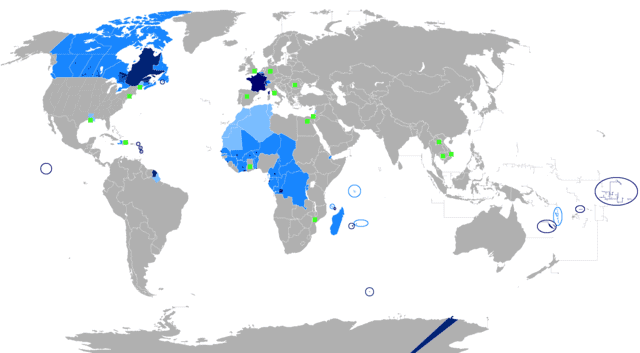
French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d’oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France’s past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.
Read More About French language / Source
Punjabi language

Punjabi (Gurmukhi, Shahmukhi) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Punjabi people and native to the Punjab region of India and Pakistan. It has approximately 113 million native speakers. The larger part – 80.5 million as of 2017 – are in Pakistan, where Punjabi has more speakers than any other language but no official recognition at the national or provincial level. In India, Punjabi is spoken by 31.1 million people (as of 2011) and has official status in the state of Punjab. The language is spoken among a significant overseas diaspora, particularly in Canada, the United States and the United Kingdom.It has approximately 113 million native speakers. The larger part – 80.5 million as of 2017 – are in Pakistan, where Punjabi has more speakers than any other language but no official recognition at the national or provincial level. In India, Punjabi is spoken by 31.1 million people (as of 2011) and has official status in the state of Punjab. The language is spoken among a significant overseas diaspora, particularly in Canada, the United States and the United Kingdom.
Read More About Punjabi language / Source
Vietnamese language
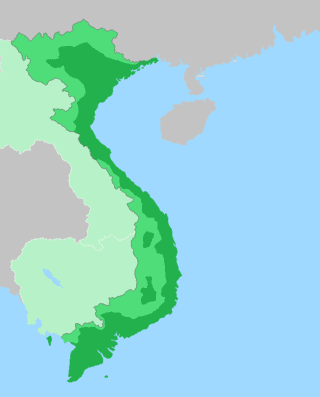
Vietnamese is an Austroasiatic language that originated in Vietnam, where it is the national and official language. It is by far the most spoken Austroasiatic language with over 70 million native speakers, at least seven times more than Khmer, the next most spoken Austroasiatic language. Its vocabulary has had significant influence from Chinese and French. It is the native language of the Vietnamese (Kinh) people, as well as a second language or first language for other ethnic groups in Vietnam. As a result of emigration, Vietnamese speakers are also found in other parts of Southeast Asia, East Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia. Vietnamese has also been officially recognized as a minority language in the Czech Republic.
Read More About Vietnamese language / Source
Tamil language
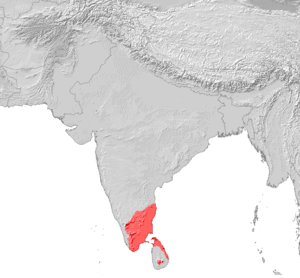
Tamil is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is the official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, as well as two sovereign nations, Singapore and Sri Lanka. In India, it is also the official language of the Union Territory of Puducherry. Tamil is spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors.
Read More About Tamil language / Source
Bhojpuri language

Bhojpuri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in northern-eastern India and the Terai region of Nepal. It is chiefly spoken in western Bihar and eastern Uttar Pradesh. Sociolinguistically, Bhojpuri is often considered one of several Hindi dialects. The language is a minority language in Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, South Africa, Suriname and Trinidad and Tobago.
Read More About Bhojpuri language / Source
Tagalog language
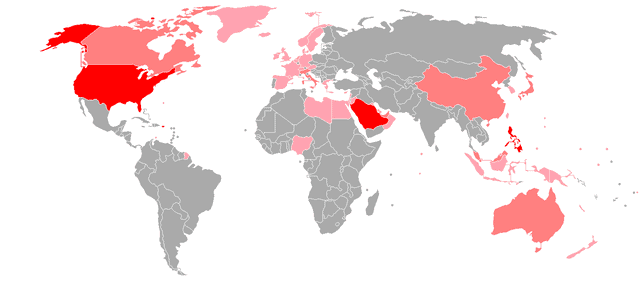
Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority. Its standardized form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of two official languages alongside English.
Read More About Tagalog language / Source
Marwari language
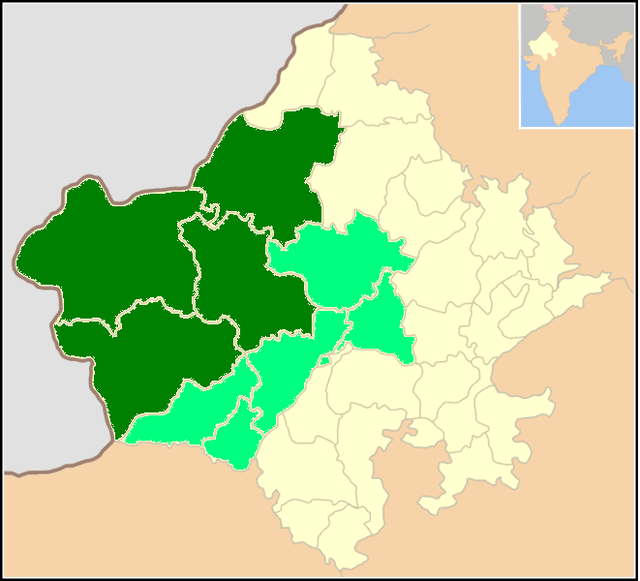
Marwari is a Rajasthani dialect spoken in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Marwari is also found in the neighbouring state of Gujarat and Haryana, Eastern Pakistan and some migrant communities in Nepal. With some 7.8 million or so speakers, it is one of the largest varieties of Rajasthani. Most speakers live in Rajasthan, with a quarter million in Sindh and a tenth that number in Nepal. There are two dozen dialects of Marwari.
Read More About Marwari language / Source
Magahi language
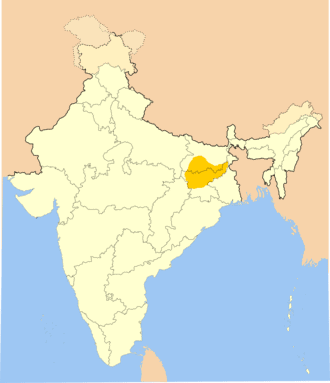
The Magahi language, also known as Magadhi, is a language spoken in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal states of eastern India. Magadhi Prakrit was the ancestor of Magahi, from which the latter’s name derives. It has a very rich and old tradition of folk songs and stories. It is spoken in nine districts of Bihar (Gaya, Patna, Jehanabad, Aurangabad, Nalanda, Sheikhpura, Nawada, Lakhisarai, Arwal), eight districts of Jharkhand (Hazaribag, Palamu, Chatra, Koderma, Jamtara, Bokaro, Dhanbad, Giridih) and in West Bengal’s Malda district. There are around 20,700,000 speakers of Magahi, including speakers of Khortha which is considered a dialect of Magahi.
Read More About Magahi language / Source
Thai language
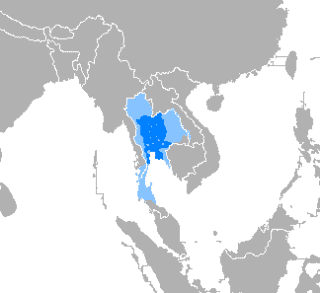
Thai, Central Thai, is the national language of Thailand and de facto official language; it is the first language of the Central Thai people and most Thai Chinese, depending on age. It is a member of the Tai group of the Kra–Dai language family, and one of over 60 languages of Thailand. Over half of Thai vocabulary is derived from or borrowed from Pali, Sanskrit, Mon and Old Khmer. It is a tonal and analytic language, similar to Chinese and Vietnamese.
Read More About Thai language / Source
Gujarati language
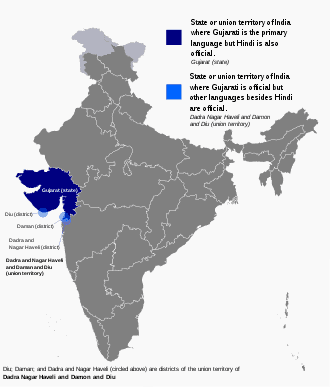
Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is part of the greater Indo-European language family. Gujarati is descended from Old Gujarati (c. 1100–1500 CE). In India, it is the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.
Read More About Gujarati language / Source
Malayalam
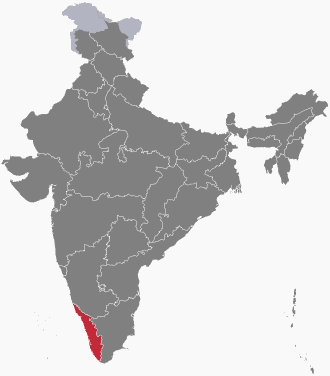
Malayalam is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India and is spoken by 2.88% of Indians. Malayalam has official language status in the state of Kerala and in the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé) and is spoken by 34 million people worldwide. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with significant number of speakers in the Nilgiris, Kanyakumari, and Coimbatore, Tenkasi, Theni districts of Tamil Nadu and Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka. Due to Malayali expatriates in the Persian Gulf, Malayalam is also widely spoken in the Gulf countries.
Read More About Malayalam / Source
Odia language
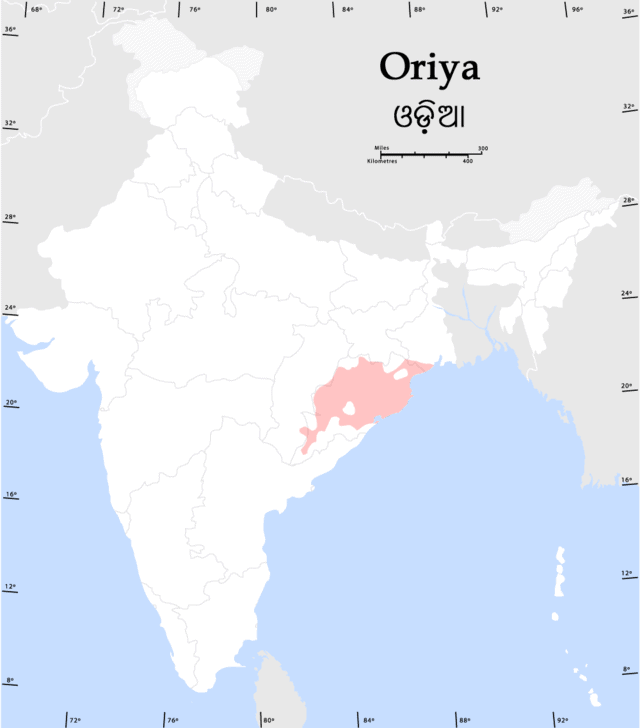
Odia is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the official language in Odisha (formerly known as Orissa) where native speakers make up 82% of the population, also spoken in parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh, Odia is one of the many official languages of India; it is the official language of Odisha and the second official language of Jharkhand. The language is also spoken by a sizeable population of at least 1 million people in Chhattisgarh.
Read More About Odia language / Source
Fula language
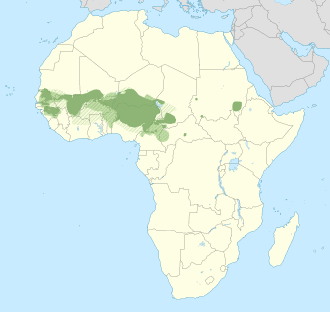
Fula, is a Senegambian language spoken as a set of various dialects in a continuum that stretches across some 20 countries in West and Central Africa by more than 65 million people. Along with other related languages such as Serer and Wolof, it belongs to the Senegambian branch within the Niger–Congo family, which does not have tones, unlike most other Niger–Congo languages. More broadly, it belongs to the Atlantic geographic grouping within Niger–Congo. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people (“Fulani”, Fula: Fulɓe) from the Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley. It is also spoken as a second language by various peoples in the region, such as the Kirdi of northern Cameroon and northeastern Nigeria.
Read More About Fula language / Source
Azerbaijani language
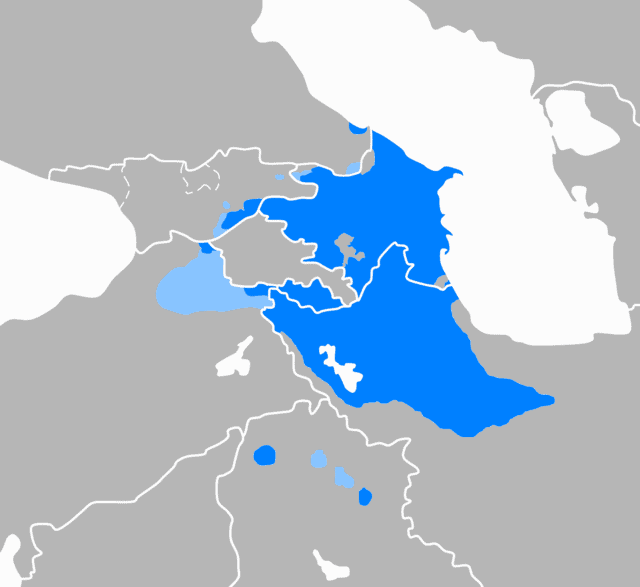
Azerbaijani, also referred to as Azeri Turkish, is a Turkic language spoken primarily by the Azerbaijani people, who live mainly in the Republic of Azerbaijan where the North Azerbaijani variety is spoken, and in the Azerbaijan region of Iran, where the South Azerbaijani variety is spoken. Although there is a very high degree of mutual intelligibility between both forms of Azerbaijani, there are significant differences in phonology, lexicon, morphology, syntax and sources of loanwords.
Read More About Azerbaijani language / Source
Balochi language
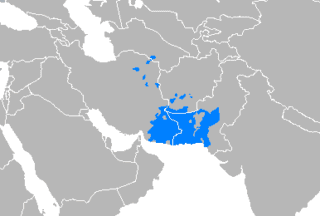
Balochi is a Northwestern Iranian language spoken primarily in the Balochistan region divided between Pakistan, Iran and Afghanistan. It is spoken by 3 to 5 million people. In addition to Pakistan, Iran and Afghanistan, it is also spoken in Oman, the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Turkmenistan, East Africa and in diaspora communities in other parts of the world.
Read More About Balochi language / Source
Uzbek language
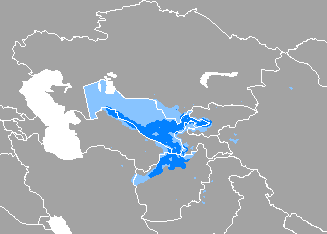
Uzbek is a Turkic language that is the first official and only declared national language of Uzbekistan. The language of Uzbeks is spoken by some 27 million native speakers in Uzbekistan and elsewhere in Central Asia, making it the second-most widely spoken Turkic language after Turkish.
Read More About Uzbek language / Source
Igbo language
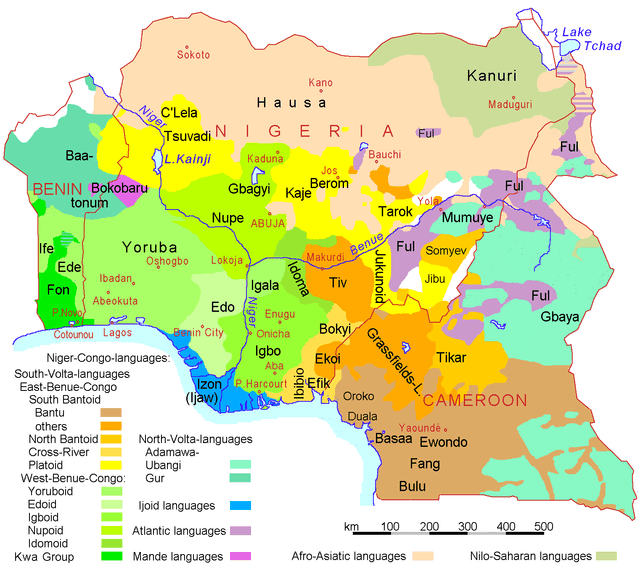
Igbo is the principal native language of the Igbo people, an ethnic group of southeastern Nigeria. A standard literary language was developed in 1972 based on the Owerri (Isuama) and Umuahia (such as Ohuhu) dialects, though it omits the nasalization and aspiration of those varieties.[citation needed] Related Igboid languages such as Ika, Ukwuani and Ogba are dialects of Igbo. Igbo is recognized as a major language in Nigeria, a minority in Equatorial Guinea and Cameroon.
Read More About Igbo language / Source
Awadhi language
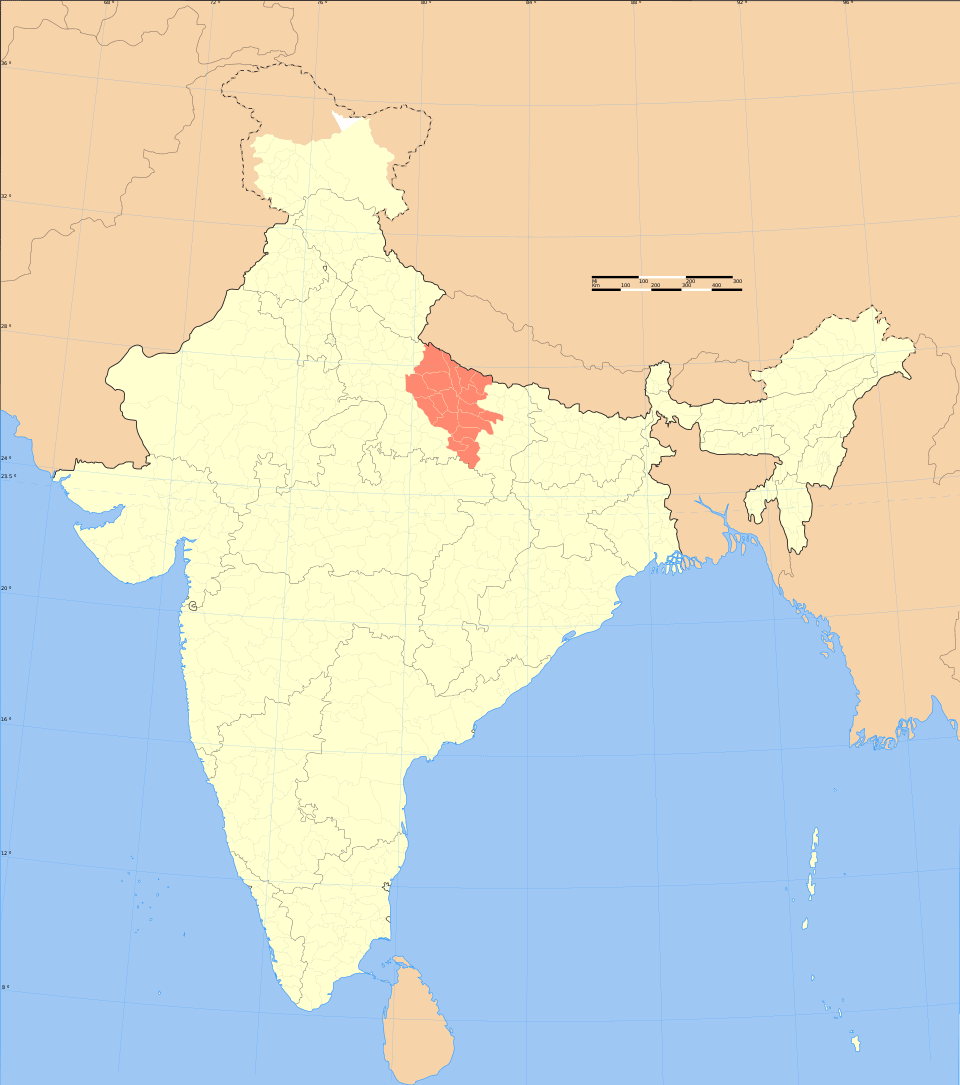
Awadhi is an Eastern Hindi language of the Indo-Aryan branch spoken in northern India. It is primarily spoken in the Awadh region of present-day Uttar Pradesh, India. The name Awadh is connected to Ayodhya, the ancient town, which is regarded as the homeland of the Hindu god Rama. It was, along with Braj Bhasha, used widely as a literary vehicle before being displaced by Hindustani in the 19th century.
Read More About Awadhi language / Source
Dutch language
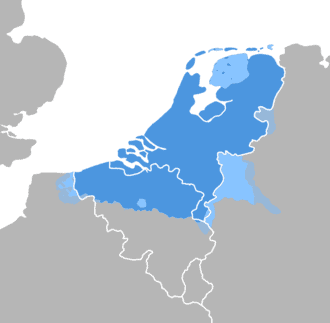
Dutch (Nederlands) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 24 million people as a first language and 5 million people as a second language, constituting the majority of people in the Netherlands (where it is the only official language countrywide) and Belgium (as one of three official languages). It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives English and German.
Read More About Dutch language / Source
Kurdish languages
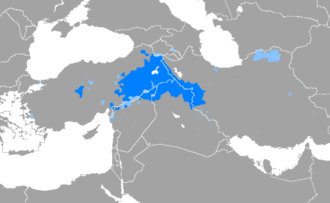
The Kurdish languages constitute a dialect continuum, belonging to the Iranian language family, spoken by Kurds in the geo-cultural region of Kurdistan and the Kurdish diaspora. The three Kurdish languages are Northern Kurdish (Kurmanji), Central Kurdish (Sorani), and Southern Kurdish (Xwarîn). A separate group of non-Kurdish Northwestern Iranian languages, the Zaza–Gorani languages, are also spoken by several million ethnic Kurds. The majority of the Kurds speak Kurmanji. Most Kurdish texts are written in Kurmanji and Sorani. Kurmanji is written in the Hawar alphabet, a derivation of the Latin script, and Sorani is written in the Sorani alphabet, a derivation of Arabic script.
Read More About Kurdish languages / Source
Malagasy language

Malagasy is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Most people in Madagascar speak it as a first language, as do some people of Malagasy descent elsewhere. The Malagasy language is the westernmost member of the Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family, a grouping that includes languages from Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. In fact, Malagasy’s distinctiveness from nearby African languages had already been noted by early scholars, such as the Dutch scholar Adriaan Reland in 1708.
Read More About Malagasy language / Source
Sinhala language

Sinhala, also known as Sinhalese, is an Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Buddhist peoples of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. Sinhala is also spoken as the first language by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 4 million people as of 2001. Sinhala is written using the Sinhala script, which is one of the Brahmic scripts, a descendant of the ancient Indian Brahmi script closely related to the Kadamba script.
Read More About Sinhala language / Source
Zhuang languages
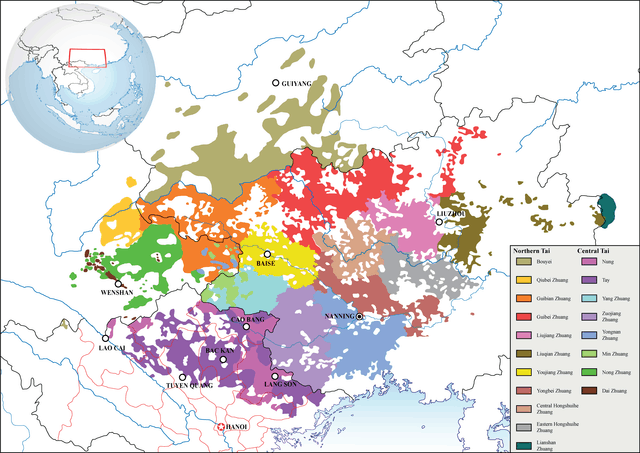
The Zhuang languages are any of more than a dozen Tai languages spoken by the Zhuang people of Southern China in the province of Guangxi and adjacent parts of Yunnan and Guangdong. The Zhuang languages do not form a monophyletic linguistic unit, as northern and southern Zhuang languages are more closely related to other Tai languages than to each other. Northern Zhuang languages form a dialect continuum with Northern Tai varieties across the provincial border in Guizhou, which are designated as Bouyei, whereas Southern Zhuang languages form another dialect continuum with Central Tai varieties such as Nung, Tay and Caolan in Vietnam. Standard Zhuang is based on the Northern Zhuang dialect of Wuming.
Read More About Zhuang languages / Source
Turkmen language
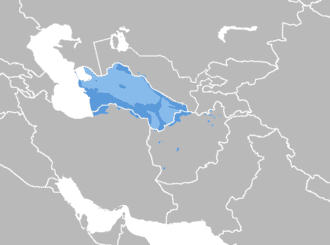
Turkmen, also referred to as Turkmen Turkic or Turkmen Turkish, is a Turkic language spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia, mainly of Turkmenistan, Iran and Afghanistan. It has an estimated five million native speakers in Turkmenistan, a further 719,000 speakers in Northeastern Iran and 1.5 million people in Northwestern Afghanistan. Turkmen has official status in Turkmenistan, but it does not have official status in Iran or Afghanistan, where big communities of ethnic Turkmens live. Turkmen is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Turkmen communities of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and by diaspora communities, primarily in Turkey and Russia.
Read More About Turkmen language / Source
Assamese language
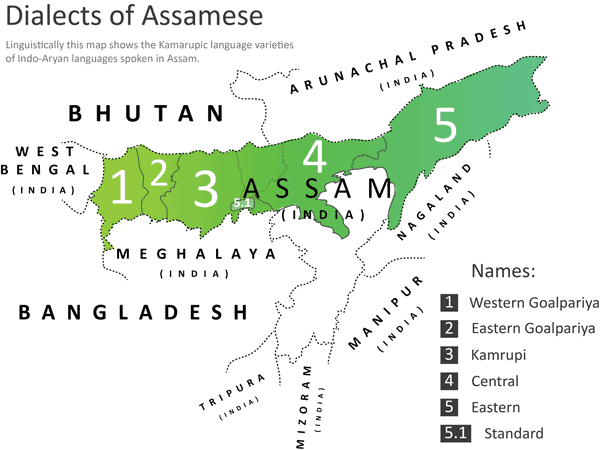
Assamese, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken mainly in the northeast Indian state of Assam, where it is an official language. It is the easternmost Indo-European language, spoken by over 14 million speakers, and serves as lingua franca of the region. Nefamese is an Assamese-based pidgin used in Arunachal Pradesh and Nagamese, an Assamese-based Creole language is widely used in Nagaland. The Kamtapuri language of Rangpur division of Bangladesh and Cooch Behar and Jalpaiguri districts of India are linguistically closer to Assamese, though the speakers identify with the Bengali culture and the literary language. In the past, it was the court language of the Ahom kingdom from the 17th century.
Read More About Assamese language / Source
Madurese language

Madurese is a language of the Madurese people of Madura Island and Eastern Java, Indonesia; it is also spoken on the neighbouring small Kangean Islands and Sapudi Islands, as well as by migrants to other parts of Indonesia, namely the eastern salient of Java (comprising Pasuruan, Surabaya, Malang to Banyuwangi), the Masalembu Islands and even some on Kalimantan. The Kangean dialect may be a separate language. It was traditionally written in the Javanese script, but the Latin script and the Pegon script (based on Arabic script) is now more commonly used. The number of speakers, though shrinking, is estimated to be 8–13 million, making it one of the most widely spoken languages in the country. Bawean, a variant of Madurese, is also spoken by Baweanese (or Boyan) descendants in Malaysia and Singapore.
Madurese is a Malayo-Sumbawan language of the Malayo-Polynesian language family, a branch of the larger Austronesian language family. Thus, despite apparent geographic spread, Madurese is more related to Balinese, Malay, Sasak and Sundanese, than it is to Javanese, the language used on the island of Java just across Madura Island.
Read More About Madurese language / Source
Somali language
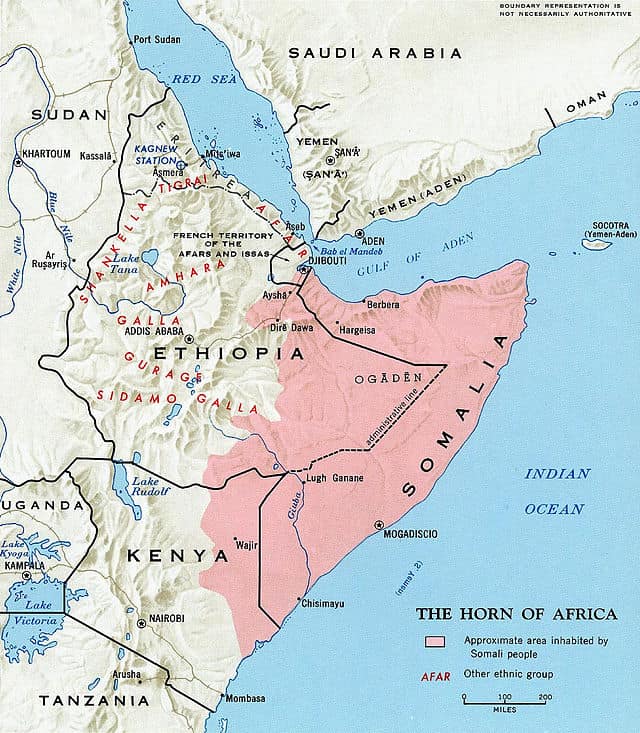
Somali is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken as a mother tongue by Somalis in Greater Somalia and the Somali diaspora. Somali is an official language of Somalia and Somaliland, a national language in Djibouti, and a working language in the Somali Region of Ethiopia and also in North Eastern Kenya. It is used as an adoptive language by a few neighboring ethnic minority groups and individuals. The Somali language is written officially with the Latin alphabet.
Read More About Somali language / Source
Haryanvi language
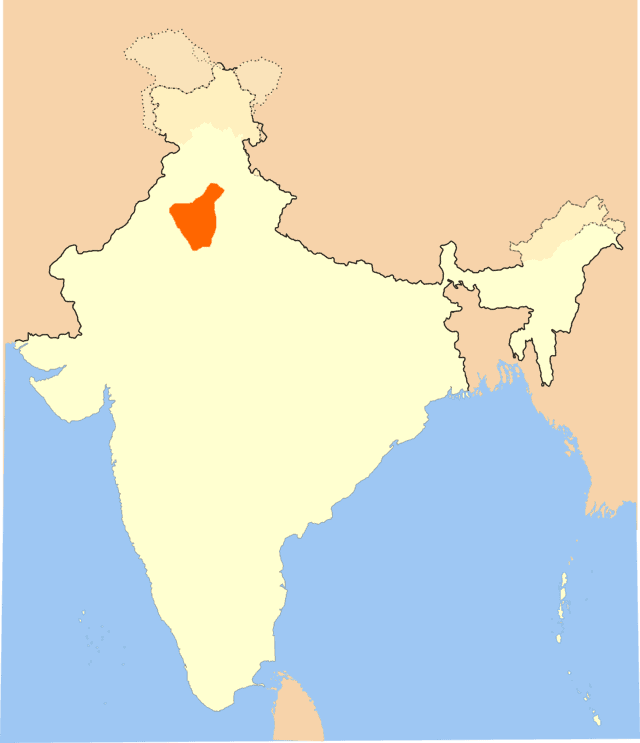
Haryanvi is a Central Indo-Aryan language or dialect spoken in Haryana, India. It is also spoken in metropolitan cities like Delhi and Kolkata to a lesser extent. Haryanvi is considered to be a Western Hindi dialect, like Khariboli and Braj and it is written in Devanagari script.
Read More About Haryanvi language / Source
Hungarian language
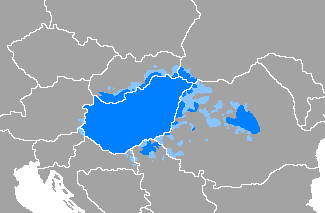
Hungarian (magyar nyelv) is a Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by communities of Hungarians in present-day Slovakia, western Ukraine (Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Mur region) and eastern Austria.
Read More About Hungarian language / Source
Chhattisgarhi language
Chhattisgarhi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by 18 million people in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. Chhattisgarhi has been known by the name Khaltahi to surrounding hill-people and by the name Loriya to speakers in neighboring regions of Odisha. The speakers are concentrated in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and in adjacent areas of Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Jharkhand. Chhattisgarhi cultural and political movements, with origins from the 1920s, affirmed Chhattisgarhi linguistic and cultural identity and sought greater autonomy within India. It was finally given statehood on 1st November 2000.
Read More About Chhattisgarhi language / Source
Chewa language
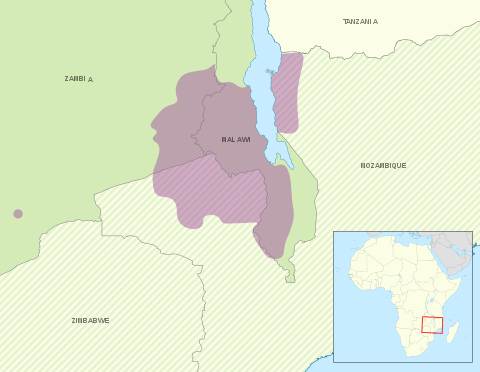
Chewa (also known as Nyanja ) is a Bantu language spoken in much of Southern, Southeast and East Africa, namely the countries of Malawi and Zambia, where it is an official language, and Mozambique and Zimbabwe where it is a recognised minority language. The noun class prefix chi- is used for languages, so the language is usually called Chichewa and Chinyanja (spelled Cinianja in Mozambique). In Malawi, the name was officially changed from Chinyanja to Chichewa in 1968 at the insistence of President Hastings Kamuzu Banda (himself of the Chewa people), and this is still the name most commonly used in Malawi today. In Zambia, the language is generally known as Nyanja or Cinyanja/Chinyanja ‘(language) of the lake’ (referring to Lake Malawi).Chewa belongs to the same language group (Guthrie Zone N) as Tumbuka, Sena and Nsenga.
Read More About Chewa language / Source
Deccan Marathi
Berar-Deccan Marathi, is a possible language of the Marathi–Konkani group, or perhaps just a regional dialect of Marathi. Glottolog reports that it is closely related to Varhadi-Nagpuri. (Sub)dialects are Bijapuri (of Bijapur district, Karnataka) and Kalvadi (of Dharwad district). These have been counted among the Marathi dialects, and it is not clear just how distinct they are from standard Marathi, with the distinct Deccani language perhaps being Deccani Urdu.
Berar-Deccan Marathi shares the names of Deccani Urdu: Dakhini, Dakhni, Dakini, Dakkani, Dakkhani, etc. Ethnologue says the speakers are Muslim and that the language is written in the Nastaliq (primarily) and Devanagari scripts, but again this may be due to confusion with Deccani Urdu.
Read More About Deccan Marathi / Source
Akan language
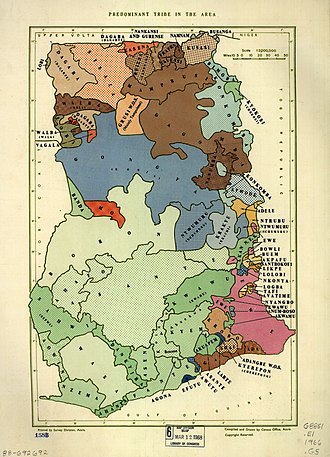
Akan is a Central Tano language and the principal native language of the Akan people of Ghana, spoken over much of the southern half of Ghana. About 80% of Ghana’s population can speak Akan, about 44% of Ghanaians are native speakers. It is also spoken in parts of Côte d’Ivoire. Four dialects have been developed as literary standards with distinct orthographies: Fante, Bono, Asante, and Akuapem, collectively known as Twi; which, despite being mutually intelligible, were inaccessible in written form to speakers of the other standards until the Akan Orthography Committee (AOC)’s development of a common Akan orthography in 1978, based mainly on Akuapem Twi.
Read More About Akan language / Source
Kazakh language
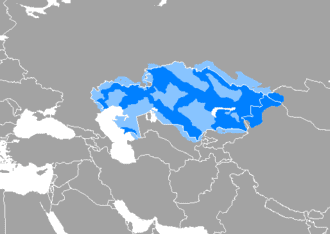
Kazakh, or Qazaq, is a Turkic language of the Kipchak branch spoken in Central Asia. It is closely related to Nogai, Kyrgyz and Karakalpak. Kazakh is the official language of Kazakhstan and a significant minority language in the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang, China and in the Bayan-Ölgii Province of Mongolia. Kazakh is also spoken by many ethnic Kazakhs through the former Soviet Union (some 472,000 in Russia according to the 2010 Russian Census), Germany, Turkey.
Read More About Kazakh language / Source
Northern Min
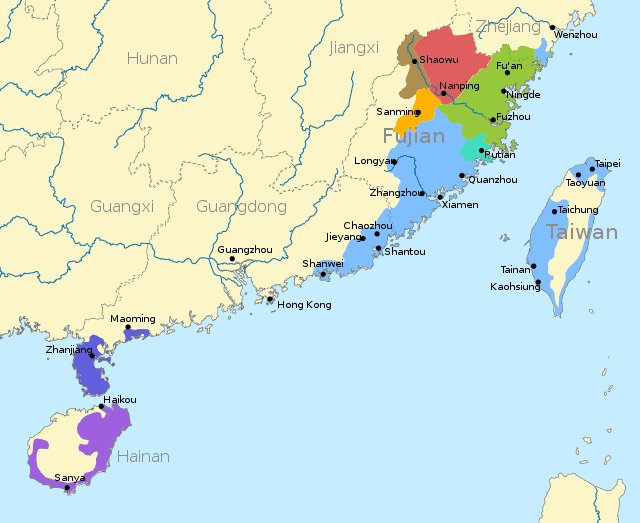
Northern Min, is a group of mutually intelligible Min varieties spoken in Nanping prefecture of northwestern Fujian. Early classifications of varieties of Chinese, such as those of Li Fang-Kuei in 1937 and Yuan Jiahua in 1960, divided Min into Northern and Southern subgroups. However, in a 1963 report on a survey of Fujian, Pan Maoding and colleagues argued that the primary split was between inland and coastal groups. In a reclassification that has been followed by most dialectologists since, they restricted the term Northern Min to inland dialects of Nanping prefecture, and classified the coastal dialects of Fuzhou and Ningde as Eastern Min.
Read More About Northern Min / Source
Sylheti language
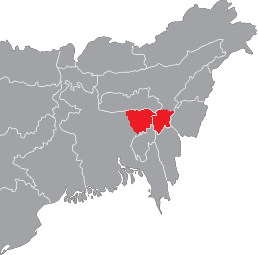
Sylheti is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language spoken by an estimated 11 million people, primarily in the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh, the Barak Valley and the Hojai district of Assam as well as in northern parts of Tripura in India. Outside of these regions, there are substantial numbers of Sylheti speakers in Meghalaya, Manipur and Nagaland; as well as diaspora communities in the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Middle East.
Read More About Sylheti language / Source
Zulu language
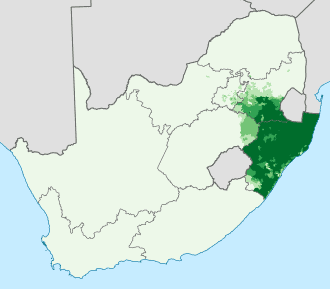
Zulu or isiZulu as an endonym, is a Southern Bantu language of the Nguni branch spoken in Southern Africa. It is the language of the Zulu people, with about 12 million native speakers, who primarily inhabit the province of KwaZulu-Natal of South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa (24% of the population), and it is understood by over 50% of its population. It became one of South Africa’s 11 official languages in 1994.
Read More About Zulu language / Source
Czech language
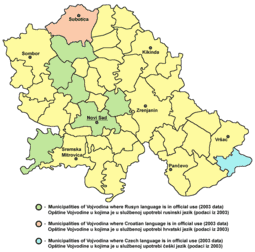
Czech, is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group. Spoken by over 13 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic (Czechia). Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as Polish to a lesser degree. Like other Slavic languages, Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German.
Read More About Czech language / Source
Dhundari language
Dhundhari (also known as Jaipuri) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Dhundhar region of northeastern Rajasthan state, India. Dhundari-speaking people are found in four districts – Jaipur, Sawai Madhopur, Dausa, and Tonk. With some 1.5 million speakers, it is not the largest speaking language in Rajasthan, though fairly used in the regions mentioned above. Dhundhari has no official status in the government in India and is not used as a language of education. Dhundhari is still spoken widely in and around Jaipur.
Read More About Dhundari language / Source
Haitian Creole
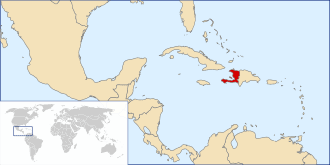
Haitian Creole, commonly referred to as simply Creole, is a French-based creole language spoken by 10–12 million people worldwide, and is one of the two official languages of Haiti, where it is the native language of a majority of the population. The language emerged from contact between French settlers and enslaved Africans during the Atlantic slave trade in the French colony of Saint-Domingue (now Haiti). Although its vocabulary is mostly taken from phonetic 18th-century French, its grammar and sentence structure is that of a West African language, paticularly the Fon language and Igbo language. It also has influences from Spanish, English, Portuguese, Taino, and other West African languages. It is not mutually intelligible with standard French, and has its own distinctive grammar. Haitians are the largest community in the world speaking a modern creole language.
Read More About Haitian Creole / Source
Eastern Min
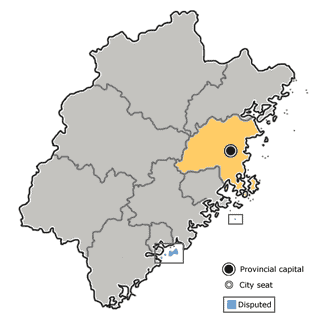
Eastern Min or Min Dong, is a branch of the Min group of Sinitic languages of China. The prestige form and most-cited representative form is the Fuzhou dialect, the speech of the capital and largest city of Fujian. Eastern Min varieties are mainly spoken in the eastern part of Fujian Province of the People’s Republic of China, in and near the cities of Fuzhou and Ningde. They are also widely encountered as the mother tongue on the Matsu Islands controlled by the Republic of China. Additionally, the inhabitants of Taishun and Cangnan to the north of Fujian in Zhejiang also speak Eastern Min varieties. Eastern Min generally coexists with the official standard Chinese in all these areas.
Read More About Eastern Min / Source
Ilocano language
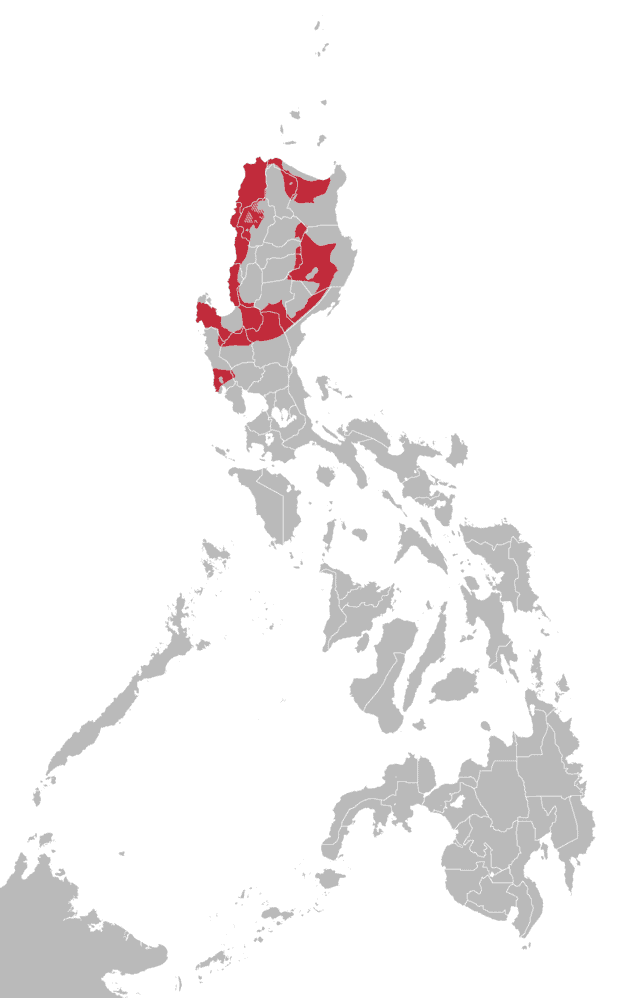
Ilocano is an Austronesian language spoken in the Philippines. It is the third most-spoken native language in the country. As an Austronesian language, it is related to Malay (Indonesian and Malaysian), Tetum, Chamorro, Fijian, Maori, Hawaiian, Samoan, Tahitian, Paiwan and Malagasy. It is closely related to some of the other Austronesian languages of Northern Luzon, and has slight mutual intelligibility with the Balangao language and the eastern dialects of the Bontoc language.
Read More About Ilocano language / Source
Quechuan languages
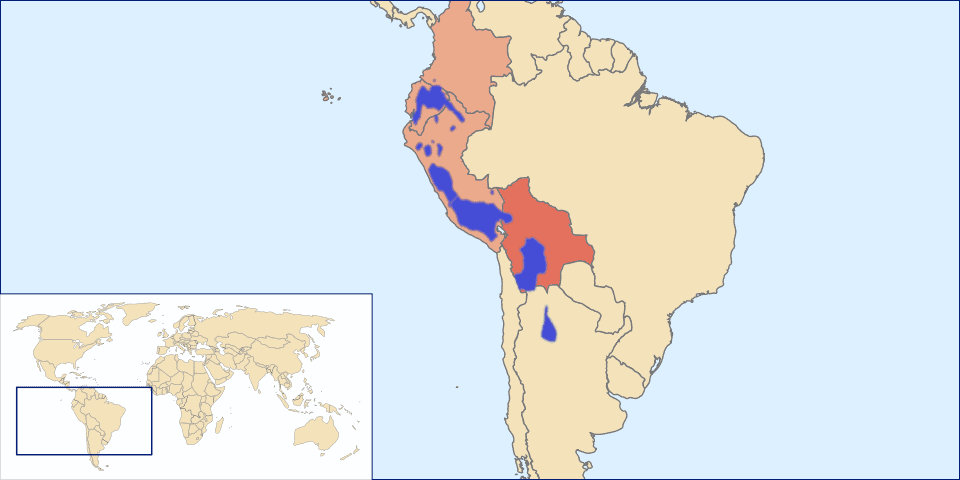
Quechua, usually called Runasimi (“people’s language”) in Quechuan languages, is an indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with a total of probably some 8–10 million speakers. Approximately 25% (7.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spaniards encouraged its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence of the 1780s. As a result, Quechua variants are still widely spoken today, being the co-official language of many regions and the second most spoken language family in Peru.
Read More About Quechuan languages / Source
Kirundi
Kirundi, also known as Rundi, is a Bantu language spoken by 9 million people in Burundi and adjacent parts of Tanzania and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, as well as in Uganda. It is the official language of Burundi. Kirundi is mutually intelligible with Kinyarwanda, an official language of Rwanda, and the two form part of the wider dialect continuum known as Rwanda-Rundi.
Read More About Kirundi / Source
Swedish language
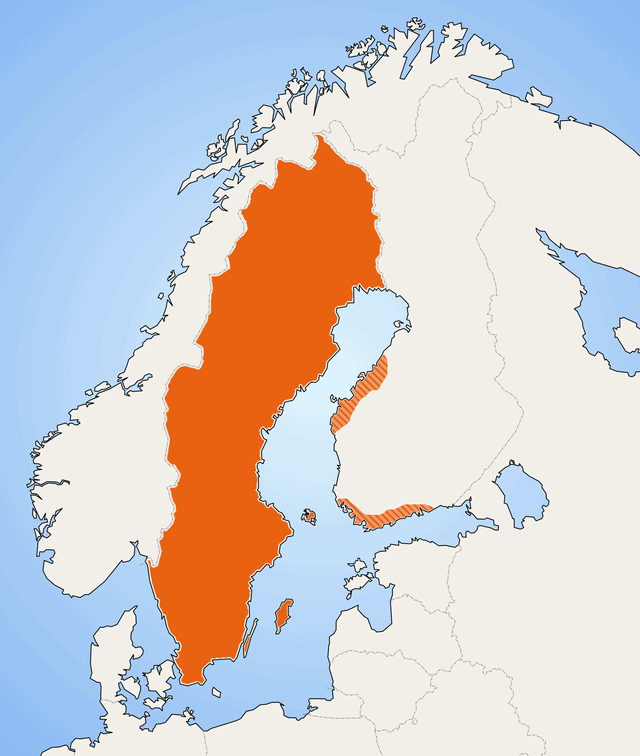
Swedish is a North Germanic language spoken natively by 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden (as the sole official language) and in parts of Finland, where it has equal legal standing with Finnish. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is largely dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Written Norwegian and Danish are usually more easily understood by Swedish speakers than the spoken languages, due to the differences in tone, accent and intonation. Swedish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Era. It has more speakers than any other North Germanic language.
Read More About Swedish language / Source
Hmong language
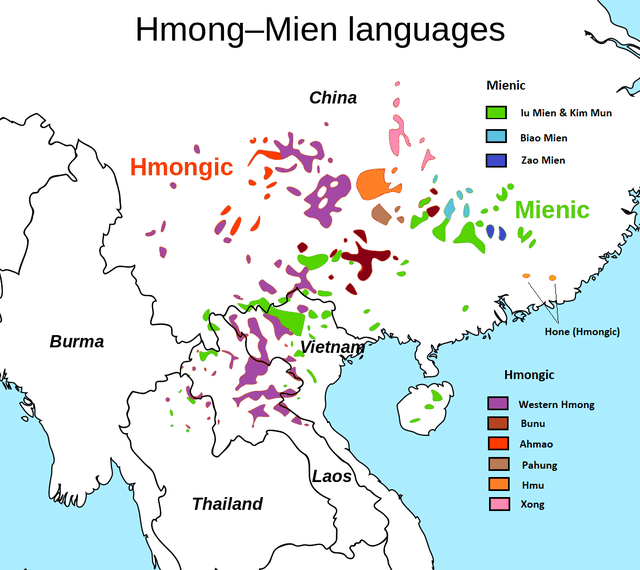
Hmong / Mong, known as Miao in China, is a dialect continuum of the West Hmongic branch of the Hmongic languages spoken by the Hmong of Sichuan, Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Hainan, northern Vietnam, Thailand, and Laos. There are some 2.7 million speakers of varieties that are largely mutually intelligible, including over 280,000 Hmong Americans as of 2013. Over half of all Hmong speakers speak the various dialects in China, where the Dananshan (大南山) dialect forms the basis of the standard language. However, Hmong Daw (White) and Mong Njua (Green) are widely known only in Laos and the United States; Dananshan is more widely known in the native region of Hmong.
Read More About Hmong language / Source
Shona language
Shona (chiShona) is a Bantu language of the Shona people of Zimbabwe. It is one of the most widely spoken Bantu languages. According to Ethnologue, Shona, comprising the Karanga, Zezuru and Korekore dialects, is spoken by about 10.8 million people. The Manyika and Ndau dialects of Shona are listed separately by Ethnologue, and are spoken by 1,025,000 and 2,380,000 people, respectively. The larger group of historically related languages—called Shona languages by linguists—also includes Ndau (Eastern Shona) and Karanga (Western Shona). Speakers of those languages prefer their distinct identities and usually reject any connection to the term Shona.
Read More About Shona language / Source
Mossi language
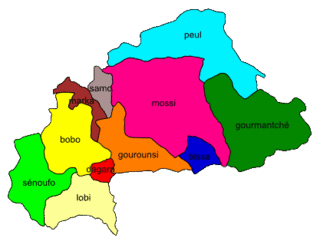
The Mossi language is a Gur language of the Oti–Volta branch and one of two official regional languages of Burkina Faso, closely related to the Frafra language spoken just across the border in the northern half of Ghana and less-closely to Dagbani and Mampruli farther south. It is the language of the Mossi people, spoken by approximately 5 million people in Burkina Faso, plus another 60,000+ in Mali and Togo.
Read More About Mossi language / Source
Xhosa language
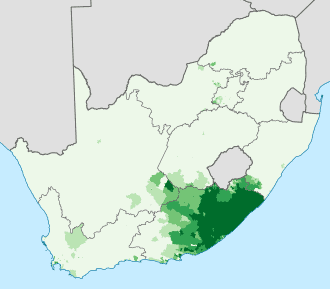
Xhosa also isiXhosa as an endonym, is a Nguni Bantu language and one of the official languages of South Africa and Zimbabwe. Xhosa is spoken as a first language by approximately 8.2 million people and by another 11 million as a second language in South Africa, mostly in Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Gauteng and Northern Cape. It has perhaps the heaviest functional load of click consonants in a Bantu language (approximately tied with Yeyi), with one count finding that 10% of basic vocabulary items contained a click.
Read More About Xhosa language / Source
Belarusian language
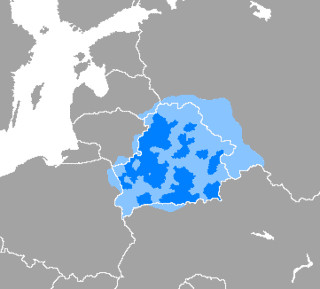
Belarusian is an East Slavic language spoken by the Belarusians. It is one of the two official languages in the Republic of Belarus under the current Constitution (Article 17), along with Russian. Additionally, it is spoken in some parts of Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, and Ukraine by Belarusian minorities in those countries.
Before Belarus gained independence in 1991, the language was only known in English as Byelorussian or Belorussian, the compound term retaining the English-language name for the Russian language in its second part, or alternatively as White Ruthenian () or White Russian. Following independence, it has acquired the additional name, Belarusian, in English.The first attempt to standardise and codify the language was undertaken following the Russian Revolution in 1917. As one of the East Slavic languages, Belarusian shares many grammatical and lexical features with other members of the group. To some extent, Russian, Rusyn, Ukrainian, and Belarusian retain a degree of mutual intelligibility. Its predecessor stage is known in Western academia as Ruthenian (14th to 17th centuries), in turn descended from what is referred to in modern linguistics as Old East Slavic (10th to 13th centuries).
Read More About Belarusian language / Source
Konkani language

Konkani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Konkani people, primarily along the western coastal region (Konkan) of India. It is one of the 22 Scheduled languages mentioned in the 8th schedule of the Indian Constitution and the official language of the Indian state of Goa. The first Konkani inscription is dated 1187 A.D. It is a minority language in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
Read More About Konkani language / Source
Yue Chinese
Yue is a group of similar Sinitic languages spoken in Southern China, particularly in Liangguang (the Guangdong and Guangxi provinces). The name Cantonese is often used for the whole group, but linguists prefer to reserve that name for the variety used in Guangzhou (Canton), Wuzhou (Ngchow), Hong Kong and Macau, which is the prestige dialect. Taishanese, from the coastal area of Jiangmen (Kongmoon) located southwest of Guangzhou, was the language of most of the 19th-century emigrants from Guangdong to Southeast Asia and North America. Most later migrants have been speakers of Cantonese. Yue varieties are not mutually intelligible with other varieties of Chinese. They are among the most conservative varieties with regard to the final consonants and tonal categories of Middle Chinese, but have lost several distinctions in the initial and medial consonants that other Chinese varieties have retained.
Read More About Yue Chinese / Source
Jin Chinese

Jin is a group of Chinese dialects or languages spoken by roughly 63 million people in northern China. Its geographical distribution covers most of Shanxi province except for the lower Fen River valley, much of central Inner Mongolia and adjoining areas in Hebei, Henan, and Shaanxi provinces. The status of Jin is disputed among linguists; some prefer to classify it as a dialect of Mandarin, but others set it apart as a closely related, but separate sister-language to Mandarin.
Read More About Jin Chinese / Source
Gan Chinese

Gan, Gann or Kan is a group of Sinitic languages spoken natively by many people in the Jiangxi province of China, as well as significant populations in surrounding regions such as Hunan, Hubei, Anhui, and Fujian. Gan is a member of the Sinitic languages of the Sino-Tibetan language family, and Hakka is the closest Chinese variety to Gan in terms of phonetics. Different dialects of Gan exist; the Nanchang dialect is usually taken as representative.
Read More About Gan Chinese / Source
Greek language
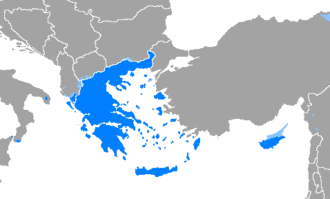
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, Albania, other parts of the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea. It has the longest documented history of any living Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for over 2,600 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems.
Read More About Greek language / Source
Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda is an official language of Rwanda and a dialect of the Rwanda-Rundi language spoken by at least 10 million people in Rwanda, Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo and adjacent parts of southern Uganda where it is known as Rufumbira. The mutually intelligible Kirundi dialect is the official language of neighbouring Burundi. Kinyabwisha and Kinyamulenge are the mutually intelligible dialects spoken in North Kivu and South Kivu provinces of neighbouring DR Congo.
Read More About Kinyarwanda / Source
Uyghur language
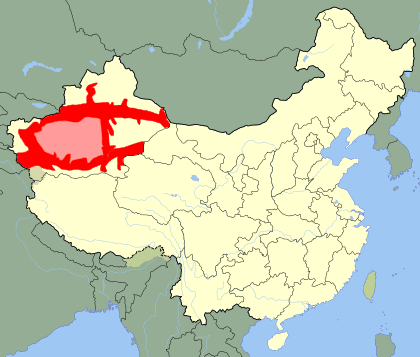
The Uyghur or Uighur language, is a Turkic language, written in a Uyghur Perso-Arabic script, with 10 to 15 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur speakers are located in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan and various other countries have Uyghur-speaking expatriate communities. Uyghur is an official language of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region and is widely used in both social and official spheres, as well as in print, television and radio and is used as a common language by other ethnic minorities in Xinjiang.
Read More About Uyghur language / Source
Hiligaynon language
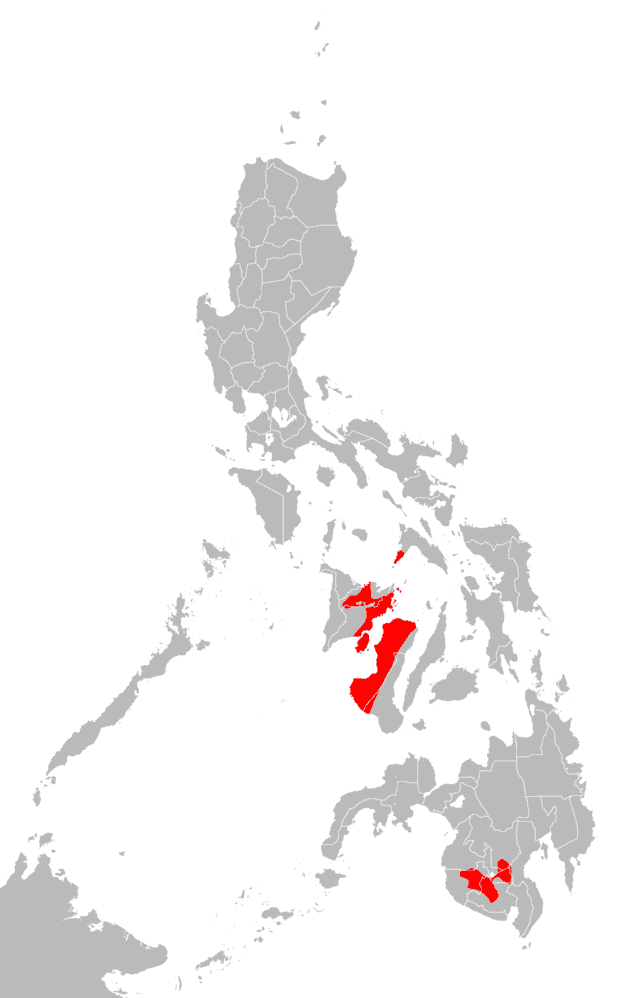
Hiligaynon, also often referred colloquially simply as Ilonggo, is an Austronesian regional language spoken in the Philippines by about 9.1 million people, mainly in Western Visayas and Soccsksargen, most of whom belong to the Hiligaynon people. It is the second-most widely spoken language in the Visayas and belongs to the Bisayan languages, and is more distantly related to other Philippine languages.
Read More About Hiligaynon language / Source
Javanese language
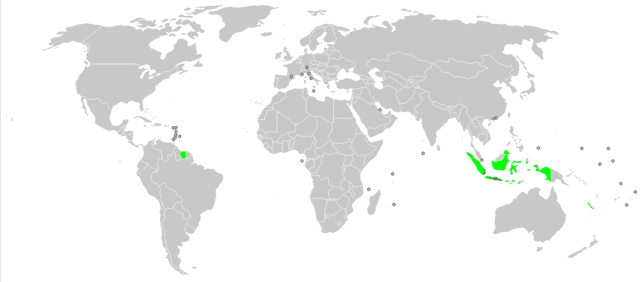
Javanese, is the language of the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, in Indonesia. There are also pockets of Javanese speakers on the northern coast of western Java. It is the native language of more than 98 million people (more than 42% of the total population of Indonesia). Javanese is the largest of the Austronesian languages in number of native speakers. It has several regional dialects and a number of clearly distinct status styles.
Read More About Javanese language / Source
Turkish language
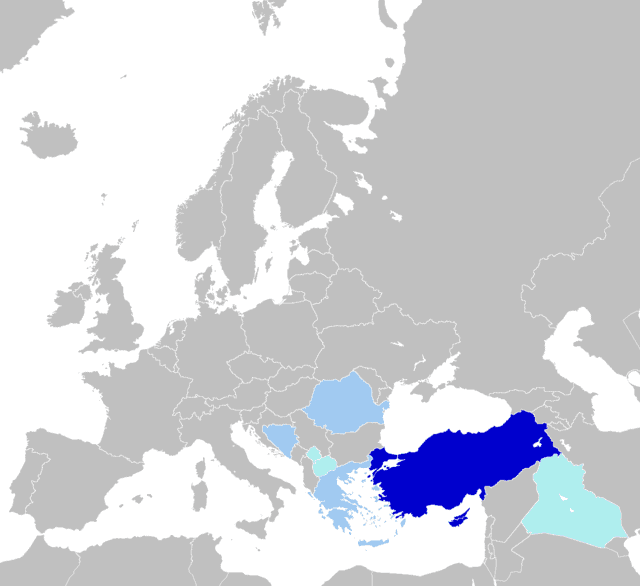
Turkish, also referred to as Istanbul Turkish (İstanbul Türkçesi) or Turkey Turkish (Türkiye Türkçesi), is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, with around 70 to 80 million speakers, the national language of Turkey. Outside its native country, significant smaller groups of speakers exist in Iraq, Syria, Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Northern Cyprus, Greece, the Caucasus, and other parts of Europe and Central Asia. Cyprus has requested that the European Union add Turkish as an official language, even though Turkey is not a member state.
Read More About Turkish language / Source
Italian language
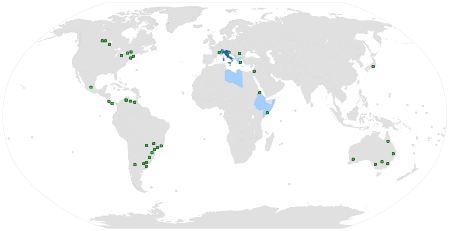
Italian is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. Italian is, by most measures and together with Sardinian, the closest language to Latin, from which it descends via Vulgar Latin. Italian is an official language in Italy, Switzerland (Ticino and the Grisons), San Marino, and Vatican City. It has an official minority status in western Istria (Croatia and Slovenia). It formerly had official status in Albania, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro (Kotor), Greece (Ionian Islands and Dodecanese) and is generally understood in Corsica by Corsican speakers (in facts, many linguists classify it as an Italian dialect). It also used to be an official language in the former Italian East Africa and Italian North Africa, where it still plays a significant role in various sectors. Italian is also spoken by large expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia. Italian is included under the languages covered by the European Charter for Regional or Minority languages in Bosnia and Herzegovina and in Romania, although Italian is neither a co-official nor a protected language in these countries. Many speakers of Italian are native bilinguals of both Italian (either in its standard form or regional varieties) and other regional languages.
Read More About Italian language / Source
Southern Min
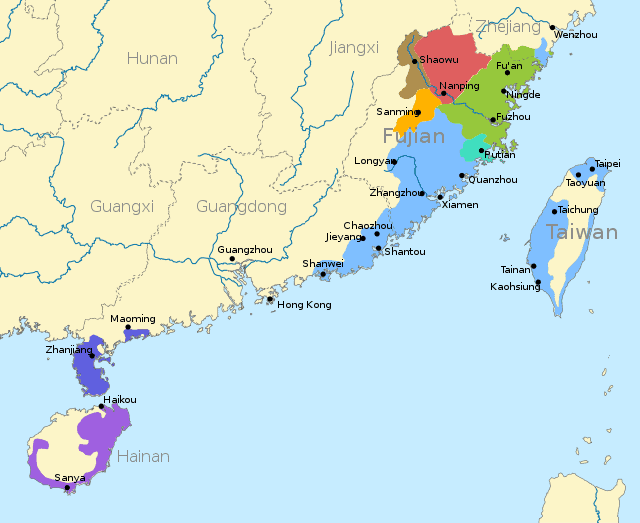
Southern Min, Minnan or Banlam, is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages that form a branch of Min Chinese spoken in Fujian (especially the Minnan region), most of Taiwan (many citizens are descendants of settlers from Fujian), Eastern Guangdong, Hainan and Southern Zhejiang. The Minnan dialects are also spoken by descendants of emigrants from these areas in diaspora, most notably the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and New York City. It is the most populous branch of Min Chinese, spoken by an estimated 48 million people in ca. 2017–2018.In common parlance and in the narrower sense, Southern Min refers to the Quanzhang or Hokkien-Taiwanese variety of Southern Min originating from Southern Fujian in Mainland China. This is spoken mainly in Fujian, Taiwan, as well as certain parts of Southeast Asia. The Quanzhang variety is often called simply “Minnan Proper” (simplified Chinese: 闽南语; traditional Chinese: 閩南語). It is considered the mainstream Southern Min Chinese Language.
Read More About Southern Min / Source
Persian language

Persian, is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian, Dari Persian (officially named Dari since 1958) and Tajiki Persian (officially named Tajik since the Soviet era). It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a derivation of Cyrillic.
Read More About Persian language / Source
Polish language
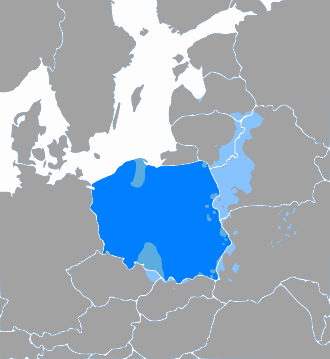
Polish is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by Polish minorities in other countries. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world – it is the sixth-most-spoken language of the European Union.
Read More About Polish language / Source
Kannada
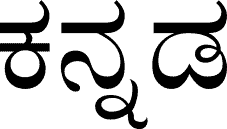
Kannada is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in the southwestern region of India. The language is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the states of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Kerala and Goa; and also by Kannadigas abroad. The language had roughly 43 million native speakers by 2011. Kannada is also spoken as a second and third language by over 12.9 million non-native speakers in Karnataka, which adds up to 56.9 million speakers. It is one of the scheduled languages of India and the official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful empires of South and Central India, such as the Chalukya dynasty, the Rashtrakuta dynasty, the Vijayanagara Empire and the Hoysala Empire.
Read More About Kannada / Source
Xiang Chinese

Xiang or Hsiang, is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages, spoken mainly in Hunan province but also in northern Guangxi and parts of neighboring Guizhou and Hubei provinces. Scholars divided Xiang into five subgroups, Chang-Yi, Lou-Shao, Hengzhou, Chen-Xu and Yong-Quan. Among those, Lou-shao, also known as Old Xiang, still exhibits the three-way distinction of Middle Chinese obstruents, preserving the voiced stops, fricatives, and affricates. Xiang has also been heavily influenced by Mandarin, which adjoins three of the four sides of the Xiang speaking territory, and Gan in Jiangxi Province, from where a large population immigrated to Hunan during the Ming Dynasty.
Read More About Xiang Chinese / Source
Sundanese language
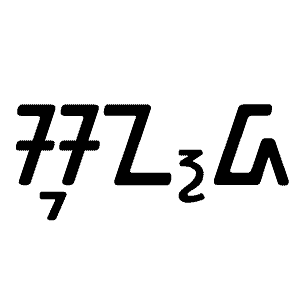
Sundanese is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Sundanese. It has approximately 39 million native speakers in the western third of Java; they represent about 15% of Indonesia’s total population. According to American linguist Robert Blust, Sundanese is closely related to the Malayic languages, as well as to language groups spoken in Borneo such as the Land Dayak languages or the Kayan–Murik languages, based on high lexical similarities between these languages. It is more distantly related to Madurese and Javanese.
Read More About Sundanese language / Source
Hausa language
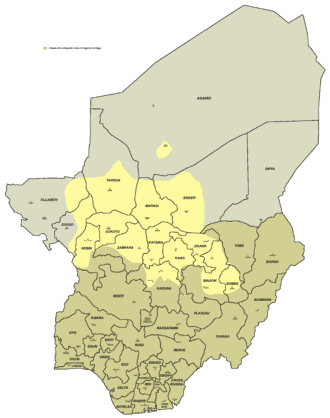
Hausa is a Chadic language spoken by the Hausa people, mainly within the territories of Niger and the northern half of Nigeria, and with significant minorities in Chad, Ghana, and Cameroon. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Ethnologues estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 47 million people and as a second language by another 25 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 72 million. According to more recent estimations, Hausa would be spoken by 100–150 million people.
Read More About Hausa language / Source
Burmese language
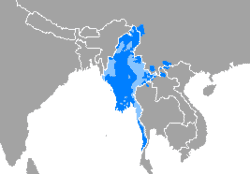
Burmese is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken in Myanmar where it is an official language and the language of the Bamar people, the country’s principal ethnic group. Although the Constitution of Myanmar officially recognizes the English name of the language as the Myanmar language, most English speakers continue to refer to the language as Burmese, after Burma, the previous name for Myanmar. In 2007, it was spoken as a first language by 33 million, primarily the Bamar (Burman) people and related ethnic groups, and as a second language by 10 million, particularly ethnic minorities in Myanmar and neighboring countries. In 2014 the Burmese population was 36.39 million, and has been estimated at 38.2 million as of April 2020.
Read More About Burmese language / Source
Hakka Chinese

Hakka is a language group of varieties of Chinese, spoken natively by the Hakka people throughout Southern China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Macau and throughout the diaspora areas of East Asia, Southeast Asia and in overseas Chinese communities around the world. Due to its primary usage in scattered isolated regions where communication is limited to the local area, Hakka has developed numerous varieties or dialects, spoken in different provinces, such as Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Fujian, Sichuan, Hunan, Jiangxi and Guizhou, as well as in Hong Kong, Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia and Indonesia. Hakka is not mutually intelligible with Yue, Wu, Southern Min, Mandarin or other branches of Chinese, and itself contains a few mutually unintelligible varieties. It is most closely related to Gan and is sometimes classified as a variety of Gan, with a few northern Hakka varieties even being partially mutually intelligible with southern Gan. There is also a possibility that the similarities are just a result of shared areal features.
Read More About Hakka Chinese / Source
Ukrainian language
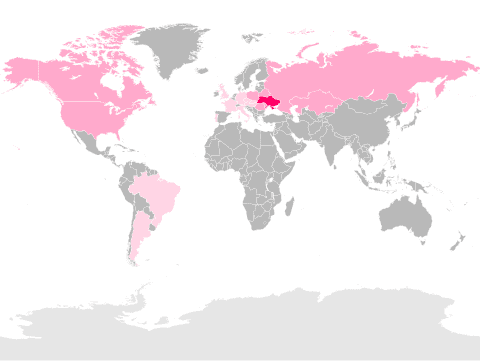
Ukrainian, historically also Ruthenian is an East Slavic language. It is the official state language of Ukraine and one of the three official languages in the unrecognized state of Transnistria, the other two being Moldovan and Russian. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic script (see Ukrainian alphabet).
Read More About Ukrainian language / Source
Yoruba language
Yoruba is a language spoken in West Africa, most prominently Southwestern Nigeria. It is spoken by the ethnic Yoruba people. The number of Yoruba speakers is estimated at between 45 and 55 million. As a pluricentric language, it is primarily spoken in a dialectal area spanning Nigeria, Benin and Togo, with smaller migrated communities in Cote d’Ivoire, Sierra Leone and The Gambia.
Read More About Yoruba language / Source
Maithili language
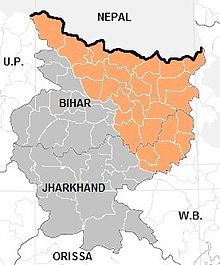
Maithili is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian subcontinent, mainly spoken in India and Nepal. In India, it is spoken in the states of Bihar and Jharkhand and is one of the 22 recognised Indian languages. In Nepal, it is spoken in the eastern Terai and is the second most prevalent language of Nepal. Tirhuta was formerly the primary script for written Maithili. Less commonly, it was also written in the local variant of Kaithi. Today it is written in the Devanagari script.
Read More About Maithili language / Source
Sindhi language

Sindhi is an Indo-Aryan language of the historical Sindh region in the western part of the Indian subcontinent, spoken by the Sindhi people. It is the official language of the Pakistani province of Sindh. In India, Sindhi is one of the scheduled languages officially recognized by the central government, though Sindhi is not an official language of any of the states in India. According to the preliminary results of Pakistan’s 2017 census, Sindhi is the first language of 30.26 million people, or 14.57% of the country’s population. In India, it was the first language of 1.68 million as of the 2011 census.
Read More About Sindhi language / Source
Amharic
Amharic is an Ethiopian Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amharas and as a lingua franca by other populations residing in major cities and towns of Ethiopia. The Amharic language possibly originated as result of a pidginization process with a Cushitic substratum and a Semitic superstratum to enable communication between people who spoke a mix of different languages. The language serves as the working language of Ethiopia, and is also the working language of several of the states within the Ethiopian federal system. With 31,800,000 mother-tongue speakers as of 2018, plus another 25,100,000 second language speakers, Amharic is the second-most common language of Ethiopia (after Oromo) and second-most commonly spoken Semitic language in the world (after Arabic).
Read More About Amharic / Source
Romanian language
Romanian is a Balkan Romance language spoken by approximately 24–26 million people as a native language, primarily in Romania and Moldova, and by another 4 million people as a second language. According to another estimate, there are about 34 million people worldwide who can speak Romanian, of whom 30 million speak it as a native language. It is an official and national language of both Romania and Moldova and is one of the official languages of the European Union.
Read More About Romanian language / Source
Oromo language
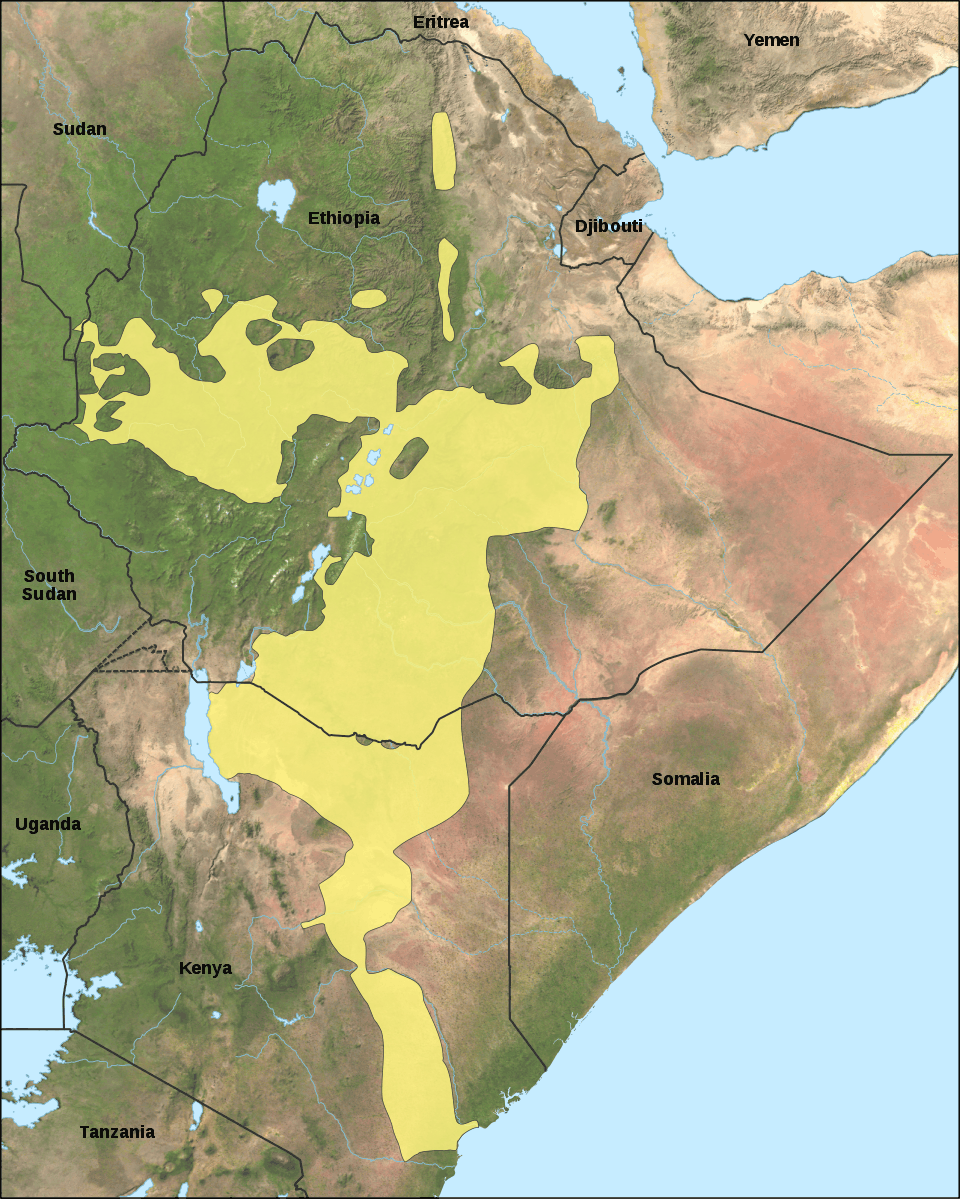
Oromo is an Afroasiatic language that belongs to the Cushitic branch. It is native to the Ethiopian state of Oromia and spoken predominantly by the Oromo people and neighbouring ethnic groups in the Horn of Africa. With 33.8% Oromo speakers, followed by 29.3% Amharic speakers, Oromo is the most widely spoken language in Ethiopia. It is also the most widely spoken Cushitic language and the fourth-most widely spoken language of Africa, after Arabic, Hausa and Swahili. Forms of Oromo are spoken as a first language by more than 35 million Oromo people in Ethiopia and by an additional half-million in parts of northern and eastern Kenya. It is also spoken by smaller numbers of emigrants in other African countries such as South Africa, Libya, Egypt and Sudan.
Read More About Oromo language / Source
Cebuano language
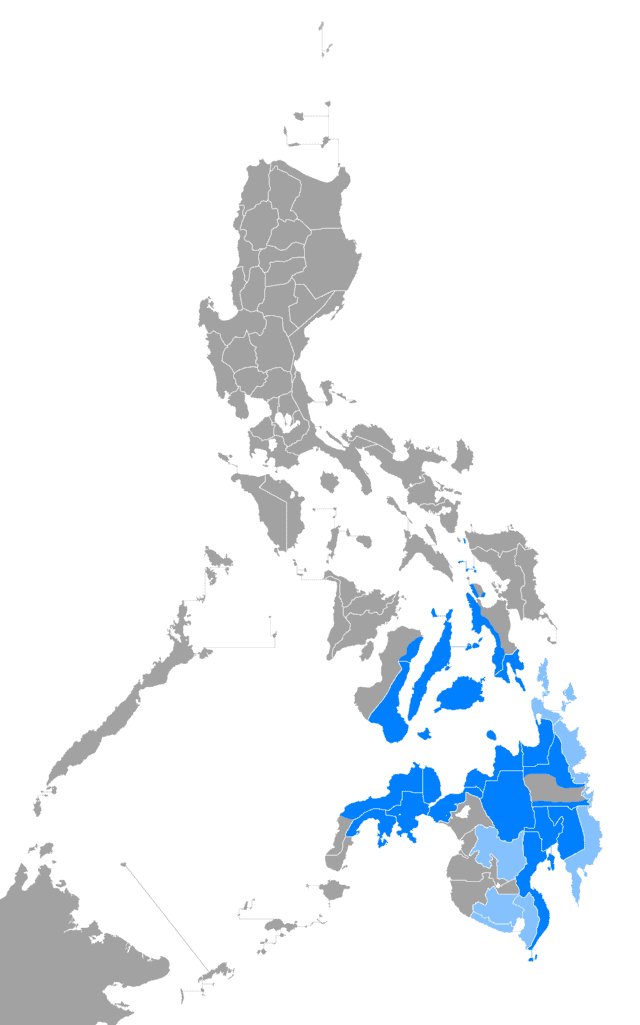
Cebuano, also referred to by most of its speakers as Bisaya or Binisaya (translated into English as Visayan, though this should not be confused with other Bisayan languages), is an Austronesian language, spoken in the southern Philippines. Specifically, it flourishes in Central Visayas, western parts of Eastern Visayas and on most of Mindanao. It originated on the island of Cebu, and now is spoken primarily by various Visayan ethnolinguistic groups who are native to those areas, primarily the Cebuanos. While Tagalog has the largest number of native speakers among the languages of the Philippines, Cebuano had the largest native-language-speaking population in the Philippines, from the 1950s until about the 1980s. It is by far the most widely spoken of the Bisayan languages.
Read More About Cebuano language / Source
Serbo-Croatian
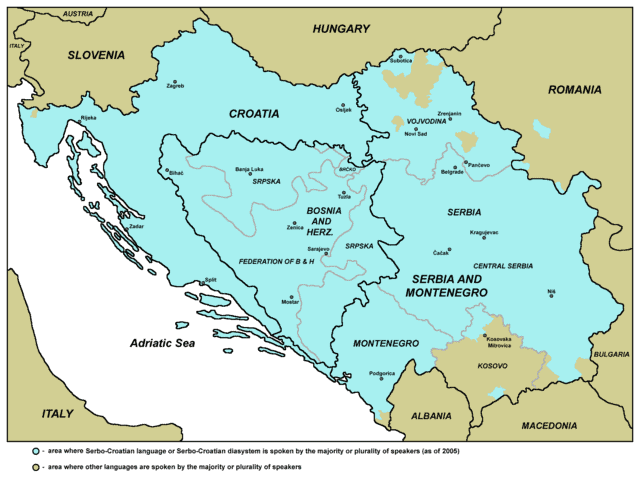
Serbo-Croatian also called Serbo-Croat, Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin.
Read More About Serbo-Croatian / Source
Saraiki language

Saraiki is an Indo-Aryan language of the Lahnda group, spoken in the south-western half of the province of Punjab in Pakistan. It was previously known as Multani, after its main dialect. Saraiki is to a high degree mutually intelligible with Standard Punjabi and shares with it a large portion of its vocabulary and morphology. At the same time in its phonology it is radically different (particularly in the lack of tones, the preservation of the voiced aspirates and the development of implosive consonants), and has important grammatical features in common with the Sindhi language spoken to the south.
Read More About Saraiki language / Source
Nepali language
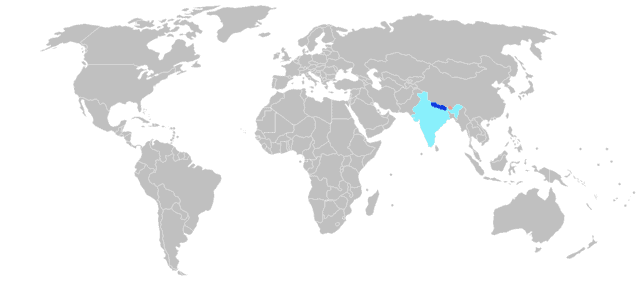
Nepali is an Indo-Aryan language of the sub-branch of Eastern Pahari. It is the official language of Nepal and one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. Also known by the endonym Khas kura (Devanagari: खस कुरा), the language is also called Gorkhali or Parbatiya in some contexts. It is spoken mainly in Nepal and by about a quarter of the population in Bhutan. In India, Nepali has official status in the state of Sikkim and in the Darjeeling Sadar subdivision and Kalimpong district of West Bengal. It has a significant number of speakers in the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mizoram and Uttarakhand. It is also spoken in Myanmar and by the Nepali diaspora worldwide. Nepali developed in proximity to a number of Indo-Aryan languages, most notably the other Pahari languages and Maithili and shows Sanskrit influence. However, owing to Nepal’s location, it has also been influenced by Tibeto-Burman languages. Nepali is mainly differentiated from Central Pahari, both in grammar and vocabulary, by Tibeto-Burman idioms owing to close contact with this language group.
Read More About Nepali language / Source
Chittagonian language

Chittagonian, also known by its endonym Chatgaya is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Chittagong Division in Bangladesh. It is generally considered to be a nonstandard dialect of Bengali because its speakers identify with Bengali culture and Standard Bengali as literary language, but the two are not mutually intelligible. It is estimated (2009) that Chittagonian has 13–16 million speakers, principally in Bangladesh.
Read More About Chittagonian language / Source
Khmer language
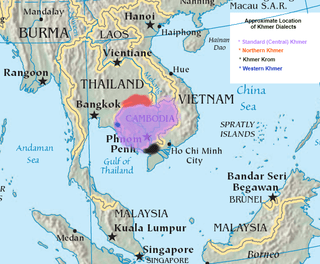
Khmer is the language of the Khmer people and the official language of Cambodia. With approximately 16 million speakers, it is the second most widely spoken Austroasiatic language (after Vietnamese). Khmer has been influenced considerably by Sanskrit and Pali, especially in the royal and religious registers, through Hinduism and Buddhism. It is also the earliest recorded and earliest written language of the Mon–Khmer family, predating Mon and Vietnamese, due to Old Khmer being the language of the historical empires of Chenla, Angkor and, presumably, their earlier predecessor state, Funan.
Read More About Khmer language / Source







