List of 86 Heritage Sites in Italy
Italy is a country with a rich history and culture, and its heritage sites reflect that. From ancient ruins to UNESCO World Heritage Sites, Italy is a great destination for cultural exploration. Here is a list of some of the most notable heritage sites in the country.
Historic Centre of Naples

Considering that the site is of exceptional value. It is one of the most ancient cities in Europe, whose contemporary urban fabric preserves the elements of its long and eventful history. Its setting on the Bay of Naples gives it an outstanding universal value which has had a profound influence in many parts of Europe and beyond. — Motivation of UNESCO
The historic center, or Centro Storico, of Naples, Italy represents the historic nucleus of the city, spanning 27 centuries.
Almost the entirety of the historic center, approximately 1021 hectares, was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1995, and included in the list of historic assets to be protected; its particular uniqueness lying in the almost total conservation and use of its ancient Greek road layout.
Read More About Historic Centre of Naples / Source
Rock Drawings in Valcamonica

The rock drawings in Valcamonica (Camonica Valley) are located in the Province of Brescia, Italy, and constitute the largest collections of prehistoric petroglyphs in the world. The collection was recognized by UNESCO in 1979 and was Italy’s first recognized World Heritage Site. UNESCO has formally recognized more than 140,000 figures and symbols, but new discoveries have increased the number of catalogued incisions to between 200,000 and 300,000. The petroglyphs are spread on all surfaces of the valley, but concentrated in the areas of Darfo Boario Terme, Capo di Ponte, Nadro, Cimbergo and Paspardo.
Read More About Rock Drawings in Valcamonica / Source
San Paolo Fuori le Mura

The Papal Basilica of Saint Paul Outside the Walls (Italian: Basilica Papale di San Paolo fuori le Mura), commonly known as Saint Paul’s Outside the Walls, is one of Rome’s four major papal basilicas, along with the basilicas of Saint John in the Lateran, Saint Peter’s, and Saint Mary Major, as well as one of the Seven Pilgrim Churches of Rome.
The Basilica is within Italian territory, but the Holy See owns the Basilica in a regime of extraterritoriality, with Italy recognizing its full ownership and conceding it “the immunity granted by international law to the headquarters of the diplomatic agents of foreign States”.James Michael Harvey was named Archpriest of the basilica in 2012.
Read More About San Paolo Fuori le Mura / Source
Santa Maria delle Grazie

Santa Maria delle Grazie (“Holy Mary of Grace”) is a church and Dominican convent in Milan, northern Italy, and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The convent contains the mural of The Last Supper by Leonardo da Vinci, which is in the refectory.
Read More About Santa Maria delle Grazie / Source
Historic Centre of Florence

The historic centre of Florence is part of quartiere 1 of the Italian city of Florence. This quarter was named a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1982.Built on the site of an Etruscan settlement, Florence, the symbol of the Renaissance, rose to economic and cultural pre-eminence under the Medici in the 15th and 16th centuries. Its 600 years of extraordinary artistic activity can be seen above all in the 13th-century cathedral (Santa Maria del Fiore), the Church of Santa Croce, the Uffizi and the Pitti Palace, the work of great masters such as Giotto, Filippo Brunelleschi, Sandro Botticelli and Michelangelo.
Read More About Historic Centre of Florence / Source
Venetian Lagoon

The Venetian Lagoon (Italian: Laguna di Venezia; Venetian: Łaguna de Venesia) is an enclosed bay of the Adriatic Sea, in northern Italy, in which the city of Venice is situated. Its name in the Italian and Venetian languages, Laguna Veneta—cognate of Latin lacus, “lake”—has provided the English name for an enclosed, shallow embayment of salt water, a lagoon.
Read More About Venetian Lagoon / Source
Piazza del Duomo, Pisa

The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites are places of importance to cultural or natural heritage as described in the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Cultural heritage consists of monuments (such as architectural works, monumental sculptures, or inscriptions), groups of buildings, and sites (including archaeological sites). Natural features (consisting of physical and biological formations), geological and physiographical formations (including habitats of threatened species of animals and plants), and natural sites which are important from the point of view of science, conservation or natural beauty, are defined as natural heritage. Italy ratified the convention on June 23, 1978.As of 2021, Italy has 58 listed sites, making it the state party with the most World Heritage Sites, just above China (56). The first site in Italy, the Rock Drawings in Valcamonica, was listed at the 3rd Session of the World Heritage Committee, held in Cairo and Luxor, Egypt, in 1979. Twenty-five Italian sites were added during the 1990s, including 10 sites added at the 21st session held in Naples in 1997. Italy has served as a member of the World Heritage Committee five times, 1978–1985, 1987–1993, 1993–1999, 1999–2001, and 2021–2025.Out of Italy’s 58 heritage sites, 53 are cultural and 5 are natural. Seven sites are transnational. The Historic Centre of Rome is shared with the Vatican; the Monte San Giorgio and Rhaetian Railway with Switzerland; the Venetian Works of Defence with Croatia and Montenegro; the Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps with 5 other countries; The Great Spa Towns of Europe with 6 other countries; and the Ancient and Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians and Other Regions of Europe are shared with 17 other countries. In addition, Italy has 31 sites on the tentative list.
Read More About Piazza del Duomo, Pisa / Source
San Gimignano

San Gimignano (Italian pronunciation: [san dʒimiɲˈɲaːno]) is a small walled medieval hill town in the province of Siena, Tuscany, north-central Italy. Known as the Town of Fine Towers, San Gimignano is famous for its medieval architecture, unique in the preservation of about a dozen of its tower houses, which, with its hilltop setting and encircling walls, form “an unforgettable skyline”. Within the walls, the well-preserved buildings include notable examples of both Romanesque and Gothic architecture, with outstanding examples of secular buildings as well as churches. The Palazzo Comunale, the Collegiate Church and Church of Sant’ Agostino contain frescos, including cycles dating from the 14th and 15th centuries. The “Historic Centre of San Gimignano” is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The town also is known for saffron, the Golden Ham, and its white wine, Vernaccia di San Gimignano, produced from the ancient variety of Vernaccia grape which is grown on the sandstone hillsides of the area.
Read More About San Gimignano / Source
The Sassi and the Park of the Rupestrian Churches of Matera

The Sassi di Matera are two districts (Sasso Caveoso and Sasso Barisano) of the Italian city of Matera, Basilicata, well-known for their ancient cave dwellings inhabited since the Paleolithic period.
The “Sassi” have been described by Fodor’s as “one of the most unique landscapes in Europe”. Along with the park of the Rupestrian Churches, it was named a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1993.
Read More About The Sassi and the Park of the Rupestrian Churches of Matera / Source
City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto

City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto is a World Heritage Site in Italy, which protects buildings by the architect Andrea Palladio. UNESCO inscribed the site on the World Heritage List in 1994. At first the site was called “Vicenza, City of Palladio” and only buildings in the immediate area of Vicenza were included.
Various types of buildings were represented in the original site, which included the Basilica Palladiana, Teatro Olimpico and palazzi in the city itself, along with a few villas in the vicinity. However, most of Palladio’s surviving villas lay outside the site. In 1996 the site was expanded. Its present name reflects the fact that it includes all the Palladian Villas of the Veneto. City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto also has some examples of ecclesiastical architecture, including the relatively small church at Maser. In total there are 47 Palladian buildings registered in the UNESCO list in the Veneto region.There is another important group of urban buildings by Palladio in Venice, a city which also has World Heritage Site status. Venice has notable examples of ecclesiastical architecture by Palladio, including the San Giorgio Maggiore (church), Venice.
Read More About City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto / Source
Historic Centre of Siena

Siena ( see-EN-ə, Italian: [ˈsjɛːna, ˈsjeːna] (listen); Latin: Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centuries. Siena is also home to the oldest bank in the world, the Monte dei Paschi bank, which has been operating continuously since 1472.Several significant Renaissance painters worked and were born in Siena, among them Duccio, Ambrogio Lorenzetti, Simone Martini and Sassetta, and influenced the course of Italian and European art.The University of Siena, originally called Studium Senese, was founded in 1240, making it one of the oldest universities in continuous operation in the world.Siena was one of the most important cities in medieval Europe, and its historic centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. From January until the end of September of 2021 it had about 217,000 arrivals, with the largest numbers of foreign visitors coming from Germany, France and the Netherlands. Siena is famous for its cuisine, art, museums, medieval cityscape and the Palio, a horse race held twice a year in Piazza del Campo.
Read More About Historic Centre of Siena / Source
Crespi d'Adda

Crespi d’Adda is a village in northern Italian and hamlet (frazione) of Capriate San Gervasio, a municipality in the province of Bergamo, Lombardy. It is a historic settlement and an outstanding example of the 19th and early 20th-century “company towns” built in Europe and North America by enlightened industrialists to meet the workers’ needs. The site is still intact and is partly used for industrial purposes, although changing economic and social conditions now threaten its survival. Since 1995 it has been on UNESCO’s list of World Heritage Sites.
Read More About Crespi d'Adda / Source
Po Delta

The Po ( POH, Italian: [ˈpɔ]; Latin: Padus or Ēridanus; Ancient Ligurian: Bodincus or Bodencus) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy starting from the Cottian Alps. The river’s length is either 652 km (405 mi) or 682 km (424 mi), if the Maira, a right bank tributary, is included. The headwaters of the Po are a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face of Monviso. The Po then extends along the 45th parallel north before ending at a delta projecting into the Adriatic Sea near Venice.
It is characterized by its large discharge (several rivers over 1,000 km have a discharge inferior or equal to the Po). It is, with the Rhône and Nile, one of the three Mediterranean rivers with the largest water discharge. As a result of its characteristics, the river is subject to heavy flooding. Consequently, over half its length is controlled with embankments.The river flows through many important Italian cities, including Turin, Piacenza, Cremona and Ferrara. It is connected to Milan through a net of channels called navigli, which Leonardo da Vinci helped design. Near the end of its course, it creates a wide delta (with hundreds of small channels and five main ones, called Po di Maestra, Po della Pila, Po delle Tolle, Po di Gnocca and Po di Goro) at the southern part of which is Comacchio, an area famous for eels. The Po valley was the territory of Roman Cisalpine Gaul, divided into Cispadane Gaul (south of the Po) and Transpadane Gaul (north of the Po).
Read More About Po Delta / Source
Castel del Monte

Castel del Monte (Italian for “Castle of the Mountain”; Barese: Castìdde du Monte) is a 13th-century citadel and castle situated on a hill in Andria in the Apulia region of southeast Italy. It was built during the 1240s by King Frederick II, who had inherited the lands from his mother Constance of Sicily. In the 18th century, the castle’s interior marbles and remaining furnishings were removed. It has neither a moat nor a drawbridge and some considered it never to have been intended as a defensive fortress. However, archaeological work has suggested that it originally had a curtain wall. Described by the Enciclopedia Italiana as “the most fascinating castle built by Frederick II”, the site is protected as a World Heritage Site. It also appears on the Italian version of the one cent Euro coin.
Read More About Castel del Monte / Source
Alberobello

Alberobello (Italian: [ˌalberoˈbɛllo]; literally “beautiful tree”; Barese: Ajarubbédde) is a small town and comune of the Metropolitan City of Bari, Apulia, southern Italy. It has 10,237 inhabitants (2022) and is famous for its unique trullo buildings. The trulli of Alberobello have been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage site since 1996.
Read More About Alberobello / Source
Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna

Ravenna ( rə-VEN-ə, Italian: [raˈvenna], also locally [raˈvɛnna], Romagnol: Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the capital of the Ostrogothic Kingdom until it was re-conquered in 540 by the Byzantine Empire. Afterwards, the city formed the centre of the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna until the last exarch was executed by the Lombards in 751.
Although it is an inland city, Ravenna is connected to the Adriatic Sea by the Candiano Canal. It is known for its well-preserved late Roman and Byzantine architecture, with eight buildings comprising the UNESCO World Heritage Site “Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna”.
Read More About Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna / Source
Historic Centre of the City of Pienza
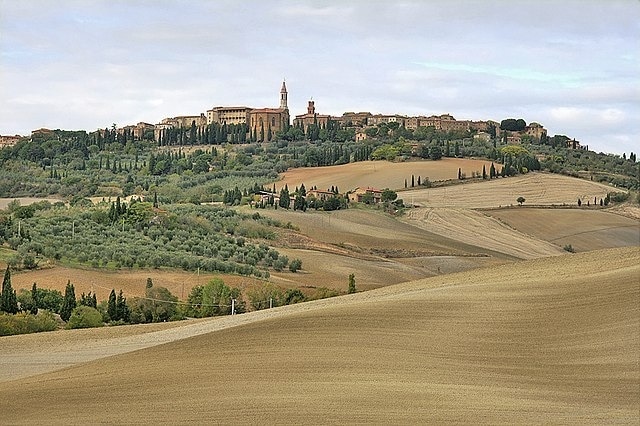

Pienza (Italian pronunciation: [piˈɛntsa]) is a town and comune in the province of Siena, Tuscany, in the historical region of Val d’Orcia. Situated between the towns of Montepulciano and Montalcino, it is considered the “touchstone of Renaissance urbanism”.In 1996, UNESCO declared the town a World Heritage Site, and in 2004 the entire valley, the Val d’Orcia, was included on the list of UNESCO’s World Cultural Landscapes.
Read More About Historic Centre of the City of Pienza / Source
Aqueduct of Vanvitelli

The Aqueduct of Vanvitelli or Caroline Aqueduct is a 38 km aqueduct that supplied water to the Reggia di Caserta and the San Leucio complex from the foot of the Taburno massif and springs of the Fizzo Contrada, in the territory of Bucciano.
Mostly underground, the aqueduct is noted for its well-preserved, three-tier, 529-metre-long (1,736 ft) tufa-arched section bridging the Valle di Maddaloni between Monte Longano (to the east) and Monte Garzano (to the west). This section was modelled after Roman arched aqueducts, is 55.8 metres (183 ft) high at its highest point, crosses what is now highway SP335 — and was designated a World Heritage Site in 1997.
Commissioned by Charles of Bourbon, the aqueduct was designed by and named after Luigi Vanvitelli. Construction began in March 1753 and it opened on 7 May 1762. It is located in SS265, 81020 Valle di Maddaloni CE, Italy.
Read More About Aqueduct of Vanvitelli / Source
San Leucio

San Leucio is a frazione of the comune of Caserta, in the region of Campania in southern Italy. It is most notable for a resort developed around an old silk factory, named a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1997.
It is located 3.5 km northwest of Caserta, at 145 m above sea level.
Read More About San Leucio / Source
Residences of the Royal House of Savoy

The Residences of the Royal House of Savoy are a group of buildings in Turin and the Metropolitan City of Turin, in Piedmont (northern Italy). It was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Sites list in 1997.
Read More About Residences of the Royal House of Savoy / Source
Botanical Garden (Orto Botanico), Padua

The Orto Botanico di Padova is a botanical garden in Padua, in the northeastern part of Italy. Founded in 1545 by the Venetian Republic, it is the world’s oldest academic botanical garden that is still in its original location. The garden – affiliated with the University of Padua – currently covers roughly 22,000 square meters, and is known for its special collections and historical design.
Read More About Botanical Garden (Orto Botanico), Padua / Source
Porto Venere

Porto Venere (Italian pronunciation: [ˈpɔrto ˈvɛːnere]; until 1991 Portovenere; Ligurian: Pòrtivene) is a town and comune (municipality) located on the Ligurian coast of Italy in the province of La Spezia. It comprises the three villages of Fezzano, Le Grazie and Porto Venere, and the three islands of Palmaria, Tino and Tinetto. In 1997 Porto Venere and the villages of Cinque Terre were designated by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
Read More About Porto Venere / Source
Cathedral

Modena Cathedral (Italian: Cattedrale Metropolitana di Santa Maria Assunta e San Geminiano but colloquially known as simply Duomo di Modena) is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Modena, Italy, dedicated to the Assumption of the Virgin Mary and Saint Geminianus. Formerly the seat of the Diocese, later Archdiocese, of Modena, it has been since 1986 the archiepiscopal seat of the Archdiocese of Modena-Nonantola. Consecrated in 1184, it is an important Romanesque building in Europe, and along with its bell tower, the Torre della Ghirlandina, is designated as a World Heritage Site.
Read More About Cathedral / Source
Archaeological Areas of Pompei, Herculaneum and Torre Annunziata

Pompeii (, Latin: [pɔmˈpei̯.iː]) was an ancient city located in what is now the comune of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried under 4 to 6 m (13 to 20 ft) of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD.
Largely preserved under the ash, the excavated city offered a unique snapshot of Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, although much of the detailed evidence of the everyday life of its inhabitants was lost in the excavations. It was a wealthy town, with a population of ca. 11,000 in AD 79, enjoying many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and works of art which were the main attractions for the early excavators. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash. Over time, they decayed, leaving voids that archaeologists found could be used as moulds to make plaster casts of unique, and often gruesome, figures in their final moments of life. The numerous graffiti carved on the walls and inside rooms provide a wealth of examples of the largely lost Vulgar Latin spoken colloquially at the time, contrasting with the formal language of the classical writers.
Pompeii is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is one of the most popular tourist attractions in Italy, with approximately 2.5 million visitors annually.After many excavations prior to 1960 that had uncovered most of the city but left it in decay, further major excavations were banned or limited to targeted, prioritised areas. In 2018, these led to new discoveries in some previously unexplored areas of the city.
Read More About Archaeological Areas of Pompei, Herculaneum and Torre Annunziata / Source
Amalfi Coast (Costiera Amalfitana)

The Amalfi Coast (Italian: Costiera amalfitana) is a stretch of coastline in southern Italy overlooking the Tyrrhenian Sea and the Gulf of Salerno. It is located south of the Sorrentine Peninsula and north of the Cilentan Coast.
Celebrated worldwide for its Mediterranean landscape and natural diversity, the Coast is named after the town of Amalfi, which makes up its main historical and political centre. It is a very popular jet set destination, and has been an attraction to upper-class Europeans since the 18th century, when it was a frequent stopover on their Grand Tours. Attracting international tourists of all classes annually, the Amalfi Coast was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1997.
Read More About Amalfi Coast (Costiera Amalfitana) / Source
Valle dei Templi

The Valle dei Templi (Italian: [ˈvalle dei ˈtɛmpli]; Sicilian: Vaddi di li Tempri), or Valley of the Temples, is an archaeological site in Agrigento (ancient Greek Akragas), Sicily. It is one of the most outstanding examples of ancient Greek art and architecture, and is one of the main attractions of Sicily.
The term “valley” is a misnomer, the site being located on a ridge outside the town of Agrigento.
Read More About Valle dei Templi / Source
Villa Romana del Casale

The Villa Romana del Casale (Sicilian: Villa Rumana dû Casali) is a large and elaborate Roman villa or palace located about 3 km from the town of Piazza Armerina, Sicily. Excavations have revealed one of the richest, largest, and varied collections of Roman mosaics in the world, for which the site has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The villa and artwork contained within date to the early 4th century AD.
The mosaic and opus sectile floors cover some 3,500 m2 and are almost unique in their excellent state of preservation due to the landslide and floods that covered the remains.Although less well-known, an extraordinary collection of frescoes covered not only the interior rooms, but also the exterior walls.
Read More About Villa Romana del Casale / Source
Su Nuraxi di Barumini

Su Nuraxi is a nuragic archaeological site in Barumini, Sardinia, Italy. Su Nuraxi simply means “The Nuraghe” in Campidanese, the southern variant of the Sardinian language.
Su Nuraxi is a settlement consisting of a seventeenth century BC Nuraghe, a bastion of four corner towers plus a central one, and a village inhabited from the thirteenth to the sixth century BC, developed around the Nuraghe. They are considered by scholars the most impressive expression of the Nuragic civilization and were included in the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in 1997 as Su Nuraxi di Barumini.
Read More About Su Nuraxi di Barumini / Source
Archaeological Area and the Patriarchal Basilica of Aquileia

Basilica di Santa Maria Assunta (Italian: Basilica Patriarcale di Santa Maria Assunta is the principal church in the town of Aquileia, in the Province of Udine and the region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Italy.
The original church dated back to the fourth century. The current basilica was built in the eleventh century and rebuilt again in the thirteenth century. It is located on Via Sacra, overlooking the Piazza del Capitolo, along with the bell tower and baptistery.
Read More About Archaeological Area and the Patriarchal Basilica of Aquileia / Source
Historic Centre of Urbino

Urbino (UK: ur-BEE-noh; Italian: [urˈbiːno] (listen); Romagnol: Urbìn) is a walled city in the Marche region of Italy, south-west of Pesaro, a World Heritage Site notable for a remarkable historical legacy of independent Renaissance culture, especially under the patronage of Federico da Montefeltro, duke of Urbino from 1444 to 1482. The town, nestled on a high sloping hillside, retains much of its picturesque medieval aspect. It hosts the University of Urbino, founded in 1506, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Urbino. Its best-known architectural piece is the Palazzo Ducale, rebuilt by Luciano Laurana.
Read More About Historic Centre of Urbino / Source
Cilento and Vallo di Diano National Park

Cilento, Vallo di Diano and Alburni National Park (Italian Parco Nazionale del Cilento, Vallo di Diano e Alburni) is an Italian national park in the Province of Salerno, in Campania in southern Italy. It includes much of the Cilento, the Vallo di Diano and the Monti Alburni. It was founded in 1991, and was formerly known as the Parco Nazionale del Cilento e Vallo di Diano.
Read More About Cilento and Vallo di Diano National Park / Source
Villa Adriana

Hadrian’s Villa (Italian: Villa Adriana) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising the ruins and archaeological remains of a large villa complex built c. AD 120 by Roman Emperor Hadrian at Tivoli outside Rome. The site is owned by the Republic of Italy and has been managed since 2014 by the Polo Museale del Lazio.
Read More About Villa Adriana / Source
City of Verona

Verona ( və-ROH-nə, Italian: [veˈroːna] (listen); Venetian: Verona or Veròna) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region, and is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in northeastern Italy. The metropolitan area of Verona covers an area of 1,426 km2 (550.58 sq mi) and has a population of 714,310 inhabitants. It is one of the main tourist destinations in northern Italy because of its artistic heritage and several annual fairs and shows as well as the opera season in the Arena, an ancient Roman amphitheater.
Between the 13th and 14th century, the city was ruled by the della Scala Family. Under the rule of the family, in particular of Cangrande I della Scala, the city experienced great prosperity, becoming rich and powerful and being surrounded by new walls. The Della Scala era is survived in numerous monuments around Verona.
Two of William Shakespeare’s plays are set in Verona: Romeo and Juliet (which also features Romeo’s visit to Mantua) and The Two Gentlemen of Verona. It is unknown if Shakespeare ever visited Verona or Italy, but his plays have lured many visitors to Verona and surrounding cities. Verona was also the birthplace of Isotta Nogarola, who is said to be the first major female humanist and one of the most important humanists of the Renaissance. In November 2000 the city was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO because of its urban structure and architecture.
The city is scheduled to host the 2026 Winter Olympics closing ceremonies.
Read More About City of Verona / Source
Isole Eolie (Aeolian Islands)

The Aeolian Islands ( ee-OH-lee-ən; Italian: Isole Eolie [ˈiːzole eˈɔːlje]; Sicilian: Ìsuli Eoli), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( LIP-ə-ree, Italian: [ˈliːpari]) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named after Aeolus, the mythical ruler of the winds. The islands’ inhabitants are known as Aeolians (Italian: Eoliani). The islands had a permanent population of 14,224 at the 2011 census; the latest official estimate is 15,419 as of 1 January 2019. The Aeolian Islands are a popular tourist destination in the summer and attract up to 600,000 visitors annually.
There are seven significant islands: Lipari, Vulcano, Salina, Stromboli, Filicudi, Alicudi and Panarea, and a set of minor islands and rocks.
Read More About Isole Eolie (Aeolian Islands) / Source
Assisi, the Basilica of San Francesco and Other Franciscan Sites

The Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi (Italian: Basilica di San Francesco d’Assisi; Latin: Basilica Sancti Francisci Assisiensis) is the mother church of the Roman Catholic Order of Friars Minor Conventual in Assisi, a town in the Umbria region in central Italy, where Saint Francis was born and died. It is a Papal minor basilica and one of the most important places of Christian pilgrimage in Italy. With its accompanying friary, Sacro Convento, the basilica is a distinctive landmark to those approaching Assisi. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2000.
The basilica, which was begun in 1228, is built into the side of a hill and comprises two churches (known as the Upper Church and the Lower Church) and a crypt, where the remains of the saint are interred. The interior of the Upper Church is an important early example of the Gothic style in Italy. The Upper and Lower Churches are decorated with frescoes by numerous late medieval painters from the Roman and Tuscan schools, and include works by Cimabue, Giotto, Simone Martini, Pietro Lorenzetti and possibly Pietro Cavallini. The range and quality of the works give the basilica a unique importance in demonstrating the outstanding development of Italian art of this period, especially if compared with the rest of Christian Europe.
Read More About Assisi, the Basilica of San Francesco and Other Franciscan Sites / Source
Villa d'Este, Tivoli

The Villa d’Este is a 16th-century villa in Tivoli, near Rome, famous for its terraced hillside Italian Renaissance garden and especially for its profusion of fountains. It is now an Italian state museum, and is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Read More About Villa d'Este, Tivoli / Source
Val di Noto

Val di Noto (English: Province of Noto) is a historical and geographical area encompassing the south-eastern third of Sicily; it is dominated by the limestone Hyblaean plateau. Historically, it was one of the three valli of Sicily.
Read More About Val di Noto / Source
Sacri Monti of Piedmont and Lombardy

The Sacri Monti (plural of Sacro Monte, Italian for “Sacred Mountain”) of Piedmont and Lombardy are a series of nine calvaries or groups of chapels and other architectural features created in northern Italy during the late sixteenth century and the seventeenth century. They are dedicated to various aspects of the Christian faith and are considered of great beauty by virtue of the skill with which they have been integrated into the surrounding natural landscape of hills, forests and lakes. They also house important artistic materials in the form of wall paintings and statuary. In 2003, they were named as a World Heritage Site.
Read More About Sacri Monti of Piedmont and Lombardy / Source
Val d'Orcia

The Val d’Orcia or Valdorcia (Italian pronunciation: [ˌvalˈdortʃa]) is a region of Tuscany, central Italy, which extends from the hills south of Siena to Monte Amiata. Its gentle, cultivated hills are occasionally broken by gullies and by picturesque towns and villages such as Pienza (rebuilt as an “ideal town” in the 15th century under the patronage of Pope Pius II), Radicofani (home to the notorious brigand-hero Ghino di Tacco) and Montalcino (the Brunello di Montalcino is counted among the most prestigious of Italian wines). Its landscape has been depicted in works of art from Renaissance painting to modern photography.
Read More About Val d'Orcia / Source
Etruscan Necropolises of Cerveteri and Tarquinia

Cerveteri (Italian: [tʃerˈvɛːteri]) is a town and comune of northern Lazio in the region of the Metropolitan City of Rome. Known by the ancient Romans as Caere, and previously by the Etruscans as Caisra or Cisra, and as Agylla (or Άγυλλα) by the Greeks, its modern name derives from Caere Vetus used in the 13th century to distinguish it from Caere Novum (the current town).
It is the site of the ancient Etruscan city which was one of the most important Etruscan cities with an area more than 15 times larger than today’s town.
Caere was one of the city-states of the Etruscan League and at its height, around 600 BC, its population was perhaps around 25,000 – 40,000 people.
Read More About Etruscan Necropolises of Cerveteri and Tarquinia / Source
Syracuse and the Rocky Necropolis of Pantalica

The Necropolis of Pantalica is a collection of cemeteries with rock-cut chamber tombs in southeast Sicily, Italy. Dating from the 13th to the 7th centuries BC, there was thought to be over 5,000 tombs, although the most recent estimate suggests a figure of just under 4,000. They extend around the flanks of a large promontory located at the junction of the Anapo river with its tributary, the Calcinara, about 23 km (14 mi) northwest of Syracuse. Together with the city of Syracuse, Pantalica was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2005.
Read More About Syracuse and the Rocky Necropolis of Pantalica / Source
Genoa: Le Strade Nuove and the system of the Palazzi dei Rolli

Genoa: Le Strade Nuove and the system of the Palazzi dei Rolli is a UNESCO World Heritage Site which includes a number of streets and palaces in the center of Genoa, in Northwestern Italy.
The Strade Nuove (Italian for “New Streets”) are a group of streets built by the Genoese aristocracy during the expansion of the city at a time when the Republic of Genoa was at the height of its financial and seafaring power. These are Via Giuseppe Garibaldi (1558-1583, formerly Strada Maggiore or Strada Nuova) and Via Balbi (1602-1620, formerly Strada Balbi), later followed by Via Cairoli (1778-1786, formerly Strada Nuovissima).
The Palazzi dei Rolli (Italian for “Palaces of the Lists”) are a group of palaces – most of which also date from the late 16th and early 17th centuries – which were associated to a particular system of ‘public lodging’ in private residences, whereby notable guests on State visit to the Republic were hosted in one of these palaces on behalf of the State.
On 13 July 13, 2006, forty-two of the 163 palaces originally included in one the five public list called “Rolli” (Italian for “lists”) were selected as a World Heritage Site by the UNESCO special committee meeting in Vilnius (Lithuania). The site includes an ensemble of Renaissance and Baroque palaces along the so-called ‘new streets’ (Strade Nuove), which offer an extraordinary variety of different solutions, achieving universal value in adapting to the particular characteristics of the site and to the requirements of a specific social and economic organization. They also offer an original example of a public network of private residences designated to host state visits.
On January 20, 2007, UNESCO unveiled a plaque in via Garibaldi, the former Strada Nuova, explaining the reasons for inclusion of the Strade Nuove and the system of the Palazzi dei Rolli within the World Heritage Sites:
The largest homes, various in shape and distribution, that were chosen at random in the lists (rolli) to host visits of state. The buildings, often built on sloping land, formed of a stepped atrium – courtyard – staircase – garden and rich interior decorations, express a singular social and economic identity and commencement of modern age urban architecture in Europe.Some of the Palazzi dei Rolli are used today as public buildings, museums, offices and private residences. Among the palaces open to the public, Palazzo Rosso, Palazzo Bianco and Palazzo Doria Tursi jointly constitute the Strada Nuova Museums located in via Garibaldi.
Read More About Genoa: Le Strade Nuove and the system of the Palazzi dei Rolli / Source
Mantua and Sabbioneta

Mantua ( MAN-tew-ə; Italian: Mantova and Latin: Mantua) is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture. In 2017, it was named as the European Capital of Gastronomy, included in the Eastern Lombardy District (together with the cities of Bergamo, Brescia, and Cremona).
In 2008, Mantua’s centro storico (old town) and Sabbioneta were declared by UNESCO to be a World Heritage Site. Mantua’s historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family has made it one of the main artistic, cultural, and especially musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole. Having one of the most splendid courts of Europe of the fifteenth, sixteenth, and early seventeenth centuries. Mantua is noted for its significant role in the history of opera; the city is also known for its architectural treasures and artifacts, elegant palaces, and the medieval and Renaissance cityscape. It is the city where the composer Monteverdi premiered his opera L’Orfeo and to where Romeo was banished in Shakespeare’s play Romeo and Juliet. It is the nearest town to the birthplace of the Roman poet Virgil, who is commemorated by a statue at the lakeside park “Piazza Virgiliana”.
Mantua is surrounded on three sides by artificial lakes, created during the 12th century as the city’s defence system. These lakes receive water from the Mincio River, a tributary of the Po River which descends from Lake Garda. The three lakes are called Lago Superiore, Lago di Mezzo, and Lago Inferiore (“Upper”, “Middle”, and “Lower” Lakes, respectively). A fourth lake, Lake Pajolo, which once served as a defensive water ring around the city, dried up at the end of the 18th century.
The area and its environs are important not only in naturalistic terms, but also anthropologically and historically; research has highlighted a number of human settlements scattered between Barche di Solferino and Bande di Cavriana, Castellaro and Isolone del Mincio. These dated, without interruption, from Neolithic times (5th–4th millennium BC) to the Bronze Age (2nd–1st millennium BC) and the Gallic phases (2nd–1st centuries BC), and ended with Roman residential settlements, which could be traced to the 3rd century AD.
In 2017, Legambiente ranked Mantua as the best Italian city for the quality of the life and environment.
Read More About Mantua and Sabbioneta / Source
Dolomites

The Dolomites (Italian: Dolomiti [doloˈmiːti]; Ladin: Dolomites; German: Dolomiten [doloˈmiːtn̩] (listen); Venetian: Dołomiti [doɰoˈmiti]: Friulian: Dolomitis), also known as the Dolomite Mountains, Dolomite Alps or Dolomitic Alps, are a mountain range located in northeastern Italy. They form part of the Southern Limestone Alps and extend from the River Adige in the west to the Piave Valley (Pieve di Cadore) in the east. The northern and southern borders are defined by the Puster Valley and the Sugana Valley (Italian: Valsugana). The Dolomites are located in the regions of Veneto, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Friuli Venezia Giulia, covering an area shared between the provinces of Belluno, Vicenza, Verona, Trentino, South Tyrol, Udine and Pordenone.
Other mountain groups of similar geological structure are spread along the River Piave to the east – Dolomiti d’Oltrepiave; and far away over the Adige River to the west – Dolomiti di Brenta (Western Dolomites). A smaller group is called Piccole Dolomiti (Little Dolomites), located between the provinces of Trentino, Verona, and Vicenza.
The Dolomiti Bellunesi National Park and many other regional parks are located in the Dolomites. In August 2009, the Dolomites were declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.The Adamello-Brenta UNESCO Global Geopark is also in the Dolomites.
Read More About Dolomites / Source
Monte San Giorgio

Monte San Giorgio is a mountain and UNESCO World Heritage Site on the border between Switzerland and Italy. It is part of the Lugano Prealps, overlooking Lake Lugano in the Swiss Canton of Ticino.
Monte San Giorgio is a wooded mountain, rising to 1,097 m (3,600 feet) above sea level. It has a roughly pyramidal shape, with a steep north edge sloping towards Lake Lugano and a more shallow South Slope extending towards the Po Plain. The eastern (Swiss) side of the mountain, between the municipalities of Brusino Arsizio, Riva San Vitale, and Meride, was listed as a World Heritage Site in 2003. This was in recognition of its cultural, biological, and especially paleontological significance. The site is renowned for its fossil content, one of the best known records of marine life in the Middle Triassic period. The Italian region west of Poncione d’Arzo (Porto Ceresio) was added as an extension to the World Heritage Site in 2010.
Read More About Monte San Giorgio / Source
Places of the Longobards in Italy.

Longobards in Italy: Places of Power (568–774 A.D.) (Italian: Longobardi in Italia: i luoghi del potere) is seven groups of historic buildings that reflect the achievements of the Germanic tribe of the Lombards (also referred to as Longobards), who settled in Italy during the sixth century and established a Lombard Kingdom which ended in 774 A.D.
The groups comprise monasteries, church buildings, and fortresses and became UNESCO World Heritage Sites in June 2011 as they testify “to the Lombards’ major role in the spiritual and cultural development of Medieval European Christianity”.
Read More About Places of the Longobards in Italy. / Source
Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps

Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps are a series of prehistoric pile dwelling (or stilt house) settlements in and around the Alps built from about 5000 to 500 BC on the edges of lakes, rivers or wetlands. In 2011, 111 sites located variously in Switzerland (56), Italy (19), Germany (18), France (11), Austria (5) and Slovenia (2) were added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list. In Slovenia, these were the first World Heritage Sites to be listed for their cultural value.Excavations conducted at some of the sites have yielded evidence regarding prehistoric life and the way communities interacted with their environment during the Neolithic and Bronze Ages in Alpine Europe. These settlements are a unique group of exceptionally well-preserved and culturally rich archaeological sites, which constitute one of the most important sources for the study of early agrarian societies in the region.Contrary to popular belief, the dwellings were not erected over water, but on nearby marshy land. They were set on piles to protect against occasional flooding. Because the lakes have grown in size over time, many of the original piles are now under water, giving modern observers the false impression that they have always been this way.
Read More About Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps / Source
Medici Villas and Gardens in Tuscany

The Medici villas are a series of rural building complexes in Tuscany which were owned by members of the Medici family between the 15th century and the 17th century. The villas served several functions: they were the country palaces of the Medici, scattered over the territory that they ruled, demonstrating their power and wealth. They were also recreational resorts for the leisure and pleasure of their owners; and, more prosaically, they were the centre of agricultural activities on the surrounding estates. In 2013, the Medici villas were added to UNESCO’s World Heritage list.
Read More About Medici Villas and Gardens in Tuscany / Source
Vineyard Landscape of Piedmont: Langhe-Roero and Monferrato

Vineyard Landscape of Piedmont: Langhe-Roero and Monferrato is the official name of a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising “five distinct wine-growing areas with outstanding landscapes” plus the Castle of Grinzane Cavour in the region of Piedmont, Italy.The site, which extends over hilly areas of Langhe and Montferrat, is one of the most important wine producing zones in Italy.
Located in the center of Piedmont region (North West of Italy), the site is inscribed as a “cultural landscape”, since it is a result of the combined work of nature and man. The site is inscribed in the UNESCO World Heritage List thanks to the outstanding value of its wine culture, which has shaped the landscape over the centuries.
Read More About Vineyard Landscape of Piedmont: Langhe-Roero and Monferrato / Source
Arab-Norman Palermo and the Cathedral Churches of Cefalù and Monreale

Arab-Norman Palermo and the Cathedral Churches of Cefalù and Monreale is a series of nine religious and civic structures located on the northern coast of Sicily dating from the era of the Norman Kingdom of Sicily (1130-1194): two palaces, three churches, a cathedral, and a bridge in Palermo, as well as the cathedrals of Cefalù and Monreale. They have been designated together as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. This dedication took place in 2015.The new Norman rulers built various structures in what has become known as the Arab-Norman style. They incorporated the best practices of Arab and Byzantine architecture into their own art. Although a different builder constructed each of the sites, they are linked together because of their shared architecture and time period. These sites work to create a shared identity among the areas that they are built in. This is because many people chose to visit the sites together, not just one at a time. Providing not only a steady revenue of tourism, but also a revenue of tourists that have visited each of the sites and bring that experience with them.
Currently all of the buildings are under continuous restoration and care. This care varies from site to site but most often consists of topical restoration (cleaning, maintaining murals, etc), research (what the building might have looked like originally and what was done there), and structural restoration (making sure the building is safe and structurally sound).
Read More About Arab-Norman Palermo and the Cathedral Churches of Cefalù and Monreale / Source
Ancient and Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians and Other Regions of Europe

Ancient and Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians and Other Regions of Europe is a transnational serial nature UNESCO World Heritage Site, encompassing 94 component parts (forests of European beech, Fagus sylvatica) in 18 European countries. Together, the sites protect the largest and least disturbed forests dominated by the beech tree. In many of these stands (especially those in the Carpathians), these forests here were allowed to proceed without interruption or interference since the last ice age. These sites document the undisturbed postglacial repopulation of the species.
Venetian Works of Defence between the 16th and 17th centuries: Stato da Terra – Western Stato da Mar

Venetian Works of Defence between the 16th and 17th centuries: Stato da Terra – Western Stato da Mar is a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising six bastion forts built by the Republic of Venice on its mainland domains (Stato da Terra) and its Domains of the Sea (Stato da Mar).
With the increase in firearm warfare in the Renaissance came significant shifts in military strategy and fort design. One of these changes was the development of the bastion fort, or alla moderna fortifications, with a polygon-shaped fortress with bulwarks at the corners. These designs originated from the Republic of Venice, but would soon spread throughout Europe and remain the standard for defence until the 19th century. In 2017, six of these fortifications in Italy, Croatia, and Montenegro were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage list. These six sites provide quintessential examples of this fort design, demonstrate the influence of Renaissance-era Venice, and pay testimony to a major advancement in the history of warfare.
Ivrea, Industrial City of the 20th Century

Ivrea (Italian: [iˈvrɛːa]; Piedmontese: Ivrèja [iˈʋrɛja]; French: Ivrée; Latin: Eporedia) is a town and comune of the Metropolitan City of Turin in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy. Situated on the road leading to the Aosta Valley (part of the medieval Via Francigena), it straddles the Dora Baltea and is regarded as the centre of the Canavese area. Ivrea lies in a basin that in prehistoric times formed a large lake. Today five smaller lakes — Sirio, San Michele, Pistono, Nero and Campagna — are found in the area around the town.
On July 1, 2018, the site which is known as “Industrial City of the 20th Century” was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Read More About Ivrea, Industrial City of the 20th Century / Source
The Prosecco Hills of Conegliano and Valdobbiadene

Conegliano (Italian: [koneʎˈʎaːno]; Venetian: Conejan) is a town and comune of the Veneto region, Italy, in the province of Treviso, about 30 kilometres (19 mi) north by rail from the town of Treviso. The population of the city is of 35,023 people. The remains of a 10th-century castle are situated on a hill that dominates the town. Formerly belonging to the Bishop of Vittorio Veneto, what remains is a bell tower, which now houses a small museum, and outer walls.
On 7 July 2019, Le Colline del Prosecco di Conegliano e Valdobbiadene was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Read More About The Prosecco Hills of Conegliano and Valdobbiadene / Source
The Great Spa Towns of Europe

The Great Spa Towns of Europe is a transnational World Heritage Site consisting of a selection of 11 spa towns across seven European countries. They were developed around natural mineral water springs. From the early 18th century to the 1930s, Western Europe experienced an increase in spa and bathing culture, leading to the construction of elaborate bath houses. These would often include gardens, casinos, theatres, and villas surrounding the springs and the bath houses.
Read More About The Great Spa Towns of Europe / Source
Padua's fourteenth-century fresco cycles

Padua’s fourteenth-century fresco cycles is a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Padua, Italy, listed in 2021.
The site comprises eight buildings, both religious and secular, in four clusters. They house fresco cycles that were painted between 1302 and 1397 by several prominent painters: Giotto, Guariento di Arpo, Giusto de’ Menabuoi, Altichiero da Zevio, Jacopo d’Avanzi, and Jacopo da Verona. The frescos are innovative in their way of depicting the allegorical narrative and use new way of perspective. Emotions of characters are shown in a realistic manner. In some frescos, the patron who commissioned them is depicted as one of the characters in a story. This new fresco style formed the inspirational basis for centuries of fresco work in the Italian Renaissance and beyond.
Read More About Padua's fourteenth-century fresco cycles / Source
The Porticoes of Bologna

The Porticoes of Bologna are an important cultural and architectural heritage of Bologna, Italy and represent a symbol of the city together with the numerous towers. No other city in the world has as many porticoes as Bologna: all together, they cover more than 38 kilometres (24 mi) only in the historic center, but can reach up to 53 kilometres (33 mi) if those outside the medieval city walls are also considered.On account of their cultural and artistic significance, in 2021 the porticoes of Bologna have been declared an UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Read More About The Porticoes of Bologna / Source
Lake Maggiore

Lake Maggiore (UK: , US: ; Italian: Lago Maggiore [ˈlaːɡo madˈdʒoːre]; Western Lombard: Lagh Maggior; Piedmontese: Lagh Magior; literally ‘Greater Lake’) or Verbano (pronounced [verˈbaːno]; Latin: Lacus Verbanus) is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest lake in Italy and the largest in southern Switzerland. The lake and its shoreline are divided between the Italian regions of Piedmont and Lombardy and the Swiss canton of Ticino. Located halfway between Lake Orta and Lake Lugano, Lake Maggiore extends for about 65 kilometres (40 miles) between Locarno and Arona.
The climate is mild in both summer and winter, producing Mediterranean vegetation, with many gardens growing rare and exotic plants. Well-known gardens include those of the Borromean and Brissago Islands, that of the Villa Taranto in Verbania, and the Alpinia Botanical Garden above Stresa.
Lake Maggiore is drained by the Ticino river, a main tributary of the Po. Its basin also collects the waters of several large lakes, notably Lake Lugano (through the Tresa), Lake Orta (through the Toce) and Lake Varese (through the Bardello).
Read More About Lake Maggiore / Source
Giardini Botanici Hanbury

The Giardini Botanici Hanbury, also known as Villa Hanbury, are major botanical gardens operated by the University of Genoa. They are located at Corso Montecarlo 43, Mortola Inferiore, several km west of Ventimiglia, Italy.
Read More About Giardini Botanici Hanbury / Source
Orvieto

Orvieto (Italian: [orˈvjɛːto]) is a city and comune in the Province of Terni, southwestern Umbria, Italy, situated on the flat summit of a large butte of volcanic tuff. The city rises dramatically above the almost-vertical faces of tuff cliffs that are completed by defensive walls built of the same stone.
Read More About Orvieto / Source
Appian Way

The Appian Way (Latin and Italian: Via Appia) is one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, in southeast Italy. Its importance is indicated by its common name, recorded by Statius, of Appia longarum… regina viarum (“the Appian Way, the queen of the long roads”).
The road is named after Appius Claudius Caecus, the Roman censor who began and completed the first section as a military road to the south in 312 BC during the Samnite Wars.
Read More About Appian Way / Source
Villas of the Papal Nobility

Viterbo (Italian: provincia di Viterbo) is a province in the Lazio region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Viterbo.
Read More About Villas of the Papal Nobility / Source
Salento and the "Barocco Leccese

Salento (Salentino: Salentu, Salentino Griko: Σαλέντο) is a cultural, historical and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apulia in Southern Italy. It is a sub-peninsula of the Italian Peninsula, sometimes described as the “heel” of the Italian “boot”.
It encompasses the entire administrative area of the province of Lecce, a large part of the province of Brindisi and part of that of Taranto.
The peninsula is also known as Terra d’Otranto, and in the past Sallentina. In ancient times it was called variously Calabria or Messapia.
Read More About Salento and the "Barocco Leccese / Source
Cattolica Monastery in Stilo

The Cattolica di Stilo is a Byzantine church in the comune of Stilo (Province of Reggio), Calabria, southern Italy. It is a national monument.
Read More About Cattolica Monastery in Stilo / Source
Archipelago of La Maddalena

The Maddalena Archipelago is a group of islands in the Strait of Bonifacio between Corsica (France) and Sardinia (Italy). The whole archipelago makes the territory of the La Maddalena comune in Sardinia.
Read More About Archipelago of La Maddalena / Source
Mothia Island

Motya was an ancient and powerful city on San Pantaleo Island off the west coast of Sicily, in the Stagnone Lagoon between Drepanum (modern Trapani) and Lilybaeum (modern Marsala). It is within the present-day commune of Marsala, Italy.
Many of the city’s ancient monuments have been excavated and are visible today.Motya has become known for the marble statue of the Motya Charioteer, found in 1979 and on display at the local Giuseppe Whitaker museum.
Read More About Mothia Island / Source
Bradyseism in the Flegrea Area

The Phlegraean Fields (Italian: Campi Flegrei [ˈkampi fleˈɡrɛi]; Neapolitan: Campe Flegree, from Ancient Greek φλέγω phlego ‘to burn’) is a large region of supervolcanic calderas situated to the west of Naples, Italy. It was declared a regional park in 2003. The area of the caldera consists of 24 craters and volcanic edifices; most of them lie under water. Hydrothermal activity can be observed at Lucrino, Agnano and the town of Pozzuoli. There are also effusive gaseous manifestations in the Solfatara crater, the mythological home of the Roman god of fire, Vulcan.
This area is monitored by the Vesuvius Observatory. It is considered a supervolcano.The area also features bradyseismic phenomena, which are most evident at the Macellum of Pozzuoli (misidentified as a temple of Serapis): bands of boreholes left by marine molluscs on marble columns show that the level of the site in relation to sea level has varied.
Read More About Bradyseism in the Flegrea Area / Source
Cascata delle Marmore

The Cascata delle Marmore (Italian: [kaˈskaːta delle ˈmarmore]) or Marmore Falls is a man-made waterfall created by the ancient Romans. Its total height is 165 m (541 feet), making it the tallest man-made waterfall in the world.
It is located 7.7 km from Terni, a provincial capital of the Italian region of Umbria.
Its source is a portion of the waters of the river Velino (the rest of the river flows into a hydroelectric power plant), after flowing through Piediluco lake near the community of Marmore (italian). It pours into the valley below formed by the river Nera. Its flow is turned on and off according to a published schedule, to satisfy the needs of tourists and the power company alike. Tourists try to be there the moment the gates are opened to see the powerful rush of water.
Read More About Cascata delle Marmore / Source
Pelagos: The Cetacean Sanctuary
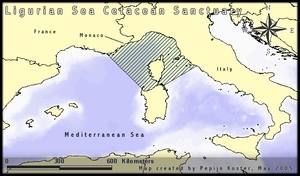
Originally called the International Ligurian Sea Cetacean Sanctuary (Ligurian Sea Sanctuary), what is now known as the Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals is a Marine Protected Area aimed at the protection of marine mammals (cetaceans). It covers an area of approximately 84,000 km2, comprising the waters between Toulon (French Riviera), Capo Falcone (western Sardinia), Capo Ferro (eastern Sardinia) and Fosso Chiarone (Tuscany).
The sanctuary is located in the Ligurian basin of the Mediterranean Sea. In this area all the cetaceans occurring in the Mediterranean can be found at regular intervals. It is believed to be the main feeding ground for Fin Whales in the Mediterranean basin.
The sanctuary was established on 25 November 1999 and is the first (and currently the only) international / High Seas MPA in the world covering areas of the Mediterranean seas of France, Italy, and Monaco.
To underline the importance of the sanctuary, it has been added to the Specially Protected Areas of Mediterranean Importance (SPAMI) list of the 1999 Barcelona Convention.
Read More About Pelagos: The Cetacean Sanctuary / Source
Island of Asinara
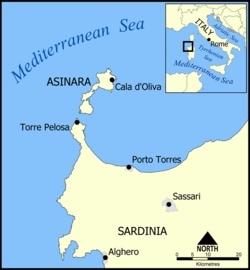
Asinara is an Italian island of 52 km2 (20 sq mi) in area. The name is Italian for “donkey-inhabited”, but it is thought to derive from the Latin “sinuaria”, and meaning sinus-shaped. The island is virtually uninhabited. The census of population of 2001 lists one man. The island is located off the north-western tip of Sardinia, and is mountainous in geography with steep, rocky coasts. Because fresh water is scarce, trees are sparse and low scrub is the predominant vegetation. Part of the national parks system of Italy, the island was recently converted to a wildlife and marine preserve. It is home to a population of wild Albino donkeys from which the island may take its name.
Read More About Island of Asinara / Source
Sulcis Iglesiente

The Iglesiente is a traditional and geographical subdivision of Sardinia, Italy. It encompasses the northern province of Carbonia-Iglesias and the south-western one of the province of Medio Campidano, and its main center is Iglesias.
Languages spoken include Italian and Sardinian (Campidanesu).
Read More About Sulcis Iglesiente / Source
The Marble Basin of Carrara

Carrara marble, Luna marble to the Romans, is a type of white or blue-grey marble popular for use in sculpture and building decor. It has been quarried since Roman times in the mountains just outside the city of Carrara in the province of Massa and Carrara in the Lunigiana, the northernmost tip of modern-day Tuscany, Italy.
More marble has been extracted from the over 650 quarry sites near Carrara than from any other place. The pure white statuario grade was used for monumental sculpture, as “it has a high tensile strength, can take a high gloss polish and holds very fine detail”. By the late 20th century this had now run out, and the considerable ongoing production is of stone with a greyish tint, or streaks of black or grey on white. This is still attractive as an architectural facing, or for tiles.
Read More About The Marble Basin of Carrara / Source
The Transhumance: The Royal Shepherd's Track

Volterra: Historical City and Cultural Landscape

Volterra (Italian pronunciation: [volˈtɛrra]; Latin: Volaterrae) is a walled mountaintop town in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its history dates from before the 8th century BC and it has substantial structures from the Etruscan, Roman, and Medieval periods.
Read More About Volterra: Historical City and Cultural Landscape / Source
The Aniene valley and Villa Gregoriana in Tivoli

The Aniene (pronounced [aˈnjɛːne]; Latin: Aniō), formerly known as the Teverone, is a 99-kilometer (62 mi) river in Lazio, Italy. It originates in the Apennines at Trevi nel Lazio and flows westward past Subiaco, Vicovaro, and Tivoli to join the Tiber in northern Rome. It formed the principal valley east of ancient Rome and became an important water source as the city’s population expanded. The falls at Tivoli were noted for their beauty. Historic bridges across the river include the Ponte Nomentano, Ponte Mammolo, Ponte Salario, and Ponte di San Francesco, all of which were originally fortified with towers.
Read More About The Aniene valley and Villa Gregoriana in Tivoli / Source
The Murge of Altamura

The Altopiano delle Murge (Italian for “Murge plateau”) is a karst topographic plateau of rectangular shape in southern Italy. Most of it lies within Apulia and corresponds with the sub-region known as Murgia or Le Murge. The plateau lies mainly in the Metropolitan City of Bari and the province of Barletta-Andria-Trani, but extends into the provinces of Brindisi and Taranto to the south, and into Matera in Basilicata to the west. The name is believed to originate from the Latin murex, meaning “sharp stone”.
Read More About The Murge of Altamura / Source
Citadel of Alessandria

The Cittadella of Alessandria (Italian: Cittadella di Alessandria) is a star fort and citadel in the city of Alessandria, Italy. It was built in the 18th century by the Kingdom of Sardinia, and today it is one of the best preserved fortifications of that era. It is one of the few fortifications in Europe still in their original environment, since there are no buildings blocking the views of the ramparts, or a road that surrounds the ditches.
On 10 March 1821, during the Piedmont insurrection, the blue, red and black tricolour of the Carbonari was raised on the Cittadella’s bastions by Colonel Ansaldi. This was the first use of a tricolour flag in the history of Italy.The Cittadella has been Italy’s tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 2006.
Read More About Citadel of Alessandria / Source
Mont Blanc massif

The Mont Blanc massif (French: Massif du Mont-Blanc; Italian: Massiccio del Monte Bianco) is a mountain range in the Alps, located mostly in France and Italy, but also straddling Switzerland at its northeastern end. It contains eleven major independent summits, each over 4,000 metres (13,123 ft) in height. It is named after Mont Blanc (4,808 metres (15,774 ft)), the highest point in western Europe and the European Union. Because of its considerable overall altitude, a large proportion of the massif is covered by glaciers, which include the Mer de Glace and the Miage Glacier – the longest glaciers in France and Italy, respectively.
The massif forms a watershed between the vast catchments of the rivers Rhône and Po, and a tripoint between France, Italy and Switzerland; it also marks the border between two climate regions by separating the northern and western Alps from the southern Alps. The mountains of the massif consist mostly of granite and gneiss rocks and at high altitudes the vegetation is an arctic-alpine flora.
The valleys that delimit the massif were used as communication routes by the Romans until they left around the 5th century AD. The region remained of some military importance through to the mid-20th century. A peasant farming economy operated within these valleys for many centuries until the glaciers and mountains were “discovered” by the outside world in the 18th century. Word of these impressive sights began to spread, and Mont Blanc was first climbed in 1786, marking the start of the sport of mountaineering. The region is now a major tourist destination, drawing in over six million visitors per year. It provides a wide range of opportunities for outdoor recreation and activities such as sight-seeing, hiking, rock climbing, mountaineering and skiing. Around one hundred people a year die across its mountains and, occasionally, bodies have been lost and entombed in its glaciers for decades.
Access into the mountains is facilitated by cable cars, mountain railways and mountain huts which offer overnight refuge to climbers and skiers. The long-distance Tour du Mont Blanc hiking trail circumnavigates the whole massif in an 11-day trek of 170 kilometres (110 mi). The Mont Blanc Tunnel connects the French town of Chamonix on the northern side with the Italian town of Courmayeur in the south. The high mountains have provided many opportunities for scientific research, including neutrino measurements within the tunnel and impact of climate change on its highest slopes. Recent rises in average temperatures have led to significant glacial retreat across the massif and an awareness of the need for better environmental protection, including a call for World Heritage Site status.
Read More About Mont Blanc massif / Source
The cultural landscape of the Benedictine settlements in medieval Italy

Mediterranean Alps

Cuneo (Italian), or Coni (Piedmontese), is a province in the southwest of the Piedmont region of Italy. To the west it borders on the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur (departments of Alpes-Maritimes, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and Hautes-Alpes). To the north it borders with the Metropolitan City of Turin. To the east it borders with the province of Asti. To the south it borders with the Ligurian provinces of Savona and Imperia. It is also known as La Provincia Granda, Piedmontese for “The Big Province”, because it is the fourth-largest province in Italy (following the provinces of Sassari, South Tyrol and Foggia) and the largest one in Piedmont. Briga Marittima and Tenda were part of this province before cession to France in 1947.
Read More About Mediterranean Alps / Source
The Cultural Landscape of Civita di Bagnoregio

Civita di Bagnoregio is a town in the Province of Viterbo in central Italy, a suburb of the comune of Bagnoregio, 1 kilometre (0.6 mi) east from it. It is about 120 kilometres (75 mi) north of Rome. The only access is a footbridge from the nearby town, with a toll introduced in 2013. Due to the toll, communal taxes were abolished in Civita and nearby Bagnoregio. Due to its unstable foundation that often erodes, Civita is famously known as “the dying city”.
Read More About The Cultural Landscape of Civita di Bagnoregio / Source
Evaporite karst and caves of Emilia Romagna Region

Via Francigena in Italy

The Via Francigena (Italian: [ˈviːa franˈtʃiːdʒena]) is an ancient road and pilgrimage route running from the cathedral city of Canterbury in England, through France and Switzerland, to Rome and then to Apulia, Italy, where there were ports of embarkation for the Holy Land. It was known in Italy as the “Via Francigena” (“the road that comes from France”) or the “Via Romea Francigena” (“the road to Rome that comes from France”). In medieval times it was an important road and pilgrimage route for those wishing to visit the Holy See and the tombs of the apostles Peter and Paul.
Read More About Via Francigena in Italy / Source
The domus de janas.

Domus de Janas (Sardinian: “House of the Fairies” or, alternatively, “House of Witches”) are a type of pre-Nuragic rock-cut chamber tomb found in Sardinia. They consist of several chambers quarried out by the people of the San Ciriaco through Ozieri cultures and subsequent cultures, resembling houses in their layout.
Built mostly between 3400 and 2700 BC, they date to the late Neolithic, Chalcolithic and early Bronze Age, including the Bell Beaker period. A necropolis of them at the site of Anghelu Ruju, near Alghero, consists of 38 tombs. Other large sites are those of Montessu, near Villaperuccio, and of Sant’Andrea Priu at Bonorva. Many other domus de janas can be found throughout the island, with the exception of Gallura (where the deceased were usually buried in megalithic circles, such as that those of Li Muri).
The shape of the internal chambers can vary from that of a rounded hut with conical or triangular ceiling. The walls are often decorated with reliefs or etchings depicting magical and religious symbols such as spirals, zig-zag motifs and bull’s horns.Carved or painted false doors appear in about 20 tombs mostly located in northwestern Sardinia,: 137–9 an example being some of the tombs of the necropolis of Anghelu Ruju, which are variously datable from the Ozieri to the Bonnanaro cultures (c.3200 – 1600 BCE). The earliest examples predate the appearance of false doors in Ancient Egyptian tombs. These false doors usually appear on the back wall of the main chamber, and are represented by horizontal and vertical frames and a projecting lintel. Sometimes the door is topped with painted or carved U-shaped bull horns, inscribed inside each other in a variable number.
The corpses, painted with red ochre like the tomb’s walls, were buried together with common life objects, jewels and tools. According to archaeologist Giovanni Lilliu, they were buried under shells of molluscs; according to other theories, they were left outside the tomb, being put inside only after they had reduced to a skeleton.
Read More About The domus de janas. / Source
Eocene Marine Biodiversity of the Alpone Valley

The Province of Verona (Italian: Provincia di Verona) is a province in the Veneto administrative region of Italy. On its northwestern border, Lake Garda – Italy’s largest – is divided between Verona and the provinces of Brescia (Lombardy region) and Trentino (Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol region). Its capital is the city of Verona. The city is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.The province is cosmopolitan in nature. It is bordered by Italian Tyrol in the north, Province of Vicenza and Province of Padua in the east. Province of Rovigo and Province of Mantua in south and Lake Garda in the west. From north to south the maximum extent of the province is 50 miles while it is 25 miles from east to west.
Read More About Eocene Marine Biodiversity of the Alpone Valley / Source
Historical theatres of the Marche Region

This nomination comprises 61 theatres in the Marche region. They date from the 16th to the 19th century and are often located in smaller towns, sometimes in municipal buildings or manor houses. The design of the theatres changed through centuries. They were visited by all social classes. They preserve rich libraries of text and musical sheets. The Teatro dell’Aquila in Fermo is pictured.
Read More About Historical theatres of the Marche Region / Source




