List of 1453 Minerals Available on Earth
Halite

Halite , commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride (NaCl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on inclusion of other materials, impurities, and structural or isotopic abnormalities in the crystals. It commonly occurs with other evaporite deposit minerals such as several of the sulfates, halides, and borates. The name halite is derived from the Ancient Greek word for “salt”, ἅλς (háls).
Read More About Halite / Source
Abelsonite

Abelsonite is a nickel porphyrin mineral with chemical formula C31H32N4Ni. It was discovered in 1969 in the U.S. State of Utah and described in 1975. The mineral is named after geochemist Philip H. Abelson. It is the only known crystalline geoporphyrin.
Read More About Abelsonite / Source
Abenakiite-(Ce)

Abenakiite-(Ce) is a mineral of sodium, cerium, neodymium, lanthanum, praseodymium, thorium, samarium, oxygen, sulfur, carbon, phosphorus, and silicon with a chemical formula Na26Ce6(SiO3)6(PO4)6(CO3)6(S4+O2)O. The silicate groups may be given as the cyclic Si6O18 grouping. The mineral is named after the Abenaki, an Algonquian Indian tribe of New England. Its Mohs scale rating is 4 to 5.
Read More About Abenakiite-(Ce) / Source
Abernathyite

Abernathyite is a mineral with formula K(UO2)(AsO4)·3H2O. The mineral is named after Jesse Evrett Abernathy (1913–1963) who first noted it in 1953 in the U.S. State of Utah. It was described as a new mineral species in 1956. Abernathyite is yellow and occurs as small crystals.
Read More About Abernathyite / Source
Abhurite

Abhurite is a mineral of tin, oxygen, hydrogen, and chlorine with the formula Sn21O6(OH)14Cl16 or Sn3O(OH)2Cl2. It is named after its type locality, a shipwreck with tin ingots at Sharm Abhur, a cove near Jeddah in the Red Sea. Abhurite forms alongside other tin minerals like romarchite and cassiterite.
Read More About Abhurite / Source
Abramovite

Abramovite is a very rare mineral from the sulfides and sulfosalt categories. It has the chemical formula Pb2SnInBiS7. It occurs as tiny elongated lamellar-shaped crystals, up 1 mm × 0.2 mm in size, and is characterized by its non-commensurate structure.
Read More About Abramovite / Source
Zabuyelite

Zabuyelite is the natural mineral form of lithium carbonate, with a formula Li2CO3. It was discovered in 1987 at Lake Zabuye, Tibet, after which it is named. It forms colorless vitreous monoclinic crystals.
It occurs as inclusions within halite in lithium rich evaporites and as solid phase in fluid inclusions in the mineral spodumene. Associated minerals include halite, gaylussite and northupite in the Tibet locality.In addition to the Tibetan salt lake it has been reported from Bikita and Kamativi
in Zimbabwe, from Kings Mountain, Cleveland County, North Carolina, US and the Tanco pegmatite, Bernic Lake, Manitoba, Canada.
Read More About Zabuyelite / Source
Zaccagnaite
Zaccagnaite is a mineral, with a formula Zn4Al2CO3(OH)12·3H2O. It occurs as white hexagonal crystals associated with calcite in cavites in Carrara marble of the Italian Alps and is thought to have formed by hydrothermal alteration of sphalerite in an aluminium rich environment. It is named after Domenico Zaccagna (1851–1940), an Italian mineral collector.
Read More About Zaccagnaite / Source
Zaherite

Zaherite is a mineral, a complex sulfate of aluminium, formula Al12(OH)26(SO4)5·20H2O. It was discovered in the Salt range, Punjab, Pakistan by M. A. Zaher of the Bangladesh Geological Survey after whom it is named in 1977. This mineral would be extremely soluble in water and unlikely to persist anywhere except in the most arid of environments. It spontaneously, and reversibly dehydrates around room temperature. Its color is white to blue-green.
Read More About Zaherite / Source
Zaïrite

Zaïrite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Bi(Fe3+,Al)3[(OH)6|(PO4)2]. The name was given from where it was locally discovered in Eta-Etu, Kivu, Congo (Zaïre) in 1975.
Read More About Zaïrite / Source
Zakharovite

Zakharovite is a mineral, a silicate of sodium and manganese; formula Na4Mn5Si10O24(OH)6·6H2O. It has a yellow colour with a pearly lustre. Discovered in 1982 in the Kola peninsula of Northern Russia, it is named after Evgeny Evgenevich Zakharov (1902–1980), the director of the Moscow Institute of Geological Exploration.
Read More About Zakharovite / Source
Zanazziite

Zanazziite is a complex hydrated phosphate mineral from the roscherite group. It is a magnesium beryllium phosphate mineral. Zanazziite arises as barrel-shaped crystals and can reach up to 4 mm. It grows alongside quartz minerals. It is found in the crevices of Lavra da Ilha pegmatite, near Taquaral, in northeastern Minas Gerais, Brazil. Zanazziite is named after Pier F. Zanazzi. Zanazziite has an ideal chemical formula of Ca2Mg5Be4(PO4)6(OH)4·6H2O.
Read More About Zanazziite / Source
Zaratite

Zaratite is a bright emerald green nickel carbonate mineral with formula Ni3CO3(OH)4·4H2O. Zaratite crystallizes in the isometric crystal system as massive to mammillary encrustations and vein fillings. It has a specific gravity of 2.6 and a Mohs hardness of 3 to 3.5. It has no cleavage and is brittle to conchoidal fracture. The luster is vitreous to greasy.
It is a rare secondary mineral formed by hydration or alteration of the primary nickel and iron bearing minerals, chromite, pentlandite, pyrrhotite, and millerite, during the serpentinization of ultramafic rocks. Hellyerite, NiCO3·6H2O, is a related mineral.
It was found originally in Galicia, Spain in 1851, and named after Spanish diplomat and dramatist Antonio Gil y Zárate (1793–1861).
Read More About Zaratite / Source
Zavaritskite

Zavaritskite is a rare mineral of the halide class, bismuth oxyhalide with the chemical formula (BiO)F. It is named after the Soviet geologist and petrographer, academician of the USSR Academy of Sciences Alexander Nikolaevich Zavaritsky. It was discovered in 1962 by Soviet scientists. Zavaritskite is part of matlockite group of minerals.
Read More About Zavaritskite / Source
Zektzerite

The mineral zektzerite is a member of the tuhualite group and was first found in 1966 by Seattle mineralogist Benjamin Bartlett “Bart” Cannon. It was discovered in the Willow creek basin below Silver Star mountain in miarolitic cavities within the alkaline arfvedsonite granite phase of the Golden Horn batholith, Okanogan County, Washington. It is named for Jack Zektzer (born 1936), mathematician and mineral collector of Seattle, Washington.The mineral was misidentified as alkali beryl (morganite) at that time. Subsequently, in September, 1975, additional specimens of the mineral were found in a “float boulder” (a glacial erratic, or dropstone) on the north side of Kangaroo Ridge at an approximate elevation of 6,500 feet (2,000 m); it was recognized that the material was not beryl.
Read More About Zektzerite / Source
Zellerite

Zellerite is a uranium mineral, named after its discoverer, geologist Howard Davis Zeller. It has a type locality of the Lucky MC uranium mine in Wyoming, USA. It was approved by the IMA in 1965, but was first published a year after its approval.
Read More About Zellerite / Source
Zemannite

Zemannite is a very rare oxide mineral with the chemical formula Mg0.5ZnFe3+[TeO3]3·4.5H2O. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system and forms small prismatic brown crystals. Because of the rarity and small crystal size, zemannite has no applications and serves as a collector’s item.
Read More About Zemannite / Source
Zeolite
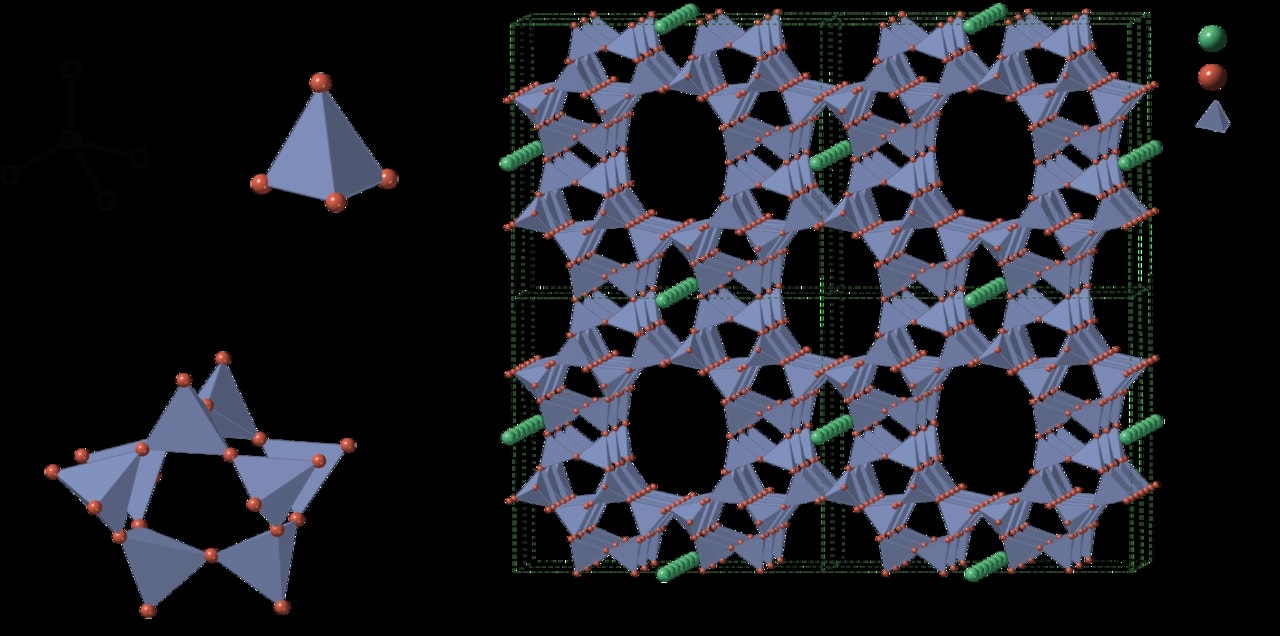
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula Mn+1/n(AlO2)−(SiO2)x・yH2O where Mn+1/n is either a metal ion or H+. These positive ions can be exchanged for others in a contacting electrolyte solution. H+ exchanged zeolites are particularly useful as solid acid catalysts.The term zeolite was originally coined in 1756 by Swedish mineralogist Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who observed that rapidly heating a material, believed to have been stilbite, produced large amounts of steam from water that had been adsorbed by the material. Based on this, he called the material zeolite, from the Greek ζέω (zéō), meaning “to boil” and λίθος (líthos), meaning “stone”.Zeolites occur naturally but are also produced industrially on a large scale. As of December 2018, 253 unique zeolite frameworks have been identified, and over 40 naturally occurring zeolite frameworks are known. Every new zeolite structure that is obtained is examined by the International Zeolite Association Structure Commission (IZA-SC) and receives a three letter designation.
Read More About Zeolite / Source
Zajacite-(Ce)

Gagarinite-(Ce) previously zajacite-(Ce) is a rare radioactive fluoride mineral with formula Na(REExCa1−x)(REEyCa1−y)F6. REE refers to rare-earth elements, mostly those belonging to the lanthanide series. It crystallizes in the trigonal rhombohedral system and has a white vitreous appearance with a conchoidal fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 and a specific gravity of 4.44 to 4.55. Zajacite is transparent with refractive indices nω = 1.483 and nε = 1.503. Gagarinite-(Y) is a yttrium-rich analog.
It occurs as creamy to white anhedral to subhedral grains in pegmatite and aplite pods or lenses in a peralkaline igneous intrusion.
It was discovered in 1993 at Strange Lake, Quebec – Labrador, (56°20’N, 64°10’W) and was initially named for Ihor Stephan Zajac, who led the expedition responsible for its discovery, and who first recognized the presence of the new mineral. The mineral was renamed gagarinite-(Ce) in 2010 by the IMA. The new name is for Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin (1934–1968).
Read More About Zajacite-(Ce) / Source
Zhonghuacerite-(Ce)

Kukharenkoite-(Ce) is a barium cerium fluoride carbonate mineral, formula Ba2CeF(CO3)3. It was identified from samples found in the Mont-Saint-Hilaire alkaline intrusive complex, Quebec, and the Khibiny Massif, Kola peninsula, Russia. It was named for Russian mineralogist Alexander A. Kukharenko (1914–1993).The similar zhonghuacerite, a cerium containing mineral from China, is considered to be either kukharenkoite-(Ce) or huanghoite-(Ce) rather than a valid mineral.
Read More About Zhonghuacerite-(Ce) / Source
Zinalsite
NounEdit. zinalsite (plural zinalsites). (mineralogy) A supposed zinc aluminium silicate mineral, not officially recognised.
Read More About Zinalsite / Source
Zeunerite

Zeunerite is a green copper uranium arsenate mineral with formula Cu(UO2)2(AsO4)2•(10-16)H2O. It is a member of the autunite group. The associated mineral metazeunerite is a dehydration product of zeunerite.
Zeunerite occurs as a secondary mineral in the oxidized weathering zone of hydrothermal uranium ore deposits which contain arsenic. Olivenite, mansfieldite, scorodite, azurite and malachite are found in association with zeunerite.It was first described in 1872 for an occurrence in the Schneeberg District, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany. It was named for Gustav Anton Zeuner (1828–1907).
Read More About Zeunerite / Source
Zhanghengite

Zhanghengite is a mineral consisting of 80% copper and zinc, 10% iron with the balance made up of chromium and aluminium. Its color is golden yellow. It was discovered in 1986 during the analysis of the Bo Xian meteorite and is named after Zhang Heng, an ancient Chinese astronomer.
Read More About Zhanghengite / Source
Zhangpeishanite
Zhangpeishanite is a mineral named after Zhang Peishan (Chinese: 张培善), a Chinese mineralogist at the Institute of Geology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in recognition of his contributions to studying the mineralogy Bayan Obo deposit, where the mineral is mined. The Bayan Obo deposit is also known for being a world class deposit. The mineral got approved by the IMA in 2006 but was published two years after its approval. The mineral consists of barium chloride fluoride.
Read More About Zhangpeishanite / Source
Zharchikhite
Zharchikhite is a halide mineral, a hydroxyl fluoride of aluminium; formula AlF(OH)2. It forms colourless, transparent crystals. Discovered in 1968, it is named after its original locality, the Zharchinskoya Deposit, which is in Buryatia, Russia.
Read More About Zharchikhite / Source
Abswurmbachite
Abswurmbachite is a copper manganese silicate mineral ((Cu,Mn2+)Mn3+6O8SiO4). It was first described in 1991 and named after Irmgard Abs-Wurmbach (born 1938), a German mineralogist. It crystallizes in the tetragonal system. Its Mohs scale rating is 6.5 and a specific gravity of 4.96. It has a metallic luster and its color is jet black, with light brown streaks.
Read More About Abswurmbachite / Source
Acanthite

Acanthite is a form of silver sulfide with the chemical formula Ag2S. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and is the stable form of silver sulfide below 173 °C (343 °F). Argentite is the stable form above that temperature. As argentite cools below that temperature its cubic form is distorted to the monoclinic form of acanthite. Below 173 °C acanthite forms directly. Acanthite is the only stable form in normal air temperature.
Read More About Acanthite / Source
Achávalite

Achávalite a selenide mineral that is a member of the nickeline group. It has only been found in a single Argentinian mine system, being first discovered in 1939 in a selenide deposit. The type locality is Cacheuta mine, Sierra de Cacheuta, Mendoza, Argentina.
Read More About Achávalite / Source
Actinolite

Actinolite is an amphibole silicate mineral with the chemical formula Ca2(Mg4.5-2.5Fe2+0.5-2.5)Si8O22(OH)2.
Read More About Actinolite / Source
Acuminite
Acuminite is a rare halide mineral with chemical formula: SrAlF4(OH)·(H2O). Its name comes from the Latin word acumen, meaning “spear point”. Its Mohs scale rating is 3.5.
Acumenite has only been described from its type locality of the cryolite deposit in Ivigtut, Greenland.
Read More About Acuminite / Source
Adamite

Adamite is a zinc arsenate hydroxide mineral, Zn2AsO4OH. It is a mineral that typically occurs in the oxidized or weathered zone above zinc ore occurrences. Pure adamite is colorless, but usually it possess yellow color due to Fe compounds admixture. Tints of green also occur and are connected with copper substitutions in the mineral structure. Olivenite is a copper arsenate that is isostructural with adamite and there is considerable substitution between zinc and copper resulting in an intermediate called cuproadamite. Zincolivenite is a recently discovered mineral being an intermediate mineral with formula CuZn(AsO4)(OH). Manganese, cobalt, and nickel also substitute in the structure. An analogous zinc phosphate, tarbuttite, is known.
Read More About Adamite / Source
Adamsite-(Y)

Adamsite-(Y) (previously IMA 1999-020), chemical formula NaY(CO3)2·6H2O is a mineral of sodium, yttrium, carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. It is named after Frank Dawson Adams (1859–1942), professor of geology, McGill University. Its Mohs scale rating is 3.
Read More About Adamsite-(Y) / Source
Zhemchuzhnikovite

Zhemchuzhnikovite is an oxalate mineral of organic origin; formula NaMg(FeAl)C2O4·8H2O. It forms smokey green crystals with a vitreous lustre and is found in Russian coal mines. It is named after Yury Zhemchuzhnikov (1885–1957), a Russian clay mineralogist.
Read More About Zhemchuzhnikovite / Source
Adelite

The rare mineral adelite, is a calcium, magnesium, arsenate with chemical formula CaMgAsO4OH. It forms a solid solution series with the vanadium-bearing mineral gottlobite. Various transition metals substitute for magnesium and lead replaces calcium leading to a variety of similar minerals in the adelite – duftite group.
Adelite forms variably colored (blue, green, yellow and grey) crystals in the orthorhombic crystal system. The form is typically massive. It has a Mohs hardness rating of 5 and a specific gravity of 3.73 to 3.79.
It was first described in 1891 from Värmland, Sweden. Its name comes from the Greek word for indistinct.
Read More About Adelite / Source
Admontite
Admontite is a hydrated magnesium borate mineral with formula MgB6O10·7H2O.
Occurrence – In a gypsum deposit.
Associations: gypsum, anhydrite, hexahydrite, löweite, eugsterite, pyrite, quartz.
It is named after Admont, Austria. Its Mohs scale rating is 2 to 3.
Read More About Admontite / Source
Ziesite

Ziesite is a copper vanadate mineral with formula: β-Cu2V2O7. It was discovered in 1980 as monoclinic crystals occurring as volcanic sublimates around fumaroles in the crater of the Izalco Volcano, El Salvador. It is named after Emanuel George Zies (1883–1981), an American geochemist who studied Izalco in the 1930s.
Closely related is blossite, also a copper vanadate with formula of α-Cu2V2O7. It forms orthorhombic crystals. Blossite was also first described for specimens from the Izalco volcano.
Ziesite and blossite are polymorphs, different crystal structure for the same chemical composition and are quite similar in physical properties.
Associated minerals include stoiberite, shcherbinaite, bannermanite, fingerite, mcbirneyite, blossite, chalcocyanite and chalcanthite.
Read More About Ziesite / Source
Aegirine

Aegirine is a member of the clinopyroxene group of inosilicate minerals. Aegirine is the sodium endmember of the aegirine-augite series. Aegirine has the chemical formula NaFeSi2O6 in which the iron is present as Fe3+. In the aegirine-augite series the sodium is variably replaced by calcium with iron(II) and magnesium replacing the iron(III) to balance the charge. Aluminium also substitutes for the iron(III). Acmite is a fibrous, green-colored variety.
Aegirine occurs as dark green monoclinic prismatic crystals. It has a glassy luster and perfect cleavage. Its Mohs hardness varies from 5 to 6, and its specific gravity is between 3.2 and 3.4.
This mineral commonly occurs in alkalic igneous rocks, nepheline syenites, carbonatites and pegmatites. It also appears in regionally
metamorphosed schists, gneisses, and iron formations; in blueschist facies rocks, and from sodium metasomatism in granulites. It may occur as an authigenic mineral in shales and marls. It occurs in association with potassic feldspar, nepheline, riebeckite, arfvedsonite, aenigmatite, astrophyllite, catapleiite, eudialyte, serandite and apophyllite.Localities include Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada; Kongsberg, Norway; Narsarssuk, Greenland; Kola Peninsula, Russia; Magnet Cove, Arkansas, US; Kenya; Scotland and Nigeria.
The acmite variety was first described in 1821, at Kongsberg, Norway, and the aegirine variety in 1835 for an occurrence in Rundemyr, Øvre Eiker, Buskerud, Norway. Aegirine was named after Ægir, the Norse god of the sea. A synonym for the mineral is acmite (from Greek ἀκμή “point, edge”) in reference to the typical pointed crystals.It is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Aegirine / Source
Aenigmatite

Aenigmatite, also known as Cossyrite after Cossyra, the ancient name of Pantelleria, is a sodium, iron, titanium inosilicate mineral. The chemical formula is Na2Fe2+5TiSi6O20 and its structure consists of single tetrahedral chains with a repeat unit of four and complex side branches. It forms brown to black triclinic lamellar crystals. It has Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and specific gravity of 3.74 to 3.85. Aenigmatite forms a solid-solution series with wilkinsonite, Na2Fe2+4Fe3+2Si6O20.
Aenigmatite is primarily found in peralkaline volcanic rocks, pegmatites, and granites as well as silica-poor intrusive rocks. It was first described by August Breithaupt in 1865 for an occurrence in the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of southwest Greenland. Its name comes from αίνιγμα, the Greek word for “riddle”.
It was also reported from the Kaidun meteorite, possibly a Mars meteorite, which landed in March 1980 in South Yemen. Other notable studied occurrences include:
Narsaarsuk and elsewhere in Greenland.
The Khibiny and Lovozero alkaline massifs on Kola Peninsula, Russia.
The Yenisei Range, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia.
The volcanic island of Pantelleria, Italy.
In the US, from Granite Mountain, near Little Rock, Pulaski County, Arkansas, and Santa Rosa, Sonoma County, California.
In Australia, from Warrumbungle volcano, Nandewar volcano, and the Mount Warning complex, New South Wales; and the Peak Range Province, Queensland.
In Canada, from Mount Edziza, the Ilgachuz and Rainbow Range shield complexes.
From Logan Point quarry, Dunedin volcano, New Zealand.
Read More About Aenigmatite / Source
Aerinite

Aerinite (Ca4(Al,Fe,Mg)10Si12O35(OH)12CO3·12H2O) is a bluish-purple inosilicate mineral. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and occurs as fibrous or compact masses and coatings. It has a dark, vitreous luster, a specific gravity of 2.48 and a Mohs hardness of 3.
It is a low-temperature hydrothermal phase occurring in zeolite facies alteration of dolerites. Associated minerals include prehnite, scolecite and mesolite.Its name comes from a Greek root “aerinos,” meaning “atmosphere” or “sky blue”. It was first described by Lasaulx (1876) from a specimen in the Wroclaw museum that was obtained in Aragon, Spain. In 1882, the geologist Luis Mariano Vidal found the mineral in situ in Caserras del Castillo, a locality that currently belongs to the municipality of Estopiñán del Castillo, in Huesca (Spain).
Read More About Aerinite / Source
Aerugite

Aerugite is a rare complex nickel arsenate mineral with a variably reported formula: Ni9(AsO4)2AsO6. It forms green to deep blue-green trigonal crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 4 and a specific gravity of 5.85 to 5.95.
It was first described in 1858 in either the South Terres mine of Cornwall, England or in Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany. The origin is disputed. The most common occurrence is as an incrustation on furnace walls in which ores are roasted. Its name comes from the Latin word aerugo for copper rust.
Read More About Aerugite / Source
Aeschynite-(Ce)
Aeschynite-(Ce) (or Aschynite, Eschinite, Eschynite) is a rare earth mineral of cerium, calcium, iron, thorium, titanium, niobium, oxygen, and hydrogen with chemical formula (Ce,Ca,Fe,Th)(Ti,Nb)2(O,OH)6. Its name comes from the Greek word αισχύνη (“aeschyne”) for “shame” because early chemists had difficulty with separations of titanium from zirconium.The “-(Ce)” means it has more cerium than the yttrium variety aeschynite-(Y). Its Mohs scale rating is 5–6.
Read More About Aeschynite-(Ce) / Source
Aeschynite-(Nd)
Aeschynite-(Nd) is a rare earth mineral of neodymium, cerium, calcium, thorium, titanium, niobium, oxygen, and hydrogen with the chemical formula (Nd,Ce,Ca,Th)(Ti,Nb)2(O,OH)6. Its name comes from the Greek word for “shame”. Its Mohs scale rating is 5 to 6. It is a member of the hydroxide minerals.
It was first reported for an occurrence in Bayan Obo, Inner Mongolia in 1982. In that rare earth mining deposit it occurs in veins within metamorphosed dolomite and slate. It occurs associated with aegirine, riebeckite, barite, fluorite, albite, phlogopite and magnetite. The IMA symbol is Aes-Nd.
Read More About Aeschynite-(Nd) / Source
Aeschynite-(Y)

Aeschynite-(Y) (or Aeschinite-(Y), Aeschynite-(Yt), Blomstrandine, Priorite) is a rare earth mineral of yttrium, calcium, iron, thorium, titanium, niobium, oxygen, and hydrogen with the chemical formula (Y,Ca,Fe,Th)(Ti,Nb)2(O,OH)6. Its name comes from the Greek word for “shame”. Its Mohs scale rating is 5 to 6.
Read More About Aeschynite-(Y) / Source
Afghanite

Afghanite, (Na,K)22Ca10[Si24Al24O96](SO4)6Cl6, is a hydrous sodium, calcium, potassium, sulfate, chloride, carbonate alumino-silicate mineral. Afghanite is a feldspathoid of the cancrinite group and typically occurs with sodalite group minerals. It forms blue to colorless, typically massive crystals in the trigonal crystal system. The lowering of the symmetry from typical (for cancrinite group) hexagonal one is due to ordering of Si and Al. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 2.55 to 2.65. It has refractive index values of nω=1.523 and nε=1.529. It has one direction of perfect cleavage and exhibits conchoidal fracture. It fluoresces a bright orange.
It was discovered in 1968 in the Lapis-lazuli Mine, Sar-e-Sang, Badakhshan Province, Afghanistan and takes its name from that country. It has also been described from localities in Germany, Italy, the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan, near Lake Baikal in Siberia, New York and Newfoundland. It occurs as veinlets in lazurite crystals in the Afghan location and in altered limestone xenoliths within pumice in Pitigliano, Tuscany, Italy.It is used as a gemstone.
Read More About Afghanite / Source
Afwillite

Afwillite is a calcium hydroxide nesosilicate mineral with formula Ca3(SiO3OH)2·2H2O. It occurs as glassy, colorless to white prismatic monoclinic crystals. Its Mohs scale hardness is between 3 and 4. It occurs as an alteration mineral in contact metamorphism of limestone. It occurs in association with apophyllite, natrolite, thaumasite, merwinite, spurrite, gehlenite, ettringite,
portlandite, hillebrandite, foshagite, brucite and calcite.It was first described in 1925 for an occurrence in the Dutoitspan Mine, Kimberley, South Africa and was named for Alpheus Fuller Williams (1874–1953), a past official of the De Beers diamond company.Afwillite is typically found in veins of spurrite and it belongs to the nesosilicate sub-class. It is monoclinic, its space group is P2 and its point group is 2.
Read More About Afwillite / Source
Agardite

Agardite is a mineral group consisting of agardite-(Y), agardite-(Ce), agardite-(Nd), and agardite-(La). They comprise a group of minerals that are hydrous hydrated arsenates of rare-earth elements (REE) and copper, with the general chemical formula (REE,Ca)Cu6(AsO4)3(OH)6·3H2O. Yttrium, cerium, neodymium, lanthanum, as well as trace to minor amounts of other REEs, are present in their structure. Agardite-(Y) is probably the most often found representative. They form needle-like yellow-green (variably hued) crystals in the hexagonal crystal system. Agardite minerals are a member of the mixite structure group, which has the general chemical formula Cu2+6A(TO4)3(OH)6·3H2O, where A is a REE, Al, Ca, Pb, or Bi, and T is P or As. In addition to the four agardite minerals, the other members of the mixite mineral group are calciopetersite, goudeyite, mixite, petersite-(Ce), petersite-(Y), plumboagardite, and zálesíite.Agardite-(Y) from the Bou Skour mine in Djebel Sarhro, Morocco was the first of the agardite-group minerals to be characterized. It was described by Dietrich in 1969 and was named after Jules Agard, a French geologist at the Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières, Orléans, France. Agardite-group minerals have subsequently been found in Germany, Czech Republic, Greece, Italy, Japan, Namibia, Poland, Spain, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Read More About Agardite / Source
Agrellite

Agrellite (NaCa2Si4O10F) is a rare triclinic inosilicate mineral with four-periodic single chains of silica tetrahedra.
It is a white to grey translucent mineral, with a pearly luster and white streak. It has a mohs hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 2.8. Its type locality is the Kipawa Alkaline Complex, Quebec, Canada, where it occurs as tabular laths in pegmatite lenses. Other localities include Murmansk Oblast, Russia, Dara-i-Pioz Glacier, Tajikistan, and Saima Complex, Liaoning, China. Common associates at the type locality include Zircon, Eudialyte, Vlasovite, Miserite, Mosandrite-(Ce), and Calcite.Agrellite displays pink fluorescence strongly under shortwave and weakly under longwave ultraviolet light. The fluorescent activator is dominantly Mn2+, with minor Eu2+, Sm3+, and Dy3+.It is named in honor of Stuart Olof Agrell (1913–1996), a British mineralogist at Cambridge University.
Read More About Agrellite / Source
Agrinierite

Agrinierite (chemical formula K2(Ca,Sr)(UO2)3O3(OH)2·5H2O) is a mineral often found in the oxidation zone of uranium deposits. The IMA symbol is Agn. It is named for Henry Agrinier (1928–1971), an engineer for the Commissariat à l’Énergie Atomique.
Read More About Agrinierite / Source
Aguilarite

Aguilarite is an uncommon sulfosalt mineral with formula Ag4SeS. It was described in 1891 and named for discoverer Ponciano Aguilar.
Read More About Aguilarite / Source
Aheylite

Aheylite is a rare phosphate mineral with formula (Fe2+Zn)Al6[(OH)4|(PO4)2]2·4(H2O). It occurs as pale blue to pale green triclinic crystal masses. Aheylite was made the newest member of the turquoise group in 1984 by International Mineralogical Association Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names.
Read More About Aheylite / Source
Ahlfeldite

Ahlfeldite ((Ni, Co)SeO3]·2H2O) is a mineral of secondary origin. It is named after Friedrich Ahlfeld (1892–1982), a German-Bolivian mining engineer and geologist. Its type locality is Virgen de Surumi mine, Pakajake Canyon, Chayanta Province, Potosí Department, Bolivia.
Read More About Ahlfeldite / Source
Aikinite

Aikinite is a sulfide mineral of lead, copper and bismuth with formula PbCuBiS3. It forms black to grey or reddish brown acicular orthorhombic crystals with a Mohs hardness of 2 to 2.5 and a specific gravity of 6.1 to 6.8. It was originally found in 1843 in the Beryozovskoye deposit, Ural Mountains. It is named after Arthur Aikin (1773–1854), an English geologist.
It has been found in Western Tasmania, in mines located near Dundas, Tasmania
Read More About Aikinite / Source
Zinclipscombite

Zinclipscombite is a dark-green to brown zinc iron phosphate mineral with the formula Zn(Fe3+)2(PO4)2(OH)2. It occurs as fibrous spheres and exhibits tetragonal crystal structure.In the classification of non-silicate minerals zinclipscombite is in the lipscombite group, which also includes lipscombite.
Read More About Zinclipscombite / Source
Ajoite

Ajoite is a hydrated sodium potassium copper aluminium silicate hydroxide mineral. Ajoite has the chemical formula (Na,K)Cu7AlSi9O24(OH)6·3H2O, and minor Mn, Fe and Ca are usually also present in the structure. Ajoite is used as a minor ore of copper.
Read More About Ajoite / Source
Zincmelanterite
Zincmelanterite is a mineral, a sulfate of zinc, copper and iron with the chemical formula (Zn,Cu,Fe)SO4·7H2O. It is a soft monoclinic yellow green mineral with Mohs hardness of 2 and a specific gravity of 2.02.
It was discovered in 1920 in the Vulcan mining district of Gunnison County, Colorado, United States, and is named for its zinc content and its resemblance to melanterite.
Read More About Zincmelanterite / Source
Akaganeite

Akaganeite, also written as the deprecated Akaganéite, is a chloride-containing iron(III) oxide-hydroxide mineral, formed by the weathering of pyrrhotite (Fe1−xS).
Akaganeite is often described as the β phase of anhydrous ferric oxyhydroxide FeOOH, but some chloride (or fluoride) ions are normally included in the structure, so a more accurate formula is FeO0.833(OH)1.167Cl0.167.Nickel may substitute for iron, yielding the more general formula (Fe3+,Ni2+)8(OH,O)16Cl1.25Akaganeite has a metallic luster and a brownish yellow streak. Its crystal structure is monoclinic and similar to that of hollandite BaMn8O16, characterised by the presence of tunnels parallel to the c-axis of the tetragonal lattice. These tunnels are partially occupied by chloride anions that give to the crystal its structural stability.
Read More About Akaganeite / Source
Zincobotryogen

Zincobotryogen is a hydrous sulfate mineral with the chemical formula (Zn,Mg,Mn)Fe3+(SO4)2(OH)·7H2O. It forms bright orange red monoclinic prismatic crystals that exhibit a vitreous to greasy luster. Its specific gravity is 2.201 and it has a Mohs hardness of 2.5.
It is a rare secondary mineral which forms in arid climates by alteration of other zinc minerals. It was named for its zinc content and it relationship to botryogen. It has been reported from the Xitieshan Mine, Qinghai, Northwest Region, China; Rammelsberg mine, near Goslar, Harz Mountains, Germany; the Bisbee district of Arizona and various mines in Colorado.
Read More About Zincobotryogen / Source
Akatoreite
Akatoreite ((Mn2+, Fe2+)9Al2[(OH)3|HSi4O13]) is a mineral found in New Zealand. The IMA symbol is Aka.
Read More About Akatoreite / Source
Zincochromite

Zincochromite is a zinc chromium oxide mineral with the formula ZnCr2O4. It is the zinc analogue of chromite, hence the name. It was first described in 1987 as an occurrence in a uranium deposit near Lake Onega, Russia. It has also been reported from Dolo Hill, New South Wales, Australia, and from the Tarkwa Mine in the Ashanti gold belt of Ghana.
Read More About Zincochromite / Source
Akdalaite
Akdalaite (IMA symbol: Akd) is a very rare mineral found in Kazakhstan and has the formula 5Al2O3·H2O. It was formerly believed to be 4Al2O3·H2O. It is therefore the same as tohdite an artificially produced phase. Studies on the crystal structure and spectra indicate that this is an aluminium oxide hydroxide.
Read More About Akdalaite / Source
Zincolivenite

Zincolivenite is a copper zinc arsenate mineral with formula CuZn(AsO4)(OH) that is a member of the olivenite group. Its colors range from green to blue, and its name comes from its composition of zinc and olivenite.It was first described from St Constantine, Lavrion District Mines, Laurium, Attica, Greece. It was approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 2006.
Read More About Zincolivenite / Source
Åkermanite

Åkermanite (Ca2Mg[Si2O7]) is a melilite mineral of the sorosilicate group, containing calcium, magnesium, silicon, and oxygen. It is a product of contact metamorphism of siliceous limestones and dolomites, and rocks of sanidinite facies. Sanidinite facies represent the highest conditions of temperature of contact metamorphism and are characterized by the absence of hydrous minerals. It has a density of 2.944 g/cm3. Åkermanite ranks a 5 or 6 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, and can be found gray, green, brown, or colorless. It has a white streak and a vitreous or resinous luster. It has a tetragonal crystal system and a good, or distinct, cleavage. It is the end member in a solid solution series beginning with gehlenite (Ca2Al[AlSiO7]).The mineral is named for Anders Richard Åkerman (1837–1922), a Swedish metallurgist. It has been found at Monte Somma and Vesuvius, and Monte Cavalluccio near Rome. It was “grandfathered” in as a species of mineral because it was described prior to 1959, before the founding of the International Mineralogical Association.
Read More About Åkermanite / Source
Zinkenite

Zinkenite is a steel-gray metallic sulfosalt mineral composed of lead antimony sulfide Pb9Sb22S42. Zinkenite occurs as acicular needle-like crystals.It was first described in 1826 for an occurrence in the Harz Mountains, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany and named after its discoverer, German mineralogist and mining geologist, Johann Karl Ludwig Zinken (1790–1862).
Read More About Zinkenite / Source
Akhtenskite
Akhtenskite is a manganese oxide mineral with the chemical formula of MnO2 (or: ε-Mn4+O2) that was named after the Akhtensk deposit in Russia, where it was first discovered and noted in 1979. It can be found in the Akhtensk brown ironstone deposit, in the southern Ural Mountains, on Mt. Zarod, on the Sikhote-Alin Mountains, and in the Primorskiy Krai, all in Russia.Its crystals are usually hexagonal in shape, with flakiness and plating, usually because it replaced a mineral. Akhtenskite is a polymorphous with the much more widespread pyrolusite. It occurs in mixtures with “psilomelane” (recently renamed to romanechite) and with other manganese oxides in an iron oxide deposit, most likely bacterially altered from a previous mineral in the Akhtensk deposit. It also occurs in crusts of ferromanganese minerals on oceanic rocks. Its chemical makeup is 63% oxygen and 37% manganese.
Some minerals that are commonly associated with akhtenskite are: todorokite, pyrolusite, nsutite, goethite, and cryptomelane.
Read More About Akhtenskite / Source
Akimotoite
Akimotoite is a rare silicate mineral in the ilmenite group of minerals, with the chemical formula (Mg,Fe)SiO3. It is polymorphous with pyroxene and with bridgmanite, a natural silicate perovskite that is the most abundant mineral in Earth’s silicate mantle. Akimotoite has a vitreous luster, is colorless, and has a white or colorless streak. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system in space group R3. It is the silicon analogue of geikielite (MgTiO3).
Read More About Akimotoite / Source
Zinnwaldite

Zinnwaldite, KLiFeAl(AlSi3)O10(OH,F)2, potassium lithium iron aluminium silicate hydroxide fluoride is a silicate mineral in the mica group. The IMA status is as a series between siderophyllite (KFe2Al(Al2Si2)O10(F,OH)2) and polylithionite (KLi2AlSi4O10(F,OH)2) and not considered a valid mineral species.
Read More About Zinnwaldite / Source
Akrochordite

Akrochordite is a rare hydrated arsenate mineral with the chemical formula (Mn,Mg)4(AsO4)2(OH)4·4H2O and represents a small group of rare manganese (Mn) arsenates and, similarly to most other Mn-bearing arsenates, possess pinkish colour. It is typically associated with metamorphic Mn deposits.
Read More About Akrochordite / Source
Aksaite
Aksaite (Mg[B6O7(OH)6]·2H2O) is a mineral found in Kazakhstan.
Read More About Aksaite / Source
Zippeite

Zippeite is a hydrous potassium uranium sulfate mineral with formula: K4(UO2)6(SO4)3(OH)10·4(H2O). It forms yellow to reddish brown monoclinic-prismatic crystals with perfect cleavage. The typical form is as encrustations and pulverulent earthy masses. It forms as efflorescent encrustations in underground uranium mines. It has a Mohs hardness of 2 and a specific gravity of 3.66. It is strongly fluorescent yellow under ultraviolet light and is moderately radioactive.
Read More About Zippeite / Source
Aktashite

Aktashite is a rare arsenic sulfosalt mineral with formula Cu6Hg3As4S12. It is a copper mercury-bearing sulfosalt and is the only sulfosalt mineral with essential Cu and Hg yet known. It is of hydrothermal origin. It was published without approval of the IMA-CNMNC, but recognized as valid species by the IMA-CNMNC Sulfosalts Subcommittee (2008).
Read More About Aktashite / Source
Zircon

Zircon is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is ZrSiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the range of substitution in zircon is (Zr1–y, REEy)(SiO4)1–x(OH)4x–y. Zircon precipitates from silicate melts and has relatively high concentrations of high field strength incompatible elements. For example, hafnium is almost always present in quantities ranging from 1 to 4%. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural color of zircon varies between colorless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue, and green.
The name derives from the Persian zargun, meaning “gold-hued”. This word is changed into “jargoon”, a term applied to light-colored zircons. The English word “zircon” is derived from Zirkon, which is the German adaptation of this word. Yellow, orange, and red zircon is also known as “hyacinth”, from the flower hyacinthus, whose name is of Ancient Greek origin.
Read More About Zircon / Source
Alabandite

Alabandite or alabandine is a rarely occurring manganese sulfide mineral. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system with the chemical composition Mn2+S and develops commonly massive to granular aggregates, but rarely also cubic or octahedral crystals to 1 cm.
Read More About Alabandite / Source
Zirconolite

Zirconolite is a mineral, calcium zirconium titanate; formula CaZrTi2O7. Some examples of the mineral may also contain thorium, uranium, cerium, niobium and iron; the presence of thorium or uranium would make the mineral radioactive. It is black or brown in color.
Read More About Zirconolite / Source
Alacránite

Alacránite (As8S9) is an arsenic sulfide mineral first discovered in the Uzon caldera, Kamchatka, Russia. It was named for its occurrence in the Alacrán silver/arsenic/antimony mine. Pampa Larga, Chile. It is generally more rare than realgar and orpiment. Its origin is hydrothermal. It occurs as subhedral to euhedral tabular orange to pale gray crystals that are transparent to translucent. It has a yellow-orange streak with a hardness of 1.5. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It occurs with realgar and uzonite as flattened and prismatic grains up to 0.5 mm across.
Read More About Alacránite / Source
Zircophyllite
Zircophyllite is a complex mineral, formula (K,Na)3(Mn,Fe)2+7(Zr,Ti,Nb)2Si8O24(OH,F)7. It crystallizes in the triclinic – pinacoidal crystal class as dark brown to black micaceous plates. It has perfect 001 cleavage, a Mohs hardness of 4 to 4.5 and a specific gravity of 3.34. Its indices of refraction are nα=1.708 nβ=1.738 nγ=1.747 and it has a 2V optical angle of 62°.
It occurs with natrolite in alkali pegmatites. It was discovered in 1972 in the Korgeredabinsh massif, Tuva, Russia and is named for its zirconium content and its relationship to astrophyllite. It is also known from the Mont Saint-Hilaire intrusive complex of Québec, Canada.
Zircophyllite is radioactive, but the radioactivity is barely detectable.
Read More About Zircophyllite / Source
Zirkelite
Zirkelite is an oxide mineral with the chemical formula (Ca,Th,Ce)Zr(Ti,Nb)2O7. It occurs as well-formed fine sized isometric crystals. It is a black, brown or yellow mineral with a hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 4.7.
Read More About Zirkelite / Source
Znucalite

Znucalite or CaZn11(UO2)(CO3)3(OH)20·4(H2O) is a rare, radioactive, white to pale cream colored uranium-containing carbonate mineral, hydrated calcium zinc uranyl carbonate hydroxide. Znucalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system, often forming aggregates or crusts, and is found as a rare secondary species in carbonate-hosted (meaning it is mined from carbonate containing formations such as limestone) polymetallic veins, and nearby oxidizing uranium veins; on dump material and coating mine walls, apparently of post-mine origin. It fluoresces yellow-green under UV light.It was first described in 1989, after being discovered in Lill Mine, Černojamské deposit (Black pits deposit) in the Czech Republic. It was named in 1990 by Petr Ondruš, František Veselovský, and R. Rybka for its constituent elements.
Read More About Znucalite / Source
Zoisite

Zoisite, first known as saualpite, after its type locality, is a calcium aluminum hydroxy sorosilicate belonging to the epidote group of minerals. Its chemical formula is Ca2Al3(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH).
Zoisite occurs as prismatic, orthorhombic (2/m 2/m 2/m) crystals or in massive form, being found in metamorphic and pegmatitic rock. Zoisite may be blue to violet, green, brown, pink, yellow, gray, or colorless. Blue crystals are known under the name tanzanite. It has a vitreous luster and a conchoidal to uneven fracture. When euhedral, zoisite crystals are striated parallel to the principal axis (c-axis). Also parallel to the principal axis is one direction of perfect cleavage. The mineral is between 6 and 7 on the Mohs hardness scale, and its specific gravity ranges from 3.10 to 3.38, depending on the variety. It streaks white and is said to be brittle. Clinozoisite is a more common monoclinic polymorph of Ca2Al3(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH).
Transparent material is fashioned into gemstones while translucent-to-opaque material is usually carved.
The mineral was described by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1805. He named it after the Carniolan naturalist Sigmund Zois, who sent him its specimens from Saualpe in Carinthia. Zois realized that this was an unknown mineral when it was brought to him by a mineral dealer, presumed to be Simon Prešern, in 1797.Sources of zoisite include Tanzania (tanzanite), Kenya (anyolite), Norway (thulite), Switzerland, Austria, India, Pakistan, and the U.S. state of Washington.
Read More About Zoisite / Source
Zorite

Zorite is a silicate mineral with the chemical formula of Na2Ti(Si,Al)3O9·nH2O. It is named because of its pink color, after the Russian word “zoria” which refers to the rosy hue of the sky at dawn. It is primarily found in Mount Karnasurta, Lovozero Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia. The Lovozero Massif is an area with an igneous mountain range, home to various types of minerals such as eudialyte, loparite, and natrosilitite.
Crystallographically, zorite belongs in the orthorhombic group, which has 3 axes, a, b, and c that are of unequal lengths (a≠b≠c) that form 90° with each other. It also belongs in the point group 2/m2/m2/m. The state of aggregation for zorite is acicular. Zorite has perfect cleavage along the planes {010} and {001}, while having poor cleavage along the plane {110}. Zorite is anisotropic, which means that the velocity of light is not the same in all directions. It belongs in the biaxial group, because it is an orthorhombic mineral. Under plane polarized light, zorite displays different colors depending on the angle that the light hits the mineral. This quality is called pleochroism and zorite is rose along the x-axis, colorless along the y-axis, and bluish along the z-axis. The index of refraction of zorite is 1.59, which is the velocity of light through vacuum over the velocity of light through zorite. Zorite is studied to better understand silicate structures.
In 2003, zorite was looked into to analyze the symmetry and topology of a family of three minerals found in Russia, Nenadkevichite, Labuntsovite, and Zorite. Zorite was also studied to comprehend how silicate structures change when an element is replaced, for example when the sodium is replaced with potassium, caesium and phosphorus. Furthermore, because of its rarity, zorite is one of the collectors’ items coveted for its scarcity, as well as it being a valuable source to understanding silicate topology.
Read More About Zorite / Source
Zunyite

Zunyite is a sorosilicate mineral, Al13Si5O20(OH,F)18Cl, composed of aluminium, silicon, hydrogen, chlorine, oxygen, and fluorine.
Read More About Zunyite / Source
Zussmanite

Zussmanite is a hydrated iron-rich silicate mineral with the chemical formula K(Fe2+,Mg,Mn)13[AlSi17O42](OH)14. It occurs as pale green crystals with perfect cleavage.
Read More About Zussmanite / Source
Alamosite

Alamosite (Pb12Si12O36) is a colorless silicate mineral named after the place where it was discovered, Álamos, Sonora, Mexico. It is a rare secondary mineral occurring in the oxidized zones of lead-rich deposits. For example, the infobox picture shows its association with black leadhillite.
Read More About Alamosite / Source
Alarsite

Alarsite (AlAsO4) is an aluminium arsenate mineral with its name derived from its composition: aluminium and arsenate. It occurs as brittle subhedral grains which exhibit trigonal symmetry. It has a Mohs hardness of 5-5.5 and a specific gravity of 3.32. It is semitransparent, colorless with pale yellow tints and shows a vitreous luster. It is optically uniaxial (+) with refractive indices of nω = 1.596 and nε = 1.608.
It was reported from fumaroles in the Tolbachik volcano, Kamchatka, Far Eastern Region, Russia. It occurs in association with fedotovite, klyuchevskite, lammerite, nabokoite, atlasovite, langbeinite, hematite and tenorite.
Read More About Alarsite / Source
Albite

Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula NaAlSi3O8. It is a tectosilicate. Its color is usually pure white, hence its name from Latin, albus. It is a common constituent in felsic rocks.
Read More About Albite / Source
Albrechtschraufite
Albrechtschraufite (IMA symbol: Asf) is a very rare complex hydrated calcium and magnesium-bearing uranyl fluoride carbonate mineral with formula Ca4Mg(UO2)2(CO3)6F2·17H2O. Its molar weight is 1,428.98 g, color yellow-green, streak white, density 2.6 g/cm3, Mohs hardness 2-3, and luster is vitreous (glassy). It is named after Albrecht Schrauf (1837–1897), Professor of Mineralogy, University of Vienna. Its type locality is Jáchymov, Jáchymov District, Krušné Hory Mountains, Karlovy Vary Region, Bohemia, Czech Republic.
Read More About Albrechtschraufite / Source
Aldermanite

Aldermanite is a rare hydrated phosphate mineral with formula Mg5Al12(PO4)8(OH)22·32H2O. It is named after Arthur Richard Alderman (1901–1980), Professor of Geology and Mineralogy, University of Adelaide. Its type locality is Moculta Phosphate Quarry (Klemm’s Quarry), Angaston, Barossa Valley, North Mount Lofty Ranges, Mount Lofty Ranges, South Australia, Australia.
Read More About Aldermanite / Source
Aleksite

Aleksite (IMA symbol: Alk) is a rare lead bismuth tellurium sulfosalt mineral with formula PbBi2Te2S2.
Read More About Aleksite / Source
Alforsite
Alforsite is a barium phosphate chloride mineral with formula: Ba5(PO4)3Cl. It was discovered in 1981, and named to honor geologist John T. Alfors (1930–2005) of the California Geological Survey for his work in the area where it was discovered.
Alforsite is a hexagonal colorless crystal in the chemical class phosphates and the group apatite. It is found in certain parts of central California, primarily Fresno, Mariposa, and Tulare Counties. It has also been found in Baja California, Mexico.
Alforsite is a constituent of the apatite group of minerals. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system with a point group of 6/m and space group P63/m. It occurs as colorless grains that are hard to distinguish from fluoroapatite, as they both display low birefringence and high relief.
Read More About Alforsite / Source
Algodonite

Algodonite is a copper arsenide mineral with formula: Cu6As. It is a gray white metallic mineral crystallizing in the hexagonal system. It has a Mohs hardness of 4 and a specific gravity of 8.38 – 8.72.
It was first described in 1857 from the Algodones silver mine, Coquimbo, Chile.
Read More About Algodonite / Source
Aliettite

Aliettite is a complex phyllosilicate mineral of the smectite group with a formula of (Ca0.2Mg6(Si,Al)8O20(OH)4·4H2O) or [Mg3Si4O10(OH)2](Ca0.5,Na)0.33(Al,Mg,Fe2+)2−3(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2·n(H2O).It is a soft, colorless to pale yellow or green earthy mineral which crystallizes in the monoclinic system as minute tabular to platy crystals.It was first described in 1968 for an occurrence in Monte Chiaro, Albareto, Parma Province, Emilia-Romagna, Italy and named for the Italian mineralogist Andrea Alietti (born 1923).It occurs in serpentinized ophiolites and their residual soil. It also occurs in altered dolomite. Associated minerals include talc, chlorite, serpentine and calcite. In addition to the type locality in Italy it has been reported from Kinshasa, Katanga; the Chelyabinsk Oblast of the southern Urals and the Turii alkaline Massif of the Kola Peninsula in Russia; the Zirabulak Mountains of Uzbekistan; and the Goldstrike Mine of Eureka County, Nevada, US.
Read More About Aliettite / Source
Allabogdanite
Allabogdanite is a very rare phosphide mineral with the chemical formula (Fe,Ni)2P, found in 1994 in a meteorite. It was described for an occurrence in the Onello meteorite in the Onello River basin, Sakha Republic; Yakutia, Russia; associated with
taenite, schreibersite, kamacite, graphite and awaruite. It was named for Russian geologist Alla Bogdanova.In a June 2021 study, scientists reported the discovery of terrestrial allabogdanite in a sedimentary formation. It is located in the Negev desert of Israel, just southwest of the Dead Sea.
Read More About Allabogdanite / Source
Allactite

Allactite is a rare arsenate mineral of metamorphosed manganese zinc ore deposits. It is found in Sweden and New Jersey, US. Its name originated from Greek αλλάκτειν (allaktein) meaning “to change”, referring to the strong pleochroism of the mineral.
Read More About Allactite / Source
Allanite

Allanite (also called orthite) is a sorosilicate group of minerals within the broader epidote group that contain a significant amount of rare-earth elements. The mineral occurs mainly in metamorphosed clay-rich sediments and felsic igneous rocks. It has the general formula A2M3Si3O12[OH], where the A sites can contain large cations such as Ca2+, Sr2+, and rare-earth elements, and the M sites admit Al3+, Fe3+, Mn3+, Fe2+, or Mg2+ among others. However, a large amount of additional elements, including Th, U, Be, Zr, P, Ba, Cr and others may be present in the mineral. The International Mineralogical Association lists four minerals in the allanite group, each recognized as a unique mineral: allanite-(Ce), allanite-(La), allanite-(Nd), and allanite-(Y), depending on the dominant rare earth present: cerium, lanthanum, neodymium or yttrium.
Allanite contains up to 20% rare-earth elements and is a valuable source of them. The inclusion of thorium and other radioactive elements in allanite results in some interesting phenomena. Allanite often has a pleochroic halo of radiation damage in the minerals immediately adjacent. Also highly radioactive grains of allanite often have their structure disrupted or are metamict. The age of allanite grains that have not been destroyed by radiation can be determined using different techniques.Allanite is usually black in color, but can be brown or brown-violet. It is often coated with a yellow-brown alteration product, likely limonite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and forms prismatic crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5–6 and a specific gravity of 3.5–4.2. It is also pyrognomic, meaning that it becomes incandescent at a relatively low temperature of about 95 °C.
It was discovered in 1810 and named for the Scottish mineralogist Thomas Allan (1777–1833). The type locality is Aluk Island, Greenland, where it was first discovered by Karl Ludwig Giesecke.
Read More About Allanite / Source
Allanpringite

Allanpringite is a phosphate mineral named after Australian mineralogist Allan Pring of the South Australian Museum. Allanpringite is a Fe3+ analogue Al-phosphate mineral wavellite, but it has a different crystal symmetry – monoclinic instead of orthorhombic in wavellite. It forms needle-like crystals, which are always twinned and form parallel bundles up to about 2 mm long. They are often found in association with other iron phosphates in abandoned iron mines.
Read More About Allanpringite / Source
Allargentum

Allargentum is a mineral from the class of antimonides, superclass of sulfides and sulfosalts (sometimes ascribed to the natural elements and alloys class), with formula written as Ag1−xSbx, where x = 0.09–0.16. This moderately rare mineral is found in silver ores and is therefore named from the Greek ἄλλος (allos, “another”) and the Latin argentum (“silver”). Its Vickers hardness is 172–203.
Read More About Allargentum / Source
Alleghanyite

Alleghanyite is a moderately rare humite mineral with formula Mn5(SiO4)2(OH)2, belonging to the nesosilicates class. In general its occurrences are related with metamorphic (metamorphosed) manganese deposits. The mineral is named after Alleghany County, North Carolina, US.
Read More About Alleghanyite / Source
Alloclasite
Alloclasite ((Co,Fe)AsS) is a sulfosalt mineral (IMA symbol: Acl). It is a member of the arsenopyrite group. Alloclasite crystallizes in the monoclinic system and typically forms as columnar to radiating acicular prismatic clusters. It is an opaque steel-gray to silver-white, with a metallic luster and a black streak. It is brittle with perfect cleavage, a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 5.91–5.95.It was first described in 1866 for an occurrence in Romania. Its name is derived from Greek for “other” and “to break,” in reference to its distinct cleavage which distinguished it from the similar appearing mineral marcasite.The mineral is monoclinic in the P21 space group.
Read More About Alloclasite / Source
Alluaivite
Alluaivite is a rare mineral of the eudialyte group, with complex formula written as Na19(Ca,Mn)6(Ti,Nb)3Si26O74Cl·2H2O. It is unique among the eudialyte group as the only titanosilicate (other representatives of the group are usually zirconosilicates). The two dual-nature minerals of the group, being both titano- and zirconosilicates, are labyrinthite and dualite. They both contain alluaivite module in their structures. Alluaivite is named after Mt. Alluaiv in Lovozero Tundry massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia, where it is found in ultra-agpaitic, hyperalkaline pegmatites.
Read More About Alluaivite / Source
Alluaudite

Alluaudite is a relatively common alkaline manganese iron phosphate mineral with the chemical formula (Na,Ca)Mn2+(Fe3+,Mn2+,Fe2+,Mg)2(PO4)3. It occurs as metasomatic replacement in granitic pegmatites and within phosphatic nodules in shales.It was first described in 1848 for an occurrence in Skellefteå, Västerbotten, Sweden. It was named by Alexis Damour after François Alluaud (II) (1778–1866). The mineral structure was first described in 1955.
Read More About Alluaudite / Source
Almandine

Almandine , also known as almandite, is a species of mineral belonging to the garnet group. The name is a corruption of alabandicus, which is the name applied by Pliny the Elder to a stone found or worked at Alabanda, a town in Caria in Asia Minor. Almandine is an iron alumina garnet, of deep red color, inclining to purple. It is frequently cut with a convex face, or en cabochon, and is then known as carbuncle. Viewed through the spectroscope in a strong light, it generally shows three characteristic absorption bands.Almandine is one end-member of a mineral solid solution series, with the other end member being the garnet pyrope. The almandine crystal formula is: Fe3Al2(SiO4)3. Magnesium substitutes for the iron with increasingly pyrope-rich composition.
Almandine, Fe2+3Al2Si3O12, is the ferrous iron end member of the class of garnet minerals representing an important group of rock-forming silicates, which are the main constituents of the Earth’s crust, upper mantle and transition zone. Almandine crystallizes in the cubic space group Ia3d, with unit-cell parameter a ≈ 11.512 Å at 100 K.Almandine is antiferromagnetic with the Néel temperature of 7.5 K. It contains two equivalent magnetic sublattices.
Read More About Almandine / Source
Almarudite
Almarudite (IMA symbol: Alr) is an extremely rare alkaline manganese beryllium silicate mineral of the cyclosilicates (ring silicates) class, with the chemical formula K([ ],Na)2(Mn2+,Fe2+,Mg)2(Be,Al)3[Si12O30], from the volcanic environment of the Eifel Mountains in Germany.
Read More About Almarudite / Source
Alsakharovite-Zn
Alsakharovite-Zn (IMA symbol: Ask-Zn) is an extremely rare alkaline strontium zinc titanium silicate mineral from the cyclosilicates class, with the chemical formula NaSrKZn(Ti,Nb)4(Si4O12)2(O,OH)4·7H2O, from alkaline pegmatites. It belongs to the labuntsovite group.The mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic system with space group Cm.
Read More About Alsakharovite-Zn / Source
Alstonite

Alstonite, also known as bromlite, is a low temperature hydrothermal mineral that is a rare double carbonate of calcium and barium with the formula BaCa(CO3)2, sometimes with some strontium. Barytocalcite and paralstonite have the same formula but different structures, so these three minerals are said to be trimorphous. Alstonite is triclinic but barytocalcite is monoclinic and paralstonite is trigonal. The species was named Bromlite by Thomas Thomson in 1837 after the Bromley-Hill mine, and alstonite by August Breithaupt of the Freiberg Mining Academy in 1841, after Alston, Cumbria, the base of operations of the mineral dealer from whom the first samples were obtained by Thomson in 1834. Both of these names have been in common use.
Read More About Alstonite / Source
Altaite

Altaite, or lead telluride, is a yellowish white mineral with an isometric crystal structure. Altaite is in the galena group of minerals as it shares many of properties of galena. Altaite has an unusually high density for a light-colored mineral. Altaite and other rare tellurides are classified in the sulfide mineral class (Dana classification).
Altaite was discovered in 1845 in the Altai Mountains. Besides these mountains altaite can also be found in Zyryanovsk, Kazakhstan; the Ritchie Creek Deposit in Price County, Wisconsin; the Koch-Bulak gold deposit in Kazakhstan; Moctezuma, Mexico; and Coquimbo, Chile among other locations.
Read More About Altaite / Source
Althausite

Althausite is a relatively simple magnesium phosphate mineral with formula Mg2(PO4)(OH,F). It is very rare. Original occurrences are magnesite deposits among serpentinites. It is named after Egon Althaus (born 1933), a mineralogist at the University of Karlsruhe, Germany.
Read More About Althausite / Source
Althupite

Althupite (IMA symbol: Ahp) is a rare aluminium thorium uranyl phosphate mineral with complex formula written as AlTh(UO2)7(PO4)4O2(OH)5·15H2O, from a granitic pegmatite. It is named after its composition (ALuminium, THorium, Uranium, and Phosphorus).
Read More About Althupite / Source
Altisite
Altisite (IMA symbol: Ati) is an exceedingly rare alkaline titanium aluminosilicate chloride mineral with formula Na3K6Ti2Al2Si8O26Cl3, from alkaline pegmatites. It is named after its composition (ALuminium, TItanium, and SIlicon).The mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with space group C2/m.
Read More About Altisite / Source
Alum-(K)

Alum-(K) is a hydrous potassium aluminium sulfate mineral with formula KAl(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is the mineral form of potassium alum and is referred to as potassium alum in older sources. It is a member of the alum group.It occurs as colorless to white, soft isometric crystals and efflorescence coatings. Rare crystals are octahedral in form if occurring as precipitates from neutral water solution, but cubic in form if the solution is alkaline.It occurs as a precipitate around volcanic fumaroles and solfataras. It also occurs as an alteration in argillaceous sediments or coal beds which contain oxidizing sulfide minerals (pyrite or marcasite). Occurs associated with alunogen, pickeringite, epsomite, melanterite, gypsum and native sulfur.Occurrences include Mount Vesuvius, Italy and Alum Cave, Sevier County, Tennessee.
Read More About Alum-(K) / Source
Aluminite

Aluminite is a hydrous aluminium sulfate mineral with formula: Al2SO4(OH)4·7H2O. It is an earthy white to gray-white monoclinic mineral which almost never exhibits crystal form. It forms botryoidal to mammillary clay-like masses. It has a very soft Mohs hardness of 1–2 and a specific gravity of 1.66–1.82.
It forms in clay and lignite deposits as an oxidation product of pyrite and marcasite along with aluminium silicates. It also occurs in volcanic sublimates, in native sulfur deposits and rarely in caves. It occurs in association with basaluminite, gibbsite, epsomite, gypsum, celestine, dolomite and goethite.It was first described in 1807 from Halle, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany and named for its aluminium content. It is also known as alley stone, halite and websterite (named after Orcadian geologist Thomas Webster).
Aluminite is used by tile and masonry workers to reduce the setting time of mortars.
Read More About Aluminite / Source
Aluminium

Aluminium (aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals; about one-third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, forming a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, nonmagnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope: 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the twelfth-most common element in the universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiometric dating.
Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity towards oxygen leads to aluminium’s common association with oxygen in nature in the form of oxides; for this reason, aluminium is found on Earth primarily in rocks in the crust, where it is the third-most abundant element, after oxygen and silicon, rather than in the mantle, and virtually never as the free metal. It is obtained industrially by mining bauxite, a sedimentary rock rich in aluminium minerals.
The discovery of aluminium was announced in 1825 by Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. The first industrial production of aluminium was initiated by French chemist Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville in 1856. Aluminium became much more available to the public with the Hall–Héroult process developed independently by French engineer Paul Héroult and American engineer Charles Martin Hall in 1886, and the mass production of aluminium led to its extensive use in industry and everyday life. In World Wars I and II, aluminium was a crucial strategic resource for aviation. In 1954, aluminium became the most produced non-ferrous metal, surpassing copper. In the 21st century, most aluminium was consumed in transportation, engineering, construction, and packaging in the United States, Western Europe, and Japan.
Despite its prevalence in the environment, no living organism is known to use aluminium salts for metabolism, but aluminium is well tolerated by plants and animals. Because of the abundance of these salts, the potential for a biological role for them is of interest, and studies continue.
Read More About Aluminium / Source
Alunite
Alunite is a hydroxylated aluminium potassium sulfate mineral, formula KAl3(SO4)2(OH)6. It was first observed in the 15th century at Tolfa, near Rome, where it was mined for the manufacture of alum. First called aluminilite by J.C. Delamétherie in 1797, this name was contracted by François Beudant three decades later to alunite.
Alunite crystals morphologically are rhombohedra with interfacial angles of 90° 50′, causing them to resemble cubes. Crystal symmetry is trigonal. Minute glistening crystals have also been found loose in cavities in altered rhyolite. Alunite varies in color from white to yellow gray. The hardness on the Mohs scale is 4 and the specific gravity is between 2.6 and 2.8. It is insoluble in water or weak acids, but soluble in sulfuric acid.
Sodium can substitute for potassium in the mineral, and when the sodium content is high, is called natroalunite.
Alunite is an analog of jarosite, where aluminium replaces Fe3+. Alunite occurs as a secondary mineral on iron sulfate ores.
Alunite occurs as veins and replacement masses in trachyte, rhyolite, and similar potassium rich volcanic rocks. It is formed by the action of sulfuric acid bearing solutions on these rocks during the oxidation and leaching of metal sulfide deposits. Alunite also is found near volcanic fumaroles. The white, finely granular masses closely resemble finely granular limestone, dolomite, anhydrite, and magnesite in appearance. The more compact kinds from Hungary are so hard and tough that they have been used for millstones.Historically extensive deposits were mined in Tuscany and Hungary, and at Bulahdelah, New South Wales, Australia. It is currently mined at Tolfa, Italy. In the United States it is found in the San Juan district of Colorado; Goldfield, Nevada; the ghost town of Alunite, Utah near Marysvale; and Red Mountain near Patagonia, Arizona. The Arizona occurrence lies appropriately above a canyon named Alum Gulch. Alunite is mined as an ore of both potassium and aluminium at Marysvale. Some of the ore deposits were located by airborne and satellite multispectral imaging.
An article in the May/June 2019 issue of Archaeology magazine states that in China, in Henan province, an assortment of ceramic objects and jars were found, dating back 2000 years. In one of the jars, a mixture of alunite and potassium nitrate was found. The mixture was then thought to be a “mixture of immortality” mentioned in ancient Chinese texts. Obviously, this does not appear to have succeeded.
Read More About Alunite / Source
Alunogen

Alunogen (from French alun, “alum”), also called feather alum and hair salt is a colourless to white (although often coloured by impurities, such as iron substituting for aluminium) fibrous to needle-like aluminium sulfate mineral. It has the chemical formula Al2(SO4)3·17H2O.It is often found on the walls of mines and quarries as a secondary mineral. It can be found in the oxidation zones of some ore deposits as well as on burning coal dumps (i.e., as the product of millosevichite hydration). It also forms as a low temperature deposit in fumaroles. It occurs associated with pyrite, marcasite, halotrichite, pickeringite, epsomite, potash alum, melanterite and gypsum.The crystallochemical formula, can be written as: [Al(H2O)6]2(SO4)3.5H2O. The second formula shows that H2O in the alunogen formula occurs both as ligand (coordinative form) and loosely bound (crystallization) form.
Read More About Alunogen / Source
Amakinite
Amakinite (IMA symbol: Amk) is a semi transparent yellow-green hydroxide mineral belonging to the brucite group that was discovered in 1962. Its chemical formula is written as (Fe2+,Mg)(OH)2. It usually occurs in the form of splotchy, anhedral crystals forming within a group or structure in other minerals or rocks, such as kimberlite (occurring in diamond-rich eruptive pipe). Its composition is as follows:
Magnesium 5.82% Mg 9.66% MgO
Manganese 6.58% Mn 8.50% MnO
Iron 46.84% Fe 60.26% FeO
Hydrogen 2.42% H 21.58% H2O
Oxygen 38.34% OAmakinite is slightly magnetic and was named for the Amakin Expedition, which prospected the diamond deposits of Yakutia in the Russian Far East.
Read More About Amakinite / Source
Amarantite

Amarantite is an amaranth-red to brownish mineral with the general formula of Fe3+2O(SO4)2·7H2O or Fe3+SO4(OH)·3H2O.The name comes from the Greek word αμάραντος which means amaranth, an imaginary undying red flower, in allusion to its color.Amarantite is triclinic, which means crystallographically, it has only one symmetry fold. It must be rotated 360 degrees to be exactly the same. Due to it being triclinic it falls into the biaxial optical class, the axis degrees do not equal 90 degrees and the sides of each axis are not the same length. Amarantite is anisotropic, which means, the velocity of light varies with crystallographic direction, and there is more than one refractive index.Amarantite is a very rare mineral and can only be found in a couple of places such as Carocoles, Chile. Although it is a source of iron, there is not enough amarantite to be mined for iron. However, when found in crystal form its red orange color gives it value as a collectors item.
Read More About Amarantite / Source
Amblygonite

Amblygonite ( ) is a fluorophosphate mineral, (Li,Na)AlPO4(F,OH), composed of lithium, sodium, aluminium, phosphate, fluoride and hydroxide. The mineral occurs in pegmatite deposits and is easily mistaken for albite and other feldspars. Its density, cleavage and flame test for lithium are diagnostic. Amblygonite forms a series with montebrasite, the low fluorine endmember. Geologic occurrence is in granite pegmatites, high-temperature tin veins, and greisens. Amblygonite occurs with spodumene, apatite, lepidolite, tourmaline, and other lithium-bearing minerals in pegmatite veins. It contains about 10% lithium, and has been utilized as a source of lithium. The chief commercial sources have historically been the deposits of California and France.
Read More About Amblygonite / Source
Ameghinite
Ameghinite, Na[H4B3O7] or NaB3O3(OH)4, is a mineral found in Argentina. It is a soft mineral with a Mohs hardness of 2–3. Ameghinite has a monoclinic crystal system.
It was first described in 1967 for an occurrence in the Tincalayu Mine, Salar Del Hombre Muerto, Salta, Argentina. It was named for Argentine geologist brothers, Carlos Ameghino (1865–1936) and Florentino Ameghino (1854–1911).
Read More About Ameghinite / Source
Amesite

Amesite is a mineral with general formula of Mg2Al2SiO5(OH)4.Amesite crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system. It contains three axes of unequal length, not at right angles.
It was first described in 1876 for an occurrence in the Chester Emery Mines, Chester, Hampden County, Massachusetts. It was named for mine owner James Ames. It occurs in an environment of low-grade metamorphism affecting rocks with high aluminium and magnesium content. It occurs associated with vesuvianite, chlorite, magnetite, rutile, diaspore, grossular, calcite, diopside and clinozoisite in various locations.Amesite is an uncommon silicate mineral which has been reported from a variety of locations worldwide. Amesite has the first reported natural occurrence of the 6R polytype for a trioctahedral 1:1 layer silicate.
Read More About Amesite / Source
Amicite

Amicite is a silicate mineral of the zeolite family. It has a general formula of K2Na2Al4Si4O16·5(H2O). Amicite was described in 1979 from specimens obtained at the Höwenegg quarry in Immendingen, Hegau, in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, which is consequently its type locality. The name is in honor of Giovanni Battista Amici (1786–1863) a botanist, physicist, optician, and inventor of microscope optical elements.
Read More About Amicite / Source
Amphibole

Amphibole is a group of inosilicate minerals, forming prism or needlelike crystals, composed of double chain SiO4 tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures. Its IMA symbol is Amp. Amphiboles can be green, black, colorless, white, yellow, blue, or brown. The International Mineralogical Association currently classifies amphiboles as a mineral supergroup, within which are two groups and several subgroups.
Read More About Amphibole / Source
Analcime

Analcime (; from Ancient Greek ἀνάλκιμος (análkimos) ‘not strong’) or analcite is a white, gray, or colorless tectosilicate mineral. Analcime consists of hydrated sodium aluminium silicate in cubic crystalline form. Its chemical formula is NaAlSi2O6·H2O. Minor amounts of potassium and calcium substitute for sodium. A silver-bearing synthetic variety also exists (Ag-analcite). Analcime is usually classified as a zeolite mineral, but structurally and chemically it is more similar to the feldspathoids. Analcime isn’t classified as an isometric crystal, as although the crystal structure appears to be isometric, it is usually off only by a fraction of an angle. However, there are truly isometric samples of the mineral, which makes its classification even more difficult. Due to the differences between the samples being too slight, there’s no merit from having multiple species names, so as a result analcime is a common example for minerals occurring in multiple crystal systems and space groups. It was first described by French geologist Déodat de Dolomieu, who called it zéolithe dure, meaning hard zeolite. It was found in lava in Cyclops, Italy. The mineral is IMA approved, and had been grandfathered, meaning the name analcime is believed to refer to a valid species til this day.
Read More About Analcime / Source
Anandite
Anandite is a rare phyllosilicate with formula (Ba,K)(Fe2+,Mg)3(Si,Al,Fe)4O10(S,OH)2. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It is black in color with a glassy luster and a near perfect cleavage.It was first described in 1967 for an occurrence in the Wilagedera Prospect of the North Western Province of Sri Lanka in bands of iron ore. It has also been found in Big Creek in Fresno County and in Trumball Peak in Mariposa County, California as well as the Sterling Mine in New Jersey. It was named for Ananda Kentish Coomaraswamy (1877–1947), who was the director of the Mineral Survey of Ceylon, Sri Lanka at that time.Anandite is a member of the mica group of minerals. Other minerals that anandite is associated with include: magnetite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, pyrrhotite and baryte.
Read More About Anandite / Source
Anapaite

Anapaite is a calcium–iron phosphate mineral with formula: Ca2Fe2+(PO4)2·4H2O. It is a mineral that typically occurs in cavities in fossil bearing sedimentary rocks. It is also found in phosphate bearing iron ores and rarely in pegmatites. It is commonly found with goethite, siderite and vivianite.It was named after the type locality on the Black Sea coastal region of Anapa, Taman Peninsula, Russia. Noted localities include Kertch (Crimea, Ukraine), Bellver de Cerdanya (Lleida, Catalonia, Spain) and Valdarno, Tuscany, Italy.
Read More About Anapaite / Source
Anatase

Anatase is a metastable mineral form of titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a tetragonal crystal structure. Although colorless or white when pure, anatase in nature is usually a black solid due to impurities. Three other polymorphs (or mineral forms) of titanium dioxide are known to occur naturally: brookite, akaogiite, and rutile, with rutile being the most common and most stable of the bunch. Anatase is formed at relatively low temperatures and found in minor concentrations in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Thin films of TiO2-coated glass show antifogging and self-cleaning properties under ultraviolet radiation.Anatase is always found as small, isolated, and sharply developed crystals, and like rutile, it crystallizes in a tetragonal system. Anatase is metastable at all temperatures and pressures, with rutile being the equilibrium polymorph. Nevertheless, anatase is often the first titanium dioxide phase to form in many processes due to its lower surface energy, with a transformation to rutile taking place at elevated temperatures. Although the degree of symmetry is the same for both anatase and rutile phases, there is no relation between the interfacial angles of the two minerals, except in the prism-zone of 45° and 90°. The common octahedral crystal habit of anatase, with four perfect cleavage planes, has an angle over its polar edge of 82°9′, whereas rutile octahedra only have a polar edge angle of 56°52½’. The steeper angle gives anatase crystals a longer vertical axis and skinnier appearance than rutile, which led French mineralogist René Just Haüy to name the mineral anatase in 1801, from the Greek anatasis (“extension”). Additional important differences exist between the physical characters of anatase and rutile. For example, anatase is less hard (5.5–6 vs. 6–6.5 on the Mohs scale) and less dense (specific gravity about 3.9 vs. 4.2) than rutile. Anatase is also optically negative, whereas rutile is optically positive. Anatase has a more strongly adamantine or metallic-adamantine luster than that of rutile as well.
Read More About Anatase / Source
Ancylite

Ancylite is a group of hydrous strontium carbonate minerals containing cerium, lanthanum and minor amounts of other rare-earth elements. The chemical formula is Sr(Ce,La)(CO3)2(OH)·H2O with ancylite-Ce enriched in cerium and ancylite-La in lanthanum.Ancylite was first described in 1899 for an occurrence in the Narsarsuk pegmatite in west Greenland and named from the Ancient Greek: αυκιλος for curved in reference to its rounded or distorted crystal form.
Read More About Ancylite / Source
Andalusite

Andalusite is an aluminium nesosilicate mineral with the chemical formula Al2SiO5. This mineral was called andalousite by Delamétehrie, who thought it came from Andalusia, Spain. It soon became clear that it was a locality error, and that the specimens studied were actually from El Cardoso de la Sierra, in the Spanish province of Guadalajara, not Andalusia.Andalusite is trimorphic with kyanite and sillimanite, being the lower pressure mid temperature polymorph. At higher temperatures and pressures, andalusite may convert to sillimanite. Thus, as with its other polymorphs, andalusite is an aluminosilicate index mineral, providing clues to depth and pressures involved in producing the host rock.
Read More About Andalusite / Source
Andersonite

Andersonite, Na2Ca(UO2)(CO3)3·6H2O, or hydrated sodium calcium uranyl carbonate is a rare uranium carbonate mineral that was first described in 1948. Named after Charles Alfred Anderson (1902–1990) of the United States Geological Survey, who first described the mineral species, it is found in sandstone-hosted uranium deposits. It has a high vitreous to pearly luster and is fluorescent. Andersonite specimens will usually glow a bright lemon yellow (or green with blue hints depending on the deposit) in ultraviolet light. It is commonly found as translucent small rhombohedral crystals that have angles close to 90 degrees although its crystal system is nominally trigonal. Its Mohs hardness is 2.5, with an average specific gravity of 2.8.
It occurs in the oxidized zone of uranium-bearing polymetallic ore deposits. It also may occur as an efflorescent crust on the walls and timbers of uranium mines. As this mineral is water-soluble, samples must be stored in dry conditions. It occurs with schrockingerite, bayleyite, schwarzites, boltwoodite, liebigite and gypsum.It was first described in 1948 for an occurrence in the Hillside Mine near Bagdad, Eureka District, Yavapai County, Arizona.
Read More About Andersonite / Source
Andesine

Andesine is a silicate mineral, a member of the plagioclase feldspar solid solution series. Its chemical formula is (Ca, Na)(Al, Si)4O8, where Ca/(Ca + Na) (% anorthite) is between 30 and 50%. The formula may be written as Na0.7-0.5Ca0.3-0.5Al1.3-1.5Si2.7-2.5O8.The plagioclase feldspars are a continuous solid solution series and as such the accurate identification of individual members requires detailed optical study, chemical analysis or density measurements. Refractive indices and specific gravity increase directly with calcium content.It is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Andesine / Source
Andorite

Andorite is a sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula PbAgSb3S6.
It was first described in 1892 for an occurrence in the Baia Sprie mine, Baia Sprie, in what is now Maramureș County, Romania, and named for Hungarian amateur mineralogist Andor von Semsey (1833–1923). Andorite occurs in low-temperature polymetallic hydrothermal veins. It occurs associated with stibnite, sphalerite, baryte, fluorite, siderite, cassiterite, arsenopyrite, stannite, zinkenite, tetrahedrite, pyrite, alunite, quartz, pyrargyrite, stephanite and rhodochrosite.
Read More About Andorite / Source
Andradite

Andradite is a mineral species of the garnet group. It is a nesosilicate, with formula Ca3Fe2Si3O12.
Andradite includes three varieties:
Melanite: Black in color, referred to as “titanian andradite”.
Demantoid: Vivid green in color, one of the most valuable and rare stones in the gemological world.
Topazolite: Yellow-green in color and sometimes of high enough quality to be cut into a faceted gemstone, it is rarer than demantoid.It was first described in 1868 for an occurrence in Drammen, Buskerud, Norway. Andradite was named after the Brazilian statesman, naturalist, professor and poet José Bonifácio de Andrada e Silva (1763–1838).
Read More About Andradite / Source
Andyrobertsite

Andyrobertsite is a rare, complex arsenate mineral with a blue color. It is found in the Tsumeb mine in Namibia and named after Andrew C. Roberts (b. 1950), mineralogist with the Geological Survey of Canada. A Ca-rich analogue (with Ca instead of Cd) is called calcioandyrobertsite and has a more greenish tint.
Read More About Andyrobertsite / Source
Anglesite

Anglesite is a lead sulfate mineral with the chemical formula PbSO4. It occurs as an oxidation product of primary lead sulfide ore, galena. Anglesite occurs as prismatic orthorhombic crystals and earthy masses, and is isomorphous with barite and celestine. It contains 74% of lead by mass and therefore has a high specific gravity of 6.3. Anglesite’s color is white or gray with pale yellow streaks. It may be dark gray if impure.
It was first recognized as a mineral species by William Withering in 1783, who discovered it in the Parys copper-mine in Anglesey; the name anglesite, from this locality, was given by F. S. Beudant in 1832. The crystals from Anglesey, which were formerly found abundantly on a matrix of dull limonite, are small in size and simple in form, being usually bounded by four faces of a prism and four faces of a dome; they are brownish-yellow in colour owing to a stain of limonite. Crystals from some other localities, notably from Monteponi in Sardinia, are transparent and colourless, possessed of a brilliant adamantine lustre, and usually modified by numerous bright faces. The variety of combinations and habits presented by the crystals is very extensive, nearly two hundred distinct forms being figured by V. von Lang in his monograph of the species; without measurement of the angles the crystals are frequently difficult to decipher. There are distinct cleavages parallel to the faces of the prism (110) and the basal plane (001), but these are not so well developed as in the isomorphous minerals barite and celestite.Anglesite is a mineral of secondary origin, having been formed by the oxidation of galena in the upper parts of mineral lodes where these have been affected by weathering processes. At Monteponi the crystals encrust cavities in glistening granular galena; and from Leadhills, in Scotland, pseudomorphs of anglesite after galena are known. At most localities it is found as isolated crystals in the lead-bearing lodes, but at some places, in Australia and Mexico, it occurs as large masses, and is then mined as an ore of lead.Anglesite is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Anglesite / Source
Anhydrite

Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with the orthorhombic barium (baryte) and strontium (celestine) sulfates, as might be expected from the chemical formulas. Distinctly developed crystals are somewhat rare, the mineral usually presenting the form of cleavage masses. The Mohs hardness is 3.5, and the specific gravity is 2.9. The color is white, sometimes greyish, bluish, or purple. On the best developed of the three cleavages, the lustre is pearly; on other surfaces it is glassy. When exposed to water, anhydrite readily transforms to the more commonly occurring gypsum, (CaSO4·2H2O) by the absorption of water. This transformation is reversible, with gypsum or calcium sulfate hemihydrate forming anhydrite by heating to around 200 °C (400 °F) under normal atmospheric conditions. Anhydrite is commonly associated with calcite, halite, and sulfides such as galena, chalcopyrite, molybdenite, and pyrite in vein deposits.
Read More About Anhydrite / Source
Ankerite

Ankerite is a calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese carbonate mineral of the group of rhombohedral carbonates with the chemical formula Ca(Fe,Mg,Mn)(CO3)2. In composition it is closely related to dolomite, but differs from this in having magnesium replaced by varying amounts of iron(II) and manganese. It forms a series with dolomite and kutnohorite.The crystallographic and physical characters resemble those of dolomite and siderite. The angle between the perfect rhombohedral cleavages is 73° 48′, the hardness is 3.5 to 4, and the specific gravity is 2.9 to 3.1. The color is white, grey or reddish to yellowish brown.Ankerite occurs with siderite in metamorphosed ironstones and sedimentary banded iron formations. It also occurs in carbonatites. In sediments it occurs as authigenic, diagenetic minerals and as a product of hydrothermal deposition. It is one of the minerals of the dolomite-siderite series, to which the terms brown-spar, pearl-spar and bitter-spar have been historically loosely applied.It was first recognized as a distinct species by W. von Haidinger in 1825, and named for Matthias Joseph Anker (1771–1843) of Styria, an Austrian mineralogist.It has been found in Western Tasmania, in mines in Dundas, Tasmania.
Read More About Ankerite / Source
Annabergite

Annabergite is an arsenate mineral consisting of a hydrous nickel
arsenate, Ni3(AsO4)2·8H2O, crystallizing in the monoclinic system and isomorphous with vivianite and erythrite. Crystals are minute and capillary and rarely met with, the mineral occurring usually as soft earthy masses and encrustations. A fine apple-green color is its characteristic feature. It was long known (since 1758) under the name nickel bloom; the name annabergite was proposed by H. J. Brooke and W H. Miller in 1852, from Annaberg in Saxony, one of the localities of the mineral. It occurs with ores of nickel, of which it is a product of alteration. A variety, from Creetown in Kirkcudbrightshire, in which a portion of the nickel is replaced by calcium, has been called dudgeonite, after P. Dudgeon, who found it.Closely related is cabrerite wherein some of the nickel is replaced by magnesium. It is named for Sierra Cabrera in Spain where it was originally found.
Read More About Annabergite / Source
Annite

Annite is a phyllosilicate mineral in the mica family. It has a chemical formula of KFe32+AlSi3O10(OH)2. Annite is the iron end member of the biotite mica group, the iron rich analogue of magnesium rich phlogopite. Annite is monoclinic and contains tabular crystals and cleavage fragments with pseudohexagonal outlines. There are contact twins with composition surface {001} and twin axis {310}.Annite was first described in 1868 for the first noted occurrence in Cape Ann, Rockport, Essex County, Massachusetts, US. It also occurs on Pikes Peak, El Paso County, Colorado. It occurs in igneous and metamorphic rocks that are deficient in magnesium and is associated with fluorite and zircon in the type locality.
Read More About Annite / Source
Anorthite

Anorthite is the calcium endmember of the plagioclase feldspar mineral series. The chemical formula of pure anorthite is CaAl2Si2O8. Anorthite is found in mafic igneous rocks. Anorthite is rare on the Earth but abundant on the Moon.
Read More About Anorthite / Source
Anorthoclase

The mineral anorthoclase ((Na,K)AlSi3O8) is a crystalline solid solution in the alkali feldspar series, in which the sodium-aluminium silicate member exists in larger proportion. It typically consists of between 10 and 36 percent of KAlSi3O8 and between 64 and 90 percent of NaAlSi3O8.
Read More About Anorthoclase / Source
Antarcticite
Antarcticite is an uncommon calcium chloride hexahydrate mineral with formula CaCl2·6H2O. It forms colorless acicular trigonal crystals. It is hygroscopic and has a low specific gravity of 1.715.
As its name implies, it was first described in 1965 for an occurrence in Antarctica where it occurs as crystalline precipitate from a highly saline brine in Don Juan Pond, in the west end of Wright Valley, Victoria Land. This discovery was made by Japanese geochemists Tetsuya Torii and Joyo Ossaka. It was also reported from brine in Bristol Dry Lake, California, and stratified brine within blue holes on North Andros Island in the Bahamas. It has also been noted within fluid inclusions within quartz in pegmatite bodies in the Bushveld complex of South Africa. It occurs in association with halite, gypsum and celestine in the California dry lake.A similar mineral, sinjarite, the dihydrate of calcium chloride, crystallizes in the tetragonal system. Sinjarite is semitransparent, with pale pink color. Hydrophilite is a now discredited calcium chloride mineral that is considered to be either antarcticite or sinjarite.
Read More About Antarcticite / Source
Anthonyite

Anthonyite is a hydrous secondary copper halide mineral with chemical formula of Cu(OH,Cl)2·3(H2O).
It was discovered in 1963 in the Centennial mine, Calumet, Houghton County, Michigan, United States. It was discovered by the University of Arizona mineralogist John W. Anthony (1920–1992), who named it for himself.
Anthonyite is lavender in color, has a Mohs hardness of 2 and crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system.
Anthonyite occurs as an alteration of native copper in basalt in fractures and cavities by circulation of chloride rich groundwater or connate fluids. The similar orthorhombic mineral calumetite occurs by the same process. It occurs associated with tremolite, quartz, epidote, monazite, native copper, cuprite and paratacamite in the Centennial mine area. It also occurs in the Cole mine, at Bisbee, Cochise County, Arizona; and Villa Hermosa, Sonora, Mexico. It occurs as a slag mineral in Richelsdorf, Hesse, Germany and Laurium, Greece.
Read More About Anthonyite / Source
Anthophyllite

Anthophyllite is an orthorhombic amphibole mineral: ☐Mg2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2 (☐ is for a vacancy, a point defect in the crystal structure), magnesium iron inosilicate hydroxide. Anthophyllite is polymorphic with cummingtonite. Some forms of anthophyllite are lamellar or fibrous and are classed as asbestos. The name is derived from the Latin word anthophyllum, meaning clove, an allusion to the most common color of the mineral. The Anthophyllite crystal is characterized by its perfect cleavage along directions 126 degrees and 54 degrees.
Read More About Anthophyllite / Source
Antigorite

Antigorite is a lamellated, monoclinic mineral in the phyllosilicate serpentine subgroup with the ideal chemical formula of (Mg,Fe2+)3Si2O5(OH)4. It is the high-pressure polymorph of serpentine and is commonly found in metamorphosed serpentinites. Antigorite, and its serpentine polymorphs, play an important role in subduction zone dynamics due to their relative weakness and high weight percent of water (up to 13 weight % H2O). It is named after its type locality, the Geisspfad serpentinite, Valle Antigorio in the border region of Italy/Switzerland and is commonly used as a gemstone in jewelry and carvings.
Read More About Antigorite / Source
Antimony

Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from Latin: stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name kohl. The earliest known description of the metal in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio.
China is the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan. The industrial methods for refining antimony from stibnite are roasting followed by reduction with carbon, or direct reduction of stibnite with iron.
The largest applications for metallic antimony are in alloys with lead and tin, which have improved properties for solders, bullets, and plain bearings. It improves the rigidity of lead-alloy plates in lead–acid batteries. Antimony trioxide is a prominent additive for halogen-containing flame retardants. Antimony is used as a dopant in semiconductor devices.
Read More About Antimony / Source
Antitaenite
Antitaenite is a meteoritic metal alloy mineral composed of iron (Fe) and 20–40% nickel (Ni), (and traces of other elements) that has a face centered cubic crystal structure.
There are three known Fe-Ni meteoritic minerals: kamacite, taenite, and tetrataenite.
The existence of antitaenite as a new mineral species, occurring in both iron meteorites and in chondrites, was first proposed in 1995 but the IMA has not approved paramagnetic antitaenite; instead the organization regards it as a variety of taenite. Gamma (fcc) Fe-Ni alloys with low-Ni (about 25% Ni) are probably inhomogeneous on a nanometer scale.Antitaenite and taenite have the same crystal structure (face centered cubic) and can have the same chemical composition (same proportions of Fe and Ni) but they differ in their electronic structures: taenite has a high magnetic moment whereas antitaenite has a low magnetic moment. This difference in electronic structure was first established in 1999 and arises from a high-magnetic-moment to low-magnetic-moment transition occurring in the Fe-Ni bi-metallic alloy series. The same electronic structure transition is believed to be a causal factor in Invar behaviour.
Read More About Antitaenite / Source
Antlerite

Antlerite is a greenish hydrous copper sulfate mineral, with the formula Cu3(SO4)(OH)4. It occurs in tabular, acicular, or fibrous crystals with a vitreous luster. Originally believed to be a rare mineral, antlerite was found to be the primary ore of the oxidised zones in several copper mines across the world, including the Chuquicamata mine in Chile, and the Antler mine in Arizona, US from which it takes its name. It is chemically and optically similar in many respects to other copper minerals such as malachite and brochantite, though it can be distinguished from the former by a lack of effervescence in hydrochloric acid.
Antlerite is a common corrosion product on bronze sculptures located in urban areas, where atmospheric sulfur dioxide (a common pollutant) is present. Antlerite forms mainly in sheltered areas where weathering is low, which permits accumulation of copper ions and enhancement in the acidity of water films. In exposed areas, the main corrosion product is brochantite.
Antlerite specimens
Read More About Antlerite / Source
Apachite
Apachite is a copper silicate mineral with a general formula of Cu9Si10O29·11H2O. The name is associated with the Apache tribe residents of the area near the Christmas copper mine in the Dripping Spring Mountains of Gila County, Arizona, the location where apachite was first described in 1980.Apachite has monoclinic crystal symmetry, displaying 3 axes of unequal length with two of the axes perpendicular to each other as well as one angle oriented less than 90°. The mineral has a maximum birefringence value of δ = 0.040 which describes the difference between the highest and lowest index of refraction for the mineral. Apachite is an anisotropic mineral, so the velocity of light varies for this mineral.
It occurs in retrograde metamorphic environment as fractures cutting garnet diopside skarn. It occurs associated with kinoite, gilalite, stringhamite, junitoite, clinohedrite, xonotlite, apophyllite, calcite and tobermorite.
Read More About Apachite / Source
Apatite

Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of OH−, F− and Cl− ion, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of the three most common endmembers is written as Ca10(PO4)6(OH,F,Cl)2, and the crystal unit cell formulae of the individual minerals are written as Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, Ca10(PO4)6F2 and Ca10(PO4)6Cl2.
The mineral was named apatite by the German geologist Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1786, although the specific mineral he had described was reclassified as fluorapatite in 1860 by the German mineralogist Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg. Apatite is often mistaken for other minerals. This tendency is reflected in the mineral’s name, which is derived from the Greek word ἀπατάω (apatáō), which means to deceive.
Read More About Apatite / Source
Aphthitalite

Aphthitalite is a potassium sulfate mineral with the chemical formula: (K,Na)3Na(SO4)2.
It was first described in 1835 for an occurrence on Mount Vesuvius, Italy. The name is from the Greek άφθητος, “unalterable”, and άλας, “salt”, for its stability in air. It occurs as fumarolic incrustations in volcanic environments, as small crystals and masses in evaporite deposits and in guano deposits. It occurs associated with thenardite, jarosite, sylvite and hematite in fumaroles; with blodite, syngenite, mirabilite, picromerite, borax and halite in evaporites; and with syngenite, whitlockite, monetite, niter and gypsum in guano deposits.
Read More About Aphthitalite / Source
Apophyllite

The name apophyllite refers to a specific group of phyllosilicates, a class of minerals. Originally, the group name referred to a specific mineral, but was redefined in 1978 to stand for a class of minerals of similar chemical makeup that comprise a solid solution series, and includes the members fluorapophyllite-(K), fluorapophyllite-(Na), hydroxyapophyllite-(K). The name apophyllite is derived from the Greek apophyllízo (ἀποφυλλίζω), meaning ‘it flakes off’, a reference to this class’s tendency to flake apart when heated, due to water loss. Exfoliation of apophyllite is also possible by treating it with acids or simply by rubbing it. These minerals are typically found as secondary minerals in vesicles in basalt or other volcanic rocks. A recent change (2008) in the nomenclature system used for this group was approved by the International Mineralogical Association, removing the prefixes from the species names and using suffixes to designate the species. A subsequent nomenclature change approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 2013 renamed the minerals to include both suffixes and prefixes, as shown above.Though relatively unfamiliar to the general public, apophyllites are fairly prevalent around the world, with specimens coming from some of the world’s most well-known mineral localities. These localities include: Jalgaon, India; the Harz Mountains of Germany, Mont Saint-Hilaire in Canada, and Kongsberg, Norway, with other locations in Scotland, Ireland, Brazil, Japan, and throughout the United States.
Read More About Apophyllite / Source
Aragonite

Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, CaCO3 (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments.
The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called flos-ferri (“flowers of iron”) from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines.
Read More About Aragonite / Source
Arcanite

Arcanite is a potassium sulfate mineral with formula: K2SO4.
Arcanite was first described in 1845 for an occurrence in old pine railroad ties in the Santa Ana tin mine, Trabuco Canyon, Santa Ana Mountains, Orange County, California, US. It has also been reported from hydrothermal deposits in the Cesano geothermal field, Latium, Italy; in bat guano on the Chincha Islands of Peru; and in caves in Western Australia, South Africa and Namibia.
Read More About Arcanite / Source
Archerite

Archerite (IMA symbol: Aht) is a phosphate mineral with chemical formula (K,NH4)H2PO4. It’s named after Michael Archer (born 25 March 1945), professor of Biology, University of New South Wales. Its type locality is Petrogale Cave, Madura Roadhouse, Dundas Shire, Western Australia. It occurs in guano containing caves as wall encrustations and stalactites.
Read More About Archerite / Source
Arctite

Arctite (Na2Ca4(PO4)3F) is a colourless mineral found in the Kola Peninsula northern Russia. Its IMA symbol is Arc. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 and has a specific gravity of 3.13. Arctite is transparent with a vitreous lustre. Arctite has a perfect cleavage and a trigonal crystal system. It is also a naturally occurring antiperovskite.Common associates of arctite include aegirine, natisite, lomonosovite, umbite and thenardite.
Read More About Arctite / Source
Arcubisite

Arcubisite (Ag6CuBiS4) is a sulfosalt mineral occurring with cryolite in Greenland. It is named after its composition (ARgentum, CUprum, and BISmuth). Its IMA symbol is Acb.
Read More About Arcubisite / Source
Ardaite

Ardaite is a very rare sulfosalt mineral with chemical formula Pb19Sb13S35Cl7 in the monoclinic crystal system, named after the Arda River, which passes through the type locality. It was discovered in 1978 and approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 1980. It was the second well-defined natural chlorosulfosalt, after dadsonite.
Greenish gray or bluish green in color, its luster is metallic. Ardaite occurs as 50 µm fine-grained aggregates of acicular crystals associated with galena, pyrostilpnite, anglesite, nadorite, and chlorine-bearing robinsonite and semseyite, in the Madjarovo polymetallic ore deposit in Bulgaria. Ardaite has a hardness of 2.5 to 3 on Mohs scale and a density of approximately 6.44.The type locality is the Madjarovo polymetallic ore deposit in the Rhodope Mountains. Later its occurrence was proved in the Gruvåsen deposit, near Filipstad, Bergslagen, Sweden.
Read More About Ardaite / Source
Arfvedsonite

Arfvedsonite is a sodium amphibole mineral with composition: [Na][Na2][(Fe2+)4Fe3+][(OH)2|Si8O22]. It crystallizes in the monoclinic prismatic crystal system and typically occurs as greenish black to bluish grey fibrous to radiating or stellate prisms.
It is a rather rare mineral occurring in nepheline syenite intrusions and agpaitic (peralkaline) pegmatites and granites as the Golden Horn batholith in Okanogan County, Washington (type locality for zektzerite). Occurrences include Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada; the Ilímaussaq complex in Southern Greenland; and in pegmatites of the Kola Peninsula, Russia. Its mineral association includes nepheline, albite, aegirine, riebeckite, katophorite and quartz.Arfvedsonite was discovered in 1823 and named for the Swedish chemist Johan August Arfwedson (1792–1841).
Read More About Arfvedsonite / Source
Argentite

In mineralogy, argentite (from Latin argentum ‘ silver’) is cubic silver sulfide (Ag2S), which can only exist at temperatures above 173 °C (343 °F), 177 °C (351 °F), or 179 °C (354 °F). When it cools to ordinary temperatures it turns into its monoclinic polymorph, acanthite. The International Mineralogical Association has decided to reject argentite as a proper mineral.The name “argentite” sometimes also refers to pseudomorphs of argentite: specimens of acanthite which still display some of the outward signs of the cubic crystal form, even though their actual crystal structure is monoclinic due to the lower temperature. This form of acanthite is occasionally found as uneven cubes and octahedra, but more often as dendritic or earthy masses, with a blackish lead-grey color and metallic luster.Argentite belongs to the galena group. Cleavage, which is so prominent a feature in galena, here presents only in traces. The mineral is perfectly sectile and has a shining streak; hardness 2.5, specific gravity is 7.2–7.4. It occurs in mineral veins, and when found in large masses, as in Mexico and in the Comstock Lode in Nevada, it forms an important ore of silver. The mineral was mentioned in 1529 by G. Agricola, but the name argentite was not used till 1845 and is due to W. Haidinger. Old names for the species are Glaserz, silver-glance and vitreous silver. A related copper-rich mineral occurring e.g. in Jalpa, Zacatecas, Mexico, is known as jalpaite.
Read More About Argentite / Source
Argutite
Argutite (GeO2) is a rare germanium oxide mineral. It is a member of the rutile group.
It was first described for an occurrence in the Argut deposit, central Pyrenees, Haute-Garonne, France in 1983. The type locality is within a zinc ore deposit within lower Paleozoic sedimentary rocks that have undergone metamorphism. Associated minerals include sphalerite, cassiterite, siderite and briartite.
Read More About Argutite / Source
Argyrodite

Argyrodite is an uncommon silver germanium sulfide mineral with formula Ag8GeS6. The color is iron-black with a purplish tinge, and the luster metallic.
Discovered by Clemens Winkler in 1886, it is of interest as it was described shortly after the element germanium was isolated, 15 years after it had been postulated by Mendeleev. It was first described for an occurrence in the Himmelsfürst Mine, Erzgebirge, Freiberg, Saxony, Germany.The Freiberg mineral had previously been imperfectly described by August Breithaupt under the name “Plusinglanz”, and Bolivian crystals were incorrectly described in 1849 as crystallized brongniardite.Isomorphous with argyrodite is the corresponding tin bearing mineral Ag8SnS6, also found in Bolivia as pseudocubic crystals, and known by the name canfieldite. There is also a related mineral, putzite, with composition (Cu4.7Ag3.3)GeS6.
Argyrodite gets its name from the Greek words that loosely translate into “rich in silver”.
Read More About Argyrodite / Source
Armalcolite

Armalcolite is a titanium-rich mineral with the chemical formula (Mg,Fe2+)Ti2O5. It was first found at Tranquility Base on the Moon in 1969 during the Apollo 11 mission, and is named for Armstrong, Aldrin and Collins, the three Apollo 11 astronauts. Together with tranquillityite and pyroxferroite, it is one of three new minerals that were discovered on the Moon. Armalcolite was later identified at various locations on Earth and has been synthesized in the laboratory. (Tranquillityite and pyroxferroite were also later found at various locations on Earth). The synthesis requires low pressures, high temperatures and rapid quenching from about 1,000 °C to the ambient temperature. Armalcolite breaks down to a mixture of magnesium-rich ilmenite and rutile at temperatures below 1,000 °C, but the conversion slows down with cooling. Because of this quenching requirement, armalcolite is relatively rare and is usually found in association with ilmenite and rutile, among other minerals.
Read More About Armalcolite / Source
Arsendescloizite

Arsendescloizite is a lead-zinc mineral, approved by the IMA in 1982. It is an arsenate analog of descloizite. Its first description was published in 1982.
Read More About Arsendescloizite / Source
Arsenic

Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry.
The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds.A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, hamsters, goats, chickens, and presumably other species. A role in human metabolism is not known. However, arsenic poisoning occurs in multicellular life if quantities are larger than needed. Arsenic contamination of groundwater is a problem that affects millions of people across the world.
The United States’ Environmental Protection Agency states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health. The United States’ Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic as number 1 in its 2001 Priority List of Hazardous Substances at Superfund sites. Arsenic is classified as a Group-A carcinogen.
Read More About Arsenic / Source
Arseniosiderite

Arseniosiderite is a rare arsenate mineral formed by the oxidation of other arsenic-containing minerals, such as scorodite or arsenopyrite. It occurs in association with beudantite, carminite, dussertite, pharmacolite, pitticite, adamite and erythrite. The name arseniosiderite reflects two major elements of the mineral, arsenic and iron (Greek sideros means iron).
Read More About Arseniosiderite / Source
Arsenoclasite
Arsenoclasite (originally arsenoklasite) is a red or dark orange brown mineral with formula Mn5(AsO4)2(OH)4. The name comes from the Greek words αρσενικόν (for arsenic) and κλάσις (for cleavage), as arsenoclasite contains arsenic and has perfect cleavage. The mineral was discovered in 1931 in Långban, Sweden.
Read More About Arsenoclasite / Source
Arsenolite

Arsenolite is an arsenic mineral, chemical formula As4O6. It is formed as an oxidation product of arsenic sulfides. Commonly found as small octahedra it is white, but impurities of realgar or orpiment may give it a pink or yellow hue. It can be associated with its dimorph claudetite (a monoclinic form of As2O3) as well as realgar (As4S4), orpiment (As2S3) and erythrite, Co3(AsO4)2·8H2O.Arsenolite belongs to the minerals which are highly toxic.
Read More About Arsenolite / Source
Arsenopyrite

Arsenopyrite (IMA symbol: Apy) is an iron arsenic sulfide (FeAsS). It is a hard (Mohs 5.5-6) metallic, opaque, steel grey to silver white mineral with a relatively high specific gravity of 6.1. When dissolved in nitric acid, it releases elemental sulfur. When arsenopyrite is heated, it produces sulfur and arsenic vapor. With 46% arsenic content, arsenopyrite, along with orpiment, is a principal ore of arsenic. When deposits of arsenopyrite become exposed to the atmosphere, the mineral slowly converts into iron arsenates. Arsenopyrite is generally an acid-consuming sulfide mineral, unlike iron pyrite which can lead to acid mine drainage.The crystal habit, hardness, density, and garlic odour when struck are diagnostic. Arsenopyrite in older literature may be referred to as mispickel, a name of German origin.Arsenopyrite also can be associated with significant amounts of gold. Consequently, it serves as an indicator of gold bearing reefs. Many arsenopyrite gold ores are refractory, i.e. the gold is not easily cyanide leached from the mineral matrix.
Arsenopyrite is found in high temperature hydrothermal veins, in pegmatites, and in areas of contact metamorphism or metasomatism.
Read More About Arsenopyrite / Source
Arthurite

Arthurite is a mineral composed of divalent copper and iron ions in combination with trivalent arsenate, phosphate and sulfate ions with hydrogen and oxygen. Initially discovered by Sir Arthur Russell in 1954 at Hingston Down Consols mine in Calstock, Cornwall, England, arthurite is formed as a resultant mineral in the oxidation region of some copper deposits by the variation of enargite or arsenopyrite. The chemical formula of Arthurite is CuFe23+(AsO4,PO4,SO4)2(O,OH)2•4H2O.Arthurite is named after Arthur W. G. Kingsbury (1906–1968), a British mineralogist, and Sir Arthur Russell (1878–1964), a collector of minerals.
Read More About Arthurite / Source
Artinite

Artinite is a hydrated basic magnesium carbonate mineral with formula: Mg2(CO3)(OH)2·3H2O. It forms white silky monoclinic prismatic crystals that are often in radial arrays or encrustations. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a specific gravity of 2.
It occurs in low-temperature hydrothermal veins and in serpentinized ultramafic rocks. Associated minerals include brucite, hydromagnesite, pyroaurite, chrysotile, aragonite, calcite, dolomite and magnesite.It was first reported in 1902 in Lombardy, Italy. It was named for Italian mineralogist, Ettore Artini (1866–1928).
Read More About Artinite / Source
Artroeite

Artroeite (PbAlF3(OH)2) is a mineral found in Arizona. It is named for the late American chemist Arthur Roe (1912–1993).
Read More About Artroeite / Source
Asbecasite

Asbecasite is a calcium titanium beryllium arsenite silicate mineral with the chemical formula Ca3(Ti,Sn4+)Be2(AsO3)6(SiO4)2. Its type locality is the Binn valley in Switzerland.
Read More About Asbecasite / Source
Ashburtonite

Ashburtonite is a rare lead copper silicate-bicarbonate mineral with formula: HPb4Cu2+4Si4O12(HCO3)4(OH)4Cl.
Read More About Ashburtonite / Source
Ashoverite
Ashoverite is one of three polymorphs of zinc hydroxide, Zn(OH)2. It is a rare mineral first found in a limestone quarry near Ashover, Derbyshire, England, in 1988. It has also been found in the Harz mountain range in Germany, and in Namibia.
The mineral was discovered after samples of the polymorph sweetite were sent to labs by S. A. Rust. Some specimens contained what appeared to be baryte but, which on further examination, were found to be a previously undescribed mineral.
Read More About Ashoverite / Source
Asisite

Asisite (Pb7SiO8Cl2) is a yellow tetragonal mineral. It is found at Kombat Mine, Kombat, Grootfontein District, Otjozondjupa Region, Namibia. It was named for a farm, Asis, which covers the mine where it was found. It was discovered in 1988.
Read More About Asisite / Source
Astrophyllite

Astrophyllite is a very rare, brown to golden-yellow hydrous potassium iron titanium silicate mineral. Belonging to the astrophyllite group, astrophyllite may be classed either as an inosilicate, phyllosilicate, or an intermediate between the two. It forms an isomorphous series with kupletskite, to which it is visually identical and often intimately associated. Astrophyllite is of interest primarily to scientists and collectors.
Heavy, soft and fragile, astrophyllite typically forms as bladed, radiating stellate aggregates. It is this crystal habit that gives astrophyllite its name, from the Greek words astron meaning “star” and phyllon meaning “leaf”. Its great submetallic gleam and darkness contrast sharply with the light (felsic) matrix the mineral is regularly found within. Astrophyllite is usually opaque to translucent, but may be transparent in thin specimens.
As the crystals themselves possess perfect cleavage, they are typically left in situ, the entire aggregate often cut into slabs and polished. Owing to its limited availability and high cost, astrophyllite is seldom seen in an ornamental capacity. It is sometimes used in jewellery where it is fashioned into cabochons.
Found in cavities and fissures in unusual felsic igneous rocks, astrophyllite is associated with feldspar, mica, titanite, zircon, nepheline, and aegirine. Common impurities include magnesium, aluminium, calcium, zirconium, niobium, and tantalum. It was first discovered in 1854 at its type locality; Laven Island, Norway. Kupletskite was not known until 1956, over a hundred years later.
Astrophyllite is found in a few scarce, remote localities: Mont-Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada; Pikes Peak, Colorado, US; Narsarsuk and Kangerdluarsuk, Greenland; Brevig, Norway; and the Kola Peninsula, Russia.
Read More About Astrophyllite / Source
Atacamite

Atacamite is a copper halide mineral: a copper(II) chloride hydroxide with formula Cu2Cl(OH)3. It was first described for deposits in the Atacama Desert of Chile in 1802 by Dmitri de Gallitzin. The Atacama Desert is also the namesake of the mineral.
Read More About Atacamite / Source
Athabascaite
Athabascaite is a member of the copper selenide minerals, and forms with other copper selenides. It was first discovered by S. Kaiman in 1949 while he was researching radioactive materials around Lake Athabasca. Kaiman was conducting research near Uranium City, Saskatchewan where mass amounts of uranium mines were present.
Read More About Athabascaite / Source
Atheneite
Atheneite is a rare palladium, mercury arsenide mineral with the chemical formula (Pd,Hg)3 associated with palladium–gold deposits. Its composition parallels that of arsenopalladinite (Pd8(As,Sb)3), isomertieite (Pd11Sb2As2) and meritieite-II (Pd8(Sb,As)3) (Cabral, 2002).
Read More About Atheneite / Source
Aubertite
Aubertite is a mineral with the chemical formula CuAl(SO4)2Cl·14H2O. It is colored blue. Its crystals are triclinic pedial. It is transparent. It has vitreous luster. It is not radioactive. Aubertite is rated 2-3 on the Mohs Scale. The sample was collected by J. Aubert (born 1929), assistant director, National Institute of Geophysics, France, in the year 1961. Its type locality is Queténa Mine, Toki Cu deposit, Chuquicamata District, Calama, El Loa Province, Antofagasta Region, Chile.
Read More About Aubertite / Source
Augelite

Augelite is an aluminium phosphate mineral with formula: Al2(PO4)(OH)3. The shade varies from colorless to white, yellow or rose. Its crystal system is monoclinic.It was first described by Christian Wilhelm Blomstrand for an occurrence in Västanå iron mine at Scania, Sweden in 1868 and derives its name from the Greek αύγή in reference to its pearly lustre.It occurs as a product of metamorphism of phosphate bearing peraluminous sediments and in high-temperature hydrothermal ore deposits. It occurs in association with attakolite, svanbergite, lazulite, hematite, trolleite, berlinite, rutile, pyrophyllite, baryte, arsenopyrite, stannite, pyrite, andorite, cassiterite and zinkenite.
Read More About Augelite / Source
Augite

Augite is a common rock-forming pyroxene mineral with formula (Ca,Na)(Mg,Fe,Al,Ti)(Si,Al)2O6. The crystals are monoclinic and prismatic. Augite has two prominent cleavages, meeting at angles near 90 degrees.
Read More About Augite / Source
Aurichalcite

Aurichalcite is a carbonate mineral, usually found as a secondary mineral in copper and zinc deposits. Its chemical formula is (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6. The zinc to copper ratio is about 5:4. Copper (Cu2+) gives aurichalcite its green-blue colors.
Read More About Aurichalcite / Source
Auricupride

Auricupride is a natural alloy that combines copper and gold. Its chemical formula is Cu3Au. The alloy crystallizes in the cubic crystal system in the L12 structure type and occurs as malleable grains or platey masses. It is an opaque yellow with a reddish tint. It has a hardness of 3.5 and a specific gravity of 11.5.A variant called tetra-auricupride (CuAu) exists. Silver may be present resulting in the variety argentocuproauride (Cu3(Au,Ag)).It was first described in 1950 for an occurrence in the Ural Mountains Russia. It occurs as low temperature unmixing product in serpentinites and as reduction “halos” in redbed deposits. It is most often found in Chile, Argentina, Tasmania, Russia, Cyprus, Switzerland and South Africa.
Read More About Auricupride / Source
Aurostibite

Aurostibite is an isometric gold antimonide mineral which is a member of the pyrite group. Aurostibite was discovered in 1952 and can be found in hydrothermal gold-quartz veins, in sulfur-deficient environments that contain other antimony minerals. The mineral can be found in Yellowknife in the Northwest Territories of Canada, and the Timiskaming District in Ontario, Canada. Antimonides are rare and are normally placed in the sulfide class by mineralogists.
Read More About Aurostibite / Source
Austinite

Austinite is a member of the adelite-descloizite group, adelite subgroup, the zinc (Zn) end member of the copper-Zn series with conichalcite. It is the zinc analogue of cobaltaustinite and nickelaustinite. At one time “brickerite” was thought to be a different species, but it is now considered to be identical to austinite. Austinite is named in honour of Austin Flint Rogers (1877–1957), American mineralogist from Stanford University, California, US.
Read More About Austinite / Source
Autunite

Autunite (hydrated calcium uranyl phosphate), with formula Ca(UO2)2(PO4)2·10–12H2O, is a yellow-greenish fluorescent phosphate mineral with a hardness of 2–2+1⁄2. Autunite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and often occurs as tabular square crystals, commonly in small crusts or in fan-like masses. Due to the moderate uranium content of 48.27% it is radioactive and also used as uranium ore. Autunite fluoresces bright green to lime green under UV light. The mineral is also called calco-uranite, but this name is rarely used and effectively outdated.Autunite was discovered in 1852 near Autun, France, which is also autunite’s namesake. It occurs as an oxidation product of uranium minerals in granite pegmatites and hydrothermal deposits. Associate minerals include metaautunite, torbernite, phosphuranylite, saleeite, uranophane and sabugalite.
Read More About Autunite / Source
Avicennite
Avicennite (thallium(III) oxide) is an oxide mineral. It was discovered around the Dzhuzumli village, Samarqand, Uzbekistan. It is named after Avicenna, a Persian doctor and polymath.
Read More About Avicennite / Source
Avogadrite

Avogadrite ((K,Cs)BF4) is a potassium-caesium tetrafluoroborate in the halide class. Avogadrite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group Pnma) with cell parameters a 8.66 Å, b 5.48 Å and c Å 7.03.
Read More About Avogadrite / Source
Awaruite

Awaruite is a naturally occurring alloy of nickel and iron with a composition from Ni2Fe to Ni3Fe.
Awaruite occurs in river placer deposits derived from serpentinized peridotites and ophiolites. It also occurs as a rare component of meteorites. It occurs in association with native gold and magnetite in placers; with copper, heazlewoodite, pentlandite, violarite, chromite, and
millerite in peridotites; with kamacite, allabogdanite, schreibersite and graphite in meteorites.It was first described in 1885 for an occurrence along Gorge River, near Awarua Bay, South Island, New Zealand, its type locality.Awaruite is also known as josephinite in an occurrence in Josephine County, Oregon where it is found as placer nuggets in stream channels and masses in serpentinized portions of the Josephine peridotite. Some nuggets contain andradite garnet.An occurrence of awaruite is being developed commercially as an ore mineral in a large low grade deposit in central British Columbia, some 90 km northwest of Fort St. James. In the deposit awaruite occurs disseminated in the Mount Sidney Williams ultramafic/ophiolite complex.
Read More About Awaruite / Source
Axinite

Axinite is a brown to violet-brown, or reddish-brown bladed group of minerals composed of calcium aluminium boro-silicate, (Ca,Fe,Mn)3Al2BO3Si4O12OH. Axinite is pyroelectric and piezoelectric.
The axinite group includes:
Axinite-(Fe) or ferroaxinite, Ca2Fe2+Al2BOSi4O15(OH) iron rich, clove-brown, brown, plum-blue, pearl-gray
Axinite-(Mg) or magnesioaxinite, Ca2MgAl2BOSi4O15(OH) magnesium rich, pale blue to pale violet; light brown to light pink
Axinite-(Mn) or manganaxinite, Ca2Mn2+Al2BOSi4O15(OH) manganese rich, honey-yellow, clove-brown, brown to blue
Tinzenite, (CaFe2+Mn2+)3Al2BOSi4O15(OH) iron – manganese intermediate, yellow, brownish yellow-greenAxinite is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Axinite / Source
Azurite

Azurite is a soft, deep-blue copper mineral produced by weathering of copper ore deposits. During the early 19th century, it was also known as chessylite, after the type locality at Chessy-les-Mines near Lyon, France. The mineral, a basic carbonate with the chemical formula Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2, has been known since ancient times, and was mentioned in Pliny the Elder’s Natural History under the Greek name kuanos (κυανός: “deep blue,” root of English cyan) and the Latin name caeruleum. Copper (Cu2+) gives it its blue color. Since antiquity, azurite’s exceptionally deep and clear blue has been associated with low-humidity desert and winter skies. The modern English name of the mineral reflects this association, since both azurite and azure are derived via Arabic from the Persian lazhward (لاژورد), an area known for its deposits of another deep-blue stone, lapis lazuli (“stone of azure”).
Read More About Azurite / Source
Babefphite
Babefphite is a rare phosphate mineral with the general formula BaBe(PO4)(F,OH). The name is given for its composition (Ba meaning barium, Be meaning beryllium, F meaning fluorine, and P for phosphorus).
Read More About Babefphite / Source
Babingtonite

Babingtonite is a calcium iron manganese inosilicate mineral with the formula Ca2(Fe,Mn)FeSi5O14(OH). It is unusual in that iron(III) completely replaces the aluminium so typical of silicate minerals. It is a very dark green to black translucent (in thin crystals or splinters) mineral crystallizing in the triclinic system with typically radial short prismatic clusters and druzy coatings. It occurs with zeolite minerals in cavities in volcanic rocks. Babingtonite contains both iron(II) and iron(III) and shows weak magnetism. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 3.3.
It was first described in 1824 from samples from Arendal, Aust-Agder, Norway (which is its type locality) and was named after the Irish physician and mineralogist William Babington (1757–1833).It is the official mineral (mineral emblem) of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The first published report of babingtonite in Massachusetts was by Francis Alger in 1844, who credited Thomas Nuttall with its discovery in Charlestown (now Somerville). The location was the Granite Street quarry, formerly known as the Milk Row quarry.
Read More About Babingtonite / Source
Baddeleyite

Baddeleyite is a rare zirconium oxide mineral (ZrO2 or zirconia), occurring in a variety of monoclinic prismatic crystal forms. It is transparent to translucent, has high indices of refraction, and ranges from colorless to yellow, green, and dark brown. See etymology below.
Baddeleyite is a refractory mineral, with a melting point of 2700 °C. Hafnium is a substituting impurity and may be present in quantities ranging from 0.1 to several percent.
It can be found in igneous rocks containing potassium feldspar and plagioclase. Baddeleyite is commonly not found with zircon (ZrSiO4), because it forms in silica-undersaturated rocks, such as mafic rocks. This is because, when silica is free in the system (silica-saturated/oversaturated), zircon is the dominating phase, not baddeleyite. It belongs to the monoclinic-prismatic class, of the P21/c crystal system. It has been used for geochronology.
Read More About Baddeleyite / Source
Bakerite
Bakerite is the common name given to hydrated calcium boro-silicate hydroxide, a borosilicate mineral (chemical formula Ca4B4(BO4)(SiO4)3(OH)3·(H2O)) that occurs in volcanic rocks in the Baker, California area. Discredited mineral: IMA2016-A.
It was first described in 1903 for an occurrence in the Corkscrew Canyon Mine of the Black Mountains, Furnace Creek District, Death Valley National Park, Inyo County, California, US. It was named for Richard C. Baker, a director of the Pacific Coast Borax Company.
Read More About Bakerite / Source
Balangeroite

Balangeroite is found in one of the most important chrysotile mines in Europe, the Balangero Serpentinite. Hence, it is usually mistaken as an asbestiform in an assemblage of other mineral phases like chrysotile, magnetite and Fe-Ni alloys. However, Balangeroite does not lead to serious health problems caused by asbestos fibers.
Read More About Balangeroite / Source
Banalsite
Banalsite is a rare barium, sodium aluminium silicate mineral with formula: BaNa2Al4Si4O16. Banalsite is a tectosilicate of the feldspar group.
Banalsite and its strontium analogue, stronalsite (SrNa2Al4Si4O16), constitute a complete solid solution series. In addition limited solid solution with calcium exists between these and lisetite: CaNa2Al4Si4O16.It was first described in 1944 for an occurrence in the Benallt Mine, Rhiw, Llanfaelrhys, Lleyn Peninsula, Gwynedd (Caernarvonshire), Wales. The name is derived from the chemical symbols of its composition. It has also been reported from Långban, Värmland, Sweden and from the Kalahari manganese field, Cape Province, South Africa. It has recently been reported from the nepheline syenites of the Zhidoy massif, Eastern Sayan, Siberia, Russia; the Prairie Lake complex of alkaline rocks and carbonatites, Superior Alkaline Province, northwestern Ontario, Canada; the Pilansberg peralkaline complex, South Africa; the Sakharjok alkaline complex in the Kola Alkaline Province, Kola Peninsula of northwestern Russia (the Gremyakha–Vyrmes peralkaline complex, and the Turiy Mys complex of ultramafic–alkaline rocks and carbonatites).
Read More About Banalsite / Source
Bannisterite

Bannisterite is a mineral named in honor of mineralogist and x-ray crystallographer Dr. Frederick Allen Bannister (1901-1970). It is a calcium-dominant member of the ganophyllite group, and was previously identified as ganophyllite in 1936, but otherwise it is structurally related to the stilpnomelane group. It was approved by the IMA in 1967.
Read More About Bannisterite / Source
Baotite

Baotite Ba4Ti4(Ti, Nb, Fe)4(Si4O12)O16Cl is a rare mineral recognized as having a unique four-fold silicate ring. Crystals are tetragonal, though commonly deformed to the extent of appearing monoclinic. Named for the locality of first discovery, Baotou, China, baotite has been found in hydrothermal veins and alkalic rocks in various locations around the world.
Read More About Baotite / Source
Bararite

Bararite is a natural form of ammonium fluorosilicate (also known as hexafluorosilicate or fluosilicate). It has chemical formula (NH4)2SiF6 and trigonal crystal structure. This mineral was once classified as part of cryptohalite. Bararite is named after the place where it was first described, Barari, India. It is found at the fumaroles of volcanoes (Vesuvius, Italy), over burning coal seams (Barari, India), and in burning piles of anthracite (Pennsylvania, U.S.). It is a sublimation product that forms with cryptohalite, sal ammoniac, and native sulfur.
Read More About Bararite / Source
Baratovite

Baratovite is a very rare cyclosilicate mineral named after Rauf Baratovich Baratov from Tajikistan. It was discovered in 1974 at Dara-Pioz glacier, Tajikistan, and was approved by the International Mineralogical Association only a year later in 1975. The glacier gives home to 133 valid species, and is the type locality of 33 minerals, one of which is baratovite.
Read More About Baratovite / Source
Barrerite

Barrerite is a tectosilicate mineral and a member of the zeolite family. It is one of the rarer zeolites. It was named for Richard Barrer, a New Zealand-born chemist.Barrerite crystal are white to pinkish, with a vitreous-glassy luster. The crystal system is orthorhombic and is flat and tabular in appearance. It has a Mohs hardness of 3 to 4 and its cleavage is perfect. Barrerite has a white streak and a density of 2.13.
It was first described in 1974 for an occurrence in Sardinia at Sant’ Efisio Tower on Cape Pula in Cagliari Province. It has also been reported from Rocky Pass, Kuiu Island, Alaska, and a few other localities.
Read More About Barrerite / Source
Barstowite

Barstowite, formula Pb4[Cl6|CO3]•H2O, is a transparent to white mineral in the monoclinic system. It has a Mohs hardness of 3, a white streak and an adamantine lustre.The type locality for Barstowite is Bounds Cliff, St Endellion, Cornwall in the United Kingdom. It is named after Richard W. Barstow (1947–1982), a Cornish mineral collector.
Read More About Barstowite / Source
Baryte

Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate (BaSO4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The baryte group consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), anglesite (lead sulfate), and anhydrite (calcium sulfate). Baryte and celestine form a solid solution (Ba,Sr)SO4.
Read More About Baryte / Source
Barytocalcite

Barytocalcite is an anhydrous barium calcium carbonate mineral with the chemical formula BaCa(CO3)2. It is trimorphous with alstonite and paralstonite, that is to say the three minerals have the same formula but different structures. Baryte and quartz pseudomorphs after barytocalcite have been observed.Barytocalcite crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, typically as massive to druzy accumulations of transparent white to yellow to grey aggregates of slender prismatic crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 4 and a specific gravity of 3.64 to 3.71.It was first described in 1824 for an occurrence in the Blagill Mine in North Pennines, Cumbria (Cumberland), England, and named for its composition.
Read More About Barytocalcite / Source
Bassanite

Bassanite is a calcium sulfate mineral with formula CaSO4·1/2H2O or 2CaSO4·H2O. In other words it has half a water molecule per CaSO4 unit, hence its synonym calcium sulfate hemihydrate.
Bassanite was first described in 1910 for an occurrence on Mount Vesuvius. It was named for Italian paleontologist Francesco Bassani (1853–1916).At Vesuvius it occurs as alterations from gypsum within leucite tephrite and as fumarole deposits. It occurs in dry lake beds in California and Australia. It also occurs interlayered with gypsum in caves.H. Schmidt and coinvestigators reported in 2011 that under dry conditions, the structure is monoclinic with space group C2, but at 75% humidity, the structure is trigonal with space group P3221. This reflects the incorporation of additional water of hydration, such that the trigonal form has the formula CaSO4·0.625H2O
Read More About Bassanite / Source
Bastnäsite

The mineral bastnäsite (or bastnaesite) is one of a family of three carbonate-fluoride minerals, which includes bastnäsite-(Ce) with a formula of (Ce, La)CO3F, bastnäsite-(La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F, and bastnäsite-(Y) with a formula of (Y, Ce)CO3F. Some of the bastnäsites contain OH− instead of F− and receive the name of hydroxylbastnasite. Most bastnäsite is bastnäsite-(Ce), and cerium is by far the most common of the rare earths in this class of minerals. Bastnäsite and the phosphate mineral monazite are the two largest sources of cerium and other rare-earth elements.
Bastnäsite was first described by the Swedish chemist Wilhelm Hisinger in 1838. It is named for the Bastnäs mine near Riddarhyttan, Västmanland, Sweden.
Bastnäsite also occurs as very high-quality specimens at the Zagi Mountains, Pakistan.
Bastnäsite occurs in alkali granite and syenite and in associated pegmatites. It also occurs in carbonatites and in associated fenites and other metasomatites.
Read More About Bastnäsite / Source
Baumhauerite

Baumhauerite (Pb3As4S9) is a rare lead sulfosalt mineral. It crystallizes in the triclinic system, is gray-black to blue-gray and its lustre is metallic to dull. Baumhauerite has a hardness of 3.
Baumhauerite occurs as small crystals embedded in dolomitic marble. It is found primarily in the Lengenbach Quarry, Binnental, in the Valais region of Switzerland, the mineral is named after German mineralogist Heinrich Adolph Baumhauer (1848–1926), who discovered it at Lengenbach, famous among mineralogists for its array of rare minerals, in 1902. Baumhauerite has also been reported at Sterling Hill, New Jersey, United States, typically in association with molybdenite, and in aggregates at Hemlo, Thunder Bay, Ontario, Canada.
Read More About Baumhauerite / Source
Bavenite

Bavenite is a calcium beryllium aluminosilicate, and it is a part of the Bavenite-Bohseite series. Its name originates from its type locality, which is Baveno, Italy. This mineral is approved by the IMA, and got grandfathered, meaning it is still believed to refer to a valid mineral species. It was discovered in 1901 in a pink granite mined in Lago Maggiore. When bavenite was discovered, it was considered as a member of the zeolite series. Later it was removed from the series as unlike zeolites, bavenite loses the water stored in its crystal lattice in a way higher temperature, between 210 and 320 °C. It is a cheap mineral considering its rarity.
Read More About Bavenite / Source
Bayldonite

Bayldonite (BAIL-done-ite) is a rare secondary mineral with the chemical formula PbCu3(AsO4)2(OH)2. It was first discovered in Penberthy Croft Mine, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is named after its discoverer, John Bayldon (1837(8) – 1872). Specimens are also found in Tsumeb, Namibia, and Arizona, United States. It is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Bayldonite / Source
Bayleyite

Bayleyite is a uranium carbonate mineral with the chemical formula: Mg2(UO2)(CO3)3·18(H2O). It is a secondary mineral which contains magnesium, uranium and carbon. It is a bright yellow color. Its crystal habit is acicular but is more commonly found as crusts on uranium bearing ores. It has a Mohs hardness of about 2-2.5.
Read More About Bayleyite / Source
Bazzite

Bazzite is a beryllium scandium cyclosilicate mineral with chemical formula Be3Sc2Si6O18 (Be3(Sc,Fe)2Si6O18 or Be3(Sc,Al)2Si6O18). It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system typically as small blue hexagonal crystals up to 2 cm length. It has a Mohs hardness of 6.5-7 and a specific gravity of 2.77 to 2.85.
It is hard to distinguish from blue beryl.
Occurs in miarolitic cavities in granite, in alpine veins and in scandium bearing granitic pegmatites. It occurs associated with quartz, orthoclase, muscovite, laumontite, albite, hematite, calcite, chlorite, fluorite, beryl and bavenite.It was first described from an occurrence in Baveno, Italy. Named after the discoverer, the Italian engineer Alessandro E. Bazzi.
Read More About Bazzite / Source
Becquerelite

Becquerelite is a uranium mineral with the chemical formula: Ca(UO2)6O4(OH)6·8(H2O). It is a secondary mineral which contains calcium and is a bright yellow colour. It has a Mohs hardness of about 2.
It was named after the French physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel (1852–1908), who discovered radioactivity in 1896. Becquerelite contains about 70% uranium by weight.
It is mainly mined in Kasolo of the former Zaire, in the present day Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Read More About Becquerelite / Source
Benitoite

Benitoite is a rare blue barium titanium cyclosilicate, found in hydrothermally altered serpentinite. It forms in low temperature, high pressure environments typical of subduction zones at convergent plate boundaries. Benitoite fluoresces under short wave ultraviolet light, appearing bright blue to bluish white in color. The more rarely seen clear to white benitoite crystals fluoresce red under long-wave UV light.
It was discovered in 1907 by prospector James M. Couch in the San Benito Mountains roughly halfway between San Francisco and Los Angeles. Due to its similar color, Couch originally believed it to be sapphire, a variety of corundum. In 1909, a sample was sent to the University of California, Berkeley, where mineralogist Dr. George D. Louderback realized it was a previously unknown mineral. Corundum (sapphire) has a defined Mohs hardness of 9, while benitoite is much softer. He named it benitoite for its occurrence near the headwaters of the San Benito River in San Benito County, California.Benitoite occurs in a number of isolated locations globally, but gemstone quality material has only been found in California at the Benito Gem Mine where it was first discovered. It has been correctly identified in Montana, Arkansas, Japan, and Australia although they formed under slightly different conditions and only grow large enough to be considered an accessory mineral. In 1985 benitoite was named as the official state gem of California.Non-gem crystals of benitoite can have a very rare, six-pointed twinned form.
Read More About Benitoite / Source
Benstonite

Benstonite is a mineral with formula Ba6Ca6Mg(CO3)13. Discovered in 1954, the mineral was described in 1961 and named after Orlando J. Benston (1901–1966).
Read More About Benstonite / Source
Bentorite

Bentorite is a mineral with the chemical formula Ca6(Cr,Al)2(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O. It is colored violet to light violet. Its crystals are hexagonal to dihexagonal dipyramidal. It is transparent and has vitreous luster. It has perfect cleavage. It is not radioactive. Bentorite is rated 2 on the Mohs Scale.
The mineral was first described in 1980 by Shulamit Gross for an occurrence in the Hatrurim Formation of Danian age along the western margin of the Dead Sea, Israel. It was named by its discoverer, Shulamit Gross, for Yaakov Ben-Tor (1910–2002), Professor at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and the University of California, San Diego, California, US, for his contributions to geology and mineralogy in Israel.
Read More About Bentorite / Source
Beraunite

Beraunite is an iron phosphate mineral. It was first described by August Breithaupt for an occurrence in Beraun currently in the Czech Republic. Beraunite occurs as a secondary mineral in iron ore deposits, and as an alteration product of primary phosphate minerals in granite pegmatites.
Beraunite crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with point group 2/m. Beraunite’s formula is Fe2+ Fe3+5(OH)5(PO4)4·4H2O. Aluminium and zinc may substitute in the structure.
Read More About Beraunite / Source
Berborite

Berborite is a beryllium borate mineral with the chemical formula Be2(BO3)(OH,F)·(H2O). It is colorless and leaves a white streak. Its crystals are hexagonal to pyramidal. It is transparent and has vitreous luster. It is not radioactive. Berborite is rated 3 on the Mohs Scale.Berborite occurs in 1T, 2T, 2H polytypes.It was first described in 1967 for an occurrence in the Lupikko Mine, Ladoga Region Karelia Republic, Russia. It has also been reported from Tvedalen, Larvik, Vestfold, and Siktesøya Island, Langesundsfjord, Porsgrunn, Telemark, Norway. It occurs in serpentine altered dolomite in association with skarn enriched in tungsten, strontium, beryllium and boron in the Keralia occurrence and in vugs with natrolite and thomsonite in Norway.
Read More About Berborite / Source
Bergenite

Bergenite is a rare uranyl phosphate of the more specific phosphuranylite group. The phosphuranylite-type sheet in bergenite is a new isomer of the group, with the uranyl phosphate tetrahedra varying in an up-up-down, same-same-opposite (uuduudSSOSSO) orientation. All bergenite samples have been found in old mine dump sites. Uranyl minerals are a large constituent of uranium deposits.The phosphuranylites are one of the two major groups of the uranyl series, and are the most extensive of the uranium minerals. Uranyl phosphates include 45 different minerals, at least 16 of which belong to the phosphuranylite type topology, including dumontite, vanmeersscheite, upalite, and the most characteristic, phosphuranylite. As explained by Frost et al., the uranyl phosphates display diverse chemical and structural features, which often exhibit the geochemical conditions present during formation.
Read More About Bergenite / Source
Berlinite

Berlinite (aluminium phosphate, chemical formula AlPO4 or Al(PO4)) is a rare high-temperature hydrothermal or metasomatic phosphate mineral. It has the same crystal structure as quartz with a low temperature polytype isostructural with α–quartz and a high temperature polytype isostructural with β–quartz. Berlinite can vary from colorless to greyish or pale pink and has translucent crystals.It was first described in 1868 for an occurrence in the Västanå iron mine, Scania, Sweden and named for Nils Johan Berlin (1812–1891) of Lund University.It occurs as a rare mineral in high-temperature hydrothermal or metasomatic deposits. Associated minerals include augelite, attakolite, kyanite, pyrophyllite, scorzalite, lazulite, gatumbaite, burangaite, amblygonite, phosphosiderite, purpurite, apatite, muscovite, quartz, hematite in granite pegmatites. It also occurs with alunite, aragonite, collophane, crandallite, francoanellite, gypsum, huntite, hydromagnesite, leucophosphite, nesquehonite, niter, and nitrocalcite in the Paddy’s River copper mine in the Brindabella Mountains of Australia.
Read More About Berlinite / Source
Berryite

Berryite is a mineral with the formula Pb3(Ag,Cu)5Bi7S16. It occurs as gray to blue-gray monoclinic prisms. It is opaque and has a metallic luster. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 and a specific gravity of 6.7.
It was first identified in 1965 using X-ray diffraction by mineralogist Leonard Gascoigne Berry (1914–1982). It is found in Park and San Juan counties in Colorado. It occurs in sulfide bearing quartz veins in Colorado and with siderite-rich cryolite in Ivigtut, Greenland.
Read More About Berryite / Source
Berthierite

Berthierite is a mineral, a sulfide of iron and antimony with formula FeSb2S4. It is steel grey in colour with a metallic lustre which can be covered by an iridescent tarnish. Because of its appearance it is often mistaken for stibnite.
It was discovered in France in 1827 and named for the French chemist, Pierre Berthier (1782–1861).
Read More About Berthierite / Source
Bertrandite

Bertrandite is a beryllium sorosilicate hydroxide mineral with composition: Be4Si2O7(OH)2. Bertrandite is a colorless to pale yellow orthorhombic mineral with a hardness of 6-7.
It is commonly found in beryllium rich pegmatites and is in part an alteration of beryl. Bertrandite often occurs as a pseudomorphic replacement of beryl. Associated minerals include beryl, phenakite, herderite, tourmaline, muscovite, fluorite and quartz.It, with beryl, are ores of beryllium.
It was discovered near Nantes, France in 1883 and named after French mineralogist, Emile Bertrand (1844–1909).One of the world’s largest deposits of bertrandite is Spor Mountain, Thomas Range, Utah which is currently the source of most of the world’s beryllium production.
Read More About Bertrandite / Source
Beryl

Beryl ( BERR-əl) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2Si6O18. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and aquamarine. Naturally occurring, hexagonal crystals of beryl can be up to several meters in size, but terminated crystals are relatively rare. Pure beryl is colorless, but it is frequently tinted by impurities; possible colors are green, blue, yellow, pink, and red (the rarest). It is an ore source of beryllium.
Read More About Beryl / Source
Beryllonite

Beryllonite is a rare sodium beryllium phosphate mineral with formula NaBePO4. The tabular to prismatic monoclinic crystals vary from colorless to white or pale yellowish, and are transparent with a vitreous luster. Twinning is common and occurs in several forms. It exhibits perfect cleavage in one direction. The hardness is 5.5 to 6 and the specific gravity is 2.8. Refractive indices are nα = 1.552, nβ = 1.558 and nγ = 1.561. A few crystals have been cut and faceted, but, as the refractive index is no higher than that of quartz, they do not make very brilliant gemstones.It occurs as a secondary beryllium mineral in granitic and alkalic pegmatites. It was first described from complex crystals and as broken fragments in the disintegrated material of a granitic vein at Stoneham, Oxford County, Maine where it is associated with feldspar, smoky quartz, beryl and columbite. It was discovered by James Dwight Dana in 1888, and named beryllonite for its beryllium content.
Read More About Beryllonite / Source
Beudantite

Beudandite is a secondary mineral occurring in the oxidized zones of polymetallic deposits. It is a lead, iron, arsenate, sulfate with endmember formula: PbFe3(OH)6SO4AsO4.
Beudantite is in a subgroup of the alunite group. It is the arsenate analogue of the phosphate corkite. Beudantite also forms a solid-solution with segnitite and plumbojarosite.It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system and shows a variety of crystal habits including tabular, acute rhombohedral, pseudo-cubic and pseudo-cuboctahedral.
It occurs in association with carminite, scorodite, mimetite, dussertite, arseniosiderite, pharmacosiderite, olivenite, bayldonite, duftite, anglesite, cerussite and azurite.
Read More About Beudantite / Source
Bicchulite

Bicchulite has an ideal chemical formula of 2CaO•Al2O2•SiO2•H2O, which was formularized from the hydrothermal synthesis of synthetic gehlenite (2CaO•Al2O3•SiO2). Also, bicchulite was sighted in the mines of Japan with related minerals. This sodalite-type structured bicchulite has an uncommon ratio of aluminium to silicon, causing difficulties deciphering the structure. Because of bicchulite’s structure it has a powdery texture, which leads to complications in obtaining information on the mineral’s physical properties. Despite this problem, the color, specific gravity, and crystal size of bicchulite are known. Although bicchulite was only discovered about 40 years ago, technology has been rapidly advancing, allowing more accurate results to be made from experiments done today.
Read More About Bicchulite / Source
Biehlite

Biehlite is an exceptionally rare mineral, an antimony arsenic bearing molybdate with formula [(Sb,As)O]2MoO4. It comes from Tsumeb.
Read More About Biehlite / Source
Bilibinskite
Bilibinskite is an Au – Cu – Pb telluride. It is a rare mineral that was named after Soviet geologist Yuri Bilibin (1901–1952), who researched the geology of gold deposits during the time of the USSR.
Read More About Bilibinskite / Source
Bílinite
Bílinite (Fe2+Fe23+(SO4)·22H2O) is an iron sulfate mineral. It is a product of the oxidation of pyrite in water. It is an acidic mineral that has a pH of less than 3 and is harmful to the environment when it comes from acid rock drainage (Keith et al., 2001).
Bílinite was first discovered near Bílina, Czech Republic which is why the mineral was named ‘bílinite’ (Palache, et al., 1969). This mineral possibly occurs on Mars.
Read More About Bílinite / Source
Billietite

Billietite is an uncommon mineral of uranium that contains barium. It has the chemical formula: Ba(UO2)6O4(OH)6•8H2O. It usually occurs as clear yellow orthorhombic crystals.
Billietite is named after Valere Louis Billiet (1903–1945), Belgian crystallographer at the University of Ghent, Ghent, Belgium.
Billietite was discovered in the locality of the Shinkolobwe uranium mine in the Haut-Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
Read More About Billietite / Source
Billwiseite
Billwiseite is a very rare oxide mineral found at the pegmatite commonly referred to as “Stak Nala” located within a few hundred yards from the village of Toghla in the Stak Nala, Gilgit-Baltistan Pakistan. It has only been found as a coating on a single crystal of lepidolite. The sole rock containing Billwiseite is kept at the Royal Ontario Museum, catalogue number M5595.It contains four relatively uncommon elements: antimony, niobium, tantalum, and tungsten. It is named after William Wise, a mineralogist from the University of California, Santa Barbara.It was discovered by an international group of geologists, and accepted by the IMA in 2010. Its discovery was announced in Mineralogical Magazine in 2011, and was described in detail in 2012 in The Canadian Mineralogist by Hawthrone et al.
Read More About Billwiseite / Source
Biotite

Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula K(Mg,Fe)3AlSi3O10(F,OH)2. It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron-endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more aluminous end-members include siderophyllite and eastonite. Biotite was regarded as a mineral species by the International Mineralogical Association until 1998, when its status was changed to a mineral group. The term biotite is still used to describe unanalysed dark micas in the field. Biotite was named by J.F.L. Hausmann in 1847 in honor of the French physicist Jean-Baptiste Biot, who performed early research into the many optical properties of mica.Members of the biotite group are sheet silicates. Iron, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen form sheets that are weakly bound together by potassium ions. The term “iron mica” is sometimes used for iron-rich biotite, but the term also refers to a flaky micaceous form of haematite, and the field term Lepidomelane for unanalysed iron-rich Biotite avoids this ambiguity. Biotite is also sometimes called “black mica” as opposed to “white mica” (muscovite) – both form in the same rocks, and in some instances side by side.
Read More About Biotite / Source
Birnessite

Birnessite (nominally MnO2·nH2O), also known as δ-MnO2, is a hydrous manganese dioxide mineral with a chemical formula of Na0.7Ca0.3Mn7O14·2.8H2O. It is the main manganese mineral species at the Earth’s surface, and commonly occurs as fine-grained, poorly crystallized aggregates in soils, sediments, grain and rock coatings (e.g., desert varnish), and marine ferromanganese nodules and crusts. It was discovered at Birness, Aberdeenshire, Scotland.
Read More About Birnessite / Source
Bischofite

Bischofite is a hydrous magnesium chloride mineral with formula MgCl2·6H2O. It belongs to halides and is a sea salt concentrate. It contains many macro- and micro-elements vital for human health, in much higher concentrations than can be found in sea or ocean salt. The main bischofite compound is magnesium chloride (up to 350 g/L), moreover, it contains about 70 other elements as impurities, including potassium, sodium, bromine, boron, calcium, silicon, molybdenum, silver, zinc, iron and copper.
Read More About Bischofite / Source
Bismite

Bismite is a bismuth oxide mineral, bismuth trioxide or Bi2O3. It is a monoclinic mineral, but the typical form of occurrence is massive and clay-like with no macroscopic crystals. The color varies from green to yellow. It has a Mohs hardness of 4 to 5 and a specific gravity of 8.5 to 9.5, quite high for a nonmetallic mineral.
Bismite is a secondary oxidation zone mineral which forms from primary bismuth minerals.
It was first described from Goldfield, Nevada in 1868, and later from the Schneeberg District, Ore Mountains, Saxony, Germany.
Read More About Bismite / Source
Bismuth

Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known.
Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be weakly radioactive. The metal’s only primordial isotope, bismuth-209, experiences alpha decay at such a rate that its half-life is more than the estimated age of the universe.Bismuth metal has been known since ancient times. Before modern analytical methods bismuth’s metallurgical similarities to lead and tin often led it to be confused with those metals. The etymology of “bismuth” is uncertain. The name may come from mid-sixteenth century New Latin translations of the German words weiße Masse or Wismuth, meaning ‘white mass’, which were rendered as bisemutum or bisemutium.
Read More About Bismuth / Source
Bismuthinite

Bismuthinite is a mineral consisting of bismuth sulfide (Bi2S3). It is an important ore for bismuth. The crystals are steel-grey to off-white with a metallic luster. It is soft enough to be scratched with a fingernail and rather dense.
Bismuthinite forms a series with the lead, copper, bismuth mineral aikinite (PbCuBiS3).
It occurs in hydrothermal veins with tourmaline-bearing copper veins associated with granite, in some high temperature gold veins, and in recent volcanic exhalation deposits. Associated minerals include native bismuth, aikinite, arsenopyrite, stannite, galena, pyrite, chalcopyrite, tourmaline, wolframite, cassiterite and quartz.It was first reported in 1832 from the mines of Potosí, Bolivia.
Read More About Bismuthinite / Source
Bismutite

Bismutite or bismuthite is a bismuth carbonate mineral with formula Bi2(CO3)O2 (bismuth subcarbonate). Bismutite occurs as an oxidation product of other bismuth minerals such as bismuthinite and native bismuth in hydrothermal veins and pegmatites. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and typically occurs as earthy to fibrous masses.It was first described in 1841 for an occurrence in Saxony.The term bismuthite has been used in the past for bismuthinite.
Read More About Bismutite / Source
Bityite
Bityite is considered a rare mineral, and it is an endmember to the margarite mica sub-group found within the phyllosilicate group. The mineral was first described by Antoine François Alfred Lacroix in 1908, and later its chemical composition was concluded by Professor Hugo Strunz. Bityite has a close association with beryl, and it generally crystallizes in pseudomorphs after it, or in cavities associated with reformed beryl crystals. The mineral is considered a late-stage constituent in lithium bearing pegmatites, and has only been encountered in a few localities throughout the world. The mineral was named by Lacroix after Mt. Bity, Madagascar from where it was first discovered.
Read More About Bityite / Source
Bixbyite

Bixbyite is a manganese iron oxide mineral with chemical formula: (Mn,Fe)2O3. The iron/manganese ratio is quite variable and many specimens have almost no iron. It is a metallic dark black with a Mohs hardness of 6.0 – 6.5. It is a somewhat rare mineral sought after by collectors as it typically forms euhedral isometric crystals exhibiting various cubes, octahedra, and dodecahedra.
It is commonly associated with beryl, quartz, spessartine, hematite, pseudobrookite, hausmannite, braunite and topaz in pneumatolytic or hydrothermal veins and cavities and in metamorphic rocks. It can also be found in lithophysal cavities in rhyolite. Typical localities are Jhabua and Chhindwara districts, India and the Thomas Range in Juab County, Utah. It is also reported from San Luis Potosi, Mexico; northern Patagonia, Argentina; Girona, Catalonia, Spain; Sweden, Germany, Namibia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa.Bixbyite was named for the American mineralogist Maynard Bixby (1853–1935), responsible for its discovery in 1897. It should not be confused with bixbite, a red form of beryl; to avoid confusion, this name has been deprecated from the CIBJO and the IMA.
Read More About Bixbyite / Source
Blödite

Blödite or bloedite is a hydrated sodium magnesium sulfate mineral with formula: Na2Mg(SO4)2·4H2O. The mineral is clear to yellow in color often darkened by inclusions and forms monoclinic crystals.
Blödite was first described in 1821 for an occurrence in a salt deposit in Ischler Salzberg, Bad Ischl, Gmunden, Austria and named for German mineralogist and chemist Karl August Blöde (1773–1820).It is found worldwide in evaporitic sedimentary environments such as the Great Salt Lake, Utah.
Read More About Blödite / Source
Blossite
Blossite is an anhydrous copper vanadate mineral with the formula: Cu2+V5+2O7. Blossite was named for mineralogist F. Donald Bloss of Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Read More About Blossite / Source
Bobfergusonite
Bobfergusonite is a mineral with formula Na2Mn5FeAl(PO4)6. The mineral varies in color from green-brown to red-brown. It was discovered in 1986 in Manitoba, Canada, and named for Robert Bury Ferguson (born 1920). As of 2012, the mineral has only been found in Canada and Argentina.
Read More About Bobfergusonite / Source
Boehmite

Boehmite or böhmite is an aluminium oxide hydroxide (γ-AlO(OH)) mineral, a component of the aluminium ore bauxite. It is dimorphous with diaspore. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic dipyramidal system and is typically massive in habit. It is white with tints of yellow, green, brown or red due to impurities. It has a vitreous to pearly luster, a Mohs hardness of 3 to 3.5 and a specific gravity of 3.00 to 3.07. It is colorless in thin section, optically biaxial positive with refractive indices of nα = 1.644 – 1.648, nβ = 1.654 – 1.657 and nγ = 1.661 – 1.668.
Boehmite occurs in tropical laterites and bauxites developed on alumino-silicate bedrock. It also occurs as a hydrothermal alteration product of corundum and nepheline. It occurs with kaolinite, gibbsite and diaspore in bauxite deposits; and with nepheline, gibbsite, diaspore, natrolite and analcime in nepheline pegmatites. Industrially, it is used as an inexpensive flame retardant additive for fire-safe polymers.
It was first described by J. de Lapparent in 1927 for an occurrence in the bauxites of Mas Rouge, Les Baux-de-Provence, France, and named for the Bohemian-German chemist Johann Böhm (1895–1952) who carried out X-ray studies of aluminium oxide hydroxides in 1925 (and not for the German geologist Johannes Böhm (1857–1938) as often stated).
Read More About Boehmite / Source
Boleite

Boleite is a complex halide mineral with formula: KPb26Ag9Cu24(OH)48Cl62. It was first described in 1891 as an oxychloride mineral. It is an isometric mineral which forms in deep-blue cubes. There are numerous minerals related to boleite, such as pseudoboleite, cumengite, and diaboleite, and these all have the same complex crystal structure. They all contain bright-blue cubic forms and are formed in altered zones of lead and copper deposits, produced during the reaction of chloride bearing solutions with primary sulfide minerals.
Read More About Boleite / Source
Boltwoodite

Boltwoodite is a hydrated potassium uranyl silicate mineral with formula HK(UO2)(SiO4)·1.5(H2O). It is formed from the oxidation and alteration of primary uranium ores. It takes the form of a crust on some sandstones that bear uranium. These crusts tend to be yellowish with a silky or vitreous luster.
Read More About Boltwoodite / Source
Bonaccordite

Bonaccordite is a rare mineral discovered in 1974. Its chemical formula is Ni2FeBO5 and it is a mineral of the ludwigite group. It usually crystallizes in long, cylindrical prisms that form within another source. It is named after the area of Bon Accord, where it was first found. There have also been findings of bonaccordite within nuclear plants at multiple companies. It builds up a deposit within the machines and is a very hard mineral to clean out because it is resistant to ordinary techniques.
Read More About Bonaccordite / Source
Boracite

Boracite is a magnesium borate mineral with formula: Mg3B7O13Cl. It occurs as blue green, colorless, gray, yellow to white crystals in the orthorhombic – pyramidal crystal system. Boracite also shows pseudo-isometric cubical and octahedral forms. These are thought to be the result of transition from an unstable high temperature isometric form on cooling. Penetration twins are not unusual. It occurs as well formed crystals and dispersed grains often embedded within gypsum and anhydrite crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 7 to 7.5 and a specific gravity of 2.9. Refractive index values are nα = 1.658 – 1.662, nβ = 1.662 – 1.667 and nγ = 1.668 – 1.673. It has a conchoidal fracture and does not show cleavage. It is insoluble in water (not to be confused with borax, which is soluble in water).
Boracite is typically found in evaporite sequences associated with gypsum, anhydrite, halite, sylvite, carnallite, kainite and hilgardite. It was first described in 1789 for specimens from its type locality of Kalkberg hill, Lüneburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. It is also found near Sussex, New Brunswick.The name is derived from its boron content (19 to 20% boron by mass).
Read More About Boracite / Source
Borax

Borax (also referred to as sodium borate, tincal and tincar ) is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated or anhydrous borate of sodium, with the chemical formula Na2H20B4O17. It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution.
It is commonly available in powder or granular form and has many industrial and household uses, including as a pesticide, as a metal soldering flux, as a component of glass, enamel, and pottery glazes, for tanning of skins and hides, for artificial aging of wood, as a preservative against wood fungus, and as a pharmaceutic alkalizer. In chemical laboratories, it is used as a buffering agent.The terms tincal and tincar refer to native borax, historically mined from dry lake beds in various parts of Asia.
Read More About Borax / Source
Bornite

Bornite, also known as peacock ore, is a sulfide mineral with chemical composition Cu5FeS4 that crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (pseudo-cubic).
Read More About Bornite / Source
Botallackite

Botallackite, chemical formula Cu2(OH)3Cl is a secondary copper mineral, named for its type locality at the Botallack Mine, St Just in Penwith, Cornwall. It is polymorphous with atacamite, paratacamite and clinoatacamite.Botallackite crystallises in the monoclinic crystal system. It is mountain-green to green in colour, with one distinct to good cleavage.
Read More About Botallackite / Source
Botryogen

Botryogen is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula: MgFe3+(SO4)2(OH)·7H2O. It is also known as quetenite.It crystallizes in the monoclinic prismatic system and typically occurs as vitreous bright yellow to red botryoidal to reniform masses and radiating crystal prisms. It has a specific gravity in the range 2 to 2.1 and Mohs hardness in the range of 2 to 2.5.It occurs in arid climates as a secondary alteration product of pyrite-bearing deposits.It was first described in 1828 for an occurrence in the Falu mine of Falun, Dalarna, Sweden. It was named for its grape like appearance from Greek botrys for “bunch of grapes” and genos meaning “to bear”.
Read More About Botryogen / Source
Boulangerite

Boulangerite is an uncommon monoclinic orthorhombic sulfosalt mineral, lead antimony sulfide, formula Pb5Sb4S11. It was named in 1837 in honor of French mining engineer Charles Boulanger (1810–1849), and had been a valid species since pre-IMA. It was first described prior to 1959, and is now grandfathered.
Read More About Boulangerite / Source
Bournonite

Bournonite is a sulfosalt mineral species, trithioantimoniate of lead and copper with the formula PbCuSbS3.It was first mentioned by Philip Rashleigh in 1797 as an ore of antimony and was more completely described in 1804 by French crystallographer and mineralogist Jacques Louis, Comte de Bournon (1751–1825), after whom it was named. The name given by Bournon himself (in 1813) was endellione, since used in the form endellionite, after St Endellion, the locality in Cornwall where the mineral was first found.The crystals are orthorhombic, and are generally tabular in habit owing to the predominance of the basal pinacoid; numerous smooth bright faces are often developed on the edges and corners of the crystals. They are usually twinned, the twin-plane being a face of the prism (m); the angle between the faces of this prism being nearly a right angle (86° 20′), the twinning gives rise to cruciform groups and when it is often repeated the group has the appearance of a cog-wheel, hence the name Rãdelerz (wheel-ore) of the Kapnik miners. The repeated twinning gives rise to twin-lamellae, which may be detected on the fractured surfaces, even of the massive material.It is a mineral in medium temperature hydrothermal vein deposits. It commonly occurs with galena, tetrahedrite, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, stibnite, zinkenite, siderite, quartz, rhodochrosite, dolomite and barite.It was first described for an occurrence in Wheal Boys in the parish of St Endellion in Cornwall, it was found associated with jamesonite, sphalerite and siderite. Later, still better crystals were found in another Cornish mine, namely, Herodsfoot mine near Liskeard, which was worked for argentiferous galena. Fine crystals of large size have been found with quartz and siderite in the mines at Neudorf in the Harz, and with sphalerite and tetrahedrite at Cavnic near Baia Mare in Romania. It has been reported from a large number of other localities.
Read More About Bournonite / Source
Bowieite
Bowieite is a rhodium-iridium-platinum sulfide mineral (Rh,Ir,Pt)2S3, found in platinum-alloy nuggets from Goodnews Bay, Alaska. It was named (by the IMA in 1984) after the British scientist Stanley Bowie (1917–2008), in recognition of his work on identification of opaque minerals.The mineral crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system (space group Pbcn).
Read More About Bowieite / Source
tornado torrent

Tornado is one of the lightest and fastest torrent searching app in the Play Store which you can use to search and download popular content including free movies, free books, free games, free music and many more!
Read More About tornado torrent / Source
Braggite

Braggite is a sulfide mineral of platinum, palladium and nickel with chemical formula: (Pt, Pd, Ni)S. It is a dense (specific gravity of 10), steel grey, opaque mineral which crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system. It is the central member in the platinum group end-members cooperite and vysotskite.
It was first described in 1932 for an occurrence in the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa. Its name came from William Henry Bragg (1862–1942) and his son, William Lawrence Bragg (1890–1971). It was the first mineral that was discovered with the assistance of X rays.It occurs as magmatic segregations in layered igneous intrusions such as Bushveld, the Stillwater igneous complex, the Lac des Îles igneous complex, the island of Rùm intrusive, the Great Dyke and many others. It is one of the most common platinum group minerals.
Read More About Braggite / Source
Brassite

Brassite is a rare arsenate mineral with the chemical formula Mg(AsO3OH)·4(H2O). It was named brassite, in 1973, to honor French chemist R`ejane Brasse, who first synthesized the compound. The type locality for brassite is Jáchymov of the Czech Republic.It occurs as an alteration of magnesium carbonate minerals by arsenic bearing solutions. It occurs associated with pharmacolite, picropharmacolite, weilite, haidingerite, rauenthalite, native arsenic, realgar and dolomite.
Read More About Brassite / Source
Braunite

Braunite is a silicate mineral containing both di- and tri-valent manganese with the chemical formula:
Mn2+Mn3+6[O8|SiO4]. Common impurities include iron, calcium, boron, barium, titanium, aluminium, and magnesium.
Braunite forms grey/black tetragonal crystals and has a Mohs hardness of 6 – 6.5.
It was named after the Wilhelm von Braun (1790–1872) of Gotha, Thuringia, Germany.A calcium iron bearing variant, named braunite II (formula: Ca(Mn3+,Fe3+)14SiO24), was discovered and described in 1967 from Kalahari, Cape Province, South Africa.
Read More About Braunite / Source
Brazilianite

Brazilianite, whose name derives from its country of origin, Brazil, is a typically yellow-green phosphate mineral, most commonly found in phosphate-rich pegmatites.
It occurs in the form of perfect crystals grouped in druses, in pegmatites, and is often of precious-stone quality. One noted deposit of brazilianite is in the surroundings of Conselheiro Pena, in Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Some of these are found on leaves of muscovite with their strong silvery glitter, ingrown in their parent rock. The crystals, dark greenish-yellow to olive-green, sometimes measure up to 12 cm (4.7 in) in length and 8 cm (3.1 in) in width. Crystals of similar shape and dimensions have been discovered in another deposit in Minas Gerais, near Mantena, but they lack the perfection of the crystal form. Many brazilianite specimens found in mineral collections originated from the Palermo and the Charles Davis mines in Grafton County, New Hampshire.
Read More About Brazilianite / Source
Breithauptite

Breithauptite is a nickel antimonide mineral with the simple formula NiSb. Breithauptite is a metallic opaque copper-red mineral crystallizing in the hexagonal – dihexagonal dipyramidal crystal system. It is typically massive to reniform in habit, but is observed as tabular crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 8.23.
It occurs in hydrothermal calcite veins associated with cobalt–nickel–silver ores.
It was first described in 1840 from the Harz Mountains, Lower Saxony, Germany and in 1845 for occurrences in the Cobalt and Thunder Bay districts of Ontario, Canada. It was named to honor Saxon mineralogist Johann Friedrich August Breithaupt (1791–1873).
Read More About Breithauptite / Source
Brewsterite

Brewsterite is the name of a series of tectosilicate minerals of the zeolite group. Prior to 1997, brewsterite was recognized as a mineral species, but a reclassification in 1997 by the International Mineralogical Association changed it to a series name, with the mineral species being named brewsterite-Sr and brewsterite-Ba. Brewsterite-Sr, the more common of these, is a hydrous strontium and aluminium silicate, (Sr,Ba)2Al4Si12O32·10H2O. Small amounts of barium is usually present replacing part of the strontium. The appropriate species name depends on the dominant element. The species are visually indistinguishable, and the series name brewsterite is still used whenever testing has not been performed.
It is generally considered to be monoclinic, though optical studies have suggested it might be triclinic. It has one plane of perfect cleavage. The color is white, yellow-white, or gray. The Mohs’ hardness is 5. It is transparent to translucent. The crystals are prismatic. Brewsterite is isomorphous with heulandite.
It is named after Sir David Brewster (1781–1868) who described it in 1822. The type locality for the series and for brewsterite-Sr is Strontian, Argyll, Scotland.
It is a hydrothermal mineral occurring in volcanic rocks such as basalt. Grayish crystals are found at the Giant’s Causeway in County Antrim. It is found with harmotome in the lead mines at Strontian in Argyllshire.
Read More About Brewsterite / Source
Brezinaite
Brezinaite, discovered in 1969, is a rare mineral composed of chromium and sulfur. It is found in meteorites, such as the Tucson Ring meteorite (Irwin-Ainsa meteorite), its type locality. It was also found in the New Baltimore meteorite and the Sikhote-Alin meteorite. Brezinaite was named in honour of Aristides Brezina (1848–1909), a past director of the Mineralogy-Petrology Section of the Natural History Museum, Vienna, Austria.
Read More About Brezinaite / Source
Brianite

Brianite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Na2CaMg(PO4)2. It was first identified in an iron meteorite. This mineral is named after Brian Harold Mason (1917–2009), a pioneer in meteoritics.It was first reported from the Dayton meteorite in Montgomery County, Ohio in 1966. It occurs in phosphate nodules within the meteorite. Associated minerals include: panethite, whitlockite, albite, enstatite, schreibersite, kamacite, taenite, graphite, sphalerite and troilite.
Read More About Brianite / Source
Brianyoungite

Brianyoungite is a secondary zinc carbonate mineral. The Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification (CNMNC) of the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) classifies it as a carbonate with the formula Zn3(CO3)(OH)4, but sulfate groups SO4 also occupy the carbonate CO3 positions, in the ratio of about one sulfate to three carbonates, so other sources give the formula as Zn3(CO3,SO4)(OH)4, and Gaines et al. classify the mineral as a compound carbonate. It is
similar in appearance to hydrozincite, another zinc carbonate. It was discovered in 1991 and designated IMA1991-053. In 1993 it was named “brianyoungite” after Brian Young (born 1947), a field geologist with the British Geological Survey, who provided the first specimens.
Read More About Brianyoungite / Source
Briartite
Briartite is an opaque iron-grey metallic sulfide mineral, Cu2(Zn,Fe)GeS4 with traces of Ga and Sn, found as inclusions in other germanium-gallium-bearing sulfides.It was discovered at the Prince Léopold Mine, Kipushi, Shaba, Congo (Léopoldville) in 1965 by Francotte and others, and named for Gaston Briart who had studied formations at Kipushi.Briartite is also found in Namibia, Greece, and Spain.
Read More About Briartite / Source
Silicate perovskite
Silicate perovskite is either (Mg,Fe)SiO3 (the magnesium end-member is called bridgmanite) or CaSiO3 (calcium silicate known as davemaoite) when arranged in a perovskite structure. Silicate perovskites are not stable at Earth’s surface, and mainly exist in the lower part of Earth’s mantle, between about 670 and 2,700 km (420 and 1,680 mi) depth. They are thought to form the main mineral phases, together with ferropericlase.
Read More About Silicate perovskite / Source
Brochantite

Brochantite is a sulfate mineral, one of a number of cupric sulfates. Its chemical formula is Cu4SO4(OH)6. Formed in arid climates or in rapidly oxidizing copper sulfide deposits, it was named by Armand Lévy for his fellow Frenchman, geologist and mineralogist A. J. M. Brochant de Villiers.Crystals of brochantite can range from emerald green to black-green to blue-green, and can be acicular or prismatic. Brochantite is often associated with minerals such as malachite, azurite, and chrysocolla, and may form pseudomorphs with these minerals.
The mineral is found in a number of locations around the world, notably the southwestern United States (especially Arizona), Serifos in Greece and Chile.
Brochantite is a common corrosion product on bronze sculptures located in urban areas, where atmospheric sulfur dioxide (a common pollutant) is present. Brochantitie forms mainly in exposed areas where weathering prevents accumulation copper ions and enhancement in the acidity of water films. In sheltered areas, the main corrosion product is antlerite.
Read More About Brochantite / Source
Brockite

Brockite is a rare earth phosphate mineral with formula: (Ca,Th,Ce)PO4·H2O. It crystallizes in the hexagonal system in the chiral space group 180 or its enantiomorph 181. It is typically granular to massive with only rare occurrence of stubby crystals. It is radioactive due to the thorium content.
Read More About Brockite / Source
Bromargyrite

Bromyrite or bromargyrite is a natural mineral form of silver bromide found mainly in Mexico and Chile. Hardness is 1.5 to 2. Related are chlorargyrite and iodyrite.
It was first described in 1859 for an occurrence in Plateros, Zacatecas, Mexico where it occurred in a silver deposit as an oxidation product of primary ore minerals. It occurs in arid environments along with native silver, iodargyrite and smithsonite along with iron and manganese oxide minerals.
Read More About Bromargyrite / Source
Bromellite

Bromellite, whose name derives from the Swedish chemist Magnus von Bromell (1670–1731), is a white oxide mineral, found in complex pegmatitic manganese-iron deposits, but is more frequently made synthetically. This is a rare mineral to encounter in its natural state, but it has been made synthetically for over 40 years.
Read More About Bromellite / Source
Bronzite

Bronzite is a member of the pyroxene group of minerals, belonging with enstatite and hypersthene to the orthorhombic series of the group. Rather than a distinct species, it is really a ferriferous variety of enstatite, which owing to partial alteration has acquired a bronze-like sub-metallic luster on the cleavage surfaces.Enstatite is magnesium silicate, MgSiO3, with the magnesium partly replaced by small amounts (up to about 12%) of Fe+2. In the bronzite variety, (Mg,Fe)SiO3, the iron(II) oxide ranges from about 12 to 30%, and with still more iron there is a passage to hypersthene. The ferriferous varieties are liable to a particular kind of alteration, known as schillerization, which results in the separation of the iron as very fine films of oxide and hydroxides along the cleavage cracks of the mineral. The cleavage surfaces therefore exhibit a metallic sheen or schiller, which is even more pronounced in hypersthene than in bronzite. The color of bronzite is green or brown; its specific gravity is about 3.3–3.4, varying with the amount of iron present. The refractive indices and optic angle increase with iron content. The enstatite endmember has a positive optic sign, whereas bronzite and hypersthene both show a negative optic sign.Like enstatite, bronzite is a constituent of many mafic to ultramafic igneous rocks, such as, norite, gabbro, and especially peridotite, and of the serpentinites which have been derived from them. It also occurs in some crystalline schist. Bronzitite, a pyroxenite of bronzite composition, is noted in the cumulate rocks of the Stillwater igneous complex of Montana.
Read More About Bronzite / Source
Brookite

Brookite is the orthorhombic variant of titanium dioxide (TiO2), which occurs in four known natural polymorphic forms (minerals with the same composition but different structure). The other three of these forms are akaogiite (monoclinic), anatase (tetragonal) and rutile (tetragonal). Brookite is rare compared to anatase and rutile and, like these forms, it exhibits photocatalytic activity. Brookite also has a larger cell volume than either anatase or rutile, with 8 TiO2 groups per unit cell, compared with 4 for anatase and 2 for rutile. Iron (Fe), tantalum (Ta) and niobium (Nb) are common impurities in brookite.Brookite was named in 1825 by French mineralogist Armand Lévy for Henry James Brooke (1771–1857), an English crystallographer, mineralogist and wool trader.Arkansite is a variety of brookite from Magnet Cove, Arkansas, US. It is also found in the Murun Massif on the Olyokma-Chara Plateau of Eastern Siberia, Russia, part of the Aldan Shield.At temperatures above about 750 °C, brookite will revert to the rutile structure.
Read More About Brookite / Source
Brownleeite
Brownleeite is a silicide mineral with chemical formula MnSi. It was discovered by researchers of the Johnson Space Center in Houston while analyzing the Pi Puppid particle shower of the comet 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup. The only other known natural manganese silicide is mavlyanovite, Mn5Si3.
Read More About Brownleeite / Source
Brownmillerite

Brownmillerite is a rare oxide mineral with chemical formula Ca2(Al,Fe)2O5. It is named for Lorrin Thomas Brownmiller (1902–1990), chief chemist of the Alpha Portland Cement Company, Easton, Pennsylvania.
Read More About Brownmillerite / Source
Brucite

Brucite is the mineral form of magnesium hydroxide, with the chemical formula Mg(OH)2. It is a common alteration product of periclase in marble; a low-temperature hydrothermal vein mineral in metamorphosed limestones and chlorite schists; and formed during serpentinization of dunites. Brucite is often found in association with serpentine, calcite, aragonite, dolomite, magnesite, hydromagnesite, artinite, talc and chrysotile.
It adopts a layered CdI2-like structure with hydrogen-bonds between the layers.
Read More About Brucite / Source
Brushite

Brushite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula CaHPO4·2H2O. Crystals of the pure compound belong to the monoclinic space group C2/c and are colorless. It is the phosphate analogue of the arsenate pharmacolite.
Read More About Brushite / Source
Buddingtonite
Buddingtonite is an ammonium feldspar with formula: NH4AlSi3O8 (note: some sources add 0.5H2O to the formula). It forms by hydrothermal alteration of primary feldspar minerals. It is an indicator of possible gold and silver deposits, as they can become concentrated by hydrothermal processes. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system and is colorless to white with a vitreous luster. Its structure is analogous to that of high sanidine (KAlSi3O8). Buddingtonite has a hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 2.32.
Buddingtonite was discovered in 1964 at the Sulfur Bank mine near Clear Lake in Lake County, California. Clear Lake is at the north end of The Geysers geothermal area. It also occurs in the Tonopah, Nevada area and in hydrothermal areas in New Zealand and Japan. It has also been reported from the sedimentary Phosphoria Formation in Idaho, South Dakota, Wyoming, and Montana. It occurs in the oil shale deposit, near Proserpine, Queensland, Australia.It was named for Arthur Francis Buddington (1890–1980), a petrologist at Princeton University.
Read More About Buddingtonite / Source
Bukovite

Bukovite is a rare selenide mineral with formula Tl2Cu3FeSe4. It is a brown to black metallic mineral which crystallizes in the tetragonal system.It was first described in 1971 for an occurrence in the Bukov uranium mine, Rožná deposit, Vysočina Region, Moravia, Czech Republic. It has also been reported in Skrikerum, near Tryserum, Kalmar, Sweden; near Vernet-la-Varenne, Puy-de-Dôme, France; and Tuminico, Sierra de Cacho, La Rioja Province, Argentina.
Read More About Bukovite / Source
Bukovskyite

Bukovskyite (also known as “clay of Kutná Hora”) is an iron arsenate sulfate mineral with formula: Fe2(AsO4)(SO4)(OH)·7H2O which forms nodules with a reniform (kidney-shaped) surface. Under a microscope, these nodules appear as a collection of minute needles similar to gypsum. Some can be seen with the naked eye and occur inside the nodules.
Bukovskyite was first described from pit heaps from the Middle Ages, where sulfate ores had been mined at Kank, north of Kutná Hora in Bohemia, Czech Republic, and other old deposits in the vicinity. Only recently defined and acknowledged, it was approved by the IMA in 1969.
Bukovskyite was collected a long time ago from the overgrown pit heaps by the inhabitants of Kutná Hora. It was used for poisoning fieldmice and other field vermin. This poisonous clay, known also by the place name as “clay of Kutná Hora”‘, was widely known and it was considered to be ‘arsenic’ (arsenic trioxide). In 1901 Antonín Bukovský (1865–1950), a Czech chemist, who studied minerals of old pit heaps, proved it was an arsenate.
Read More About Bukovskyite / Source
Bultfonteinite

Bultfonteinite, originally dutoitspanite, is a pink to colorless mineral with chemical formula Ca2SiO2(OH,F)4. It was discovered in 1903 or 1904 in the Bultfontein mine in South Africa, for which the mineral is named, and described in 1932.
Read More About Bultfonteinite / Source
Bunsenite

Bunsenite is the naturally occurring form of nickel(II) oxide, NiO. It occurs as rare dark green crystal coatings. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system and occurs as well formed cubic, octahedral and dodecahedral crystals. It is a member of the periclase group.
It was first described in 1868 for a sample from a hydrothermal nickel–uranium vein from Johanngeorgenstadt, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany and named for German chemist Robert William Eberhard Bunsen (1811–1899). Other occurrences include west of the Scotia talc mine near Bon Accord, Barberton district, Transvaal, South Africa and from Kambalda south of Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. The South African occurrence has evidence of thermal metamorphism of a nickel-rich meteorite. It occurs associated with native bismuth, annabergite, aerugite, xanthiosite in Germany; and with liebenbergite, trevorite, nickeloan serpentine, nickeloan ludwigite, violarite, millerite, gaspeite, nimite and bonaccordite in the South African occurrence.
Read More About Bunsenite / Source
Bustamite

Bustamite is a calcium manganese inosilicate (chain silicate) and a member of the wollastonite group. Magnesium, zinc and iron are common impurities substituting for manganese. Bustamite is the high-temperature polymorph of CaMnSi2O6 and johannsenite is the low temperature polymorph. The inversion takes place at 830 °C (1,530 °F), but may be very slow.Bustamite could be confused with light-colored rhodonite or pyroxmangite, but both these minerals are biaxial (+) whereas bustamite is biaxial (-).
Read More About Bustamite / Source
Bystrite
Bystrite is a silicate mineral with the formula (Na,K)7Ca(Si6Al6)O24S4.5•(H2O), and a member of the cancrinite mineral group. It is a hexagonal crystal, with a 3m point group. The mineral may have been named after the Malaya Bystraya deposits in Russia, where it was found.Bystrite is a cancrinite mineral and exhibits similar physical properties, composition and structure as other cancrinites.
Read More About Bystrite / Source
Cabalzarite

Cabalzarite is a rare arsenate mineral with the chemical formula Ca(Mg,Al,Fe3+)2[AsO4]2•2(H2O,OH). It is a member of the tsumcorite group. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and typically occurs as clusters of crystals or granular aggregates.It was first described for samples from an abandoned manganese mine in Falotta, Graubünden, Switzerland and named for Swiss amateur mineralogist Walter Cabalzar. It was approved as a new mineral by the IMA in 1997. It has also been reported from the Aghbar mine in Ouarzazate Province, Morocco.
Read More About Cabalzarite / Source
Cabriite
Cabriite (Pd2SnCu) is a mineral first found in the eastern Siberian region of Russia and named for the Canadian mineralogist Louis J. Cabri (born 1934).
Read More About Cabriite / Source
Cacoxenite

Cacoxenite is an iron aluminium phosphate mineral with formula: Fe3+24Al(PO4)17O6(OH)12·17(H2O). Cacoxenite is associated with iron ores. The name comes from the Greek κăκός for “bad” or “evil” and ξένος for “guest” because the phosphorus content of cacoxenite lessens the quality of iron smelted from ore containing it.It was first described in 1825 for an occurrence in the Hrbek Mine, Bohemia, Czech Republic. It occurs as a secondary phase in oxidized magnetite and limonite deposits. It also occurs in novaculites and in iron and phosphorus rich sediments.
Read More About Cacoxenite / Source
Cadmium

Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds, and like mercury, it has a lower melting point than the transition metals in groups 3 through 11. Cadmium and its congeners in group 12 are often not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled d or f electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. The average concentration of cadmium in Earth’s crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered in 1817 simultaneously by Stromeyer and Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate.
Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores and is a byproduct of zinc production. Cadmium was used for a long time as a corrosion-resistant plating on steel, and cadmium compounds are used as red, orange, and yellow pigments, to color glass, and to stabilize plastic. Cadmium use is generally decreasing because it is toxic (it is specifically listed in the European Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive) and nickel-cadmium batteries have been replaced with nickel-metal hydride and lithium-ion batteries. One of its few new uses is in cadmium telluride solar panels.
Although cadmium has no known biological function in higher organisms, a cadmium-dependent carbonic anhydrase has been found in marine diatoms.
Read More About Cadmium / Source
Cadmoindite

Cadmoindite (CdIn2S4) is a rare cadmium indium sulfide mineral discovered in Siberia around the vent of a high-temperature (450–600 °C) fumarole at the Kudriavy volcano, Iturup Island in the Kuril Islands. It has also been reported from the Kateřina Coal Mine in Bohemia, Czech Republic.
Read More About Cadmoindite / Source
Cadmoselite

Cadmoselite is a rare cadmium selenide mineral with chemical formula CdSe. Cadmoselite crystallizes in the hexagonal system and occurs as black to pale grey opaque crystals and grains.
It was first described in 1957 for an occurrence in Tuva. The mineral occurs as interstitial grains in sandstone formed under reducing alkaline diagenetic conditions.
Read More About Cadmoselite / Source
Cadwaladerite

Cadwaladerite is a rare aluminium halide mineral with formula: AlCl(OH)2·4(H2O). It was reported for an amorphous substance associated with sulfate minerals and embedded in a halite crystal cluster. Its status is uncertain due to inadequate data.
It was first described in 1941 for an occurrence in mine dumps of the Victoria Segunda mine Cerros Pintados, Iquique province, Tarapacá Region, Chile. It was named for Charles Meigs Biddle Cadwalader, president of the Academy of Natural Sciences. Lesukite was discredited (IMA2018-H).
Read More About Cadwaladerite / Source
Cafarsite

Cafarsite (Ca8(Ti,Fe2+,Fe3+,Mn)6–7(AsO3)12·4H2O)
is a rare calcium iron arsenite mineral. Manganese and titanium occur with iron in the formula.
It was first described in 1966 for an occurrence in the Binn Valley, Valais, Switzerland. Its name is from the composition, calcium, ferrum (iron), and arsenic. It has also been reported from Piedmont, Italy and the Hemlo gold mine in the Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada.
Read More About Cafarsite / Source
Cafetite

Cafetite is a rare titanium oxide mineral with formula (Ca,Mg)(Fe,Al)2Ti4O12·4(H2O). It is named for its composition, Ca-Fe-Ti.It was first described in 1959 for an occurrence in the Afrikanda Massif, Afrikanda, Kola Peninsula, Murmanskaja Oblast, Northern Region, Russia. It is also reported from the Khibiny and Kovdor massifs of the Kola Peninsula and from Meagher County, Montana, US.It occurs in pegmatites in a pyroxenite intrusion as crystals in miarolitic cavities. It occurs associated with ilmenite, titaniferous magnetite, titanite, anatase, perovskite, baddeleyite, phlogopite, clinochlore and kassite.
Read More About Cafetite / Source
Cahnite

Cahnite (Cahnit in German, Cahnita in Spanish, Канит in Russian) is a brittle white or colorless mineral that has perfect cleavage and is usually transparent. It usually forms tetragonal-shaped crystals and it has a hardness of 3 mohs. Cahnite was discovered in the year 1921. It was named Cahnite to honor Lazard Cahn (1865–1940), who was a mineral collector and dealer. It is usually found in the Franklin Mine, in Franklin, New Jersey, but has also been found in Japan as well as in the Vallerano quarries in Rome, Italy. The geological environment that it occurs in is in pegmatites cutting a changed zinc orebody.
The chemical formula for cahnite is Ca2B[AsO4](OH)4. It is made up of 26.91% calcium, 3.63% boron, 25.15% arsenic, 1.35% hydrogen, and 42.96% oxygen. It has a molecular weight of 297.91 grams. Cahnite is not radioactive. Cahnite is associated with these other minerals: willemite, rhodonite, pyrochroite, hedyphane, datolite, and baryte.
Read More About Cahnite / Source
Calaverite

Calaverite, or gold telluride, is an uncommon telluride of gold, a metallic mineral with the chemical formula AuTe2, with approximately 3% of the gold replaced by silver. It was first discovered in Calaveras County, California in 1861, and was named for the county in 1868.
The mineral often has a metallic luster, and its color may range from a silvery white to a brassy yellow. It is closely related to the gold-silver telluride mineral sylvanite, which, however, contains significantly more silver. Another AuTe2 mineral (but with a quite different crystal structure) is krennerite. Calaverite and sylvanite represent the major telluride ores of gold, although such ores are minor sources of gold in general. As a major gold mineral found in Western Australia, calaverite played a major role in the 1890s gold rushes in that area.
Read More About Calaverite / Source
Calciborite

Calciborite, CaB2O4, is a rare calcium borate mineral.
It was first described in 1955 in the Novofrolovskoye copper–boron deposit, near Krasnoturinsk, Turinsk district, Northern Ural Mountains, Russia. It occurs in a skarn deposit formed in limestone adjacent to a quartz diorite intrusive. It occurs associated with: sibirskite (another rare calcium borate mineral), calcite, dolomite, garnet, magnetite and pyroxene. It has also been reported from the Fuka mine of Okayama Prefecture, Japan.
Read More About Calciborite / Source
Calcite

Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses.
Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable.
Read More About Calcite / Source
Calderite

Calderite is a mineral in the garnet group with the chemical formula (Mn2+, Ca)3(Fe3+, Al)2(SiO4)3.
It is dark reddish brown to dark yellowish in color and generally granular massive in form.It was named for geologist James Calder who worked on the geology of India. The name was first applied to a rock in manganese deposits in Katkamsandi, Hazaribagh district, Bihar and at Netra, Balaghat district, Madhya Pradesh, India.
later transferred to its predominant mineral. In 1909 it was described as a mineral from Otjosondu, Otjozondjupa Region, Namibia.
Read More About Calderite / Source
Caledonite

Caledonite, whose name derives from Caledonia, the historical name of its place of discovery (Scotland), is a richly colored blue-green sulfate-carbonate mineral of lead and copper with an orthorhombic crystal structure. It is an uncommon mineral found in the oxidized zones of copper-lead deposits.
Read More About Caledonite / Source
Calomel

Calomel is a mercury chloride mineral with formula Hg2Cl2 (see mercury(I) chloride). The name derives from Greek kalos (beautiful) and melas (black) because it turns black on reaction with ammonia. This was known to alchemists.Calomel occurs as a secondary mineral which forms as an alteration product in mercury deposits. It occurs with native mercury, amalgam, cinnabar, mercurian tetrahedrite, eglestonite, terlinguaite, montroydite, kleinite, moschelite, kadyrelite, kuzminite, chursinite, kelyanite, calcite, limonite and various clay minerals.The type locality is Moschellandsburg, Alsenz-Obermoschel, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Read More About Calomel / Source
Calumetite

Calumetite is a natural rarely occurring mineral. It was discovered in 1963 at the Centennial Mine near Calumet, Michigan, United States. Calumetite was first discovered along with anthonyite. It has a chemical formula of Cu(OH,Cl)2•2(H2O).
Read More About Calumetite / Source
Campigliaite
Campigliaite is a copper and manganese sulfate mineral with a chemical formula of Cu4Mn(SO4)2(OH)6·4H2O. It has a chemical formula and also a crystal structure similar to niedermayrite, with Cd(II) cation replacing by Mn(II). The formation of campigliaite is related to the oxidation of sulfide minerals to form sulfate solutions with ilvaite associated with the presence of manganese. Campigliaite is a rare secondary mineral formed when metallic sulfide skarn deposits are oxidized. While there are several related associations, there is no abundant source for this mineral due to its rare process of formation. Based on its crystallographic data and chemical formula, campigliaite is placed in the devillite group and considered the manganese analogue of devillite. Campigliaite belongs to the copper oxysalt minerals as well followed by the subgroup M=M-T sheets. The infinite sheet structures that campigliaite has are characterized by strongly bonded polyhedral sheets, which are linked in the third dimension by weaker hydrogen bonds.
Read More About Campigliaite / Source
Canasite

Canasite is a mineral whose name is derived from its chemical composition of calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), and silicon (Si). It was approved in 1959 by IMA.
Read More About Canasite / Source
Canavesite

Canavesite, Mg2(HBO3)(CO3)∙5H2O, is a rare carboborate mineral from the abandoned Brosso mine in Italy. Canavesite is a secondary mineral that occurs due to the weathering of ludwigite-magnetite skarn on the surface of mine walls. The physical properties consist of milky-white rosette-like aggregates of elongated transparent fibers shown in figure one. It has the crystal symmetry of a monoclinic with a diffraction symbol of 2/mP-/-.
Read More About Canavesite / Source
Cancrinite

Cancrinite is a complex carbonate and silicate of sodium, calcium and aluminium with the formula Na6Ca2[(CO3)2|Al6Si6O24]·2H2O. It is classed as a member of the feldspathoid group of minerals; the alkali feldspars that are poor in silica. Yellow, orange, pink, white or even blue, it has a vitreous or pearly luster; a hardness of 5–6 and an uneven conchoidal fracture. It is unusual among the silicate minerals in that it will effervesce with hydrochloric acid due to the associated carbonate ions.
Found originally in 1839 in the Ural Mountains, it is named after Georg von Cancrin, a Russian minister of finance.
Read More About Cancrinite / Source
Canfieldite

Canfieldite is a rare silver tin sulfide mineral with formula: Ag8SnS6. The mineral typically contains variable amounts of germanium substitution in the tin site and tellurium in the sulfur site. There is a complete series between canfieldite and its germanium analogue, argyrodite. It forms black orthorhombic crystals which often appear to be cubic in form due to twinning. The most typical form is as botryoidal rounded grape-like masses. Its Mohs hardness is 2.5 and the specific gravity is 6.28. Canfieldite exhibits conchoidal fracturing and no cleavage.
Canfieldite was first described in 1893 from an occurrence in Colquechaca, Potosí Department, Bolivia. It was named for Frederick Alexander Canfield (1849–1926), an American mining engineer.
Read More About Canfieldite / Source
Carletonite

Carletonite is a rare silicate mineral with formula KNa4Ca4(CO3)4Si8O18(F,OH)·(H2O).
It is a phyllosilicate and a member of the apophyllite group. Its tetragonal crystals are a translucent blue, white, colorless or pink with a vitreous to dull lustre. It has a density of 2.45 and a hardness of 4-4.5.
It was discovered by G.Y Chao and named for the school he attended, Carleton University of Ottawa. It was first described in 1969 for an occurrence at Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec. The type locality at Mont Saint–Hilaire is the only reported occurrence.It occurs in hornfels and siliceous marble xenoliths within and adjacent to a nepheline syenite intrusion. It occurs in association with quartz, narsarsukite, calcite, fluorite, ancylite, molybdenite, leucosphenite, lorenzenite, galena, albite, pectolite, apophyllite, leifite, microcline and arfvedsonite.
Read More About Carletonite / Source
Carlosruizite
Carlosruizite is a sulfate or selenate – iodate mineral with chemical formula: K6(Na,K)4Na6Mg10(SeO4)12(IO3)12·12H2O. It has a low density (specific gravity of 3.36), colorless to pale yellow, transparent mineral which crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system. It forms a series with fuenzalidaite.
It was first discovered in 1994 in the locality of Zapiga, Tarapacá Region of Chile. Its name came from Carlos Ruiz Fuller (1916–1997), founder of the Institute of Geological Investigations.It is found in samples of iquiqueite leached from caliche amarillo (yellow nitrate ore).
Read More About Carlosruizite / Source
Carlsbergite

Carlsbergite is a nitride mineral that has the chemical formula CrN, or chromium nitride.
It is named after the Carlsberg Foundation which backed the recovery of the Agpalilik fragment of the Cape York meteorite in which the mineral was first described.It occurs in meteorites along the grain boundaries of kamacite (nickel-rich native iron) or troilite (FeS: iron sulfide) in the form of tiny plates. It occurs associated with kamacite, taenite, daubreelite, troilite and sphalerite, (Zn,Fe)S.In addition to the Cape York meteorite, carlsbergite has been reported from:
the North Chile meteorite in the Antofagasta Province, Chile
the Nentmannsdorf meteorite of Bahretal, Erzgebirge, Saxony
the Okinawa Trough, Senkaku Islands, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan
the Uwet meteorite of Cross River State, Nigeria
the Sikhote-Alin meteorite, Sikhote-Alin Mountains, Russia
the Hex River Mountains meteorite from the Cape Winelands District, Western Cape Province, South Africa
the Canyon Diablo meteorite of Meteor Crater, Coconino County, Arizona
the Smithonia meteorite of Oglethorpe County, Georgia
the Kenton County meteorite of Kenton County, Kentucky
the Lombard meteorite of Broadwater County, Montana
the Murphy meteorite of Cherokee County and the Lick Creek meteorite of Davidson County, North Carolina
the New Baltimore meteorite of Somerset County, Pennsylvania
Read More About Carlsbergite / Source
Carminite

Carminite (PbFe3+2(AsO4)2(OH)2) is an anhydrous arsenate mineral containing hydroxyl. It is a rare secondary mineral that is structurally related to palermoite (Li2SrAl4(PO4)4(OH)4). Sewardite (CaFe3+2(AsO4)2(OH)2) is an analogue of carminite, with calcium in sewardite in place of the lead in carminite. Mawbyite is a dimorph (same formula, different structure) of carminite; mawbyite is monoclinic and carminite is orthorhombic. It has a molar mass of 639.87 g. It was discovered in 1850 and named for the characteristic carmine colour.
Read More About Carminite / Source
Carnallite

Carnallite (also carnalite) is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated potassium magnesium chloride with formula KCl.MgCl2·6(H2O). It is variably colored yellow to white, reddish, and sometimes colorless or blue. It is usually massive to fibrous with rare pseudohexagonal orthorhombic crystals. The mineral is deliquescent (absorbs moisture from the surrounding air) and specimens must be stored in an airtight container.
Carnallite occurs with a sequence of potassium and magnesium evaporite minerals: sylvite, kainite, picromerite, polyhalite, and kieserite. Carnallite is an uncommon double chloride mineral that only forms under specific environmental conditions in an evaporating sea or sedimentary basin. It is mined for both potassium and magnesium and occurs in the evaporite deposits of Carlsbad, New Mexico; the Paradox Basin in Colorado and Utah; Stassfurt, Germany; the Perm Basin, Russia; and the Williston Basin in Saskatchewan, Canada. These deposits date from the Devonian through the Permian Periods. In contrast, both Israel and Jordan produce potash from the Dead Sea by using evaporation pans to further concentrate the brine until carnallite precipitates, dredging the carnallite from the pans, and processing to remove the magnesium chloride from the potassium chloride.Carnallite was first described in 1856 from its type location of Stassfurt Deposit, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It was named for the Prussian mining engineer Rudolf von Carnall (1804–1874).
Read More About Carnallite / Source
Carnotite

Carnotite is a potassium uranium vanadate radioactive mineral with chemical formula K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O. The water content can vary and small amounts of calcium, barium, magnesium, iron, and sodium are often present.
Read More About Carnotite / Source
Carobbiite
Carobbiite, chemical formula KF (potassium fluoride), is a rare, soft (Mohs 2 – 2.5), colourless cubic mineral. It is found at Monte Somma, Somma-Vesuvius Complex, Province of Naples, Campania, Italy. It was discovered in 1956 by Italian geologist Guido Carobbi (1900–1983). It has also been reported from Hokkaido, Japan.
Read More About Carobbiite / Source
Carpathite

Carpathite is a very rare hydrocarbon mineral, consisting of exceptionally pure coronene (C24H12), a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. The name has been spelled karpatite and the mineral was improperly renamed pendletonite.
Read More About Carpathite / Source
Carpholite

Carpholite is a manganese silicate mineral with formula Mn2+Al2Si2O6(OH)4. It occurs as yellow clusters of slender prisms or needles. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system.
The carpholite group includes ferrocarpholite, magnesiocarpholite, vanadiocarpholite, and potassiccarpholite.
Read More About Carpholite / Source
Carrollite

Carrollite, CuCo2S4, is a sulfide of copper and cobalt, often with substantial substitution of nickel for the metal ions, and a member of the linnaeite group. It is named after the type locality in Carroll County, Maryland, US, at the Patapsco mine, Sykesville.
Read More About Carrollite / Source
Caryopilite

Caryopilite (synonymous with ectropite and ektropite) is a brown-colored mineral with formula (Mn2+,Mg)3Si2O5(OH)4. The mineral was discovered in 1889 from a mine in Sweden. It was named for the Greek words for walnut and felt in reference to its appearance.
Read More About Caryopilite / Source
Cassiterite

Cassiterite is a tin oxide mineral, SnO2. It is generally opaque, but it is translucent in thin crystals. Its luster and multiple crystal faces produce a desirable gem. Cassiterite was the chief tin ore throughout ancient history and remains the most important source of tin today.
Read More About Cassiterite / Source
Cattierite

Cattierite (CoS2) is a cobalt sulfide mineral found in the Democratic Republic of Congo. It was discovered together with the nickel sulfide vaesite by Johannes F. Vaes, a Belgian mineralogist and named after Felicien Cattier, who was chairman of the board of the Union Minière du Haut-Katanga.The mineral belongs to the pyrite group, in which all minerals share the same building principle. The metal in the oxidation state +2 forms a sodium chloride structure together with the anion S22−. This formalism recognizes that the sulfur atoms in pyrite occur in pairs with clear S-S bonds.
It occurs with pyrite, chalcopyrite and members of the linnaeite – polydymite group in ore deposits in carbonate rocks. In addition to the type locality in the Katanga district it is reported from Gansberg, Black Forest, Germany; near Filipstad, Varmland, Sweden; Bald Knob, near Sparta, Alleghany County, North Carolina and in the Fletcher mine of Reynolds County, Missouri.
Read More About Cattierite / Source
Cavansite

Cavansite, whose name is derived from its chemical composition, calcium vanadium silicate, is a deep blue hydrous calcium vanadium phyllosilicate mineral, occurring as a secondary mineral in basaltic and andesitic rocks along with a variety of zeolite minerals. It’s blue coloring comes from vanadium, a metal ion. Discovered in 1967 in Malheur County, Oregon, cavansite is a relatively rare mineral. It is polymorphic with the even rarer mineral, pentagonite. It is most frequently found in Pune, India and in the Deccan Traps, a large igneous province.
Read More About Cavansite / Source
Celadonite

Celadonite is a mica group mineral, a phyllosilicate of potassium, iron in both oxidation states, aluminium and hydroxide with formula K(Mg,Fe2+)(Fe3+,Al)[Si4O10](OH)2.
It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and usually forms massive aggregates of prismatic crystallites or in dull clay masses. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 2 and a specific gravity of 3. Typically occurs as dull gray-green to bluish green masses. It forms vesicle fillings and linings in altered basaltic lavas. Early research suggests this mineral has ties to weakly metamorphosed plutonic rocks during formation, and is also found with montmorillonite clays or zeolite crystals. Association with zeolites may indicate these minerals favor the same underlying conditions of crystal growth.It was first described in 1847 on Monte Baldo, near Verona, Italy. The name is from the French celadon, for sea-green. It is one of two minerals, along with glauconite, used in making the pigment known as green earth.Common impurities are manganese, calcium and sodium (previously known as natrium).
Read More About Celadonite / Source
Celestine (mineral)

Celestine (the IMA-accepted name) or celestite is a mineral consisting of strontium sulfate (SrSO4). The mineral is named for its occasional delicate blue color. Celestine and the carbonate mineral strontianite are the principal sources of the element strontium, commonly used in fireworks and in various metal alloys.
Read More About Celestine (mineral) / Source
Celsian

Celsian is an uncommon feldspar mineral, barium aluminosilicate, BaAl2Si2O8. The mineral occurs in contact metamorphic rocks with significant barium content. Its crystal system is monoclinic, and it is white, yellow, or transparent in appearance. In pure form, it is transparent. Synthetic barium aluminosilicate is used as a ceramic in dental fillings and other applications.
The mineral is named after Anders Celsius (1701–1744).
Read More About Celsian / Source
Cerite

Cerite is a complex silicate mineral group containing cerium, formula (Ce,La,Ca)9(Mg,Fe3+)(SiO4)6(SiO3OH)(OH)3. The cerium and lanthanum content varies with the Ce rich species (cerite-(Ce)) and the La rich species (cerite-(La)). Analysis of a sample from the Mountain Pass carbonatite gave 35.05% Ce2O3 and 30.04% La2O3.Cerite was first described in 1803 for an occurrence in Bastnäs in Västmanland, Sweden. The lanthanum rich species, cerite-(La) was first described for an occurrence in the Khibina massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia in 2002.
Read More About Cerite / Source
Cerium

Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the oxidation state of +3 characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is also considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure.
Despite always occurring in combination with the other rare-earth elements in minerals such as those of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, cerium is easy to extract from its ores, as it can be distinguished among the lanthanides by its unique ability to be oxidized to the +4 state in aqueous solution. It is the most common of the lanthanides, followed by neodymium, lanthanum, and praseodymium. It is the 25th-most abundant element, making up 66 ppm of the Earth’s crust, half as much as chlorine and five times as much as lead.
Cerium was the first of the lanthanides to be discovered, in Bastnäs, Sweden, by Jöns Jakob Berzelius and Wilhelm Hisinger in 1803, and independently by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in Germany in the same year. In 1839 Carl Gustaf Mosander became the first to isolate the metal. Today, cerium and its compounds have a variety of uses: for example, cerium(IV) oxide is used to polish glass and is an important part of catalytic converters. Cerium metal is used in ferrocerium lighters for its pyrophoric properties. Cerium-doped YAG phosphor is used in conjunction with blue light-emitting diodes to produce white light in most commercial white LED light sources.
Read More About Cerium / Source
Cerussite

Cerussite (also known as lead carbonate or white lead ore) is a mineral consisting of lead carbonate (PbCO3), and is an important ore of lead. The name is from the Latin cerussa, white lead. Cerussa nativa was mentioned by Conrad Gessner in 1565, and in 1832 F. S. Beudant applied the name céruse to the mineral, whilst the present form, cerussite, is due to W. Haidinger (1845). Miners’ names in early use were lead-spar and white-lead-ore.Cerussite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system and is isomorphous with aragonite. Like aragonite it is very frequently twinned, the compound crystals being pseudo-hexagonal in form. Three crystals are usually twinned together on two faces of the prism, producing six-rayed stellate groups with the individual crystals intercrossing at angles of nearly 60°. Crystals are of frequent occurrence and they usually have very bright and smooth faces. The mineral also occurs in compact granular masses, and sometimes in fibrous forms. The mineral is usually colorless or white, sometimes grey or greenish in tint and varies from transparent to translucent with an adamantine lustre. It is very brittle, and has a conchoidal fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 3 to 3.75 and a specific gravity of 6.5. A variety containing 7% of zinc carbonate, replacing lead carbonate, is known as iglesiasite, from Iglesias in Sardinia, where it is found.The mineral may be readily recognized by its characteristic twinning, in conjunction with the adamantine lustre and high specific gravity. It dissolves with effervescence in dilute nitric acid. A blowpipe test will cause it to fuse very readily, and gives indications for lead.Finely crystallized specimens have been obtained from the Friedrichssegen mine in Lahnstein in Rhineland-Palatinate, Johanngeorgenstadt in Saxony, Stříbro in the Czech Republic, Phoenixville in Pennsylvania, Broken Hill in New South Wales, and several other localities. Delicate acicular crystals of considerable length were found long ago in the Pentire Glaze mine near St Minver in Cornwall. Cerussite is often found in considerable quantities, and has a lead content of up to 77.5%.Lead(II) carbonate is practically insoluble in neutral water (solubility product [Pb2+][CO32−] ≈ 1.5×10−13 at 25 °C), but will dissolve in dilute acids.
Read More About Cerussite / Source
Cervandonite

Cervandonite is a rare arsenosilicate mineral. It has a chemical formula (Ce,Nd,La)(Fe3+,Fe2+,Ti4+,Al)3SiAs(Si,As)O13 or (Ce,Nd,La)(Fe3+,Fe2+,Ti,Al)3O2(Si2O7)(As3+O3)(OH). It has a monoclinic crustal structure with supercell (Z=6), the crystal structure was established as a trigonal subcell, with space group R3m and a = 6.508(1)Ǻ, c = 18.520(3) Ǻ, V 679.4(2) Ǻ3, and Z=3. It was first described by Buhler Armbruster in 1988, but it has proven to be problem due to the extreme scarcity of single crystals and its unusual replacement of silicon and arsenic. Cervandonite is named after the location where it was first described, Pizzo Cervandone (Scherbadung), Italy in the Central Alps.
Read More About Cervandonite / Source
Cervantite

Cervantite is an antimony oxide mineral with formula Sb3+Sb5+O4 (antimony tetroxide).
It was first described in 1850 for an occurrence in Cervantes, Sierra de Ancares, Lugo, Galicia, Spain, and named for the locality. The mineral was questioned and disapproved, but re-approved and verified in 1962 based on material from the Zajaca-Stolice district, Brasina, Serbia. It occurs as a secondary alteration product of antimony bearing minerals, mainly stibnite.
Read More About Cervantite / Source
Cesanite
Cesanite is the end member of the apatite-wilkeite-ellestadite series that substitutes all of apatite’s phosphate ions with sulfate ions and balances the difference in charge by replacing several calcium ions with sodium ions. Currently very few sites bearing cesanite have been found and are limited to a geothermal field in Cesano, Italy from which its name is derived, Măgurici Cave in Romania, and in the San Salvador Island caves in the Bahamas.
Read More About Cesanite / Source
Cesbronite

Cesbronite is a copper-tellurium oxysalt mineral with the chemical formula Cu3Te6+O4(OH)4 (IMA 17-C). It is colored green and its crystals are orthorhombic dipyramidal. Cesbronite is rated 3 on the Mohs Scale. It is named after Fabien Cesbron (born 1938), a French mineralogist.
Read More About Cesbronite / Source
Chabazite

Chabazite (UK: ) is a tectosilicate mineral of the zeolite group, closely related to gmelinite, with the chemical formula (Ca,K2,Na2,Mg)Al2Si4O12•6H2O. Recognized varieties include Chabazite-Ca, Chabazite-K, Chabazite-Na, and Chabazite-Sr, depending on the prominence of the indicated cation.
Chabazite crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system with typically rhombohedral shaped crystals that are pseudo-cubic. The crystals are typically twinned, and both contact twinning and penetration twinning may be observed. They may be colorless, white, orange, brown, pink, green, or yellow. The hardness ranges from 3 to 5 and the specific gravity from 2.0 to 2.2. The luster is vitreous.
It was named chabasie in 1792 by Bosc d’Antic and later changed to the current spelling.
Chabazite occurs most commonly in voids and amygdules in basaltic rocks.
Chabazite is found in India, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, the Giants Causeway in Northern Ireland, Bohemia, Italy, Germany, along the Bay of Fundy in Nova Scotia, Oregon, Arizona, and New Jersey.
Read More About Chabazite / Source
Chaidamuite
Chaidamuite is a rare zinc – iron sulfate mineral with chemical formula: ZnFe3+(SO4)2(OH)·4H2O.
It was first described for an occurrence in the Xitieshan mine south of Mt. Qilianshan in the Chaidamu basin, Qinghai Province, China and was named for the locality. It occurs as an oxidation phase in a lead zinc deposit. In the type locality it is associated with the rare minerals: coquimbite, copiapite, butlerite and zincobotryogen. In addition to the Chinese occurrence it has been reported from the Getchell Mine in the Potosi District in Humboldt County, Nevada.
Read More About Chaidamuite / Source
Chalcanthite

Chalcanthite (from Ancient Greek χάλκανθον (khálkanthon), from χαλκός (khalkós) ‘copper’, and ἄνθος (ánthos) ‘flower, bloom’) is a richly colored blue-green water-soluble sulfate mineral CuSO4 · 5H2O. It is commonly found in the late-stage oxidation zones of copper deposits. Due to its ready solubility, chalcanthite is more common in arid regions.
Chalcanthite is a pentahydrate and the most common member of a group of similar hydrated sulfates, the chalcanthite group. These other sulfates are identical in chemical composition to chalcanthite, with the exception of replacement of the copper ion by either manganese as jokokuite, iron as melanterite, or magnesium as pentahydrite.Other names include blue stone, blue vitriol, and copper vitriol.
Read More About Chalcanthite / Source
Chalcocite

Chalcocite , copper(I) sulfide (Cu2S), is an important copper ore mineral. It is opaque and dark gray to black, with a metallic luster. It has a hardness of 2.5–3 on the Mohs scale. It is a sulfide with a monoclinic crystal system.
The term chalcocite comes from the alteration of the obsolete name chalcosine, from the Greek khalkos, meaning “copper”. It is also known as redruthite, vitreous copper, or copper-glance.
Read More About Chalcocite / Source
Chalconatronite

Chalconatronite is a carbonate mineral and rare secondary copper mineral that contains copper, sodium, carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, its chemical formula is Na2Cu(CO3)2•3(H2O). Chalconatronite is partially soluble in water, and only decomposes, although chalconatronite is soluble while cold, in dilute acids. The name comes from the mineral’s compounds, copper (“chalcos” in Greek) and natron, naturally forming sodium carbonate. The mineral is thought to be formed by water carrying alkali carbonates (possibly from soil) reacting with bronze. Similar minerals include malachite, azurite, and other copper carbonates. Chalconatronite has also been found and recorded in Australia, Germany, and Colorado.
Read More About Chalconatronite / Source
Chalcophyllite

Chalcophyllite is a rare secondary copper arsenate mineral occurring in the oxidized zones of some arsenic-bearing copper deposits. It was first described from material collected in Germany. At one time chalcophyllite from Wheal Tamar in Cornwall, England, was called tamarite, but this name is now discredited (not to be confused with the amphibole mineral taramite, which is quite different). At Wheal Gorland a specimen exhibiting partial replacement of liriconite, Cu2Al(AsO4)(OH)4•(4H2O), by chalcophyllite has been found. The mineral is named from the Greek, chalco “copper” and fyllon, “leaf”, in allusion to its composition and platy structure. It is a classic Cornish mineral that can be confused with tabular spangolite.
Read More About Chalcophyllite / Source
Chalcopyrite

Chalcopyrite ( KAL-kə-PY-ryte, -koh-) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black.On exposure to air, chalcopyrite tarnishes to a variety of oxides, hydroxides, and sulfates. Associated copper minerals include the sulfides bornite (Cu5FeS4), chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS), digenite (Cu9S5); carbonates such as malachite and azurite, and rarely oxides such as cuprite (Cu2O). It is rarely found in association with native copper. Chalcopyrite is a conductor of electricity.Copper can be extracted from chalcopyrite ore using various methods. The two predominant methods are pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy, the former being the most commercially viable.
Read More About Chalcopyrite / Source
Challacolloite

Challacolloite, KPb2Cl5, is a rare halide mineral. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system (with space group P21/c) and occurs as white fumarolic encrustations on lava. It occurs as intergrowths with cotunnite.It was first described from a finding at the Challacollo Mine, Iquique, Chile and thereafter identified in specimens from the 1855 Mount Vesuvius eruption and from the Kudryavyi volcano in the Kuriles and also from the Satsuma-Iwojima volcano in Japan. It was recognized as a valid mineral species by the IMA (International Mineralogical Association) in 2005.Artificially grown KPb2Cl5 crystals are used for lasers.
Read More About Challacolloite / Source
Chambersite

Chambersite is a manganese borate mineral with formula Mn3B7O13Cl. It is a member of the borate mineral series that includes other minerals such as ericaite (Fe3B7O13Cl) and boracite (Mg3B7O13Cl). When chambersite was first discovered, it was the second chemical analogue of boracite to be found in nature. It was discovered as a mineral at Barber’s Hill salt dome in Texas in 1957 and in 1971 at the Dongshuichang deposit in Jixian, Tianjin, China. Chambersite occurs associated with the evaporite minerals halite, anhydrite, and gypsum.
Read More About Chambersite / Source
Chamosite

Chamosite is the Fe2+end member of the chlorite group. A hydrous aluminium silicate of iron, which is produced in an environment of low to moderate grade of metamorphosed iron deposits, as gray or black crystals in oolitic iron ore. Like other chlorites, it is a product of the hydrothermal alteration of pyroxenes, amphiboles and biotite in igneous rock. The composition of chlorite is often related to that of the original igneous mineral so that more Fe-rich chlorites are commonly found as replacements of the Fe-rich ferromagnesian minerals (Deer et al., 1992).
Read More About Chamosite / Source
Changbaiite
Changbaiite (PbNb2O6) is a member of the oxide mineral class in which the mineral contains oxygen which is grouped along with one or two metal ion. Changbaiite is classified as a multiple Oxide XY2O6 and it generally has an ionic bond. Furthermore, it is also orthorhombic at a temperature of 25 °C and it changes to orthorhombic-tetragonal at 570 °C.
Read More About Changbaiite / Source
Chaoite
Chaoite, or white carbon, is a mineral described as an allotrope of carbon whose existence is disputed. It was discovered in shock-fused graphite gneiss from the Ries crater in Bavaria. It has been described as slightly harder than graphite, with a reflection colour of grey to white. From its electron diffraction pattern, the mineral has been considered to have a carbyne structure, the linear acetylenic carbon allotrope of carbon. A later report has called this identification, and the very existence of carbyne phases, into question, arguing that the new reflections in the diffraction pattern are due to clay impurities.
Read More About Chaoite / Source
Chapmanite

Chapmanite is a rare silicate mineral belonging to the nesosilicate group, discovered in 1924, and named in honour of the late Edward John Chapman (1821–1904), a geology professor at the University of Toronto. Chemically, it is an iron antimony silicate, closely related to bismutoferrite, and may contain aluminium impurities. It is closely associated with silver mines, most notably the Keeley mine in Ontario, Canada, found in quartz veinlets containing graphite in gneiss. It takes the form of a powdery, yellow-green, semitransparent solid, and leaves a streak of the same color. Early German texts have referred to the mineral as antimon-hypochlorite.
It was recently rediscovered in the southern hemisphere at the abandoned Argent lead mine in Bushveld series rocks of South Africa.
Read More About Chapmanite / Source
Charlesite

Charlesite is a sulfate mineral of the ettringite group. Charlesite was named in 1945 after Dr. Charles Palache mineralogist and professor at Harvard University for his work on minerals. This mineral is extremely rare, and when it is found it is often in crystal (but not gem) form. Its crystals are soft hexagonal, that can vary in color. Colors can range from clear to white, or even a pale yellow or pink. The brittle mineral’s Mohs hardness is 2.5 with a specific gravity of 1.79. Though transparent to the eye the mineral has a white streak.
Read More About Charlesite / Source
Charoite

Charoite K(Ca,Na)2Si4O10(OH,F)•H2O is a rare silicate mineral, first described in 1978. It was believed to be named after the Chara River, but due to the river being 70 km away from its discovery place, now it is believed to be named after the Russian word chary, meaning magic or charms. When it was discovered, it was thought to be a fake, dyed purple to give it its striking appearance.
Read More About Charoite / Source
Chatkalite
Chatkalite is a copper, iron, tin sulfide mineral with formula Cu6Fe2+Sn2S8. It crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system and forms as rounded disseminations within tetrahedrite in quartz veins.
Read More About Chatkalite / Source
Chesterite
Chesterite is a rare silicate mineral that can be compared to amphiboles, micas, and jimthompsonite. Its chemical formula is (Mg,Fe)17Si20O54(OH)6. Chesterite is named after Chester, Vermont, where it was first described in 1977. The specific geologic setting within its origin is the Carleton talc quarry in Chester, Vermont.Chesterite has an orthorhombic crystal structure, which means it has three crystallographic axes of unequal length. All of the axes are perpendicular to each other. The stacking sequence for chesterite, which is found in micas, is very similar to orthopyroxenes and orthoamphiboles. Chesterite is an anisotropic mineral; therefore, it allows light to travel through it at different velocities when viewed at different angles. Chesterite is usually found in thin sheets within ultramafic rocks.A polytype of chesterite could be anthophyllite, which has a similar crystal structure. Chesterite is used for research on stacking formations and symmetry point groups that could be possible polymorphs or polysomes of the amphibole-anthophyllite groups. Chesterite has no direct usage, but some geologists or scientists generally classify it under the amphibole-anthophyllite group.
Read More About Chesterite / Source
Chibaite

Chibaite is a rare silicate mineral. It is a silica clathrate with formula SiO2•n(CH4,C2H6,C3H8,i-C4H10) (n = 3/17 (max)). The mineral is cubic (diploidal class, m3) and the silica hosts or traps various hydrocarbon molecules, such as methane, ethane, propane and isobutane.Chibaite was first described for specimens collected from Arakawa, Minamibōsō, Chiba Prefecture, Honshu Island, Japan. The mineral was approved by the IMA in 2009.
Read More About Chibaite / Source
Childrenite

Childrenite is a rare hydrated phosphate mineral with elements iron, manganese, aluminium, phosphorus, oxygen and hydrogen. Its chemical formula is (Fe2+,Mn)2+AlPO4(OH)2•H2O and it has a molecular weight of 229.83 g/mol. Its specific gravity is 3.2 and it has a Mohs hardness of 4.5 to 5. It is usually translucent and non-fluorescent, with imperfect cleavage. It has a vitreous lustre with a white streak, and is brown or yellow in color. It has a conchoidal, uneven fracture, and an orthorhombic crystal system.
Read More About Childrenite / Source
Chiolite

Chiolite is a tetragonal-ditetragonal dipyramidal mineral, composed of sodium, fluorine, and aluminium. The name originates from the combination of the Greek words for snow (χιώυ) and stone (λίθος). It is an allusion to its similarity and appearance to cryolite (ice stone). Chiolite is an IMA approved mineral that has been grandfathered, meaning the name chiolite is believed to refer to a valid species to this day. Synonyms of chiolite are arksudite, arksutite, chodneffite, chodnewite and nipholith. It was first discovered in the Ilmen mountains, Russia, in 1846. Chiolite has been a valid species from the same year of its discovery.
Read More About Chiolite / Source
Chlorargyrite

Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric – hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to columnar in occurrence it also has been found as colorless to variably yellow cubic crystals. The color changes to brown or purple on exposure to light. It is quite soft with a Mohs hardness of 1 to 2 and dense with a specific gravity of 5.55. It is also known as cerargyrite and, when weathered by desert air, as horn silver. Bromian chlorargyrite (or embolite) is also common. Chlorargyrite is water-insoluble.
It occurs associated with native silver, cerussite, iodargyrite, atacamite, malachite, jarosite and various iron–manganese oxides.It was first described in 1875 for occurrences in the Broken Hill district, New South Wales, Australia. The rich Bridal Chamber deposit at Lake Valley, Sierra County, New Mexico was almost pure chlorargyrite. The name is from the Greek, chloros for “pale green” and Latin for silver, argentum.
Read More About Chlorargyrite / Source
Chlorite

The chlorites are the group of phyllosilicate minerals common in low-grade metamorphic rocks and in altered igneous rocks. Greenschist, formed by metamorphism of basalt or other low-silica volcanic rock, typically contains significant amounts of chlorite.
Chlorite minerals show a wide variety of compositions, in which magnesium, iron, aluminium, and silicon substitute for each other in the crystal structure. A complete solid solution series exists between the two most common end members, magnesium-rich clinochlore and iron-rich chamosite. In addition, manganese, zinc, lithium, and calcium species are known. The great range in composition results in considerable variation in physical, optical, and X-ray properties. Similarly, the range of chemical composition allows chlorite group minerals to exist over a wide range of temperature and pressure conditions. For this reason chlorite minerals are ubiquitous minerals within low and medium temperature metamorphic rocks, some igneous rocks, hydrothermal rocks and deeply buried sediments.
The name chlorite is from the Greek chloros (χλωρός), meaning “green”, in reference to its color. Chlorite minerals do not contain the element chlorine, also named from the same Greek root.
Read More About Chlorite / Source
Chloritoid

Chloritoid is a silicate mineral of metamorphic origin. It is an iron magnesium manganese alumino-silicate hydroxide with formula (Fe, Mg, Mn)2Al4Si2O10(OH)4. It occurs as greenish grey to black platy micaceous crystals and foliated masses. Its Mohs hardness is 6.5, unusually high for a platy mineral, and it has a specific gravity of 3.52 to 3.57. It typically occurs in phyllites, schists and marbles.
Both monoclinic and triclinic polytypes exist and both are pseudohexagonal.It was first described in 1837 from localities in the Ural Mountains region of Russia. It was named for its similarity to the chlorite group of minerals.
Read More About Chloritoid / Source
Chlormayenite
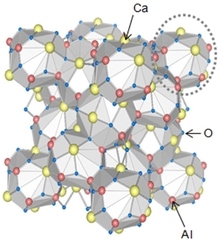
Chlormayenite (after Mayen, Germany), Ca12Al14O32[☐4Cl2], is a rare calcium aluminium oxide mineral of cubic symmetry.
It was originally reported from Eifel volcanic complex (Germany) in 1964. It is also found at pyrometamorphic sites such as in the Hatrurim Formation of Israel and in some burned coal dumps.It occurs in thermally altered limestone xenoliths within basalts in Mayen, Germany and Klöch, Styria, Austria. In the Hatrurim of Israel it occurs in thermally altered limestones. It occurs with calcite, ettringite, wollastonite, larnite, brownmillerite, gehlenite, diopside, pyrrhotite, grossular, spinel, afwillite, jennite, portlandite, jasmundite, melilite, kalsilite and corundum in the limestone xenoliths. In the Hatrurim it occurs with spurrite, larnite, grossite and brownmillerite.Synthetic Ca12Al14O33 and Ca12Al14O32(OH)2 are known, they are stabilized by moisture instead of chlorine. The formula can be written as [Ca12Al14O32]O, which refers to the unique feature: anion diffusion process.Chlormayenite is also found as calcium aluminate in cement where its formula is also written as 11CaO·7 Al2O3·CaCl2, or C11A7CaCl2 in the cement chemist notation.
Read More About Chlormayenite / Source
Chlorocalcite
Chlorocalcite is a rare potassium calcium chloride evaporite mineral with formula: KCaCl3. It is found in active volcanic fumaroles.
It was first described in 1872 for an occurrence on Mount Vesuvius and given the name for its calcium content previous to discovering that it also contained potassium. It has also been reported from the Desdemona Mine, Peine, Lower Saxony, Germany.
Read More About Chlorocalcite / Source
Chloroxiphite

Chloroxiphite is a rare olive green to pistacio green lead copper halide mineral with formula: Pb3CuO2Cl2(OH)2.
It was first discovered in 1923 in the Mendip Hills, Somerset, England associated with mendipite. Like mendipite it is an oxychloride mineral and formed from the alteration of lead ore (galena) by secondary oxidation. In addition to mendipite, it occurs with diaboleite, parkinsonite, wulfenite, cerussite and hydrocerussite. Its name comes from the Greek words (χλωρός) “green”, describing its color, and (ζιφος) “blade” as its crystal form is long blade-like crystals that often show the growth pattern and time taken to form.
Read More About Chloroxiphite / Source
Chondrodite

Chondrodite is a nesosilicate mineral with formula (Mg,Fe)5(SiO4)2(F,OH,O)2. Although it is a fairly rare mineral, it is the most frequently encountered member of the humite group of minerals. It is formed in hydrothermal deposits from locally metamorphosed dolomite. It is also found associated with skarn and serpentinite.
It was discovered in 1817 at Pargas in Finland, and named from the Greek for “granule”, which is a common habit for this mineral.
Read More About Chondrodite / Source
Chrisstanleyite
Chrisstanleyite, Ag2Pd3Se4, is a selenide mineral that crystallizes in high saline, acidic hydrothermal solution at low temperatures as part of selenide vein inclusions in and alongside calcite veins. It tends to be found in assemblages of other selenides: jagueite, naumannite, fischesserite, oosterboschite, and tiemannite, and it is a solid solution mineral with jagueite Cu2Pd3Se4 in which it shares a unique crystal structure that has not been identified elsewhere (Paar et al. 1998; Nickel 2002; Paar et al. 2004). Chrisstanleyite and jagueite are unlike the other minerals of the selenide family as they do not have a sulfide analogue (Topa et al. 2006). First discovered by Werner Paar from a sample received from Hope’s Nose, Torquay, Devon, England, chrisstanleyite has since been discovered in the Pilbara region of Western Australia and in El Chire, La Rioja, Argentina. Chrisstanleyite was named after the Deputy Head and Associate Keeper at the Department of Mineralogy at The Natural History Museum in London.
Read More About Chrisstanleyite / Source
Christite

Christite is a mineral with the chemical formula TlHgAsS3. It is named after Dr. Charles L. Christ, a member of the U.S. Geological Survey. It usually comes in a crimson red or bright orange color. It has a density of 6.2 and has a rating between 1 and 2 on Mohs Hardness Scale. Christite has an adamantine luster and leaves behind an orange streak. Its crystal system is monoclinic with possible crystal classes of twofold symmetry, mirror plane symmetry, and twofold with a mirror plane. This means it can have radial symmetry, mirror plane symmetry, or mirror plane symmetry perpendicular to the two-fold axis. It is an anisotropic mineral, which means that it exhibits different properties when measured in different directions. In plane polarized light, its color is golden yellow. It is birefringent, which means that it has two distinct indices of refraction. This can be seen when one looks through the microscope with both polars crossed and sees the mineral change colors when it is rotated.
Read More About Christite / Source
Chromite

Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can substitute for iron in variable amounts as it forms a solid solution with magnesiochromite (MgCr2O4). A substitution of the element aluminium can also occur, leading to hercynite (FeAl2O4). Chromite today is mined particularly to make stainless steel through the production of ferrochrome (FeCr), which is an iron-chromium alloy.Chromite grains are commonly found in large mafic igneous intrusions such as the Bushveld in South Africa and India. Chromite is iron-black in color with a metallic luster, a dark brown streak and a hardness on the Mohs scale of 5.5.
Read More About Chromite / Source
Chromium

Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating (electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared light. The name of the element is derived from the Greek word χρῶμα, chrōma, meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored.
Industrial production of chromium proceeds from chromite ore (mostly FeCr2O4) to produce ferrochromium, an iron-chromium alloy, by means of aluminothermic or silicothermic reactions. Ferrochromium is then used to produce alloys such as stainless steel. Pure chromium metal is produced by a different process: roasting and leaching of chromite to separate it from iron, followed by reduction with carbon and then aluminium.
In the United States, trivalent chromium (Cr(III)) ion is considered an essential nutrient in humans for insulin, sugar, and lipid metabolism. However, in 2014, the European Food Safety Authority, acting for the European Union, concluded that there was insufficient evidence for chromium to be recognized as essential.While chromium metal and Cr(III) ions are considered non-toxic, hexavalent chromium, Cr(VI), is toxic and carcinogenic. According to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), chromium trioxide that is used in industrial electroplating processes is a “substance of very high concern” (SVHC).Abandoned chromium production sites often require environmental cleanup.
Read More About Chromium / Source
Chrysoberyl

The mineral or gemstone chrysoberyl is an aluminate of beryllium with the formula BeAl2O4. The name chrysoberyl is derived from the Greek words χρυσός chrysos and βήρυλλος beryllos, meaning “a gold-white spar”. Despite the similarity of their names, chrysoberyl and beryl are two completely different gemstones, although they both contain beryllium. Chrysoberyl is the third-hardest frequently encountered natural gemstone and lies at 8.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, between corundum (9) and topaz (8).An interesting feature of its crystals are the cyclic twins called trillings. These twinned crystals have a hexagonal appearance, but are the result of a triplet of twins with each “twin” oriented at 120° to its neighbors and taking up 120° of the cyclic trilling. If only two of the three possible twin orientations are present, a “V”-shaped twin results.
Ordinary chrysoberyl is yellowish-green and transparent to translucent. When the mineral exhibits good pale green to yellow color and is transparent, then it is used as a gemstone. The three main varieties of chrysoberyl are: ordinary yellow-to-green chrysoberyl, cat’s eye or cymophane, and alexandrite. Yellow-green chrysoberyl was referred to as “chrysolite” during the Victorian and Edwardian eras, which caused confusion since that name has also been used for the mineral olivine (“peridot” as a gemstone); that name is no longer used in the gemological nomenclature.
Alexandrite, a strongly pleochroic (trichroic) gem, will exhibit emerald green, red and orange-yellow colors depending on viewing direction in partially polarised light. However, its most distinctive property is that it also changes color in artificial (tungsten/halogen) light compared to daylight. The color change from red to green is due to strong absorption of light in a narrow yellow portion of the spectrum, while allowing large bands of more blue-green and red wavelengths to be transmitted. Which of these prevails to give the perceived hue depends on the spectral balance of the illumination. Fine-quality alexandrite has a green to bluish-green color in daylight (relatively blue illumination of high color temperature), changing to a red to purplish-red color in incandescent light (relatively yellow illumination). However, fine-color material is extremely rare. Less-desirable stones may have daylight colors of yellowish-green and incandescent colors of brownish red.Cymophane is popularly known as “cat’s eye”. This variety exhibits pleasing chatoyancy or opalescence that reminds one of the eye of a cat. When cut to produce a cabochon, the mineral forms a light-green specimen with a silky band of light extending across the surface of the stone.
Read More About Chrysoberyl / Source
Chrysocolla

Chrysocolla ( KRIS-ə-KOL-ə) is a hydrated copper phyllosilicate mineral and mineraloid with formula Cu2–xAlx(H2Si2O5)(OH)4•nH2O (x<1) or (Cu,Al)2H2Si2O5(OH)4•nH2O).The structure of the mineral has been questioned, as a 2006 spectrographic study suggest material identified as chrysocolla may be a mixture of the copper hydroxide spertiniite and chalcedony.
Read More About Chrysocolla / Source
Chrysotile

Chrysotile or white asbestos is the most commonly encountered form of asbestos, accounting for approximately 95% of the asbestos in the United States and a similar proportion in other countries. It is a soft, fibrous silicate mineral in the serpentine subgroup of phyllosilicates; as such, it is distinct from other asbestiform minerals in the amphibole group. Its idealized chemical formula is Mg3(Si2O5)(OH)4. The material has physical properties which make it desirable for inclusion in building materials, but poses serious health risks when dispersed into air and inhaled.
Read More About Chrysotile / Source
Chvaleticeite
Chvaleticeite is a monoclinic hexahydrite manganese magnesium sulfate mineral with formula: (Mn2+, Mg)[SO4]·6(H2O). It occurs in the oxidized zone of manganese silicate deposits with pyrite and rhodochrosite that have undergone regional and contact metamorphism. It is defined as the manganese dominant member of the hexahydrite group.
Chvaleticeite is named after the city Chvaletice, Bohemia, in the Czech Republic. Chvaleticeite and minerals like it have been studied for their hydrogen bonding and incongruent melting properties as they are predicted to form in the relative environments of Mars and other bodies in the solar system.
Read More About Chvaleticeite / Source
Cinnabar

Cinnabar (; from Ancient Greek κιννάβαρι (kinnábari)), or cinnabarite , is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining elemental mercury and is the historic source for the brilliant red or scarlet pigment termed vermilion and associated red mercury pigments.
Cinnabar generally occurs as a vein-filling mineral associated with recent volcanic activity and alkaline hot springs. The mineral resembles quartz in symmetry and in its exhibiting birefringence. Cinnabar has a mean refractive index near 3.2, a hardness between 2.0 and 2.5, and a specific gravity of approximately 8.1. The color and properties derive from a structure that is a hexagonal crystalline lattice belonging to the trigonal crystal system, crystals that sometimes exhibit twinning.
Cinnabar has been used for its color since antiquity in the Near East, including as a rouge-type cosmetic, in the New World since the Olmec culture, and in China since as early as the Yangshao culture, where it was used in coloring stoneware.
Associated modern precautions for use and handling of cinnabar arise from the toxicity of the mercury component, which was recognized as early as ancient Rome.
Read More About Cinnabar / Source
Clarkeite
Clarkeite is a uranium oxide mineral with the chemical formula(Na,Ca,Pb)2(UO2)2(O,OH)3 or (Na,Ca,Pb)(UO2)O(OH)•0-1H2O.
Its color varies from dark brown to reddish orange. Clarkeite forms by oxidation and replacement of uraninite late during pegmatite crystallization. Although uraninite-bearing granite pegmatites are common, clarkeite is rare and occurs intimately intergrown with other uranium minerals.
It is known from only two localities; the Spruce Pine pegmatite district in western North Carolina, US, and Rajputana, in the Ajmer district, India. Clarkeite is the only known naturally occurring high-temperature uranate. The general formula for ideal clarkeite is Na[(UO2)O(OH)](H2O)0–1.
It was named for Frank Wigglesworth Clarke (1847–1931), American mineral chemist, and former chief chemist of the United States Geological Survey.
Read More About Clarkeite / Source
Claudetite
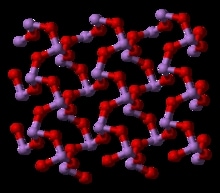
Claudetite is an arsenic oxide mineral with chemical formula As2O3. Claudetite is formed as an oxidation product of arsenic sulfides and is colorless or white. It can be associated with arsenolite (the cubic form of As2O3) as well as realgar (As4S4), orpiment (As2S3) and native sulfur.It was first described in 1868 for an occurrence in the San Domingo mines, Algarve, Portugal. It was first described by and named for the French chemist Frederick Claudet.
Read More About Claudetite / Source
Clausthalite

Clausthalite is a lead selenide mineral, PbSe. It forms a solid solution series with galena PbS.
Read More About Clausthalite / Source
Clearcreekite
Clearcreekite is a carbonate mineral, polymorphous with peterbaylissite. The chemical formula of clearcreekite is Hg1+3CO3(OH)∙2H2O. It has a pale greenish yellow color and streak with tabular subhedral crystals and good cleavage on {001}. It is transparent with vitreous luster and uneven fracture. Its density (calculated from the idealized formula) is 6.96 g/cm3. The mineral is monoclinic with the space group P2/c. Clearcreekite is an extremely rare mineral from the Clear Creek mercury mine, New Idria district, San Benito County, California. It was probably formed after the alteration of other mercury minerals such as cinnabar. The mineral is named after the locality where it was found.
Read More About Clearcreekite / Source
Cleusonite
Cleusonite is a member of the crichtonite group of minerals with the chemical formula (Pb,Sr)(U4+,U6+)(Fe2+,Zn)2(Ti,Fe2+,Fe3+)18(O,OH)38. This group of minerals contains approximately thirteen complex metal titanates. The structures of minerals of this group is complicated by frequent fine-scale twinning and metamictization due to radioactive elements. The crichtonite group consists of members of related mineral species of the type A{BC2D6E12}O38 which are characterized by their predominant cations (as seen in crichtonite (Sr), senaite (Pb), davidite (REE + U), landauite (Na), loveringite (Ca), lindsleyite (Ba), and mathiasite (K).
Read More About Cleusonite / Source
Clinoclase

Clinoclase is a hydrous copper arsenate mineral, Cu3AsO4(OH)3. Clinoclase is a rare secondary copper mineral and forms acicular crystals in the fractured weathered zone above copper sulfide deposits. It occurs in vitreous, translucent dark blue to dark greenish blue colored crystals and botryoidal masses. The crystal system is monoclinic 2/m. It has a hardness of 2.5 – 3 and a relative density of 4.3. Associated minerals include malachite, olivenite, quartz, limonite, adamite, azurite, and brochantite among others.
Clinoclase was discovered in 1830 in the county of Cornwall in England. Found at Broken Hill New South Wales, Australia and associated with copper ore deposits in Arizona, California, Montana, New Mexico, Nevada, and Utah in the United States. Also found in France, Germany, Czech Republic, Austria, Romania, Russia, and The Democratic Republic of The Congo.
Abichite is another name for clinoclase.
The type locality for clinoclase is the Wheal Gorland mine at St Day, Cornwall in the United Kingdom.
Read More About Clinoclase / Source
Clinohedrite
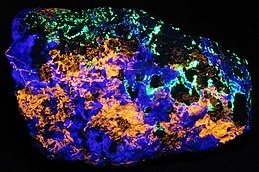
Clinohedrite is a rare silicate mineral. Its chemical composition is a hydrous calcium-zinc silicate; CaZn(SiO4)·H2O. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and typically occurs as veinlets and fracture coatings. It is commonly colorless, white to pale amethyst in color. It has perfect cleavage and the crystalline habit has a brilliant luster. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 3.28 – 3.33.Under short wave ultraviolet light it fluoresces a rich orange color. It is frequently associated with minerals such as hardystonite (fluoresces violet blue), esperite (fluoresces bright yellow), calcite (fluoresces orange-red), franklinite (non-fluorescent) and willemite (fluoresces green).Clinohedrite was found primarily at the Franklin zinc mines in New Jersey, the type locality, but has also been reported from the Christmas mine, Gila County, Arizona, and the Western Quinling gold belt, Gansu Province, China.It was first described in 1898 and was named for its crystal morphology from the Greek klino for incline, and hedra for face.
Read More About Clinohedrite / Source
Clinohumite

Clinohumite is an uncommon member of the humite group, a magnesium silicate according to the chemical formula (Mg, Fe)9(SiO4)4(F,OH)2. The formula can be thought of as four olivine (Mg2SiO4), plus one brucite (Mg(OH)2). Indeed, the mineral is essentially a hydrated olivine and occurs in altered ultramafic rocks and carbonatites. Most commonly found as tiny indistinct grains, large euhedral clinohumite crystals are sought by collectors and occasionally fashioned into bright, yellow-orange gemstones. Only two sources of gem-quality material are known: the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan, and the Taymyr region of northern Siberia. It is one of two humite group minerals that have been cut into gems, the other being the much more common chondrodite.
Read More About Clinohumite / Source
Clinoptilolite

Clinoptilolite is a natural zeolite composed of a microporous arrangement of silica and alumina tetrahedra. It has the complex formula (Na,K,Ca)2–3Al3(Al,Si)2Si13O36•12H2O. It forms as white, green to reddish tabular monoclinic tectosilicate crystals with a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 2.1 to 2.2. It commonly occurs as a devitrification product of volcanic glass shards in tuff and as vesicle fillings in basalts, andesites and rhyolites. It was described in 1969 from an occurrence in the Barstow Formation, San Bernardino County, California. Sodium levels in clinoptilolite are generally higher than potassium levels, as is the case with the San Bernardino Barstow Formation, but there are sources that are potassium-rich and have minimal sodium.It forms a series with heulandite:
Clinoptilolite-Ca – heulandite-Ca solid solution series
Clinoptilolite-K – heulandite-K solid solution series
Clinoptilolite-Na – heulandite-Na solid solution seriesUse of clinoptilolite in industry and academia focuses on its ion exchange properties having a strong exchange affinity for ammonium (NH4+). A typical example of this is in its use as an enzyme-based urea sensor.The name is derived from the Greek words klino (κλίνω; “oblique”), ptylon (φτερών; “feather”), and lithos (λίθος; “stone”).
Read More About Clinoptilolite / Source
Clinozoisite

Clinozoisite is a complex calcium aluminium sorosilicate mineral with formula: Ca2Al3(Si2O7)(SiO4)O(OH). It forms a continuous solid solution series with epidote by substitution of iron(III) in the aluminium (m3 site) and is also called aluminium epidote.Clinothulite is a manganese bearing variety with a pinkish hue due to substitution of Mn(III) in the aluminium site.It was originally discovered in 1896 in East Tyrol, Austria, and is so-named because of its resemblance to zoisite and its monoclinic crystal structure.It occurs in rocks which have undergone low to medium grade regional metamorphism and in contact metamorphism of high calcium sedimentary rocks. It also occurs in saussurite alteration
of plagioclase.Jadeite bearing pyroxene minerals have suggested Clinozoisite and paragonite are associated and derived from lawsonite releasing Quartz and water via the following reaction:
4
CaAl
2
Si
2
O
8
(
H
2
O
)
2
+
NaAlSi
2
O
6
↽
−
−
⇀
2
Ca
2
Al
3
Si
3
O
12
(
OH
)
+
NaAl
3
Si
3
O
10
(
OH
)
2
+
SiO
2
+
6
H
2
O
{displaystyle {ce {4CaAl2Si2O8(H2O)2 + NaAlSi2O6 <=> 2Ca2Al3Si3O12(OH) + NaAl3Si3O10(OH)2 + SiO2 + 6H2O}}}
Read More About Clinozoisite / Source
Clintonite

Clintonite is a calcium magnesium aluminium phyllosilicate mineral. It is a member of the margarite group of micas and the subgroup often referred to as the “brittle” micas. Clintonite has the chemical formulaCa(Mg,Al)3(Al3Si)O10(OH)2. Like other micas and chlorites, clintonite is monoclinic in crystal form and has a perfect basal cleavage parallel to the flat surface of the plates or scales. The Mohs hardness of clintonite is 6.5, and the specific gravity is 3.0 to 3.1. It occurs as variably colored, colorless, green, yellow, red, to reddish-brown masses and radial clusters.
The brittle micas differ chemically from the micas in containing less silica and no alkalis, and from the chlorites in containing much less water; in many respects, they are intermediate between the micas and chlorites. Clintonite and its iron-rich variety xanthophyllite are sometimes considered the calcium analogues of the phlogopites.Typical formation environment is in serpentinized Dolomitic limestone and contact metamorphosed skarns. It occurs with talc, spinel, grossular, vesuvianite, clinopyroxene, monticellite, chondrodite, phlogopite, chlorite, quartz, calcite and dolomite.Clintonite was first described in 1843 for an occurrence in Orange County, New York. It was named for De Witt Clinton (1769–1828).
Read More About Clintonite / Source
Cobaltite

Cobaltite is a sulfide mineral composed of cobalt, arsenic, and sulfur, CoAsS. Its impurities may contain up to 10% iron and variable amounts of nickel. Structurally, it resembles pyrite (FeS2) with one of the sulfur atoms replaced by an arsenic atom.
Although rare, it is mined as a significant source of the strategically important metal cobalt. Secondary weathering incrustations of erythrite, hydrated cobalt arsenate, are common. A variety containing much iron replacing cobalt, and known as ferrocobaltite (German: Stahlkobalt), was found at Siegen in Westphalia.The name is from the German, Kobold, “underground spirit” in allusion to the “refusal” of cobaltiferous ores to smelt as they are expected to, including the foul-smelling, poisonous fumes the ores gave off. Cobaltite, which contains both arsenic and sulfur, was one of these ores.
It occurs in high-temperature hydrothermal deposits and contact metamorphic rocks. It occurs in association with magnetite, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, skutterudite, allanite, zoisite, scapolite, titanite, and calcite along with numerous other Co–Ni sulfides and arsenides. It was described as early as 1832.It is found chiefly in Sweden, Norway, Germany, Cornwall, England, Canada, La Cobaltera, Chile, Australia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Morocco. Crystals have also been found at Khetri in Rajasthan, and under the name sehta the mineral was used by Indian jewellers for producing a blue enamel on gold and silver ornaments.Cobaltite can be separated from other minerals by selective, pH controlled, flotation methods, where cobalt recovery usually involves hydrometallurgy. It can also be processed with pyrometallurgical methods, such as flash smelting.
Read More About Cobaltite / Source
Coccinite

Coccinite is a rare mercury iodide mineral with chemical formula of HgI2, mercury(II) iodide.
It was first discovered in Casas Viejas, Mexico; it has also been reported from Broken Hill, New South Wales, and from a uranium mine in Thuringia and old mercury workings in the Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany. At the Thuringia deposit the mineral occurs as a sublimation product resulting from fires associated with pyrite-bearing graptolitic slate.
Read More About Coccinite / Source
Coconinoite

Coconinoite is a uranium ore that was discovered in Coconino County, Arizona. It is a phosphate mineral; or uranyl phosphate mineral along with other subclass uranium U6+ minerals like blatonite, boltwoodite, metazeunerite and rutherfordine.
Read More About Coconinoite / Source
Coesite
Coesite is a form (polymorph) of silicon dioxide Si O2 that is formed when very high pressure (2–3 gigapascals), and moderately high temperature (700 °C, 1,300 °F), are applied to quartz. Coesite was first synthesized by Loring Coes Jr., a chemist at the Norton Company, in 1953.
Read More About Coesite / Source
Coffinite

Coffinite is a uranium-bearing silicate mineral with formula: U(SiO4)1−x(OH)4x.
It occurs as black incrustations, dark to pale-brown in thin section. It has a grayish-black streak. It has a brittle to conchoidal fracture. The hardness of coffinite is between 5 and 6.
It was first described in 1954 for an occurrence at the La Sal No. 2 Mine, Beaver Mesa, Mesa County, Colorado, US, and named for American geologist Reuben Clare Coffin (1886–1972).
It has widespread global occurrence in Colorado Plateau-type uranium ore deposits of uranium and vanadium. It replaces organic matter in sandstone and in hydrothermal vein type deposits. It occurs in association with uraninite, thorite, pyrite, marcasite, roscoelite, clay minerals and amorphous organic matter.
Read More About Coffinite / Source
Cohenite
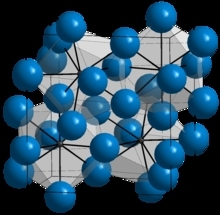
Cohenite is a naturally occurring iron carbide mineral with the chemical structure (Fe, Ni, Co)3C. This forms a hard, shiny, silver mineral which was named by E. Weinschenk in 1889 after the German mineralogist Emil Cohen, who first described and analysed material from the Magura meteorite found near Slanica, Žilina Region, Slovakia. Cohenite is found in rod-like crystals in iron meteorites.On Earth cohenite is stable only in rocks which formed in a strongly reducing environment and contain native iron deposits. Such conditions existed in some places where molten magmas invaded coal deposits, e.g. on Disko Island in Greenland, or at the Bühl near Kassel in Germany.Associated minerals include native iron, schreibersite, troilite and wustite.Similar iron carbides occur also in technical iron alloys and are called cementite.
Read More About Cohenite / Source
Colemanite

Colemanite (Ca2B6O11·5H2O) or (CaB3O4(OH)3·H2O) is a borate mineral found in evaporite deposits of alkaline lacustrine environments. Colemanite is a secondary mineral that forms by alteration of borax and ulexite.It was first described in 1884 for an occurrence near Furnace Creek in Death Valley and was named after William Tell Coleman (1824–1893), owner of the mine “Harmony Borax Works” where it was first found. At the time, Coleman had alternatively proposed the name “smithite” instead after his business associate Francis Marion Smith.
Read More About Colemanite / Source
Colimaite
Colimaite, the naturally occurring analog of synthetic K3VS4, is a sulfide mineral discovered in southwestern Mexico. The potassium-vanadium sulfide was collected from the crater of the Colima volcano. The mineral colimaite is named after the locality of this volcano and has been approved in 2007, along with its mineral name, by the Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification (CNMNC). It has been given the International Mineralogical Association number of IMA 2007–045.
Read More About Colimaite / Source
Collinsite

Collinsite is a mineral with chemical formula Ca2(Mg,Fe2+)(PO4)2•2H2O. It was discovered in British Columbia, Canada, and formally described in 1927. It was named in honor of William Henry Collins (1878–1937), director of the Geological Survey of Canada. There are three varieties of the mineral: magnesian collinsite, zincian collinsite, and strontian collinsite. The crystal structure consists of polyhedral chains linked by weak hydrogen bonds.
Read More About Collinsite / Source
Coloradoite

Coloradoite, also known as mercury telluride (HgTe), is a rare telluride ore associated with metallic deposit (especially gold and silver). Gold usually occurs within tellurides, such as coloradoite, as a high-finess native metal.The quest for mining led to the discovery of telluride ores which were found to be associated with metals. Tellurides are ingrown into ores containing these precious metals and are also responsible for a significant amount of these metals being produced. Coloradoite, a member of the coordination subclass of tellurides, is a covalent compound that is isostructural with sphalerite (ZnS). Its chemical properties are highly instrumental in distinguishing it from other tellurides. It was first discovered in Colorado in 1877. Since then, other deposits have been found. Although it plays an important role in the geology of minerals, it can also be used for other purposes.
Read More About Coloradoite / Source
Columbite

Columbite, also called niobite, niobite-tantalite and columbate, of general chemical formula (FeII,MnII)Nb2O6, is a black mineral group that is an ore of niobium. It has a submetallic luster and a high density and is a niobate of iron and manganese. This mineral group was first found in Haddam, Connecticut, in the United States. It forms a series with the tantalum-dominant analogue ferrotantalite and one with the manganese-dominant analogue manganocolumbite. The iron-rich member of the columbite group is ferrocolumbite. Some tin and tungsten may be present in the mineral. Yttrocolumbite is the yttrium-rich columbite with the formula (Y,U,Fe)(Nb,Ta)O4. It is a radioactive mineral found in Mozambique.
Columbite has the same composition and crystal symmetry (orthorhombic) as tantalite. In fact, the two are often grouped together as a semi-singular mineral series called columbite-tantalite or coltan in many mineral guides. However, tantalite has a much greater specific gravity than columbite, more than 8.0 compared to columbite’s 5.2.Columbite is also very similar to tapiolite. Those minerals have the same chemical composition but different crystal symmetry: orthorhombic for columbite and tetragonal for tapiolite. The largest documented single crystal of columbite consisted of plates 6 mm (0.24 in) thick measuring 76 cm × 61 cm (30 in × 24 in).Columbite contains varying amounts of thorium and uranium, which makes it radioactive to various degrees.
Read More About Columbite / Source
Combeite

Combeite is a rare silicate mineral with the formula Na2Ca2Si3O9. It has a trigonal crystal system.
Read More About Combeite / Source
Conichalcite

Conichalcite, CaCu(AsO4)(OH), is a relatively common arsenate mineral related to duftite (PbCu(AsO4)(OH)). It is green, often botryoidal, and occurs in the oxidation zone of some metal deposits. It occurs with limonite, malachite, beudantite, adamite, cuproadamite, olivenite and smithsonite.
Read More About Conichalcite / Source
Connellite

Connellite is a rare mineral species, a hydrous copper chloro-sulfate, Cu19(OH)32(SO4)Cl4·3H2O, crystallizing in the hexagonal system. It occurs as tufts of very delicate acicular crystals of a fine blue color, and is associated with other copper minerals of secondary origin, such as cuprite and malachite. Its occurrence in Cornwall, England, was noted by Philip Rashleigh in 1802, and it was first examined chemically by Prof Arthur Connell FRSE in 1847, after whom it is named.The type locality is Wheal Providence at Carbis Bay in Cornwall. Outside Cornwall it has been found in over 200 locations worldwide including Namaqualand in South Africa and at Bisbee, Arizona (US).
Read More About Connellite / Source
Cooperite

Cooperite is a grey mineral consisting of platinum sulfide (PtS), generally in combinations with sulfides of other elements such as palladium and nickel (PdS and NiS). Its general formula is (Pt,Pd,Ni)S. It is a dimorph of braggite.It is mined as an ore of platinum and platinum group metals such as palladium. It occurs in South Africa in minable quantities and an old mine near Mount Washington on Vancouver Island.It was first described in 1928 for occurrences in the Bushveld Igneous Complex and named after South African metallurgist Richard A. Cooper who first characterized it.
Read More About Cooperite / Source
Copiapite

Copiapite is a hydrated iron sulfate mineral with formula: Fe2+Fe3+4(SO4)6(OH)2·20(H2O). Copiapite can also refer to a mineral group, the copiapite group.
Copiapite is strictly a secondary mineral forming from the weathering or oxidation of iron sulfide minerals or sulfide-rich coal. Its most common occurrence is as the end member mineral from the rapid oxidation of pyrite. It also occurs rarely with fumaroles. It occurs with melanterite, alunogen, fibroferrite, halotrichite, botryogen, butlerite and amarantite. It is by far the most common mineral in the copiapite group.
It rarely occurs as single crystals, is in the triclinic crystal system, and is pale to bright yellow. It is soluble in water, changing the water color to deep orange or orangish-red. In solution copiapite is very acidic. In high concentrations a negative pH can occur, as reported in waters draining from Richmond Mine at Iron Mountain, California. Copiapite can easily be distinguished from native sulfur because it does not give off an odor when dissolved in water. It can be distinguished from similar appearing uranium minerals, such as carnotite, by its lack of radioactivity. The only way to differentiate between the minerals in the copiapite group is by X-ray diffraction.
Copiapite was first described in 1833 for an occurrence near Copiapó, Atacama, Chile. It is sometimes known as yellow copperas. Other occurrences are in California, Nevada, and in the filled paleo sinkholes and caves of Missouri.
Read More About Copiapite / Source
Native copper

Native copper is an uncombined form of copper that occurs as a natural mineral. Copper is one of the few metallic elements to occur in native form, although it most commonly occurs in oxidized states and mixed with other elements. Native copper was an important ore of copper in historic times and was used by pre-historic peoples.
Native copper occurs rarely as isometric cubic and octahedral crystals, but more typically as irregular masses and fracture fillings. It has a reddish, orangish, and/or brownish color on fresh surfaces, but typically is weathered and coated with a green tarnish of copper(II) carbonate (also known as patina or verdigris). Its specific gravity is 8.9 and its hardness is 2.5–3.The mines of the Keweenaw native copper deposits of Upper Michigan were major copper producers in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and are the largest deposits of native copper in the world. Native Americans mined copper on a small scale at this and many other locations, and evidence exists of copper trading routes throughout North America among native peoples, proven by isotopic analysis. The first commercial mines in the Keweenaw Peninsula (which is nicknamed the “Copper Country” and “Copper Island”) opened in the 1840s. Isle Royale in western Lake Superior was also a site of many tons of native copper. Some of it was extracted by native peoples, but only one of several commercial attempts at mining turned a profit there. An archived record of native copper originally found up river from Lake Superior, on the west branch of the Ontonagon River, via being dragged by a glacier is seen in the Ontonagon Boulder now in the possession of the Department of Mineral Sciences, National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution.
Another major native copper deposit is in Coro Coro, Bolivia.
The name copper comes from the Greek kyprios, “of Cyprus”, the location of copper mines since pre-historic times.
Read More About Native copper / Source
Corderoite

Corderoite is an extremely rare mercury sulfide chloride mineral with formula Hg3S2Cl2. It crystallizes in the isometric crystal system. It is soft, 1.5 to 2 on the Mohs scale, and varies in color from light gray to black and rarely pink or yellow.
It was first described in 1974 for occurrences in the McDermitt Mercury mine in Humboldt County, Nevada. The name is from the old name of the mine, the Old Cordero Mine.
Read More About Corderoite / Source
Cordierite

Cordierite (mineralogy) or iolite (gemology) is a magnesium iron aluminium cyclosilicate. Iron is almost always present and a solid solution exists between Mg-rich cordierite and Fe-rich sekaninaite with a series formula: (Mg,Fe)2Al3(Si5AlO18) to (Fe,Mg)2Al3(Si5AlO18). A high-temperature polymorph exists, indialite, which is isostructural with beryl and has a random distribution of Al in the (Si,Al)6O18 rings.
Read More About Cordierite / Source
Corkite

Corkite is a phosphate mineral in the beudantite subgroup of the alunite group. Corkite is the phosphate analogue of beudantite and with it, a complete solid solution range exists. Corkite will also form a solid solution with kintoreite.
Corkite is named after County Cork, Ireland; the location where the first notable amount was discovered in 1869. Like many of the other minerals in the beudantite group, corkite is a relatively uncommon, secondary mineral that occurs in oxidation zones near hydrothermal base metal deposits. It occurs associated with pyromorphite, malachite, plumbojarosite, limonite and quartz.
Read More About Corkite / Source
Cornubite

Cornubite is a rare secondary copper arsenate mineral with formula: Cu5(AsO4)2(OH)4. It was first described for its discovery in 1958 in Wheal Carpenter, Gwinear, Cornwall, England, UK. The name is from Cornubia, the medieval Latin name for Cornwall. It is a dimorph of Cornwallite, and the arsenic analogue of pseudomalachite.
Read More About Cornubite / Source
Cornwallite

Cornwallite is an uncommon copper arsenate mineral with formula Cu5(AsO4)2(OH)4. It forms a series with the phosphate pseudomalachite and is a dimorph of the triclinic cornubite. It is a green monoclinic mineral which forms as radial to fibrous encrustations.
Read More About Cornwallite / Source
Corundum

Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange.
The name “corundum” is derived from the Tamil-Dravidian word kurundam (ruby-sapphire) (appearing in Sanskrit as kuruvinda).Because of corundum’s hardness (pure corundum is defined to have 9.0 on the Mohs scale), it can scratch almost all other minerals. It is commonly used as an abrasive on sandpaper and on large tools used in machining metals, plastics, and wood. Emery, a variety of corundum with no value as a gemstone, is commonly used as an abrasive. It is a black granular form of corundum, in which the mineral is intimately mixed with magnetite, hematite, or hercynite.In addition to its hardness, corundum has a density of 4.02 g/cm3 (251 lb/cu ft), which is unusually high for a transparent mineral composed of the low-atomic mass elements aluminium and oxygen.
Read More About Corundum / Source
Cotunnite

Cotunnite is the natural mineral form of lead(II) chloride (PbCl2). Unlike the pure compound, which is white, cotunnite can be white, yellow, or green. The density of mineral samples spans range 5.3–5.8 g/cm3. The hardness on the Mohs scale is 1.5–2. The crystal structure is orthorhombic dipyramidal and the point group is 2/m 2/m 2/m. Each Pb has a coordination number of 9. Cotunnite occurs near volcanoes: Vesuvius, Italy; Tarapacá, Chile; and Tolbachik, Russia.It was first described in 1825 from an occurrence on Mount Vesuvius, Naples Province, Campania, Italy. It was named for Domenico Cotugno (Cotunnius) (1736–1822), Italian physician and Professor of Anatomy.It was first recognized in volcanic fumarole deposits. It occurs as a secondary alteration product in lead ore deposits. It has also been reported as an alteration of archaeological objects that contain lead.It occurs in association with galena, cerussite, anglesite and matlockite in the Caracoles, Chile. At the Tolbachik volcano on the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia it occurs with the rare to uncommon minerals tenorite, ponomarevite, sofiite, burnsite, ilinskite, georgbokite, chloromenite, halite, sylvite and native gold.
Read More About Cotunnite / Source
Covellite

Covellite (also known as covelline) is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is commonly a secondary mineral in limited abundance and although it is not an important ore of copper itself, it is well known to mineral collectors.The mineral is generally found in zones of secondary enrichment (supergene) of copper sulfide deposits. Commonly found as coatings on chalcocite, chalcopyrite, bornite, enargite, pyrite, and other sulfides, it often occurs as pseudomorphic replacements of other minerals. The first records are from Mount Vesuvius, formally named in 1832 after N. Covelli.
Read More About Covellite / Source
Coyoteite
Coyoteite is a hydrated sodium iron sulfide mineral. The mineral was named coyoteite after Coyote Peak near Orick, California where it was discovered (along with another rare mineral, orickite).This mineral is unstable under normal atmospheric conditions, making it rare at the surface. The mineral was first described in a petrographic study of a sample of a mafic diatreme at Coyote Peak. The largest piece of coyoteite found on that specimen has the dimensions of 0.2 × 0.4 mm.
Read More About Coyoteite / Source
Creedite

Creedite is a calcium aluminium sulfate fluoro hydroxide mineral with formula: Ca3Al2SO4(F,OH)10·2(H2O). Creedite forms colorless to white to purple monoclinic prismatic crystals. It often occurs as acicular radiating sprays of fine prisms. It is translucent to transparent with indices of refraction of nα = 1.461 nβ = 1.478 nγ = 1.485. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 2.7.
Creedite was first described in 1916 from the Creede Quadrangle in Mineral County, Colorado. It is a product of intense oxidation of ore deposits.
Read More About Creedite / Source
Cristobalite

Cristobalite is a mineral polymorph of silica that is formed at very high temperatures. It has the same chemical formula as quartz, SiO2, but a distinct crystal structure. Both quartz and cristobalite are polymorphs with all the members of the quartz group, which also include coesite, tridymite and stishovite. It is named after Cerro San Cristóbal in Pachuca Municipality, Hidalgo, Mexico.
It is used in dentistry as a component of alginate impression materials as well as for making models of teeth.
Read More About Cristobalite / Source
Crocoite

Crocoite is a mineral consisting of lead chromate, PbCrO4, and crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system. It is identical in composition with the artificial product chrome yellow used as a paint pigment.
Read More About Crocoite / Source
Cronstedtite

Cronstedtite is a complex iron silicate mineral belonging to the serpentine group of minerals. Its chemical formula is Fe2+2Fe3+(Si,Fe3+O5)(OH)4.
It was discovered in 1821 and named in honor of Swedish mineralogist Axel Fredrik Cronstedt (1722–1765). It has been found in Bohemia in the Czech Republic and in Cornwall, England.
Cronstedtite is a major constituent of CM chondrites, a carbonaceous chondrite group exhibiting varying degrees of aqueous alteration. Cronstedtite abundance decreases with increasing alteration.
Read More About Cronstedtite / Source
Crookesite

Crookesite is a selenide mineral composed of copper and selenium with variable thallium and silver.
Read More About Crookesite / Source
Crossite

Crossite is an inosilicate double chain sodic amphibole and is a rare silicate mineral belonging to the riebeckite group. It is considered an intermediate between the amphiboles glaucophane and magnesioriebeckite, which form a series. IMA status: discredited 1997.
Crossite is named after Charles Whitman Cross, an American USGS petrologist.
Read More About Crossite / Source
Cryolite

Cryolite (Na3AlF6, sodium hexafluoroaluminate) is an uncommon mineral identified with the once-large deposit at Ivittuut on the west coast of Greenland, mined commercially until 1987.
Read More About Cryolite / Source
Cryptomelane

Cryptomelane is a potassium manganese oxide mineral with formula K(Mn4+,Mn2+)8O16.
In 1942 the name cryptomelane was proposed as part of an effort to sort out the manganese oxide minerals referred to as psilomelane. Cryptomelane was identified and defined based on X-ray diffraction studies of samples from Tombstone, Arizona; Deming, New Mexico; Mena, Arkansas; and Philipsburg, Montana.Cryptomelane was approved in 1982 by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA). The type locality is the Tombstone District, Cochise County, Arizona, US. The name comes from the Greek for hidden and black, in reference to the confusion and difficulty in recognition of the various black manganese oxide minerals referred to as psilomelane, the collective term for hard manganese oxides.It is of rather common occurrence in oxidized manganese deposits where it occurs as replacements and open space fillings in veins and vugs. It occurs in association with pyrolusite, nsutite, braunite, chalcophanite, manganite and various other manganese oxides.
Read More About Cryptomelane / Source
Cubanite

Cubanite is a copper iron sulfide mineral that commonly occurs as a minor alteration mineral in magmatic sulfide deposits. It has the chemical formula CuFe2S3 and when found, it has a bronze to brass-yellow appearance. On the Mohs hardness scale, cubanite falls between 3.5 and 4 and has a orthorhombic crystal system. Cubanite is chemically similar to chalcopyrite, however it is the less common copper iron sulfide mineral due to crystallization requirements.
Cubanite occurs in high temperature hydrothermal mineral deposits with pyrrhotite and pentlandite as intergrowths with chalcopyrite. It results from exsolution from chalcopyrite at temperatures below 200 to 210 °C. If cubanite is exposed to temperatures above 210 °C, it will transform into isocubanite. After this transformation, if it begins to cool, it will not revert to cubanite. Upon its transformation to isocubanite it will lose its highly magnetic property due to its change from an orthorhombic to a cubic crystal structure. Cubanite has been identified on chondrites and within dust grain samples and has improved the precision of copper isotope analysis.
Read More About Cubanite / Source
Cumengeite

Cumengeite, also known as cumengite, is a secondary mineral that was named after mining engineer Bernard Louis Philippe Édouard Cumenge, who found the first specimens. It is easily confused with diaboleite. It is a valid species that was first described prior to 1959, and is grandfathered now, but it has been a valid species since 1893, since pre-IMA. It is the hydroxychloride of lead and copper.
Read More About Cumengeite / Source
Cummingtonite

Cummingtonite ( KUM-ing-tə-nyte) is a metamorphic amphibole with the chemical composition (Mg,Fe2+)2(Mg,Fe2+)5Si8O22(OH)2, magnesium iron silicate hydroxide.
Monoclinic cummingtonite is compositionally similar and polymorphic with orthorhombic anthophyllite, which is a much more common form of magnesium-rich amphibole, the latter being metastable.
Cummingtonite shares few compositional similarities with alkali amphiboles such as arfvedsonite, glaucophane-riebeckite. There is little solubility between these minerals due to different crystal habit and inability of substitution between alkali elements and ferro-magnesian elements within the amphibole structure.
Read More About Cummingtonite / Source
Cupalite
Cupalite is a rare mineral which is mostly composed of copper and aluminium, but might contain up to several percent of zinc or iron; its chemical structure is therefore described by an approximate formula (Cu,Zn)Al or (Cu,Fe)Al. It was discovered in 1985 in placers derived from serpentine, in association with another rare mineral khatyrkite (CuAl2). Both minerals are thus far restricted to the area of the Iomrautvaam, in the Khatyrka ultramafic (silicon-poor) zone of the Koryak–Kamchatka fold area, Koryak Mountains, Anadyrsky District, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia. The mineral name derives from cuprum (Latin for copper) and aluminium. Its holotype (defining sample) is preserved in the Mining Museum in Saint Petersburg, and parts of it can be found in other museums, such as Museo di Storia Naturale di Firenze.
Read More About Cupalite / Source
Cuprite

Cuprite is an oxide mineral composed of copper(I) oxide Cu2O, and is a minor ore of copper.
Its dark crystals with red internal reflections are in the isometric system hexoctahedral class, appearing as cubic, octahedral, or dodecahedral forms, or in combinations. Penetration twins frequently occur. In spite of its nice color, it is rarely used for jewelry because of its low Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4. It has a relatively high specific gravity of 6.1, imperfect cleavage and is brittle to conchoidal fracture. The luster is sub-metallic to brilliant adamantine. The “chalcotrichite” (from Ancient Greek: χαλκός θρίξ τριχός, “plush copper ore”) variety typically shows greatly elongated (parallel to [001]) capillary or needle like crystals forms.
It is a secondary mineral which forms in the oxidized zone of copper sulfide deposits. It frequently occurs in association with native copper, azurite, chrysocolla, malachite, tenorite and a variety of iron oxide minerals. It is known as ruby copper due to its distinctive red color.
Cuprite was first described by Wilhelm Karl Ritter von Haidinger in 1845 and the name derives from the Latin cuprum for its copper content.Cuprite is found in the Ural Mountains, Altai Mountains, and Sardinia, and in more isolated locations in Cornwall, France, Arizona, Chile, Bolivia, and Namibia.
Read More About Cuprite / Source
Cuprosklodowskite

Cuprosklodowskite is a secondary uranium mineral formed by alteration of earlier uranium minerals. Its empirical formula is Cu(UO2)2(HSiO4)2·6(H2O). Cuprosklodowskite is a nesosilicate mineral, It is grass green to dark green in color, and its crystal habit is typically acicular, flat bladed crystals. It is a strongly radioactive mineral.
Cuprosklodowskite was discovered in 1933 at the Kalongwe deposit in (then) Katanga province, Belgian Congo, the type locality. It was named in the mistaken belief that the mineral was the copper analogue of sklodowskite, which in turn was named for Marie Skłodowska Curie (1867–1934).
It occurs in association with becquerelite, brochantite, uranophane, kasolite, vandenbrandeite, liebigite
and compreignacite.
Read More About Cuprosklodowskite / Source
Cuprospinel
Cuprospinel is a mineral. Cuprospinel is an inverse spinel with the chemical formula CuFe2O4, where copper substitutes some of the iron cations in the structure. Its structure is similar to that of magnetite, Fe3O4, yet with slightly different chemical and physical properties due to the presence of copper.
The type locality of cuprospinel is Baie Verte, Newfoundland, Canada, where the mineral was found in an exposed ore dump. The mineral was first characterized by Ernest Henry Nickel, a mineralogist with the Department of Energy, Mines and Resources in Australia, in 1973. Cuprospinel is also found in other places, for example, in Hubei province, China and at Tolbachik volcano in Kamchatka, Russia.
Read More About Cuprospinel / Source
Curite

Curite is a lead uranium oxide mineral with formula: Pb3(UO2)8O8(OH)6·3(H2O). It is named after the physicists Marie and Pierre Curie, who are both known for their work on radioactivity. The type locality is the Shinkolobwe Mine.
Read More About Curite / Source
Cuspidine

Cuspidine is a fluorine bearing calcium silicate mineral (sorosilicate) with formula: Ca4(Si2O7)(F,OH)2. Cuspidine crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system and occurs as acicular to spear shaped pale red to light brown crystals. It is a member of the wöhlerite group.
Cuspidine was first described in 1876 for an occurrence in Monte Somma, Italy. The name is from the Greek cuspis for spear from its characteristic crystal form. Cuspidine occurs as crystals in tuff from Monte Somma. In the Franklin, New Jersey mine area it occurs in contact metamorphosed limestone. In Dupezeh Mountain, Iraq, it occurs in melilite bearing skarn. Associated minerals include augite, hornblende, diopside, grossular, biotite, phlogopite, monticellite, wollastonite, calcite, spinel, magnetite and perovskite.
Read More About Cuspidine / Source
Cyanotrichite

Cyanotrichite is a hydrous copper aluminium sulfate mineral with formula Cu4Al2[(OH)12|SO4]·2H2O, also known as lettsomite. Cyanotrichite forms velvety radial acicular crystal aggregates of extremely fine fibers. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and forms translucent bright blue acicular crystal clusters or drusey coatings. The Mohs hardness is 2 and the specific gravity ranges from 2.74 to 2.95. Refractive indices are nα=1.588 nβ=1.617 nγ=1.655.
Read More About Cyanotrichite / Source
Cylindrite

Cylindrite is a sulfosalt mineral containing tin, lead, antimony and iron with formula: Pb3Sn4FeSb2S14. It forms triclinic pinacoidal crystals which often occur as tubes or cylinders which are in fact rolled sheets. It has a black to lead grey metallic colour with a Mohs hardness of 2 to 3 and a specific gravity of 5.4.
It was first discovered in the Santa Cruz mine, Oruro Department, Bolivia in 1893. The name arises from its curious cylindrical crystal which it forms almost uniquely among minerals.
Read More About Cylindrite / Source
Cymrite

Cymrite is a silicate mineral with the chemical formula BaAl2Si2(O,OH)8·H2O. The mineral is named for Cymru, which is the Welsh word for Wales.Cymrite, with perfect cleavage and a monoclinic crystalline system, falls in the silicate group. Silicates are formed of Silicon and Oxygen bonding together to form tetrahedra. The symmetry of Cymrite is classified as having a mirror plane. It has a moderate relief, meaning the contrast between the mineral and the epoxy of a thin section makes cymrite easily visible. The birefringence of the mineral is 0.01. Cymrite, being monoclinic is anisotropic with two optic axes.
Read More About Cymrite / Source
Cyrilovite

Cyrilovite (NaFe33+(PO4)2(OH)4·2(H2O)) is a hydrous sodium iron phosphate mineral. It is isomorphous and isostructural with wardite, the sodium aluminium counterpart.Cyrilovite is found in granitic pegmatites. It was first discovered in 1953 in a pegmatite at Cyrilov, near Velké Meźiřiči, West Moravia, Czech Republic.
Read More About Cyrilovite / Source
Danalite

Danalite is an iron beryllium silicate sulfide mineral with formula: Fe2+4Be3(SiO4)3S.
It is a rare mineral which occurs in granites, tin bearing pegmatites, contact metamorphic skarns, gneisses and in hydrothermal deposits. It occurs in association with magnetite, garnet, fluorite, albite, cassiterite, pyrite, muscovite, arsenopyrite, quartz, and chlorite.Danalite was first described in 1866 from a deposit in Essex County, Massachusetts and named for American mineralogist James Dwight Dana (1813–1895).It has been found in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Sierra County, New Mexico; Yavapai County, Arizona; Needlepoint Mountain, British Columbia; Walrus Island, James Bay, Quebec; Sweden; Cornwall, England; Imalka and Transbaikal, Russia; Kazakhstan; Somalia; Tasmania; Western Australia and Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan.
Read More About Danalite / Source
Danburite

Danburite is a calcium boron silicate mineral with a chemical formula of CaB2(SiO4)2.It has a Mohs hardness of 7 to 7.5 and a specific gravity of 3.0. The mineral has an orthorhombic crystal form. It is usually colourless, like quartz, but can also be either pale yellow or yellowish-brown. It typically occurs in contact metamorphic rocks.
The Dana classification of minerals categorizes danburite as a sorosilicate, while the Strunz classification scheme lists it as a tectosilicate; its structure can be interpreted as either.
Its crystal symmetry and form are similar to topaz; however, topaz is a calcium fluorine bearing nesosilicate. The clarity, resilience, and strong dispersion of danburite make it valuable as cut stones for jewelry.
It is named for Danbury, Connecticut, United States, where it was first discovered in 1839 by Charles Upham Shephard.
Read More About Danburite / Source
Datolite

Datolite is a calcium boron hydroxide nesosilicate, CaBSiO4(OH). It was first observed by Jens Esmark in 1806, and named by him from δατεῖσθαι, “to divide,” and λίθος, “stone,” in allusion to the granular structure
of the massive mineral.Datolite crystallizes in the monoclinic system forming prismatic crystals and nodular masses. The luster is vitreous and may be brown, yellow, light green or colorless. The Mohs hardness is 5.5 and the specific gravity is 2.8 – 3.0.
The type localities are in the diabases of the Connecticut River valley and Arendal, Aust-Agder, Norway. Associated minerals include prehnite, danburite, babingtonite, epidote, native copper, calcite, quartz and zeolites. It is common in the copper deposits of the Lake Superior region of Michigan. It occurs as a secondary mineral in mafic igneous rocks often filling vesicles along with zeolites in basalt. Unlike most localities throughout the world, the occurrence of datolite in the Lake Superior region is usually fine grained in texture and possesses colored banding. Much of the coloration is due to the inclusion of copper or associated minerals in progressive stages of hydrothermal precipitation.
Botryolite is a botryoidal form of datolite.
Read More About Datolite / Source
Daubréeite
Daubréeite is a rare bismuth oxohalide mineral with formula BiO(OH,Cl). It is a creamy-white to yellow-brown, soft, earthy clay–like mineral which crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system. It is a member of the matlockite group.It was first described for an occurrence in the Constanicia mine, Tazna, Bolivia, in 1876. It was named for French mineralogist Gabriel Auguste Daubrée (1814–1896). At the Tanza location it occurs as a secondary mineral formed by the oxidation of native bismuth or bismuthinite. It occurs with clay minerals. In addition to its discovery location it has also been reported from the Tintic District in the East Tintic Mountains of Juab County, Utah; in the Josephine Creek District of Josephine County, Oregon; in the Manhattan District of Nye County, Nevada; and the Rio Marina Mine on Elba, Italy.
Read More About Daubréeite / Source
Daubréelite

Daubréelite is a rare sulfide mineral. It crystallizes with cubic symmetry and has chemical composition of Fe2+Cr3+2S4. It usually occurs as black platy aggregates.
Read More About Daubréelite / Source
Davemaoite
Davemaoite is a high-pressure calcium silicate perovskite (
CaSiO
3
{displaystyle {ce {CaSiO3}}}
) mineral with a distinctive cubic crystal structure. It is named after geophysicist Ho-kwang (Dave) Mao, who pioneered in many discoveries in high-pressure geochemistry and geophysics.It is one of three main minerals in Earth’s lower mantle, making up around 5–7% of the material there. Significantly, davemaoite can host uranium and thorium, radioactive isotopes which produce heat through radioactive decay and contribute greatly to heating within this region giving the material a major role in how heat flows deep below the earth’s surface.Davemaoite has been artificially synthesized in the laboratory, but was thought to be too extreme to exist in the Earth’s crust. Then in 2021, the mineral was discovered as specks within a diamond that formed between 660 and 900 km beneath the Earth’s surface, within the mantle. The diamond had been extracted from the Orapa diamond mine in Botswana. The discovery was made by focusing a high-energy beam of X-rays on precise spots within the diamond using a technique known as synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Subsequently, a reappraisal of the data from the Orapa diamond and its inclusion cast doubt on the attribution to calcium silicate perovskite. Instead, the data were reinterpreted in terms of a diamond from the shallow part of the mantle with inclusions of minerals commonly found in microinclusions.Calcium silicate is found in other forms, such as wollastonite in the crust and breyite in the middle and lower regions of the mantle. However, this version can exist only at very high pressure of around 200,000 times that found at Earth’s surface.
Read More About Davemaoite / Source
Davidite

Davidite is a rare earth oxide mineral with chemical end members La and Ce. It exists in two forms:
Davidite-(La) (La,Ce,Ca)(Y,U)(Ti,Fe3+)20O38 discovered at Radium Hill mine, South Australia in 1906 and named by Douglas Mawson for Australian geologist Tannatt William Edgeworth David (1858-1934).
Davidite-(Ce) (Ce,Le)(Y,U)(Ti,Fe3+)20O38 first described in 1960 from Vemork, Iveland, Norway.
Read More About Davidite / Source
Dawsonite

Dawsonite is a mineral composed of sodium aluminium carbonate hydroxide, chemical formula NaAlCO3(OH)2. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. It is not mined for ore. It was discovered in 1874 during the construction of the Redpath Museum in a feldspathic dike on the campus of McGill University on the Island of Montreal, Canada. It is named after geologist Sir John William Dawson (1820–1899).The type material is preserved in the collection of the Redpath Museum.
Read More About Dawsonite / Source
Delafossite

Delafossite is a copper iron oxide mineral with formula CuFeO2 or Cu1+Fe3+O2. It is a member of the delafossite mineral group, which has the general formula ABO2, a group characterized by sheets of linearly coordinated A cations stacked between edge-shared octahedral layers (BO6). Delafossite, along with other minerals of the ABO2 group, is known for its wide range of electrical properties, its conductivity varying from insulating to metallic. Delafossite is usually a secondary mineral that crystallizes in association with oxidized copper and rarely occurs as a primary mineral.
Read More About Delafossite / Source
Delvauxite
Delvauxite, also known as borickite, is a yellow to brown to dark brown amorphous mineral, sometimes forming a botryoidal mass. Its chemical formula is CaFe4(PO4,SO4)2(OH)8•(4-6)H2O. and it may sometimes form stalactites.
It was first described in 1838 by Belgian chemist, Dumont and dedicate to J.S.P.J. Delvaux de Fenffe (1782–1863). It was found in Bernau, Liege, Belgium and Stredocesky, Czech Republic.
Read More About Delvauxite / Source
Demesmaekerite

Demesmaekerite is a rare uranium selenite mineral with the chemical formula: Pb2Cu5(UO2)2(SeO3)6(OH)6·2H2O.
It is named after the Belgian mineralogist Gaston Demesmaeker, who worked at the Musonoi Mine in Katanga. It is a secondary mineral which contains lead, copper and selenium, it is a bottle green to brown/yellow color, its crystal habit varies depending on where it is found. It has pleochroic attributes, which means depending on which axis it is seen, the gem displays different colors, which is an optical phenomenon. On the X axis it displays a yellow-green color, and on the Y the gem is seen in a brown color. Demesmaekerite has a very strong radioactivity, 1,629,108.74, measured in GRapi (Gamma Ray American Petroleum Institute Units). It is mostly made out of oxygen (22.1%), uranium (21.92%) which causes its irradiative attributes, selenium (21.81%), lead (19.08%) which is a poisonous chemical element and copper (14.63%), but also contains hydrogen (0.46%).It can be found associated with other rare selenium-bearing uranium ores, such as haynesite, guilleminite, marthozite and piretite.
Read More About Demesmaekerite / Source
Derriksite

Derriksite is a very rare uranium mineral with the chemical formula Cu4(UO2)(SeO3)2(OH)6•H2O. It is a secondary mineral that contains copper, uranium and the rarer selenium. It is a bright green to duller bottle green colour. Its crystal habit is acicular, it is most likely to be found along with the uranyl selenium mineral demesmaekerite, but derriksite is much rarer than demesmaekerite. It is named after Jean Marie Francois Joseph Derriks (1912–1992), geologist and administrator of the Union Minière du Haut Katanga (UMHK). It has a Mohs hardness of about 2.
Read More About Derriksite / Source
Descloizite

Descloizite is a rare mineral species consisting of basic lead and zinc vanadate, (Pb, Zn)2(OH)VO4, crystallizing in the orthorhombic crystal system and isomorphous with olivenite. Appreciable gallium and germanium may also be incorporated into the crystal structure.
The color is deep cherry-red to brown or black, and the crystals are transparent or translucent with a greasy lustre; the streak is orange-yellow to brown; specific gravity 5.9 to 6.2; hardness 31/2. A variety known as cuprodescloizite is dull green in color; it contains a considerable amount of copper replacing zinc and some arsenic replacing vanadium. There is also an arsenate analogue called arsendescloizite.
Read More About Descloizite / Source
Devilline

Devilline is a sulfate mineral with the chemical formula CaCu4(SO4)2(OH)6•3H2O. The name originates from the French chemist’s name, Henri Etienne Sainte-Claire Deville (1818–1881).
Devilline crystallizes in the monoclinic system. Crystallographically, it contains three vectors of unequal lengths and two pairs of vectors are perpendicular while the other pair makes an angle other than 90°. Devilline is prismatic and belongs to the crystal class 2/m. This mineral belongs to the space group P 21/c. Devilline is an anisotropic mineral, meaning that the mineral has different properties in different directions. Optically, this mineral is biaxial negative, meaning that it contains two optic axes. Devilline has a moderate mineral relief. Mineral relief refers to the way a mineral appears to stand out when viewed under polarized light and it is dependent on the mineral’s index of refraction.
Devilline is a rare and unusual secondary mineral found in the oxidized portions of copper sulfide ore deposits. Because Devilline occurs in such oxidation zones, this mineral often is of post-mining origin. Devilline is found in mines all around the world.
Read More About Devilline / Source
Diaboleite

Diaboleite is a blue-colored mineral with formula Pb2CuCl2(OH)4. It was discovered in England in 1923 and named diaboleite, from the Greek word διά and boleite, meaning “distinct from boleite”. The mineral has since been found in a number of countries.
Read More About Diaboleite / Source
Diadochite

Diadochite is a phospho-sulfate mineral. It is a secondary mineral formed by the weathering and hydration of other minerals. Its formula is Fe2(PO4)(SO4)OH·5H2O. Well crystallized forms are referred to as destinezite, which has been given official recognition by the International Mineralogical Association with diadochite being the poorly formed to amorphous variety.It has a greenish yellow to brown colour and forms nodules or crusts. Its appearance has been compared to cauliflower.
Identified originally in Belgium in 1831, it has been found in many places throughout the world.
It occurs as a secondary mineral in mineral gossans, coal deposits, phosphate rich pegmatites and cave guano deposits.
Read More About Diadochite / Source
Diamond

Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth.
Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a very high refractive index and a relatively high optical dispersion.
Most natural diamonds have ages between 1 billion and 3.5 billion years. Most were formed at depths between 150 and 250 kilometres (93 and 155 mi) in the Earth’s mantle, although a few have come from as deep as 800 kilometres (500 mi). Under high pressure and temperature, carbon-containing fluids dissolved various minerals and replaced them with diamonds. Much more recently (hundreds to tens of million years ago), they were carried to the surface in volcanic eruptions and deposited in igneous rocks known as kimberlites and lamproites.
Synthetic diamonds can be grown from high-purity carbon under high pressures and temperatures or from hydrocarbon gases by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Imitation diamonds can also be made out of materials such as cubic zirconia and silicon carbide. Natural, synthetic and imitation diamonds are most commonly distinguished using optical techniques or thermal conductivity measurements.
Read More About Diamond / Source
Diaspore

Diaspore , also known as diasporite, empholite, kayserite, or tanatarite, is an aluminium oxide hydroxide mineral, α-AlO(OH), crystallizing in the orthorhombic system and isomorphous with goethite. It occurs sometimes as flattened crystals, but usually as lamellar or scaly masses, the flattened surface being a direction of perfect cleavage on which the lustre is markedly pearly in character. It is colorless or greyish-white, yellowish, sometimes violet in color, and varies from translucent to transparent. It may be readily distinguished from other colorless transparent minerals with a perfect cleavage and pearly luster—like mica, talc, brucite and gypsum—by its greater hardness of 6.5 to 7. The specific gravity is 3.4. When heated before the blowpipe it decrepitates violently, breaking up into white pearly scales.The mineral occurs as an alteration product of corundum or emery and is found in granular limestone and other crystalline rocks. Well-developed crystals are found in the emery deposits of the Urals and at Chester, Massachusetts, US and in kaolin at Schemnitz in Hungary. If obtainable in large quantity, it would be of economic importance as a source of aluminium.Diaspore, along with gibbsite and boehmite, is a major component of the aluminium ore bauxite.It was first described in 1801 for an occurrence in Mramorsk Zavod, Sverdlovskaya Oblast, Middle Urals, Russia. The name, which was coined by René Just Haüy, is from the Ancient Greek διασπείρω meaning “to scatter”, in allusion to its decrepitation on heating.Csarite, ottomanite, Turkizite and zultanite are trade names for gem-quality diaspore (also known as Turkish diaspore) from the İlbir Mountains of southwest Turkey.
Read More About Diaspore / Source
Dickite

Dickite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) is a phyllosilicate clay mineral named after the metallurgical chemist Allan Brugh Dick, who first described it. It is chemically composed of 20.90% aluminium, 21.76% silicon, 1.56% hydrogen and 55.78% oxygen. It has the same composition as kaolinite, nacrite, and halloysite, but with a different crystal structure (polymorph). Dickite sometimes contains impurities such as titanium, iron, magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium.Dickite occurs with other clays and requires x-ray diffraction for its positive identification. Dickite is an important alteration indicator in hydrothermal systems as well as occurring in soils and shales.
Dickite’s type location is in Pant-y-Gaseg, Amlwch, Isle of Anglesey, Wales, United Kingdom, where it was first described in 1888. Dickite appears in locations with similar qualities and is found in China, Jamaica, France, Germany, United Kingdom, United States, Italy, Belgium and Canada.
Read More About Dickite / Source
Digenite

Digenite is a copper sulfide mineral with formula: Cu9S5. Digenite is a black to dark blue opaque mineral that crystallizes with a trigonal – hexagonal scalenohedral structure. In habit it is usually massive, but does often show pseudo-cubic forms. It has poor to indistinct cleavage and a brittle fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3 and a specific gravity of 5.6. It is found in copper sulfide deposits of both primary and supergene occurrences. It is typically associated with and often intergrown with chalcocite, covellite, djurleite, bornite, chalcopyrite and pyrite. The type locality is Sangerhausen, Thuringia, Germany, in copper slate deposits.
Read More About Digenite / Source
Dimorphite
Dimorphite, chemical name arsenic sesquisulfide (As4S3), is a very rare orange-yellow arsenic sulfide mineral. In nature, dimorphite forms primarily by deposition in volcanic fumaroles at temperatures of 70–80 °C (158–176 °F). Dimorphite was first discovered in such a fumarole near Naples, Italy in 1849 by the mineralologist Arcangelo Scacchi (1810–1893). Since its discovery, dimorphite has been found in the Alacrán silver mine near Copiapó, Chile. It has also been reported from Cerro de Pasco, Peru, and the Lavrion District Mines in Attica, Greece.
Read More About Dimorphite / Source
Diopside

Diopside is a monoclinic pyroxene mineral with composition MgCaSi2O6. It forms complete solid solution series with hedenbergite (FeCaSi2O6) and augite, and partial solid solutions with orthopyroxene and pigeonite. It forms variably colored, but typically dull green crystals in the monoclinic prismatic class. It has two distinct prismatic cleavages at 87 and 93° typical of the pyroxene series. It has a Mohs hardness of six, a Vickers hardness of 7.7 GPa at a load of 0.98 N, and a specific gravity of 3.25 to 3.55. It is transparent to translucent with indices of refraction of nα=1.663–1.699, nβ=1.671–1.705, and nγ=1.693–1.728. The optic angle is 58° to 63°.
Read More About Diopside / Source
Dioptase

Dioptase is an intense emerald-green to bluish-green copper cyclosilicate mineral. It is transparent to translucent. Its luster is vitreous to sub-adamantine. Its formula is Cu6Si6O18·6H2O (also reported as CuSiO2(OH)2). It has a hardness of 5, the same as tooth enamel. Its specific gravity is 3.28–3.35, and it has two perfect and one very good cleavage directions. Additionally, dioptase is very fragile, and specimens must be handled with great care. It is a trigonal mineral, forming 6-sided crystals that are terminated by rhombohedra.
It is popular with mineral collectors and is sometimes cut into small gems. It can also be ground up and used as a pigment for painting.
Read More About Dioptase / Source
Djerfisherite

Djerfisherite is an alkali copper–iron sulfide mineral and a member of the djerfisherite group.
The chemical composition is somewhat variable. A Russian study from 1979 on djerfisherite from the Kola Peninsula found the formula K6Na(Fe,Cu)24S26Cl, but a study in 2007 of a samples from Siberia found no detectable sodium and states that the formula K6(Fe,Cu,Ni)25S26Cl is considered the most appropriate. Both crystallographic studies have 58 atoms per unit cell. Sulfur atoms are in three nonequivalent locations, containing 12, 6, and 8 atoms per unit cell. The later study put a copper atom where the earlier study put a sodium atom. More information on the structure and other questions is available, as well as 3-D models.The Webmineral “Mineralogy Database” site gives the “chemical formula” as K6Na(Fe2+,Cu,Ni)25S26Cl, apparently in error, and an “empirical formula” as K6NaFe2+19Cu4NiS26Cl.Its type locality is the Kota-Kota meteorite (Marimba meteorite), Malawi. It was first described in 1966 and named after professor Daniel Jerome Fisher (1896–1988), University of Chicago. It has been reported from meteorites, copper-nickel hydrothermal deposits, skarn, pegmatite, kimberlites and alkalic intrusive complexes. Associated minerals include kamacite, troilite, schreibersite, clinoenstatite, tridymite, cristobalite, daubreelite, graphite, roedderite, alabandite, talnakhite,
pentlandite, chalcopyrite, magnetite, valleriite, sphalerite and platinum minerals.
Read More About Djerfisherite / Source
Djurleite

Djurleite is a copper sulfide mineral of secondary origin with formula Cu31S16 that crystallizes with monoclinic-prismatic symmetry. It is typically massive in form, but does at times develop thin tabular to prismatic crystals. It occurs with other supergene minerals such as chalcocite, covellite and digenite in the enriched zone of copper orebodies. It is a member of the chalcocite group, and very similar to chalcocite, Cu2S, in its composition and properties, but the two minerals can be distinguished from each other by x-ray powder diffraction. Intergrowths and transformations between djurleite, digenite and chalcocite are common. Many of the reported associations of digenite and djurleite, however, identified by powder diffraction, could be anilite and djurleite, as anilite transforms to digenite during grinding.Djurleite was named for the Swedish chemist Seved Djurle (1928–2000), from the University of Uppsala, Sweden, who first synthesized the mineral in 1958, prior to its discovery in nature. The natural material was first described in 1962 by E H Roseboom Jr, of the US Geological Survey, from occurrences at the type locality, Barranca del Cobre, Chihuahua, Mexico.
Read More About Djurleite / Source
Dmitryivanovite
Dmitryivanovite is a natural mineral composed of calcium, aluminium and oxygen, with the molecular formula CaAl2O4. It was reported in 2009 in a calcium-aluminium-rich inclusion in the carbonaceous chondrite meteorite 470 (NWA470) CH3, which landed in North Africa. The mineral name was chosen to honor Dmitriy A. Ivanov (1962–1986), a geologist, mineralogist, and petrologist who died on a field expedition.It is the high-pressure CaAl2O4 dimorph of krotite.
Read More About Dmitryivanovite / Source
Dollaseite-(Ce)

Dollaseite-(Ce) is a sorosilicate end-member epidote rare-earth mineral which was discovered by Per Geijer (1927) in the Ostanmossa mine (Östanmossa gruva), Norberg district, Sweden. Dollaseite-(Ce), although not very well known, is part of a broad epidote group of minerals which are primarily silicates, the most abundant type of minerals on earth. Dollaseite-(Ce) forms as dark-brown subhedral crystals primarily in Swedish mines. With the ideal chemical formula, CaREE3+Mg2AlSi3O11,(OH)F, dollaseite-(Ce) can be partially identified by its content of the rare earth element cerium.
Read More About Dollaseite-(Ce) / Source
Dolomite (mineral)

Dolomite is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally CaMg(CO3)2. The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic rock type is dolostone.
Read More About Dolomite (mineral) / Source
Domeykite

Domeykite is a copper arsenide mineral, Cu3As. It crystallizes in the isometric system, although crystals are very rare. It typically forms as irregular masses or botryoidal forms. It is an opaque, white to gray (weathers brassy) metallic mineral with a Mohs hardness of 3 to 3.5 and a specific gravity of 7.2 to 8.1It was first described in 1845 in the Algodones mines, Coquimbo, Chile. It was named after Polish mineralogist Ignacy Domeyko (1802–1889) by Wilhelm Haidinger.
Read More About Domeykite / Source
Donnayite-(Y)

Donnayite-(Y) is a rare-earth carbonate mineral containing the rare-earth metal yttrium. It was first discovered in 1978 at Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec. Donnayite was subsequently identified and named after Joseph D. H. Donnay and his wife, Gabrielle Donnay. Both were prominent mineralogists and crystallographers, and J. D. H. Donnay was awarded the Roebling Award by the Mineralogical Society of America in 1971 for his emphasis on the importance of optical mineralogy and crystal morphology. Donnayite tends to occur in small quantities in the pegmatite dykes and miarolitic cavities of mountainous regions. It crystallizes in this environment with increasing alkalinity values until the alkalinity suddenly drops during the last stage of crystallization. This results in increasing amounts of Na carbonates and REE minerals. First discovered at Mont St-Hilaire, donnayite has since been found in the Southern Ural Mountains of Russia and the Narssarssuk pegmatite of South Greenland. Donnayite crystals tend to be small and the color is commonly pale yellow to yellow with a white streak and a vitreous luster. Donnayite crystals usually display trigonal or hexagonal symmetry and have a hardness of 3. Twinning is extremely common in this mineral. Minerals closely related to donnayite include synchysite, calcite, sphalerite, microcline, and analcime. Donnayite is isomorphous with weloganite and mckelveyite.
Read More About Donnayite-(Y) / Source
Doyleite

Doyleite is a rare aluminum trihydroxide mineral named in honor of its discoverer, the Canadian physician Earl Joseph (Jess) Doyle. It was first definitively described in 1985 (although a partial description was published in 1979) and it is approved by the IMA. It was described from Mont Saint-Hilaire, where it is extremely rare.
Read More About Doyleite / Source
Dresserite

Dresserite is a mineral of the dresserite group, named in honor of John Alexander Dresser, geologist. It was approved by the IMA in 1968, but only a year after was it published. The rare mineral can only be found in Francon quarry, Canada. The quarry is located in the middle of the city of Montréal, but had been closed in 1981 and will not reopen in the future.
Read More About Dresserite / Source
Drysdallite

Drysdallite is a rare molybdenum selenium sulfide mineral with formula Mo(Se,S)2. It crystallizes in the hexagonal system as small pyramidal crystals or in cleavable masses. It is an opaque metallic mineral with a Mohs hardness of 1 to 1.5 and a specific gravity of 6.25. Like molybdenite it is pliable with perfect cleavage.
It was first described in 1973 for an occurrence in an oxidized uranium deposit near Solwezi, Zambia. It was named for Alan Roy Drysdall, the director of the Zambian geological survey.
Read More About Drysdallite / Source
Duftite

Duftite is a relatively common arsenate mineral with the formula CuPb(AsO4)(OH), related to conichalcite. It is green and often forms botryoidal aggregates. It is a member of the adelite-descloizite Group, Conichalcite-Duftite Series. Duftite and conichalcite specimens from Tsumeb are commonly zoned in color and composition. Microprobe analyses and X-ray powder-diffraction studies indicate extensive substitution of Zn for Cu, and Ca for Pb in the duftite structure. This indicates a solid solution among conichalcite, CaCu(AsO4 )(OH), austinite, CaZn(AsO4)(OH) and duftite PbCu(AsO4)(OH), all of them belonging to the adelite group of arsenates. It was named after Mining Councilor G Duft, Director of the Otavi Mine and Railroad Company, Tsumeb, Namibia. The type locality is the Tsumeb Mine, Tsumeb, Otjikoto Region, Namibia.
Read More About Duftite / Source
Dumortierite

Dumortierite is a fibrous variably colored aluminium boro-silicate mineral, Al7BO3(SiO4)3O3. Dumortierite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system typically forming fibrous aggregates of slender prismatic crystals. The crystals are vitreous and vary in color from brown, blue, and green to more rare violet and pink. Substitution of iron and other tri-valent elements for aluminium result in the color variations. It has a Mohs hardness of 7 and a specific gravity of 3.3 to 3.4. Crystals show pleochroism from red to blue to violet. Dumortierite quartz is blue colored quartz containing abundant dumortierite inclusions.
Dumortierite was first described in 1881 for an occurrence in Chaponost, in the Rhône-Alps of France and named for the French paleontologist Eugène Dumortier (1803–1873). It typically occurs in high temperature aluminium rich regional metamorphic rocks, those resulting from contact metamorphism and also in boron rich pegmatites. The most extensive investigation on dumortierite was done on samples from the high grade metamorphic Gfohl unit in Austria by Fuchs et al. (2005).
It is used in the manufacture of high grade porcelain. It is sometimes mistaken for sodalite and has been used as imitation lapis lazuli.
Sources of Dumortierite include Austria, Brazil, Canada, France, Italy, Madagascar, Namibia, Nevada, Norway, Peru, Poland, Russia and Sri Lanka.
Read More About Dumortierite / Source
Dundasite

Dundasite is a rare lead aluminium carbonate mineral. The mineral is named after the type locality, Dundas, Tasmania, Australia. The mineral was first discovered in the Adelaide Proprietary Mine. Dundasite was first described by William Frederick Petterd in 1893.Dundasite is an uncommon secondary mineral occurring in the oxidized zone of lead ore deposits. It commonly overgrows crocoite. It may also be overgrown by yellow cerussite. It may be associated with cerussite, plattnerite, azurite, malachite, pyromorphite, mimetite, beudantite, duftite, crocoite, gibbsite, allophane and limonite.Besides its type location on Tasmania, the mineral has also been found in New Zealand, Mainland Australia, China, Belgium, Germany, France, Greece, United Kingdom, Ireland, Italy, Austria, Czech Republic, Namibia, and the US.
Read More About Dundasite / Source
Dypingite

Dypingite is a hydrated magnesium carbonate mineral with the formula: Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·5H2O. Its type locality is the Dypingdal serpentine-magnesite deposit, Snarum, Norway.
Read More About Dypingite / Source
Dyscrasite

The silver antimonide mineral dyscrasite has the chemical formula Ag3Sb. It is an opaque, silver white, metallic mineral which crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. It forms pyramidal crystals up to 5 cm (2.0 in) and can also form cylindrical and prismatic crystals.
Read More About Dyscrasite / Source
Dzhalindite
Dzhalindite is a rare indium hydroxide mineral discovered in Siberia. Its chemical formula is In(OH)3.
It was first described in 1963 for an occurrence in the Dzhalinda tin deposit, Malyi Khingan Range, Khabarovskiy Kray, Far-Eastern Region, Russia.It has also been reported from Mount Pleasant, New Brunswick, Canada; the Flambeau mine, Ladysmith, Rusk County, Wisconsin, US; in the Mangabeira tin deposit, Goiás, Brazil; Attica, mines of the Lavrion District, Greece; Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany; the Krušné Hory Mountains of Bohemia, Czech Republic; the Chubu Region, Honshu Island, Japan; and the Arashan Massif of Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
Read More About Dzhalindite / Source
Edenite

Edenite is a double chain silicate mineral of the amphibole group with the general chemical composition NaCa2Mg5(Si7Al)O22(OH)2. Edenite is named for the locality of Edenville, Orange County, New York, where it was first described.
Read More About Edenite / Source
Edingtonite

Edingtonite is a white, gray, brown, colorless, pink or yellow zeolite mineral. Its chemical formula is BaAl2Si3O10·4H2O. It has varieties with tetragonal, orthorhombic or triclinic crystals.The mineral occurs within cavities in nepheline syenites, carbonatites, in
hydrothermal veins and various mafic rocks. It occurs associated with thomsonite, analcime, natrolite, harmotome, brewsterite, prehnite and calcite.The mineral was first reported by and named for Scottish mineral collector James Edington (1787–1844). Other sources (including the mineralogist Haidinger) credit Scottish geologist and mineralogist Thomas Edington (1814-1859). However, as the mineral was named in 1825, the former accreditation must be the true one.
Read More About Edingtonite / Source
Edscottite
Edscottite is an iron carbide mineral, with the formula Fe5C2. It was previously known to occur during iron smelting, but in 2019 was identified as occurring in nature, but not naturally occurring on earth, when it was discovered in a meteorite.The source, the Wedderburn meteorite, was found in 1951 just outside Wedderburn in Australia, and is held in the Museums Victoria collection.During a re-investigation of a section of the meteorite housed at the University of California, Los Angeles, Chi Ma and Alan Rubin verified the presence of a new mineral. They named it edscottite in honor of Edward (Ed) R. D. Scott of the University of Hawaii, USA, a pioneering cosmochemist.
Read More About Edscottite / Source
Efremovite
Efremovite is a rare ammonium sulfate mineral with the chemical formula: (NH4)2Mg2(SO4)3. It is a white to gray cubic mineral. This anhydrous sulfate occurs as constituent in sulfate crusts of burning coal dumps. It is hygroscopic and when exposed to humid air it slowly converts to the hydrate form, boussingaultite.It was first described in 1989 for an occurrence in the Chelyabinsk coal basin, Southern Urals, Russia. It was named for Russian geologist Ivan Antonovich Yefremov (1907–1972). It has also been reported from several coal mining areas across Europe. It occurs in association with native sulfur, kladnoite, mascagnite, and boussingaultite.
Read More About Efremovite / Source
Ekanite

Ekanite is an uncommon silicate mineral with chemical formula Ca2ThSi8O20 or (Ca,Fe,Pb)2(Th,U)Si8O20. It is a member of the steacyite group. It is among the few gemstones that are naturally radioactive. Most ekanite is mined in Sri Lanka, although deposits also occur in Russia and North America. Clear and well-colored stones are rare as the radioactivity tends to degrade the crystal matrix over time in a process known as metamictization.
The type locality is Eheliyagoda, Ratnapura District, Sabaragamuwa Province, Sri Lanka, where it was first described in 1955 by F. L. D. Ekanayake, a Sri Lankan scientist, and it is named after him.In Sri Lanka the mineral specimens occur as detrital pebbles. In the Tombstone Mountains of Yukon, Canada, the mineral is found in a syenitic glacial erratic boulder. In the Alban Hills of Italy it is found in volcanic ejecta.
Read More About Ekanite / Source
Elaliite
Elaliite is a mineral with formula Fe9PO12 (or Fe2+8Fe3+(PO4)O8) that was first synthesized in a laboratory in the 1980s and later identified in natural material in 2022 at which time the official mineral designation was given. The mineral is orthorhombic, with space group Cmmm (space group 65).
Read More About Elaliite / Source
Elbaite

Elbaite, a sodium, lithium, aluminium boro-silicate, with the chemical composition Na(Li1.5Al1.5)Al6Si6O18(BO3)3(OH)4, is a mineral species belonging to the six-member ring cyclosilicate tourmaline group.
Elbaite forms three series, with dravite, with fluor-liddicoatite, and with schorl. Due to these series, specimens with the ideal endmember formula are not found occurring naturally.
As a gemstone, elbaite is a desirable member of the tourmaline group because of the variety and depth of its colours and quality of the crystals. Originally discovered on the island of Elba, Italy in 1913, it has since been found in many parts of the world. In 1994, a major locality was discovered in Canada, at O’Grady Lakes in the Yukon.
Elbaite forms in igneous and metamorphic rocks and veins in association with lepidolite, microcline, and spodumene in granite pegmatites; with andalusite and biotite in schist; and with molybdenite and cassiterite in massive hydrothermal replacement deposits.
Elbaite is allochromatic, meaning trace amounts of impurities can tint crystals, and it can be strongly pleochroic. Every color of the rainbow may be represented by elbaite, some exhibiting multicolor zonation. Microscopic acicular inclusions in some elbaite crystals show the Cat’s eye effect in polished cabochons.
Read More About Elbaite / Source
Elkinstantonite
Elkinstantonite is a mineral with formula Fe4(PO4)2O that was first generated in a laboratory in the 1980s and first identified from natural origins in 2022, when the official mineral designation was also given. It is monoclinic, with space group P21/c (space group 14).
Read More About Elkinstantonite / Source
Emmonsite

Emmonsite, also known as durdenite, is an iron tellurite mineral with the formula: Fe2(TeO3)3·2(H2O). Emmonsite forms triclinic crystals. It is of a yellowish-green color, with a vitreous luster, and a hardness of 5 on the Moh scale.
Emmonsite was first described in 1885 for an occurrence in the Tombstone District, Cochise County, Arizona. It was named for the American geologist, Samuel Franklin Emmons, (1841–1911), of the United States Geological Survey.Emmonsite is found, often with quartz or cerussite in the Tombstone, Arizona area. It is also associated with native tellurium, tellurite, native gold, pyrite, rodalquilarite, mackayite, sonoraite, cuzticite and eztlite.
Read More About Emmonsite / Source
Empressite

Empressite is a mineral form of silver telluride, AgTe.
It is a rare, grey, orthorhombic mineral with which can form compact masses, rarely as bipyramidal crystals.
Recent crystallographic analysis has confirmed that empressite is a distinct mineral with orthorhombic crystal structure, different from the hexagonal Ag5−xTe3 with which empressite has been commonly confused in mineralogy literature.
At the same time, empressite does not appear on the equilibrium Ag-Te phase diagram, and therefore it is only metastable at ambient conditions. Given infinite time, it would phase separate into pure Ag5Te3 and pure Te.
The name empressite comes from the location of its discovery – the Empress Josephine mine, Saguache County, Colorado, US. It was first described in 1914.
Read More About Empressite / Source
Enargite

Enargite is a copper arsenic sulfosalt mineral with formula Cu3AsS4. It takes its name from the Greek word enarge, “distinct”. Enargite is a steel gray, blackish gray, to violet black mineral with metallic luster. It forms slender orthorhombic prisms as well as massive aggregates. It has a hardness of 3 and a specific gravity of 4.45.
Enargite is dimorph of the tetragonal luzonite.
Read More About Enargite / Source
Enstatite

Enstatite is a mineral; the magnesium endmember of the pyroxene silicate mineral series enstatite (MgSiO3) – ferrosilite (FeSiO3). The magnesium rich members of the solid solution series are common rock-forming minerals found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. The intermediate composition, (Mg,Fe)SiO3, has historically been known as hypersthene, although this name has been formally abandoned and replaced by orthopyroxene. When determined petrographically or chemically the composition is given as relative proportions of enstatite (En) and ferrosilite (Fs) (e.g., En80Fs20).
Read More About Enstatite / Source
Eosphorite

Eosphorite is a brown (occasionally pink) manganese hydrous phosphate mineral with chemical formula: MnAl(PO4)(OH)2·H2O. It is used as a gemstone.Eosphorite crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It forms slender prismatic crystals which often form radiating or spherical clusters. The crystals often show pseudo–orthorhombic forms due to twinning.Eosphorite forms a series with childrenite, the iron rich member, with divalent iron replacing most of the manganese in the crystal lattice. The two endmembers are isostructural but differ in their properties, such as crystal habit, coloration, and optical properties.
It was first described in 1878 for an occurrence in the Branchville Mica Mine in Branchville, Fairfield County, Connecticut, US. Its name is derived from the Greek έωσφορος for “dawn-bearing,” because of its pink color. It occurs worldwide typically as a secondary mineral in phosphate rich granitic pegmatites in association with rhodochrosite, lithiophilite, triphylite, triploidite, dickinsonite, albite, cookeite, apatite, beryllonite, hydroxyl-herderite, and tourmaline. An attractive combination of eosphorite and rose quartz occurs at Taquaral, Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Read More About Eosphorite / Source
Ephesite

Ephesite is a rare member of the mica silicate mineral group, phyllosilicate. It is restricted to quartz-free, alumina rich mineral assemblages and has been found in South African deposits in the Postmasburg district as well as Ephesus, Turkey.
Read More About Ephesite / Source
Epidote

Epsomite

Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O.
Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massive encrustations. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. The Mohs hardness is 2 to 2.5 and it has a low specific gravity of 1.67.
It is readily soluble in water. It absorbs water from the air and converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure.
Read More About Epsomite / Source
Ericssonite
Ericssonite has a general formula of BaMn2FeO[Si2O7](OH). It was discovered in 1967 and named after John Ericsson (July 31, 1803 – March 8, 1889), a well known Swedish American inventor, engineer and designer of the iron-clad ship USS Monitor. Ericssonite was discovered in the Jakobsberg Mine in Värmland, Sweden.Ericcsonite is monoclinic; this means it contains three unequal vectors, two of these vector angles are perpendicular while the other is at an angle greater than 90°. Optically ericssonite is anisotropic which means that the mineral has more than one index of refraction, causing light to vary in speed depending on which axis it is traveling through. Since ericssonite is monoclinic, containing three unequal vectors, it has three indices of refraction. Ericssonite is usually a deep reddish-black in color. Ericssonite is only found in the Langban mine in Sweden, associated with a metamorphic manganese orebody. Also it is always inter-grown with orthoericssonite, which is almost identical to ericssonite except it contains extra silicon and oxygen in its chemical formula.
Read More About Ericssonite / Source
Erionite

Erionite is a naturally occurring fibrous mineral that belongs to a group of minerals called zeolites. It usually is found in volcanic ash that has been altered by weathering and ground water. Erionite forms brittle, wool-like fibrous masses in the hollows of rock formations and has an internal molecular structure similar to chabazite. Some properties of erionite are similar to the properties of asbestos; however, erionite is not currently regulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and there are no occupational exposure limits for erionite fibers. Erionite was first described by A.S. Eakle in 1898, as white woolly fibrous masses in cavities in rhyolite lava near Durkee, Oregon. It was originally thought to be another relatively rare zeolite named offretite, which is very similar to erionite in appearance and chemical composition.
Read More About Erionite / Source
Erythrite

Erythrite or red cobalt is a secondary hydrated cobalt arsenate mineral with the formula Co3(AsO4)2•8H2O. Erythrite and annabergite, chemical formula Ni3(AsO4)2•8H2O, or nickel arsenate form a complete series with the general formula (Co,Ni)3(AsO4)2•8H2O.
Erythrite crystallizes in the monoclinic system and forms prismatic crystals. The color is crimson to pink and occurs as a secondary coating known as cobalt bloom on cobalt arsenide minerals. Well-formed crystals are rare, with most of the mineral manifesting in crusts or small reniform aggregates.
Erythrite was first described in 1832 for an occurrence in Grube Daniel, Schneeberg, Saxony, and takes its name from the Greek έρυθρος (erythros), meaning red. Historically, erythrite itself has not been an economically important mineral, but the prospector may use it as a guide to associated cobalt and native silver.Erythrite occurs as a secondary mineral in the oxide zone of Co–Ni–As bearing mineral deposits. It occurs in association with cobaltite, skutterudite, symplesite, roselite-beta, scorodite, pharmacosiderite, adamite, morenosite, retgersite, and malachite.Notable localities are Cobalt, Ontario; La Cobaltera, Chile, Schneeberg, Saxony, Germany; Joachimsthal, Czech Republic; Cornwall, England; Bou Azzer, Morocco; the Blackbird mine, Lemhi County, Idaho; Sara Alicia mine, near Alamos, Sonora, Mexico; Mt. Cobalt, Queensland and the Dome Rock copper mine, Mingary, South Australia.
Read More About Erythrite / Source
Eskolaite

Eskolaite is a rare chromium oxide mineral (chromium(III) oxide Cr2O3).
Read More About Eskolaite / Source
Esperite

Esperite is a rare complex calcium lead zinc silicate (PbCa3Zn4(SiO4)4) related to beryllonite and trimerite that used to be called calcium larsenite. It was named in honor of Esper F. Larsen Jr. (1879–1961), petrologist of Harvard University.Esperite has a white, greasy appearance in daylight and is much prized for its brilliant yellow green fluorescence under shortwave ultraviolet light. It is found in association with calcite, franklinite, willemite, hardystonite and clinohedrite. It has also been found as prismatic crystals up to 1 mm in length at the El Dragon Mine, Potosi, Bolivia in association with allophane, chalcomenite, clinochalcomenite and barite.
Read More About Esperite / Source
Ettringite

Ettringite is a hydrous calcium aluminium sulfate mineral with formula: Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O. It is a colorless to yellow mineral crystallizing in the trigonal system. The prismatic crystals are typically colorless, turning white on partial dehydration. It is part of the ettringite-group which includes other sulfates such as thaumasite and bentorite.
Read More About Ettringite / Source
Euchlorine
Euchlorine (KNaCu3(SO4)3O) is a rare emerald-green colored sulfate mineral found naturally occurring as a sublimate in fumaroles around volcanic eruptions. It was first discovered in fumaroles of the 1868 eruption at Mount Vesuvius in Campania, Italy by Arcangelo Scacchi. The name ‘euchlorine’ comes from the Greek word εΰχλωρος meaning “pale green” in reference to the mineral’s color, other reported spellings include euclorina, euchlorin, and euchlorite.The ideal formula of euchlorine is KNaCu3(SO4)3O though calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) occasionally substitute into the crystal lattice. Euchlorine is structurally related to puninite (Na2Cu3(SO4)3O) and fedotovite (K2Cu3(SO4)3O), all of which are included in the euchlorine group of minerals.One of the distinguishing physical properties helpful for identifying euchlorine in hand sample is its streak, which is a pistachio-green color. If trying to find euchlorine in the field, wear protective clothing as the volcanic fumaroles around which it occurs can be very hot (approximately 300 to 650°C, 580 to 1200°F) and can cause severe steam burns if not adequately protected.
Read More About Euchlorine / Source
Euchroite

Euchroite is a hydrated copper arsenate hydroxide mineral with formula: Cu2AsO4OH·3H2O. It is a vitreous green to emerald green mineral crystallizing in the orthorhombic system. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 – 4.0 and a specific gravity of 3.39 – 3.45. It was first described in 1823 in Ľubietová, Slovakia.
Read More About Euchroite / Source
Euclase

Euclase is a beryllium aluminium hydroxide silicate mineral (BeAlSiO4(OH)). It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system and is typically massive to fibrous as well as in slender prismatic crystals. It is related to beryl (Be3Al2Si6O18) and other beryllium minerals. It is a product of the decomposition of beryl in pegmatites.
Euclase crystals are noted for their blue color, ranging from very pale to dark blue. The mineral may also be colorless, white, or light green. Cleavage is perfect, parallel to the clinopinacoid, and this suggested to René Just Haüy the name euclase, from the Greek εὖ, easily, and κλάσις, fracture. The ready cleavage renders the crystals fragile with a tendency to chip, and thus detracts from its use for personal ornament. When cut, it resembles certain kinds of beryl and topaz, from which it may be distinguished by its specific gravity (3.1). Its hardness (7.5) is similar to beryl (7.5 – 8), and a bit less than that of topaz (8).
It was first reported in 1792 from the Orenburg district in the southern Urals, Russia, where it is found with topaz and chrysoberyl in the gold-bearing gravels of the Sanarka (nowadays probably, Sakmara River, Mednogorsk district, Orenburgskaya Oblast’). Its type locality is Ouro Prêto, Minas Gerais, Southeast Region, Brazil, where it occurs with topaz. It is found rarely in the mica-schist of the Rauris in the Austrian Alps.
Read More About Euclase / Source
Eucryptite

Eucryptite is a lithium bearing aluminium silicate mineral with formula LiAlSiO4. It crystallizes in the trigonal – rhombohedral crystal system. It typically occurs as granular to massive in form and may pseudomorphically replace spodumene. It has a brittle to conchoidal fracture and indistinct cleavage. It is transparent to translucent and varies from colorless to white to brown. It has a Mohs hardness of 6.5 and a specific gravity of 2.67. Optically it is uniaxial positive with refractive index values of nω = 1.570 – 1.573 and nε = 1.583 – 1.587.
Its typical occurrence is in lithium-rich pegmatites in association with albite, spodumene, petalite, amblygonite, lepidolite and quartz.It occurs as a secondary alteration product of spodumene. It was first described in 1880 for an occurrence at its type locality, Branchville, Connecticut. Its name was from the Greek for well concealed, for its typical occurrence embedded in albite.
Read More About Eucryptite / Source
Eudialyte

Eudialyte, whose name derives from the Greek phrase Εὖ διάλυτος, eu dialytos, meaning “well decomposable”, is a somewhat rare, nine member ring cyclosilicate mineral, which forms in alkaline igneous rocks, such as nepheline syenites. Its name alludes to its ready solubility in acid.Eudialyte was first described in 1819 for an occurrence in nepheline syenite of the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of southwest Greenland.
Read More About Eudialyte / Source
Eudialyte group
Eudialyte group is a group of complex trigonal zircono- and, more rarely, titanosilicate minerals with general formula [N(1)N(2)N(3)N(4)N(5)]3[M(1a)M(1b)]3M(2)3M(4)Z3[Si24O72]O’4X2, where N(1) and N(2) and N(3) and N(5) = Na+ and more rarely H3O+ or H2O, N(4) = Na+, Sr2+, Mn2+ and more rarely H3O+ or H2O or K+ or Ca2+ or REE3+ (rare earth elements), M(1) and M(1b) = Ca2+, M(1a) = Ca2+ or Mn2+ or Fe2+, M(2) = Fe (both II and III), Mn and rarely Na+, K+ or Zr4+, M(3) = Si, Nb and rarely W, Ti and [] (vacancy), M(4) = Si and or rarely [], Z Zr4+ and or rarely Ti4+, and X = OH−, Cl− and more rarely CO32− or F−. Some of the eudialyte-like structures can even be more complex, however, in general, its typical feature is the presence of [Si3O9]6− and [Si9O27]18− ring silicate groups. Space group is usually R3m or R-3m but may be reduced to R3 due to cation ordering. Like other zirconosilicates, the eudialyte group minerals possess alkaline ion-exchange properties, as microporous materials.
Read More About Eudialyte group / Source
Euxenite

Euxenite, or euxenite-(Y) (the official mineralogical name), is a brownish black mineral with a metallic luster.
Read More About Euxenite / Source
Eveite

Eveite is a manganese arsenate mineral in the olivenite group. Its chemical formula is Mn2AsO4OH. It is found only in Långban, Filipstad, Värmland, Sweden and at the Sterling Mine in New Jersey, United States. It is a dimorph of sarkinite and is isostructural with adamite. The name, for the biblical “Eve”, comes from its structural similarities to adamite and is also a reference to its apple-green color. It can also be pale yellow. Eveite is an orthorhombic mineral, which means it has three crystallographic axes of unequal lengths which are at 90° to one another.
Eveite is anisotropic, which means that its physical and optical properties differ with respect to direction. It has high relief, which is the apparent topography exhibited by minerals in thin section as a consequence of refractive index. It is biaxial, so it has two optic axes and three indices of refraction n depending on the crystallographic direction. The refractive index is the ratio of the velocity of light in vacuum to that in the mineral. The difference between the highest and lowest indices of refraction is called the birefringence, so the birefringence of eveite is β = 0.032.
Eveite is significant because it was the first mineral to show Mn2+ atoms in five-fold coordination, which is otherwise undocumented in mineral structures. It is therefore an important addition to the olivenite group. Because it shows up in very small quantities and in only two locations, it has no commercial use. It is relatively low-density and is associated with high-hydrate and low-density arsenates in open cavities, which contributes to its rarity.
Read More About Eveite / Source
Evenkite

Evenkite is a rare hydrocarbon mineral with formula C24H50; specifically, H3C–(CH2)22–CH3, the alkane n-tetracosane. It occurs as very soft (Mohs hardness 1) transparent crystals, colorless to yellow, with a waxy luster. The softness is a characteristic of crystalline long-chain alkanes, which are the main constituents of paraffin wax.Evenkite one of very few minerals that consist of crystalline hydrocarbons, which include carpathite (pure crystalline coronene, a polyaromatic hydrocarbon). It is also one of the few non-porous minerals that floats on water. It has been claimed to be the same as hatchettite.
Read More About Evenkite / Source
Eveslogite
Eveslogite is a complex inosilicate mineral with a chemical formula (Ca,K,Na,Sr,Ba)48[(Ti,Nb,Fe,Mn)12(OH)12Si48O144](F,OH,Cl)14 found on Mt. Eveslogchorr in Khibiny Mountains, on the Kola peninsula, Russia. It was named after the place it was found. This silicate mineral occurs as an anchimonomineral veinlet that cross-cuts poikilitic nepheline syenite. This mineral appears to resemble yuksporite, as it forms similar placated fine fibrous of approximately 0.05 to 0.005mm that aggregates outwardly. The color of eveslogite is yellow or rather light brown. In addition, it is a semitransparent mineral that has a white streak and a vitreous luster. Its crystal system is monoclinic and possesses a hardness (Mohs) of 5. This newly discovered mineral belongs to the astrophyllite group of minerals and contains structures that are composed of titanosilicate layers (Krivovichev et al., 2004). Limited information about this mineral exists due to the few research studies carried out since its recent discovery.
Read More About Eveslogite / Source
Fabianite
Fabianite is a borate mineral with the chemical formula CaB3O5(OH). It is colorless and leaves a white streak. Its crystals are monoclinic prismatic. It is transparent and fluorescent. It has vitreous luster. It is not radioactive. Fabianite is rated 6 on the Mohs Scale. It was named for Hans-Joachim Fabian, a German geologist.
Read More About Fabianite / Source
Farneseite
Farneseite is a mineral from the cancrinite sodalite group with 14 layer stacking. It is a complex silicate mineral with formula (Na,Ca,K)56(Al6Si6O24)7(SO4)12·6H2O. It was named after a location in Farnese, Lazio, Italy. It is a member of the cancrinite-sodalite group, approved in 2004 as a new mineral species. The group is characterized by the number of stacking layers making up each member, with farneseite being one of newest minerals in the group with a 14 layer stacking structure. It is a clear transparent mineral and has a hexagonal crystal system with crystal class of 6/m and space group of P63/m. The specimens discovered in Farnese were in a pyroclastic rock from the Làtera Cauldera region.In the volcanic region of Latium, Italy, a few scientists found some crystals with hexagonal morphology while doing a study of the cancrinite-group minerals. These crystals were in a rock sample they had collected from a small village called Farnese in the Viterbo Province, north of Rome. They believed the substance to be sacrofanite, but after several diagnostic tests they observed the powder IR spectrum of the sample showed some differences from sacrofanite. They then performed a complete chemical and structural analysis which confirmed that the substance indeed was a new feldspathoid species related to the cancrinite-sodalite group. The cancrinite group are minerals with hexagonal and trigonal crystal systems with various anions and cations located in cages within the main frame. The crystal structures of the members of the group are characterized by the six membered rings of SiO4 and Al04 tetrahedra. The layers are lined up along the c axis in the ABCABABACBACAC… fashion.
Read More About Farneseite / Source
Faujasite

Faujasite (FAU-type zeolite) is a mineral group in the zeolite family of silicate minerals. The group consists of faujasite-Na, faujasite-Mg and faujasite-Ca. They all share the same basic formula (Na2,Ca,Mg)3.5[Al7Si17O48]·32(H2O) by varying the amounts of sodium, magnesium and calcium. Faujasite occurs as a rare mineral in several locations worldwide.
Faujasite materials are widely synthesized industrially. The relatively low-silica (Si/Al<2) synthetic faujasite is called Zeolite X and the high-silica (Si/Al>2) one is called Zeolite Y. In addition, the aluminum component in zeolite Y can be removed by acid-treatment and/or steam-treatment, and the resulting faujasite is called USY (Ultrastable zeolite Y). USY is used in fluid catalytic cracking process as a catalyst.
Read More About Faujasite / Source
Faustite
The IMA approved mineral faustite, named after the American mineralogist and petrologist with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Dr. George Tobias Faust, is a member of the triclinic turquoise group of hydrous phosphates with the following chemical composition:
ZnAl6(PO4)4(OH)8·4H2O
Some divalent copper generally replaces the zinc position. Faustite is the zinc rich analogue of turquoise having almost four times as much zinc than copper in its crystal structure. Trivalent (ferric) iron may replace some of the aluminum. Minor amounts of calcium may also be present. It has a hardness of 4.5 – 5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and aside from having a slightly lower hardness, it may be difficult to distinguish it from turquoise in hand specimens.
Faustite has a blue-green to apple green color in polished cabochons, and may be presented as a turquoise imitation, and it may also be treated with stabilizers for jewelry making.
Read More About Faustite / Source
Fayalite

Fayalite (Fe2SiO4, commonly abbreviated to Fa) is the iron-rich end-member of the olivine solid-solution series. In common with all minerals in the olivine group, fayalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group Pbnm) with cell parameters a 4.82 Å, b 10.48 Å and c 6.09 Å.
Fayalite forms solid solution series with the magnesium olivine endmember forsterite (Mg2SiO4) and also with the manganese rich olivine endmember tephroite (Mn2SiO4).
Iron rich olivine is a relatively common constituent of acidic and alkaline igneous rocks such as volcanic obsidians, rhyolites, trachytes and phonolites and plutonic quartz syenites where it is associated with amphiboles. Its main occurrence is in ultramafic volcanic and plutonic rocks and less commonly in felsic plutonic rocks and rarely in granite pegmatite. It also occurs in lithophysae in obsidian. It also occurs in medium-grade thermally metamorphosed iron-rich sediments and in impure carbonate rocks.Fayalite is stable with quartz at low pressures, whereas more magnesian olivine is not, because of the reaction olivine + quartz = orthopyroxene. Iron stabilizes the olivine + quartz pair. The pressure and compositional dependence of the reaction can be used to calculate constraints on pressures at which assemblages of olivine + quartz formed.
Fayalite can also react with oxygen to produce magnetite + quartz: the three minerals together make up the “FMQ” oxygen buffer. The reaction is used to control the fugacity of oxygen in laboratory experiments. It can also be used to calculate the fugacity of oxygen recorded by mineral assemblages in metamorphic and igneous processes.
At high pressure, fayalite undergoes a phase transition to ahrensite, the iron-bearing analogue of ringwoodite, i.e., contrary to forsterite there is no intermediate form analogous to wadsleyite; under the conditions prevailing in the upper mantle of the Earth, the transition would occur at ca. 6–7 GPa, i.e., at substantially lower pressure than the phase transitions of forsterite. In high-pressure experiments, the transformation may be delayed, so that it may remain stable to pressures of almost 35 GPa (see fig.), at which point it may become amorphous rather than take on a crystalline structure such as ahrensite.
The name fayalite is derived from Faial (Fayal) Island in the Azores where it was first described in 1840.
Read More About Fayalite / Source
Feldspar

Feldspars (sometimes spelled felspars) are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the plagioclase (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the alkali (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth’s crust, and 41% of the Earth’s continental crust by weight.Feldspars crystallize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks.
Read More About Feldspar / Source
Feldspathoid
The feldspathoids are a group of tectosilicate minerals which resemble feldspars but have a different structure and much lower silica content. They occur in rare and unusual types of igneous rocks, and are usually not found in rocks containing primary quartz. A notable exception where feldspathoids and quartz-bearing rocks are found together is the Red Hill Syenite.Foid, a contraction of the term feldspathoid, is applied to any igneous rock containing up to 60% modal feldspathoid minerals. For example, a syenite with significant nepheline present can be termed a nepheline-bearing syenite or nepheline syenite, with the term nepheline replaceable by any foid mineral. Such terminology is used in the Streckeisen (QAPF) classification of igneous rocks.
Read More About Feldspathoid / Source
Felsőbányaite

Felsőbányaite or basaluminite is a hydrated aluminium sulfate mineral with formula: Al4(SO4)(OH)10·4H2O. It is a rare white to pale yellow mineral which typically occurs as globular masses and incrustations or as minute rhombic crystals. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system.It occurs as a weathering product under acidic conditions associated with pyrite or marcasite decomposition. Associated minerals include hydrobasaluminite, hydroargillite, meta-aluminite, allophane, gibbsite, gypsum and aragonite.Felsőbányaite was first described in 1853 for an occurrence in the Baia Sprie mine, Baia Sprie (Felsőbánya), Maramureș County, Romania, and named for the locality. The mineral name basaluminite was used for an occurrence of the same mineral in England in 1948 and discredited by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) in 2006.
Read More About Felsőbányaite / Source
Ferberite

Ferberite is the iron endmember of the manganese – iron wolframite solid solution series. The manganese endmember is hübnerite. Ferberite is a black monoclinic mineral composed of iron(II) tungstate, FeWO4.
Ferberite and hübnerite often contain both divalent cations of iron and manganese, with wolframite as the intermediate species for which the solid solution series is named.Ferberite occurs as granular masses and as slender prismatic crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 4.5 and a specific gravity of 7.4 to 7.5. Ferberite typically occurs in pegmatites, granitic greisens, and high temperature hydrothermal deposits. It is a minor ore of tungsten.
Ferberite was discovered in 1863 in Sierra Almagrera, Spain, and named after the German mineralogist Moritz Rudolph Ferber (1805–1875).
Read More About Ferberite / Source
Fergusonite

Fergusonite is a mineral comprising a complex oxide of various rare-earth elements. The general chemical formula of fergusonite is (Y,REE)NbO4, where REE = rare-earth elements in solid solution with Y. Yttrium is usually dominant (the mineral in this case being referred to as fergusonite-(Y)), but sometimes Ce or Nd may be the major rare-earth component (in fergusonite-(Ce) and fergusonite-(Nd), respectively). The other rare-earth elements are present in smaller amounts, and tantalum sometimes substitutes for some of the niobium. There are Fergusonite-beta-(Nd), Fergusonite-beta-(Y), Fergusonite-beta-(Ce) forms too, but they are classified as 4.DG.10 in the Nickel–Strunz system. The mineral has tetragonal crystal symmetry and the same structure as scheelite (calcium tungstate, CaWO4), but can be metamict (amorphous) due to radiation damage from its small content of thorium. It is found as needle-like or prismatic crystals in pegmatite. It was named after British politician and mineral collector Robert Ferguson of Raith (1767–1840).
Read More About Fergusonite / Source
Feroxyhyte
Feroxyhyte is an oxide/hydroxide of iron, δ-Fe3+O(OH). Feroxyhyte crystallizes in the hexagonal system. It forms as brown rounded to concretionary masses. Feroxyhyte is opaque, magnetic, has a yellow streak, and has a relative density of 4.2.It occurs in manganese-iron nodules on the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean floors. It is also found in the Baltic, White, and Kara Seas. Forms under high pressure conditions and reverts to goethite on exposure to surface conditions. It also occurs as cement and coatings on clasts in poorly drained soils and sediments, formed by the rapid oxidation of iron(II) oxide compounds.It was first described in 1976 for an occurrence in soils at its type locality: Kolomyya, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, Ukraine.
Read More About Feroxyhyte / Source
Ferrierite

The ferrierite group of zeolite minerals (the FER structure) consists of three very similar species: ferrierite-Mg, ferrierite-Na, and ferrierite-K, based on the dominant cation in the A location. ferrierite-Mg and ferrierite-K are orthorhombic minerals and ferrierite-Na is monoclinic with highly variable cationic composition (Na,K)2Mg(Si,Al)18O36(OH)·9H2O. Calcium and other ions are often also present. They are found in vitreous to pearly, often radiating, spherical aggregates of thin blade-shaped transparent to translucent crystals.
Ferrierite typically occurs as an alteration mineral in basaltic rocks and in tuffaceous sediments. In North America, it is found at Kamloops Lake, BC, Canada (the original type locality) and Leavitt Lake, California. Ferrierite was named for Canadian geologist and mining engineer Walter Frederick Ferrier (1865–1950).
Read More About Ferrierite / Source
Ferrihydrite

Ferrihydrite (Fh) is a widespread hydrous ferric oxyhydroxide mineral at the Earth’s surface, and a likely constituent in extraterrestrial materials. It forms in several types of environments, from freshwater to marine systems, aquifers to hydrothermal hot springs and scales, soils, and areas affected by mining. It can be precipitated directly from oxygenated iron-rich aqueous solutions, or by bacteria either as a result of a metabolic activity or passive sorption of dissolved iron followed by nucleation reactions. Ferrihydrite also occurs in the core of the ferritin protein from many living organisms, for the purpose of intra-cellular iron storage.
Read More About Ferrihydrite / Source
Ferrimolybdite

Ferrimolybdite is a hydrous iron molybdate mineral with formula: Fe3+2(MoO4)3·8(H2O) or Fe3+2(MoO4)3·n(H2O). It forms coatings and radial aggregates of soft yellow needles which crystallize in the orthorhombic system.
Read More About Ferrimolybdite / Source
Ferro-actinolite
Ferro-actinolite is the ferrous iron-rich endmember of the actinolite-tremolite continuous solid solution series of the double chain calcareous amphibole group of inosilicate minerals. All the series members belong to the monoclinic crystal system.
The following formula comparison indicates the position of individual well-known members within the series:
tremolite: ☐Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2
actinolite: ☐Ca2(Mg4.5-2.5Fe2+0.5-2.5)Si8O22(OH)2
ferro-actinolite: ☐Ca2(Mg2.5-0.0Fe2+2.5-5.0)Si8O22(OH)2Some other substitute cations that may replace either Ca, Mg, or Fe include potassium (K), aluminium (Al), manganese (Mn), titanium (Ti), and chromium (Cr). A fluorine (F) anion may partially replace the hydroxyl (OH).
Read More About Ferro-actinolite / Source
Ferrogedrite

Ferrogedrite is an amphibole mineral with the complex chemical formula of ☐Fe2+2(Fe2+3Al2)(Si6Al2)O22(OH)2. It is sodium and calcium poor, making it part of the magnesium-iron-manganese-lithium amphibole subgroup. Defined as less than 1.00 apfu (atoms per formula unit) of Na + Ca and consisting of greater than 1.00 apfu of (Mg, Fe2+, Mn2+, Li) separating it from the calcic-sodic amphiboles.: 12–78 It is related to anthophyllite amphibole and gedrite through coupled substitution of (Al, Fe3+) for (Mg, Fe2+, Mn) and Al for Si. and determined by the content of silicon in the standard cell.
Read More About Ferrogedrite / Source
Ferrohortonolite
Ferrohortonolite is a mineral variety in the olivine series composed of 70% to 90% fayalite and 30% to 10% forsterite or Fe/(Fe+Mg) ratio of 0.7 to 0.9. It is from the obsolete hortonolite terminology for the olivine series.It has been reported from Mount Gillies, Queensland, Australia; the Ilimaussaq complex of west Greenland; Pantelleria Island, Sicily; and from Choc village on Saint Lucia.
Read More About Ferrohortonolite / Source
Ferronigerite-2N1S

Ferronigerite-2N1S is an iron, tin, alumino-hydroxide mineral that naturally occurs around sillimanite-quartz veins. Ferronigerite-2N1S belongs to the nigerite group, högbomite supergroup. The other constituents of the nigerite group are ferronigerite-6N6S, magnesionigerite-2N1S, magnesionigerite-6N6S, zinconigerite-2N1S and zinconigerite-6N6S. The 2N1S ending stands for the nolanite and spinel structural layers.Ferronigerite-2N1S was first discovered in the Kabba province of central Nigeria in 1944; it was originally named Nigerite. Its name was later changed to nigerite-6H then to nigerite-6T and in 2003 ferronigertie-2N1S was approved by the International Mineralogical Association.
Read More About Ferronigerite-2N1S / Source
Ferropericlase
Ferropericlase or magnesiowüstite is a magnesium/iron oxide with the chemical formula (Mg,Fe)O that is interpreted to be one of the main constituents of the Earth’s lower mantle together with the silicate perovskite ((Mg,Fe)SiO3), a magnesium/iron silicate with a perovskite structure. Ferropericlase has been found as inclusions in a few natural diamonds. An unusually high iron content in one suite of diamonds has been associated with an origin from the lowermost mantle. Discrete ultralow-velocity zones in the deepest parts of the mantle, near the Earth’s core, are thought to be blobs of ferropericlase, as seismic waves are significantly slowed as they pass through them, and ferropericlase is known to have this effect at the high pressures and temperatures found deep within the Earth’s mantle. In May 2018, ferropericlase was shown to be anisotropic in specific ways in the high pressures of the lower mantle, and these anisotropies may help seismologists and geologists to confirm whether those ultra-low velocity zones are indeed ferropericlase, by passing seismic waves through them from various different directions and observing the exact amount of change in the velocity of those waves.
Read More About Ferropericlase / Source
Ferroselite

Orthorhombic ferroselite and its isometric polymorph dzharkenite are iron selenides of general formula FeSe2 precipitated under reducing conditions in anoxic environments. They are a source of selenium in the Rocky Mountains where selenium occurrence is associated with Upper Cretaceous shale deposits.
In the frame of safety assessment calculations made for deep disposal of high-level radioactive waste, ferroselite and dzharkenite are also considered in geochemical calculations as one of the mineral phases limiting the solubility of Selenium-79.
Read More About Ferroselite / Source
Fettelite

Fettelite, also known as sanguinite, is a mercury-sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula Ag16HgAs4S15. The mineral was first described by Wang and Paniagua (1996) who named it after M. Fettel, a German field geologist who collected the first samples from Odenwald. It was first collected in the Nieder-Beerbach mine, 10 km south of Darmstadt, Odenwald, Germany. Its normal occurrence is in hydrothermal veins, which can cut gabbro-diorite intrusives. It is closely related to other rare minerals like dervillite, daomanite, vaughanite and criddleite which are also found in the same type locality as fettelite.Fettelite occurs as clusters of hexagonal flakes. These flakes can get up to 0.2 mm across and around 5-10 µm thick. In more complex hexagonal tablets, somewhat larger sub parallel aggregates can be measured. The birefringence of Fettelite is moderate white to grayish brown.
Read More About Fettelite / Source
Fichtelite

Fichtelite is a rare white mineral found in fossilized wood from Bavaria. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It is a cyclic hydrocarbon: dimethyl-isopropyl-perhydrophenanthrene, C19H34. It is very soft with a Mohs hardness of 1, the same as talc. Its specific gravity is very low at 1.032, just slightly denser than water.
It was first described in 1841 and named for the location, Fichtelgebirge, Bavaria, Germany. It has been reported from fossilized pine wood from a peat bog and in organic-rich modern marine sediments.
Read More About Fichtelite / Source
Fingerite
Fingerite is a copper vanadate mineral with formula: β-Cu2V2O5. It was discovered as triclinic crystals occurring as volcanic sublimates around fumaroles in the crater of the Izalco Volcano, El Salvador.
Associated minerals include thenardite, euchlorine, stoiberite, shcherbinaite, ziesite, bannermanite, chalcocyanite and chalcanthite. The mineral also dissolves in water.Fingerite is named for Dr. Larry W. Finger (b. 1940) of the Geophysical Laboratory, Carnegie Institution of Washington.
Read More About Fingerite / Source
Fletcherite
Fletcherite is a rare thiospinel sulfide mineral with formula Cu(Ni,Co)2S4. It is an opaque metallic steel gray mineral which crystallizes in the cubic crystal system. It is a member of the linnaeite group.
It was first described in 1977 for an occurrence in the Fletcher Mine, Viburnum Trend (New Lead Belt), near Centerville, Reynolds County, Missouri.It occurs as a dissemination within copper sulfide minerals in mineralization replacing dolomite at the type locality in the Fletcher
mine where it is associated with vaesite, pyrite, covellite, chalcopyrite, bornite and digenite. In an occurrence in Kalgoorlie, Australia it is found in black slate associated with pyrrhotite.
Read More About Fletcherite / Source
Fluckite

Fluckite is an arsenate mineral with the chemical formula CaMnH2(AsO4)2·2(H2O).Fluckite’s mineral crystallography is triclinic meaning it has three axis of different length and three different interior angles that do not equal 90°. Because fluckite possesses three axes with different angles and lengths it is an anisotropic mineral. This means that it has more than one optic axis. This mineral is a member of the P1 space group meaning that it can be rotated 360° degrees and inverted to obtain the original figure. Optically, this mineral has positive biaxial birefringence, which can be shown obtaining an interference figure that is blue in the upper right and lower left quadrants of the figure while looking down the c- axis. Fluckite possesses moderate optical relief which is the degree to which the mineral stands out from the mounting medium.
Read More About Fluckite / Source
Fluellite

Fluellite is a mineral with the chemical formula Al2(PO4)F2(OH)•7H2O. The name is from its chemical composition, being a fluate of alumine (French).It was first described in 1824 for an occurrence in the Stenna Gwyn Mine, St Stephen-in-Brannel, St Austell District, Cornwall, England.It is a rare secondary mineral found in complex granite pegmatites where it forms by weathering of earlier phosphate minerals. It is found in association with fluorapatite, wavellite, phosphosiderite, strengite, aldermanite, cacoxenite, variscite, turquoise, fluorite and quartz.
Read More About Fluellite / Source
Fluoborite

Fluoborite has a chemical formula of Mg3(BO3)(F,OH)3. Its name comes from its main chemical components, FLUOrine and BORon. It was first described in 1926.Fluoborite’s crystal system is hexagonal, meaning it has one six-fold axis of rotation. It also has a mirror plane perpendicular to the c-axis. Fluoborite is uniaxial, just like all other hexagonal minerals. Uniaxial means it has only one optic axis. It is anisotropic. Its relief is low, and it is birefringent.
There are three major settings fluoborite is found. It is found in skarns developed in metamorphosed boron-rich magnesium rocks, contact metamorphosed marble, and in contact metasomatic magnetite deposits. There are two major type localities for fluoborite. One is Tall Mine, Kallmora, Norberg, Västmanland, Sweden. It is an iron mine in a contact metasomatic magnetite deposit. The other type locality is the Huerta del Vinagre mine, Spain.It occurs associated with ludwigite, chondrodite, magnetite and calcite in the Tallgruvan, Sweden occurrence. It occurs with mooreite, willemite, fluorite, hydrozincite, pyrochroite, zincite and rhodochrosite at Sterling Hill, New Jersey.
Read More About Fluoborite / Source
Fluocerite
Fluocerite, also known as tysonite, is a mineral consisting of cerium and lanthanum fluorides, with the chemical formula (Ce,La)F3. The end members are classified as two different mineral types depending on the cation, fluocerite-(Ce) and fluocerite-(La), corresponding respectively to lanthanum trifluoride and cerium trifluoride. Both crystallize in the trigonal system.Fluocerite-(Ce) was first described (without the Ce) in 1845 from hydrothermal veins in granite in Sweden. Fluocerite-(La) was first described in 1969 from the type locality in central Kazakhstan. The name tysonite was given in 1880 to the same type of mineral found in Colorado. Tysonite-type structure is used for rare-earth fluorides with the P3c1 space group structure.
Read More About Fluocerite / Source
Fluor-buergerite

Fluor-buergerite, originally named buergerite, is a mineral species belonging to the tourmaline group. It was first described for an occurrence in rhyolitic cavities near Mexquitic, San Luis Potosi, Mexico. It was approved as a mineral in 1966 by the IMA and named in honor of Martin J. Buerger (1903–1986), professor of mineralogy at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It has also been reported from Minas Gerais, Brazil, and the Central Bohemia Region of the Czech Republic.
Read More About Fluor-buergerite / Source
Fluor-liddicoatite
Fluor-liddicoatite is a rare member of the tourmaline group of minerals, elbaite subgroup, and the theoretical calcium endmember of the elbaite-fluor-liddicoatite series; the pure end-member has not yet been found in nature. Fluor-liddicoatite is indistinguishable from elbaite by X-ray diffraction techniques. It forms a series with elbaite and probably also with olenite. Liddiocoatite is currently a non-approved mineral name, but Aurisicchio et al. (1999) and Breaks et al. (2008) found OH-dominant species. Formulae are
Fluor-liddicoatite Ca(Li2Al)Al6(BO3)3Si6O18(OH)3F
Elbaite Na(Al1.5Li1.5)Al6(BO3)3Si6O18(OH)4
Olenite NaAl9B3Si6O27O3(OH)Fluor-liddicoatite was named in 1977 after Richard T. Liddicoat (1918–2002) gemmologist and president of the Gemological Institute of America, who is well known for introducing the GIA diamond grading system in 1953.
Read More About Fluor-liddicoatite / Source
Fluor-uvite

Fluor-uvite is a tourmaline mineral with the chemical formula CaMg3(Al5Mg)(Si6O18)(BO3)3(OH)3F. It is a rare mineral that is found in calcium rich contact metamorphic rocks with increased amounts of boron. Uvite is trigonal hexagonal, which means that it has three equal length axes at 120 degrees, all perpendicular to its fourth axis which has a different length. Uvite is part of the space group 3m. Uvite’s hardness has been measured to be 7.5 on the Mohs hardness scale. The color of uvite widely varies, depending on the sample, but is mostly deep green or brown. In regard to uvite’s optical properties, it is uniaxial (-) and anisotropic, meaning that the velocity of light in the mineral depends on the path that it takes. In plane polarized light, uvite is colorless to pale yellow and shows weak pleochroism.Uvite was first found in 1929 in Uva Province, Sri Lanka, hence the name.Uvite has no use, but is commonly found in mineral specimen collections. The mineral is sought after by collectors because of its pronounced colors, crystal structure, and often large crystal size.
Read More About Fluor-uvite / Source
Fluorapatite

Fluorapatite, often with the alternate spelling of fluoroapatite, is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F (calcium fluorophosphate). Fluorapatite is a hard crystalline solid. Although samples can have various color (green, brown, blue, yellow, violet, or colorless), the pure mineral is colorless, as expected for a material lacking transition metals. Along with hydroxylapatite, it can be a component of tooth enamel, but for industrial use both minerals are mined in the form of phosphate rock, whose usual mineral composition is primarily fluorapatite but often with significant amounts of the other.Fluorapatite crystallizes in a hexagonal crystal system. It is often combined as a solid solution with hydroxylapatite (Ca5(PO4)3OH or Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2) in biological matrices. Chlorapatite (Ca5(PO4)3Cl) is another related structure. Industrially, the mineral is an important source of both phosphoric and hydrofluoric acids.
Fluorapatite as a mineral is the most common phosphate mineral. It occurs widely as an accessory mineral in igneous rocks and in calcium rich metamorphic rocks. It commonly occurs as a detrital or diagenic mineral in sedimentary rocks and is an essential component of phosphorite ore deposits. It occurs as a residual mineral in lateritic soils.Fluorapatite is found in the teeth of sharks and other fishes in varying concentrations. It is also present in human teeth that have been exposed to fluoride ions, for example, through water fluoridation or by using fluoride-containing toothpaste. The presence of fluorapatite helps prevent tooth decay or dental caries. Fluoroapatite has a mild bacteriostatic property as well, which helps decrease the proliferation of Streptococcus mutans, the predominant bacterium related to dental caries.
Read More About Fluorapatite / Source
Apophyllite-(KF)

Apophyllite-(KF) or fluorapophyllite is a mineral of the apophyllite group, with the chemical formula of KCa4Si8O20(F,OH)·8(H2O). It gets the first half of its name, “fluor”, from containing more fluorine than hydroxide compared to the other minerals in the apophyllite group.
Fluorapophyllite crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system. Tetragonal minerals have three axes of different lengths and angles of 90 degrees. Fluorapophyllite is an anisotropic mineral and has low relief. This mineral belongs to the uniaxial (+) optical class, which means its indicatrix has a prolate sphenoid shape with a circular section, principal section, and one optic axis.Among the apophyllite group, fluorapophyllite is the most abundant compared to the other two minerals in the group, hydroxyapophyllite and natroapophyllite. It is popular among many mineral collectors because of the large, well-developed crystals they form and the multiple colors they come in. The most wanted variation of fluorapophyllite is the green colored variant, which is found in India. Fluorapophyllite is also found in New Jersey of the United States. This mineral is found as a secondary mineral in vesicles in volcanic rocks such as basalt.
Read More About Apophyllite-(KF) / Source
Fluorcanasite
Fluorcanasite is a rare calcium, potassium, sodium fluoride silicate mineral, discovered in the Kirovsk mine’s dumps, in Russia. It has been approved by the IMA in 2007. The name fluorcanasite is a portmanteau word, and was made by blending fluorine, a chemical element that can be found in the mineral, and canasite, as the mineral is close to canasite in several ways (analogue of said mineral and a member of the canasite group). Fluorcanasite is also close to frankamenite.
Read More About Fluorcanasite / Source
Fluorcaphite

Fluorcaphite is a mineral with the chemical formula (Ca,Sr,Ce,Na)5(PO4)3F. It is found in the Kola Peninsula in Russia. Its crystals are hexagonal (dipyramidal class) and are transparent with a vitreous luster. It is light to bright yellow, leaves a white streak and is rated five on the Mohs Scale. Fluorcaphite is radioactive.
Read More About Fluorcaphite / Source
Fluorellestadite

Fluorellestadite is a rare nesosilicate of calcium, with sulfate and fluorine, with the chemical formula Ca10(SiO4)3(SO4)3F2. It is a member of the apatite group, and forms a series with hydroxylellestadite.
Read More About Fluorellestadite / Source
Fluorite

Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite.Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics are also usable in the far-ultraviolet and mid-infrared ranges, where conventional glasses are too opaque for use.
Read More About Fluorite / Source
Fluoro-richterite

Fluororichterite is a rare amphibole with formula Na(NaCa)Mg5Si8O22F2.
Read More About Fluoro-richterite / Source
Fontarnauite

Fontarnauite is a relatively recently described, rare sulfate, borate mineral with the chemical formula (Na,K)2(Sr,Ca)(SO4)[B5O8(OH)]·2H2O. It is found in an evaporite boron deposit. It coexists with other evaporite boron minerals, especially probertite. It is monoclinic, crystallizing in the space group P21/c.It was named for Ramon Fontarnau i Griera, a materials scientist of the University of Barcelona.
Read More About Fontarnauite / Source
Fornacite

Fornacite is a rare lead, copper chromate arsenate hydroxide mineral with the formula: Pb2Cu(CrO4)(AsO4)(OH). It forms a series with the phosphate mineral vauquelinite. It forms variably green to yellow, translucent to transparent crystals in the monoclinic – prismatic crystal system. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.3 and a specific gravity of 6.27.
It was first described in 1915 and named after Lucien Lewis Forneau (1867–1930) the governor of the French Congo. Its type locality is in Reneville, Republic of Congo.It occurs in the oxidized zone of ore deposits and is associated with dioptase, wulfenite, hemihedrite, phoenicochroite, duftite, mimetite, shattuckite, chrysocolla, hemimorphite, willemite and fluorite.
Read More About Fornacite / Source
Forsterite

Forsterite (Mg2SiO4; commonly abbreviated as Fo; also known as white olivine) is the magnesium-rich end-member of the olivine solid solution series. It is isomorphous with the iron-rich end-member, fayalite. Forsterite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group Pbnm) with cell parameters a 4.75 Å (0.475 nm), b 10.20 Å (1.020 nm) and c 5.98 Å (0.598 nm).Forsterite is associated with igneous and metamorphic rocks and has also been found in meteorites. In 2005 it was also found in cometary dust returned by the Stardust probe. In 2011 it was observed as tiny crystals in the dusty clouds of gas around a forming star.Two polymorphs of forsterite are known: wadsleyite (also orthorhombic) and ringwoodite (isometric, Cubic crystal system). Both are mainly known from meteorites.
Peridot is the gemstone variety of forsterite olivine.
Read More About Forsterite / Source
Fougèrite
Fougèrite is a relatively recently described naturally occurring green rust mineral. It is the archetype of the fougèrite group in the larger hydrotalcite supergroup of naturally occurring layered double hydroxides. The structure is based on brucite-like layers containing Fe2+ and Fe3+ cations, O2− and OH− anions, with loosely bound [CO3]2− groups and H2O molecules between the layers. Fougèrite crystallizes in trigonal system. The ideal formula for fougèrite is [Fe2+4Fe3+2(OH)12][CO3]·3H2O. Higher degrees of oxidation produce the other members of the fougèrite group, namely trébeurdenite, [Fe2+2Fe3+4O2(OH)10][CO3]·3H2O and mössbauerite, [Fe3+6O4(OH)8][CO3]·3H2O.
Fougèrite was first found in forested soils near Fougères, Brittany, France, and recognised as a valid mineral species by the International Mineralogical Association in 2002. It is blue-green to bluish-gray in colour, and resembles clay minerals in habit, forming hexagonal platelets of submicron diameter. In this environment, it is intimately intergrown with trébeurdenite, to give varying overall ratios of Fe2+:Fe3+. The existence of two intergrown fixed-composition phases has been demonstrated by Mössbauer spectroscopy. The mineral is unstable in air, and decomposes by oxidation, dehydration and decarbonation, to ferrihydrite, and ultimately to lepidocrocite or goethite, Fe3+O(OH).
Read More About Fougèrite / Source
Fourmarierite

Fourmarierite is a secondary uranium-lead mineral. It was named for the Belgian geologist Paul Fourmarier (1877–1970). Its chemical formula is Pb(UO2)4O3(OH)4•4H2O.
Read More About Fourmarierite / Source
Fraipontite

Fraipontite is a zinc aluminium silicate mineral with a formula of (Zn,Al)3(Si,Al)2O5(OH)4.It is a member of the kaolinite-serpentine mineral group and occurs as an oxidation product of zinc deposits. It occurs with smithsonite, gebhardite, willemite, cerussite and sauconite.It was first described in 1927 for an occurrence in Vieille Montagne, Verviers, Liège Province, Belgium. It was named for Julien Jean Joseph Fraipont (1857–1910), and Charles de Fraipont, geologists of Liege, Belgium. In addition to the type locality in Belgium, it has been reported from Tsumeb, Namibia; Laurium, Greece; Swaledale, North Yorkshire, England; the Silver Bill mine, Cochise County, Arizona, the Blanchard Mine, Socorro County, New Mexico and the Mohawk mine, San Bernardino County, California in the US; and from the Ojuela mine, Mapimi, Durango, Mexico.A synonym of the fraipontite is the zinalsite, which was reported in 1956 for an occurrence in Kazakhstan.
Read More About Fraipontite / Source
Francevillite

Francevillite is a uranyl-group vanadate mineral in the tyuyamunite series. Its chemical formula is (Ba,Pb)(UO2)2V2O8·5(H2O). Francevillite is a strongly radioactive mineral. It is typically orange, yellow or brownish yellow. It forms a series with curienite.
Read More About Francevillite / Source
Franckeite

Franckeite, chemical formula Pb5Sn3Sb2S14, belongs to a family of complex sulfide minerals. Franckeite is a sulfosalt. It is closely related to cylindrite.
It was first described in 1893 for an occurrence in Chocaya, Potosí Department, Bolivia. It is named after the mining engineers, Carl and Ernest Francke. It can be found in Bolivia at Poopó in Oruro and at Las Aminas, southeast of Chocaya, in Potosi. Franckeite has an average density of 5.7 and can be both grayish black, blackish gray in color.
It occurs in hydrothermal silver-tin deposits in Bolivia and in contact metamorphosed limestone deposit in the Kalkar quarry in California. It occurs with cylindrite, teallite, plagionite, zinkenite, cassiterite, wurtzite, pyrrhotite,
marcasite, arsenopyrite, galena, pyrite, sphalerite, siderite and stannite.
Read More About Franckeite / Source
Frankamenite
Frankamenite is the fluorine-dominate variation of the rare mineral canasite with a general formula of K3Na3Ca5(Si12O30)[F,(OH)]4·(H2O).Frankamenite belongs to the triclinic crystal system, with the bases of its structure containing Ca-Na mixed octahedra joined by octagonal tubes SiO4 of the composition (Si12O30). Frankamenite has six Ca-Na mixed positions distributed amongst these octahedra, reflecting its varying compositions.Frankamenite was named for the Russian mineralogist-crystallographer V. A. Frank-Kamentsky (1915–1994), who discovered the mineral.Frankamenite occurs in association with the rare mineral charoite, which is found only in the Murun Massif of the Olyokma-Chara Plateau, Aldan Shield, Sakha Republic, Yakutia, Siberia, Russia. Here, metasomatism enriches a syenite massif with potassium when it comes into contact with a limestone at around 200–250 °C. This metamorphic process produces a potassium feldspar metasomatite, the typical geological environment for canasite and, therefore, frankamenite. Frankamenite and charoitein are exclusive to the Sakha Republic in this sort of environment, as mineralogists have yet to discover the minerals elsewhere.
Read More About Frankamenite / Source
Frankdicksonite
Frankdicksonite is a halide mineral with the chemical formula BaF2 which corresponds to the chemical compound barium fluoride. It occurs in the Carlin gold deposit of Eureka County, Nevada as cubic crystals sized between 0.1 and 4 mm, and is of hydrothermal origin. Its only associated mineral is quartz and the frankdicksonite crystals are always completely encapsulated in it. Frankdicksonite has fluorite crystal structure with a cubic symmetry and the lattice constant a = 619.64 pm. Its Vickers hardness on the {111} cleavage crystal faces varies between 88 and 94 kg/mm2 and is close to that of the synthetic barium fluoride (95 kg/mm2). Its refractive index (1.475) is almost identical to that of BaF2 (1.474). Under electron irradiation, it emits strong blue cathodoluminescence. The major impurity in frankdicksonite is strontium with concentrations up to 0.5% by weight. Also present are silicon (0.02%) and magnesium (0.0015%); other impurities have concentrations below 0.0015%.Although synthetic barium fluoride has been commonly known from at least 1846, it had not been found in nature. The natural existence of barium fluoride was predicted by Michael Fleischer in 1970. Later in the same year, the mineral was discovered by Arthur S. Radtke and named after Frank W. Dickson (born 1922), professor of Geochemistry at Stanford University in recognition of his contributions to geology and geochemistry of low-temperature ore deposits. Frankdicksonite was officially recognized by the Commission of New Minerals and Mineral Names in 1974.
Read More About Frankdicksonite / Source
Frankhawthorneite
Frankhawthorneite Cu2Te6+O4(OH)2 is a monoclinic copper tellurate mineral (space group P21/n) named after Prof. Frank Christopher Hawthorne (born 1946), University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada. It was discovered at Centennial Eureka Mine, Tintic District, East Tintic Mountains, Juab County, Utah, in 1995. It has a leaf green color.
Read More About Frankhawthorneite / Source
Franklinite

Franklinite is an oxide mineral belonging to the normal spinel subgroup’s iron (Fe) series, with the formula Zn2+Fe23+O4.
As with another spinel member magnetite, both ferrous (2+) and ferric (3+) iron may be present in franklinite samples. Divalent iron and/or manganese (Mn) may commonly accompany zinc (Zn) and trivalent manganese may substitute for some ferric iron.
At its type locality, franklinite can be found with a wide array of minerals, many of which are fluorescent. More commonly, it occurs with willemite, calcite, and zincite. In these rocks, it forms as disseminated small black crystals with their octahedral faces visible at times. It may rarely be found as a single large euhedral crystal.
Franklinite is a major ore of the element zinc. It is named after its local discovery at the Franklin Mine and Sterling Hill Mines in New Jersey.
Read More About Franklinite / Source
Franklinphilite
Franklinphilite is a phyllosilicate of the stilpnomelane group. Known from only two localities (with a third unconfirmed locality in Switzerland) It was found exclusively from the Franklin and Sterling Hill mines in Franklin, Sussex County, New Jersey. until 2013, when a locality in Wales was confirmed
Read More About Franklinphilite / Source
Freibergite

Freibergite is a complex sulfosalt mineral of silver, copper, iron, antimony and arsenic with formula (Ag,Cu,Fe)12(Sb,As)4S13. It has cubic crystals and is formed in hydrothermal deposits. It forms one solid solution series with tetrahedrite and another with argentotennantite. Freibergite is an opaque, metallic steel grey to black and leaves a reddish-black streak. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4.0 and a specific gravity of 4.85 – 5. It is typically massive to granular in habit with no cleavage and an irregular fracture.
The mineral was first described in 1853 from an occurrence in the silver mines of the type locality at Freiberg, Saxony.
Read More About Freibergite / Source
Freieslebenite

Freieslebenite is a sulfosalt mineral composed of antimony, lead, and silver. Sulfosalt minerals are complex sulfide minerals with the formula: AmBnSp. The formula of freieslebenite is AgPbSbS3.
Freieslebenite was discovered in approximately 1773 in the Himmelsfurst mines of Freiberg, Saxony, Germany. The mineral was initially called Schilf-Glaserz; however, in 1845 it was given the current name Freieslebenite after the Mining Commissioner of Saxony, Johann Carl Freiesleben (1774–1846).
Read More About Freieslebenite / Source
Fukuchilite

Fukuchilite, Cu3FeS8, is a copper iron sulfide named after the Japanese mineralogist Nobuyo Fukuchi (1877–1934), that occurs in ore bodies of gypsum-anhydrite at the intersection points of small masses of barite, covellite, gypsum and pyrite, and is mostly found in the Hanawa mine in the Akita prefecture of Honshū, Japan where it was first discovered in 1969. It occurs in masses within the third geologic unit of the Kuroko type deposits within the mine.
As a copper, iron sulfide, it is placed in the same group as bornite and chalcopyrite, and most fukuchilite locations are found in relatively close proximity to these minerals. Fukuchilite was found to have a reflection color very similar to bornite and bright pinkish brown in air, while being a purplish brown in oil. Also, it was found to have a reactivity lower than pyrite, but distinctly higher than bornite. It has a Mohs hardness of 4–6, a specific gravity of 4.9, and a sub metallic luster, composed of 11.1% iron, 37.9% copper, and 51.00% of sulfur.It is in the isotropic cubic crystal system with symmetry: (2/m3), space group P a3. Much relating to the structure of the mineral is still under debate, and some believe that fukuchilite might actually be a form of villamaninite (Cu,Ni,Co,Fe)S2, but fukuchilite currently still holds its mineral status as there is currently not enough evidence to discredit an already accepted and titled mineral.
Read More About Fukuchilite / Source
Gabrielite

Gabrielite is a rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with a chemical formula of Tl6Ag3Cu6(As,Sb)9S21 or Tl2AgCu2As3S7.It was first reported in 2002 for its occurrence in the Lengenbach quarry, Binntal, Valais, Switzerland, and named after Walter Gabriel (born 1943), a Swiss mineral photographer.
This region was transformed during the greenschist-garnet/amphibolite facies of metamorphism. Due to this many rare sulfosalts like gabrielite are found in this part of Switzerland.
Read More About Gabrielite / Source
Gadolinite

Gadolinite, sometimes known as ytterbite, is a silicate mineral consisting principally of the silicates of cerium, lanthanum, neodymium, yttrium, beryllium, and iron with the formula (Ce,La,Nd,Y)2FeBe2Si2O10. It is called gadolinite-(Ce) or gadolinite-(Y), depending on the prominent composing element (Y if yttrium predominates, and Ce if cerium). It may contain 35.5% yttria sub-group rare earths, 2.2% ceria earths, as much as to 11.6% BeO, and traces of thorium. It is found in Sweden, Norway, and the US (Texas and Colorado).
Read More About Gadolinite / Source
Gahnite

Gahnite, ZnAl2O4, is a rare mineral belonging to the spinel group. It forms octahedral crystals which may be green, blue, yellow, brown or grey. It often forms as an alteration product of sphalerite in altered massive sulphide deposits such as at Broken Hill, Australia. Other occurrences include Falun, Sweden where it is found in pegmatites and skarns; and, in the United States, Charlemont, Massachusetts; Spruce Pine, North Carolina; White Picacho district, Arizona; Topsham, Maine; and Franklin, New Jersey.It was first described in 1807 for an occurrence in the Falu mine, Falun, Dalarna, Sweden, and named after the Swedish chemist, Johan Gottlieb Gahn (1745–1818), the discoverer of the element manganese. It is sometimes called zinc spinel.
Read More About Gahnite / Source
Galaxite

Galaxite, also known as ‘mangan-spinel’ is an isometric mineral belonging to the spinel group of oxides with the ideal chemical formula Mn2+Al2O4.Galaxite is the manganese (Mn) rich endmember of the aluminium (Al) series of the spinel group. Divalent iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg) readily substitute for the manganese in the crystal structure. Trivalent iron may also substitute for the aluminium. Thus, reflecting most natural samples, the formula may be better represented as (Mn,Fe2+,Mg)(Al,Fe3+)2O4.Galaxite generally occurs as small granular aggregates with a red-brownish tone. It has a vitreous luster and leaves a brownish-red streak. It is rated 7.5 on the Mohs Scale.It was first described in 1932 for an occurrence at Bald Knob, Alleghany County, North Carolina near its namesakes, the town of Galax, Virginia, named after the plant galax or wandflower which grows in the area.It occurs in carbonate-rich metamorphosed manganese ore deposits. It occurs associated with alleghanyite, rhodonite, sonolite, spessartine, tephroite, kutnohorite, manganhumite, jacobsite, kellyite and alabandite in the Bald Knob area. Associated minerals include katoptrite, magnetite, manganostibite, magnussonite, tephroite, manganhumite and manganosite in the Brattfors mine area of Nordmark, Värmland, Sweden.It is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Galaxite / Source
Galena

Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system often showing octahedral forms. It is often associated with the minerals sphalerite, calcite and fluorite.
Read More About Galena / Source
Galkhaite

Galkhaite is a rare and chemically complex sulfosalt mineral from a group of natural thioarsenites. Its formula is (Cs,Tl)(Hg,Cu,Zn)6(As,Sb)4S12, making the mineral the only known natural Cs-Hg and Cs-As phase. It occurs in Carlin-type hydrothermal deposits.
Read More About Galkhaite / Source
Gananite
Gananite (simplified Chinese: 赣南矿; traditional Chinese: 贛南礦; pinyin: gànnánkuàng) is a rare bismuth fluoride mineral form of bismuth trifluoride with a general formula of BiF3. Gananite is an isotropic mineral, it belongs to the space group P43m. This means that gananite does not show any colors in cross polarized light, because when polarized light passes through it, it does not split into two perpendicular rays. In other words, because gananite is an isometric mineral, it does not exhibit double refraction. Moreover, this tells us that this mineral is not birefringent. Its color in plane-polarized light is blackish-brown, and it does not show pleochroism.
Read More About Gananite / Source
Ganophyllite
Ganophyllite is a phyllosilicate mineral. It was named by Axel Hamberg in 1890 from the Greek words for leaf (φύλλον) and luster (γανωμα); the latter one was chosen due to the lustrous cleavages. The mineral was approved by the IMA in 1959, and it is a grandfathered mineral, meaning its name is still believed to refer to an existing species until this day. Tamaite is the calcium analogue, while eggletonite is the natrium analogue of said mineral.
Read More About Ganophyllite / Source
Garnet

Garnets ( ) are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different species are pyrope, almandine, spessartine, grossular (varieties of which are hessonite or cinnamon-stone and tsavorite), uvarovite and andradite. The garnets make up two solid solution series: pyrope-almandine-spessartine (pyralspite), with the composition range [Mg,Fe,Mn]3Al2(SiO4)3; and uvarovite-grossular-andradite (ugrandite), with the composition range Ca3[Cr,Al,Fe]2(SiO4)3.
Read More About Garnet / Source
Gaspéite

Gaspéite, a very rare nickel carbonate mineral, with the formula (Ni,Fe,Mg)CO3, is named for the place it was first described, in the Gaspé Peninsula, Québec, Canada.
Gaspéite is the nickel rich member of the calcite group. A solid solution series exists between all members of this group with divalent cations readily exchanged within the common crystal structure. It forms massive to reniform papillary aggregates in fractures, botryoidal concretions in laterite or fracture infill. It is also present as stains and patinas on iron oxide boxworks of gossanous material.
Read More About Gaspéite / Source
Gatehouseite
Gatehouseite is a manganese hydroxy phosphate mineral with formula Mn5(PO4)2(OH)4. First discovered in 1987, it was identified as a new mineral species in 1992 and named for Bryan M. K. C. Gatehouse (born 1932). As of 2012, it is known from only one mine in South Australia.
Read More About Gatehouseite / Source
Gaylussite

Gaylussite is a carbonate mineral, a hydrated sodium calcium carbonate, formula Na2Ca(CO3)2·5H2O. It occurs as translucent, vitreous white to grey to yellow monoclinic prismatic crystals. It is an unstable mineral which dehydrates in dry air and decomposes in water.
Read More About Gaylussite / Source
Gedrite

Gedrite is a crystal belonging to the orthorhombic ferromagnesian subgroup of the amphibole supergroup of the double chain inosilicate minerals with the ideal chemical formula Mg2(Mg3Al2)(Si6Al2)O22(OH)2.
Gedrite is the magnesium (Mg) rich endmember of a solid solution series, with divalent magnesium cations readily replaced with ferrous iron (Fe), leading to the iron rich endmember ‘ferrogedrite’, with the formula: Fe2+2(Fe2+3Al2)(Si6Al2)O22(OH)2. However, pure endmembers are very rare, with often either one of the mentioned cations dominating the composition. Thus, the formula can be written in such a way to express common intermediary gedrite samples:
(Mg,Fe)2+2(Mg,Fe)2+3Al2(Al2Si6O22)(OH)2.
Divalent manganese (Mn) may substitute for some of the magnesium. Trivalent or ferric iron, or titanium4+ may replace some of the aluminum (Al). Fluorine and chlorine are common substitutes for the hydroxyl (OH) in amphoboles. Other chemical impurities may include calcium, sodium, and potassium.
Gedrite also forms a series with another ferromagnesian amphibole, anthophyllite.
Gedrite occurs in contact and medium to high grade metamorphic rocks in association with garnet, cordierite, anthophyllite, cummingtonite, sapphirine, sillimanite, kyanite, quartz, staurolite and biotite.Gedrite was first described for an occurrence in Gèdre, Hautes-Pyrenees, France in 1836.
Read More About Gedrite / Source
Geerite
Geerite is a copper sulfide mineral with the chemical formula Cu8S5. The mineral is named after the original collector, Adam Geer, of Utica, New York, US.
Read More About Geerite / Source
Gehlenite

Gehlenite, (Ca2Al[AlSiO7]), is a sorosilicate, Al-rich endmember of the melilite complete solid solution series with akermanite.
The type locality is in the Monzoni Mountains, Fassa Valley in Trentino in Italy, and is named after Adolf Ferdinand Gehlen (1775–1815) by A.J. Fuchs in 1815.
Read More About Gehlenite / Source
Geigerite
Geigerite is a mineral, a complex hydrous manganese arsenate with formula: Mn5(AsO3OH)2(AsO4)2·10H2O. It forms triclinic pinacoidal, vitreous, colorless to red to brown crystals. It has a Mohs hardness of 3 and a specific gravity of 3.05.It was discovered in Grischun, Switzerland in 1989. It was named
in honor of Thomas Geiger (1886–1976), Wiesendangen, Switzerland, who studied the Falotta manganese ores.
Read More About Geigerite / Source
Geikielite

Geikielite is a magnesium titanium oxide mineral with formula: MgTiO3. It is a member of the ilmenite group. It crystallizes in the trigonal system forming typically opaque, black to reddish black crystals.
It was first described in 1892 for an occurrence in the Ceylonese gem bearing gravel placers. It was named for Scottish geologist Sir Archibald Geikie (1835–1924). It occurs in metamorphosed impure magnesian limestones, in serpentinite derived from ultramafic rocks, in kimberlites and carbonatites. Associated minerals include rutile, spinel, clinohumite, perovskite, diopside, serpentine, forsterite, brucite, hydrotalcite, chlorite and calcite.
Read More About Geikielite / Source
Gembone
Gembone, also known as gem bone, agatized dinosaur bone, or dinogem, is mineralized bone, often dinosaur bone, which occurs when minerals from groundwater are deposited within the bones. It is one of five gemstones created from organisms (the others being pearl, ammolite, amber and jet). Many minerals can be found in gembone including agate, hematite, iron, pyrite, jasper, marcasite, quartz or other crystal. Aside from their use in jewelry, scientists can use this type of specimen to perform research into the anatomic structure of ancient species.
Read More About Gembone / Source
Geocronite

Geocronite is a mineral, a mixed sulfosalt containing lead, antimony, and arsenic with a formula of Pb14(Sb, As)6S23. Geocronite is the antimony-rich endmember of a solid solution series. The arsenic-rich endmember is named jordanite. It occurs as grey, black, to silvery white monoclinic crystals. It is found in hydrothermal veins usually associated with other similar minerals, particularly the sulfides of iron and copper.
The mineral has been found in Spain, Ireland and Sweden where it was first identified in 1839.
Read More About Geocronite / Source
Georgerobinsonite
Georgerobinsonite, named for George Willard Robinson, is a lead chromate mineral with formula Pb4(CrO4)2(OH)2FCl. It exhibits very small, transparent crystals with a bright orange-red color. It was obtained from the Mammoth–St. Anthony Mine in Arizona in the 1940s and identified in 2009.
Read More About Georgerobinsonite / Source
Germanite

Germanite is a rare copper iron germanium sulfide mineral, Cu26Fe4Ge4S32. It was first discovered in 1922, and named for its germanium content. It is only a minor source of this important semiconductor element, which is mainly derived from the processing of the zinc sulfide mineral sphalerite. Germanite contains gallium, zinc, molybdenum, arsenic, and vanadium as impurities.Its type locality is the Tsumeb Mine in Namibia where it occurs in a hydrothermal polymetallic ore deposit in dolomite in association with renierite, pyrite, tennantite, enargite, galena, sphalerite, digenite, bornite and chalcopyrite. It has also been reported from Argentina, Armenia, Bulgaria, Cuba, Democratic Republic of Congo (Zaire), Finland, France, Greece, Japan, Republic of Congo (Brazzaville), Russia and the United States.
Read More About Germanite / Source
Gersdorffite

Gersdorffite is a nickel arsenic sulfide mineral with formula NiAsS. It crystallizes in the isometric system showing diploidal symmetry. It occurs as euhedral to massive opaque, metallic grey-black to silver white forms. Gersdorffite belongs to a solid solution series with cobaltite, CoAsS. Antimony freely substitutes also leading to ullmannite, NiSbS. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 5.9 to 6.33.
Gersdorffite has three crystallisation forms: Gersdorffite-P213 (NiAsS), Gersdorffite-Pa3 (Ni(As,S)2) and Gersdorffite-Pca21 (NiAsS). Gersdorffite occurs as a hydrothermal vein mineral along with other nickel sulfides. Associated minerals include nickeline, nickel-skutterudite, cobaltite, ullmannite, maucherite, löllingite, platinum-group minerals, millerite, pyrite, marcasite, and chalcopyrite.
Gersdorffite was first described in 1843 and named in 1845 for Johann von Gersdorff (1781–1849), owner of the nickel mine at Schladming, Austria the type locality.
Read More About Gersdorffite / Source
Getchellite

Getchellite is a rare sulfide of arsenic and antimony, AsSbS3, that was discovered by B. G. Weissberg of the New Zealand Department of Scientific and Industrial Research in 1963, and approved as a new species by the International Mineralogical Association in 1965. Many metal sulfides are grey to black, but a few are brightly colored. Orpiment is yellow to brownish gold, cinnabar is deep red and getchellite is a bright orange red.
Read More About Getchellite / Source
Gibbsite

Gibbsite, Al(OH)3, is one of the mineral forms of aluminium hydroxide. It is often designated as γ-Al(OH)3 : 2 (but sometimes as α-Al(OH)3.). It is also sometimes called hydrargillite (or hydrargyllite).
Gibbsite is an important ore of aluminium in that it is one of three main phases that make up the rock bauxite.
Gibbsite has three named structural polymorphs or polytypes: bayerite (designated often as α-Al(OH)3,: 2 but sometimes as β-Al(OH)3), doyleite, and nordstrandite. Gibbsite can be monoclinic or triclinic, while bayerite is monoclinic.: 13 Doyleite and nordstrandite are triclinic forms.: 13
Read More About Gibbsite / Source
Gilalite

Gilalite is a copper silicate mineral with chemical composition of Cu5Si6O17·7(H2O).It occurs as a retrograde metamorphic phase in a calc-silicate and sulfide skarn deposit. It occurs as fracture fillings and incrustations associated with diopside crystals. It is commonly found in the form of spherules of radial fibers.
It was first described for an occurrence in the Christmas porphyry copper mine in Gila County, Arizona in 1980 along with the mineral apachite. It derives its name from this locality. It has also been reported from the Goodsprings District, Clark County, Nevada; Juazeiro do Norte, Ceara State, Brazil and a slag area in Lavrion District, Attica, Greece.
Read More About Gilalite / Source
Gismondine

Gismondine is a mineral with the chemical formula CaAl2Si2O8·4(H2O). It is a zeolite or hydrated alumino-silicate. It forms colorless, bipyramidal crystals of orthorhombic symmetry.
Gismondine was named for Italian mineralogist Carlo Giuseppe Gismondi (1762–1824). It has been found in Iceland, Ireland, and Italy.
Read More About Gismondine / Source
Glauberite

Glauberite is a monoclinic sodium calcium sulfate mineral with the formula Na2Ca(SO4)2.
It was first described in 1808 for material from the El Castellar Mine, Villarrubia de Santiago, Toledo, Castile-La Mancha, Spain. It was named for the extracted Glauber’s salts after the German alchemist Johann Rudolf Glauber (1604–1668).Glauberite often forms in continental and marine evaporite deposits, but may also form from hydrothermal deposits, as mineral sublimates deposited near fumaroles, in amygdules in basalt, and in nitrate deposits in arid climates. It occurs associated with halite, polyhalite, anhydrite, gypsum, thenardite, mirabilite, sassolite and blodite.Because of its solubility, glauberite is often dissolved away from the crystal matrix leaving a distinctly shaped hollow cast. Its mineral composition is readily altered into other minerals as pseudomorphs. Gypsum pseudomorphs are common due to increased humidity.
Glauberite, its cast impressions, and its pseudomorphed crystals are often easily recognizable due to its common crystal twinning, and crystal habit displayed by uniquely shaped flattened, often seeming rhombohedral, large individual ‘floater crystals’.
The mineral is commercially mined for its sulfate contents.
Read More About Glauberite / Source
Glaucochroite

Glaucochroite is a calcium manganese nesosilicate mineral with formula CaMnSiO4. It occurs in metamorphosed limestones.
It was first described in 1899 in Franklin Furnace, Sussex County, New Jersey.
Read More About Glaucochroite / Source
Glaucodot

Glaucodot is a cobalt iron arsenic sulfide mineral with formula (Co,Fe)AsS. The cobalt:iron(II) ratio is typically 3:1 with minor nickel substituting. It forms a series with arsenopyrite (FeAsS). It is an opaque grey to tin-white typically found as massive forms without external crystal form. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. The locality at Håkansboda, Sweden has rare twinned dipyramidal crystals (see photo). It is brittle with a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 5.95. It occurs in high temperature hydrothermal deposits with pyrrhotite and chalcopyrite. Glaucodot is classed as a sulfide in the arsenopyrite löllingite group.
Glaucodot was first described in 1849 in Huasco, Valparaíso Province, Chile. Its name originates from the Greek Ancient Greek: γλανκός (“blue”) in reference to its use in the dark blue glass called smalt.
Read More About Glaucodot / Source
Glauconite

Glauconite is an iron potassium phyllosilicate (mica group) mineral of characteristic green color which is very friable and has very low weathering resistance.
It crystallizes with a monoclinic geometry. Its name is derived from the Greek glaucos (γλαυκός) meaning ‘bluish green’, referring to the common blue-green color of the mineral; its sheen (mica glimmer) and blue-green color. Its color ranges from olive green, black green to bluish green, and yellowish on exposed surfaces due to oxidation. In the Mohs scale it has hardness of 2. The relative specific gravity range is 2.4 – 2.95. It is normally found as dark green rounded concretions with the dimensions of a sand grain. It can be confused with chlorite (also of green color) or with a clay mineral. Glauconite has the chemical formula (K,Na)(Fe,Al,Mg)2(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2.
Glauconite particles are one of the main components of greensand, glauconitic siltstone and glauconitic sandstone. Glauconite has been called a marl in an old and broad sense of that word. Thus references to “greensand marl” sometimes refer specifically to glauconite. The Glauconitic Marl formation is named after it, and there is a glauconitic sandstone formation in the Mannville Group of Western Canada.
Read More About Glauconite / Source
Glaucophane

Glaucophane is the name of a mineral and a mineral group belonging to the sodic amphibole supergroup of the double chain inosilicates, with the chemical formula ☐Na2(Mg3Al2)Si8O22(OH)2.
Glaucophane crystallizes in the monoclinic system.
Read More About Glaucophane / Source
Gmelinite

Gmelinite-Na is one of the rarer zeolites but the most common member of the gmelinite series, gmelinite-Ca, gmelinite-K and gmelinite-Na. It is closely related to the very similar mineral chabazite. Gmelinite was named as a single species in 1825 after Christian Gottlob Gmelin (1792–1860) professor of chemistry and mineralogist from Tübingen, Germany, and in 1997 it was raised to the status of a series.Gmelinite-Na has been synthesised from Na-bearing aluminosilicate gels. The naturally occurring mineral forms striking crystals, shallow, six sided double pyramids, which can be colorless, white, pale yellow, greenish, orange, pink, and red. They have been compared to an angular flying saucer.
Read More About Gmelinite / Source
Godovikovite

Godovikovite is a rare sulfate mineral with the chemical formula: (NH4)Al(SO4)2. Aluminium can partially be substituted by iron. Hydration of godovikovite gives the ammonium alum, tschermigite. The mineral forms cryptocrystalline, often porous, masses, usually of white colour. Single crystals are very small hexagonal blades. Typical environment for godovikovite are burning coal sites (mainly dumps). There the mineral acts, together with millosevichite, as one of the main components of so-called sulfate crust.It was first described in 1988 for an occurrence in the Chelyabinsk coal basin, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Southern Urals, Russia, and named for Russian mineralogist Aleksandrovich Godovikov (1927–1995).
Read More About Godovikovite / Source
Goethite

Goethite (, US also ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the α-polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient times for its use as a pigment (brown ochre). Evidence has been found of its use in paint pigment samples taken from the caves of Lascaux in France. It was first described in 1806 based on samples found in the Hollertszug Mine in Herdorf, Germany. The mineral was named after the German polymath and poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749–1832).
Read More About Goethite / Source
Gold

Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from Latin aurum ‘gold’) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher–atomic-number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions.
Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides).
Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is insoluble in nitric acid alone, which dissolves silver and base metals, a property long used to refine gold and confirm the presence of gold in metallic substances, giving rise to the term ‘acid test’. Gold dissolves in alkaline solutions of cyanide, which are used in mining and electroplating. Gold also dissolves in mercury, forming amalgam alloys, and as the gold acts simply as a solute, this is not a chemical reaction.
A relatively rare element, gold is a precious metal that has been used for coinage, jewelry, and other arts throughout recorded history. In the past, a gold standard was often implemented as a monetary policy. Gold coins ceased to be minted as a circulating currency in the 1930s, and the world gold standard was abandoned for a fiat currency system after the Nixon shock measures of 1971.
In 2020, the world’s largest gold producer was China, followed by Russia and Australia. A total of around 201,296 tonnes of gold exists above ground, as of 2020. This is equal to a cube with each side measuring roughly 21.7 meters (71 ft). The world consumption of new gold produced is about 50% in jewelry, 40% in investments and 10% in industry. Gold’s high malleability, ductility, resistance to corrosion and most other chemical reactions, and conductivity of electricity have led to its continued use in corrosion-resistant electrical connectors in all types of computerized devices (its chief industrial use). Gold is also used in infrared shielding, production of colored glass, gold leafing, and tooth restoration. Certain gold salts are still used as anti-inflammatories in medicine.
Goldmanite

Goldmanite is a green or greenish-brown silicate mineral of the garnet group with a chemical formula of Ca3(V3+,Al,Fe3+)2(SiO4)3.
Read More About Goldmanite / Source
Gonnardite

Gonnardite is a comparatively rare, fibrous zeolite, natrolite subgroup. Older papers claim that a complete solid solution exists between tetranatrolite and gonnardite, but tetranatrolite was discredited as a separate species in 1999. A series, based on the disorder of the silicon-aluminum in the framework, appears to exist between Na-rich gonnardite and natrolite, Na2(Si3Al2)O10·2H2O.Gonnardite was named in 1896 after Ferdinand Pierre Joseph Gonnard (1833–1923), who was Professor of Mining Engineering at the University of Lyon, France.
Read More About Gonnardite / Source
Gordaite

Gordaite is a sulfate mineral composed primarily of hydrous zinc sodium sulfate chloride hydroxide with formula: NaZn4(SO4)(OH)6Cl·6H2O. It was named for the discovery location in the Sierra Gorda district of Chile. Gordaite forms as tabular trigonal crystals.
Gordaite first appeared after a research dive in September 1984 from the Juan de Fuca Ridge of the northeastern side of the Pacific Ocean. Gordaite was also described from weathered slag deposits as a result of copper smelting in Hettstedt, Germany. The mineral exhibits a hexagonal shape with clear or white (green if cuprian – Cu2+) crystals ranging from planar to broad habit and has a point group of 3. Gordaite commonly occurs near minerals such as sphalerite, boleite and gypsum. The most recent finding occurred in the San Francisco mine in Chile where copper-zinc sulfide deposits were found.
Read More About Gordaite / Source
Gormanite

Gormanite is a phosphate mineral with the formula (Fe,Mg)3Al4(PO4)4(OH)6·2H2O. It was named after the University of Toronto professor Donald Herbert Gorman (1922-2020).
Read More About Gormanite / Source
Goslarite

Goslarite is a hydrated zinc sulfate mineral (ZnSO4 · 7 H2O) which was first found in the Rammelsberg mine, Goslar, Harz, Germany. It was described in 1847. Goslarite belongs to the epsomite group which also includes epsomite (MgSO4 · 7 H2O) and morenosite (NiSO4 · 7 H2O). Goslarite is an unstable mineral at the surface and will dehydrate to other minerals like bianchite (ZnSO4 · 6 H2O), boyleite (ZnSO4 · 4 H2O) and gunningite (ZnSO4 · H2O).
Read More About Goslarite / Source
Graftonite

Graftonite is an iron(II), manganese, calcium phosphate mineral with the chemical formula (Fe2+,Mn,Ca)3(PO4)2. It forms lamellar to granular translucent brown to red-brown to pink monoclinic prismatic crystals. It has a vitreous luster with a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 3.67 to 3.7.
It was first described from its type locality of Melvin Mountain in the town of Grafton, in Grafton County, New Hampshire.
Read More About Graftonite / Source
Grandidierite

Grandidierite is a rare mineral that was first discovered in 1902 in southern Madagascar. The mineral was named in honor of French explorer Alfred Grandidier (1836–1912) who studied the natural history of Madagascar.
Grandidierites appear bluer in color the more iron (Fe) they contain. A recently discovered gemstone, blue ominelite, is the Fe-analogue (Fe, Mg) to grandidierite (Mg, Fe).Grandidierites display strong trichroic pleochroism. That means that it can show three different colors depending on the viewing angle: dark blue-green, colorless (sometimes a very light yellow), or dark green.
While trichroism can usually help distinguish grandidierites from other gems, lazulites can occur with blue-green colors and show colorless/blue/dark blue pleochroism. Nevertheless, lazulites have somewhat higher refractive indices and specific gravity. Grandidierites also have greater hardness, with a 7.5 on the Mohs scale.
Large transparent faceted grandidierite specimens are extremely rare. The largest cut specimen currently known to the GIA weighs in at 763.5 carats.
Read More About Grandidierite / Source
Grandreefite
Grandreefite is a rare secondary lead sulfate-fluoride mineral with a general chemical formula, Pb2SO4F2. It is named for the location in which it was discovered in 1989, the Grand Reef Mine in Graham County, Arizona.
Grandreefite is monoclinic, falling in the 2/m symmetry group. Crystallographically this means, grandreefite has three axes of unequal length, with two angles at 90° to one another and a third, obtuse angle. The 2/m symmetry group indicates a two-fold axis with a perpendicular mirror plane. Grandreefite was originally classified as an orthorhombic mineral but was determined monoclinic instead upon further analysis. Pseudograndreefite, one of three other newly discovered minerals in 1989 at the Grand Reef Mine site, has orthorhombic crystallography. Optically, grandreefite is an anisotropic mineral, meaning the velocity of light varies depending on the direction through which it is passing through the mineral. Its calculated relief, i.e. its relative difference in index of refraction compared to the surrounding medium’s index of refraction, is 1.96–1.98; and its birefringence is .025.
Grandreefite, while not a valuable mineral in terms of commercial use, is useful in the sense that it is a good indicator of the very specific environment in which it forms and therefore the same conditions required to produce minerals similar to it in structure, composition, etc. For example, its structure is very similar to that of lanthanide oxide sulfates and therefore may be used to help better describe them. The Grand Reef Mine is located near a large granitic intrusion. Grandreefite is usually found in the mine in isolated veins containing hydrothermal copper, silver, and lead minerals hosted in oxidized breccias.
Read More About Grandreefite / Source
Graphite

Graphite is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large scale (300 kton/year, in 1989) for uses in pencils, lubricants, and electrodes. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. It is a good (but not excellent) conductor of both heat and electricity.
Read More About Graphite / Source
Gratonite

Gratonite is a lead-arsenic sulfosalt mineral, with the chemical composition Pb9As4S15. Gratonite was discovered in 1939 at the Excelsior Mine, Cerro de Pasco, Peru. It is named in honor of geologist L. C. Graton (1880–1970), who had a long-standing association with the Cerro de Pasco mines.
Read More About Gratonite / Source
Greenalite

Greenalite is a mineral in the kaolinite-serpentine group with the chemical composition (Fe2+,Fe3+)2-3Si2O5(OH)4. It is a member of the serpentine group.
Read More About Greenalite / Source
Greenockite

Greenockite is a rare cadmium bearing metal sulfide mineral consisting of cadmium sulfide (CdS) in crystalline form. Greenockite crystallizes in the hexagonal system. It occurs as massive encrustations and as hemimorphic six-sided pyramidal crystals which vary in color from a honey yellow through shades of red to brown. The Mohs hardness is 3 to 3.5 and the specific gravity is 4.8 to 4.9.
Greenockite belongs to the wurtzite group and is isostructural with it at high temperatures. It is also isostructural with sphalerite at low temperatures. It occurs with other sulfide minerals such as sphalerite and galena, and is the only ore mineral of cadmium. Most cadmium is recovered as a byproduct of copper, zinc, and lead mining. It is also known from the lead-zinc districts of the central United States.
It was first recognized in 1840 in Bishopton, Scotland, during the cutting of a tunnel for the Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway. The mineral was named after the land owner Lord Greenock (1783–1859).
Read More About Greenockite / Source
Gregoryite
Gregoryite is an anhydrous carbonate mineral that is rich in potassium and sodium with the chemical formula (Na2,K2,Ca)CO3. It is one of the two main ingredients of natrocarbonatite, found naturally in the lava of Ol Doinyo Lengai volcano, the other being nyerereite.Because of its anhydrous nature, gregoryite reacts quickly with the environment, causing the dark lava to be converted to white substance within hours.Gregoryite was first described in 1980 and named after the British geologist and author John Walter Gregory (1864–1932), who studied the East African Rift Valley. It occurs associated with nyerereite, alabandite, halite, sylvite, fluorite and calcite.
Read More About Gregoryite / Source
Greifensteinite

Greifensteinite is beryllium phosphate mineral with formula: Ca2Fe2+5Be4(PO4)6(OH)4·6H2O. It is the Fe2+ dominant member of the roscherite group. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system and typically forms prismatic dark olive green crystals.It was first described in Germany at Greifenstein Rocks, Ehrenfriedersdorf, and was named for the location. At the type locality, it occurs within a lithium-rich pegmatite in miarolitic cavities. It was approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 2002.
Read More About Greifensteinite / Source
Greigite
Greigite is an iron sulfide mineral with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2S4. It is the sulfur equivalent of the iron oxide magnetite (Fe3O4). It was first described in 1964 for an occurrence in San Bernardino County, California, and named after the mineralogist and physical chemist Joseph W. Greig (1895–1977).
Read More About Greigite / Source
Grossite
Grossite is a calcium aluminium oxide mineral with formula CaAl4O7. It is a colorless to white vitreous mineral which crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system.Grossite was first described 1994 for an occurrence in the Hatrurim Formation of Israel. It was named for Shulamit Gross (1923–2012) of the Geological Survey of Israel.It occurs within high temperature metamorphosed impure limestone of the Hatrurim Formation and also within calcium-aluminium rich inclusions in chondritic meteorites. Associated minerals in the Hatrurium include brownmillerite, mayenite and larnite. In meteorites it occurs with perovskite, melilite, hibonite, spinel and calcium rich pyroxene.
Read More About Grossite / Source
Grossular

Grossular is a calcium-aluminium species of the garnet group of minerals. It has the chemical formula of Ca3Al2(SiO4)3 but the calcium may, in part, be replaced by ferrous iron and the aluminium by ferric iron. The name grossular is derived from the botanical name for the gooseberry, grossularia, in reference to the green garnet of this composition that is found in Siberia. Other shades include cinnamon brown (cinnamon stone variety), red, and yellow. Grossular is a gemstone.
In geological literature, grossular has often been called grossularite. Since 1971, however, use of the term grossularite for the mineral has been discouraged by the International Mineralogical Association.
Read More About Grossular / Source
Groutite

Groutite is a manganese oxide mineral with formula Mn3+O(OH). It is a member of the diaspore group and is trimorphous with manganite and feitknechtite. It forms lustrous black crystals in the orthorhombic system.
It occurs in weathered banded iron formations, metamorphosed manganese ore bodies and hydrothermal ore environments.
It was first described in 1945 for an occurrence in the Mahnomen mine, Cuyuna Range, Crow Wing County, Minnesota and named for petrologist Frank Fitch Grout (1880–1958), of the University of Minnesota.
Read More About Groutite / Source
Grunerite

Grunerite is a mineral of the amphibole group of minerals with formula Fe7Si8O22(OH)2. It is the iron endmember of the grunerite-cummingtonite series. It forms as fibrous, columnar or massive aggregates of crystals. The crystals are monoclinic prismatic. The luster is glassy to pearly with colors ranging from green, brown to dark grey. The Mohs hardness is 5 to 6 and the specific gravity is 3.4 to 3.5.
It was discovered in 1853 and named after Emmanuel-Louis Gruner (1809–1883), the Swiss-French chemist who first analysed it.
Read More About Grunerite / Source
Guettardite
Guettardite is a rare arsenic-antimony lead sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula Pb(Sb,As)2S4. It forms gray black metallic prismatic to acicular crystals with monoclinic symmetry. It is a dimorph of the triclinic twinnite.
Read More About Guettardite / Source
Gugiaite
Gugiaite is a melilite mineral, named for the Chinese village of Gugia where it was first discovered. Its chemical formula is Ca2BeSi2O7. It occurs mostly in skarns with melanite adjacent to an alkali syenite and has no economic value. Its crystals are small tetragonal tablets with vitreous luster and perfect cleavage. It is colorless and transparent with a density of three. The mineral belongs to space group P-421m and is strongly piezoelectric.
Shortly after the discovery of gugiaite, it was noted that a new name was unnecessary as it could have been considered an end member of meliphanite, (Ca,Na)2Be(Si,Al)2(O,F)2 differing mainly in containing much less Na and F (Fleischer 1963). Recent data have confirmed that gugiaite differs from meliphanite optically and structurally (Grice and Hawthorne 2002). Gugiaite is a melilite and is distinctly different from other beryllium minerals such as meliphanite and leucophanite (Grice and Hawthorne 2002). Gugiaite is named for its locality near the village of Gugia, China (Peng et al. 1962). Incongruent information exists regarding Gugia; consequently the actual location of this village within China is unclear (de Fourestier 2005). Gujia is most often referenced as being in either Jiangsu Province or Liaoning Province (Yang et al. 2001; Mandarino 2005).
Read More About Gugiaite / Source
Guilleminite

Guilleminite (Ba(UO2)3(SeO3)2(OH)4•3H2O) is a uranium mineral named by R. Pierrot, J. Toussaint, and T. Verbeek in 1965 in honor of Jean Claude Guillemin (1923–1994), a chemist and mineralogist. It is a rare uranium/selenium mineral found at the Musonoi Mine in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.This secondary mineral also includes barium in its structure, in addition to selenium and uranium. It is bright yellow in colour and usually has an acicular crystal habit. It has a Mohs hardness of 2–3.
Read More About Guilleminite / Source
Gunningite

Gunningite is one of the minerals in the Kieserite group, with the chemical formula (Zn,Mn2+)SO4·H2O. Its name honours Henry Cecil Gunning (1901–1991) of the Geological Survey of Canada and a professor at the University of British Columbia.
Read More About Gunningite / Source
Guyanaite

Guyanaite (CrOOH) is a chromium oxide mineral that forms as an intergrowth with other chromium oxide minerals known as bracewellite (CrOOH) and grimaldiite (CrOOH) as well as eskolaite (Cr2O3) which in early findings were nearly indistinguishable from one another. These oxides formed so closely as intergrowths with one another that they were initially, and erroneously, identified as a single definite mineral previously known as merumite. Because of its complex history and the previously undiscovered nature of these chromium oxide polymorphs, the relevance of any information found in many early experiments involving the mineral formerly known as merumite in regard to guyanaite is unknown and it is implied that in any further reference of merumite it will have been composed of a mineral assemblage including guyanaite. The rare occurrence and complexity from intergrowth of naturally occurring guyanaite hinders experimental work, leading to laboratory synthesized samples which help to better experiment with the minerals.
Read More About Guyanaite / Source
Gwihabaite
Gwihabaite is a rare ammonium potassium nitrate mineral (NH4,K)(NO3). It is orthorhombic in form, colorless with a vitreous luster. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 1.77. It is deliquescent and water-soluble. The mineral is also known as nitrammite. It was first described in 1996 for an occurrence in Gcwihaba Caves (Drotsky’s Cavern, type locality), Maun, North-West District, Botswana. The spelling of the name was simplified, omitting the “c”, which represents the “click” sound used by the San people. It occurs as incrustations and efflorescences on cave surfaces formed by bacterial action on bat guano.
Read More About Gwihabaite / Source
Gypsum

Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4·2H2O. It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. Alabaster, a fine-grained white or lightly tinted variety of gypsum, has been used for sculpture by many cultures including Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Ancient Rome, the Byzantine Empire, and the Nottingham alabasters of Medieval England. Gypsum also crystallizes as translucent crystals of selenite. It forms as an evaporite mineral and as a hydration product of anhydrite.
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness defines gypsum as hardness value 2 based on scratch hardness comparison.
Read More About Gypsum / Source
Hafnon

Hafnon is a hafnium nesosilicate mineral, chemical formula (Hf,Zr)SiO4 or (Hf,Zr,Th,U,Y)SiO4. In natural zircon ZrSiO4 part of the zirconium is replaced by the very similar hafnium and so natural zircon is never pure ZrSiO4. A zircon with 100% hafnium substitution can be made synthetically and is hafnon.
Hafnon occurs as transparent red to red orange tetragonal crystals with a hardness of 7.5.Hafnon occurs naturally in tantalum-bearing granite pegmatites in the Zambezia district, Mozambique and in
weathered pegmatites at Mount Holland, Western Australia. It has also been reported from locations in Ontario, Quebec and Manitoba, Canada; North Carolina, United States; and in Zimbabwe.
Read More About Hafnon / Source
Hagendorfite

Hagendorfite is an iron phosphate mineral with the chemical formula of (Na,Ca)MnFe2(PO4)3 and is named after where the mineral was discovered, Hagendorf-Süd, Bavaria, Germany.Hagendorfite is in the monoclinic crystal class; the mineral’s internal symmetry consists of three axes with unequal length. Furthermore, the angles between two of the axes is 90° while the other angle is less than 90°. Monoclinic minerals contain a twofold rotation axis where they can be rotated 360° and have the crystal face repeat every 180°. They also have the characteristic mirror plane, which can produce a perfect mirror image when divided in two.
Hagendorfite belongs to the monoclinic crystal class, so it is assigned to the biaxial optical class. Hagendorfite’s optic sign, which is negative, is proven by examining its interference figure. Biaxial minerals, including Hagendorfite, have three indices of refraction which may or may not correspond with the mineral’s unequally lengthened axes. A refractive index will provide the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum with the speed of light in the mineral. A single refractive index is given when two rays of light vibrate in the mineral’s circular section and move along the optic axes.
Read More About Hagendorfite / Source
Haggertyite
Haggertyite is a rare barium, iron, magnesium, titanate mineral: Ba(Fe2+6Ti5Mg)O19 first described in 1996 from the Crater of Diamonds State Park near Murfreesboro in Pike County, Arkansas. The microscopic metallic mineral crystallizes in the hexagonal system and forms tiny hexagonal plates associated with richterite and serpentinitized olivine of mafic xenoliths in the lamproite host rock. It is an iron(II) rich member of the magnetoplumbite group. It is a light grey opaque mineral with calculated Mohs hardness of 5.
It was named for geophysicist Stephen E. Haggerty (born 1938) of the Florida International University.
Read More About Haggertyite / Source
Haidingerite

Haidingerite is a calcium arsenate mineral with formula Ca(AsO3OH)·H2O. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system as short prismatic to equant
crystals. It typically occurs as scaly, botryoidal or fibrous coatings. It is soft, Mohs hardness of 2 to 2.5, and has a specific gravity of 2.95. It has refractive indices of nα = 1.590, nβ = 1.602 and nγ = 1.638.It was originally discovered in 1827 in Jáchymov, Czech Republic. It was named to honor Austrian mineralogist Wilhelm Karl Ritter von Haidinger (1795–1871). It occurs as a dehydration product of pharmacolite in the Getchell Mine, Nevada.
Read More About Haidingerite / Source
Haiweeite

Haiweeite is a mineral of uranium and has the chemical formula: Ca[(UO2)2Si5O12(OH)2]·3(H2O). It is a secondary mineral of uranium, a product of oxidation. It has a greenish yellow color. It has a Mohs hardness of about 3.5 and is fluorescent under UV light.
It was named after the Haiwee Reservoir, Inyo County, California, US, where it was first found.
Read More About Haiweeite / Source
Håleniusite-(La)

Håleniusite-(La), chemical formula (La,Ce)OF. is a yellow isometric mineral. It has a dull, earthy lustre. The geological setting of håleniusite-(La) is in vugs and leaching zones of massive ferriallanite-(Ce), intimately intergrown with cerite-(Ce) and bastnäsite-(La).
It was discovered in 1986 at Bastnäs mines, Riddarhyttan, Skinnskatteberg, Västmanland, Sweden and named in honour of Ulf Hålenius, director of the mineralogy department at the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm, Sweden.
Read More About Håleniusite-(La) / Source
Halite (mineral)

Halite , commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride (NaCl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on inclusion of other materials, impurities, and structural or isotopic abnormalities in the crystals. It commonly occurs with other evaporite deposit minerals such as several of the sulfates, halides, and borates. The name halite is derived from the Ancient Greek word for “salt”, ἅλς (háls).
Read More About Halite (mineral) / Source
Halloysite

Halloysite is an aluminosilicate clay mineral with the empirical formula Al2Si2O5(OH)4. Its main constituents are oxygen (55.78%), silicon (21.76%), aluminium (20.90%), and hydrogen (1.56%). It is a member of the kaolinte group. Halloysite typically forms by hydrothermal alteration of alumino-silicate minerals. It can occur intermixed with dickite, kaolinite, montmorillonite and other clay minerals. X-ray diffraction studies are required for positive identification. It was first described in 1826, and subsequently named after, the Belgian geologist Omalius d’Halloy.
Read More About Halloysite / Source
Halotrichite

Halotrichite, also known as feather alum, is a highly hydrated sulfate of aluminium and iron. Its chemical formula is FeAl2(SO4)4·22H2O. It forms fibrous monoclinic crystals. The crystals are water-soluble.
It is formed by the weathering and decomposition of pyrite commonly near or in volcanic vents. The locations of natural occurrences include: the Atacama Desert, Chile; Dresden in Saxony, Germany; San Juan County, Utah; Iceland and Mont Saint-Hilaire, Canada.
The name is from Latin: halotrichum for salt hair which accurately describes the precipitate/evaporite mineral.
Gallery
Read More About Halotrichite / Source
Hambergite

Hambergite (Be2BO3OH) is a beryllium borate mineral named after Swedish explorer and mineralogist Axel Hamberg (1863–1933). The mineral occurs as white or colorless orthorhombic crystals.
Read More About Hambergite / Source
Hanksite

Hanksite is a sulfate mineral, distinguished as one of only a handful that contain both carbonate and sulfate ion groups. It has the chemical formula Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl.
Read More About Hanksite / Source
Hapkeite
Hapkeite is a mineral discovered in the Dhofar 280 meteorite found in 2000 in Oman on the Arabian peninsula. The meteorite is believed to originate from the Moon; specifically, it appears to be a fragment of lunar highland breccia. Hapkeite’s composition is of silicon and iron, and it is similar to other silicon-iron minerals found on Earth. An impact on the Moon is thought to have launched the partially molten or vaporized material into orbit.
Due to its 1:2 composition of silicon-iron, hapkeite was given the chemical formula Fe2Si. It occurs as opaque, yellowish to silvery microscopic isometric crystals.
It is named after Bruce Hapke, who predicted the presence and importance of vapor-deposited coatings on lunar soil grains (space weathering).Beside hapkeite, other natural iron silicide minerals include gupeiite, naqite, linzhiite, luobusaite, suessite, xifengite, and zangboite.
Read More About Hapkeite / Source
Hardystonite

Hardystonite is a rare calcium zinc silicate mineral first described from the Franklin, New Jersey, U.S. zinc deposits. It often contains lead, which was detrimental to the zinc smelting process, so it was not a useful ore mineral. Like many of the famous Franklin minerals, hardystonite responds to short wave ultraviolet (254 nm wavelength) light, emitting a fluorescence from dark purple to bright violet blue. In daylight, it is white to gray to light pink in color, sometimes with a vitreous or greasy luster. It is very rarely found as well formed crystals, and these are usually rectangular in appearance and rock-locked.
Hardystonite has a chemical composition of Ca2ZnSi2O7. It is frequently found with willemite (fluoresces green), calcite (fluoresces red), and clinohedrite (fluoresces orange). Hardystonite can be found altered to clinohedrite CaZn(SiO4)·H2O through direct hydrothermal alteration.
Other minerals often associated with hardystonite are franklinite, diopside, andradite garnet, and esperite (fluoresces yellow).
It was first described in 1899 by J.E. Wolff, when the New Jersey Zinc Company mines were located in what was called Franklin Furnace, in Hardyston Township, New Jersey.
Read More About Hardystonite / Source
Harmotome

Harmotome is a mineral, one of the rarer zeolites; a hydrated barium silicate with formula: (Ba0.5,Ca0.5,Na,K)5Al5,Si11O32·12(H2O). It forms vitreous white well defined monoclinic crystals, often associated with calcite and other zeolites. It has a Mohs hardness of 4 to 5 and a specific gravity of 2.44 to 2.5.
Read More About Harmotome / Source
Hauerite

Hauerite is a manganese sulfide mineral with the chemical formula MnS2. It forms reddish brown or black octahedral crystals with the pyrite structure and it is usually found associated with the sulfides of other transition metals such as rambergite. It occurs in low temperature, sulfur rich environments associated with solfataras and salt deposits in association with native sulfur, realgar, gypsum and calcite.It was discovered in Austro-Hungarian Monarchy in Kalinka (now Vígľašská Huta-Kalinka village) sulfur deposit near Detva in what is now Slovakia in 1846 and named after the Austrian geologists, Joseph Ritter von Hauer (1778–1863) and Franz Ritter von Hauer (1822–1899).It is found in Texas, USA; the Ural Mountains of Russia, and Sicily, Italy.Under high pressure conditions (P>11 GPa), Hauerite undergoes a large collapse in unit cell volume (22 %) driven by a spin-state transition.
Read More About Hauerite / Source
Hausmannite

Hausmannite is a complex oxide, or a mixed oxide, of manganese containing both di- and tri-valent manganese. Its chemical formula can be represented as MnIIMnIII2O4, or more simply noted as MnO·Mn2O3, or Mn3O4, as commonly done for magnetite (Fe3O4), the corresponding iron oxide. It belongs to the spinel group and forms tetragonal crystals. Hausmannite is a brown to black metallic mineral with Mohs hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 4.8.
The type locality is Oehrenstock (Öhrenstock), Ilmenau, Thuringian Forest, Thuringia, Germany, where it was first described in 1813. Locations include Batesville, Arkansas, US; Ilfeld, Germany; Langban, Sweden; and the Ural Mountains, Russia. High quality samples have been found in South Africa and Namibia where it is associated with other manganese oxides, pyrolusite and psilomelane and the iron-manganese mineral bixbyite. Wilhelm Haidinger (1827) named it in honour of Johann Friedrich Ludwig Hausmann (1782–1859), Professor of Mineralogy, University of Göttingen, Germany.
Read More About Hausmannite / Source
Hauyne

Hauyne or haüyne, also called hauynite or haüynite ( ah-WEE-nyte), is a tectosilicate sulfate mineral with endmember formula Na3Ca(Si3Al3)O12(SO4). As much as 5 wt % K2O may be present, and also H2O and Cl. It is a feldspathoid and a member of the sodalite group. Hauyne was first described in 1807 from samples discovered in Vesuvian lavas in Monte Somma, Italy, and was named in 1807 by Brunn-Neergard for the French crystallographer René Just Haüy (1743–1822). It is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Hauyne / Source
Hawleyite

Hawleyite is a rare sulfide mineral in the sphalerite group, dimorphous and easily confused with greenockite. Chemically, it is cadmium sulfide, and occurs as a bright yellow coating on sphalerite or siderite in vugs, deposited by meteoric water.It was discovered in 1955 in the Hector-Calumet mine, Keno-Galena Hill area, Yukon Territory and named in honour of mineralogist James Edwin Hawley (1897–1965), a professor at Queen’s University in Ontario, Canada.
Read More About Hawleyite / Source
Haxonite
Haxonite is an iron nickel carbide mineral found in iron meteorites and carbonaceous chondrites. It has a chemical formula of (Fe,Ni)23C6, crystallises in the cubic crystal system and has a Mohs hardness of 5+1⁄2 – 6.It was first described in 1971, and named after Howard J. Axon (1924–1992), metallurgist at the University of Manchester, Manchester, England. Co-type localities are the Toluca meteorite, Xiquipilco, Mexico and the Canyon Diablo meteorite, Meteor Crater, Coconino County, Arizona, US.It occurs associated with kamacite, taenite, schreibersite, cohenite, pentlandite and magnetite.
Read More About Haxonite / Source
Hazenite
Hazenite is a hydrous phosphate mineral with chemical formula of KNaMg2(PO4)2 · 14 H2O, therefore a hydrous alkali magnesium phosphate. It is a member of the struvite group.It was first described for an occurrence adjacent to Mono Lake, California, and named after Robert M. Hazen of the Carnegie Institute. It was approved as a new mineral on February 28, 2008 by the Commission on New Minerals of the International Mineralogical Association.
It occurs as crystal clusters associated with decomposed cyanobacteria remnants on calcite or aragonite. It is precipitated by microbes when the lake has been dry for so long that phosphorus levels build up, poisoning the microbes. They dispose of the excess phosphorus by excreting hazenite crystals. The crystals disappear when it rains or the lake level rises.
Read More About Hazenite / Source
Heazlewoodite

Heazlewoodite, Ni3S2, is a rare sulfur-poor nickel sulfide mineral found in serpentinitized dunite. It occurs as disseminations and masses of opaque, metallic light bronze to brassy yellow grains which crystallize in the trigonal crystal system. It has a hardness of 4, a specific gravity of 5.82. Heazlewoodite was first described in 1896 from Heazlewood, Tasmania, Australia.
Read More About Heazlewoodite / Source
Hectorite

Hectorite is a rare soft, greasy, white clay mineral with a chemical formula of Na0.3(Mg,Li)3Si4O10(OH)2.Hectorite was first described in 1941 and named for an occurrence in the United States near Hector (in San Bernardino County, California, 30 miles east of Barstow.) Hectorite occurs with bentonite as an alteration product of clinoptilolite from volcanic ash and tuff with a high glass content. Hectorite is also found in the beige/brown clay ghassoul, mined in the Atlas Mountains in Morocco. A large deposit of hectorite is also found at the Thacker Pass lithium deposit, located within the McDermitt Caldera in Nevada. The Thacker Pass lithium deposit could be a significant source of lithium.Despite its rarity, it is economically viable as the Hector mine sits over a large deposit of the mineral. Hectorite is mostly used in making cosmetics, but has uses in chemical and other industrial applications, and is a mineral source for refined lithium metal.
Read More About Hectorite / Source
Hedenbergite

Hedenbergite, CaFeSi2O6, is the iron rich end member of the pyroxene group having a monoclinic crystal system. The mineral is extremely rarely found as a pure substance, and usually has to be synthesized in a lab. It was named in 1819 after M.A. Ludwig Hedenberg, who was the first to define hedenbergite as a mineral. Contact metamorphic rocks high in iron are the primary geologic setting for hedenbergite. This mineral is unique because it can be found in chondrites and skarns (calc–silicate metamorphic rocks). Since it is a member of the pyroxene family, there is a great deal of interest in its importance to general geologic processes.
Read More About Hedenbergite / Source
Hellyerite

Hellyerite, NiCO3·6(H2O), is an hydrated nickel carbonate mineral. It is light blue to bright green in colour, has a hardness of 2.5, a vitreous luster, a white streak and crystallises in the monoclinic system. The crystal habit is as platy and mammillary encrustations on its matrix.
Read More About Hellyerite / Source
Hematite

Hematite , also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of Fe2O3. It has the same crystal structure as corundum (Al2O3) and ilmenite (FeTiO3). With this it forms a complete solid solution at temperatures above 950 °C (1,740 °F).
Hematite naturally occurs in black to steel or silver-gray, brown to reddish-brown, or red colors. It is mined as an important ore mineral of iron. It is electrically conductive. Hematite varieties include kidney ore, martite (pseudomorphs after magnetite), iron rose and specularite (specular hematite). While these forms vary, they all have a rust-red streak. Hematite is not only harder than pure iron, but also much more brittle. Maghemite is a polymorph of hematite (γ-Fe2O3) with the same chemical formula, but with a spinel structure like magnetite.
Large deposits of hematite are found in banded iron formations. Gray hematite is typically found in places that have still, standing water or mineral hot springs, such as those in Yellowstone National Park in North America. The mineral can precipitate in the water and collect in layers at the bottom of the lake, spring, or other standing water. Hematite can also occur in the absence of water, usually as the result of volcanic activity.
Clay-sized hematite crystals can also occur as a secondary mineral formed by weathering processes in soil, and along with other iron oxides or oxyhydroxides such as goethite, which is responsible for the red color of many tropical, ancient, or otherwise highly weathered soils.
Read More About Hematite / Source
Hemihedrite

Hemihedrite is a rare lead zinc chromate silicate mineral with formula Pb10Zn(CrO4)6(SiO4)2(F,OH)2. It forms a series with the copper analogue iranite.
Read More About Hemihedrite / Source
Hemimorphite

Hemimorphite is the chemical compound Zn4(Si2O7)(OH)2·H2O, a component of mineral calamine. It is a silicate mineral which, together with smithsonite (ZnCO3), has been historically mined from the upper parts of zinc and lead ores. Both compounds were originally believed to be the same mineral and classified as calamine. In the second half of the 18th century, it was discovered that these two different compounds were both present in calamine. They closely resemble one another.
The silicate was the rarer of the two and was named hemimorphite because of the hemimorph development of its crystals. This unusual form, which is typical of only a few minerals, means that the crystals are terminated by dissimilar faces. Hemimorphite most commonly forms crystalline crusts and layers, also massive, granular, rounded and reniform aggregates, concentrically striated, or finely needle-shaped, fibrous or stalactitic, and rarely fan-shaped clusters of crystals.
Some specimens show strong green fluorescence in shortwave ultraviolet light (253.7 nm) and weak light pink fluorescence in longwave UV.
Read More About Hemimorphite / Source
Hemusite

Hemusite is a very rare isometric gray mineral containing copper, molybdenum, sulfur, and tin with chemical formula Cu6SnMoS8. It was discovered by Bulgarian mineralogist Georgi Terziev in 1963. He also described it and named it after Haemus, the ancient name of Stara planina (Balkan) mountains in Europe. The type locality is Chelopech copper ore deposit, Bulgaria. Later tiny deposits of hemusite were found in Ozernovskoe deposit, Kamchatka, Russia; Kawazu mine, Rendaiji, Shimoda city, Chūbu region, Honshu Island, Japan; Iriki mine, Iriki, Satsuma-gun, Kagoshima Prefecture, Kyushu Region, Japan; Kochbulak deposit, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Hemusite occurs as rounded isometric grains and aggregates usually about 0.05 mm in diameter and in association with enargite, luzonite, colusite, stannoidite, renierite, tennantite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, and other minerals.
Read More About Hemusite / Source
Hendricksite
Hendricksite is a member of the trioctahedral micas group. The mineral was named by Clifford Frondel and Jun Ito in honor of Sterling Brown Hendricks, who studied micas. It was approved in 1966 by the IMA.
Read More About Hendricksite / Source
Heptasartorite
Heptasartorite is a very rare mineral with formula Tl7Pb22As55S108. It belongs to sartorite homologous series. It is related to other recently approved minerals of the series: enneasartorite and hendekasartorite. All three minerals come from a quarry in Lengenbach, Switzerland, which is famous of thallium minerals. Chemically similar minerals include edenharterite and hutchinsonite.
Read More About Heptasartorite / Source
Herbertsmithite

Herbertsmithite is a mineral with chemical structure ZnCu3(OH)6Cl2. It is named after the mineralogist Herbert Smith (1872–1953) and was first found in 1972 in Chile. It is polymorphous with kapellasite and closely related to paratacamite. Herbertsmithite is generally found in and around Anarak, Iran, hence its other name, anarakite.
Herbertsmithite is associated with copper mineralizations in syenitic porphyries and granites in Chile and in Triassic dolomite formations in Iran. It has also been reported from the Osborn District in the Big Horn Mountains of Maricopa County, Arizona and the Lavrion District Mines of Attica, Greece.Herbertsmithite has a vitreous luster and is fairly transparent with a light-green to blue green color. Herbertsmithite has a Mohs hardness of between 3 and 3.5 and is known to have a brittle tenacity. The crystal’s density has been calculated at 3.76 g/cm3.
Herbertsmithite, in a pure synthetic form, was discovered in 2012 to be able to exhibit the properties of a quantum spin liquid, a generalized form of strongly correlated quantum spin liquid due to its Kagome lattice structure. Herbertsmithite is the first mineral known to exhibit this unique state of magnetism: it is neither a ferromagnet with mostly aligned magnetic particles, nor is it an antiferromagnet with mostly opposed adjacent magnetic particles; rather its magnetic particles have constantly fluctuating scattered orientations.
Optical conductivity observations suggest the magnetic state in herbertsmithite is a type of emergent gauge field of a gapless U(1) Dirac spin liquid. Other experiments and some numerical calculations suggest instead that it is a
Z
2
{displaystyle mathbb {Z} _{2}}
spin liquid (or in other words, has a
Z
2
{displaystyle mathbb {Z} _{2}}
topological order). To clarify the situation, it is useful to carry out a number of experiments.
Read More About Herbertsmithite / Source
Hercynite

Hercynite is a spinel mineral with the formula FeAl2O4.
It occurs in high-grade metamorphosed iron rich argillaceous sediments as well as in mafic and ultramafic igneous rocks. Due to its hardness it also is found in placers.It was first described in 1847 and its name originates from the Latin name for the Harz, Silva Hercynia, where the species was first found.Hercynite is a spinel of regular symmetry and normal cation distribution, but some disorder occurs in its structure. It consists of ferrous (Fe2+) ions and aluminium ions (Al3+), however some ferric ions (Fe3+) may be located in the structure of hercynite.Melting point of this mineral is inbetween 1,692–1,767 °C (3,078–3,213 °F).
Read More About Hercynite / Source
Herderite

Herderite is a phosphate mineral belonging to the apatite, phosphate group, with formula CaBe(PO4)(F,OH). It forms monoclinic crystals, often twinned and variable in colour from colourless through yellow to green. It forms a series with the more common hydroxylherderite, which has more hydroxyl ion than fluoride.It is found in many parts of the world, often in pegmatites and associated with other apatite minerals.
It was first described in 1828 for an occurrence in the Sauberg Mine, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany. It was named for Saxon mining official Sigmund August Wolfgang von Herder (1776–1838).
Read More About Herderite / Source
Hermannjahnite
Hermannjahnite is a rare sulfate mineral with the relatively simple formula CuZn(SO4)2. It is one of many fumarolic minerals discovered on the Tolbachik volcano.
Read More About Hermannjahnite / Source
Hessite

Hessite is a mineral form of disilver telluride (Ag2Te). It is a soft, dark grey telluride mineral which forms monoclinic crystals.
It is named after Germain Henri Hess (1802–1850).
Hessite is found in the US in Eagle County, Colorado and in Calaveras County, California and in many other locations.
Stützite (Ag7Te4) and empressite (AgTe) are related silver telluride minerals.
Read More About Hessite / Source
Heulandite

Heulandite is the name of a series of tecto-silicate minerals of the zeolite group. Prior to 1997, heulandite was recognized as a mineral species, but a reclassification in 1997 by the International Mineralogical Association changed it to a series name, with the mineral species being named:
Heulandite-Ca
Heulandite-Na
Heulandite-K
Heulandite-Sr
Heulandite-Ba (described in 2002).Heulandite-Ca, the most common of these, is a hydrous calcium and aluminium silicate, (Ca,Na)2−3Al3(Al,Si)2Si13O36·12H2O. Small amounts of sodium and potassium are usually present replacing part of the calcium. Strontium replaces calcium in the heulandite-Sr variety. The appropriate species name depends on the dominant element. The species are visually indistinguishable, and the series name heulandite is still used whenever testing has not been performed.
Read More About Heulandite / Source
Hexaferrum
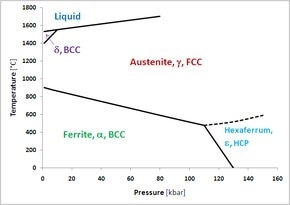
Hexaferrum and epsilon iron (ε-Fe) are synonyms for the hexagonal close-packed (HCP) phase of iron that is stable only at extremely high pressure.
A 1964 study at the University of Rochester mixed 99.8% pure α-iron powder with sodium chloride, and pressed a 0.5-mm diameter pellet between the flat faces of two diamond anvils. The deformation of the NaCl lattice, as measured by x-ray diffraction (XRD), served as a pressure indicator. At a pressure of 13 GPa and room temperature, the body-centered cubic (BCC) ferrite powder transformed to the HCP phase in Figure 1. When the pressure was lowered, ε-Fe transformed back to ferrite (α-Fe) rapidly. A specific volume change of −0.20 cm3/mole ± 0.03 was measured. Hexaferrum, much like austenite, is more dense than ferrite at the phase boundary. A shock wave experiment confirmed the diamond anvil results. Epsilon was chosen for the new phase to correspond with the HCP form of cobalt.The triple point between the alpha, gamma and epsilon phases in the unary phase diagram of iron has been calculated as T = 770 K and P = 11 GPa, although it was determined at a lower temperature of T = 750 K (477 °C) in Figure 1. The Pearson symbol for hexaferrum is hP2 and its space group is P63/mmc.Another study concerning the ferrite-hexaferrum transformation metallographically determined that it is a martensitic rather than equilibrium transformation.While hexaferrum is purely academic in metallurgical engineering, it may have significance in geology. The pressure and temperature of Earth’s iron core are on the order of 150–350 GPa and 3000 ± 1000 °C. An extrapolation of the austenite-hexaferrum phase boundary in Figure 1 suggests hexaferrum could be stable or metastable in Earth’s core. For this reason, many experimental studies have investigated the properties of HCP iron under extreme pressures and temperatures. Figure 2 shows the compressional behaviour of ε-iron at room temperature up to a pressure as would be encountered halfway through the outer core of the Earth; there are no points at pressures lower than approximately 6 GPa, because this allotrope is not thermodynamically stable at low pressures but will slowly transform into α-iron.
Read More About Hexaferrum / Source
Hiärneite
Hiärneite is an oxide mineral named after the Swedish geologist Urban Hiärne (1641-1727). The mineral can be found in rocks that mainly consists of fine grained phlogopite. Hiärneite is the first known mineral that contains both of the chemical elements antimony and zirconium. The mineral was described in 1997 for its occurrence in a skarn environment in Långban iron–manganese deposit of the Filipstad district, Värmland, Sweden.
Read More About Hiärneite / Source
Hibonite

Hibonite is a mineral with the chemical formula (Ca,Ce)(Al,Ti,Mg)12O19, occurring in various colours, with a hardness of 7.5–8.0 and a hexagonal crystal structure. It is rare, but is found in high-grade metamorphic rocks on Madagascar. Some presolar grains in primitive meteorites consist of hibonite. Hibonite also is a common mineral in the Ca-Al-rich inclusions found in some chondritic meteorites. Hibonite is closely related to hibonite-Fe (IMA 2009-027, (Fe,Mg)Al12O19)) an alteration mineral from the Allende meteorite. Hibonites were among the first minerals to form as the disk of gas and dust swirling around the young sun cooled.A very rare gem, hibonite was discovered in 1953 in Madagascar by Paul Hibon, a French prospector.
Read More About Hibonite / Source
Hilgardite

Hilgardite is a borate mineral with the chemical formula Ca2B5O9Cl·H2O. It is transparent and has vitreous luster. It is colorless to light pink with a white streak. It is rated 5 on the Mohs Scale.
It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system. Crystals occur as distorted tabular triangles and are hemimorphic, polytypes exist.It was named for geologist Eugene W. Hilgard (1833–1916). It was first described in 1937 for an occurrence in the Choctaw Salt Dome of Iberville Parish, Louisiana, US. It occurs as an uncommon accessory mineral in evaporite deposits and salt domes worldwide. In addition to the type locality it has been reported in Wayne County, Mississippi and in the Louann Salt Formation, Clarke County, Alabama in the United States and at the Penobsquis and Salt Springs evaporites, near Sussex, New Brunswick, Canada. In Europe it is reported from the Konigshall-Hindenburg potash mine near Göttingen, Lower Saxony, Germany and in the Boulby potash mine, Whitby, Yorkshire, England. In Asia it is reported from the Chelkar salt dome, Uralsk district, Kazakhstan; the Ilga Basin, eastern Siberia, Russia and the Sedom Formation, Mount Sedom, Dead Sea, Israel.
Read More About Hilgardite / Source
Hisingerite

Hisingerite is an iron(III) phyllosilicate mineral with formula FeIII2Si2O5(OH)4 · 2 H2O. A black or dark brown, lustrous secondary mineral, it is formed by the weathering or hydrothermal alteration of other iron silicate and sulfide minerals.It was first described in 1828 for an occurrence in Riddarhyttan, Vastmanland, Sweden. It was named after Wilhelm Hisinger (1766–1852), a Swedish chemist.There are also aluminian hisingerite variety in which one of the iron atoms is replaced by aluminium and chrome-alumina-hisingerite variety in which chromium substitutes for iron.
Read More About Hisingerite / Source
Hodgkinsonite

Hodgkinsonite is a rare zinc manganese silicate mineral Zn2MnSiO4(OH)2. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and typically forms radiating to acicular prismatic crystals with variable color from pink, yellow-red to deep red. Hodgkinsonite was discovered in 1913 by H. H. Hodgkinson, for whom it is named in Franklin, New Jersey, and it is only found in that area.
Read More About Hodgkinsonite / Source
Hoelite

Hoelite is a mineral, discovered in 1922 at Mt. Pyramide, Spitsbergen, Norway and named after Norwegian geologist Adolf Hoel (1879–1964). Its chemical formula is C14H8O2 (9,10-anthraquinone).It is a very rare organic mineral which occurs in coal fire environments in association with sal ammoniac and native sulfur.
Read More About Hoelite / Source
Hollandite

Hollandite (chemical formula: Ba(Mn4+6Mn3+2)O16) is an oxide mineral. It is the barium-manganese (III) endmember of the coronadite group.A mineral, with the chemical composition BaMn4+6Fe3+2O16, that was first found in the Kajlidongri mine in the Jhabua district of Madhya Pradesh, India, had the name hollandite until it was reclassified as ferrihollandite by the International Mineralogical Association in 2012. Ferrihollandite is the barium-iron (III) endmember of the coronadite group.Rare quartz inclusion
Read More About Hollandite / Source
Holmquistite

Holmquistite is a lithium magnesium aluminium inosilicate mineral with chemical formula Li2(Mg,Fe2+)3Al2Si8O22(OH)2. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system as prismatic crystals up to 10 cm (3.9 in) or as massive aggregates. It has a Mohs hardness of 5-6 and a specific gravity of 2.95 to 3.13.
Color could vary from black, dark violet to light sky blue.
It occurs as metasomatic replacements on the margins of lithium rich pegmatites.
It was first described in 1913 from an occurrence in Utö, near Stockholm, Sweden. It was named for the Swedish petrologist Per Johan Holmquist (1866–1946).
Read More About Holmquistite / Source
Homilite
Homilite is a borosilicate mineral belonging to the gadolinite group of minerals with formula Ca2(Fe,Mg)B2Si2O10.
It occurs as brown monoclinic crystals (space group P21/a) within feldspar masses in pegmatite and was discovered in 1876 in Stoko island, Langesundfiord, Norway. The name is from the Greek for to occur together, in allusion to its association with meliphanite and
allanite.
Read More About Homilite / Source
Hopeite

Hopeite is a hydrated zinc phosphate with formula: Zn3(PO4)2·4H2O. It is a rare mineral used mainly as a collectors specimen.
Hopeite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system with prismatic, vitreous white to yellow crystals. It also forms druzy encrustations and reniform (kidney-shaped) masses. The related mineral parahopeite, which has the same composition but different crystal structure, is triclinic. The minerals are formed through oxidation of sphalerite by the presence of phosphate-rich solutions
It was first described in 1822 from Moresnet, Liège Province, Belgium and is named after Scottish chemist, Thomas Charles Hope (1766–1844) of the University of Edinburgh.
It has been found in Zambia associated with lazulite.
Hopeite is one of the 2 conversion minerals arising from the application of the rust converter ‘Fertan’.
Read More About Hopeite / Source
Hornblende

Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
The general formula is (Ca,Na)2−3(Mg,Fe,Al)5(Al,Si)8O22(OH,F)2.
Read More About Hornblende / Source
Howlite

Howlite, a calcium borosilicate hydroxide (Ca2B5SiO9(OH)5), is a borate mineral found in evaporite deposits.
Read More About Howlite / Source
Hsianghualite

Hsianghualite is a tectosilicate (framework silicate) of lithium, calcium and beryllium, with fluorine, a member of the zeolite group. It was discovered in 1958 and named for the type locality, Hsiang Hua, 香花, meaning fragrant flower.
Read More About Hsianghualite / Source
Hubeite

The mineral hubeite, Ca2Mn2+Fe3+[Si4O12(OH)]·(H2O)2, is a sorosilicate of the Si4O13 group. Structurally it also belongs to the Akatoreite group. It was found and named after the province of Hubei, China. It is common to iron ores in a mine of that region. It occurs mainly as aggregates of fan like crystals. It is dark to pale brown, has orange-brown streak and is vitreous. Hubeite has a hardness of 5.5 in the Mohs scale, one good cleavage and conchoidal fracture. It is triclinic with a space group of P1*. The structure of hubeite is very uncommon, and in fact there is only one other mineral that fits the Si4O13 group, which is ruizite.
Read More About Hubeite / Source
Hübnerite

Hübnerite or hubnerite is a mineral consisting of manganese tungsten oxide (chemical formula MnWO4). It is the manganese endmember of the manganese–iron wolframite solid solution series.
It forms reddish brown to black monoclinic prismatic submetallic crystals. The crystals are typically flattened and occur with fine striations. It has a high specific gravity of 7.15 and a Mohs hardness of 4.5. It is transparent to translucent with perfect cleavage. Refractive index values are nα = 2.170 – 2.200, nβ = 2.220, and nγ = 2.300 – 2.320.
Typical occurrence is in association with high-temperature hydrothermal vein deposits and altered granites with greisen, granite pegmatites and in alluvial deposits. It occurs associated with cassiterite, arsenopyrite, molybdenite, tourmaline, topaz, rhodochrosite and fluorite.It was first described in 1865 for an occurrence in the Erie and Enterprise veins, Mammoth district, Nye County, Nevada, and named after the German mining engineer and metallurgist, Adolf Hübner from Freiberg, Saxony.
Read More About Hübnerite / Source
Huemulite

Huemulite is a mineral with formula Na4Mg(V10O28)·24H2O that is yellow to orange in color. It was first discovered in Argentina in 1959 and described in 1966. The mineral is named for the Huemul mine in which it was discovered.
Read More About Huemulite / Source
Humite

Humite is a mineral found in the volcanically ejected masses of Vesuvius. It was first described in 1813 and named for Abraham Hume (1749–1838).
Read More About Humite / Source
Huntite

Huntite is a carbonate mineral with the chemical formula Mg3Ca(CO3)4. Huntite crystallizes in the trigonal system and typically occurs as platy crystals and powdery masses. For most of recorded history its main use was as a white pigment. Today the most common industrial use of huntite is as a natural mixture with hydromagnesite as a flame retardant or fire retardant additive for polymers.
Read More About Huntite / Source
Hureaulite

Hureaulite is a manganese phosphate with the formula Mn2+5(PO3OH)2(PO4)2·4H2O. It was discovered in 1825 and named in 1826 for the type locality, Les Hureaux, Saint-Sylvestre, Haute-Vienne, Limousin, France. It is sometimes written as huréaulite, but the IMA does not recommend this for English language text.A complete series exists from lithiophilite, LiMn2+PO4 to triphylite, LiFe2+PO4, including hureaulite, strengite, FePO4·2H2O, stewartite, Mn2+Fe3+2(OH,PO4)2·8H2O, and sicklerite, (LiMn2+,Fe3+)PO4.
Read More About Hureaulite / Source
Hutchinsonite

Hutchinsonite is a sulfosalt mineral of thallium, arsenic and lead with formula (Tl,Pb)2As5S9. Hutchinsonite is a rare hydrothermal mineral.
It was first discovered in a sample from Binnental, Switzerland in 1903 and named after Cambridge mineralogist Arthur Hutchinson, F.R.S. (1866–1937) in 1904.
Read More About Hutchinsonite / Source
Huttonite
Huttonite is a thorium nesosilicate mineral with the chemical formula ThSiO4 and which crystallizes in the monoclinic system. It is dimorphous with tetragonal thorite, and isostructual with monazite. An uncommon mineral, huttonite forms transparent or translucent cream–colored crystals. It was first identified in samples of beach sands from the West Coast region of New Zealand by the mineralogist Colin Osborne Hutton (1910–1971). Owing to its rarity, huttonite is not an industrially useful mineral.
Read More About Huttonite / Source
Hydroboracite

Hydroboracite is a hydrated borate mineral (hence the name) of calcium and magnesium, whose chemical composition is CaMgB6O8(OH)6·3H2O. It was discovered in 1834 in the Inder lake, Atyrau Province, Kazakhstan. Hydroboracite is a minor borate ore mineral.
Read More About Hydroboracite / Source
Hydrogrossular

Hydrogrossular is a calcium aluminium garnet series (formula: Ca3Al2(SiO4)3−x(OH)4x, with hydroxide (OH) partially replacing silica (SiO4)). The endmembers of the hydrogarnet family (grossular, hibschite, and katoite) depend on the degree of substitution (x):
grossular: x = 0
hibschite: 0.2 < x < 1.5
katoite: 1.5 < x < 3.Hydrogrossular is a garnet variety in which a Si4+ is missing from a tetrahedral site. Charge balance is maintained by bonding a H+ to each of the four oxygens surrounding the vacant site.
Hydrogrossular is found in massive crystal habit, sometimes grown in with idocrase.Hydrogrossular is translucent to opaque, and found in green to bluish green, pink, white, and gray. The cause of the green color is chromium, and possibly iron. Pink hydrogrossular is caused by the presence of manganese. Hydrogrossular may have dark gray to black small inclusions. It has similarities to jade, and has the misnomers Transvaal jade, and African jade.Hydrogrossular is sometimes used as a gemstone, being cabochon cut, or made into beads. Sources for green and pink hydrogrossular are South Africa, Canada, and the United States. White hydrogrossular is sourced from Burma and China.
Read More About Hydrogrossular / Source
Hydrohalite
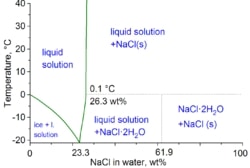
Hydrohalite is a mineral that occurs in saturated halite brines at cold temperatures (below 0.1 °C). It was first described in 1847 in Dürrnberg, Austria. It exists in cold weather.
Hydrohalite has a high nucleation energy, and solutions will normally need to be supercooled for crystals to form. The cryohydric point is at −21.2 °C (−6.2 °F). Above this temperature, liquid water saturated with salt can exist in equilibrium with hydrohalite. Hydrohalite has a strong positive temperature coefficient of solubility, unlike halite. Hydrohalite decomposes at 0.1°C, giving a salty brine and solid halite. Under pressure, hydrohalite is stable between 7,900 and 11,600 atmospheres pressure. The decomposition point increases at the rate of 0.007K per atmosphere (for 1–1000 atmospheres). The maximum decomposition temperature is at 25.8°C under 9400 atmospheres. Above this pressure the decomposition point goes down.
Read More About Hydrohalite / Source
Hydrokenoelsmoreite

Hydrokenoelsmoreite is a hydrous tungsten oxide mineral with formula □2W2O6(H2O). Hydrokenoelsmoreite is a colorless to white, translucent isometric mineral. It has a Mohs hardness of 3, exhibits no cleavage and has a splintery fracture. It has a vitreous to adamantine luster. It is optically isotropic with an index of refraction of n = 2.24.
It forms from the oxidation of ferberite within granitic pegmatite dykes and in pegmatitic greisen veins. It has a structure based on a defect pyrochlore lattice (A2B2O6O’).
It was first described for an occurrence in Elsmore Hill, New South Wales, Australia from where it takes its name.
Read More About Hydrokenoelsmoreite / Source
Hydromagnesite

Hydromagnesite is a hydrated magnesium carbonate mineral with the formula Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·4H2O.
It generally occurs associated with the weathering products of magnesium containing minerals such as serpentine or brucite. It occurs as incrustations and vein or fracture fillings in ultramafic rocks and serpentinites, and occurs in hydrothermally altered dolomite and marble. Hydromagnesite commonly appears in caves as speleothems and “moonmilk”, deposited from water that has seeped through magnesium rich rocks. It is the most common cave carbonate after calcite and aragonite. The mineral thermally decomposes, over a temperature range of approximately 220 °C to 550 °C, releasing water and carbon dioxide leaving a magnesium oxide residue.
Hydromagnesite was first described in 1836 for an occurrence in Hoboken, New Jersey.Stromatolites in an alkaline (pH greater than 9) freshwater lake (Salda Gölü) in southern Turkey are made of hydromagnesite precipitated by diatoms and cyanobacteria.
Microbial deposition of hydromagnesite is also reported from playas in British Columbia. The hydromagnesite-magnesite playas near Atlin, British Columbia are some of the most studied deposits of hydromagnesite. These deposits have been characterized in the context of a biogeochemical model for CO2 sequestration.One of the largest deposits of hydromagnesite exists in Greece. It consists of a natural mixture with huntite. Local people have used the white mineral as a source of material for whitewashing buildings for centuries. In the mid 20th century the minerals, ground to a fine powder, found use as a filler for rubber shoe soles. The locals used the granite mills designed for grinding wheat. Commercial exploitation of the minerals began in the late 70s and early 80s with the mineral being exported worldwide. The Greek deposit is still operated commercially, although the world’s largest commercially operated reserves are in Turkey.
Read More About Hydromagnesite / Source
Hydrotalcite

Hydrotalcite or formerly also Völknerite is a layered double hydroxide (LDH) of general formula Mg6Al2CO3(OH)16·4H2O, whose name is derived from its resemblance with talc and its high water content. Multiple structures containing loosely bound carbonate ions exist. The easily exchanged carbonates allow for applications of the mineral in wastewater treatment and nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Read More About Hydrotalcite / Source
Hydroxyapatite

Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. Hydroxyapatite is the hydroxyl endmember of the complex apatite group. The OH− ion can be replaced by fluoride, chloride or carbonate, producing fluorapatite or chlorapatite. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system. Pure hydroxyapatite powder is white. Naturally occurring apatites can, however, also have brown, yellow, or green colorations, comparable to the discolorations of dental fluorosis.
Up to 50% by volume and 70% by weight of human bone is a modified form of hydroxyapatite, known as bone mineral. Carbonated calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite is the main mineral of which dental enamel and dentin are composed. Hydroxyapatite crystals are also found in pathological calcifications such as those found in breast tumors, as well as calcifications within the pineal gland (and other structures of the brain) known as corpora arenacea or “brain sand”.
Read More About Hydroxyapatite / Source
Hydrozincite

Hydrozincite, also known as zinc bloom or marionite, is a white carbonate mineral consisting of Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6. It is usually found in massive rather than crystalline form.
It occurs as an oxidation product of zinc ores and as post mine incrustations. It occurs associated with smithsonite, hemimorphite, willemite, cerussite, aurichalcite, calcite and limonite.It was first described in 1853 for an occurrence in Bad Bleiberg, Carinthia, Austria and named for its chemical content.
Read More About Hydrozincite / Source
Ianbruceite

Ianbruceite is a rare hydrated zinc arsenate with the formula [Zn2(OH)(H2O)(AsO4)](H2O)2; material from the Driggith mine has traces of cobalt. It was first discovered at Tsumeb, approved by the International Mineralogical Association as a new mineral species in 2011, reference IMA2011-49, and named for Ian Bruce, who founded “Crystal Classics” in the early 1990s, and was heavily involved in attempts to reopen the famous Tsumeb mine for specimen mining.
In 2013 new occurrences of ianbruceite were reported from the neighbouring Driggith and Potts Gill mines on High Pike in the Caldbeck Fells, Cumbria, England. Here the mineral is probably a post-mining product. Caldbeck Fells and Tsumeb are the only reported localities for ianbruceite to date (May 2013).
Read More About Ianbruceite / Source
Ichnusaite
Ichnusaite (pronounced iknusa-ait) is a very rarely found mineral. Ichnusaite is a natural compound of thorium and molybdenum with the formula Th(MoO4)2·3H2O. It was discovered in Su Seinargiu, Sarroch, Cagliari, Sardegna, Italy in 2013. The name is from the old Greek name of Sardinia, Ιχνουσσα, Ichnusa. This locality is also a place of discovery of the second natural thorium molybdate – nuragheite.
Read More About Ichnusaite / Source
Icosahedrite
Icosahedrite is the first known naturally occurring quasicrystal phase. It has the composition Al63Cu24Fe13 and is a mineral approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 2010. Its discovery followed a 10-year-long systematic search by an international team of scientists led by Luca Bindi and Paul J. Steinhardt to find the first natural quasicrystal.It occurs as tiny grains in a small sample labelled “khatyrkite” (catalog number 46407/G, housed in The Museum of Natural History, University of Florence, Italy), collected from an outcrop of weathered serpentinite in the Khatyrka ultramafic zone of the Koryak-Kamchatka area, Koryak Mountains, Russia. The rock sample also contains spinel, diopside, forsterite, nepheline, sodalite, corundum, stishovite, khatyrkite, cupalite and an unnamed AlCuFe alloy. Evidence shows that the sample is actually extraterrestrial in origin, delivered to the Earth by a CV3 carbonaceous chondrite asteroid that dates back 4.5 Gya. A geological expedition has identified the exact place of the original discovery and found more specimens of the meteorite.
The same Al-Cu-Fe quasicrystal phase had previously been created in the laboratory by Japanese experimental metallurgists in the late 1980s.The concept of quasicrystals — along with the term — was first introduced in 1984 by Steinhardt and Dov Levine, both then at the University of Pennsylvania. The first synthetic quasicrystal, a combination of aluminium and manganese, was reported in 1984 by Israeli materials scientist Dan Shechtman and colleagues at the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology, a finding for which Shechtman won the 2011 Nobel Prize for Chemistry.
Read More About Icosahedrite / Source
Idrialite

Idrialite is a rare hydrocarbon mineral with approximate chemical formula C22H14.Idrialite usually occurs as soft orthorhombic crystals, is usually greenish yellow to light brown in color with bluish fluorescence. It is named after Idrija, town in Slovenia, where its occurrence was first described.The mineral has also been called idrialine, and branderz in German It has also been called inflammable cinnabar due to its combustibility and association with cinnabar ores in the source locality. A mineral found in the Skaggs Springs location of California was described in 1925 and named curtisite, but was eventually found to consist of the same compounds as idrialite, in somewhat different amounts. Thus curtisite is now considered to be merely a variety of idrialite.
Read More About Idrialite / Source
Ikaite

Ikaite is the mineral name for the hexahydrate of calcium carbonate, CaCO3·6H2O. Ikaite tends to form very steep or spiky pyramidal crystals, often radially arranged, of varied sizes from thumbnail size aggregates to gigantic salient spurs. It is only found in a metastable state and decomposes rapidly by losing most of its water content once removed from near-freezing water. This “melting mineral” is more commonly known through its pseudomorphs.
Read More About Ikaite / Source
Illite

Illite is a group of closely related non-expanding clay minerals. Illite is a secondary mineral precipitate, and an example of a phyllosilicate, or layered alumino-silicate. Its structure is a 2:1 sandwich of silica tetrahedron (T) – alumina octahedron (O) – silica tetrahedron (T) layers. The space between this T-O-T sequence of layers is occupied by poorly hydrated potassium cations which are responsible for the absence of swelling. Structurally, illite is quite similar to muscovite with slightly more silicon, magnesium, iron, and water and slightly less tetrahedral aluminium and interlayer potassium. The chemical formula is given as (K,H3O)(Al,Mg,Fe)2(Si,Al)4O10[(OH)2·(H2O)], but there is considerable ion (isomorphic) substitution. It occurs as aggregates of small monoclinic grey to white crystals. Due to the small size, positive identification usually requires x-ray diffraction or SEM-EDS (automated mineralogy) analysis. Illite occurs as an altered product of muscovite and feldspar in weathering and hydrothermal environments; it may be a component of sericite. It is common in sediments, soils, and argillaceous sedimentary rocks as well as in some low grade metamorphic rocks. The iron-rich member of the illite group, glauconite, in sediments can be differentiated by x-ray analysis.The cation-exchange capacity (CEC) of illite is smaller than that of smectite but higher than that of kaolinite, typically around 20 – 30 meq/100 g.
Illite was first described for occurrences in the Maquoketa shale in Calhoun County, Illinois, US, in 1937. The name was derived from its type location in Illinois.Illite is also called hydromica or hydromuscovite. Brammallite is a sodium rich analogue. Avalite is a chromium bearing variety which has been described form Mt. Avala, Belgrade, Serbia.Zipao ‘jade’ is an ornamental form of illite showing bands of red-purple and pale yellow-green. It may be carved into pendants and other ornaments.
Read More About Illite / Source
Ilmenite

Ilmenite is a titanium-iron oxide mineral with the idealized formula FeTiO3. It is a weakly magnetic black or steel-gray solid. Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing inks, fabrics, plastics, paper, sunscreen, food and cosmetics.
Read More About Ilmenite / Source
Ilsemannite

Ilsemannite is an uncommon amorphous complex heterovalent molybdenum oxide, that was first published in 1871, and has been a valid species since pre-IMA. It is a grandfathered mineral, meaning the name ilsemannite is still believed to refer to a valid species. However, it is likely that specimens formed under different conditions, in different localities do not have the same composition, and may even be a mixture of compounds. Furthermore, it is hard to analyze the specimens due to them being a mixture, hence why adequate analyses are lacking of said mineral. Ilsemannite is believed to be identical to synthetic molybdic oxide.
Read More About Ilsemannite / Source
Ilvaite

Ilvaite is a sorosilicate of iron and calcium with formula: CaFe2+2Fe3+Si2O7O(OH). Both manganese and magnesium substitute in the structure. Ilvaite crystallizes in the monoclinic system in black prismatic crystals and columnar masses. It is black to brownish black to gray and opaque. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 3.8 to 4.1. Ilvaite is structurally related to lawsonite.
It occurs in contact metamorphic rocks and skarn ore deposits. It also occurs less commonly in syenites.
Ilvaite was first described in 1811 on the island of Elba and the name ilvaite from the Latin name Ilva of the island. Sometimes referred to as yenite.
Read More About Ilvaite / Source
Imogolite

Imogolite is an aluminium silicate clay mineral with the chemical formula Al2SiO3(OH)4. It occurs in soils formed from volcanic ash and was first described in 1962 for an occurrence in Uemura, Kumamoto prefecture, Kyushu Region, Japan. Its name originates from the Japanese word imogo, which refers to the brownish yellow soil derived from volcanic ash. It occurs together with allophane, quartz, cristobalite, gibbsite, vermiculite and limonite.Imogolite consists of a network of nanotubes with an outer diameter of ca. 2 nm and an inner diameter of ca. 1 nm. The tube walls are formed by continuous Al(OH)3 (gibbsite) sheets and orthosilicate anions (O3SiOH groups). Owing to its tubular structure, natural availability, and low toxicity, imogolite has potential applications in polymer composites, fuel gas storage, absorbents, and as a catalyst support in chemical catalysis.
Read More About Imogolite / Source
Inderite

Inderite, also known as Lesserite, is a mineral that was named after its source, the Inder lake, near the Inder Mountains in Kazakhstan. The samples were described in English by the soviet mineralogist Boldyreva in 1937. It is a rare secondary mineral but common in salt, potassium and borate deposits.
Read More About Inderite / Source
Indite
Indite is an extremely rare indium-iron sulfide mineral, found in Siberia. Its chemical formula is FeIn2S4.
It occurs as replacement of cassiterite in hydrothermal deposits. It is associated with dzhalindite, cassiterite and quartz. It was first described in 1963 for an occurrence in the Dzhalinda tin deposit, Malyi Khingan Range, Khabarovskiy Kray, Far-Eastern Region, Russia.
Read More About Indite / Source
Indium

Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts per million of the Earth’s crust. Indium has a melting point higher than sodium and gallium, but lower than lithium and tin. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and it is largely intermediate between the two in terms of its properties. Indium was discovered in 1863 by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter by spectroscopic methods. They named it for the indigo blue line in its spectrum. Indium was isolated the next year.
Indium is a minor component in zinc sulfide ores and is produced as a byproduct of zinc refinement. It is most notably used in the semiconductor industry, in low-melting-point metal alloys such as solders, in soft-metal high-vacuum seals, and in the production of transparent conductive coatings of indium tin oxide (ITO) on glass. Indium is considered a technology-critical element.
Indium has no biological role. Its compounds are toxic when injected into the bloodstream. Most occupational exposure is through ingestion, from which indium compounds are not absorbed well, and inhalation, from which they are moderately absorbed.
Read More About Indium / Source
Inesite

Inesite is a hydrous calcium manganese silicate mineral. Its chemical formula is Ca2Mn7Si10O28(OH)2•5(H2O). Inesite is an inosilicate with a triclinic crystal system. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6, and a specific gravity of 3.0. Its name originates from the Greek Ίνες (ines), “fibers” in allusion to its color and habit.
Read More About Inesite / Source
Inyoite

Inyoite, named after Inyo County, California, where it was discovered in 1914, is a colourless monoclinic mineral. It turns white on dehydration. Its chemical formula is Ca(H4B3O7)(OH)·4H2O or CaB3O3(OH)5·4H2O. Associated minerals include priceite, meyerhofferite, colemanite, hydroboracite, ulexite and gypsum.
Read More About Inyoite / Source
Iodargyrite

Iodyrite or iodargyrite is a natural mineral form of silver iodide.
Related minerals are chlorargyrite and bromargyrite.
Read More About Iodargyrite / Source
Iranite

Iranite (Persian: ایرانیت) is a triclinic lead copper chromate silicate mineral with formula Pb10Cu(CrO4)6(SiO4)2(F,OH)2. It was first described from an occurrence in Iran. It is the copper analogue of hemihedrite (Pb10Zn(CrO4)6(SiO4)2(F,OH)2).It occurs as an oxidation product of hydrothermal lead-bearing veins. Associated minerals include dioptase, fornacite, wulfenite, mimetite, cerussite and diaboleite. It was first described in 1970 for an occurrence in the Sebarz Mine, northeast of Anarak, Iran.
Read More About Iranite / Source
Iridium

Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density of 22.56 g/cm3 (0.815 lb/cu in) as defined by experimental X-ray crystallography. It is one of the most corrosion-resistant metals, even at temperatures as high as 2,000 °C (3,630 °F). However, corrosion-resistance is not quantifiable in absolute terms; although only certain molten salts and halogens are corrosive to solid iridium, finely divided iridium dust is much more reactive and can be flammable, whereas gold dust is not flammable but can be attacked by substances that iridium resists, such as aqua regia.
Iridium was discovered in 1803 among insoluble impurities in natural platinum. Smithson Tennant, the primary discoverer, named it after the Greek goddess Iris, personification of the rainbow, because of the striking and diverse colors of its salts. Iridium is one of the rarest elements in Earth’s crust, with annual production and consumption of only 3 tonnes (6.6 thousand pounds). 191Ir and 193Ir are the only two naturally occurring isotopes of iridium, as well as the only stable isotopes; the latter is the more abundant.
The dominant uses of iridium are the metal itself and its alloys, as in high-performance spark plugs, crucibles for recrystallization of semiconductors at high temperatures, and electrodes for the production of chlorine in the chloralkali process. Important compounds of iridium are chlorides and iodides in industrial catalysis. Iridium is a component of some OLEDs.
Iridium is found in meteorites in much higher abundance than in the Earth’s crust. For this reason, the unusually high abundance of iridium in the clay layer at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary gave rise to the Alvarez hypothesis that the impact of a massive extraterrestrial object caused the extinction of dinosaurs and many other species 66 million years ago, now known to be produced by the impact that formed the Chicxulub crater. Similarly, an iridium anomaly in core samples from the Pacific Ocean suggested the Eltanin impact of about 2.5 million years ago.It is thought that the total amount of iridium in the planet Earth is much higher than that observed in crustal rocks, but as with other platinum-group metals, the high density and tendency of iridium to bond with iron caused most iridium to descend below the crust when the planet was young and still molten.
Read More About Iridium / Source
Telluric iron

Telluric iron, also called native iron, is iron that originated on Earth, and is found in a metallic form rather than as an ore. Telluric iron is extremely rare, with only one known major deposit in the world, located in Greenland.
Read More About Telluric iron / Source
Ixiolite

Ixiolite is an accessory oxide mineral found in granitic pegmatites. It is an oxide with the general chemical formula (Ta,Nb,Sn,Mn,Fe)4O8 or (Ta,Mn,Nb)O2.
Read More About Ixiolite / Source
Jacobsite

Jacobsite is a manganese iron oxide mineral. It is in the spinel group and forms a solid solution series with magnetite. The chemical formula is (Mn,Mg)Fe2O4 or with oxidation states and substitutions:
(Mn2+,Fe2+,Mg)(Fe3+,Mn3+)2O4.
It occurs as a primary phase or as alteration of other manganese minerals during metamorphism of manganese deposits. Typical associated minerals include hausmannite, galaxite, braunite, pyrolusite, coronadite, hematite and magnetite. It is a ferrimagnetic substance, which is weakly attracted by a magnet.
It was first described in 1869 and named for the Jakobsberg Mine, Nordmark, Filipstad, Värmland, Sweden.
Read More About Jacobsite / Source
Jadarite

Jadarite is a white, earthy monoclinic silicate mineral, sodium lithium boron silicate hydroxide (LiNaSiB3O7(OH) or Na2OLi2O(SiO2)2(B2O3)3H2O).
Read More About Jadarite / Source
Jadeite

Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition NaAlSi2O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, but is most often found in shades of green or white. Jadeite is formed only in subduction zones on continental margins, where rock undergoes metamorphism at high pressure but relatively low temperature.
Jadeite is the principal mineral making up the most valuable form of jade, a precious stone particularly prized in China. Most gem-quality jadeite jade comes from northern Myanmar. Jade tools and implements have been found at Stone Age sites, showing that the mineral has been prized by humans since before the beginning of written history.
Read More About Jadeite / Source
Jaffeite
Jaffeite is a hydrated calcium silicate with the following chemical formula: Ca6Si2O7(OH)6
Read More About Jaffeite / Source
Jalpaite

Jalpaite is a rare copper silver sulfide mineral with formula Ag3CuS2.
It was first described in 1858 for an occurrence in the Leonora Mine, Jalpa, Zacatecas, Mexico and named for the locality. It occurs in low temperature hydrothermal veins at temperatures less than 117 °C (243 °F). Associated minerals include acanthite, mckinstryite, galena, sphalerite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, stromeyerite, polybasite, pearceite, tetrahedrite–tennantite and native silver.
Read More About Jalpaite / Source
Jamesonite

Jamesonite is a sulfosalt mineral, a lead, iron, antimony sulfide with formula Pb4FeSb6S14. With the addition of manganese it forms a series with benavidesite. It is a dark grey metallic mineral which forms acicular prismatic monoclinic crystals. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and has a specific gravity of 5.5 – 5.6. It is one of the few sulfide minerals to form fibrous or needle like crystals. It can also form large prismatic crystals similar to stibnite with which it can be associated. It is usually found in low to moderate temperature hydrothermal deposits.It was named for Scottish mineralogist Robert Jameson (1774–1854). It was first identified in 1825 in Cornwall, England. It is also reported from South Dakota and Arkansas, US; Zacatecas, Mexico; and Romania.
Read More About Jamesonite / Source
Janggunite

Janggunite is a rare manganese oxide mineral with the chemical formula Mn5−x(Mn,Fe)1+xO8(OH)6.
It was first described in 1975 for an occurrence in the Janggun mine, Bonghwa-gun, Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea and named for the locality.
Read More About Janggunite / Source
Jarosewichite
Jarosewichite is a rare manganese arsenate mineral with formula: Mn2+3Mn3+(AsO4)(OH)6. It was first described in Franklin, New Jersey which is its only reported occurrence. Its chemical composition and structure are similar to chlorophoenicite. This mineral is orthorhombic with 2/m2/m2/m point group. Its crystals are prismatic or barrel-shaped. The color of jarosewichite is dark red to black. It has subvitreous luster of fracture surfaces and reddish-orange streak. This mineral occurs with flinkite, franklinite, andradite and cahnite.
Read More About Jarosewichite / Source
Jarosite

Jarosite is a basic hydrous sulfate of potassium and ferric iron (Fe-III) with a chemical formula of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. This sulfate mineral is formed in ore deposits by the oxidation of iron sulfides. Jarosite is often produced as a byproduct during the purification and refining of zinc and is also commonly associated with acid mine drainage and acid sulfate soil environments.
Read More About Jarosite / Source
Jennite
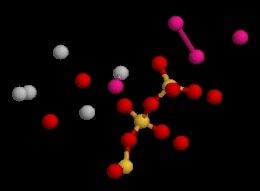
Jennite is a calcium silicate hydrate mineral of general chemical formula: Ca9Si6O18(OH)6·8H2O.
Jennite occurs as an alteration mineral in metamorphosed limestone and skarn. It typically occurs as vein and open space fillings as a late mineral phase. It also occurs in hydrated cement paste.
A first specimen of jennite found in 1966 at the Crestmore quarries (Crestmore, Riverside County, California, US) was analysed and identified as a new mineral by Carpenter in 1966 (Carpenter, 1966). They named it in honor of its discoverer: Clarence Marvin Jenni (1896–1973) director of the Geological Museum at the University of Missouri.In contrast to the first analysis made by Carpenter, jennite was found to not contain appreciable amount of sodium when the Crestmore specimen was reexamined.The structure of jennite is made of three distinct modules: ribbons of edge-sharing calcium octahedra, silicate chains of wollastonite-type running along the b axis, and additional calcium octahedra on inversion centers. The hydroxyl groups are bonded to three calcium cations while no SiOH groups are observed.Jennite transforms to metajennite at 70–90 °C (158–194 °F) by losing four water molecules.
Read More About Jennite / Source
Jeremejevite
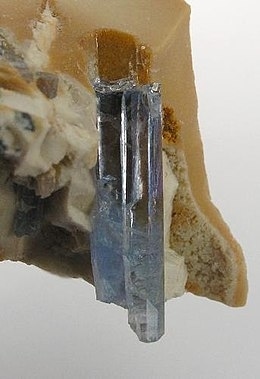
Jeremejevite is an aluminium borate mineral with variable fluoride and hydroxide ions. Its chemical formula is Al6B5O15(F,OH)3. It is considered as one of the rarest, thus one of the most expensive stones. For nearly a century, it was considered as one of the rarest gemstones in the world.It was first described in 1883 as small, single crystals in loose granitic debris in Mt. Soktui, Nerschinsk district, Adun-Chilon Mountains, Siberia. It was named after Pavel Vladimirovich Eremeev, Russian mineralogist, engineer and professor, who collected the first specimens. (Jeremejev, German) (1830–1899).
Read More About Jeremejevite / Source
Jerrygibbsite

Jerrygibbsite is a rare silicate mineral with the chemical formula (Mn,Zn)9(SiO4)4(OH)2. Jerrygibbsite was originally discovered by Pete J. Dunn in 1984, who named it after mineralogist Gerald V. Gibbs (born 1929). It has only been reported from the type locality of Franklin Furnace, New Jersey, United States, and in Namibia’s Otjozondjupa region. Jerrygibbsite is member of the leucophoenite family of the humite group. It is always found with these two minerals. It is a dimorph of sonolite.
Read More About Jerrygibbsite / Source
Jimthompsonite
Jimthompsonite is a magnesium iron silicate mineral with chemical formula (Mg,Fe2+)5Si6O16(OH)2. It is a triple chain silicate (or inosilicate) along with clinojimthompsonite and chesterite. They were described in 1977 by Burham and Veblen. They attracted great mineralogical attention because they were the first examples of new chain silicate structures among a large group known as biopyriboles whose name is derived from the words biotite, pyroxene, and amphiboles.
James B. Thompson, Jr. postulated the existence of the new biopyroles in 1970. The theory proved correct when jimthompsonite, clinojimthompsonite and chesterite were discovered in the Carlton Quarry in Windsor County, Vermont in 1977.The new minerals are found intergrown with the amphiboles anthophyllite and cummingtonite in sprays up to 5 cm long. They are all colorless to pale pinkish-brown and transparent. As for pyroxene and amphiboles, the type of chain structure dictates the angle between the two distinctive cleavages.
The cleavages of jimthompsonite are at 142 degrees and 38 degrees, and 135 degrees and 45 for chesterite; compared to the cleavage angles of pyroxene at about 94 degrees and 86 degrees and amphibole about 124 and 56 degrees.
Read More About Jimthompsonite / Source
Johannite

Johannite is a rare uranium sulfate mineral. It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system with the chemical composition Cu[UO2(OH)SO4]2·8H2O. It crystallizes in the triclinic system and develops only small prism or thin to thick tabular crystals, usually occurs as flaky or spheroidal aggregates and efflorescent coatings. Its color is emerald-green to apple-green and its streak is pale green.
Johannite is a strong radioactive mineral with a calculated activity of 87,501,143 Bq/g (to the comparison: natural potassium: 31.2 Bq/g).
Read More About Johannite / Source
Johannsenite

Johannsenite is a silicate mineral that is a member of the pyroxene family. The mineral can be produced in limestone or due a metamorphic process. The mineral is also associated with Pb-Zn mineralization.It is a relatively rare material. but is said to be abundant in the Aravaipa region of Arizona. It is commonly found as a spherulite like aggregate.The mineral is vulnerable to oxidation, hydration, and carbonation. It is also commonly altered to rhodonite.The mineral was named in 1932 after Albert Johannsen.
Read More About Johannsenite / Source
Jôkokuite

Jôkokuite is a manganese sulfate mineral with chemical formula MnSO4・5H2O. It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system. It was discovered in 1976 by Matsuo Nanbu at the Jokoku mine in Hokkaido, and is named after the location.
Read More About Jôkokuite / Source
Jolliffeite
Jolliffeite is a rare selenide mineral with formula NiAsSe or (Ni,Co)AsSe. It is the selenium analogue of the sulfide mineral gersdorffite, NiAsS, with a common impurity of cobalt, CoAsSe. It is named for its discoverer, Alfred Jolliffe, (1907–1988), a Canadian geologist of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario.
Read More About Jolliffeite / Source
Jonesite
Jonesite is a mineral with the chemical formula Ba4(K,Na)2[Ti4Al2Si10O36]*6H2O. This mineral is named after Francis Tucker Jones (1905–1993), who discovered the mineral while working as a Research Chemical Microscopist at Berkeley in CA. Jonesite has diffraction symmetry of mmm, which implies an orthorhombic system with all three axes perpendicular to each other and the angles between each axis equal to 90 degrees. In addition to symmetrical properties, Jonesite is a biaxial mineral with birefringence, which is a term to describe the difference between index of refraction. Jonesite is anisotropic, meaning the speed of light changes through the mineral, so the mineral shows color when viewed in crossed polarized light under a microscope. The mineral also has medium relief, which is a measure of how well the mineral stands out when viewed under a microscope in plane polarized light. In addition to being one of the rarest minerals in the Benitoite Gem mine located in California, Jonesite also is the first titanosilicate mineral with a porous double-layered crystal structure. This discovery is important because titanosilicate frameworks have industrial uses in energy companies and are used in containing radioactive waste.
Read More About Jonesite / Source
Jordanite

Jordanite is a sulfosalt mineral with chemical formula Pb14(As,Sb)6S23 in the monoclinic crystal system, named after the German scientist H. Jordan (1808–1887) who discovered it in 1864.
Lead-grey in colour (frequently displaying an iridescent tarnish), its streak is black and its lustre is metallic. Jordanite has a hardness of 3 on Mohs scale, has a density of approximately 6.4, and a conchoidal fracture.The type locality is the Lengenbach Quarry in the Binn Valley, Wallis, Switzerland.
Read More About Jordanite / Source
Julgoldite

Julgoldite is a member of the pumpellyite mineral series, a series of minerals characterized by the chemical bonding of silica tetrahedra with alkali and transition metal cations. Julgoldites, along with more common minerals like epidote and vesuvianite, belong to the subclass of sorosilicates, the rock-forming minerals that contain SiO4 tetrahedra that share a common oxygen to form Si2O7 ions with a charge of 6- (Deer et al., 1996). Julgoldite has been recognized for its importance in low grade metamorphism, forming under shear stress accompanied by relatively low temperatures (Coombs, 1953). Julgoldite was named in honor of Professor Julian Royce Goldsmith (1918–1999) of the University of Chicago.
Read More About Julgoldite / Source
Junitoite

Junitoite is a mineral with formula CaZn2Si2O7·H2O. It was discovered at the Christmas mine in Christmas, Arizona, and described in 1976. The mineral is named for mineral chemist Jun Ito (1926–1978).
Read More About Junitoite / Source
Jurbanite

Jurbanite is a sulfate mineral with the chemical formula AlSO4(OH)·5H2O. Its molecular weight is 230.13 g/mol. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and is dimorphous with the orthorhombic mineral rostite.
Jurbanite occurs as a secondary (post-mine) mineral in mines containing sulfide minerals.Jurbanite was first described for an occurrence in the San Manuel mine of Pinal County, Arizona and first described in 1976s. It was named for Joseph John Urban, the mineral collector who discovered it.
Read More About Jurbanite / Source
Kaatialaite

Kaatialaite (Fe(H2AsO4)3·5H2O) is a ferric arsenate mineral found in Finland.
Read More About Kaatialaite / Source
Kadyrelite
Kadyrelite is a mineral with the chemical formula Hg4(Br,Cl)2O discovered in 1987.
Read More About Kadyrelite / Source
Kaersutite

Kaersutite is a dark brown to black double chain calcic titanium bearing amphibole mineral with formula: NaCa2(Mg3Ti4+Al)(Si6Al2)O22(O)2. Ferro-kaersutite is the divalent iron rich endmember of the kaersutite group, with the iron replacing magnesium in the structure.It occurs as phenocrysts in alkalic volcanic rocks; in nodules of peridotite and gabbro in alkalic basalts; in syenites, monzonites and carbonatite tuffs. Mineral association includes titanian augite, rhoenite, olivine, ilmenite, spinel, plagioclase and titanian pargasite.It was first described in 1884 and is named for Qaersut (formerly Kaersut), Umanq district in northern Greenland.
Read More About Kaersutite / Source
Kainite

Kainite ( or ) (KMg(SO4)Cl·3H2O) is an evaporite mineral in the class of “Sulfates (selenates, etc.) with additional anions, with H2O” according to the Nickel–Strunz classification. It is a hydrated potassium-magnesium sulfate-chloride, naturally occurring in irregular granular masses or as crystalline coatings in cavities or fissures. This mineral is dull and soft, and is colored white, yellowish, grey, reddish, or blue to violet. Its name is derived from Greek καινος [kainos] (“(hitherto) unknown”), as it was the first mineral discovered that contained both sulfate and chloride as anions. Kainite forms monoclinic crystals.
Read More About Kainite / Source
Kainosite-(Y)

Kainosite is a silicate mineral that has the formula of Ca2(Y,Ce) SiO4O12(CO3)•(H2O). Kainosite was first discovered in Norway on the island of Hitterø and was named by Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld (1832–1901) in allusion to the Greek word for “unusual” for its rarity and exotic composition.Kainosite, is part of the orthorhombic crystal class minerals, which is a system that results from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs. Kainosite is a biaxial mineral, so the light entering its crystals will be polarized in two vibration directions (XYZ) for it has two optic axes. Because Kainosite is orthorhombic, the vibration directions XYZ coincide with the a,b,c crystallography axes.
Kainosite is very rare and mostly found in Russia in vugs, pegmatites, granites, and alkalic complex as an altered product of the mineral kuliokite. Classic samples have been discovered in Madawaska Mine, Bicroft Mine, and Greyhawk Mine, near Bancroft, Ontario.
Read More About Kainosite-(Y) / Source
Kalininite
Kalininite (ZnCr2S4) is a thiospinel mineral found in Russia in 1985 in the Pereval Marble Quarry, Slyudyanka (Sludyanka), Lake Baikal area, Irkutskaya Oblast’, Prebaikalia (Pribaikal’e), Eastern-Siberian Region. It was named for P. V. Kalinin, Russian mineralogist and petrologist, investigator of the southern Baikal region.
Read More About Kalininite / Source
Kalinite

Kalinite is a mineral composed of hydrated potassium aluminium sulfate (a type of alum). It is a fibrous monoclinic alum, distinct from isometric potassium alum, named in 1868. Its name comes from kalium (derived from Arabic: القَلْيَه al-qalyah “plant ashes”) which is the Latin name for potassium, hence its chemical symbol, “K”.
A proposal to remove recognition of kalinite as a mineral species was submitted to the International Mineralogical Association, however, kalinite is still on the list of approved minerals. Many older samples, however, have been found to be potassium alum.
Read More About Kalinite / Source
Kalsilite

Kalsilite (KAlSiO4) is a vitreous white to grey feldspathoidal mineral that is found in some potassium-rich lavas, such as from Chamengo Crater in Uganda. It has a relative hardness of 5.5.
Read More About Kalsilite / Source
Kamacite

Kamacite is an alloy of iron and nickel, which is found on Earth only in meteorites. According to the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) it is considered a proper nickel-rich variety of the mineral native iron. The proportion iron:nickel is between 90%:10% and 95%:5%; small quantities of other elements, such as cobalt or carbon may also be present. The mineral has a metallic luster, is gray and has no clear cleavage although its crystal structure is isometric-hexoctahedral. Its density is about 8 g/cm3 and its hardness is 4 on the Mohs scale. It is also sometimes called balkeneisen.
The name was coined in 1861 and is derived from the Greek root καμακ- “kamak” or κάμαξ “kamaks”, meaning vine-pole. It is a major constituent of iron meteorites (octahedrite and hexahedrite types). In the octahedrites it is found in bands interleaving with taenite forming Widmanstätten patterns. In hexahedrites, fine parallel lines called Neumann lines are often seen, which are evidence for structural deformation of adjacent kamacite plates due to shock from impacts.
At times kamacite can be found so closely intermixed with taenite that it is difficult to distinguish them visually, forming plessite. The largest documented kamacite crystal measured 92×54×23 cm (36.2×21.3×9.1 in).
Read More About Kamacite / Source
Kambaldaite

Kambaldaite, NaNi4(CO3)3(OH)3·3H2O, is an extremely rare hydrated sodium nickel carbonate mineral described from gossanous material associated with Kambalda type komatiitic nickel ore deposits at Kambalda, Western Australia, and Widgie Townsite nickel gossan, Widgiemooltha, Western Australia.
Kambaldaite crystallizes in the hexagonal system, is light green to blue, and forms drusy to mammilla encrustations on the matrix.
Kambaldaite was first described in 1985 from the gossan of the Otter Shoot nickel orebody, Kambalda, during mining of the gossans material. Kambaldaite, though in lesser and rarer amount, is also found in the Widgiemooltha nickel gossans, probably discovered there in the early to mid-1990s.
Read More About Kambaldaite / Source
Kamiokite

Kamiokite is an iron-molybdenum oxide mineral with the chemical formula Fe2Mo3O8. The name kamiokite is derived from the locality, the Kamioka mine in Gifu Prefecture, Japan, where this mineral was first discovered in 1975.Kamiokite is a hexagonal system with equal axes a1, a2, a3. These three axes of the kamiokite crystal are uniformly separated by 120°. Kamiokite is an anisotropic mineral, meaning that light travels through the mineral in different directions and velocities. Kamiokite is strongly pleochroic and is also birefringent.Kamiokite can be found as inclusions in domeykite, algodonite, and magnetite. Kamiokite is associated with copper arsenides found in Michigan’s Mohawk and Ahmeek copper mines. Although rare, kamiokite is predominantly found in mining environments and can indicate the presence of other minerals of interest, such as copper in the case of the Mohawk and Ahmeek mines. It is speculated that kamiokite can enhance the concentration of the copper it is hosted in.There are no known health risks associated with this mineral.
Read More About Kamiokite / Source
Kampfite

Kampfite is a rare barium silicate–carbonate–halide mineral with the chemical formula Ba12(Si11Al5)O31(CO3)8Cl5. Discovered in 1964 and described in 2001, it is named after Anthony R. Kampf. The mineral is known only from Fresno County, California.
Read More About Kampfite / Source
Kaňkite

Kankite is a mineral with the chemical formula Fe3+AsO4·3.5(H2O). Kankite is named for the locality that yielded first specimens Kaňk, Czech Republic. Kankite forms in old (1200- to 1400-year-old) mine dumps. It is yellowish-green on fresh exposure, with a paler greenish yellow on exposure to air.
Read More About Kaňkite / Source
Kanoite

Kanoite is a light pinkish brown silicate mineral that is found in metamorphic rocks. It is an inosilicate and has a chemical formula of (Mg,Mn2+)2Si2O6. It is a member of pyroxene group and clinopyroxene subgroup.
Read More About Kanoite / Source
Kaolinite

Kaolinite ( KAY-ə-lə-nyte, -lih-) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2Si2O5(OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica (SiO4) linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina (AlO6) octahedra.Kaolinite is a soft, earthy, usually white, mineral (dioctahedral phyllosilicate clay), produced by the chemical weathering of aluminium silicate minerals like feldspar. It has a low shrink–swell capacity and a low cation-exchange capacity (1–15 meq/100 g).
Rocks that are rich in kaolinite, and halloysite, are known as kaolin or china clay. In many parts of the world kaolin is colored pink-orange-red by iron oxide, giving it a distinct rust hue. Lower concentrations yield white, yellow, or light orange colors. Alternating layers are sometimes found, as at Providence Canyon State Park in Georgia, United States.
Kaolin is an important raw material in many industries and applications. Commercial grades of kaolin are supplied and transported as powder, lumps, semi-dried noodle or slurry. Global production of kaolin in 2021 was estimated to be 45 million tonnes, with a total market value of $US4.24 billion.
Read More About Kaolinite / Source
Karlite

Karlite (kar’-lite) is a silky white to light green orthorhombic borate mineral, not to be confused with tremolite-actinolite. It has a general formula of Mg7(BO3)3(OH)4Cl. Karlite is named in honor of Franz Karl (1918–1972), professor of mineralogy and petrography at Christian Albrechts University in Kiel, Germany, for his studies of the geology of the eastern Alps.
Karlite possesses moderate optical relief, the degree to which the mineral grains stand out from the mounting medium. This mineral is orthorhombic and sphenoidal, exhibiting symmetry on 222. Karlite is also enantiomorphic and dihedral. It is a member of the P212121 space group. This mineral forms optically negative biaxial birefringent crystals, meaning that the 2V angle between the optic axes is bisected by the refractive index direction. Because this mineral possesses birefringence, we know it is anisotropic and will display double refraction; it breaks light into two different rays traveling at different speeds in the mineral.
Karlite is a relatively newly discovered borate mineral occurring in clinohumite-chlorite marble in calcsilicate-carbonate lenses embedded in amphibolite. The amphibole at the original locale is situated between tectonic units “Zentralgneis” and “Schieferhulle”. Scholars assume that the high boron concentration needed for the formation of karlite is due to a contact metasomatism created by Hercynian tonalitic magmas, which make up the “Zentralgneis”, although the boron content of karlite is not of commercial importance. This mineral was originally discovered in the Furtschaglkar near the Furtschaglhaus in Austria, but has also been found in Russia and France, and was probably formed during the alpine metamorphism of the Alps.
Read More About Karlite / Source
Kasolite

Kasolite is an uncommon lead uranyl silicate monohydrate mineral. It is an IMA approved mineral, that had been a valid species before the foundation of the association, that had been first described and published in 1921 by Schoep. It is a grandfathered mineral, meaning the name kasolite is still believed to refer to a valid species to this day. The mineral’s name originates from its type locality, namely the Shinkolobwe Mine, also known as Kasolo Mine. Kasolite is possibly the lead analogue of the unnamed phase UM1956-02-SiO:CaHU, and it is the only accepted lead-uranium silicate.
Read More About Kasolite / Source
Kassite (mineral)

Kassite is a rare mineral whose chemical formula is CaTi2O4(OH)2. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system and forms radiating rosettes and pseudo-hexagonal tabular crystals which are commonly twinned. Kassite crystals are brownish pink to pale yellow in color, are translucent, and have an adamantine luster. Cleavage is distinctly visible, and the crystals are very brittle.
It was first described in 1965 in the Afrikanda pyroxenite massif, a formation on Russia’s Kola Peninsula and was named for Nikolai Grigorievich Kassin (1885–1949), a prominent Russian geologist. It occurs as miarolytic cavity fillings of alkalic pegmatites in the Kola occurrence and in nepheline syenite in the Magnet Cove igneous complex of Arkansas, US. Its mineral association includes cafetite (which with it is also polymorphous), perovskite, titanite, rutile and ilmenite.
Read More About Kassite (mineral) / Source
Katayamalite

Katayamalite is a cyclosilicate mineral that was named in honor of mineralogist and professor Nobuo Katayama. It was approved in 1982 by the International Mineralogical Association, and was first published a year later.
Read More About Katayamalite / Source
Kazakovite

Kazakovite was named in honor of Maria Efimovna Kazakova analytical chemist. It is a type locality of Karnasurt mountain, Russia. It was approved by the IMA in 1974, the same year it was discovered.
Read More About Kazakovite / Source
Kegelite

Kegelite is a complex silicate mineral with formula Pb8Al4Si8O20(SO4)2(CO3)4(OH)8.
It was first described in 1975 for an occurrence in the Tsumeb Mine, Tsumeb, Otjikoto Region, Namibia and named for Friedrich Wilhelm Kegel (?-1948), Director of mining operations at Tsumeb.
It occurs in a deeply oxidized polymetallic ore deposits in Tsumeb. Associated minerals include quartz, galena, mimetite, hematite, leadhillite, anglesite, fleischerite, melanotekite and alamosite. It has also been reported from the Zeehan district in Tasmania and from Tune, Sarpsberg, Østfold, Norway.
Read More About Kegelite / Source
Keilite
Keilite is an iron-magnesium sulfide mineral with the chemical formula (Fe,Mg)S) that is found in enstatite chondrites. Keilite is the iron-dominant analog of niningerite. Keilite is named after Klaus Keil (born 1934).
Read More About Keilite / Source
Kenhsuite

Kenhsuite is a mercury sulfide with chloride ions. It was described as a species from specimens obtained at the McDermitt mine, in Opalite, Humboldt Nevada county, (USA). The name is a tribute to Dr. Kenneth Junghwa Hsu. Professor Emeritus of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich (Switzerland).
Read More About Kenhsuite / Source
Kermesite

Kermesite or antimony oxysulfide is also known as red antimony (Sb2S2O) . The mineral’s color ranges from cherry red to a dark red to a black. Kermesite is the result of partial oxidation between stibnite (Sb2S3) and other antimony oxides such as valentinite (Sb2O3) or stibiconite (Sb3O6(OH)). Under certain conditions with oxygenated fluids the transformation of all sulfur to oxygen would occur but kermesite occurs when that transformation is halted.
Read More About Kermesite / Source
Kernite

Kernite, also known as rasorite, is a hydrated sodium borate hydroxide mineral with formula Na2B4O6(OH)2·3H2O. It is a colorless to white mineral crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system typically occurring as prismatic to acicular crystals or granular masses. It is relatively soft with Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3 and light with a specific gravity of 1.91. It exhibits perfect cleavage and a brittle fracture.
Kernite is soluble in cold water and alters to tincalconite when it dehydrates. It undergoes a non-reversible alteration to metakernite (Na2B4O7·5H2O) when heated to above 100 °C.
Read More About Kernite / Source
Kesterite

Kësterite is a sulfide mineral with a chemical formula of Cu2(Zn,Fe)SnS4. In its lattice structure, zinc and iron atoms share the same lattice sites. Kesterite is the Zn-rich variety whereas the Zn-poor form is called ferrokesterite or stannite. Owing to their similarity, kesterite is sometimes called isostannite. The synthetic form of kesterite is abbreviated as CZTS (from copper zinc tin sulfide). The name kesterite is sometimes extended to include this synthetic material and also CZTSe, which contains selenium instead of sulfur.
Read More About Kesterite / Source
Keyite

Keyite is a mineral with the chemical formula Cu2+3Zn4Cd2(AsO4)6 · 2H2O. The name comes from Charles Locke Key (born 1935), an American mineral dealer who furnished its first specimens.
Keyite is monoclinic-prismatic, meaning its crystal form has three unequal axes, two of which have 90° angles between them and one with an angle less than 90°.
Keyite belongs to the biaxial optical class, meaning it has more than one axis of anisotropy (optic axis), in which light travels with zero birefringence, and three indices of refraction, nα = 1.800, nβ, and nγ = 1.870. Being a very rare cadmium copper arsenate, keyite is only found in Tsumeb, Namibia in the Tsumeb mine, a world-famous copper mine known for its abundance of rare and unusual minerals.
Read More About Keyite / Source
Khatyrkite

Khatyrkite ( KAT-ee-ər-kyte) is a rare mineral which is mostly composed of copper and aluminium, but may contain up to about 15% of zinc or iron. Its chemical structure is described by an approximate formula (Cu,Zn)Al2 or (Cu,Fe)Al2. It was discovered in 1985 in a placer in association with another rare mineral cupalite ((Cu,Zn,Fe)Al). These two minerals have only been found at 62°39′11″N 174°30′02″E in the area of the Iomrautvaam, a tributary of the Khatyrka river, in the Koryak Mountains, in Anadyrsky District (former Beringovsky District), Chukotka, Russia. Analysis of one of the samples containing khatyrkite showed that the small rock was from a meteorite. A geological expedition has identified the exact place of the original discovery and found more specimens of the Khatyrka meteorite. The mineral’s name derives from the Khatyrka (Russian: Хатырка) zone where it was discovered. Its type specimen (defining sample) is preserved in the Mining Museum in Saint Petersburg, and parts of it can be found in other museums, such as Museo di Storia Naturale di Firenze.
Read More About Khatyrkite / Source
Kidwellite

Kidwellite in an uncommon mineral that was discovered in Arkansas in the United states. It was approved by the IMA in 1974, but it was only named in 1978 by Moore and Ito after Albert Lewis (Laws) Kidwell.
Read More About Kidwellite / Source
Kieserite

Kieserite, or magnesium sulfate monohydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula (MgSO4·H2O).
It has a vitreous luster and it is colorless, grayish-white or yellowish. Its hardness is 3.5 and crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. Gunningite is the zinc member of the kieserite group of minerals.
Read More About Kieserite / Source
Kinoite

Kinoite (Ca2Cu2Si3O8(OH)4 or Ca2Cu2Si3O10 · 2 H2O) is a light blue copper silicate mineral. It is somewhat scarce. It has a monoclinic crystal system, vitreous luster, and is transparent to translucent. It can be found in the Santa Rita Mountains, the Christmas Mine at Christmas, Arizona and a few other copper mines. Kinoite is popular with mineral collectors. Kinoite was named upon its discovery in 1970 after the pioneer Jesuit missionary Padre Eusebio Kino who worked in Arizona, Sonora and Baja California.
Read More About Kinoite / Source
Kleinite

Kleinite is a rare mineral that has only been found in the United States and Germany that occurs in hydrothermal mercury deposits. It occurs associated with calcite, gypsum and (rarely) barite or calomel. Its color can range from pale yellow/canary yellow to orange, and it is transparent to translucent. As a photosensitive mineral, its coloration darkens when exposed to light.It has been hypothesized that kleinite formed through a “reaction of cinnabar with oxidized meteoric water”, with this reaction being the source of kleinite’s nitrogen.
Read More About Kleinite / Source
Knebelite
Knebelite is a manganese variety of the fayalite-tephroite series with formula (Fe,Mn)2SiO4. It forms dark green orthorhombic crystals. It is reported from a variety of locations in Sweden as well as South Africa, Russia, British Columbia, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island.
Read More About Knebelite / Source
Knorringite
Knorringite is a mineral species belonging to the garnet group, and forms a series with the species pyrope. It was discovered in 1968 in the Kao kimberlite pipe in the Butha-Buthe District of Lesotho and is named after Oleg Von Knorring, a professor of mineralogy at the University of Leeds in England.Synthetic knorringite has the pure endmember formula Mg3Cr2(SiO4)3. As knorringite is a member of the knorringite – pyrope series, natural samples contain variable aluminium in the chromium site. Knorringite is a greenish blue color with a Mohs scale of mineral hardness of six to seven.
It occurs as a rare component within ultramafic nodules in kimberlites in association with olivine, enstatite, chrome diopside, chromian pyrope, chromian spinel, ilmenite, perovskite, zircon, diamond, omphacite, rutile, carbonates and micas. It has been reported
from the Red Ledge mine in Nevada County, California in addition to the type location in Lesotho.Knorringite is a tracer mineral in the search for diamonds in kimberlite pipes.
Read More About Knorringite / Source
Kobellite

Kobellite is a gray, fibrous, metallic mineral with the chemical formula Pb22Cu4(Bi,Sb)30S69. It is also a sulfide mineral consisting of antimony, bismuth, and lead. It is a member of the izoklakeite – berryite series with silver and iron substituting in the copper site and a varying ratio of bismuth, antimony, and lead. It crystallizes with monoclinic pyramidal crystals. The mineral can be found in ores and deposits of Hvena, Sweden; Ouray, Colorado; and Wake County, North Carolina, US. The mineral was named after Wolfgang Franz von Kobell (1803–1882), a German mineralogist.
Read More About Kobellite / Source
Kochite
Kochite is a rare silicate mineral with chemical formula of (Na,Ca)3Ca2(Mn,Ca)ZrTi[(F,O)4(Si2O7)2] or double that. Kochite is a member of the rosenbuschite group.
Read More About Kochite / Source
Kogarkoite

Kogarkoite is a sodium sulfate fluoride mineral with formula Na3(SO4)F. It has a pale blue color, a specific gravity of about 2.67 and a hardness of 3.5. The crystal is monoclinic and is a type of naturally occurring antiperovskite. Kogarkoite is named after the Russian petrologist Lia Nikolaevna Kogarko (born 1936) who discovered the mineral.
Read More About Kogarkoite / Source
Kolbeckite

Kolbeckite (scandium phosphate dihydrate) is a mineral with formula: ScPO4·2H2O. It was discovered originally at Schmiedeberg, Saxony, Germany in 1926 and is named after Friedrich L. W. Kolbeck, a German mineralogist. Kolbeckite is usually found as small clusters of crystals associated with other phosphate minerals.
Read More About Kolbeckite / Source
Kornerupine

Kornerupine (also called Prismatine) is a rare boro-silicate mineral with the chemical formula (Mg,Fe2+)4(Al,Fe3+)6(SiO4,BO4)5(O,OH)2. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic – dipyramidal crystal system as brown, green, yellow to colorless slender tourmaline like prisms or in massive fibrous forms. It has a Mohs hardness of 7 and a specific gravity of 3.3 to 3.34. Its indices of refraction are nα=1.660 – 1.671, nβ=1.673 – 1.683 and nγ=1.674 – 1.684.
It occurs in boron-rich volcanic and sedimentary rocks which have undergone high grade metamorphism. It is also found in metamorphosed anorthosite complexes.Kornerupine is valued as a gemstone when it is found in translucent green to yellow shades. The emerald green varieties are especially sought after. It forms a solid solution series with prismatine. Strongly pleochroic, it appears green or reddish brown when viewed from different directions. It has a vitreous luster.
It was first described in 1884 for an occurrence in Fiskernæs in southwest Greenland. It was named in honor of the Danish geologist, Andreas Nikolaus Kornerup Andreas Kornerup (1857–1883). Although kornerupine was named in 1884, it was not until 1912 that gem-quality material was found and it remains uncommon to this day.
Deposits are found in Burma (Myanmar), Canada (Quebec), Kenya, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, and South Africa.
Read More About Kornerupine / Source
Kosmochlor

Kosmochlor is a rare chromium sodium clinopyroxene with the chemical formula NaCr3+Si2O6.
The name is from German kosmisch, for its occurrence in meteorites, and the Greek chlor, for green. It was first reported in 1897 from the Toluca meteorite, Jiquipilco, Mexico.It occurs as a major constituent of some jadeitites and as an accessory mineral of some iron meteorites. Associated minerals include cliftonite (graphite), chromian diopside, troilite at Toluca; daubreelite, krinovite, roedderite, high albite, richterite, chromite (Canyon Diablo); and jadeite, chromite and chlorite (Burma).
Read More About Kosmochlor / Source
Kostovite

Kostovite is a rare orthorhombic-pyramidal gray white telluride mineral containing copper and gold with chemical formula AuCuTe4.It was discovered by Bulgarian mineralogist Georgi Terziev (Георги Терзиев) (1935–1972), who named it in honor of his professor Ivan Kostov (Иван Костов) (1913–2004). In 1965 kostovite was approved as a new species by the International Mineralogical Association. The type locality is the Chelopech copper ore deposit, Bulgaria. Small deposits have also been found in Kochbulak (Eastern Uzbekistan), Commoner mine (Zimbabwe), Kamchatka (Russian Far East), Ashanti (Ghana), Buckeye Gulch (Leadville, Colorado, US), Bisbee (Arizona, US), Kutemajärvi (Finland), Coranda-Hondol (Romania), Glava (Sweden), Bereznjakovskoje (Southern Urals, Russia), Moctezuma (Sonora, Mexico), Panormos Bay (Tinos Island, Greece), Guilaizhuang Mine, Tongshi complex (Linyi Prefecture, Shandong Province, China), Kalgoorlie-Boulder City, (Goldfields-Esperance region, Western Australia, Australia).
Read More About Kostovite / Source
Köttigite

Köttigite is a rare hydrated zinc arsenate which was discovered in 1849 and named by James Dwight Dana in 1850 in honour of Otto Friedrich Köttig (1824–1892), a German chemist from Schneeberg, Saxony, who made the first chemical analysis of the mineral. It has the formula Zn3(AsO4)2·8H2O and it is a dimorph of metaköttigite, which means that the two minerals have the same formula, but a different structure: köttigite is monoclinic and metaköttigite is triclinic.
There are several minerals with similar formulae but with other cations in place of the zinc. Iron forms parasymplesite Fe2+3(AsO4)2·8H2O; cobalt forms the distinctively coloured pinkish purple mineral erythrite Co3(AsO4)2·8H2O and nickel forms annabergite Ni3(AsO4)2·8H2O. Köttigite forms series with all three of these minerals and they are all members of the vivianite group.
The Vivianite Group is a group of monoclinic phosphates and arsenates with divalent cations. The group members are annabergite, arupite, babanekite, baricite, erythrite, hornesite, kottingite, manganhornesite, pakhomovskyite, parasymplesite and vivianite.
Read More About Köttigite / Source
Kovdorskite

Kovdorskite, Mg2PO4(OH)·3H2O, is a rare, hydrated, magnesium phosphate mineral. It was first described by Kapustin et al., and is found only in the Kovdor Massif near Kovdor, Kola Peninsula, Russia. It is associated with collinsite, magnesite, dolomite, hydrotalcite, apatite, magnetite, and forsterite.
Read More About Kovdorskite / Source
Kratochvílite
Kratochvilite is a rare organic mineral formed by combustion of coal or pyritic black shale deposits. It is a hydrocarbon with the formula of either C13H10 or (C6H4)2CH2. It is a polymorph of the aromatic hydrocarbon fluorene. It forms white, yellow to brown crystals in the orthorhombic system which occur often as a druzey encrustation. It has a specific gravity of 1.21 and a Mohs hardness of 1 to 2.
It was first described from the Nejedly mine in Bohemia, Czech Republic in 1937.
Read More About Kratochvílite / Source
Kremersite

Kremersite is a rare mineral which is a hydrated multiple chloride of iron, ammonium and potassium with the formula: (NH4,K)2FeCl5·H2O. Kremersite is a brown-red to orange mineral that crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. It is a water-soluble mineral that is found around volcanic fumaroles. Occurs at Vesuvius, Italy and Mount Etna, Sicily. It was discovered in 1853 and named for the German chemist, Peter Kremers (born 1827).
Read More About Kremersite / Source
Krennerite

Krennerite is an orthorhombic gold telluride mineral which can contain variable amounts of silver in the structure. The formula is AuTe2, but specimen with gold substituted by up to 24% with silver have been found ([Au0.77Ag0.24]Te2). Both of the chemically similar gold-silver tellurides, calaverite and sylvanite, are in the monoclinic crystal system, whereas krennerite is orthorhombic.
The color varies from silver-white to brass-yellow. It has a specific gravity of 8.62 and a hardness of 2.5. It occurs in high temperature, hydrothermal environments.
Krennerite was discovered in 1878 near the village of Săcărâmb, Romania, and first described by the Hungarian mineralogist Joseph Krenner (1839–1920).
Read More About Krennerite / Source
Krieselite

Krieselite is a newly discovered naturally occurring mineral. Found in the Tsumeb mine in Tsumeb, Namibia at an unknown date and unknown depth, the mineral was first cataloged in 1994. Following the acceptance as a new mineral by the International Mineralogical Association in 2003, the material has been matched to unknown samples from the same mine in Namibia from 1972.
Read More About Krieselite / Source
Kröhnkite

Kröhnkite ( Na2Cu(SO4)2•2H2O ) is a rare copper sulfate mineral named after B. Kröhnke who first researched it. Kröhnkite may be replaced by Saranchinaite, the anhydrous form of the mineral, if heated to temperatures above 200 °C (392 °F).
Read More About Kröhnkite / Source
Krotite
Krotite is a natural mineral composed of calcium, aluminium and oxygen, with the molecular formula CaAl2O4. It is the low-pressure dimorph of CaAl2O4, of which the high-pressure dimorph is named dmitryivanovite.
Krotite was reported in 2011 in a calcium-aluminium-rich inclusion (CAI) in the carbonaceous chondrite meteorite NWA (North West Africa) 1934, which landed in Morocco. The mineral name was approved by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA 2010-038) and honors Alexander N. Krot, a researcher in cosmochemistry at the University of Hawaii at Manoa in Honolulu, Hawaii.Researchers have found that the mineral, which has the same atomic arrangement as a man-made component of some types of concrete (specifically, calcium aluminate cements), forms under low pressure at a temperature of at least 1,500 °C (2,730 °F). These conditions of high temperature and low pressure are consistent with a hypothesis that the krotite grains found in the meteorite formed as high-temperature condensates from the solar nebula from which the Solar System formed, approximately 4.6 billion years ago. Thus, they are likely to be among the earliest minerals formed in the solar system.The CAI containing the krotite was said to resemble a “cracked egg” because its rim was crosscut by cracks filled with iron and aluminum hydroxides. Researchers suggest that the mineral assemblage in the CAI was at one time surrounded by a hot gas that reacted with krotite crystals on the surface of the CAI. It is likely that cracks on this rim of the CAI were filled with hydrated oxides as a result of weathering that occurred after the meteorite landed on Earth.Associated minerals include perovskite, gehlenite, hercynite, mayenite, grossite, hibonite, spinel and diopside.
Read More About Krotite / Source
Kruťaite

Kruťaite, simplified Krut’aite or krutaite, is a rare mineral with the formula CuSe2. It crystallises in the cubic crystal system. It is part of the pyrite group, being composed of Cu2+ ions and Se22− ions. The mineral is most often found as a dark grey aggregate consisting of tiny crystals no more than a millimeter in size. The crystals are opaque in any size. It has no industrial use, but it is a prized collector’s item.
Read More About Kruťaite / Source
Krutovite

Krutovite is a cubic nickel diarsenide with a chemical composition of NiAs2 and a sulfur content of 0.02-0.34 weight percent. Krutovite is composed of nickel and arsenic with trace to minor amounts of cobalt, iron, copper, sulfur, and antimony.
Read More About Krutovite / Source
Kukharenkoite-(Ce)

Kukharenkoite-(Ce) is a barium cerium fluoride carbonate mineral, formula Ba2CeF(CO3)3. It was identified from samples found in the Mont-Saint-Hilaire alkaline intrusive complex, Quebec, and the Khibiny Massif, Kola peninsula, Russia. It was named for Russian mineralogist Alexander A. Kukharenko (1914–1993).The similar zhonghuacerite, a cerium containing mineral from China, is considered to be either kukharenkoite-(Ce) or huanghoite-(Ce) rather than a valid mineral.
Read More About Kukharenkoite-(Ce) / Source
Kuratite
Kuratite, named for Dr. Gero Kurat (1938–2009), meteorite researcher and Curator of the Meteorite Collection at the Vienna Natural History Museum, was first recognized as a new mineral by the Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification in 2014 from a small meteorite sample.
Read More About Kuratite / Source
Kurnakovite

Kurnakovite is a hydrated borate of magnesium with the chemical composition MgB3O3(OH)5·5H2O. It is a member of the inderite group and is a triclinic dimorph of the monoclinic inderite.
Read More About Kurnakovite / Source
Kutnohorite

Kutnohorite is a rare calcium manganese carbonate mineral with magnesium and iron that is a member of the dolomite group. It forms a series with dolomite, and with ankerite. The end member formula is CaMn2+(CO3)2, but Mg2+ and Fe2+ commonly substitute for Mn2+, with the manganese content varying from 38% to 84%, so the formula Ca(Mn2+,Mg,Fe2+)(CO3)2 better represents the species. It was named by Professor Bukowsky in 1901 after the type locality of Kutná Hora, Bohemia, in the Czech Republic. It was originally spelt “kutnahorite” but “kutnohorite” is the current IMA-approved spelling.
Read More About Kutnohorite / Source
Kyanite

Kyanite is a typically blue aluminosilicate mineral, found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and sedimentary rock. It is the high pressure polymorph of andalusite and sillimanite, and the presence of kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates metamorphism deep in the Earth’s crust. Kyanite is also known as disthene or cyanite.Kyanite is strongly anisotropic, in that its hardness varies depending on its crystallographic direction. In kyanite, this anisotropism can be considered an identifying characteristic, along with its characteristic blue color. Its name comes from the same origin as that of the color cyan, being derived from the Ancient Greek word κύανος. This is typically rendered into English as kyanos or kuanos and means “dark blue.”
Kyanite is used as a raw material in the manufacture of ceramics and abrasives, and it is an important index mineral used by geologists to trace metamorphic zones.
Read More About Kyanite / Source
Labradorite

Labradorite is an intermediate to calcic member of the plagioclase series. It has an anorthite percentage (%An) of between 50 and 70. The specific gravity ranges from 2.68 to 2.72. The streak is white, like most silicates. The refractive index ranges from 1.559 to 1.573 and twinning is common. As with all plagioclase members, the crystal system is triclinic, and three directions of cleavage are present, two of which are nearly at right angles and are more obvious, being of good to perfect quality (while the third direction is poor). It occurs as clear, white to gray, blocky to lath shaped grains in common mafic igneous rocks such as basalt and gabbro, as well as in anorthosites.
Read More About Labradorite / Source
Lanarkite

Lanarkite is a mineral, a form of lead sulfate with formula Pb2(SO4)O. It was originally found at Leadhills in the Scottish county of Lanarkshire, hence the name. It forms white or light green, acicular monoclinic prismatic crystals, usually microscopic in size. It is an oxidation product of galena.
Read More About Lanarkite / Source
Langbeinite

Langbeinite is a potassium magnesium sulfate mineral with the chemical formula K2Mg2(SO4)3. Langbeinite crystallizes in the isometric-tetartoidal (cubic) system as transparent colorless or white with pale tints of yellow to green and violet crystalline masses. It has a vitreous luster. The Mohs hardness is 3.5 to 4 and the specific gravity is 2.83. The crystals are piezoelectric.The mineral is an ore of potassium and occurs in marine evaporite deposits in association with carnallite, halite, and sylvite.It was first described in 1891 for an occurrence in Wilhelmshall, Halberstadt, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, and named for A. Langbein of Leopoldshall, Germany.Langbeinite gives its name to the langbeinites, a family of substances with the same cubic structure, a tetrahedral anion, and large and small cations.
Related substances include hydrated salts leonite (K2Mg(SO4)2·4H2O) and picromerite (K2Mg(SO4)2·6H2O).
Read More About Langbeinite / Source
Langite

Langite is a rare hydrated copper sulfate mineral, with hydroxyl, found almost exclusively in druses of small crystals. It is formed from the oxidation of copper sulfides, and was first described in specimens from Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is dimorphous with wroewolfeite. Langite was discovered in 1864 and named after the physicist and crystallographer Viktor von Lang (1838–1921), who was Professor of Physics at the University of Vienna, Austria.
Read More About Langite / Source
Lansfordite
Lansfordite is a hydrated magnesium carbonate mineral with composition: MgCO3·5H2O. Landsfordite was discovered in 1888 in a coal mine in Lansford, Pennsylvania. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system (space group P21/c) and typically occurs as colorless to white prismatic crystals and stalactitic masses. It is a soft mineral, Mohs hardness of 2.5, with a low specific gravity of 1.7. It is transparent to translucent with refractive indices of 1.46 to 1.51. The mineral will effloresce at room temperature, producing nesquehonite.
Read More About Lansfordite / Source
Lanthanite

Lanthanites are a group of isostructural rare earth element (REE) carbonate minerals. This group comprises the minerals lanthanite-(La), lanthanite-(Ce), and lanthanite-(Nd). This mineral group has the general chemical formula of (REE)2(CO3)3·8(H2O). Lanthanites include La, Ce, and Nd as major elements and often contain subordinate amounts of other REEs including praseodymium (Pr), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu) and dysprosium (Dy). The lanthanite crystal structure consists of layers of 10-fold coordinated REE-oxygen (O) polyhedra and carbonate (CO32−) groups connected by hydrogen bonds to interlayer water molecules, forming a highly hydrated structure.
Read More About Lanthanite / Source
Laplandite-(Ce)

Laplandite has a general formula of Na4CeTiPO4Si7O18•5H2O, and is found primarily in igneous rocks. This silicate mineral has been found as inclusions in pegmatites, primarily in the Kola Peninsula in Lappland, where the mineral’s name gets its origin. Laplandite is orthorhombic, which states that crystallographically, it contains three axes of unequal lengths that all intersect at 90 degrees, perpendicular to one another. The shape of the crystal is bipyramidal, and is similar in structure to olivine or aragonite. Because of these different axes lengths, it shows anisotropism, which will allow for the visibility of birefringence. This property can give the mineral very distinct colors when viewed under cross-polarization. Laplandite has three different indices of refraction, which are measures of the speed of light in vacuum divided by the speed of light within the mineral, determined individually on each axis. Due to these different indices, Laplandite is a biaxial mineral, which states that the mineral will have two optic axes. Under the microscope, this mineral has moderate relief, which describes the contrast between Laplandite’s refractive index and the refractive index of the mounting medium on which it is placed. The relief can be seen physically as how easily you can see the boundary lines of the mineral under plane polarized light in a petrographic microscope.Because of Laplandite’s sodium solubility, it has been designated as a candidate for extracting soda from the rocks in which it is found. This readily soluble mineral has given geologists clues about the history of the source of the parent rock, as water-soluble minerals do not form near surface temperatures and pressures. Also, the formation of this type of chemical assemblage is commonly located near phosphate and rare-element deposits, giving it another important characteristic as a good indicator to where more economic minerals can be found.
Read More About Laplandite-(Ce) / Source
Larnite
Larnite is a calcium silicate mineral with formula: Ca2SiO4. It is the calcium member of the olivine group of minerals.
It was first described from an occurrence at Scawt Hill, Larne, Northern Ireland in 1929 by Cecil Edgar Tilley and named for the location. At the type locality it occurs with wollastonite, spurrite, perovskite, merwinite, melilite and
gehlenite. It occurs in contact metamorphosed limestones and chalks adjacent to basaltic intrusives.Dicalcium silicate is chemically, β–Ca2SiO4, sometimes represented by the idealized oxide formula 2CaO·SiO2 also noted C2S in the cement chemist notation (CCN). When used in the cement industry, the mineral is usually referred to as belite.
Read More About Larnite / Source
Laumontite

Laumontite is a mineral, one of the zeolite group. Its molecular formula is Ca(AlSi2O6)2 · 4H2O, a hydrated calcium-aluminium silicate. Potassium or sodium may substitute for the calcium but only in very small amounts.
It is monoclinic, space group C2/m. It forms prismatic crystals with a diamond-shaped cross-section and an angled termination. When pure, the color is colorless or white. Impurities may color it orange, brownish, gray, yellowish, pink, or reddish. It has perfect cleavage on [010] and [110] and its fracture is conchoidal. It is very brittle. The Mohs scale hardness is 3.5-4. It has a vitreous luster and a white streak.
It is found in hydrothermal deposits left in calcareous rocks, often formed as a result of secondary mineralization. Host rock types include basalt, andesite, metamorphic rocks and granites. It forms at a temperature of about 100 °C (212 °F), and becomes unstable above about 150 °C (302 °F), and so its presence in sedimentary rocks indicates that these have experienced intermediate diagenesis.The identification of laumontite goes back to the early days of mineralogy. It was first named lomonite by R. Jameson (System of Mineralogy) in 1805, and laumonite by René Just Haüy in 1809. The current name was given by K.C. von Leonhard (Handbuch der Oryktognosie) in 1821. It is named after Gillet de Laumont who collected samples from lead mines in Huelgoat, Brittany, making them the type locality.
Laumontite easily dehydrates when stored in a low humidity environment. When freshly collected, if it has not already been exposed to the environment, it can be translucent or transparent. Over a period of hours to days the loss of water turns it opaque white. In the past, this variety has been called leonhardite, though this is not a valid mineral species. The dehydrated laumontite is very friable, often falling into a powder at the slightest touch.
It is a common mineral, found worldwide. It can be locally abundant, forming seams and veins. It is frequently associated with other zeolites, including stilbite and heulandite. Notable occurrences are India; Paterson, New Jersey; Pine Creek, California; Iceland; Scotland; and the Bay of Fundy, Nova Scotia. Prehnite pseudomorphs after laumontite (epimorphs) have been found in India.
Read More About Laumontite / Source
Laurionite

Laurionite (PbCl(OH)) is a lead halide mineral. It forms colorless to white crystals in the orthorhombic crystal system and is dimorphous with paralaurionite, both members of the matlockite group.It was first described in 1887 for an occurrence in the Laurium District, Attica, Greece, and named after the town Laurium.
It occurs as an oxidation product in lead ore deposits, and is also produced on lead-bearing slag by reaction with saline solutions. It occurs associated with paralaurionite, penfieldite, fiedlerite, phosgenite, cerussite and anglesite.
Read More About Laurionite / Source
Laurite

Laurite is an opaque black, metallic ruthenium sulfide mineral with formula: RuS2. It crystallizes in the isometric system. It is in the pyrite structural group. Though it’s been found in many localities worldwide, it is extremely rare.
Laurite has a Mohs hardness of 7.5 and a specific gravity of 6.43. It can contain osmium, rhodium, iridium, and iron substituting for the ruthenium. The sulfur is present as the disulfide ion, S2−2, so the ruthenium is in the Ru(II) oxidation state.
Read More About Laurite / Source
Lautenthalite
Lautenthalite is a mineral that was named after its location, Lautenthal, Harz mountains, Germany. It can be found in several slag localities. It was approved by the IMA in 1993. It’s a member of the devilline group, and it’s the lead analogue of devilline and campigliaite. Without analytical methods, it’s hard to distinguish the mineral from both. It shows pleochroic properties, which is an optical phenomenon. Depending on which angle the mineral is inspected, the color of it differs. On the x optical axis, the mineral could be seen in a pale blue color, on the y and z axis, the mineral’s color changes to blue. It has tabular crystals and sheaflike or irregular aggregates. Lautenthalite is associated with wroewolfeite, which it tends to overgrow. It’s also associated with anglesite, devilline–serpierite, galena, linarite, brochantite and schulenbergite. It forms small singular crystals, which’s size is up to 0.5 × 0.3 × 0.03 mm.
Read More About Lautenthalite / Source
Lautite

Lautite is a rare mineral belonging to the class of sulfides and sulfosalts with the general formula CuAsS. It is orthorhombic and is known to form up to 2.3 cm long prismatic or flat crystals. It is also found as grains or masses.
First identified by Friedrich August Frenzel in 1880 in the Rudolphschacht mine near Lauta in Saxony, it was named after its type locality.Lautite is formed in veins under hydrothermal conditions at medium temperatures. Depending on the locality it is found accompanied by arsenic, tennantite, proustite, chalcopyrite, galenite, and baryte (in the type locality); by kutinaite and paxite (in Nieder-Beerbach); or by arsenic, bismuth, tennantite, loellingite, rammelsbergite, proustite, and quartz (in Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines).
Aside from the type locality, the mineral is found in other places in the Ore Mountains, in Sankt Andreasberg in the Harz mountains, Nieder-Beerbach in the Odenwald, Hausach, Schenkenzell, and Titisee-Neustadt in the Black Forest, Flatschach in Austria, Isérables in Switzerland, Cochrane in Canada, Luqu and Zoigê in China, Sirohi in India, Takab in Iran, Kombat in Namibia and Coconino County in Arizona, US.
Read More About Lautite / Source
Lavendulan

Lavendulan is an uncommon copper arsenate mineral, known for its characteristic intense electric blue colour. It belongs to the lavendulan group, which has four members:
Lavendulan NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl.5H2O
Lemanskiite NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl.5H2O
Sampleite NaCaCu5(PO4)4Cl.5H2O
Zdenekite NaPbCu5(AsO4)4Cl.5H2OLemanskiite and lavendulan are dimorphs; they have the same formula but different structures. Lemanskiite is tetragonal, but lavendulan is monoclinic. Lavendulan has the same structure as sampleite, and the two minerals form a series. It is the calcium analogue of zdenĕkite and the arsenate analogue of sampleite.
Lavendulan was originally named for the lavender color of the “type” specimen, which has since been determined to be a mixture with no relationship to modern lavendulan. The mineral which is now called lavendulan is not a lavender blue color, and has no relationship to the “type” material from Annaberg. It often contains potassium, cobalt and nickel as impurities.
Read More About Lavendulan / Source
Lawsonite

Lawsonite is a hydrous calcium aluminium sorosilicate mineral with formula CaAl2Si2O7(OH)2·H2O. Lawsonite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system in prismatic, often tabular crystals. Crystal twinning is common. It forms transparent to translucent colorless, white, and bluish to pinkish grey glassy to greasy crystals. Refractive indices are nα=1.665, nβ=1.672 – 1.676, and nγ=1.684 – 1.686. It is typically almost colorless in thin section, but some lawsonite is pleochroic from colorless to pale yellow to pale blue, depending on orientation. The mineral has a Mohs hardness of 8 and a specific gravity of 3.09. It has perfect cleavage in two directions and a brittle fracture.
Lawsonite is a metamorphic mineral typical of the blueschist facies. It also occurs as a secondary mineral in altered gabbro and diorite. Associate minerals include epidote, titanite, glaucophane, garnet and quartz. It is an uncommon constituent of eclogite.
Lawsonite was first described in 1895 for occurrences on Ring Mountain of the Tiburon peninsula, Marin County, California and was named after geologist Andrew Lawson (1861–1952) of the University of California by two of Lawson’s graduate students, Charles Palache and Frederick Leslie Ransome.
Read More About Lawsonite / Source
Lazulite

Lazulite ((Mg,Fe2+)Al2(PO4)2(OH)2) is a blue, phosphate mineral containing magnesium, iron, and aluminium phosphate. Lazulite forms one endmember of a solid solution series with the darker iron rich scorzalite.Lazulite crystallizes in the monoclinic system. Crystal habits include steep bipyramidal or wedge-shaped crystals. Lazulite has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 3.0 to 3.1. It is infusible and insoluble.
Read More About Lazulite / Source
Lazurite

Lazurite is a tectosilicate mineral with sulfate, sulfur and chloride with formula (Na,Ca)8[(S,Cl,SO4,OH)2|(Al6Si6O24)]. It is a feldspathoid and a member of the sodalite group. Lazurite crystallizes in the isometric system although well‐formed crystals are rare. It is usually massive and forms the bulk of the gemstone lapis lazuli.
Read More About Lazurite / Source
Lead

Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin plumbum) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children.
Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the group, lead tends to bond with itself; it can form chains and polyhedral structures.
Since lead is easily extracted from its ores, prehistoric people in the Near East were aware of it. Galena is a principal ore of lead which often bears silver. Interest in silver helped initiate widespread extraction and use of lead in ancient Rome. Lead production declined after the fall of Rome and did not reach comparable levels until the Industrial Revolution. Lead played
a crucial role in the development of the printing press, as movable type could be relatively easily cast from lead alloys. In 2014, the annual global production of lead was about ten million tonnes, over half of which was from recycling. Lead’s high density, low melting point, ductility and relative inertness to oxidation make it useful. These properties, combined with its relative abundance and low cost, resulted in its extensive use in construction, plumbing, batteries, bullets and shot, weights, solders, pewters, fusible alloys, white paints, leaded gasoline, and radiation shielding.
Lead’s toxicity became widely recognized in the late 19th century, although a number of well-educated ancient Greek and Roman writers were aware of this fact and even knew some of the symptoms of lead poisoning. Lead is a neurotoxin that accumulates in soft tissues and bones; it damages the nervous system and interferes with the function of biological enzymes, causing neurological disorders ranging from behavioral problems to brain damage, and also affects general health, cardiovascular, and renal systems.
Leadhillite

Leadhillite is a lead sulfate carbonate hydroxide mineral, often associated with anglesite. It has the formula Pb4SO4(CO3)2(OH)2. Leadhillite crystallises in the monoclinic system, but develops pseudo-hexagonal forms due to crystal twinning. It forms transparent to translucent variably coloured crystals with an adamantine lustre. It is quite soft with a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a relatively high specific gravity of 6.26 to 6.55.
It was discovered in 1832 in the Susannah Mine, Leadhills in the county of Lanarkshire, Scotland. It is trimorphous with susannite and macphersonite (these three minerals have the same formula, but different structures). Leadhillite is monoclinic, susannite is trigonal and macphersonite is orthorhombic. Leadhillite was named in 1832 after the locality.
Read More About Leadhillite / Source
Legrandite

Legrandite is a rare zinc arsenate mineral, Zn2(AsO4)(OH)·(H2O).
It is an uncommon secondary mineral in the oxidized zone of arsenic bearing zinc deposits and occurs rarely in granite pegmatite. Associated minerals include: adamite, paradamite, köttigite, scorodite, smithsonite, leiteite, renierite, pharmacosiderite, aurichalcite, siderite, goethite and pyrite. It has been reported from Tsumeb, Namibia; the Ojuela mine in Durango, Mexico and at Sterling Hill, New Jersey, US.It was first described in 1934 for an occurrence in the Flor de Peña Mine, Nuevo León, Mexico and named after M. Legrand, a Belgian mining engineer .
Read More About Legrandite / Source
Leifite

Leifite is a rare tectosilicate. Tectosilicates are built on a framework of tetrahedra with silicon or aluminium at the centre and oxygen at the vertices; they include feldspars and zeolites, but leifite does not belong in either of these categories. It is a member of the leifite group, which includes telyushenkoite (Cs,Na,K)Na6(Be2Al3Si15O39) and eirikite KNa6Be2(Si15Al3)O39F2). Leifite was discovered in 1915, and named after Leif Ericson who was a Norse explorer who lived around 1000 AD, and was probably the first European to land in North America, nearly 500 years before Christopher Columbus. Eirikite was named in 2007 after Eirik Raude, or Erik the Red, (950–1003), who discovered Greenland and who was the father of Leif Ericson. The third mineral in the group, telyushenkoite, was discovered in 2001. It was not named after any of Leif Ericson’s family members, but after a professor of geology in Turkmenistan.
Read More About Leifite / Source
Leightonite

Leightonite is a rare sulfate mineral with formula of K2Ca2Cu(SO4)4•2H2O.
Read More About Leightonite / Source
Lepidocrocite

Lepidocrocite (γ-FeO(OH)), also called esmeraldite or hydrohematite, is an iron oxide-hydroxide mineral. Lepidocrocite has an orthorhombic crystal structure, a hardness of 5, specific gravity of 4, a submetallic luster and a yellow-brown streak. It is red to reddish brown and forms when iron-containing substances rust underwater. Lepidocrocite is commonly found in the weathering of primary iron minerals and in iron ore deposits. It can be seen as rust scale inside old steel water pipes and water tanks.
The structure of lepidocrocite is similar to the boehmite structure found in bauxite and consists of layered iron(III) oxide octahedra bonded by hydrogen bonding via hydroxide layers. This relatively weakly bonded layering accounts for the scaley habit of the mineral.
It was first described in 1813 from the Zlaté Hory polymetallic ore deposit in Moravia, Czech Republic. The name is from the Greek lipis for scale and krokis for fibre.
Read More About Lepidocrocite / Source
Lepidolite

Lepidolite is a lilac-gray or rose-colored member of the mica group of minerals with chemical formula K(Li,Al)3(Al,Si,Rb)4O10(F,OH)2. It is the most abundant lithium-bearing mineral and is a secondary source of this metal. It is the major source of the alkali metal rubidium.
Lepidolite is found with other lithium-bearing minerals, such as spodumene, in pegmatite bodies. It has also been found in high-temperature quartz veins, greisens and granite.
Read More About Lepidolite / Source
Letovicite

Letovicite is an ammonium sulfate mineral with composition (NH4)3H(SO4)2 (IUPAC: triammonium sulfate hydrogensulfate, Nickel–Strunz classification 07.AD.20).
It is a rare colorless or white monoclinic secondary mineral formed during the burning of waste coal heaps and as a deposit in hot springs. It was first described from the Letovice region of Moravia in 1932. Geologic occurrences also include Austria, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Poland, South Africa, Tajikistan and the United States.
Read More About Letovicite / Source
Leucite

Leucite (from the Greek word leukos meaning white) is a rock-forming mineral of the feldspathoid group, silica-undersaturated and composed of potassium and aluminium tectosilicate KAlSi2O6. Crystals have the form of cubic icositetrahedra but, as first observed by Sir David Brewster in 1821, they are not optically isotropic, and are therefore pseudo-cubic. Goniometric measurements made by Gerhard vom Rath in 1873 led him to refer the crystals to the tetragonal system. Optical investigations have since proved the crystals to be still more complex in character, and to consist of several orthorhombic or monoclinic individuals, which are optically biaxial and repeatedly twinned, giving rise to twin-lamellae and to striations on the faces. When the crystals are raised to a temperature of about 500 °C they become optically isotropic and the twin-lamellae and striations disappear, although they reappear when the crystals are cooled again. This pseudo-cubic character of leucite is very similar to that of the mineral boracite.
The crystals are white or ash-grey in colour, hence the name suggested by A. G. Werner in 1701, from λευκος, ‘(matt) white’. They are transparent and glassy when fresh, albeit with a noticeably subdued ‘subvitreous’ lustre due to the low refractive index, but readily alter to become waxy/greasy and then dull and opaque; they are brittle and break with a conchoidal fracture. The Mohs hardness is 5.5, and the specific gravity 2.47. Inclusions of other minerals, arranged in concentric zones, are frequently present in the crystals. On account of the color and form of the crystals the mineral was early known as ‘white garnet’. French authors in older literature may employ René Just Haüy’s name amphigène, but ‘leucite’ is the only name for this mineral species that is recognised as official by the International Mineralogical Association.
Read More About Leucite / Source
Leucophanite

Leucophanite is an inosilicate mineral with the chemical formula (Na,Ca)2BeSi2(O.OH.F)7. It may contain cerium substituting in the calcium position.
It occurs in pegmatites and alkali igneous complexes as yellow, greenish or white triclinic crystals and has been found in Norway, Quebec and Russia.
It was first described from the Langesundfiord district of southern Norway in 1840. The name is from the Greek leucos for “white” and phanein for “to appear” in allusion to the common white color.
Read More About Leucophanite / Source
Leucophoenicite

Leucophoenicite is a mineral with formula Mn7(SiO4)3(OH)2. Generally brown to red or pink in color, the mineral gets its name from the Greek words meaning “pale purple-red”. Leucophoenicite was discovered in New Jersey, US and identified as a new mineral in 1899.
Read More About Leucophoenicite / Source
Lévyne

Levyne or levynite is a zeolite mineral, i.e. a hydrated silicate mineral. There are two forms of levyne:
Levyne-Na, the sodium dominated form (Na2,Ca,K2)Al2Si4O12·6(H2O), and
Levyne-Ca the calcium dominated form (Ca,Na2,K2)Al2Si4O12·6(H2O)Levyne crystallizes in the Trigonal – Hexagonal Scalenohedral class. It typically occurs as radiating clusters or fibrous masses that are transparent to translucent in colors ranging from white through reddish and yellowish white to gray. It has a specific gravity of 2.09 – 2.16 and a Mohs hardness of 4.0 to 4.5. It has a vitreous luster and perfect cleavage on [1011]. Typical occurrence is as an alteration and vesicle filling mineral in basalts.
It was named for French mineralogist Armand Lévy (1795–1841).
The calcium variety was first described in 1821 for an occurrence in Dalsnipa, Sandoy, Faroe Islands. The sodium variety was described in 1997 for an occurrence in Chojabaru, Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan.
Read More About Lévyne / Source
Libethenite

Libethenite is a rare copper phosphate hydroxide mineral. It forms striking, dark green orthorhombic crystals. It was discovered in 1823 in Ľubietová, Slovakia and is named after the German name of that locality (Libethen). Libethenite has also been found in the Miguel Vacas Mine, Conceição, Vila Viçosa, Évora District, Portugal, and in Tier des Carrières, Cahai, Vielsaim, Stavelot Massif, Luxembourg Province, Belgium.
Read More About Libethenite / Source
Liebigite

Liebigite is a uranium carbonate mineral with the chemical formula: Ca2(UO2)(CO3)3·11H2O. It is a secondary mineral occurring in the oxidizing zone of uranium-bearing ores. It is green to yellow green in colour. It has a Mohs hardness of about 3. Liebigite, like some other uranium minerals, is fluorescent under UV light and is also translucent. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system, but only rarely forms distinct crystals. It typically forms encrustations or granular aggregates.It was first described in 1848 for an occurrence in Adrianople, Edirne Province, Marmara Region, Turkey. It was named for German chemist Justus von Liebig (1803–1873).
Read More About Liebigite / Source
Linarite

Linarite is a somewhat rare, crystalline mineral that is known among mineral collectors for its unusually intense, pure blue color. It is formed by the oxidation of galena and chalcopyrite and other copper sulfides. It is a combined copper lead sulfate hydroxide with formula PbCuSO4(OH)2.
Linarite occurs as monoclinic prismatic to tabular crystals and irregular masses. It is easily confused with azurite, but does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid as azurite does. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a specific gravity of 5.3 – 5.5.
Linarite was first identified in 1822. It is named after the Linares Plateau, Spain. It occurs in association with brochantite, anglesite, caledonite, leadhillite, cerussite, malachite and hemimorphite.
Read More About Linarite / Source
Lindgrenite

Lindgrenite is an uncommon copper molybdate mineral with formula: Cu3(MoO4)2(OH)2. It occurs as tabular to platey monoclinic green to yellow green crystals.
Read More About Lindgrenite / Source
Linnaeite
Linnaeite is a cobalt sulfide mineral with the composition Co+2Co+32S4. It was discovered in 1845 in Västmanland, Sweden, and was named to honor Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778).Linnaeite forms a series with polydymite, Ni+2Ni+32S4. Linnaeite is found in hydrothermal veins with other cobalt and nickel sulfides in many localities around the world.
Read More About Linnaeite / Source
Lipscombite

Lipscombite (Fe2+,Mn2+)(Fe3+)2(PO4)2(OH)2 is a green gray, olive green, or black. phosphate-based mineral containing iron, manganese, and iron phosphate.
Lipscombite is often formed at meteorite impact sites where its crystals are microscopically small, because crystal-forming conditions of pressure and temperature are brief.
In the Classification of non-silicate minerals lipscombite is in the lipscombite group, which also includes zinclipscombite. This group is within the non-silicate, category 8, anhydrous phosphates, lazulite supergroup.
Read More About Lipscombite / Source
Liroconite

Liroconite is a complex mineral: Hydrated copper aluminium arsenate hydroxide, with the formula Cu2Al[(OH)4|AsO4]·4(H2O). It is a vitreous monoclinic mineral, colored bright blue to green, often associated with malachite, azurite, olivenite, and clinoclase. It is quite soft, with a Mohs hardness of 2 – 2.5, and has a specific gravity of 2.9 – 3.0.
It was first identified in 1825 in the tin and copper mines of Devon and Cornwall, England. Although it remains quite rare it has subsequently been identified in a variety of locations including France, Germany, Australia, New Jersey and California.The type locality for liroconite is Wheal Gorland in St Day, Cornwall in the United Kingdom. The largest crystal specimen on public display is in the Royal Cornwall Museum in Truro.
It occurs as a secondary mineral in copper deposits in association with olivenite, chalcophyllite, clinoclase, cornwallite, strashimirite, malachite, cuprite and limonite.
Read More About Liroconite / Source
Litharge

Litharge (from Greek lithargyros, lithos (stone) + argyros (silver) λιθάργυρος) is one of the natural mineral forms of lead(II) oxide, PbO. Litharge is a secondary mineral which forms from the oxidation of galena ores. It forms as coatings and encrustations with internal tetragonal crystal structure. It is dimorphous with the yellow orthorhombic form massicot. It forms soft (Mohs hardness of 2), red, greasy-appearing crusts with a very high specific gravity of 9.14–9.35. PbO may be prepared by heating lead metal in air at approximately 600 °C (lead melts at only 300 °C). At this temperature it is also the end product of heating of other lead oxides in air. This is often done with a set of bellows pumping air over molten lead and causing the oxidized product to slip or fall off the top into a receptacle, where it quickly solidifies in minute scales.
PbO2 –(293 °C)→ Pb12O19 –(351 °C)→ Pb12O17 –(375 °C)→ Pb3O4 –(605 °C)→ PbO
Read More About Litharge / Source
Lithiophilite

Lithiophilite is a mineral containing the element lithium. It is lithium manganese(II) phosphate with chemical formula LiMnPO4. It occurs in pegmatites often associated with triphylite, the iron end member in a solid solution series. The mineral with intermediate composition is known as sicklerite and has the chemical formula Li(Mn,Fe)PO4). The name lithiophilite is derived from the Greek philos (φιλός) “friend,” as lithiophilite is usually found with lithium.Lithiophylite is a resinous reddish to yellowish brown mineral crystallizing in the orthorhombic system often as slender prisms. It is usually associated with lepidolite, beryl, quartz, albite, amblygonite, and spodumene of pegmatitic origin. It rather readily weathers to a variety of secondary manganese phosphates and oxides. It is a late-stage mineral in some complex granite pegmatites. Members of the triphylite-lithiophilite series readily alter to secondary minerals.
The type locality is the Branchville Quarry, Branchville, Fairfield County, Connecticut where it was first reported in 1878. The largest documented single crystal of lithiophilite was found in New Hampshire, US, measured 2.44×1.83×1.22 m3 and weighed about 20 tonnes.The synthetic form of triphylite, lithium iron phosphate, is a promising material for the production of lithium-ion batteries.
Read More About Lithiophilite / Source
Livingstonite

Livingstonite is a mercury antimony sulfosalt mineral. It occurs in low-temperature hydrothermal veins associated with cinnabar, stibnite, sulfur and gypsum.
It was first described in 1874 for an occurrence in Huitzuco de los Figueroa, Guerrero, Mexico. It was named to honor Scottish explorer of Africa, David Livingstone.Its crystal structure was determined in 1957 and redetermined in 1975.
Read More About Livingstonite / Source
Lizardite

Lizardite is a mineral from the serpentine subgroup with formula Mg3(Si2O5)(OH)4, and the most common type of mineral in the subgroup. It is also a member of the kaolinite-serpentine group.Lizardite may form a solid-solution series with the nickel-bearing népouite (pure end-member: Ni3(Si2O5)(OH)4). Intermediate compositions (Mg,Ni)3(Si2O5)(OH)4 are possible, with varying proportions of magnesium and nickel. However, the lizardite end-member is much more common than pure népouite, a relatively rare mineral most often formed by the alteration of ultramafic rocks.
Extremely fine-grained, scaly lizardite (also called orthoantigorite) comprises much of the serpentine present in serpentine marbles. It is triclinic, has one direction of perfect cleavage, and may be white, yellow or green. Lizardite is translucent and soft, and may be pseudomorphous after enstatite, olivine or pyroxene, in which case the name bastite is sometimes applied. Bastite may have a silky lustre.
Read More About Lizardite / Source
Loellingite

Loellingite, also spelled löllingite, is an iron arsenide mineral with formula FeAs2. It is often found associated with arsenopyrite (FeAsS) from which it is hard to distinguish. Cobalt, nickel and sulfur substitute in the structure. The orthorhombic lollingite group includes the nickel iron arsenide rammelsbergite and the cobalt iron arsenide safflorite. Leucopyrite is an old synonym for loellingite.
It forms opaque silvery white orthorhombic prismatic crystals often exhibiting crystal twinning. It also occurs in anhedral masses and tarnishes on exposure to air. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a quite high specific gravity of 7.1 to 7.5. It becomes magnetic after heating.
Loellingite was first described in 1845 at the Lölling district in Carinthia, Austria, for which it was named.
It occurs in mesothermal ore deposits associated with skutterudite, native bismuth, nickeline, nickel-skutterudite, siderite and calcite. It has also been reported from pegmatites.
Read More About Loellingite / Source
Lonsdaleite
Lonsdaleite (named in honour of Kathleen Lonsdale), also called hexagonal diamond in reference to the crystal structure, is an allotrope of carbon with a hexagonal lattice, as opposed to the cubical lattice of conventional diamond. It is found in nature in meteorite debris; when meteors containing graphite strike the Earth, the immense heat and stress of the impact transforms the graphite into diamond, but retains graphite’s hexagonal crystal lattice. Lonsdaleite was first identified in 1967 from the Canyon Diablo meteorite, where it occurs as microscopic crystals associated with ordinary diamond.It is translucent and brownish-yellow and has an index of refraction of 2.40–2.41 and a specific gravity of 3.2–3.3 . Its hardness is theoretically superior to that of cubic diamond (up to 58% more), according to computational simulations, but natural specimens exhibited somewhat lower hardness through a large range of values (from 7–8 on Mohs hardness scale). The cause is speculated as being due to the samples having been riddled with lattice defects and impurities.In addition to meteorite deposits, hexagonal diamond has been synthesized in the laboratory (1966 or earlier; published in 1967) by compressing and heating graphite either in a static press or using explosives.
Read More About Lonsdaleite / Source
Loparite-(Ce)

Loparite-(Ce) is a granular, brittle oxide mineral of the perovskite class. It is black to dark grey and may appear grey to white in reflected light on polished thin section with reddish brown internal reflections. It has the chemical formula of (Ce,Na,Ca)(Ti,Nb)O3. Nioboloparite is a variation of Loparite-(Ce) containing niobium.Loparite occurs as a primary phase in nepheline syenite intrusions and pegmatites. It is also found replacing perovskite in carbonatites.Loparite was first described for an occurrence in the Khibiny and Lovozero massifs, Kola peninsula in northern Russia.
Crystal structures of loparite
Read More About Loparite-(Ce) / Source
Lópezite

Lópezite is a rare red chromate mineral with chemical formula: K2Cr2O7. It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system.It occurs as rare vug fillings in nitrate ores in association with tarapacáite (K2CrO4), dietzeite and ulexite in the Chilean Atacama and is reported from the Bushveld igneous complex of South Africa. Lópezite was first described in 1937 for an occurrence in Iquique Province, Chile and named after Chilean mining engineer Emiliano López Saa (1871–1959).Most lopezite offered for sale to collectors is artificially produced. Synthetic varieties also exhibit monoclinic crystals.
Read More About Lópezite / Source
Lorándite

Lorándite is a thallium arsenic sulfosalt with the chemical formula: TlAsS2. Though rare, it is the most common thallium-bearing mineral. Lorandite occurs in low-temperature hydrothermal associations and in gold and mercury ore deposits. Associated minerals include stibnite, realgar, orpiment, cinnabar, vrbaite, greigite, marcasite, pyrite, tetrahedrite, antimonian sphalerite, arsenic and barite.The mineral is being used for detection of solar neutrino via a certain nuclear reaction involving thallium. It has a monoclinic crystal structure consisting of spiral chains of AsS3 tetrahedra interconnected by thallium atoms, and can be synthesized in the laboratory.
Read More About Lorándite / Source
Loveringite
Loveringite is a rare metallic oxide mineral of the crichtonite group with the chemical formula (Ca,Ce)(Ti,Fe,Cr,Mg)21O38. It is a late-stage magmatic mineral, formed in the residual melt of mafic layered intrusions in either the olivine-chromite, pyroxene, or plagioclase-rich layers.
Read More About Loveringite / Source
Ludlamite

Ludlamite is a rare phosphate mineral with chemical formula (Fe,Mn,Mg)3(PO4)2·4H2O. It was first described in 1877 for an occurrence in Wheal Jane mine in Cornwall, England and named for English mineralogist Henry Ludlam (1824–1880).
Read More About Ludlamite / Source
Ludwigite

Ludwigite is a magnesium-iron borate mineral: Mg2FeBO5.
Ludwigite typically occurs in magnesian iron skarn and other high temperature contact metamorphic deposits. It occurs in association with magnetite, forsterite, clinohumite and the borates vonsenite and szaibelyite. It forms a solid solution series with the iron(II)-iron(III) borate mineral vonsenite.It was first described in 1874 for an occurrence in Ocna de Fier, Banat Mountains, Caraș-Severin County, Romania and named for Ernst Ludwig (1842–1915), an Austrian chemist at the University of Vienna.
Read More About Ludwigite / Source
Lulzacite

Lulzacite is a strontium-containing phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Sr2Fe2+(Fe2+,Mg)2Al4(PO4)4(OH)10.The mineral was first described in 2000 from quartzite deposits (47°42′50″N 1°29′20″W) at Saint-Aubin-des-Châteaux, Loire-Atlantique, France, and is named after Y. Lulzac, a French geologist who discovered the mineral. In this deposit, lulzacite occurs within quartz and siderite veinlets at quartzite–limestone contacts. Other minerals found in the veinlets include apatite, goyazite, and pyrite.Lulzacite crystallizes in the triclinic system with P1 space group. It is isostructural with jamesite (Pb2Zn(Fe2+,Zn)2Fe3+4(AsO4)4(OH)10).
Read More About Lulzacite / Source
Lyonsite
Lyonsite (Cu3Fe+34(VO4)6) is a rare black vanadate mineral that is opaque with a metallic lustre. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. Lyonsite often occurs as small tabular typically well formed crystals. Lyonsite has a good cleavage and a dark gray streak.
Lyonsite occurs as a sublimate in volcanic fumaroles. It is often associated with howardevansite and thenardite. It was first described in 1987 for an occurrence on the Izalco volcano, El Salvador. It was named for mineralogist John Bartholomew Lyons (1916–1998) of Dartmouth College. It has also been reported from a mine dump in the Lichtenberg Absetzer Mine of Thuringia, Germany.
Read More About Lyonsite / Source
Macdonaldite

Macdonaldite is a rare barium silicate mineral with a chemical formula of BaCa4Si16O36(OH)2·10H2O. Macdonaldite was first described in 1965 and named for Gordon A. Macdonald (1911–1978) an American volcanologist at the University of Hawaii.Macdonaldite crystallises in the orthorhombic system. Macdonaldite is anisotropic with low relief.Macdonaldite appears as veins and fracture coatings in a sanbornite and quartz bearing metamorphic rock. Macdonaldite was first described in 1965 for an occurrence near the Big Creek-Rush Creek area in Fresno County, California. It has also been reported from Mariposa and Tulare counties in California. It has also been reported from a quarry in San Venanzo, Umbria, Italy.
Read More About Macdonaldite / Source
Mackinawite

Mackinawite is an iron nickel sulfide mineral with the chemical formula (Fe,Ni)1+xS (where x = 0 to 0.11). The mineral crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system and has been described as a distorted, close packed, cubic array of S atoms with some of the gaps filled with Fe. Mackinawite occurs as opaque bronze to grey-white tabular crystals and anhedral masses. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a specific gravity of 4.17. It was first described in 1962 for an occurrence in the Mackinaw mine, Snohomish County, Washington for which it was named.
Read More About Mackinawite / Source
Madocite
Madocite is a mineral with a chemical formula of Pb17(Sb,As)16S41. Madocite was named for the locality of discovery, Madoc, Ontario, Canada. It is found in the marbles of the Precambrian Grenville Limestone. It is orthorhombic (rectangular prism with a rectangular base) and in the point group mm2. Its crystals are elongated and striated along [001] to a size of 1.5 mm.
Madocite is anisotropic and classified as having high relief. It also displays strong pleochroism.Madocite is found in small clusters in marble pits (near Madoc, Ontario), and was originally categorized in the 1920s as an unidentified sulfosalt mineral in an assemblage of pyrite, sphalerite, and jamesonite in marble. Later research was done by John L. Jambor in the 1960s who went to the site and collected samples of the assemblages.
Read More About Madocite / Source
Magadiite

Magadiite is a hydrous sodium silicate mineral (NaSi7O13(OH)3·4(H2O)) which precipitates from alkali brines as an evaporite phase. It forms as soft (Mohs hardness of 2) white powdery monoclinic crystal masses. The mineral is unstable and decomposes during diagenesis leaving a distinctive variety of chert (Magadi-type chert).The mineral was first described by Hans P. Eugster in 1967 for an occurrence in Lake Magadi, Kenya, and is also found at Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. It is also reported from alkalic intrusive syenites as in Mont Saint-Hilaire, Canada.
Read More About Magadiite / Source
Maghemite

Maghemite (Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3) is a member of the family of iron oxides. It has the same spinel ferrite structure as magnetite and is also ferrimagnetic. It is sometimes spelled as “maghaemite”.
Maghemite can be considered as an Fe(II)-deficient magnetite with formula
(
Fe
8
III
)
A
[
Fe
40
3
III
◻
8
3
]
B
O
32
{displaystyle left({ce {Fe^{III}8}}right)_{A}left[{ce {Fe_{40/3}^{III}square _{8/3}}}right]_{B}{ce {O32}}}
where
◻
{displaystyle square }
represents a vacancy, A indicates tetrahedral and B octahedral positioning.
Read More About Maghemite / Source
Magnesioferrite

Magnesioferrite is a magnesium iron oxide mineral, a member of the magnetite series of spinels.
Magnesioferrite crystallizes as black metallic octahedral crystals. It is named after its chemical composition of magnesium and ferric iron.
The density is 4.6 – 4.7 (average = 4.65), and the diaphaniety is opaque. Occurs as well-formed fine sized crystals or massive and granular.
Its hardness is 6-6.5. It has a metallic luster and a dark red streak.
Read More About Magnesioferrite / Source
Magnesiohastingsite

Magnesiohastingsite is a calcium-containing amphibole and a member of the hornblende group. It is an inosilicate (chain silicate) with the formula NaCa2(Mg4Fe3+)(Si6Al2)O22(OH)2 and molar mass 864.69 g. In synthetic magnesiohastingsite it appears that iron occurs both as ferrous iron Fe2+ and as ferric iron Fe3+, but the ideal formula features only ferric iron. It was named in 1928 by Marland P. Billings. The name is for its relationship to hastingsite and its magnesium content. Hastingsite was named for the locality in Dungannon Township, Hastings County, Ontario, Canada.Calcic (containing calcium) amphiboles include:
The tremolite – actinolite – ferro-actinolite series
The hornblende group
The kaersutite – ferro-kaersutite series
JoesmithiteThe hornblende group includes:
The edenite – ferro-edenite series
The tschermakite – ferrotschermakite series
The pargasite – ferro-pargasite series
The magnesiohastingsite – hastingsite series
The magnesiosadanagaite – sadanagaite series
Read More About Magnesiohastingsite / Source
Magnesiopascoite
Magnesiopascoite is a bright orange mineral with formula Ca2Mg(V10O28)·16H2O. It was discovered in the U.S. state of Utah and formally described in 2008. The mineral’s name derives from its status as the magnesium analogue of pascoite.
Read More About Magnesiopascoite / Source
Magnesite

Magnesite is a mineral with the chemical formula MgCO3 (magnesium carbonate). Iron, manganese, cobalt, and nickel may occur as admixtures, but only in small amounts.
Read More About Magnesite / Source
Magnetite

Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With the exception of extremely rare native iron deposits, it is the most magnetic of all the naturally occurring minerals on Earth. Naturally magnetized pieces of magnetite, called lodestone, will attract small pieces of iron, which is how ancient peoples first discovered the property of magnetism.Magnetite is black or brownish-black with a metallic luster, has a Mohs hardness of 5–6 and leaves a black streak. Small grains of magnetite are very common in igneous and metamorphic rocks.The chemical IUPAC name is iron(II,III) oxide and the common chemical name is ferrous-ferric oxide.
Read More About Magnetite / Source
Majorite
Majorite is a type of garnet mineral found in the mantle of the Earth. Its chemical formula is Mg3(MgSi)(SiO4)3. It is distinguished from other garnets in having Si in octahedral as well as tetrahedral coordination. Majorite was first described in 1970 from the Coorara Meteorite of Western Australia and has been reported from various other meteorites in which majorite is thought to result from an extraterrestrial high pressure shock event. Mantle derived xenoliths containing majorite have been reported from potassic ultramafic magmas on Malaita Island on the Ontong Java Plateau Southwest Pacific.
Read More About Majorite / Source
Malachite

Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the formula Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fractures and deep, underground spaces, where the water table and hydrothermal fluids provide the means for chemical precipitation. Individual crystals are rare, but occur as slender to acicular prisms. Pseudomorphs after more tabular or blocky azurite crystals also occur.
Read More About Malachite / Source
Malayaite

Malayaite is a calcium tin silicate mineral with formula CaSnOSiO4. It is a member of the titanite group.
Read More About Malayaite / Source
Manganite

Manganite is a mineral composed of manganese oxide-hydroxide, MnO(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic system (pseudo-orthorhombic). Crystals of manganite are prismatic and deeply striated parallel to their length; they are often grouped together in bundles. The color is dark steel-grey to iron-black, and the luster brilliant and submetallic. The streak is dark reddish brown. The hardness is 4, and the specific gravity is 4.3. There is a perfect cleavage parallel to the brachypinacoid, and less-perfect cleavage parallel to the prism faces. Twinned crystals are not infrequent.
The mineral contains 89.7% manganese sesquioxide; it dissolves in hydrochloric acid with evolution of chlorine.
Read More About Manganite / Source
Manganophyllite
Manganopyhllite is a manganese-rich variety of biotite. It was first discovered in the Harstigen mine in Sweden. The mineral was first described in 1890. The earliest use is from Edward Dana.
Read More About Manganophyllite / Source
Manganosite

Manganosite is a rare mineral composed of manganese(II) oxide MnO. It was first described in 1817 for an occurrence in the Harz Mountains, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It has also been reported from Langban and Nordmark, Sweden and at Franklin Furnace, New Jersey. It also occurs in Japan, Kyrgyzstan and Burkina Faso.It occurs in manganese nodules. It also occurs as alteration of manganese minerals such as rhodocrosite during low oxygen metamorphism and metasomatism.
Read More About Manganosite / Source
Manganvesuvianite

Manganvesuvianite is a rare mineral with formula Ca19Mn3+(Al,Mn3+,Fe3+)10(Mg,Mn2+)2(Si2O7)4(SiO4)10O(OH)9. The mineral is red to nearly black in color. Discovered in South Africa and described in 2002, it was so named for the prevalence of manganese in its composition and its relation to vesuvianite.
Read More About Manganvesuvianite / Source
Mansfieldite

Mansfieldite is an uncommon mineral that was named after an american geologist, George Rogers Mansfield. It has been considered a valid specie since 1948. It’s a member of the variscite group. Mansfieldite creates a series with scorodite, and it is the aluminium analogue of said gem. Mansfieldite is colorless in transmitted light. It is mostly made out of oxygen (47.54%). Other components include arsenic (37.1%), aluminium (13.36%) and hydrogen (2%). Mansfieldite crystals form due to hydrothermal origin in altered and mineralized andesitic pyroclastic rocks. Due to its size, mansfieldite is hard to see even under a microscope. The pink variation of the mineral is due to cobalt impurities, otherwise it is white to light gray. It can be found in the USA, Mexico, France, Algeria, England, Australia, Germany, Algeria and Kazakhstan.
Read More About Mansfieldite / Source
Marcasite

The mineral marcasite, sometimes called “white iron pyrite”, is iron sulfide (FeS2) with orthorhombic crystal structure. It is physically and crystallographically distinct from pyrite, which is iron sulfide with cubic crystal structure. Both structures do have in common that they contain the disulfide S22− ion, having a short bonding distance between the sulfur atoms. The structures differ in how these di-anions are arranged around the Fe2+ cations. Marcasite is lighter and more brittle than pyrite. Specimens of marcasite often crumble and break up due to the unstable crystal structure.
On fresh surfaces, it is pale yellow to almost white and has a bright metallic luster. It tarnishes to a yellowish or brownish color and gives a black streak. It is a brittle material that cannot be scratched with a knife. The thin, flat, tabular crystals, when joined in groups, are called “cockscombs”.
In marcasite jewellery, pyrite used as a gemstone is called “marcasite” – that is, marcasite jewellery is made from pyrite, not from the mineral marcasite. Marcasite in the scientific sense is not used as a gem due to its brittleness. In the late medieval and early modern eras, the word “marcasite” meant all iron sulfides in general, including both pyrite and the mineral marcasite. The narrower, modern scientific definition for marcasite as orthorhombic iron sulfide dates from 1845. The jewelers’ sense for the word “marcasite” pre-dates this 1845 scientific redefinition.
Read More About Marcasite / Source
Margaritasite
Margaritasite is a yellow, caesium-bearing mineral in the carnotite group. Its chemical formula is (Cs, K, H3O)2(UO2)2V2O8·H2O and its crystal system is monoclinic (space group P21/a).
Read More About Margaritasite / Source
Margarite

Margarite is a calcium rich member of the mica group of the phyllosilicates with formula: CaAl2(Al2Si2)O10(OH)2. It forms white to pinkish or yellowish gray masses or thin laminae. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It typically has a specific gravity of around 3 and a Mohs hardness of 4. It is translucent with perfect 010 cleavage and exhibits crystal twinning.
It occurs commonly as an alteration product of corundum, andalusite and other aluminous minerals. It has been reported as forming alteration pseudomorphs of chiastolite along with muscovite and paragonite. The margarite in this occurrence forms preferentially along the dark graphite rich inclusions with the chiastolite crystals.
Margarite is found in the emery deposits of Turkey and the Aegean islands, and with corundum
at several localities in the United States.
Read More About Margarite / Source
Marialite

Marialite is a silicate mineral with a chemical formula of Na4Al3Si9O24Cl if a pure endmember or Na4(AlSi3O8)3(Cl2,CO3,SO4) with increasing meionite content. Marialite is a member of the scapolite group and a solid solution exists between marialite and meionite, the calcium endmember. It is a rare mineral usually used as a collector’s stone.
Read More About Marialite / Source
Maricite

Maricite or marićite is a sodium iron phosphate mineral (NaFe2+PO4), that has two metal cations connected to a phosphate tetrahedron. It is structurally similar to the much more common mineral olivine. Maricite is brittle, usually colorless to gray, and has been found in nodules within shale beds often containing other minerals.
Maricite is most commonly known to be found in the Big Fish River area of the Yukon Territory, Canada, but it has also been found in Eastern Germany, as well as inside of various meteorites around the world. Maricite is named after Luka Maric (1899–1979) of Croatia, the longtime head of the mineralogy and petrography departments at the University of Zagreb.
Maricite is a sodium iron phosphate from the extremely diverse phosphate mineral group. In 1977 maricite was discovered in the Big Fish River area, Yukon Territory, Canada (Fleischer, Chao, and Mandarino, 1979). This is an important geologic location that has provided the discovery of several new phosphate minerals. Maricite is recognized for its possible use in sodium ion battery research as well as its role as a reaction product inside of fossil-fired electrical power generating station boilers which experience corrosion (Bridson, et al., 1997; Ong, et al., 2011).
Read More About Maricite / Source
Marrite

Marrite (mar’-ite) is a mineral with the chemical formula PbAgAsS3. It is the arsenic equivalent of freieslebenite (PbAgSbS3), but also displays close polyhedral characteristics with sicherite and diaphorite. Marrite was named in honor of geologist John Edward Marr (1857–1933) of Cambridge, England.
Read More About Marrite / Source
Marthozite

Marthozite is an orthorhombic mineral that has a general formula of Cu(UO2)3(SeO3)3(OH)2·7H2O. It was named after Belgian mineralogist Aimé Marthoz (1894-1962), former Director-general of the Union Minière du Haut Katanga – UMHK.It is usually found in cavities in selenian (selenium-containing) digenite. It is specifically found in the zones of oxidation of the Musonoi deposit in Katanga, Africa.Marthozite is orthorhombic, meaning that it has three axes of unequal lengths all orthogonal to each other. Since it is orthorhombic, marthozite is biaxial, meaning that it has three different indices of refraction. Marthozite is anisotropic, which means that it breaks light into one fast ray and one slow ray. Marthozite shows pleochroism from yellowish brown to greenish yellow.
Read More About Marthozite / Source
Mascagnite

Mascagnite is a rare ammonium sulfate mineral (NH4)2SO4. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system typically forming as stalactitic masses exhibiting good cleavage. It is soft (not higher than 2.5 on the Mohs Scale) and water-soluble. Optical properties are variable; the purest form is transparent and colorless, but opaque gray or yellow deposits are also known.
It occurs in fumaroles, as at Mount Vesuvius and associated with coal seam fires. It was named for Italian anatomist Paolo Mascagni (1752–1815) who first described the mineral.
Read More About Mascagnite / Source
Massicot

Massicot is lead (II) oxide mineral with an orthorhombic lattice structure.
Lead(II) oxide (formula: PbO) can occur in one of two lattice formats, orthorhombic and tetragonal. The red tetragonal form is called litharge. PbO can be changed from massicot to litharge (or vice versa) by controlled heating and cooling. At room temperature massicot forms soft (Mohs hardness of 2) yellow to reddish-yellow, earthy, scaley masses which are very dense, with a specific gravity of 9.64. Massicot can be found as a natural mineral, though it is only found in minor quantities. In bygone centuries it was mined. Nowadays massicot arises during industrial processing of lead and lead oxides, especially in the glass industry, which is the biggest user of PbO.
The definition of massicot as orthorhombic PbO dates from the 1840s, but the substance massicot and the name massicot has been in use since the late medieval era. There is some evidence that the ancient Romans used the substance.It may occur as an oxidation product of other lead-bearing minerals such as galena, bournonite, boulangerite, either naturally or in industrial processing. When massicot is found in a natural environment, some other minerals that may be found with it may include cerussite, litharge, minium, wulfenite, valentinite and limonite.
Read More About Massicot / Source
Masuyite

Masuyite is a uranium/lead oxide mineral with formula Pb[(UO2)3O3(OH)2]·3H2O.Masuyite was first described in 1947 for an occurrence in Katanga and named to honor Belgian geologist Gustave Masuy (1905–1945).
Read More About Masuyite / Source
Mathesiusite

Mathesiusite is a sulfate mineral containing potassium, vanadium, and uranium and has the chemical formula: K5(UO2)4(SO4)4(VO5)·4(H2O). It is a secondary mineral formed during post-mining processes.
It was discovered in the Jáchymov mining district, Czech Republic and named in 2013 after Johannes Mathesius (1504–1565), who studied minerals from the area (known then as Joachimsthal, Bohemia).
Read More About Mathesiusite / Source
Matlockite

Matlockite is a rare lead halide mineral, named after the town of Matlock in Derbyshire, England, where it was first discovered in a nearby mine. Matlockite (chemical formula: PbFCl) gives its name to the matlockite group which consists of rare minerals of a similar structure.
Read More About Matlockite / Source
Maucherite

Maucherite is a grey to reddish silver white nickel arsenide mineral. It crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system. It occurs in hydrothermal veins alongside other nickel arsenide and sulfide minerals. It is metallic and opaque with a hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 7.83. It is also known as placodine and Temiskamite. The unit cell is of symmetry group P41212 or P43212.
It has the chemical formula: Ni11As8 and commonly contains copper, iron, cobalt, antimony, and sulfur as impurities.
It was discovered in 1913 in Eisleben, Germany and was named after Wilhelm Maucher (1879–1930), a German mineral collector.
Read More About Maucherite / Source
Mawsonite
Mawsonite is a brownish orange sulfosalt mineral, containing copper, iron, tin, and sulfur: Cu6Fe2SnS8.
Read More About Mawsonite / Source
Mckelveyite-(Y)

Mckelveyite-(Y) is a hydrated sodium, barium, yttrium, and uranium–containing carbonate mineral, with the chemical formula Ba3Na(Ca,U)Y(CO3)6·3H2O.
Read More About Mckelveyite-(Y) / Source
Meionite

Meionite is a tectosilicate belonging to the scapolite group with the formula Ca4Al6Si6O24CO3. Some samples may also contain a sulfate group. It was first discovered in 1801 on Mt Somma, Vesuvius, Italy. It was named by Rene Just Haüy after μειωυ, the Greek word for less, in reference to the less acute pyramidal form as compared to Vesuvianite.
As an end-member of the scapolite solid solution, meionite has the largest cell dimension and very high thermal stability at high pressures. This indicates that meionite is one of the primary minerals in deep seated basic or intermediate magmatic processes. Meionite also breaks down to grossularite + kyanite + quartz + calcite at high pressure, similar to the upper pressure limits of anorthite . This sets its occurrence to the crustal rocks.
Read More About Meionite / Source
Melanophlogite

Melanophlogite (MEP) is a rare silicate mineral and a polymorph of silica (SiO2). It has a zeolite-like porous structure which results in relatively low and not well-defined values of its density and refractive index. Melanophlogite often overgrows crystals of sulfur or calcite and typically contains a few percent of organic and sulfur compounds. Darkening of organics in melanophlogite upon heating is a possible origin of its name, which comes from the Greek for “black” and “to be burned”.
Read More About Melanophlogite / Source
Melanterite

Melanterite is a mineral form of hydrous iron(II) sulfate: FeSO4·7H2O. It is the iron analogue of the copper sulfate chalcanthite. It alters to siderotil by loss of water. It is a secondary sulfate mineral which forms from the oxidation of primary sulfide minerals such as pyrite and marcasite in the near-surface environment. It often occurs as a post mine encrustation on old underground mine surfaces. It also occurs in coal and lignite seams exposed to humid air and as a rare sublimate phase around volcanic fumaroles. Associated minerals include pisanite, chalcanthite, epsomite, pickeringite, halotrichite and other sulfate minerals.It was first described in 1850.
Read More About Melanterite / Source
Melilite

Melilite refers to a mineral of the melilite group. Minerals of the group are solid solutions of several endmembers, the most important of which are gehlenite and åkermanite. A generalized formula for common melilite is (Ca,Na)2(Al,Mg,Fe2+)[(Al,Si)SiO7]. Discovered in 1793 near Rome, it has a yellowish, greenish-brown color. The name derives from the Greek words meli (μέλι) “honey” and lithos (λίθους) “stone”.The name refers to a group of minerals (melilite group) with chemically similar composition, nearly always minerals in åkermanite-gehlenite series.Minerals of the melilite group are sorosilicates. They have the same basic structure, of general formula A2B(T2O7). The melilite structure consist of pairs of fused TO4, where T may be Si, Al, B, in bow-tie form. Sharing one corner, the formula of the pair is T2O7. These bow-ties are linked together into sheets by the B cations. The sheets are held together by the A cations, most commonly calcium and sodium. Aluminium may sit on either the T or the B site.
Minerals with the melilite structure may show a cleavage parallel to the (001) crystallographic directions and may show weaker cleavage perpendicular to this, in the {110} directions. Melilite is tetragonal.
The important endmembers of common melilite are åkermanite Ca2Mg(Si2O7) and gehlenite Ca2Al[AlSiO7]. Many melilites also contain appreciable iron and sodium.
Some other compositions with the melilite structure include: alumoåkermanite (Ca,Na)2(Al,Mg,Fe2+)(Si2O7), okayamalite Ca2B[BSiO7], gugiaite Ca2Be[Si2O7], hardystonite Ca2Zn[Si2O7], barylite BaBe2[Si2O7],
andremeyerite BaFe2+2[Si2O7]. Some structures formed by replacing one oxygen by F or OH: leucophanite (Ca,Na)2(Be,Al)[Si2O6(F,OH)], jeffreyite (Ca,Na)2(Be,Al)[Si2O6(O,OH)], and meliphanite (Ca,Na)2(Be,Al)[Si2O6(OH,F)].
New members of this mineral group were artificially grown and became intensively studied due to their multiferroic property, i.e., they simultaneously show ferroelectric and magnetic ordering at low temperatures. This gives rise to peculiar optical properties, for example Ba2Co(Ge2O7) shows giant directional dichroism (different absorption for counter-propagating light beams) and hosts magnetically switchable chirality.
Read More About Melilite / Source
Mellite

Mellite, also called honeystone, is an unusual mineral being also an organic chemical. It is chemically identified as an aluminium salt of mellitic acid, and specifically as aluminium benzenehexacarboxylate hexadecahydrate, with the chemical formula Al2C6(COO)6·16H2O.It is a translucent honey-coloured crystal which can be polished and faceted to form striking gemstones. It crystallizes in the tetragonal system and occurs both in good crystals and as formless masses. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 2 to 2.5 and has a low specific gravity of 1.6.It was discovered originally in 1789 at Artern in Thuringia, Germany. It has subsequently also been found in Russia, Austria, the Czech Republic, and Hungary. It was named from the Greek μέλι meli “honey”, in allusion to its color.It is found associated with lignite and is assumed to be formed from plant material with aluminium derived from clay.
Read More About Mellite / Source
Melonite

Melonite is a telluride of nickel; it is a metallic mineral. Its chemical formula is NiTe2. It is opaque and white to reddish-white in color, oxidizing in air to a brown tarnish.
It was first described from the Melones and Stanislaus mine in Calaveras County, California in 1866, by Frederick Augustus Genth.
Melonite occurs as trigonal crystals, which cleave in a (0001) direction. It has a specific gravity of 7.72 and a hardness of 1–1.5 (very soft).
Read More About Melonite / Source
Mendipite

Mendipite is a rare mineral that was named in 1939 for the locality where it is found, the Mendip Hills in Somerset, England. It is an oxyhalide of lead with formula Pb3Cl2O2.
Read More About Mendipite / Source
Mendozite

Mendozite is a sulfate mineral, one of the alum series, with formula NaAl(SO4)2·11H2O. It is a hydrated form of sodium aluminium sulfate (soda alum).
It was discovered in western Argentina in 1868, probably near San Juan. The exact location has been lost, but was described as “San Juan, near Mendoza”, and it is the latter city that give the mineral its name. It occurs in evaporites, presumably from the oxidation of sulfide minerals in the presence of clays. It is very soluble in water, and so can only be found in dry regions: however, in can still effloresce (lose water of crystallisation) in extremely arid climates, altering to tamarugite (the hexahydrate).
Read More About Mendozite / Source
Meneghinite

Meneghinite is a sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula CuPb13 Sb7S24.In the orthorhombic crystal system, meneghinite has a Mohs hardness of 2+1⁄2, one perfect cleavage and a conchoidal fracture. It is a blackish lead-grey in colour and gives a black shining streak. Its lustre is metallic.Discovered in the Italian Province of Lucca in 1852, it is named after Giuseppe Meneghini (1811–1889) of the University of Pisa, who first observed the species. The Bottino Mine in Lucca is the type locality.
Read More About Meneghinite / Source
Mereheadite
Mereheadite is a rare oxychloride that can be found with Mendipite at Merehead quarry, Cranmore, Somerset, in the United Kingdom.
Most specimens are associated with calcite, mendipite or hydrous cerussite in the Manganese pods on vein two at torr works quarry (merehead quarry).
This mineral is associated with symesite which is also light yellow to orange. Symesite is found in small blotches on the calcites or mendipites; Mereheadite does not, as it is most often found in veins.
Read More About Mereheadite / Source
Merenskyite
Merenskyite is a rare telluride / bismuthinide mineral with the chemical formula (Pd,Pt)(Te,Bi)2. It is an opaque white to light gray metallic mineral that occurs as inclusions within other minerals such as chalcopyrite. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system.Merenskyite was first described in 1966 for an occurrence in the Merensky Reef of the Western Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa, and named for South African geologist Hans Merensky (1871–1952).
Read More About Merenskyite / Source
Meridianiite

Meridianiite is the mineral consisting of magnesium sulfate undecahydrate, MgSO4·11H2O. It is colorless transparent crystalline salt that precipitates from solutions saturated in Mg2+ and SO42− ions at temperatures less than 2 °C. The synthetic compound was formerly known as Fritzsche’s salt.Meridianiite is a naturally occurring mineral species found on Earth in a variety of environments including sea ice, crusts and efflorescences in coal/metal mines, cave systems, oxidized zones of sulfide deposits, salt lakes/playas and Antarctic ice-cores. It is commonly associated with other evaporite minerals such as epsomite, mirabilite, halides, and other sodium-magnesium-sulfates. There is some evidence that it was once present on the surface of Mars, and may occur in several bodies of the Solar System. As of 2012, it was the only undecahydrate sulfate known.
Read More About Meridianiite / Source
Merrillite
Merrillite is a calcium phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Ca9NaMg(PO4)7. It is an anhydrous, sodium-rich member of the merrillite group of minerals.
Read More About Merrillite / Source
Mesolite

Mesolite is a tectosilicate mineral with formula Na2Ca2(Al2Si3O10)3·8H2O. It is a member of the zeolite group and is closely related to natrolite which it also resembles in appearance.
Mesolite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and typically forms fibrous, acicular prismatic crystals or masses. Radiating sprays of needlelike crystals are not uncommon. It is vitreous in luster and clear to white in color. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 to 5.5 and a low specific gravity of 2.2 to 2.4. The refractive indices are nα=1.505 nβ=1.505 nγ=1.506.
Read More About Mesolite / Source
Messelite

Messelite is a mineral with formula Ca2(Fe2+,Mn2+)(PO4)2·2H2O. It was discovered in Germany and described in 1890. The mineral was subsequently discredited in 1940, reinstated and named neomesselite in 1955, and the name restored to messelite in 1959.
Read More About Messelite / Source
Metacinnabar

Metacinnabar is the cubic form of mercury sulfide (HgS). It is the high temperature form and trimorphous with cinnabar (trigonal structure) and the higher temperature hypercinnabar (hexagonal structure). It occurs with cinnabar in mercury deposits and is associated with native mercury, wurtzite, stibnite, marcasite, realgar, calcite, barite,
chalcedony and hydrocarbons.It was first described in 1870 for an occurrence in the Redington mine, Knoxville, Napa County, California.
Read More About Metacinnabar / Source
Metatorbernite

Metatorbernite (or meta-torbernite) is a radioactive phosphate mineral, and is a dehydration pseudomorph of torbernite. Chemically, it is a copper uranyl phosphate and usually occurs in the form of green platy deposits. It can form by direct deposition from a supersaturated solution, which produces true crystalline metatorbernite, with a dark green colour, translucent diaphaneity, and vitreous lustre. However, more commonly, it is formed by the dehydration of torbernite, which causes internal stress and breakage within the crystal lattice, resulting in crystals composed of microscopic powder held together using electrostatic force, and having a lighter green colour, opaque diaphaneity, and a relatively dull lustre. As with torbernite, it is named after the Swedish chemist Torbern Bergman. It is especially closely associated with torbernite, but is also found amongside autunite, meta-autunite and uraninite.
Read More About Metatorbernite / Source
Metazeunerite

Metazeunerite is an arsenate mineral with a chemical formula of Cu(UO2)2(AsO4)2·8H2O. The origin of this mineral is almost always from the natural dehydration process of zeunerite.Named for civil engineer Gustav A. Zeuner who worked at the School of Mines in Freiberg and its lowered hydration state.
Read More About Metazeunerite / Source
Meyerhofferite

Meyerhofferite is a hydrated borate mineral of calcium, with the chemical formula Ca2B6O6(OH)10·2H2O, CaB3O3(OH)5·H2O or Ca2(H3B3O7)2·4H2O. It occurs principally as an alteration product of inyoite, another borate mineral.
Natural meyerhofferite was discovered in 1914 in Death Valley, California It is named for German chemist Wilhelm Meyerhoffer (1864–1906), collaborator with J. H. van’t Hoff on the composition and origin of saline minerals, who first synthesized the compound.
Read More About Meyerhofferite / Source
Miargyrite

Miargyrite is a mineral, a sulfide of silver and antimony with the formula AgSbS2. It is a dimorph of cuboargyrite. Originally discovered in the Freiberg district of Germany in 1824, it has subsequently been found in many places where silver is mined. It usually occurs in low temperature hydrothermal deposits. and forms black metallic crystals which may show a dark red internal reflection. The streak is also red.
Miargyrite is named from the Greek meyon, “smaller” and argyros, “silver,” as its silver content is lower than most silver sulfides.
Read More About Miargyrite / Source
Mica

Micas ( MY-kəz) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and “books” (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites.Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing and shingles, as well as in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add “shimmer” or “frost.”
Microcline

Microcline (KAlSi3O8) is an important igneous rock-forming tectosilicate mineral. It is a potassium-rich alkali feldspar. Microcline typically contains minor amounts of sodium. It is common in granite and pegmatites. Microcline forms during slow cooling of orthoclase; it is more stable at lower temperatures than orthoclase. Sanidine is a polymorph of alkali feldspar stable at yet higher temperature. Microcline may be clear, white, pale-yellow, brick-red, or green; it is generally characterized by cross-hatch twinning that forms as a result of the transformation of monoclinic orthoclase into triclinic microcline.
The chemical compound name is potassium aluminium silicate, and it is known as E number reference E555.
Read More About Microcline / Source
Microlite

Microlite was once known as a pale-yellow, reddish-brown, or black isometric mineral composed of sodium calcium tantalum oxide with a small amount of fluorine. Its chemical formula is(Na,Ca)2Ta2O6(O,OH,F). Today it is a name of a group of oxide minerals of a similar stoichiometry having tantalum prevailing over titanium and niobium. The microlite group belongs to a large pyrochlore supergroup that occurs in pegmatites and constitutes an ore of tantalum. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 and a variable specific gravity of 4.2 to 6.4. It occurs as disseminated microscopic subtranslucent to opaque octahedral crystals with a refractive index of 2.0 to 2.2. Microlite is also called djalmaite, but both names are now obsolete.
“Microlite” occurs as a primary mineral in lithium-bearing granite pegmatites, and in miarolitic cavities in granites. Association minerals include: albite, lepidolite, topaz, beryl, tourmaline, spessartine, tantalite and fluorite.
“Microlite” was first described in 1835 for an occurrence on the Island of Uto, State of Stockholm, Sweden. Another occurrence of microlite is the Clark Ledges pegmatite, Chesterfield, Hampshire County, Massachusetts. The name is from Greek mikros for “small” and lithos for “stone.”
Read More About Microlite / Source
Miguelromeroite

Miguelromeroite is a mineral named for Miguel Romero Sanchez by Anthony Robert Kampf. The mineral, first described in 2008 was named in 2009, the same year it got approved by the International Mineralogical Association.
Read More About Miguelromeroite / Source
Millerite

Millerite is a nickel sulfide mineral, NiS. It is brassy in colour and has an acicular habit, often forming radiating masses and furry aggregates. It can be distinguished from pentlandite by crystal habit, its duller colour, and general lack of association with pyrite or pyrrhotite.
Read More About Millerite / Source
Millosevichite

Millosevichite is a rare sulfate mineral with the chemical formula Al2(SO4)3. Aluminium is often substituted by iron. It forms finely crystalline and often porous masses.
It was first described in 1913 for an occurrence in Grotta dell’Allume, Porto Levante, Vulcano Island, Lipari, Aeolian Islands, Sicily. It was named for Italian mineralogist Federico Millosevich (1875–1942) of the University of Rome.The mineral is mainly known from burning coal dumps, acting as one of the main minerals forming sulfate crust. It can be also found in volcanic solfatara environments.
It occurs with native sulfur, sal ammoniac, letovicite, alunogen and boussingaultite.
Read More About Millosevichite / Source
Mimetite

Mimetite is a lead arsenate chloride mineral (Pb5(AsO4)3Cl) which forms as a secondary mineral in lead deposits, usually by the oxidation of galena and arsenopyrite. The name derives from the Greek Μιμητής mimetes, meaning “imitator” and refers to mimetite’s resemblance to the mineral pyromorphite. This resemblance is not coincidental, as mimetite forms a mineral series with pyromorphite (Pb5(PO4)3Cl) and with vanadinite (Pb5(VO4)3Cl). Notable occurrences are Mapimi, Durango, Mexico and Tsumeb, Namibia.
Read More About Mimetite / Source
Minium (mineral)

Minium is the naturally occurring form of lead tetroxide, Pb2+2Pb4+O4 also known as red lead. Minium is a light-to-vivid red and may have brown-to-yellow tints. It typically occurs in scaly-to-earthy masses. It crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system.Minium is rare and occurs in lead-mineral deposits that have been subjected to severe oxidizing conditions. It also occurs as a result of mine fires. It is associated with cerussite, galena, litharge, massicot, mimetite, native lead, and wulfenite.It occurs in relatively small amounts throughout the world: Langhecke, Hesse; Badenweiler, Baden-Württemberg; Bleialf, Eifel district; Horhausen (Grube Holzappel), Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany. It occurs at Mies, Slovenia; Leadhills, Lanarkshire, Scotland; Castelberg St. Avold, Moselle, France; from Langban, Varmland, Sweden; Sarrabus, Sardinia, Italy; near Anarak, Iran; and Tsumeb, Namibia. In the US, mines include the Jay Gould mine, Alturas County, Idaho; the Leadville district, Lake County, Colorado; and in the Tonopah-Belmont mine, Maricopa County, Arizona. It also occurs in Eschuchapa and Guerrero, Mexico. Good specimens were produced by a mine fire at the Broken Hill mine in New South Wales, Australia.Minium has been identified as one of the pigments at Angkor Wat in Cambodia. Minium was named for the Iberian river known to the imperial Romans as Minius, now known as the Spanish Miño and the Portuguese Minho. The name was originally applied to certain forms of cinnabar that had been coated with the minium oxide; however, once the red lead contaminant was determined to be chemically distinct from cinnabar crystals, the name, minium, was applied.For properties and uses of minium see lead tetroxide.
Read More About Minium (mineral) / Source
Minnesotaite

Minnesotaite is an iron silicate mineral with formula: (Fe2+,Mg)3Si4O10(OH)2. It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system and occurs as fine needles and platelets with other silicates. It is isostructural with the pyrophyllite-talc mineral group.
Read More About Minnesotaite / Source
Minyulite

Minyulite is a rare phosphate mineral with a chemical formula of KAl2(PO4)2F·4(H2O) (redefinition, IMA21-E).It occurs as groups of radiating fine fibrous crystals within rock cracks of phosphatic ironstone. Minyulite belongs to the orthorhombic crystal system. This indicates that it has three axes of unequal length yet all are perpendicular to each other. Its cell constants are a=9.35, b=9.74 c=5.52.As for its optical properties, Minyulite is an anisotropic mineral which means the velocity of light differs when traveling through it depending on the cut of its cross-section which gives it more than one refractive index. The mineral is optically biaxial. Its birefringence value is 0.007. It has three refractive indices which are nα=1.531 nβ=1.534 nγ=1.538. Refractive indices are a ratio of the speed of light in a median with respect to the speed of light passing through the mineral.
Read More About Minyulite / Source
Mirabilite

Mirabilite, also known as Glauber’s salt, is a hydrous sodium sulfate mineral with the chemical formula Na2SO4·10H2O. It is a vitreous, colorless to white monoclinic mineral that forms as an evaporite from sodium sulfate-bearing brines. It is found around saline springs and along saline playa lakes. Associated minerals include gypsum, halite, thenardite, trona, glauberite, and epsomite.
Mirabilite is unstable and quickly dehydrates in dry air, the prismatic crystals turning into a white powder, thenardite (Na2SO4). In turn, thenardite can also absorb water and converts to mirabilite.
Mirabilite is used as a purgative and anti-inflammatory remedy in the Traditional Chinese medicine; in Mandarin, it is called máng xiāo. The name ‘mirabilite’ is based on the phrase “Sal mirabilis” (Latin for “wonderful salt”) used by Johann Rudolph Glauber when he inadvertently synthesized mirabilite.Mirabilite is found in several areas within the Mammoth Cave system, where it appears to have been mined by Late Archaic and Early Woodland peoples, probably for use as a laxative.
Four mirabilite mounds were documented on the south shore of the Great Salt Lake, Utah, United States, in January 2020. These developed where springs surfaced along the beach, which had been exposed due to lower lake elevations, and cold air helped preserve the salt precipitate. This was documented by the Utah Geological Survey as well as reported in the press.
Read More About Mirabilite / Source
Mixite

Mixite is a rare copper bismuth arsenate mineral with formula: BiCu6(AsO4)3(OH)6·3(H2O). It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system typically occurring as radiating acicular prisms and massive encrustations. The color varies from white to various shades of green and blue. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 3.8. It has an uneven fracture and a brilliant to adamantine luster.
It occurs as a secondary mineral in the oxidized zones of copper deposits. Associated minerals include: bismutite, smaltite, native bismuth, atelestite, erythrite, malachite and barite.It was discovered in 1879 near J´achymov, Czech Republic by mine engineer Anton Mixa. Mixite has also been found in Argentina, Australia, Austria, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Namibia, Poland, Spain, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the United States.Mixite is the namesake member of the mixite mineral group, which has the general chemical formula Cu2+6A(TO4)3(OH)6·3H2O, where A is a REE, Al, Ca, Pb, or Bi, and T is P or As. In addition to mixite, this mineral group contains the isostructural minerals agardite-(Y), agardite-(Ce), agardite-(Nd), agardite-(La), calciopetersite, goudeyite, petersite-(Ce), petersite-(Y), plumboagardite, and zálesíite.
Read More About Mixite / Source
Moganite

Moganite is an oxide mineral with the chemical formula SiO2 (silicon dioxide) that was discovered in 1976. It was initially described as a new form of silica from specimens found in the Barranco de Medio Almud, in the municipality of Mogán on the island of Gran Canaria, in the Canary Islands (Spain), receiving in a later work the name derived from this locality. In 1994 the International Mineralogical Association decided to disapprove it as a valid mineral, since it was considered indistinguishable from quartz. Subsequent studies allowed the IMA to rectify it in 1999, accepting it as a mineral species.
It has the same chemical composition as quartz, but a different crystal structure.This mineral has been mainly found in dry locales such as Gran Canaria and Lake Magadi. It has been reported from a variety of locations in Europe, India and the United States. Physically, it has a Mohs hardness of about 6, a dull luster and appears as a semitransparent gray in color.
Read More About Moganite / Source
Mohite
Mohite is a copper tin sulfide mineral with the chemical formula Cu2SnS3. It is colored greenish gray and leaves a gray streak. It is opaque and has metallic luster. Its crystal system is triclinic pedial. It is rated 4 on the Mohs Scale and has a specific gravity of 4.86.
Read More About Mohite / Source
Mohrite
Mohrite, (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2 · 6 H2O, is a rare ammonium iron(II) sulfate mineral originally found in the geothermal fields of Tuscany, Italy. This Fe-dominant analogue of boussingaultite is sometimes reported from burning coal dumps where it is a product of pyrite oxidation.The mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with space group P21/a.
Read More About Mohrite / Source
Moissanite

Moissanite is naturally occurring silicon carbide and its various crystalline polymorphs. It has the chemical formula SiC and is a rare mineral, discovered by the French chemist Henri Moissan in 1893. Silicon carbide is useful for commercial and industrial applications due to its hardness, optical properties and thermal conductivity.
Read More About Moissanite / Source
Molybdenite

मोलिब्डेनाइट मोलिब्डेनम डाइसल्फ़ाइड, MoS2 का एक खनिज है। ग्रेफाइट की तरह दिखने और महसूस करने में, मोलिब्डेनइट में एक चिकनाई प्रभाव होता है जो इसकी स्तरित संरचना का परिणाम होता है। परमाणु संरचना में मोलिब्डेनम परमाणुओं की एक शीट होती है जो सल्फर परमाणुओं की चादरों के बीच सैंडविच होती है। Mo-S बांड मजबूत हैं, लेकिन अलग-अलग सैंडविच जैसी त्रि-परतों के ऊपर और नीचे सल्फर परमाणुओं के बीच की बातचीत कमजोर है, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप आसान फिसलन के साथ-साथ दरार वाले विमान भी हैं।
मोलिब्डेनाइट हेक्सागोनल क्रिस्टल सिस्टम में सामान्य पॉलीटाइप 2H के रूप में और ट्राइगोनल सिस्टम में 3R पॉलीटाइप के रूप में भी क्रिस्टलीकृत होता है।
Read More About Molybdenite / Source
Molybdite

Molybdite is the naturally occurring mineral form of molybdenum trioxide MoO3. It occurs as yellow to greenish needles and crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system.
Read More About Molybdite / Source
Monazite

Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium-dominant member of the group. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. It has a hardness of 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and is relatively dense, about 4.6 to 5.7 g/cm3. There are five different most common species of monazite, depending on the relative amounts of the rare earth elements in the mineral:
monazite-(Ce), (Ce,La,Nd,Th)PO4 (the most common member),
monazite-(La), (La,Ce,Nd)PO4,
monazite-(Nd), (Nd,La,Ce)PO4,
monazite-(Sm), (Sm,Gd,Ce,Th)PO4,
monazite-(Pr), (Pr,Ce,Nd,Th)PO4.The elements in parentheses are listed in the order of their relative proportion within the mineral: lanthanum is the most common rare-earth element in monazite-(La), and so forth. Silica (SiO2) is present in trace amounts, as well as small amounts of uranium and thorium. Due to the alpha decay of thorium and uranium, monazite contains a significant amount of helium, which can be extracted by heating.The following analyses are of monazite from: (I.) Burke County, North Carolina, US; (II.) Arendal, Norway; (III.) Emmaville, New South Wales, Australia.
Monazite is an important ore for thorium, lanthanum, and cerium. It is often found in placer deposits. India, Madagascar, and South Africa have large deposits of monazite sands. The deposits in India are particularly rich in monazite.
Monazite is radioactive due to the presence of thorium and, less commonly, uranium. The radiogenic decay of uranium and thorium to lead enables monazite to be dated through monazite geochronology. Monazite crystals often have multiple distinct zones that formed through successive geologic events that lead to monazite crystallization. These domains can be dated to gain insight into the geologic history of its host rocks.
The name monazite comes from the Ancient Greek: μονάζειν, romanized: monázein (to be solitary), via German Monazit, in allusion to its isolated crystals.
Read More About Monazite / Source
Monohydrocalcite
Monohydrocalcite is a mineral that is a hydrous form of calcium carbonate, CaCO3·H2O. It was formerly also known by the name hydrocalcite, which is now discredited by the IMA. It is a trigonal mineral which is white when pure. Monohydrocalcite is not a common rock-forming mineral, but is
frequently associated with other calcium and magnesium carbonate minerals, such as calcite, aragonite, lansfordite, and nesquehonite.
Monohydrocalcite has been observed in air conditioning systems, and in moonmilk deposits in caves, both probably formed from spray of carbonate rich fluids.
It is well known in Robe on the Limestone Coast of South Australia as a component of beach sands of Lake Fellmongery and Lake Butler,
where it is believed to be formed from algal spume. Other lacustrine deposits include Lake Issyk-Kul, Kyrgyzstan, Lake Kivu, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Solar Lake, Sinai.
It has been reported as a significant component of the decomposition of ikaite
in the towers of the Ikka Fjord, West Greenland. It is also noted for its bizarre occurrences, which include inside the otoliths of the tiger shark,
the bladder of a guinea pig, the calcareous corpuscles of a cestode parasite, and the final stages of decomposition of the putrefying flesh of the giant saguaro cactus. These occurrences suggest
a biochemical origin is possible.
Read More About Monohydrocalcite / Source
Monticellite

Monticellite and kirschsteinite (commonly also spelled kirschteinite ) are gray silicate minerals of the olivine group with compositions CaMgSiO4 and CaFeSiO4, respectively. Most monticellites have the pure magnesium end-member composition but rare ferroan monticellites and magnesio-kirschsteinite are found with between 30 and 75 mol.% of the iron end member. Pure kirschsteinite is only found in synthetic systems. Monticellite is named after Teodoro Monticelli Italian mineralogist (1759–1845). Kirschsteinite is named after Egon Kirschstein, German geologist.
Like other members of the group monticellite and kirschsteinite have orthorhombic unit cells (space group Pbnm) shown in Figure 1. Iron and magnesium ions are located on the M1 inversion sites and calcium ions occupy the M2 site on mirror planes. The unit cell is somewhat larger than for the calcium free olivines forsterite and fayalite with
a = 0.4815 nm,
b = 1.108 nm and
c = 0.637 nm,and for monticellite
a = 0.4875 nm,
b = 1.1155 nm and
c = 0.6438 nm.
Read More About Monticellite / Source
Montmorillonite

Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite group, is a 2:1 clay, meaning that it has two tetrahedral sheets of silica sandwiching a central octahedral sheet of alumina. The particles are plate-shaped with an average diameter around 1 μm and a thickness of 0.96 nm; magnification of about 25,000 times, using an electron microscope, is required to “see” individual clay particles. Members of this group include, amongst others, saponite, nontronite, beidellite, and hectorite.
Montmorillonite is a subclass of smectite, a 2:1 phyllosilicate mineral characterized as having greater than 50% octahedral charge; its cation exchange capacity is due to isomorphous substitution of Mg for Al in the central alumina plane. The substitution of lower valence cations in such instances leaves the nearby oxygen atoms with a net negative charge that can attract cations. In contrast, beidellite is smectite with greater than 50% tetrahedral charge originating from isomorphous substitution of Al for Si in the silica sheet.
The individual crystals of montmorillonite clay are not tightly bound hence water can intervene, causing the clay to swell, hence montmorillonite is a characteristic component of swelling soil. The water content of montmorillonite is variable and it increases greatly in volume when it absorbs water. Chemically, it is hydrated sodium calcium aluminium magnesium silicate hydroxide (Na,Ca)0.33(Al,Mg)2(Si4O10)(OH)2·nH2O. Potassium, iron, and other cations are common substitutes, and the exact ratio of cations varies with source. It often occurs intermixed with chlorite, muscovite, illite, cookeite, and kaolinite.
Read More About Montmorillonite / Source
Mooihoekite
Mooihoekite is a copper iron sulfide mineral with chemical formula of Cu9Fe9S16. The mineral was discovered in 1972 and received its name from its discovery area, the Mooihoek mine in Transvaal, South Africa.
Read More About Mooihoekite / Source
Moolooite

Moolooite is a rare blue-green mineral with the formula Cu++(C2O4)·n(H2O) (n<1) (copper oxalate hydrate). It was discovered by Richard M Clarke and Ian R Williams in Bunbury Well, Mooloo Downs station, Murchison, Western Australia in 1986. It has an orthorhombic crystalline structure, and is formed by the interaction of bird guano with weathering copper sulfides. It is used in plastics to color them blueish-green.
A second occurrence is reported from the Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines silver mining district of Vosges Mountains, France.
Read More About Moolooite / Source
Mordenite

Mordenite is a zeolite mineral with the chemical formula, (Ca, Na2, K2)Al2Si10O24·7H2O. and it is one of the six most abundant zeolites and is used commercially.It was first described in 1864 by Henry How. He named it after the small community of Morden, Nova Scotia, Canada, along the Bay of Fundy, where it was first found.
Mordenite is orthorhombic (a,b,c unequal & all angles 90 degree). It crystallizes in the form of fibrous aggregates, masses, and vertically striated prismatic crystals. It may be colorless, white, or faintly yellow or pink. It has Mohs hardness of 5 and a density of 2.1 g/cm3. When it forms well developed crystals they are hairlike; very long, thin, and delicate.Mordenite’s molecular structure is a framework containing chains of five-membered rings of linked silicate and aluminate tetrahedra (four oxygen atoms arranged at the points of a triangular pyramid about a central silicon or aluminium atom). Its high ratio of silicon to aluminum atoms makes it more resistant to attack by acids than most other zeolites.Mordenite is one of the most abundant zeolites in altered volcanic deposits; it is found in volcanic rock such as rhyolite, andesite, and basalt. It is associated with other zeolites such as stilbite and heulandite. Good examples have been found in Iceland, India, Italy, Oregon, Washington, and Idaho. It is also found in marine sediments, as in the Ural Mountains and in dikes where water has attacked and altered volcanic glasses, as on the Isle of Arran in Scotland.
Read More About Mordenite / Source
Moschellandsbergite

Moschellandsbergite is a rare isometric mineral made up of a silver-white amalgam of mercury and silver with the chemical makeup Ag2Hg3.
It was first described in 1938 and named after Moschellandsberg Mountain near Obermoschel, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is considered a low-temperature hydrothermal mineral which occurs with metacinnabar, cinnabar, mercurian silver, tetrahedrite–tennantite, pyrite, sphalerite and chalcopyrite.
Read More About Moschellandsbergite / Source
Mosesite
Mosesite is a very rare mineral found in few locations. It is a mercury mineral found as an accessory in deposits of mercury, often in conjunction with limestone. It is known to be found in the U.S. states of Texas and Nevada, and the Mexican states of Guerrero and Querétaro. It was named after Professor Alfred J. Moses (1859–1920) for his contributions to the field of mineralogy in discovering several minerals found alongside mosesite. The mineral itself is various shades of yellow and a high occurrence of spinel twinning. It becomes isotropic when heated to 186 °C (367 °F).
Read More About Mosesite / Source
Mottramite

Mottramite is an orthorhombic anhydrous vanadate hydroxide mineral, PbCu(VO4)(OH), at the copper end of the descloizite subgroup. It was formerly called cuprodescloizite or psittacinite (this mineral characterized in 1868 by Frederick Augustus Genth). Duhamelite is a calcium- and bismuth-bearing variety of mottramite, typically with acicular habit.Mottramite is a member of the adelite-descloizite group.
Mottramite, which is a copper rich member, forms a series with descloizite, which is a zinc rich member. These two minerals usually contain significant percentages of both copper and zinc and are seldom pure. Mottramite also forms a series with duftite.It was discovered in 1876 and named for the locality, Mottram St Andrew, Cheshire, England, where ore was stockpiled, although it was probably mined from Pim Hill Mine, Shrewsbury, Shropshire, England.
Read More About Mottramite / Source
Motukoreaite

Motukoreaite is a mineral with formula Mg6Al3(OH)18[Na(H2O)6](SO4)2·6H2O (possibly more than one species). The mineral is named for Motukorea, the island in New Zealand where it was discovered. Motukoreaite was first noted in 1941 and officially described in 1977.
Read More About Motukoreaite / Source
Mullite

Mullite or porcelainite is a rare silicate mineral formed during contact metamorphism of clay minerals. It can form two stoichiometric forms: 3Al2O32SiO2 or 2Al2O3 SiO2. Unusually, mullite has no charge-balancing cations present. As a result, there are three different aluminium sites: two distorted tetrahedral and one octahedral.
Mullite was first described in 1924 for an occurrence on the Isle of Mull, Scotland. It occurs as argillaceous inclusions in volcanic rocks in the Isle of Mull, inclusions in sillimanite within a tonalite at Val Sissone, Italy and with emerylike rocks in Argyllshire, Scotland.
Read More About Mullite / Source
Mundite

Mundite is a uranium phosphate mineral with chemical formula: Al(UO2)3(PO4)2(OH)3·5(H2O). It contains aluminium and has a yellow tinge to it. It usually appears on sandstones or limestones.
Read More About Mundite / Source
Murdochite

Murdochite is a mineral combining lead and copper oxides with the chemical formula PbCu6O8−x(Cl,Br)2x (x ≤ 0.5).It was first discovered in 1953 in the Mammoth-Saint Anthony Mine in Pinal County, Arizona by Percy W. Porter, a mining engineer who handpicked a 401.5-mg sample. Porter would later submit for analysis and it was then that Fred A. Hildebrand suggested that the sample was a new mineral after taking a powder x-ray picture. It was named for Joseph Murdoch (1890–1973), American mineralogist. Murdochite was first suggested to be of a cubic structure. After this suggestion, the term “murdochite-type structure” began to be used when describing a structure that is similar to that of murdochite. Murdochite was later found to be octahedral.
Read More About Murdochite / Source
Muscovite

Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula KAl2(AlSi3O10)(F,OH)2, or (KF)2(Al2O3)3(SiO2)6(H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavage yielding remarkably thin laminae (sheets) which are often highly elastic. Sheets of muscovite 5 meters × 3 meters (16.5 feet × 10 feet) have been found in Nellore, India.Muscovite has a Mohs hardness of 2–2.25 parallel to the [001] face, 4 perpendicular to the [001] and a specific gravity of 2.76–3. It can be colorless or tinted through grays, browns, greens, yellows, or (rarely) violet or red, and can be transparent or translucent. It is anisotropic and has high birefringence. Its crystal system is monoclinic. The green, chromium-rich variety is called fuchsite; mariposite is also a chromium-rich type of muscovite.
Muscovite is the most common mica, found in granites, pegmatites, gneisses, and schists, and as a contact metamorphic rock or as a secondary mineral resulting from the alteration of topaz, feldspar, kyanite, etc. It is characteristic of peraluminous rock, in which the content of aluminum is relatively high. In pegmatites, it is often found in immense sheets that are commercially valuable. Muscovite is in demand for the manufacture of fireproofing and insulating materials and to some extent as a lubricant.
Read More About Muscovite / Source
Musgravite

Musgravite or magnesiotaaffeite-6N’3S is a rare oxide mineral used as a gemstone. Its type locality is the Ernabella Mission, Musgrave Ranges, South Australia, for which it was named following its discovery in 1967. It is a member of the taaffeite family of minerals, and its chemical formula is Be(Mg, Fe, Zn)2Al6O12. Its hardness is 8 to 8.5 on the Mohs scale. Due to its rarity, the mineral can sell for roughly USD$35,000 per carat.
Read More About Musgravite / Source
Nabalamprophyllite
Nabalamprophyllite has a general formula of Ba(Na,Ba){Na3Ti[Ti2O2Si4O14](OH,F)2}. The name is given for its composition (Naba, meaning sodium, Na and barium, Ba) and relation to other lamprophyllite-group minerals. Lamprophyllite is a rare Ti-bearing silicate mineral usually found in intrusive igneous rocks.Nabalamprophyllite is monoclinic, which means crystallographically, it contains three axes of unequal length and the angles between two of the axes are 90°, and one is less than 90°. It belongs to the space group P2/m. The mineral also has an orthorhombic polytype (nabalamprophyllite-2O). This mineral belongs to the space group Pnmn. In terms of its optical properties, nabalamprophyllite is anisotropic which means the velocity of light varies depending on direction through the mineral. Its calculated relief is 1.86 – 1.87. Its color in plane polarized light is green-brown, and it is weakly pleochroic.
The mineral has only been found in Russia, usually in association with coarse-grained igneous rocks called pegmatites. The type localities are the Inagli alkaline–ultrabasic massif, Yakutia and the Kovdor alkaline–ultrabasic massif in the Kola Peninsula.
Read More About Nabalamprophyllite / Source
Nabesite
Nabesite is a rare silicate mineral of the zeolite group with the chemical formula Na2BeSi4O10·4(H2O). It occurs as colorless to white orthorhombic crystals in thin platy mica like sheets. It has the zeolite structure. Its Mohs hardness is 5 to 6 and its specific gravity is 2.16. The reported refractive index values are nα=1.499, nβ=1.507, and nγ=1.511.
It was discovered in the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex, of southwest Greenland, and first recognized in 2000. It occurs in tugtupite-bearing albitite, a rare highly alkaline igneous rock.
Read More About Nabesite / Source
Nacrite

Nacrite Al2Si2O5(OH)4 is a clay mineral that is polymorphous (or polytypic) with kaolinite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system. X-ray diffraction analysis is required for positive identification.
Nacrite was first described in 1807 for an occurrence in Saxony, Germany. The name is from nacre in reference to the dull luster of the surface of nacrite masses scattering light with slight iridescences resembling those of the mother of pearls secreted by oysters.
Read More About Nacrite / Source
Nadorite

Nadorite is a mineral with the chemical formula PbSbO2Cl. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system and is brown, brownish-yellow or yellow in color, with a white or yellowish-white streak.Nadorite is named after Djebel Nador in Algeria, where it was first identified in 1870.
Read More About Nadorite / Source
Nagyágite

Nagyágite (Pb5Au(Te,Sb)4S(5-8)) is a rare sulfide mineral with known occurrence associated with gold ores. Nagyágite crystals are opaque, monoclinic and dark grey to black coloured.
It was first described in 1845 for an occurrence at the type locality of the Nagyág mine, Săcărâmb, Hunedoara County, Romania.It occurs in gold–tellurium epithermal hydrothermal veins. Minerals associated with nagyágite include: altaite, petzite, stutzite, sylvanite, tellurantimony, coloradoite, krennerite,
native arsenic, native gold, proustite, rhodochrosite, arsenopyrite, sphalerite, tetrahedrite, calaverite, tellurobismuthite, galena and pyrite.
Read More About Nagyágite / Source
Nahcolite

Nahcolite is a soft, colourless or white carbonate mineral with the composition of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) also called thermokalite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system.Nahcolite was first described in 1928 for an occurrence in a lava tunnel at Mount Vesuvius, Italy. Its name refers to the elements which compose it: Na, H, C, and O. It occurs as a hot spring and saline lake precipitate or efflorescence; in differentiated alkalic massifs; in fluid inclusions as a daughter mineral phase and in evaporite deposits.It occurs in association with trona, thermonatrite, thenardite, halite, gaylussite, burkeite, northupite and borax. It has been reported in a Roman conduit at Stufe de Nerone, Campi Flegrei, near Naples; in the U. S. from Searles Lake, San Bernardino County, California; in the Green River Formation, Colorado and Utah; in the Tincalayu deposit, Salar del Hombre Muerto,
Salta Province, Argentina; on Mt. Alluaiv, Lovozero Massif and Khibiny Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia; and around Mount Erebus, Victoria Land, Antarctica.
Read More About Nahcolite / Source
Naldrettite
Naldrettite is a mineral with a chemical formula of Pd2Sb. It is named after Anthony J. Naldrett (born 1933), a professor at the University of Toronto, who has made significant contributions to the International Mineralogical Association (IMA). Naldrettite is a new intermetallic mineral from the Mesamax Northwest deposit, Ungava region, Québec, Canada. Mineralization takes place around the base of basaltic dyke margins. Naldrettite is economically important because of its chemical composition (Pd2Sb). The sample in which the new mineral was discovered had high platinum group elements (PGEs) with palladium enrichment.Naldrettite occurs as anhedral grains that are commonly attached to sulfide minerals and are associated with clinochlore. It belongs to the orthorhombic crystal system and is a part of the pyramidal class. This means that all of the edge lengths (a,b,c) of the unit cell are different in length and intersect at right angles to each other. The mineral is metallic, opaque, appears bright creamy white under plane polarized light, has weak bireflectance, and does not exhibit internal reflections.
Read More About Naldrettite / Source
Nambulite

Nambulite is a lithium bearing manganese silicate mineral with the chemical formula (Li,Na)Mn4Si5O14(OH). It is named after the mineralogist, Matsuo Nambu (born 1917) of Tohoko University, Japan, who is known for his research in manganese minerals. The mineral was first discovered in the Funakozawa Mine of northeastern Japan, a metasedimentary manganese ore.Nambulite is formed from the reaction between a hydrothermal solution and rhodonite, and commonly creates veins in the host rock. Other than a collector’s gem, however, it has little economic value.
It belongs to the triclinic-pinacoidal crystal system (or triclinic-normal), meaning that it has three axes of unequal length (a, b, c), all intersecting at oblique angles with each other (none of the angles are equal to 90°). It belongs to the crystal class 1, meaning that any point on the crystal that is rotated 360° and then completely inverted will meet with an equal (but opposite) point on the crystal (see centrosymmetry). Its space group is P 1.
The three axes (a, b, c) have different indices of refraction, na=1.707, nb=1.710, nc=1.730. The index of refraction (RI) can be defined as n = cair/cmineral, where “n” is the index of refraction and “c” is the speed of light. The maximum birefringence is .023, the difference between the highest (nc=1.730) and lowest (na=1.707) indices of refraction within the mineral.
In a medium with an index of refraction equaling 1.53, Nambulite has a calculated relief of 1.71–1.73, giving it a moderate to high relief. Relief is a measure of the difference between the index of refraction of the mineral and that of the medium (often Canada balsam or other epoxy with an RI of around 1.53–1.54).Nambulite is an anisotropic crystal, where the velocity of light that passes through the crystal varies depending on the crystallographic direction. In contrast, an isotropic crystal includes all isometric crystals, and the velocity of light is equal in all directions. The mineral exhibits slight pleochroism. Pleochroism is an optical property observed when the mineral is viewed under the microscope in plane polarized light, and when it the stage of the microscope is rotated the observed colors change. The color change is due to different wavelengths being absorbed in different directions, and the color of the mineral depends on the crystallographic orientation.
Read More About Nambulite / Source
Narsarsukite

Narsarsukite is a rare silicate mineral with either the chemical formula Na2(Ti,Fe3+)Si4(O,F)11 or Na4(Ti,Fe)4[Si8O20](O,OH,F)4.It was first described in 1900 for an occurrence in the Narsarsuk pegmatite in the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of West Greenland. It has also been reported from a syenite which intruded limestone in the Sweetgrass Hills, Montana, and within hornfels and marble xenoliths in the alkalic intrusive of Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec. It occurs associated with aegirine, microcline, albite, elpidite, epididymite, taeniolite, pectolite, calcite, galena and quartz.
Read More About Narsarsukite / Source
Natrolite

Natrolite is a tectosilicate mineral species belonging to the zeolite group. It is a hydrated sodium and aluminium silicate with the formula Na2Al2Si3O10·2H2O. The type locality is Hohentwiel, Hegau, Germany.It was named natrolite by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in 1803. The name is derived from natron (νατρών), the Greek word for soda, in reference to the sodium content, and lithos (λίθος), meaning stone. Needle stone or needle-zeolite are other informal names, alluding to the common acicular habit of the crystals, which are often very slender and are aggregated in divergent tufts. The crystals are frequently epitaxial overgrowths of natrolite, mesolite, and gonnardite in various orders.
Read More About Natrolite / Source
Natron (mineral)

Natron is a naturally occurring mixture of sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3·10H2O, a kind of soda ash) and around 17% sodium bicarbonate (also called baking soda, NaHCO3) along with small quantities of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate. Natron is white to colourless when pure, varying to gray or yellow with impurities. Natron deposits are sometimes found in saline lake beds which arose in arid environments. Throughout history natron has had many practical applications that continue today in the wide range of modern uses of its constituent mineral components.
In modern mineralogy the term natron has come to mean only the sodium carbonate decahydrate (hydrated soda ash) that makes up most of the historical salt.
Read More About Natron (mineral) / Source
Natrophilite

Natrophilite is a mineral with the chemical formula NaMnPO4. In a pure form it has a yellow coloration. Its crystals are orthorhombic to dipyramidal. It is transparent to translucent. It is not radioactive. Natrophilite is rated 4.5 to 5 on the Mohs Scale.
Read More About Natrophilite / Source
Nekrasovite
See Nekrasov Cossacks for another meaningNekrasovite is a rare copper vanadium sulfosalt mineral with formula Cu26V2(Sn,As,Sb)6S32. It crystallizes in the isometric system and occurs as small grains in ore aggregates. It is a brown opaque metallic mineral with Mohs hardness of 4.5 and a specific gravity of 4.62.
It was first described in 1984 in the Khayragatsch ore deposit of eastern Uzbekistan and named for Russian mineralogist Ivan Yakovlevich Nekrasov (born 1929).
Read More About Nekrasovite / Source
Nelenite

Nelenite is a rare manganese iron phyllosilicate arsenate mineral found in Franklin Furnace, New Jersey.
Its chemical formula is (Mn,Fe)16As3Si12O36(OH)17 or (Mn,Fe)16(Si12O30)(OH)14[As3+3O6(OH)3]
Read More About Nelenite / Source
Nenadkevichite

Nenadkevichite is a rare silicate mineral containing niobium with the chemical formula (Na,Ca)(Nb,Ti)Si2O7·2H2O. It forms brown to yellow to rose colored orthorhombic dipyramidal crystals with a dull to earthy luster. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 2.86.
It was first reported in 1955 from a nepheline syenite pegmatite in the Kola Peninsula. In addition it has been reported from
Mont Saint-Hilaire, Canada; the Ilimaussaq complex, Greenland; Windhoek District, Namibia; and Zheltye Vody, Ukraine. It was named after Konstantin Avtonomovich Nenadkevich (1880–1963), Russian mineralogist and geochemist.
Read More About Nenadkevichite / Source
Nepheline

Nepheline, also called nephelite (from Ancient Greek νεφέλη (nephélē) ‘cloud’), is a rock-forming mineral in the feldspathoid group – a silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate, Na3KAl4Si4O16, that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatites. It is used in glass and ceramic manufacturing and other industries, and has been investigated as an ore of aluminium.
Read More About Nepheline / Source
Népouite

Népouite is a rare nickel silicate mineral which has the apple green colour typical of such compounds. It was named by the French mining engineer Edouard Glasser in 1907 after the place where it was first described (the type locality), the Népoui Mine, Népoui, Poya Commune, North Province, New Caledonia. The ideal formula is Ni3(Si2O5)(OH)4, but most specimens contain some magnesium, and (Ni,Mg)3(Si2O5)(OH)4 is more realistic. There is a similar mineral called lizardite (named after the Lizard Complex in Cornwall, England) in which all of the nickel is replaced by magnesium, formula Mg3(Si2O5)(OH)4. These two minerals form a series; intermediate compositions are possible, with varying proportions of nickel to magnesium.Pecoraite is another rare mineral with the same chemical formula as népouite, but a different structure; such minerals are said to be dimorphs of each other, in the same way as graphite is a dimorph of diamond. Népouite, lizardite and pecoraite are all members of the kaolinite-serpentine group.Garnierite is a green nickel ore that formed as a result of weathering of ultramafic rocks, and that occurs in many nickel deposits worldwide. It is a mixture of various nickel and magnesium phyllosilicates (sheet silicates), including népouite. Associated minerals include calcite, chlorite, goethite, halloysite, nontronite, pimelite, quartz, sepiolite, serpentine, talc and willemseite.
As well as the type locality in New Caledonia, it has been found in Australia, Austria, the Czech Republic, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Germany, Greece, Italy, Japan, Morocco, Poland, Russia, South Africa and the United States.
Read More About Népouite / Source
Neptunite

Neptunite is a silicate mineral with the formula KNa2Li(Fe2+, Mn2+)2Ti2Si8O24. With increasing manganese it forms a series with mangan-neptunite. Watatsumiite is the variety with vanadium replacing the titanium in the formula.
It was first described in 1893 for an occurrence in the Narssârssuk pegmatite of West Greenland. It is also found within natrolite veins in glaucophane schist within serpentinite in San Benito County, California, US. It also occurs in Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec and in the Kola Peninsula of Russia.The mineral is named for Neptune, Roman god of the sea because of its association with aegirine from Àgir, the Scandinavian sea-god.The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) identified an 11.78-carat faceted specimen as neptunite based on Raman spectroscopy.
Read More About Neptunite / Source
Nichromite
Nichromite (Ni,Co,Fe)(Cr,Fe,Al)2O4 is a black cubic metallic mineral and member of the spinel group. Nichromite was originally reported from the Bon Accord nickel deposit in Barberton District, South Africa. Occurring naturally in a nickel deposit, nichromite is named for chromite with dominant nickel.The atomic arrangement of the spinel group is a commonly studied structure and characteristically has four closely packed oxygen atoms. The nickel atoms are organized corresponding to a “normal” spinel arrangement.The mineral has only been found in the Bon Accord Nickel Deposit in South Africa where it is formed by replacing chromite and rimmed by trevorite.
Read More About Nichromite / Source
Nickel

Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth’s crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth’s atmosphere.
Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth’s outer and inner cores.Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an element in 1751 by Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who initially mistook the ore for a copper mineral, in the cobalt mines of Los, Hälsingland, Sweden. The element’s name comes from a mischievous sprite of German miner mythology, Nickel (similar to Old Nick), who personified the fact that copper-nickel ores resisted refinement into copper. An economically important source of nickel is the iron ore limonite, which is often 1–2% nickel. Other important nickel ore minerals include pentlandite and a mix of Ni-rich natural silicates known as garnierite. Major production sites include the Sudbury region, Canada (which is thought to be of meteoric origin), New Caledonia in the Pacific, and Norilsk, Russia.
Nickel is one of four elements (the others are iron, cobalt, and gadolinium) that are ferromagnetic at about room temperature. Alnico permanent magnets based partly on nickel are of intermediate strength between iron-based permanent magnets and rare-earth magnets. The metal is used chiefly in alloys and corrosion-resistant plating. About 68% of world production is used in stainless steel. A further 10% is used for nickel-based and copper-based alloys, 9% for plating, 7% for alloy steels, 3% in foundries, and 4% in other applications such as in rechargeable batteries, including those in electric vehicles (EVs). Nickel is widely used in coins, though nickel-plated objects sometimes provoke nickel allergy. As a compound, nickel has a number of niche chemical manufacturing uses, such as a catalyst for hydrogenation, cathodes for rechargeable batteries, pigments and metal surface treatments. Nickel is an essential nutrient for some microorganisms and plants that have enzymes with nickel as an active site.
Read More About Nickel / Source
Nickeline

Nickeline or niccolite is a mineral consisting primarily of nickel arsenide (NiAs). The naturally-occurring mineral contains roughly 43.9% nickel and 56.1% arsenic by mass, but composition of the mineral may vary slightly.Small quantities of sulfur, iron and cobalt are usually present, and sometimes the arsenic is largely replaced by antimony. This last forms an isomorphous series with breithauptite (nickel antimonide).
Read More About Nickeline / Source
Niedermayrite

Niedermayrite is a rare hydrated copper cadmium sulfate hydroxide mineral with formula: Cu4Cd(SO4)2(OH)6·4H2O. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and occurs as encrustations and well formed vitreous blue-green prismatic crystals. It has a specific gravity of 3.36.
Niedermayrite was named for Gerhard Niedermayr (born 1941), an Austrian mineralogist. It was first described in 1998 from a mine in the Lavrion District, Attica, Greece. It is also reported from the Ophir District, Tooele County, Utah. The environment is in brecciated marble. The cadmium dominant analogue of campigliaite.
Read More About Niedermayrite / Source
Niningerite
Niningerite is a magnesium-iron-manganese sulfide mineral with the chemical formula MgS that is found in enstatite chondrite meteorites. Niningerite is the magnesium-dominant analog of keilite. This mineral is named after Harvey H. Nininger.
Read More About Niningerite / Source
Nissonite

Nissonite is a very rare copper phosphate mineral with formula: Cu2Mg2(PO4)2(OH)2·5H2O. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system typically as crusts, tabular crystals, and diamond-shaped crystals. The color is blue-green. It has a light green streak, a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a specific gravity of 2.73. Cleavage is {100} distinct.
Nissonite was discovered in 1966 and was named after William H. Nisson (1912–1965). It is from Llanada copper mine, near Llanada, San Benito Co., California.
Read More About Nissonite / Source
Niter

Niter or nitre is the mineral form of potassium nitrate, KNO3. It is a soft, white, highly soluble mineral found primarily in arid climates or cave deposits.
Historically, the term niter was not well differentiated from natron, both of which have been very vaguely defined but generally refer to compounds of sodium or potassium joined with carbonate or nitrate ions.
Read More About Niter / Source
Nitratine

Nitratine or nitratite, also known as cubic niter (UK: nitre), soda niter or Chile saltpeter (UK: Chile saltpetre), is a mineral, the naturally occurring form of sodium nitrate, NaNO3. Chemically it is the sodium analogue of saltpeter. Nitratine crystallizes in the trigonal system, but rarely occurs as well formed crystals. It is isostructural with calcite. It is relatively soft and light with a Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2 and a specific gravity of 2.24 to 2.29. Its refractive indices are nω=1.587 and nε=1.336.The typical form is as coatings of white, grey to yellowish brown masses. The rare crystals when found typically have the scalenohedral form of the calcite structure. It is found only as an efflorescence in very dry environments. It is very soluble in water such that it is deliquescent and will absorb water out of the air and turn into a puddle of sodium nitrate solution when exposed to humid air.
There are nitratine deposits located in arid regions across the world such as in Chile, Mexico, Egypt, Peru, and South Africa. Chile is the only country to sell their deposits commercially as fertilizer. The salt bed that is mined contains more minerals than just nitratine often containing sulfurous minerals as well as Iodine. Around 600,000 tons of nitratine are mined in Chile each year with other products such as Iodine and sodium sulfate mined as well.Nitratine happens to be isostructural to calcite, CaCO3 a widespread naturally occurring mineral although nitratine dissolution and crystallization occur much faster than the same processes for calcite. The structural similarity makes nitratine a very useful mineral for laboratory experiments concerning pressure dissolution and other experiments such as serving as a proxy for the deformation and formation of calcite.The Saltpeter War (1480-1510) and the War of the Pacific (1879-1884) were fought over the control of saltpeter deposits.
Read More About Nitratine / Source
Nobleite

Nobleite is a rare borate mineral with the chemical formula CaB6O9(OH)2·3H2O. It was discovered in 1961, in Death Valley, California, and is named for Levi F. Noble, a USGS geologist, in honor of his contributions to the geology of the Death Valley region.
Nobleite has also been identified at two localities in Chile and Argentina.
Read More About Nobleite / Source
Nontronite

Nontronite is the iron(III) rich member of the smectite group of clay minerals. Nontronites typically have a chemical composition consisting of more than ~30% Fe2O3 and less than ~12% Al2O3 (ignited basis). Nontronite has very few economic deposits like montmorillonite. Like montmorillonite, nontronite can have variable amounts of adsorbed water associated with the interlayer surfaces and the exchange cations.
A typical structural formula for nontronite is Ca.5(Si7Al.8Fe.2)(Fe3.5Al.4Mg.1)O20(OH)4. The dioctahedral sheet of nontronite is composed mainly of trivalent iron (Fe3+) cations, although some substitution by trivalent aluminium (Al3+) and divalent magnesium (Mg2+) does occur. The tetrahedral sheet is composed mainly of silicon (Si4+), but can have substantial (about 1 in 8) substitution of either Fe3+ or Al3+, or combinations of these two cations. Thus, nontronite typically is characterised by having most (usually greater than 60%) of the layer charge located in the tetrahedral sheet. The layer charge is typically balanced by divalent calcium (Ca2+) or magnesium (Mg2+).
Nontronite forms from the weathering of biotite and basalts, precipitation of iron and silicon rich hydrothermal fluids and in deep sea hydrothermal vents. Some evidence suggests that microorganisms may play an important role in their formation. Microorganisms are also involved in reduction of structural iron in nontronite when soils undergo anoxia, and the reduced form of the clay appears to be highly reactive towards certain pollutants, perhaps contributing to the destruction of these compounds in the environment.The only known commercially viable and operational nontronite mine is located in Canterbury, New Zealand. The mine is operated by Palmer Resources and the finished products are used internationally in industrial applications (pulp & paper, surface coating) and in cosmetics marketed as New Zealand Glacial Clay.
Read More About Nontronite / Source
Norbergite

Norbergite is a nesosilicate mineral with formula Mg3(SiO4)(F,OH)2. It is a member of the humite group.
It was first described in 1926 for an occurrence in the Östanmoss iron mine in Norberg, Västmanland, Sweden, for which it is named.
It occurs in contact metamorphic zones in carbonate rocks intruded by plutonic rocks or pegmatites supplying the fluorine. Associated minerals include dolomite, calcite, tremolite, grossular, wollastonite, forsterite, monticellite, cuspidine, fluoborite, ludwigite, fluorite and phlogopite.
Read More About Norbergite / Source
Normandite

Normandite is a brittle orange brown sorosilicate mineral discovered in 1997 by Charles Normand (born 1963), of Montreal. Normandite occurs in Khibiny Massif, Kola, Russia; in Poudrette quarry, Mont-Saint-Hilaire, Quebec (type locality) and Tenerife, Canary Islands. It is found in nepheline syenite and in miarolitic cavities in nepheline syenite, associated with nepheline, albite, microcline, aegirine, natrolite, catapleiite, kupletskite, eudialyte, cancrinite, villiaumite, rinkite, and donnayite-(Y).
Normandite has a chemical formula of NaCa(Mn2+,Fe2+)(Ti,Nb,Zr)Si2O7(O,F)2. It crystallizes in the monoclinic-prismatic crystal system. It occurs as transparent to translucent orange-brown aggregates of subparallel acicular crystals up to 10 mm in length, and as patches of yellow, fibrous crystals. It has a white to very pale yellow streak and vitreous luster. It is brittle, with distinct {100} and {001} cleavages, and a conchoidal fracture. It has a specific gravity of 3.48 to 3.5, a Mohs hardness of 5 to 6 and refractive index values of nα=1.743, nβ=1.785 and nγ=1.810. It is named after Charles Normand (born 1963), Canadian geologist.
Read More About Normandite / Source
Northupite

Northupite is an uncommon evaporite mineral, with the chemical formula Na3Mg(CO3)2Cl. It occurs as colourless to dark grey or brown octahedral crystals and as globular masses. In synthetic material it forms a series with tychite (Na6Mg2(CO3)4SO4).It was discovered in 1895 at Searles Lake, San Bernardino County, California by C. H. Northup (born 1861) from San Jose, California, for whom Northupite is named.
It occurs associated with tychite, pirssonite at Searles Lake and with shortite, trona, pirssonite, gaylussite, labuntsovite, searlesite, norsethite, loughlinite, pyrite and quartz in the Green River Formation of Wyoming.
Read More About Northupite / Source
Nosean

Nosean, also known as noselite, is a mineral of the feldspathoid group with formula: Na8Al6Si6O24(SO4). H2O. It forms isometric crystals of variable color: white, grey, blue, green, to brown. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 2.3 to 2.4. It is fluorescent. It is found in low-silica igneous rocks. There is a solid solution between nosean and hauyne, which contains calcium.
It was first described in 1815 from the Rhineland in Germany and named after the German mineralogist K. W. Nose (1753–1835). The mineral is rare but widespread, found in such diverse localities as ocean islands (e.g., Tahiti) and the La Sal Range in Utah.
Read More About Nosean / Source
Nsutite

Nsutite is a manganese oxide mineral with formula: (Mn4+1−xMn2+xO2-2x(OH)2x where x = 0.06-0.07). It is found in most large manganese deposits and was first discovered in Nsuta, Ghana. Since then, it has been found worldwide. Nsutite is a dull mineral with a hardness of 6.5-8.5 and an average specific gravity of 4.45. Nustite is used as a cathode in zinc–carbon batteries, but synthetic manganese oxide is gradually replacing it.
Read More About Nsutite / Source
Nuragheite
Nuragheite is a rare natural thorium molybdate, formula Th(MoO4)2·H2O, discovered in Su Seinargiu, Sarroch, Cagliari, Sardegna, Italy. This locality is also a place of discovery of the other thorium molybdate – ichnusaite, which is a trihydrate.
Read More About Nuragheite / Source
Nyerereite
Nyerereite is a very rare sodium calcium carbonate mineral with formula Na2Ca(CO3)2. It forms colorless, platey pseudohexagonal orthorhombic crystals that are typically twinned. It has a specific gravity of 2.54 and indices of refraction of nα=1.511, nβ=1.533 and nγ=1.535. Nyerereite is not stable in contact with the atmosphere and rapidly breaks down. Collection specimens must be kept in a sealed argon environment.
It has a Hermann–Mauguin notation of mm2 and the respective space group is Cmc21. In nature Nyerereite is naturally twinned and is pseudohexagonal with triad twinning; meaning that this is a six sided crystal that apparently has a hexagonal shape but is not in the hexagonal system. Triad twinning is the intergrowth of three orthorhombic crystals that turn at their center and form hexagonally shaped crystals. Nyerereite is biaxial negative, and has a 2v of 29 degrees. It shows a center acute bisectrix and a birefringence of approximately 0.023. At high temperatures or just erupted lava nyerereite is uniaxial and shows an interference color of second order blue when twinning is not present, and when twinning is there the interference color of nyerereite is first order grey.
Read More About Nyerereite / Source
Okenite

Okenite (CaSi2O5·2H2O) is a silicate mineral that is usually associated with zeolites. It most commonly is found as small white “cotton ball” formations within basalt geodes. These formations are clusters of straight, radiating, fibrous crystals that are both bendable and fragile. It also belongs to the family of the calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) commonly found in hardened cement paste. In cement chemist notation (CCN) it is noted as CaO·2SiO2·2H2O and abbreviated as CS2H2.
Read More About Okenite / Source
Oldhamite

Oldhamite is a calcium magnesium sulfide mineral with the chemical formula (Ca,Mg)S. Ferrous iron may also be present in the mineral resulting in the chemical formula (Ca,Mg,Fe)S. It is a pale to dark brown accessory mineral in meteorites. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system, but typically occurs as anhedral grains between other minerals.
Read More About Oldhamite / Source
Olgite

Olgite is a rare blue-green colored phosphate mineral series that forms microscopic prismatic crystals that are trigonal in structure. Its chemical formula is Na(Sr,Ba)PO4.
Olgite was discredited as a mineral name in 2008 by the International Mineralogical Association and is now the series name for bario-olgite and strontio-olgite (hypothetical mineral). The substance was named after Russian mineralogist Olga Anisimovne-Vorobiova (1902–1974).
Read More About Olgite / Source
Olivenite

Olivenite is a copper arsenate mineral, formula Cu2AsO4OH. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system (pseudo-orthorhombic), and is sometimes found in small brilliant crystals of simple prismatic habit terminated by domal faces. More commonly, it occurs as globular aggregates of acicular crystals, these fibrous forms often having a velvety luster; sometimes it is lamellar in structure, or soft and earthy.
A characteristic feature, and one to which the name alludes (German, Olivenerz, of A. G. Werner, 1789), is the olive-green color, which varies in shade from blackish-green in the crystals to almost white in the finely fibrous variety known as woodcopper. The hardness is 3, and the specific gravity is 4.3. The mineral was formerly found in some abundance, associated with limonite and quartz, in the upper workings in the copper mines of the St Day district in Cornwall; also near Redruth, and in the Tintic Mining District in Utah. It is a mineral of secondary origin, a result of the oxidation of copper ores and arsenopyrite.
The arsenic of olivenite is sometimes partly replaced by a small amount of phosphorus, and in the species libethenite we have the corresponding copper phosphate Cu2PO4OH. This is found as small dark green crystals resembling olivenite at Ľubietová in the Slovak Republic, and in small amount also in Cornwall. Other members of this isomorphous group of minerals are adamite, Zn2AsO4OH, and eveite, Mn2AsO4OH.
Read More About Olivenite / Source
Olivine

The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula (Mg,Fe)2SiO4. It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth’s upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth’s subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. For this reason, olivine has been proposed as a good candidate for accelerated weathering to sequester carbon dioxide from the Earth’s oceans and atmosphere, as part of climate change mitigation. Olivine also has many other historical uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes.
The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: Mg2SiO4) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: Fe2SiO4). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and fayalite (Fa) (e.g., Fo70Fa30). Forsterite’s melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost 1,900 °C (3,450 °F), while fayalite’s is much lower – about 1,200 °C (2,190 °F). Melting temperature varies smoothly between the two endmembers, as do other properties. Olivine incorporates only minor amounts of elements other than oxygen (O), silicon (Si), magnesium (Mg) and iron (Fe). Manganese (Mn) and nickel (Ni) commonly are the additional elements present in highest concentrations.
Olivine gives its name to the group of minerals with a related structure (the olivine group) – which includes tephroite (Mn2SiO4), monticellite (CaMgSiO4), larnite (Ca2SiO4) and kirschsteinite (CaFeSiO4) (commonly also spelled kirschteinite).
Olivine’s crystal structure incorporates aspects of the orthorhombic P Bravais lattice, which arise from each silica (SiO4) unit being joined by metal divalent cations with each oxygen in SiO4 bound to three metal ions. It has a spinel-like structure similar to magnetite but uses one quadrivalent and two divalent cations M22+ M4+O4 instead of two trivalent and one divalent cations.
Read More About Olivine / Source
Olmiite

Olmiite is a rare calcium-manganese silicate that was named after an Italian mineralogist called Filippo Olmi. It was approved by the IMA in 2006, being first published in 2007, which makes it a relatively newly discovered mineral. Around 2001, a large amount of specimens believed to be poldervaartite was discovered at the N’Chwaning II mine, which is near the Wessels mine, where the latter was discovered. Only later were the researchers able to determine though their investigations that the two minerals are different, as they are visually indistinguishable. Until Renato Pagano acquired and examined the specimens, seemingly no specific investigation was carried out. Olmiite has been misidentified not only once, but twice. The cream-colored specimens were at first thought to be baryte by the mine geologist.
Read More About Olmiite / Source
Omphacite

Omphacite is a member of the clinopyroxene group of silicate minerals with formula: (Ca, Na)(Mg, Fe2+, Al)Si2O6. It is a variably deep to pale green or nearly colorless variety of clinopyroxene. It normally appears in eclogite, which is the high-pressure metamorphic rock of basalt. Omphacite is the solid solution of Fe-bearing diopside and jadeite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system with prismatic, typically twinned forms, though usually anhedral. Its space group can be P2/n or C2/c depending on the thermal history. It exhibits the typical near 90° pyroxene cleavage. It is brittle with specific gravity of 3.29 to 3.39 and a Mohs hardness of 5 to 6.
Read More About Omphacite / Source
Oneillite
Oneillite is a rare mineral of the eudialyte group with the chemical formula Na15Ca3Mn3Fe2+3Zr3NbSiO(Si3O9)2(Si9O27)2(O,OH,H2O)3(OH,Cl)2. The formula is based on the original one but extended to show the presence of cyclic silicate groups and domination of Si at the M4 site. The mineral has lowered symmetry (space group R3, instead of more specific for the group R3m one) due to Ca-Mn ordering. Similar feature is displayed by some other eudialyte-group members: aqualite, labyrinthite, raslakite, and voronkovite. Oneillite is strongly enriched in rare earth elements (REE, mainly cerium), but REE do not dominate any of its sites.
Read More About Oneillite / Source
Oosterboschite

Oosterboschite is a rare selenide mineral with the formula (Pd,Cu)7Se5. It crystallises in the orthorhombic crystal system. It has a creamy yellow colour and a Moh’s hardness of 5. It is often found as grains with no clear shape. The crystals are opaque and often no bigger than 0.4 mm.
Read More About Oosterboschite / Source
Oppenheimerite
Oppenheimerite is a very rare uranium mineral with the formula Na2(UO2)(SO4)2•3H2O. Chemically related minerals include fermiite, natrozippeite, plášilite, belakovskiite and meisserite. Most of these uranyl sulfate minerals were originally found in the Blue Lizard mine, San Juan County, Utah, US. The mineral is named after American Theoretical physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer.
Read More About Oppenheimerite / Source
Ordoñezite

Ordoñezite or ordóñezite is a rare tetragonal zinc antimonate mineral with chemical formula: ZnSb2O6.
Read More About Ordoñezite / Source
Oregonite

Oregonite, Ni2FeAs2 is a nickel iron arsenide mineral first described from Josephine Creek, Oregon, United States.
Oregonite crystallises in the hexagonal crystal system and has a Mohs hardness of 5.
Read More About Oregonite / Source
Orpiment

Orpiment is a deep-colored, orange-yellow arsenic sulfide mineral with formula As2S3. It is found in volcanic fumaroles, low-temperature hydrothermal veins, and hot springs and is formed both by sublimation and as a byproduct of the decay of another arsenic sulfide mineral, realgar.
Orpiment takes its name from the Latin auripigmentum (aurum, “gold” + pigmentum, “pigment”), due to its deep-yellow color. Orpiment once was widely used in artworks, medicine, and other applications. Because of its toxicity and instability, its usage has declined.
Read More About Orpiment / Source
Orthoclase

Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar (endmember formula KAlSi3O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for “straight fracture”, because its two cleavage planes are at right angles to each other. It is a type of potassium feldspar, also known as K-feldspar. The gem known as moonstone (see below) is largely composed of orthoclase.
Read More About Orthoclase / Source
Osarizawaite

Osarizawaite is a greenish yellow sulfate mineral with the chemical formula: PbCuAl2(SO4)2(OH)6. It has rhombohedral crystals.It was first described in 1961 for an occurrence in the oxidized zone of the Osarizawa mine, Akita Prefecture, Honshu Island, Japan.
Read More About Osarizawaite / Source
Osmium

Osmium (from Ancient Greek ὀσμή (osmḗ) ‘smell’) is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, mostly in platinum ores. Osmium is the densest naturally occurring element. When experimentally measured using X-ray crystallography, it has a density of 22.59 g/cm3. Manufacturers use its alloys with platinum, iridium, and other platinum-group metals to make fountain pen nib tipping, electrical contacts, and in other applications that require extreme durability and hardness.Osmium is among the rarest elements in the Earth’s crust, making up only 50 parts per trillion (ppt). It is estimated to be about 0.6 parts per billion in the universe and is therefore the rarest precious metal.
Read More About Osmium / Source
Osumilite

Osumilite is a very rare potassium-sodium-iron-magnesium-aluminium silicate mineral. Osumilite is part of the milarite group (also known as the milarite-osumilite group) of cyclosilicates.
Read More About Osumilite / Source
Otavite

Otavite is a rare cadmium carbonate mineral with the formula CdCO3. Otavite crystallizes in the trigonal system and forms encrustations and small scalenohedral crystals that have a pearly to adamantine luster. The color is white to reddish to yellow brown. Its Mohs hardness is 3.5 to 4 and the specific gravity is 5.04. Associated minerals include azurite, calcite, malachite, and smithsonite.
It was first described in 1906 from the Tsumeb district near Otavi, Namibia.
Read More About Otavite / Source
Ottrelite

Ottrelite is a form of chloritoid. Its empirical formula is (Mn,Fe,Mg)2Al4Si2O10(OH)4.
Read More About Ottrelite / Source
Otwayite

Otwayite, Ni2CO3(OH)2, is a hydrated nickel carbonate mineral. Otwayite is green, with a hardness of 4, a specific gravity of 3.4, and crystallises in the orthorhombic system.
Read More About Otwayite / Source
Pääkkönenite

Pääkkönenite is a metallic grey mineral with the molecular formula Sb2AsS2. It is named after Veikko Pääkkönen (1907–1980), a Finnish geologist.
Read More About Pääkkönenite / Source
Pabstite

Pabstite is a barium tin titanium silicate mineral that is found in contact metamorphosed limestone. It belongs to the benitoite group of minerals. The chemical formula of pabstite is Ba(Sn,Ti)Si3O9. It is found in Santa Cruz, California. The crystal system of the mineral is hexagonal.
Read More About Pabstite / Source
Painite

Painite is a very rare borate mineral. It was first found in Myanmar by British mineralogist and gem dealer Arthur C.D. Pain who misidentified it as ruby, until it was discovered as a new gemstone in the 1950s. When it was confirmed as a new mineral species, the mineral was named after him. Due to its rarity, painite can cost in the range of between US$50,000 to $60,000 per carat.
The chemical makeup of painite contains calcium, zirconium, boron, aluminium and oxygen (CaZrAl9O15(BO3)). The mineral also contains trace amounts of chromium and vanadium, which are responsible for Painite’s typically orange-red to brownish-red color, similar to topaz. The mineral’s rarity is due to the fact that zirconium and boron rarely interact with each other in nature. The crystals are naturally hexagonal in shape, but may also be euhedral or orthorhombic. They may also have no crystalline structure, but usually are accompanied by a crystalline structure. Until late 2004, only two had been cut into faceted gemstones.
Read More About Painite / Source
Palladium

Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them.
More than half the supply of palladium and its congener platinum is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into nontoxic substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, medicine, hydrogen purification, chemical applications, groundwater treatment, and jewelry. Palladium is a key component of fuel cells, in which hydrogen and oxygen react to produce electricity, heat, and water.
Ore deposits of palladium and other PGMs are rare. The most extensive deposits have been found in the norite belt of the Bushveld Igneous Complex covering the Transvaal Basin in South Africa, the Stillwater Complex in Montana, United States; the Sudbury Basin and Thunder Bay District of Ontario, Canada, and the Norilsk Complex in Russia. Recycling is also a source, mostly from scrapped catalytic converters. The numerous applications and limited supply sources result in considerable investment interest.
Read More About Palladium / Source
Palygorskite

Palygorskite or attapulgite is a magnesium aluminium phyllosilicate with the chemical formula (Mg,Al)2Si4O10(OH)·4(H2O) that occurs in a type of clay soil common to the Southeastern United States. It is one of the types of fuller’s earth. Some smaller deposits of this mineral can be found in Mexico, where its use is tied to the manufacture of Maya blue in pre-Columbian times.
Read More About Palygorskite / Source
Panethite
Panethite, chemical formula (Na,Ca)2(Mg,Fe)2(PO4)2, is a rare phosphate mineral that was only found in one meteorite on Earth. It was originally found in the Dayton meteorite in Ohio. It is classified as H-M symbol (2/m) with space group of P21/n. It is amber in color. It was named in the honor of Friedrich Adolf Paneth (1887–1958), a German chemist who made many contributions toward the discovery of the origin of the universe, and especially studies of meteorites.
Read More About Panethite / Source
Panguite
Panguite is a type of titanium oxide mineral first discovered as an inclusion within the Allende meteorite, and first described in 2012.The hitherto unknown meteorite mineral was named for the ancient Chinese god Pan Gu, the creator of the world through the separation of yin (earth) from yang (sky).
Read More About Panguite / Source
Papagoite

Papagoite is a rare cyclosilicate mineral. Chemically, it is a calcium copper aluminium silicate hydroxide, found as a secondary mineral on slip surfaces and in altered granodiorite veins, either in massive form or as microscopic crystals that may form spherical aggregates. Its chemical formula is Ca Cu Al Si2O6(O H)3.
It was discovered in 1960 in Ajo, Arizona, US, and was named after the Hia C-ed O’odham people (also known as the Sand Papago) who inhabit the area. This location is the only papagoite source within the United States, while worldwide it is also found in South Africa and Namibia. It is associated with aurichalcite, shattuckite, ajoite and baryte in Arizona, and with quartz, native copper and ajoite in South Africa. Its bright blue color is the mineral’s most notable characteristic.
It is used as a gemstone.
Read More About Papagoite / Source
Paragonite

Paragonite is a mineral, related to muscovite. Its empirical formula is NaAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2. A wide solvus separates muscovite from paragonite, such that there is little solid solution along the vector Na+K+ and apparent micas of intermediate composition is most commonly a microscopic (or even sub-microscopic) intergrowth of two distinct micas, one rich in K, and the other in Na. Paragonite is a common mineral in rocks metamorphosed under blueschist facies conditions along with other sodic minerals such as albite, jadeite and glaucophane. During the transition from blueschist to greenschist facies, paragonite and glaucophane are transformed into chlorite and albite. Jadeite bearing pyroxene minerals have suggested Clinozoisite and paragonite are associated and derived from lawsonite releasing Quartz and water via the following reaction:
4
CaAl
2
Si
2
O
8
(
H
2
O
)
2
+
NaAlSi
2
O
6
↽
−
−
⇀
2
Ca
2
Al
3
Si
3
O
12
(
OH
)
+
NaAl
3
Si
3
O
10
(
OH
)
2
+
SiO
2
+
6
H
2
O
{displaystyle {ce {4CaAl2Si2O8(H2O)2 + NaAlSi2O6 <=> 2Ca2Al3Si3O12(OH) + NaAl3Si3O10(OH)2 + SiO2 + 6H2O}}}
It was first described in 1843 for an occurrence at Mt. Campione, Tessin, Switzerland. The name derives from the Greek, paragon, for misleading, due to its similar appearance to talc.
Read More About Paragonite / Source
Paralaurionite

Paralaurionite is a colorless mineral consisting of a basic lead chloride PbCl(OH) that is dimorphous with laurionite. It is a member of the matlockite group. The name is derived from para-, the Greek for “near”, and laurionite, because of its polymorphic relationship to it. Bright, yellow tips of thorikosite can form on paralaurionite crystals and paralaurionite may also be intergrown with mendipite.
Read More About Paralaurionite / Source
Paramelaconite

Paramelaconite is a rare, black-colored copper(I,II) oxide mineral with formula CuI2CuII2O3 (or Cu4O3). It was discovered in the Copper Queen Mine in Bisbee, Arizona, about 1890. It was described in 1892 and more fully in 1941. Its name is derived from the Greek word for “near” and the similar mineral melaconite, now known as tenorite.
Read More About Paramelaconite / Source
Pararealgar
Pararealgar is an arsenic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula As4S4, also represented as AsS. It forms gradually from realgar under exposure to light. Its name derives from the fact that its elemental composition is identical to realgar, As4S4. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 1 – 1.5, is yellow orange in colour, and its monoclinic prismatic crystals are very brittle, easily crumbling to powder.
It is one of the sulfides of arsenic and is one of two isomers of As4S4. It forms upon exposure of the symmetrical isomer to light. Its name derives from the fact that its elemental composition is identical to realgar, As4S4.
Read More About Pararealgar / Source
Paravauxite

Paravauxite is a rare mineral that was named in 1922. Its name is a portmanteau word made by blending the Greek word for near (παρα, meaning para) and vauxite due to the chemical relationship to vauxite. It was approved by the IMA, and was first described in 1959. It is now grandfathered, meaning it is probably to remain a species.
Read More About Paravauxite / Source
Pargasite

Pargasite is a complex inosilicate mineral of the amphibole group with formula NaCa2(Mg4Al)(Si6Al2)O22(OH)2.
It was first described for an occurrence in Pargas, Finland in 1814 and named for the locality.It occurs in high temperature regional metamorphic rocks and in the skarns within contact aureoles around igneous intrusions. It also occurs in andesite volcanic rocks and altered ultramafic rocks.Pargasite is the main water-storage site in the uppermost mantle, however it becomes unstable at depths greater than 90 km (56 mi). This has significant consequences for the water storage capacity, and the solidus temperature of the lherzolite of the upper mantle.It is used as a gemstone.
Read More About Pargasite / Source
Parisite-(Ce)

Parisite is a rare mineral consisting of cerium, lanthanum and calcium fluoro-carbonate, Ca(Ce,La)2(CO3)3F2. Parisite is mostly parisite-(Ce), but when neodymium is present in the structure the mineral becomes parisite-(Nd).
It is found only as crystals, which belong to the trigonal or monoclinic pseudo-hexagonal system and usually have the form of acute double pyramids terminated by the basal planes; the faces of the hexagonal pyramids are striated horizontally, and parallel to the basal plane there is a perfect cleavage. The crystals are hair-brown in color and are translucent. The hardness is 4.5 and the specific gravity is 4.36. Light which has traversed a crystal of parisite exhibits a characteristic absorption spectrum.
At first, the only known occurrence of this mineral was in the famous emerald mine at Muzo in Colombia, South America, where it was found by J.J. Paris, who rediscovered and worked the mine in the early part of the 19th century; here it is associated with emerald in a bituminous limestone of Cretaceous age.
Closely allied to parisite, and indeed first described as such, is a mineral from the nepheline-syenite district of Julianehaab in south Greenland. To this the name synchysite has been given. The crystals are rhombohedral (as distinct from hexagonal; they have the composition CeFCa(CO3)2, and specific gravity of 2.90. At the same locality there is also found a barium-parisite, which differs from the Colombian parisite in containing barium in place of calcium, the formula being (CeF)2Ba(CO3)3: this is named cordylite on account of the club-shaped form of its hexagonal crystals. Bastnasite is a cerium lanthanum and neodymium fluoro-carbonate (CeF)CO3, from Bastnas, near Riddarhyttan, in Vestmanland, Sweden, and the Pikes Peak region in Colorado, United States.
Read More About Parisite-(Ce) / Source
Parsonsite

Parsonsite is a lead uranium phosphate mineral with chemical formula: Pb2(UO2)(PO4)2·2H2O. Parsonsite contains about 45% lead and 25% uranium. It forms elongated lathlike pseudo monoclinic crystals, radial spherulites, encrustations and powdery aggregates. It is of a light yellow colour. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5-3 and a specific gravity of 5.72 – 6.29.It was first described in 1923 for an occurrence in the Shinkolobwe mine, Katanga Copper Crescent, Democratic Republic of Congo. It was named for mineralogist Arthur Leonard Parsons (1873–1957) of the University of Toronto, Canada.
Read More About Parsonsite / Source
Parthéite
Partheite or parthéite is a calcium aluminium silicate and a member of the zeolite group of minerals, a group of silicates with large open channels throughout the crystal structure, which allow passage of liquids and gasses through the mineral. It was first discovered in 1979 in rodingitic dikes in an ophiolite zone of the Taurus Mountains in southwest Turkey. The second discovery occurred in gabbro-pegmatites in the Ural Mountains, Russia. Since its discovery and naming, the chemical formula for partheite has been revised from CaAl2Si2O8•2H2O to include not only water but hydroxyl groups as well. The framework of the mineral is interrupted due to these hydroxyl groups attaching themselves to aluminum centered oxygen tetrahedra. This type of interrupted framework is known in only one other zeolite, the mineral roggianite. As a silicate based mineral with the properties of a zeolite, partheite was first described as zeolite-like in 1984 and listed as a zeolite in 1985. Partheite and lawsonite are polymorphs. Associated minerals include prehnite, thomsonite, augite, chlorite and tremolite.
Read More About Parthéite / Source
Pascoite

Pascoite is a mineral with formula Ca3V10O28·17H2O that is red-orange to yellow in color. It was discovered in the Pasco Province of Peru, for which it is named, and described in 1914.
Read More About Pascoite / Source
Patrónite

Patronite is the vanadium sulfide mineral with formula VS4. The material is usually described as V4+(S22−)2. Structurally, it is a “linear-chain” compound with alternating bonding and nonbonding contacts between the vanadium centers. The vanadium is octa-coordinated, which is an uncommon geometry for this metal.The mineral was first described in 1906 for an occurrence in the Minas Ragra vanadium mine near Junín, Cerro de Pasco, Peru. It was named for Peruvian metallurgist Antenor Rizo-Patron (1866–1948) the discoverer of the deposit. At the type locality in Peru it occurs in fissures within a red shale likely derived from an asphaltum deposit. Associated minerals include, native sulfur, bravoite, pyrite, minasragrite, stanleyite, dwornikite, quartz and vanadium bearing lignite. It has also been reported from the Yushkinite gorge on the Middle Silova-Yakha River on the Paikhoi Range of the polar Urals of Russia and from the Tsumeb mine in Namibia.
Read More About Patrónite / Source
Paulingite
Paulingite or paulingite-K is a rare zeolite mineral that is found in vesicles in the basaltic rocks from the Columbia River near Rock Island Dam, Washington.
Paulingite was named for Linus Carl Pauling (1901–1994), professor of chemistry, California Institute of Technology and accepted by the International Mineralogical Association in 1960.
The early formation in the crystallization sequence and the high water content suggest that paulingite forms from relatively dilute pore fluids. They have a large unit cell of 3.51 nanometers and an isometric crystal system. This is the largest known inorganic unit cell apart from protein structures. Paulingite’s characteristic structure can be observed while the remaining water content decomposes. A single crystal X-ray refinement of this chemically different sample material derived three main cation positions, which are inside a so-called paulingite or Calcium (Ca), between 8-rings of neighbouring Barium (Ba), and in the centre of the non-planar 8-rings of the -cage Potassium (K).
Read More About Paulingite / Source
Paulscherrerite
Paulscherrerite, UO2(OH)2, is a newly named mineral of the schoepite subgroup of hexavalent uranium hydrate/hydroxides. It is monoclinic, but no space group has been determined because no single-crystal study has been done. Paulscherrerite occurs as a canary yellow microcrystalline powdery product with a length of ~500 nm. It forms by the weathering and ultimate pseudomorphism of uranium-lead bearing minerals such as metaschoepite. The type locality for paulscherrerite is the Number 2 Workings, Radium Ridge near Mount Painter, North Flinders Ranges, South Australia, an area where radiogenic heat has driven hydrothermal activity for millions of years. It is named for Swiss physicist Paul Scherrer, co-inventor of the Debye-Scherrer X-ray powder diffraction camera. Study of paulscherrerite and related minerals is important for understanding the mobility of uranium around mining sites, as well as designing successful strategies for the storage of nuclear weapons and the containment of nuclear waste.
Read More About Paulscherrerite / Source
Pearceite

Pearceite is one of the four so-called “ruby silvers”, pearceite Cu(Ag,Cu)6Ag9As2S11, pyrargyrite Ag3SbS3, proustite Ag3AsS3 and miargyrite AgSbS2. It was discovered in 1896 and named after Dr Richard Pearce (1837–1927), a Cornish–American chemist and metallurgist from Denver, Colorado.
Read More About Pearceite / Source
Pecoraite

Pecoraite is a nickel silicate mineral and a member of the serpentine group. It was named after geologist William Thomas Pecora. It is monoclinic and has a chemical composition of Ni3(Si2O5)(OH)4. It is associated with the weathering-and-or oxidation of meteorites or nickel sulfide minerals such as millerite. It is also found in altered ultramafic rocks. Pecoriate is typically a green, lime green, or bluegreen mineral with a waxy, or earthy luster and a mohs hardness of 2.5. Common textural habits associated with pecoraite are curved plates, spirals and tubes. It can also be granular and massive.
Read More About Pecoraite / Source
Pectolite

Pectolite is a white to gray mineral, NaCa2Si3O8(OH), sodium calcium hydroxide inosilicate. It crystallizes in the triclinic system typically occurring in radiated or fibrous crystalline masses. It has a Mohs hardness of 4.5 to 5 and a specific gravity of 2.7 to 2.9. The gemstone variety, larimar, is a pale to sky blue.
Read More About Pectolite / Source
Penfieldite

Penfieldite is a rare lead hydroxychloride mineral from the class of halides. It was named after Samuel Lewis Penfield. It has been a valid species before the founding of IMA, and was first published in 1892. It had been grandfathered, meaning the name penfieldite is still believed to refer to a valid species. When it was first described by Genth in 1892 from Laurion, Greece, the mineral had the formula of Pb3Cl4O.
Read More About Penfieldite / Source
Penikisite
Penikisite was discovered by Alan Kulan and Gunar Penikis near Rapid Creek, Yukon Territory. The mineral is a member of the bjarebyite group along with kulanite, ideally BaFe2+2Al2(PO4)3(OH)3, and bjarebyite, ideally BaMn2+2Al2(PO4)3(OH)3. It is among several new minerals that have been discovered in the Rapid Creek and Big Fish areas of Yukon Territory. Kulanite is similar in many ways to penikisite in appearance and properties. The chemical formula for penikisite is Ba(Mg,Fe,Ca)Al2(PO4)2(OH)3. It has a hardness of about 4 and a density of 3.79 g/cm3. Penikisite is unique among the bjarebyite group in being monoclinic and has a biaxial optical class. It comes in shades of blue and green and, when rubbed on a streak plate, is pale green to white in color. Although penikisite and kulanite both range from blue to green, penikisite zones are easily distinguishable from kulanite zones in kulanite-penikisite crystals because they are lighter than the darker kulanite in color. Penikisite is a phosphate and is different from kulanite in that it is a magnesium-rich phosphate whereas kulanite is an iron-rich phosphate.
Read More About Penikisite / Source
Penroseite

Penroseite is a rare selenide mineral with formula (Ni,Co,Cu)Se2. It has a gray-steel color and black streak with a hardness of 3. It is an isometric mineral, 2/m3. Penroseite was first discovered in 1925 in a Bolivian rhyolite. It was named for Richard Penrose (1863–1931), an economic geologist.
Penroseite is a rare mineral found in the Pacajake mines in Bolivia. It was discovered in 1925. It used to be found in fissure veins in the extrusive igneous rhyolite rock. It is considered as a member of the pyrite group from the perspective of its structure, with a cubic space group (Bayliss, 1989).
Penroseite makes extensive solid solutions with other minerals. For example, penroseite can be a result of alteration process of many selenides, such as olsacherite Pb2(SO4)(SeO4). Olsacherite forms very sparingly in well formed crystal covering the walls of the external side of the small cracks (Hurlbut, 1969). Another mineral related to penroseite is piretite. It occurs as an alteration product of uraninite and primary selenium-bearing sulfides, such as penroseite. Piretite forms as crusts in association with an orange masuyite-like U-Pb oxide on the surface of uraninite samples (Vochten, 1996).
Read More About Penroseite / Source
Pentagonite

Pentagonite is a rare silicate mineral with formula Ca(VO)Si4O10·4(H2O).
It was named for the unusual twinning which produces an apparent five-fold symmetry. It is a dimorph of cavansite.
Pentagonite was first described in 1973 for an occurrence in Lake Owyhee State Park, Malheur County, Oregon. It has also been reported from the Pune district of India. It occurs as fracture and cavity fillings in tuff and basalt. It occurs with cavansite, heulandite, stilbite, analcime, apophyllite and calcite.
Read More About Pentagonite / Source
Pentlandite

Pentlandite is an iron–nickel sulfide with the chemical formula (Fe,Ni)9S8. Pentlandite has a narrow variation range in nickel to iron ratios (Ni:Fe), but it is usually described as 1:1. In some cases, this ratio is skewed by the presence of pyrrhotite inclusions. It also contains minor cobalt, usually at low levels as a fraction of weight.
Pentlandite forms isometric crystals, but it is normally found in massive granular aggregates. It is brittle with a hardness of 3.5–4 and specific gravity of 4.6–5.0 and is non-magnetic. It has a yellowish bronze color and a metallic luster.Pentlandite is found in abundance within ultramafic rocks, making it one of the most important sources of mined nickel. It also occasionally occurs within mantle xenoliths and “black smoker” hydrothermal vents.
Read More About Pentlandite / Source
Perhamite

Perhamite is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca3Al7(SiO4)3(PO4)4(OH)3·16.5(H2O).
It occurs in rare isolated masses in amblygonite-rich pegmatite deposits throughout the world. It was discovered in platy sheed form of 1mm hexagonal crystals. It was first described in 1977 by P.J. Dunn and D.E. Appleman from pegmatite collected from Bell Pit, Newry, Maine. Other specimens have been found in Kapunda, South Australia, in Silver Coin mine near Humboldt County, Nevada and various locations throughout Europe.
Read More About Perhamite / Source
Periclase

Periclase is a magnesium mineral that occurs naturally in contact metamorphic rocks and is a major component of most basic refractory bricks. It is a cubic form of magnesium oxide (MgO). In nature it usually forms a solid solution with wüstite (FeO) and is then referred to as ferropericlase or magnesiowüstite.It was first described in 1840 and named from the Greek περικλάω (to break around) in allusion to its cleavage. The type locality is Monte Somma, Somma-Vesuvius Complex, Naples Province, Campania, Italy.The old term for the mineral is magnesia. Stones from the Magnesia region in ancient Anatolia contained both magnesium oxide and hydrated magnesium carbonate as well as iron oxides (such as magnetite). Thus these stones, called Stones from Magnesia in antiquity, with their unusual magnetic properties were the reason the terms magnet and magnetism were coined.
Periclase is usually found in marble produced by metamorphism of dolomitic limestones. It readily alters to brucite under near surface conditions.In addition to its type locality, it is reported from Predazzo, Trentino, Italy; Carlingford, County Louth, Ireland; Broadford, Skye and the island of Muck, Scotland; León, Spain; the Bellerberg Volcano, Eifel district, Germany; Nordmark and Långban, Varmland, Sweden; and Kopeysk, southern Ural Mountains, Russia. In the US it occurs at the Crestmore quarry, Riverside County, California; Tombstone, Arizona; Gabbs district, Nye County, Nevada. In Canada, it occurs at Oka, Quebec and in Australia, west of Cowell, Eyre Peninsula, South Australia.The crystal structure of periclase corresponds to that of halite and has been studied extensively due to its simplicity. As a consequence, the physical properties of periclase are well known, which makes the mineral a popular standard in experimental work. The mineral has been shown to remain stable at pressures up to at least 360 GPa.
Read More About Periclase / Source
Perite

Perite is a mineral that has a general chemical formula of PbBiO2Cl. The name is given for Per Adolf Geijer, a Swedish economic geologist with the Geological Survey of Sweden, who discovered the mineral in 1960 outside of Langban, Sweden. Perite is orthorhombic, space group Cmcm {C2/m 2/c 21/m}. In terms of its optical properties, Perite is anisotropic which means the velocity of light varies depending on direction through the mineral (i.e. it is birefringent). Its calculated relief is 1.45-1.461, which is moderate. It is colorless in plane polarized light, and it is weakly pleochroic. Perite is found in areas near igneous extrusions in places like the Western United States, Southern Australia, and scattered around Europe.
Read More About Perite / Source
Perovskite

Perovskite (pronunciation: ) is a calcium titanium oxide mineral composed of calcium titanate (chemical formula CaTiO3). Its name is also applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure as CaTiO3 (XIIA2+VIB4+X2−3), known as the perovskite structure. Many different cations can be embedded in this structure, allowing the development of diverse engineered materials.
Read More About Perovskite / Source
Petalite

Petalite, also known as castorite, is a lithium aluminum phyllosilicate mineral LiAlSi4O10, crystallizing in the monoclinic system. Petalite occurs as colorless, pink, grey, yellow, yellow grey, to white tabular crystals and columnar masses. It occurs in lithium-bearing pegmatites with spodumene, lepidolite, and tourmaline. Petalite is an important ore of lithium, and is converted to spodumene and quartz by heating to ~500 °C and under 3 kbar of pressure in the presence of a dense hydrous alkali borosilicate fluid with a minor carbonate component. Petalite (and secondary spodumen formed from it) is lower in iron than primary spodumene, making it a more useful source of lithium in, e.g., the production of glass. The colorless varieties are often used as gemstones.
Read More About Petalite / Source
Petrovite
Petrovite is a blue and green mineral, with the chemical formula of Na10CaCu2(SO4)8. It contains atoms of oxygen (O), sodium (Na), sulphur (S), calcium (Ca) and copper (Cu) in a porous framework. It has potential as a cathode material in sodium-ion rechargeable batteries.It was discovered in volcanic lava flows in the Kamchatka region of Russia’s far east and first described in 2020.
Read More About Petrovite / Source
Petzite

The mineral petzite, Ag3AuTe2, is a soft, steel-gray telluride mineral generally deposited by hydrothermal activity. It forms isometric crystals, and is usually associated with rare tellurium and gold minerals, often with silver, mercury, and copper.
The name comes from chemist W. Petz, who first analyzed the mineral from the type locality in Săcărâmb, Transylvania, Romania in 1845. It was described by Wilhelm Karl Ritter von Haidinger in 1845 and dedicated to W. Petz who had carried out the first analyses.It occurs with other tellurides in vein gold deposits. It is commonly associated with native gold, hessite, sylvanite, krennerite, calaverite, altaite, montbrayite, melonite,
frohbergite, tetradymite, rickardite, vulcanite and pyrite.Petzite forms together with uytenbogaardtite (Ag3AuS2) and fischesserite (Ag3AuSe2) the uytenbogaardtite group.
Read More About Petzite / Source
Pezzottaite

Pezzottaite, marketed under the name raspberyl or raspberry beryl, is a mineral species first recognized by the International Mineralogical Association in September 2003. Pezzottaite is a caesium analogue of beryl, a silicate of caesium, beryllium, lithium and aluminium, with the chemical formula Cs(Be2Li)Al2Si6O18. Named after Italian geologist and mineralogist Federico Pezzotta, pezzottaite was first thought to be either red beryl or a new variety of beryl (“caesium beryl”); unlike actual beryl, however, pezzottaite contains lithium and crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system rather than the hexagonal system.
Colors include shades of raspberry red to orange-red and pink. Recovered from miarolitic cavities in the granitic pegmatite fields of Fianarantsoa province, southern Madagascar, the pezzottaite crystals were small—no more than about 7 cm (2.8 in) in their widest dimension—and tabular or equant in habit, and few in number, most being heavily included with growth tubes and liquid feathers. Approximately 10 per cent of the rough material would also exhibit chatoyancy when polished. Most cut pezzottaite gems are under one carat (200 mg) in weight and rarely exceed two carats (400 mg).
With the exception of hardness (8 on Mohs scale), the physical and optical properties of pezzottaite—i.e., specific gravity 3.10 (average), refractive index 1.601 to 1.620, birefringence 0.008 to 0.011 (uniaxial negative)—are all higher than typical beryl. Pezzottiate is brittle with a conchoidal to irregular fracture, and streaks white. Like beryl, it has an imperfect to fair basal cleavage. Pleochroism is moderate, from pink-orange or purplish pink to pinkish purple. Pezzottaite’s absorption spectrum, as seen by a hand-held (direct vision) spectroscope, features a band at 485–500 nm with some specimens showing additional weak lines at 465 and 477 nm and a weak band at 550 to 580 nm.
Most (if not all) of the Madagascan deposits have since been exhausted. Pezzottaite has been found in at least one other locality, Afghanistan: this material was first thought to be caesium-rich morganite (pink beryl). Like morganite and red beryl, pezzottaite is believed to owe its color to radiation-induced color centres involving trivalent manganese. Pezzottaite will lose its color if heated to 450 °C for two hours, but the color can be restored with gamma irradiation.
Read More About Pezzottaite / Source
Pharmacolite

Pharmacolite is an uncommon calcium arsenate mineral with formula CaHAsO4·2(H2O). It occurs as soft, white clusters of fibrous crystals and encrustations which crystallize in the monoclinic system. It is the arsenate analogue of the sulfate gypsum and the phosphate brushite.
Read More About Pharmacolite / Source
Pharmacosiderite

Pharmacosiderite is a hydrated basic ferric arsenate, with chemical formula KFe4(AsO4)3(OH)4·(6-7)H2O and a molecular weight of 873.38 g/mol. It consists of the elements arsenic, iron, hydrogen, potassium, sodium and oxygen. It has a Mohs hardness of 2 to 3, about that of a finger nail. Its specific gravity is about 2.7 to 2.9, has indistinct cleavage, and is usually transparent or translucent. It has a yellow or white streak and a yellow, green, brown or red color. Its lustre is adamantine, vitreous and resinous, and it has conchoidal, brittle and sectile fracture.
Pharmacosiderite has an isometric crystal system, with yellowish-green, sharply defined cube crystals. Its crystals are doubly refracting, and exhibit a banded structure in polarized light. When placed in ammonium solution, a crystal changes color to a distinguishing red. Upon placing it into dilute hydrochloric acid the original color is restored.
This secondary origin mineral is normally formed in the oxidation zones of ore deposits. The alteration of arsenopyrite, tennantite and other primary arsenates can form pharmacosiderite. It can also form from precipitation of hydrothermal solutions, but only rarely. It can be found in abundance in Cornwall, Hungary and the U.S. state of Utah.
When it was first discovered, pharmacosiderite was known as cube ore. The present name, given by J. F. L. Hausmann in 1813, is made up of the Greek words for arsenic and iron, the two most significant consisting elements. Pharmakos means poison, which is related to arsenic, and sideros means iron.
Pharmacolite and picropharmacolite, which are different arsenates, are not associated besides via nomenclature. Siderite, a carbonate mineral, only shares the common element iron with pharmacosiderite.
Read More About Pharmacosiderite / Source
Phenakite

Phenakite or phenacite is a fairly rare nesosilicate mineral consisting of beryllium orthosilicate, Be2SiO4. Occasionally used as a gemstone, phenakite occurs as isolated crystals, which are rhombohedral with parallel-faced hemihedrism, and are either lenticular or prismatic in habit: the lenticular habit is determined by the development of faces of several obtuse rhombohedra and the absence of prism faces. There is no cleavage, and the fracture is conchoidal. The Mohs hardness is high, being 7.5 – 8; the specific gravity is 2.96. The crystals are sometimes perfectly colorless and transparent, but more often they are greyish or yellowish and only translucent; occasionally they are pale rose-red. In general appearance the mineral is not unlike quartz, for which indeed it has been mistaken. Its name comes from Ancient Greek: φέναξ, romanized: phénax, meaning “deceiver” due to its close visual similarity to quartz, named by Nils Gustaf Nordenskiöld in 1833.
Read More About Phenakite / Source
Phillipsite

Phillipsite is a mineral series of the zeolite group; a hydrated potassium, calcium and aluminium silicate, approximating to (Ca,Na2,K2)3Al6Si10O32·12H2O. The members of the series are phillipsite-K, phillipsite-Na and phillipsite-Ca. The crystals are monoclinic, but only complex cruciform twins are known, these being exactly like twins of harmotome which also forms a series with phillipsite-Ca. Crystals of phillipsite are, however, usually smaller and more transparent and glassy than those of harmotome. Spherical groups with a radially fibrous structure and bristled with crystals on the surface are not uncommon. The Mohs hardness is 4.5, and the specific gravity is 2.2. The species was established by Armand Lévy in 1825 and named after William Phillips. French authors use the name Christianite (after Christian VIII of Denmark), given by A. Des Cloizeaux in 1847.
Phillipsite is a mineral of secondary origin, and occurs with other zeolites in the amygdaloidal cavities of mafic volcanic rocks: for example in the basalt of the Giants Causeway in County Antrim, and near Melbourne in Victoria; and in Lencitite near Rome. Small crystals of recent formation have been observed in the masonry of the hot baths at Plombires and Bourbonne-les-Bains, in France. Minute spherical aggregates embedded in pelagic red clay were dredged by the Challenger from deep sea sedimentary deposits in the Pacific Ocean.It has been discovered that the volcanic ash that Romans employed in the mix for construction of harbor piers and sea walls contained phillipsite, and that an interaction with sea water actually causes crystalline aluminous tobermorite structures in the mortar to expand and strengthen, making the material substantially more durable than modern concrete.
Read More About Phillipsite / Source
Phlogopite

Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica.
Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O10(F,OH)2. Iron substitutes for magnesium in variable amounts leading to the more common biotite with higher iron content. For physical and optical identification, it has most of the characteristic properties of biotite.
Read More About Phlogopite / Source
Phoenicochroite

Phoenicochroite, also known as melanochroite, is a lead chromate mineral with formula Pb2OCrO4. It forms striking orange red crystals. It was first discovered in 1839 in Beryozovskoye deposit, Urals, Russia. It is named from the Greek word φοίυικος for “deep red” and χρόα for “color,” in allusion to its color.
Read More About Phoenicochroite / Source
Phosgenite

Phosgenite is a rare mineral consisting of lead carbonate chloride, (PbCl)2CO3. The tetragonal crystals are prismatic or tabular in habit: they are usually colorless and transparent, and have a brilliant adamantine lustre. Sometimes the crystals have a curious helical twist about the tetrad or principal axis. The hardness is 3 and the specific gravity 6.3. The mineral is rather sectile, and consequently was earlier known as corneous lead, (German Hornblei).
Read More About Phosgenite / Source
Phosphophyllite

Phosphophyllite (from Ancient Greek phyllon ‘leaf’, and phosphate) is a rare mineral with the chemical formula Zn2Fe(PO4)2·4H2O, composed of hydrated zinc phosphate. It is highly prized by collectors for its rarity and for its delicate bluish green colour. Phosphophyllite is rarely cut because it is fragile and brittle, and large crystals are too valuable to be broken up.
The finest phosphophyllite crystals come from Potosí, Bolivia, but it is no longer mined there. Other sources include New Hampshire, United States and Hagendorf, Bavaria, Germany. It is often found in association with the minerals chalcopyrite and triphylite.Phosphophyllite has been synthesized synthetically by the addition of diammonium phosphate to a solution of zinc and iron sulfate.
Read More About Phosphophyllite / Source
Phosphosiderite

Phosphosiderite is a rare mineral named for its main components, phosphate and iron. The siderite at the end of phosphosiderite comes from the word “sideros”, the Greek word for iron. It was published in 1890, and has been a valid species since pre-IMA. It is an IMA approved mineral which got grandfathered, meaning its name is still believed to refer to an existing species.
Read More About Phosphosiderite / Source
Phosphuranylite

Phosphuranylite is a uranyl phosphate mineral with formula KCa(H3O)3(UO2)7(PO4)4O4·8(H2O).It was first described in 1879 by Frederick Augustus Genth, from an occurrence in the Flat Rock pegmatite in Mitchell County, North Carolina, US.
Read More About Phosphuranylite / Source
Pickeringite

Pickeringite is a magnesium aluminium sulfate mineral with formula MgAl2(SO4)4·22(H2O). It forms a series with halotrichite.
It forms as an alteration product of pyrite in aluminium rich rocks and in coal seams.
It also occurs in pyrite rich hydrothermal ore deposits in arid regions. It forms in fumaroles and in caves. It occurs with kalinite, alunogen, epsomite, melanterite, copiapite and gypsum.It was first described in 1844 for an occurrence in Cerros Pintados, Pampa del Tamarugal, Iquique Province, Tarapacá Region, Chile. It was named for American linguist and philologist John Pickering (1777–1846).
Read More About Pickeringite / Source
Picropharmacolite

Picropharmacolite, Ca4Mg(AsO3OH)2(AsO4)2·11H2O, is a rare arsenate mineral. It was named in 1819 from the Greek for bitter, in allusion to its magnesium content, and its chemical similarity to pharmacolite. The mineral irhtemite, Ca4Mg(AsO3OH)2(AsO4)2·4H2O, has the same composition as picropharmacolite, except that it has only four water molecules per formula unit, instead of eleven. It may be formed by the dehydration of picropharmacolite.
Read More About Picropharmacolite / Source
Piemontite

Piemontite is a sorosilicate mineral in the monoclinic crystal system with the chemical formula Ca2(Al,Mn3+,Fe3+)3(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH). It is a member of the epidote group.Red to reddish-brown or red-black in color, Piemontite has a red streak and a vitreous lustre. Manganese (Mn3+) causes the red color.The type locality is the Prabornaz Mine, in Saint-Marcel, Aosta Valley, Italy.It occurs metamorphic rocks of the greenschist to amphibolite metamorphic facies and in low-temperature hydrothermal veins in altered volcanic rocks. It also occurs in metasomatized deposits of manganese ore. Associated minerals include: epidote, tremolite, glaucophane, orthoclase, quartz and calcite.
Read More About Piemontite / Source
Pigeonite

Pigeonite is a mineral in the clinopyroxene subgroup of the pyroxene group. It has a general formula of (Ca,Mg,Fe)(Mg,Fe)Si2O6. The calcium cation fraction can vary from 5% to 25%, with iron and magnesium making up the rest of the cations.
Pigeonite crystallizes in the monoclinic system, as does augite, and a miscibility gap exists between the two minerals. At lower temperatures, pigeonite is unstable relative to augite plus orthopyroxene. The low-temperature limit of pigeonite stability depends upon the Fe/Mg ratio in the mineral and is hotter for more Mg-rich compositions; for a Fe/Mg ratio of about 1, the temperature is about 900 °C. The presence of pigeonite in an igneous rock thus provides evidence for the crystallization temperature of the magma, and hence indirectly for the water content of that magma.
Pigeonite is found as phenocrysts in volcanic rocks on Earth and as crystals in meteorites from Mars and the Moon. In slowly cooled intrusive igneous rocks, pigeonite is rarely preserved. Slow cooling gives the calcium the necessary time to separate itself from the structure to form exsolution lamellae of calcic clinopyroxene, leaving no pigeonite present. Textural evidence of its breakdown to orthopyroxene plus augite may be present, as shown in the accompanying microscopic image.
Pigeonite is named for its type locality on Lake Superior’s shores at Pigeon Point, Minnesota, United States. It was first described in 1900.
Read More About Pigeonite / Source
Pinalite
Pinalite is a rare lead tungstate–chloride mineral with formula: Pb3WO5Cl2.
Pinalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. The orthorhombic system is described as having three crystallographic axes of unequal lengths, normally referred to as c (the longest axis), b (the second longest axis), and a (the smallest axis). These axes all have corresponding angles of 90 degrees. Pinalite belongs to the biaxial optical class, and is negative. The main difference between biaxial and axial crystals is that biaxial crystals have two optic axes.Pinalite’s structure is significant in that it is one of a kind. It is therefore important in seeing how the structures in new lead oxyhalides (containing square pyramids incorporated into sheets) are arranged. Its structure contains an extra oxygen, which therefore has a very small amount of free space and consequently protrudes into neighboring layers. The oxygen then pushes aside the chlorine atoms, leaving almost no room for the lead to occupy. This is of interest to geologists for it is such a rare occurrence of structure seen only in pinalite and its barium analog. Therefore, it could be of use to structuralists to see how this mineral was formed. Experiments have been done, using lead oxyhalides, to see the reason and sequence of events in which this mineral is executed.
Read More About Pinalite / Source
Pinnoite

Pinnoite is a magnesium borate mineral with formula: MgB2O(OH)6 or MgB2O4·3(H2O). It crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system and occurs as colorless to yellow or light green radial fibrous clusters and rarely as short prismatic crystals.
Pinnoite was first described in 1884 for an occurrence in the Stassfurt potash deposit, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany and named for the mine counselor Oberbergrat Pinno of Halle, Germany. It occurs in marine evaporite deposits and as efflorescence associated with mineral springs. It occurs with boracite and kaliborite. It also occurs in the borax mines of Death Valley in California, the Da
Quidam saline lake of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in Tibet and in Socacastro, Salta Province, Argentina.
Read More About Pinnoite / Source
Piypite

Piypite is a rare potassium, copper sulfate mineral with formula: K2Cu2O(SO4)2. It crystallizes in the tetragonal system and occurs as needlelike crystals and masses. Individual crystals are square in cross-section and often hollow. It is emerald green to black in color with a vitreous to greasy luster.It was first described in 1982 for an occurrence in the Main Fracture of the Tolbachik volcano, Kamchatka Oblast, Russia. It has also been reported from Mount Vesuvius, Italy, and in a slag deposit in the Bad Ems District in the Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Piypite occurs as a sublimate phase in a fumarole environment. Associated minerals include halite, sylvite, langbeinite, tenorite, hematite, tolbachite, dolerophanite, urusovite, aphthitalite, ponomarevite, cotunnite, chalcocyanite, sofiite, euchlorine, averievite, fedotovite, alarsite, alumoklyuchevskite, nabokoite and lammerite at the type locality in Kamchatka. On Vesuvius, it occurs with paratacamite.
Read More About Piypite / Source
Plagioclase

Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series. This was first shown by the German mineralogist Johann Friedrich Christian Hessel (1796–1872) in 1826. The series ranges from albite to anorthite endmembers (with respective compositions NaAlSi3O8 to CaAl2Si2O8), where sodium and calcium atoms can substitute for each other in the mineral’s crystal lattice structure. Plagioclase in hand samples is often identified by its polysynthetic crystal twinning or “record-groove” effect.
Plagioclase is a major constituent mineral in Earth’s crust and is consequently an important diagnostic tool in petrology for identifying the composition, origin and evolution of igneous rocks. Plagioclase is also a major constituent of rock in the highlands of the Moon. Analysis of thermal emission spectra from the surface of Mars suggests that plagioclase is the most abundant mineral in the crust of Mars.Its name comes from Ancient Greek πλάγιος (plágios) ‘oblique’, and κλάσις (klásis) ‘fracture’, in reference to its two cleavage angles.
Read More About Plagioclase / Source
Plancheite
Plancheite is a hydrated copper silicate mineral with the formula Cu8Si8O22(OH)4•(H2O). It is closely related to shattuckite in structure and appearance, and the two minerals are often confused.
Read More About Plancheite / Source
Platinum

Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish platina, a diminutive of plata “silver”.Platinum is a member of the platinum group of elements and group 10 of the periodic table of elements. It has six naturally occurring isotopes. It is one of the rarer elements in Earth’s crust, with an average abundance of approximately 5 μg/kg. It occurs in some nickel and copper ores along with some native deposits, mostly in South Africa, which accounts for ~80% of the world production. Because of its scarcity in Earth’s crust, only a few hundred tonnes are produced annually, and given its important uses, it is highly valuable and is a major precious metal commodity.Platinum is one of the least reactive metals. It has remarkable resistance to corrosion, even at high temperatures, and is therefore considered a noble metal. Consequently, platinum is often found chemically uncombined as native platinum. Because it occurs naturally in the alluvial sands of various rivers, it was first used by pre-Columbian South American natives to produce artifacts. It was referenced in European writings as early as the 16th century, but it was not until Antonio de Ulloa published a report on a new metal of Colombian origin in 1748 that it began to be investigated by scientists.
Platinum is used in catalytic converters, laboratory equipment, electrical contacts and electrodes, platinum resistance thermometers, dentistry equipment, and jewelry. Platinum is used in the glass industry to manipulate molten glass which does not “wet” platinum. As a heavy metal, it leads to health problems upon exposure to its salts; but due to its corrosion resistance, metallic platinum has not been linked to adverse health effects. Compounds containing platinum, such as cisplatin, oxaliplatin and carboplatin, are applied in chemotherapy against certain types of cancer.Pure platinum is currently less expensive than pure gold, having been so continuously since 2015, but has been twice as expensive or more, mostly prior to 2008. In early 2021, the value of platinum ranged from US$1,055 to US$1,320 per troy ounce.
Read More About Platinum / Source
Plattnerite

Plattnerite is an oxide mineral and is the beta crystalline form of lead dioxide (β-PbO2), scrutinyite being the other, alpha form. It was first reported in 1845 and named after German mineralogist Karl Friedrich Plattner. Plattnerite forms bundles of dark needle-like crystals on various minerals; the crystals are hard and brittle and have tetragonal symmetry.
Read More About Plattnerite / Source
Playfairite
Playfairite is a rare sulfosalt mineral with chemical formula Pb16Sb18S43 in the monoclinic crystal system, named after the Scottish scientist and mathematician John Playfair. It was discovered in 1966 by the Canadian mineralogist John Leslie Jambor. Lead gray to black in color, its luster is metallic. Playfairite shows strong reflection pleochroism from white to brownish gray. Playfairite has a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on Mohs scale and a specific gravity of approximately 5.72.The type locality is Taylor Pit (Concession XIV; Lot 13), Huntingdon Township, Hastings County in Ontario, Canada. Small deposits have also been found in Les Cougnasses Mine, Orpierre in the Haut-Alpes in France, Khaidarkan Sb-Hg deposit (Chaidarkan), Fergana Valley, Alai Range, Osh Oblast, Kyrgyzstan and Reese River District, Lander County, Nevada, USA.
Read More About Playfairite / Source
Plumbogummite

Plumbogummite is a rare secondary lead phosphate mineral, belonging to the alunite supergroup of minerals, crandallite subgroup. Some other members of this subgroup are:
Crandallite, CaAl3(PO4)2(OH)5·H2O, where calcium replaces lead
Goyazite, SrAl3(PO4)2(OH)5·H2O, where strontium replaces lead
Philipsbornite, PbAl3(AsO4)2(OH)5·H2O, where the arsenate group AsO4 replaces the phosphate group PO4Plumbogummite was discovered in 1819 and named in 1832 from the Latin “plumbum” for lead, and “gummi” for gum, in allusion to its lead content and appearance, which at times resembles coatings of gum.
Read More About Plumbogummite / Source
Polarite

Polarite, is an opaque, yellow-white mineral with the chemical formula Pd,(Bi,Pb). Its crystals are orthorhombic pyramidal, but can only be seen through a microscope. It has a metallic luster and leaves a white streak. Polarite is rated 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs Scale.It was first described in 1969 for an occurrence in Talnakh, Norilsk in the Polar Ural Mountains in Russia. It has also been recorded from the Bushveld igneous complex of South Africa and from Fox Gulch, Goodnews Bay, Alaska.
Read More About Polarite / Source
Pollucite

Pollucite is a zeolite mineral with the formula (Cs,Na)2Al2Si4O12·2H2O with iron, calcium, rubidium and potassium as common substituting elements. It is important as a significant ore of caesium and sometimes rubidium. It forms a solid solution series with analcime. It crystallizes in the isometric – hexoctahedral crystal system as colorless, white, gray, or rarely pink and blue masses. Well formed crystals are rare. It has a Mohs hardness of 6.5 and a specific gravity of 2.9. It has a brittle fracture and no cleavage.
Read More About Pollucite / Source
Polybasite

Polybasite is a sulfosalt mineral of silver, copper, antimony and arsenic. Its chemical formula is [(Ag,Cu)6(Sb,As)2S7][Ag9CuS4].
It forms black monoclinic crystals (thin, tabular, with six corners) which can show dark red internal reflections. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3. It is found worldwide and is an ore of silver. The name comes from the number of base metals in the mineral.
Read More About Polybasite / Source
Polycrase

Polycrase or polycrase-(Y) is a black or brown metallic complex uranium yttrium oxide mineral with the chemical formula (Y,Ca,Ce,U,Th)(Ti,Nb,Ta)2O6. It is amorphous. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 5. It is radioactive due to its uranium content (around 6%). It occurs in granitic pegmatites.
Polycrase forms a continuous series with the niobium rich rare earth oxide euxenite.
It was first described in 1870 at Rasvag, Hidra (Hittero) Island, near Flekkefjord, Norway. It is found in Sweden, Norway, and the United States.
Read More About Polycrase / Source
Polydymite

Polydymite, Ni2+Ni23+S4, is a supergene thiospinel sulfide mineral associated with the weathering of primary pentlandite nickel sulfide.
Polydymite crystallises in the isometric system, with a hardness of 4.5 to 5.5 and a specific gravity of about 4, is dark violet gray to copper-red, often with verdigris and patina from associated copper and arsenic sulfides, and is typically in amorphous to massive infill of lower saprolite ultramafic lithologies.
Polydymite is the nickel equivalent of violarite and in many cases these two minerals are formed together, potentially in solid solution.
Common contaminants of polydymite are cobalt and iron. Polydymite forms a series with linnaeite, Co+2Co+32S4.
Read More About Polydymite / Source
Polyhalite

Polyhalite is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated sulfate of potassium, calcium and magnesium with formula: K2Ca2Mg(SO4)4·2H2O. Polyhalite crystallizes in the triclinic system, although crystals are very rare. The normal habit is massive to fibrous. It is typically colorless, white to gray, although it may be brick red due to iron oxide inclusions. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 and a specific gravity of 2.8.
It occurs in sedimentary marine evaporites and is a major potassium ore mineral in the Carlsbad deposits of New Mexico. It is also present as a 2–3% contaminant of Himalayan salt.
Polyhalite was first described in 1818 for specimens from its type locality in Salzburg, Austria. The name comes from the German Polyhalit, which comes from the Ancient Greek words πολύς (polys) and ἅλς (hals), which mean “many” and “salt”, and the German ending -it (which comes from the Latin ending -ites, which originally also came from Greek), which is used like the English ending -ite to form the names of certain chemical compounds.Despite the similarity in names between polyhalite and halite (the naturally occurring form of table salt), their only connection is that both are evaporite minerals. The use of the Greek words for many and salt in polyhalite is due to polyhalite consisting of several metals that can form salts in the more general sense of the word salt used in chemistry.
Read More About Polyhalite / Source
Portlandite

Portlandite is a hydroxide-bearing mineral typically included in the oxide mineral class. It is the naturally occurring form of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and the calcium analogue of brucite (Mg(OH)2).
Read More About Portlandite / Source
Posnjakite

Posnjakite is a hydrated copper sulfate mineral. It was discovered in the Tungsten deposit of Nura-Taldy in Karaganda Region in Kazakhstan and described in 1967 by Aleksandr Ivanovich Komkov (1926–1987) and Yevgenii Ivanovich Nefedov (1910–1976) and named after geochemist Eugene Valdemar Posnjak (1888–1949).
Read More About Posnjakite / Source
Poudretteite

Poudretteite is an extremely rare mineral and gemstone that was first discovered as minute crystals in Mont St. Hilaire, Quebec, Canada, during the 1960s. The mineral was named for the Poudrette family because they operated a quarry in the Mont St. Hilaire area where poudretteite was originally found, and the quarry is currently owned by the United Kingdom based Salmon Mining Industries Inc. Poudretteite has a barely detectable radioactivity.
Read More About Poudretteite / Source
Povondraite

Povondraite is a rare silicate mineral from the tourmaline group with formula: NaFe3+3(Fe3+4,Mg2)(BO3)3Si6O18(OH)3O. It is a dark brown to black nearly opaque mineral with a resinous to splendent luster. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system as equant, distorted prisms with trigonal pyramid terminations.It occurs as rare fracture and cavity encrustations within schists derived from sedimentary rocks. Associated minerals include quartz, potassium feldspar, muscovite, schorl, riebeckite and magnesite.Discovered at the San Francisco mine, near Villa Tunari (in Alto Chapare), Bolivia, in 1976, originally it was called ferridravite, for the composition and the assumed relationship to dravite, i.e., “ferric dravite”. However later investigations yielded a new empirical formula which had no relation to the dravite. This called for renaming, and the new name, after Pavel Povondra (1924–2013), a mineralogist at the Charles University in Prague, was approved by the International Mineralogical Association in the 1990s.
Read More About Povondraite / Source
Powellite

Powellite is a calcium molybdate mineral with formula CaMoO4. Powellite crystallizes with tetragonal – dipyramidal crystal structure as transparent adamantine blue, greenish brown, yellow to grey typically anhedral forms. It exhibits distinct cleavage and has a brittle to conchoidal fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 4.25. It forms a solid solution series with scheelite (calcium tungstate, CaWO4). It has refractive index values of nω=1.974 and nε=1.984.Powellite was first described by William Harlow Melville in 1891 for an occurrence in the Peacock Mine, Adams County, Idaho and named for American explorer and geologist, John Wesley Powell (1834–1902).It occurs in hydrothermal ore deposits of molybdenum within the near surface oxidized zones. It also appears as a rare mineral phase in pegmatite, tactite and basalt. Minerals found in association with powellite include molybdenite, ferrimolybdite, stilbite, laumontite and apophyllite.
Read More About Powellite / Source
Prehnite

Prehnite is an inosilicate of calcium and aluminium with the formula: Ca2Al(AlSi3O10)(OH)2. Limited Fe3+ substitutes for aluminium in the structure. Prehnite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system, and most often forms as stalactitic or botryoidal aggregates, with only just the crests of small crystals showing any faces, which are almost always curved or composite. Very rarely will it form distinct, well-individualized crystals showing a square-like cross-section, including those found at the Jeffrey Mine in Asbestos, Quebec, Canada. Prehnite is brittle with an uneven fracture and a vitreous to pearly luster. Its hardness is 6-6.5, its specific gravity is 2.80-2.90 and its color varies from light green to yellow, but also colorless, blue, pink or white. In April 2000, rare orange prehnite was discovered in the Kalahari Manganese Fields, South Africa. Prehnite is mostly translucent, and rarely transparent.
Though not a zeolite, prehnite is found associated with minerals such as datolite, calcite, apophyllite, stilbite, laumontite, and heulandite in veins and cavities of basaltic rocks, sometimes in granites, syenites, or gneisses. It is an indicator mineral of the prehnite-pumpellyite metamorphic facies.
It was first described in 1788 for an occurrence in the Karoo dolerites of Cradock, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. It was named for Colonel Hendrik Von Prehn (1733–1785), commander of the military forces of the Dutch colony at the Cape of Good Hope from 1768 to 1780.It is used as a gemstone.Extensive deposits of gem-quality prehnite occur in the basalt tableland surrounding Wave Hill Station in the central Northern Territory, of Australia.
Read More About Prehnite / Source
Proustite

Proustite is a sulfosalt mineral consisting of silver sulfarsenide, Ag3AsS3, known also as light red silver or ruby silver ore, and an important source of the metal. It is closely allied to the corresponding sulfantimonide, pyrargyrite, from which it was distinguished by the chemical analyses of Joseph L. Proust (1754–1826) in 1804, after whom the mineral received its name.
The prismatic crystals are often terminated by the scalenohedron and the obtuse rhombohedron, thus resembling calcite (dog-tooth-spar) in habit. The color is scarlet-vermilion and the luster adamantine; crystals are transparent and very brilliant, but on exposure to light they soon become dull black and opaque. The streak is scarlet, the hardness 2 to 2.5, and the specific gravity 5.57. Its transparency differs from specimen to specimen, but most are opaque or translucent.Proustite occurs in hydrothermal deposits as a phase in the oxidized and supergene zone. It is associated with other silver minerals and sulfides such as native silver, native arsenic, xanthoconite, stephanite, acanthite, tetrahedrite and chlorargyrite.Magnificent groups of large crystals have been found at Chañarcillo in Chile; other localities which have yielded fine specimens are Freiberg and Marienberg in Saxony, Joachimsthal in Bohemia and Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines in Alsace.
Read More About Proustite / Source
Pseudomalachite

Pseudomalachite is a phosphate of copper with hydroxyl, named from the Greek for “false” and “malachite”, because of its similarity in appearance to the carbonate mineral malachite, Cu2(CO3)(OH)2. Both are green coloured secondary minerals found in oxidised zones of copper deposits, often associated with each other. Pseudomalachite is polymorphous with reichenbachite and ludjibaite. It was discovered in 1813.
Prior to 1950 it was thought that dihydrite, lunnite, ehlite, tagilite and prasin were separate mineral species, but Berry analysed specimens labelled with these names from several museums, and found that they were in fact pseudomalachite. The old names are no longer recognised by the IMA.
Read More About Pseudomalachite / Source
Pseudowollastonite

Pseudowollastonite is a high-temperature mineral phase of CaSiO3 and is polymorphous with wollastonite. Its formula can alternatively be written as Ca3Si3O9. Other names include ß-Wollastonite, and cyclowollastonite.It occurs in high temperature (pyrometamorphic) environments such as the Hatrurim Formation of the Negev Desert and the graphite mine at Pfaffenrenth near Hauzenberg, Bavaria. It also occurs in slags and cement.
Read More About Pseudowollastonite / Source
Pumpellyite

Pumpellyite is a group of closely related sorosilicate minerals:
pumpellyite-(Mg): Ca2MgAl2[Si2O6OH][SiO4](OH)2(OH)
pumpellyite-(Fe2+): Ca2Fe2+Al2[Si2O6OH][SiO4](OH)2(OH)
pumpellyite-(Fe3+): Ca2Fe3+Al2[Si2O6OH][SiO4](OH)2O
pumpellyite-(Mn2+): Ca2Mn2+Al2[Si2O6OH][SiO4](OH)2(OH)
pumpellyite-(Al): Ca2AlAl2[Si2O6OH][SiO4](OH)2OPumpellyite crystallizes in the monoclinic-prismatic crystal system. It typically occurs as blue-green to olive green fibrous to lamellar masses. It is translucent and glassy with a Mohs hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 3.2. It has refractive indices of nα=1.674–1.748, nβ=1.675–1.754 and nγ=1.688–1.764.
Pumpellyite occurs as amygdaloidal and fracture fillings in basaltic and gabbroic rocks in metamorphic terranes. It is an indicator mineral of the prehnite-pumpellyite metamorphic facies. It is associated with chlorite, epidote, quartz, calcite and prehnite.
It was first described in 1925 for occurrences in the Calumet mine, Houghton Co., Keweenaw Peninisula, Michigan and named for United States geologist, Raphael Pumpelly (1837–1923).
Read More About Pumpellyite / Source
Purpurite

Purpurite is a mineral, manganese phosphate, MnPO4 with varying amounts of iron depending upon its source. It occurs in color ranges from brownish black via purple and violet to dark red.Purpurite forms a series with the iron-bearing endmember heterosite, FePO4.
Read More About Purpurite / Source
Putnisite

Putnisite is a mineral composed of strontium, calcium, chromium, sulfur, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. It was discovered on the Polar Bear Peninsula in Shire of Dundas, Western Australia in 2007 during mining activity. Following identification and recognition by the IMA in 2012 the mineral was named after mineralogists Andrew and Christine Putnis.Putnisite has unique chemical and structural properties, and does not appear to be related to any of the existing mineralogical families. Crystals are translucent purple, but show distinct pleochroism (from pale purple to pale bluish grey, depending on the angle of observation) and leave pink streaks when rubbed on a flat surface.Putnisite occurs as small (< 0.5 mm) cube-like crystals in volcanic rock. The mineral formed during the oxidation environment within komatiite to dioritic bodies containing sulfide minerals.
Read More About Putnisite / Source
Pyrargyrite

Pyrargyrite is a sulfosalt mineral consisting of silver sulfantimonite, Ag3SbS3. Known also as dark red silver ore or ruby silver, it is an important source of the metal.
It is closely allied to, and isomorphous with, the corresponding sulfarsenide known as proustite or light red silver ore. Ruby silver or red silver ore (German Rotgültigerz) was mentioned by Georg Agricola in 1546, but the two species so closely resemble one another that they were not completely distinguished until chemical analyses of both were made.
Both crystallize in the ditrigonal pyramidal (hemimorphic-hemihedral) class of the rhombohedral system, possessing the same degree of symmetry as tourmaline. Crystals are perfectly developed and are usually prismatic in habit; they are frequently attached at one end, the hemimorphic character being then evident by the fact that the oblique striations on the prism faces are directed towards one end only of the crystal. Twinning according to several laws is not uncommon. The hexagonal prisms of pyrargyrite are usually terminated by a low hexagonal pyramid or by a drusy basal plane.
The color of pyrargyrite is usually greyish-black and the lustre metallic-adamantine; large crystals are opaque, but small ones and thin splinters are deep ruby-red by transmitted light, hence the name, from the Greek pyr and argyros, “fire-silver” in allusion to color and silver content, given by E. F. Glocker in 1831. The streak is purplish-red, thus differing markedly from the scarlet streak of proustite and affording a ready means of distinguishing the two minerals. The Mohs hardness is 2.75, and the specific gravity 5.85. The refractive indices (nω=3.084 nε=2.881) and birefringence (δ=0.203) are very high. There is no very distinct cleavage and the fracture is conchoidal. The mineral occurs in metalliferous veins with calcite, argentiferous galena, native silver, native arsenic, &c. The best crystallized specimens are from Sankt Andreasberg in the Harz, Freiberg in Saxony, and Guanajuato in Mexico. It is not uncommon in many silver mines in the United States, but rarely as distinct crystals; and it has been found in some Cornish mines.
Although the red silver ores afford a good example of isomorphism, they rarely form mixtures; pyrargyrite rarely contains as much as 3% of arsenic replacing antimony, and the same is true of antimony in proustite. Dimorphous with pyrargyrite and proustite respectively are the rare monoclinic species pyrostilpnite or fireblende (Ag3SbS3) and xanthoconite (Ag3AsS3): these four minerals thus form an isodimorphous group.
Read More About Pyrargyrite / Source
Pyrite

The mineral pyrite , or iron pyrite, also known as fool’s gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula FeS2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite’s metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of fool’s gold. The color has also led to the nicknames brass, brazzle, and Brazil, primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal.The name pyrite is derived from the Greek πυρίτης λίθος (pyritēs lithos), ‘stone or mineral which strikes fire’, in turn from πῦρ (pyr), ‘fire’. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite.By Georgius Agricola’s time, c. 1550, the term had become a generic term for all of the sulfide minerals.
Pyrite is usually found associated with other sulfides or oxides in quartz veins, sedimentary rock, and metamorphic rock, as well as in coal beds and as a replacement mineral in fossils, but has also been identified in the sclerites of scaly-foot gastropods. Despite being nicknamed “fool’s gold”, pyrite is sometimes found in association with small quantities of gold. A substantial proportion of the gold is “invisible gold” incorporated into the pyrite (see Carlin-type gold deposit). It has been suggested that the presence of both gold and arsenic is a case of coupled substitution but as of 1997 the chemical state of the gold remained controversial.
Read More About Pyrite / Source
Pyrochlore

Pyrochlore (Na,Ca)2Nb2O6(OH,F) is a mineral group of the niobium end member of the pyrochlore supergroup.
The general formula, A2B2O7 (where A and B are metals), represent a family of phases isostructural to the mineral pyrochlore.
Pyrochlores are an important class of materials in diverse technological applications such as luminescence, ionic conductivity, nuclear waste immobilization, high temperature thermal barrier coatings, automobile exhaust gas control, catalysts, solid oxide fuel cell, ionic/electrical conductors etc.
Read More About Pyrochlore / Source
Pyrolusite

Pyrolusite is a mineral consisting essentially of manganese dioxide (MnO2) and is important as an ore of manganese. It is a black, amorphous appearing mineral, often with a granular, fibrous, or columnar structure, sometimes forming reniform crusts. It has a metallic luster, a black or bluish-black streak, and readily soils the fingers. The specific gravity is about 4.8. Its name is from the Greek for fire and to wash, in reference to its use as a way to remove tints from glass.
Read More About Pyrolusite / Source
Pyromorphite

Pyromorphite is a mineral species composed of lead chlorophosphate: Pb5(PO4)3Cl, sometimes occurring in sufficient abundance to be mined as an ore of lead. Crystals are common, and have the form of a hexagonal prism terminated by the basal planes, sometimes combined with narrow faces of a hexagonal pyramid. Crystals with a barrel-like curvature are not uncommon. Globular and reniform masses are also found. It is part of a series with two other minerals: mimetite (Pb5(AsO4)3Cl) and vanadinite (Pb5(VO4)3Cl), the resemblance in external characters is so close that, as a rule, it is only possible to distinguish between them by chemical tests. They were formerly confused under the names green lead ore and brown lead ore (German: Grünbleierz and Braunbleierz).
The phosphate was first distinguished chemically by M. H. Klaproth in 1784, and it was named pyromorphite by J. F. L. Hausmann in 1813. The name is derived from the Greek for pyr (fire) and morfe (form) due to its crystallization behavior after being melted.Paecilomyces javanicus is a mold collected from a lead-polluted soil that is able to form biominerals of pyromorphite.
Read More About Pyromorphite / Source
Pyrope

The mineral pyrope is a member of the garnet group. Pyrope is the only member of the garnet family to always display red colouration in natural samples, and it is from this characteristic that it gets its name: from the Greek for fire and eye. Despite being less common than most garnets, it is a widely used gemstone with numerous alternative names, some of which are misnomers. Chrome pyrope, and Bohemian garnet are two alternative names, the usage of the latter being discouraged by the Gemological Institute of America. Misnomers include Colorado ruby, Arizona ruby, California ruby, Rocky Mountain ruby, Elie Ruby, Bohemian carbuncle, and Cape ruby.
The composition of pure pyrope is Mg3Al2(SiO4)3, although typically other elements are present in at least minor proportions—these other elements include Ca, Cr, Fe and Mn. Pyrope forms a solid solution series with almandine and spessartine, which are collectively known as the pyralspite garnets (pyrope, almandine, spessartine). Iron and manganese substitute for the magnesium in the pyrope structure. The resultant, mixed composition garnets are defined according to their pyrope-almandine ratio. The semi-precious stone rhodolite is a garnet of ~70% pyrope composition.
The origin of most pyrope is in ultramafic rocks, typically peridotite from the Earth’s mantle: these mantle-derived peridotites can be attributed both to igneous and metamorphic processes. Pyrope also occurs in ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks, as in the Dora-Maira massif in the western Alps. In that massif, nearly pure pyrope occurs in crystals to almost 12 cm (5 in) in diameter; some of that pyrope has inclusions of coesite, and some has inclusions of enstatite and sapphirine.
Pyrope is common in peridotite xenoliths from kimberlite pipes, some of which are diamond-bearing. Pyrope found in association with diamond commonly has a Cr2O3 content of 3–8%, which imparts a distinctive violet to deep purple coloration (often with a greenish tinge) and because of this is often used as a kimberlite indicator mineral in areas where erosive activity makes pinpointing the origin of the pipe difficult. These varieties are known as chrome-pyrope, or G9/G10 garnets.
Read More About Pyrope / Source
Pyrophanite

Pyrophanite is a manganese titanium oxide mineral with formula: MnTiO3. It is a member of the ilmenite group. It is a deep red to greenish black mineral which crystallizes in the trigonal system.
Read More About Pyrophanite / Source
Pyrophyllite

Pyrophyllite is a phyllosilicate mineral composed of aluminium silicate hydroxide: Al2Si4O10(OH)2. It occurs in two forms (habits): crystalline folia and compact masses; distinct crystals are not known.
The folia have a pronounced pearly luster, owing to the presence of a perfect cleavage parallel to their surfaces: they are flexible but not elastic, and are usually arranged radially in fan-like or spherical groups. This variety, when heated, exfoliates and swells up to many times its original volume, hence the name pyrophyllite, from the Greek pyro- (πυρο-, the combining form of πῦρ fire) and phyllos (a leaf), given by R. Hermann in 1829. The color of both varieties is white, pale green, greyish or yellowish; they are very soft (hardness of 1.0 to 1.5) and are greasy to the touch. The specific gravity is 2.65 – 2.85. The two varieties are thus very similar to talc.
Read More About Pyrophyllite / Source
Pyroxene

The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to Px) are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula XY(Si,Al)2O6, where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) or magnesium (Mg) and more rarely zinc, manganese or lithium, and Y represents ions of smaller size, such as chromium (Cr), aluminium (Al), magnesium (Mg), cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V) or even iron (Fe II or Fe III). Although aluminium substitutes extensively for silicon in silicates such as feldspars and amphiboles, the substitution occurs only to a limited extent in most pyroxenes. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra. Pyroxenes that crystallize in the monoclinic system are known as clinopyroxenes and those that crystallize in the orthorhombic system are known as orthopyroxenes.
The name pyroxene is derived from the Ancient Greek words for ‘fire’ (pyr πυρ) and ‘stranger’ (ksénos ξένος). Pyroxenes were so named because of their presence in volcanic lavas, where they are sometimes found as crystals embedded in volcanic glass; it was assumed they were impurities in the glass, hence the name meaning ‘fire-strangers’. However, they are simply early-forming minerals that crystallized before the lava erupted.
The upper mantle of Earth is composed mainly of olivine and pyroxene minerals. Pyroxene and feldspar are the major minerals in basalt, andesite, and gabbro rocks.
Read More About Pyroxene / Source
Pyroxferroite
Pyroxferroite (Fe2+,Ca)SiO3 is a single chain inosilicate. It is mostly composed of iron, silicon and oxygen, with smaller fractions of calcium and several other metals. Together with armalcolite and tranquillityite, it is one of the three minerals which were discovered on the Moon during the 1969 Apollo 11 mission. It was then found in Lunar and Martian meteorites as well as a mineral in the Earth’s crust. Pyroxferroite can also be produced by annealing synthetic clinopyroxene at high pressures and temperatures. The mineral is metastable and gradually decomposes at ambient conditions, but this process can take billions of years.
Read More About Pyroxferroite / Source
Pyroxmangite

Pyroxmangite has the general chemical formula of MnSiO3. It is the high-pressure, low-temperature dimorph of rhodonite.It was first described in 1913 and named for the mineral group, pyroxenes, and is known as the manganese member. It forms a series with pyroxferroite.
Pyroxmangite occurs in metamorphosed ore deposits rich in manganese. Associated minerals include spessartine, tephroite, alleghanyite, hausmannite, pyrophanite, alabandite, rhodonite and rhodochrosite.
Read More About Pyroxmangite / Source
Pyrrhotite

Pyrrhotite (pyrrhos in Greek meaning “flame-coloured”) is an iron sulfide mineral with the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2). It is a nonstoichiometric variant of FeS, the mineral known as troilite.
Pyrrhotite is also called magnetic pyrite, because the color is similar to pyrite and it is weakly magnetic. The magnetism decreases as the iron content decreases, and troilite is non-magnetic. Pyrrhotite is generally tabular and brassy/bronze in color with a metallic luster. The mineral occurs with mafic igneous rocks like norites, and may form from pyrite during metamorphic processes. Pyrrhottie is associated and mined with other sulfide minerals like pentlandite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, and magnetite, and has been found globally.
Read More About Pyrrhotite / Source
Qingsongite
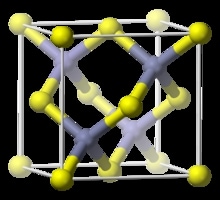
Qingsongite is a rare boron nitride mineral with cubic crystalline form. It was first described in 2009 for an occurrence as minute inclusions within chromite deposits in the Luobusa ophiolite in the Shannan Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It was recognized as a mineral in August 2013 by the International Mineralogical Association. It is named after Chinese geologist Qingsong Fang (1939–2010). Qingsongite is the only known boron mineral that is formed deep in the Earth’s mantle. Associated minerals or phases include osbornite (titanium nitride), coesite, kyanite and amorphous carbon.
Read More About Qingsongite / Source
Quartz

Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth’s continental crust, behind feldspar.Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at 573 °C (846 K; 1,063 °F). Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold.
There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia.
Quartz is the mineral defining the value of 7 on the Mohs scale of hardness, a qualitative scratch method for determining the hardness of a material to abrasion.
Read More About Quartz / Source
Quenstedtite

Quenstedtite is an uncommon iron sulfate mineral with chemical formula Fe2(SO4)3·11H2O. It forms violet or white triclinic crystals. Found in oxidized zones of pyrite-rich orebodies, especially in arid climates. It was first reported in 1888 for an occurrence in Tierra Amarilla, Copiapó Province, Atacama Region, Chile and named by G. Linck in 1889 for the German mineralogist F. A. von Quenstedt (1809–1889).
Read More About Quenstedtite / Source
Quetzalcoatlite
Quetzalcoatlite is a rare tellurium oxysalt mineral with the formula Zn6Cu3(TeO6)2(OH)6 · AgxPbyClx+2y. It also contains large amounts of silver- and lead(II)chloride with the formula AgxPbyClx+2y (x+y≤2). It has a Mohs hardness of 3 and it crystallizes in the trigonal system. It has a deep blue color. It was named after Quetzalcoatl, the Aztec and Toltec god of the sea, alluding to its color. It is not to be confused with tlalocite, which has a similar color and habit.
Read More About Quetzalcoatlite / Source
Quintinite

Quintinite is a carbonate mineral with the chemical formula Mg4Al2(OH)12CO3⋅3H2O.The mineral was named after Quintin Wight of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada (b. 1935), who was a significant contributor to mineral studies at Mont Saint-Hilaire.Quintinite is found as 2H and 3T, or 2-hexagonal and 3-trigonal, polytypes, which were originally approved as separate species, but have not been considered species since 1998. These hexagonal and trigonal forms of quintinite are both from the hexagonal crystal systems, meaning they both have similar lengths of their crystal axes and the same angles between these axes. As a hexagonal mineral, quintinite has three axes of equal length at 60 degree angles to one another and a c axis perpendicular to these three axes of a different length. 2H occurs in carbonatite at Jacupiranga, São Paulo, Brazil, in the Jacupiranga mine and 3T occurs with minerals like gonnardite and donnayite. Both polytypes occur in hydrothermal vents in alkaline rocks. Herg (1977) interpreted the Jacupiranga area as related to a hotspot. The 3T polytype was originally found in the Poudrette quarry at Mont Saint-Hilaire, which is a rare alkaline intrusive complex. The 2H polytype is pleochroic, meaning that the mineral changes colors (in this case yellow and light yellow) when viewed at different angles under a polarizing petrographic microscope. The 3T polytype, however, is not commonly pleochroic but can show green pleochroism if it is high in iron. The 3T polytype has a positive index of refraction whereas the 2H polytype can possess crystals with either a positive or a negative index of refraction.
Read More About Quintinite / Source
Qusongite
Qusongite is an extremely rare mineral with the simple formula WC, which shows the mineral to be a naturally occurring tungsten carbide. It was found in Luobusa ophiolite, China. This ophiolite is known for many natural reduced compounds, including native metals, diamond, silicides and carbides (e.g., moissanite, natural silicon carbide). Qusongite crystallizes in the hexagonal system, with space group P-6m2.
Read More About Qusongite / Source
Rakovanite

Rakovanite, Na3{H3[V10O28]}•15H20, is a member of the pascoite family. It is a transparent, brittle mineral occurring in the monoclinic crystal system. It is orange in color and has an orange-yellow colored streak. Rakovanite is soft with a Mohs hardness of 1 and a calculated density of 2.407g cm−3. It does not fluoresce in long- or short-wave ultraviolet radiation. Rakovanite crystals are up to one mm in maximum dimension and vary in habit from blocky to prismatic on [001], commonly exhibiting steps and striations parallel to [001]. Its name honors John Rakovan, professor, Department of Geology and Environmental Earth Science, Miami University.
Read More About Rakovanite / Source
Rambergite
Rambergite is a manganese sulfide mineral with formula MnS.
It has been found in anoxic marine sediments, rich in organic matter of the Gotland Deep, Baltic Sea and also in skarn in the Garpenberg area, Dalarna, Sweden. It was named after the mineralogist, Hans Ramberg (1917–1998).It is a member of the wurtzite group and is chemically related to hauerite.
Read More About Rambergite / Source
Rameauite
Rameauite is a hydrated complex uranyl oxide mineral with formula K2Ca(UO2)6OH16·H2O or K2CaU6+6O20·9H2O.
Read More About Rameauite / Source
Rammelsbergite

Rammelsbergite is a nickel arsenide mineral with formula NiAs2. It forms metallic silvery to tin white to reddish orthorhombic prismatic crystals, and is usually massive in form. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 7.1.
It was first described in 1854 from its type locality in the Schneeberg District in Saxony, Germany. It was named after the German chemist and mineralogist, Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg (1813–1899).It occurs as a hydrothermal mineral in medium temperature veins association with skutterudite, safflorite, lollingite, nickeline, native bismuth, native silver, algodonite, domeykite and uraninite.
Read More About Rammelsbergite / Source
Rapidcreekite

Rapidcreekite is a rare mineral with formula Ca2(SO4)(CO3)·4H2O. The mineral is white to colorless and occurs as groupings of acicular (needle-shaped) crystals. It was discovered in 1983 in northern Yukon, Canada, and described in 1986. Rapidcreekite is structurally and compositionally similar to gypsum.
Read More About Rapidcreekite / Source
Raslakite

Raslakite is a rare mineral of the eudialyte group with the chemical formula Na15Ca3Fe3(Na,Zr)3Zr3(Si,Nb)SiO(Si9O27)2(Si3O9)2(OH,H2O)3(Cl,OH). This formula is based on the original one, and is extended to show the presence of cyclic silicate groups. The additional silicon and oxygen shown in separation from the cyclic groups (in parentheses) are in fact connected with two 9-fold rings. The mineral has lowered symmetry (space group R3, instead of more specific for the group R3m one), similarly to some other eudialyte-group members: aqualite, labyrinthite, oneillite and voronkovite. The specific feature of raslakite is, among others, the presence of sodium and zirconium at the M2 site. Raslakite was named after Raslak Cirques located nearby the type locality.
Read More About Raslakite / Source
Raspite

Raspite is a mineral, a lead tungstate; with the formula PbWO4. It forms yellow to yellowish brown monoclinic crystals. It is the low temperature monoclinic dimorph of the tetragonal stolzite.It was discovered in 1897 at Broken Hill, New South Wales, Australia, it was named for Charles Rasp (1846–1907), German-Australian prospector, discoverer of the Broken Hill ore deposit.
Read More About Raspite / Source
Rastsvetaevite

Rastsveatevite is a rare mineral of the eudialyte group with the chemical formula Na27K8Ca12Fe3Zr6Si4[Si3O9]4[Si9O27]4(O,OH,H2O)6Cl2. Its structure is modular. It is only the third member of the group after andrianovite and davinciite with essential (site-dominating) potassium. Potassium and sodium enter both N4 and M2 sites. The mineral is named after Russian crystallographer Ramiza K. Rastsvetaeva.
Read More About Rastsvetaevite / Source
Realgar

Realgar ( ree-AL-gar, -gər), also known as “ruby sulphur” or “ruby of arsenic”, is an arsenic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula α-As4S4. It is a soft, sectile mineral occurring in monoclinic crystals, or in granular, compact, or powdery form, often in association with the related mineral, orpiment (As2S3). It is orange-red in color, melts at 320 °C, and burns with a bluish flame releasing fumes of arsenic and sulfur. Realgar is soft with a Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2 and has a specific gravity of 3.5. Its streak is orange colored. It is trimorphous with pararealgar and bonazziite.
Its name comes from the Arabic rahj al-ġār (رهج الغار, “powder of the mine”), via Medieval Latin, and its earliest record in English is in the 1390s.
Read More About Realgar / Source
Reederite-(Y)
Reederite-(Y) is a rare mineral with the formula (Na,Mn,Fe)15(Y,REE)2(CO3)9(SO3F)Cl. It is the only known mineral with fluorosulfate (fluorosulfonate). “REE” in the formula stands for rare earth elements other than yttrium, that is mostly cerium, with traces of neodymium, dysprosium, lanthanum and erbium. The formula also includes a Levinson suffix “-(Y)” pointing to the dominance of yttrium at the corresponding site. Reederite-(Y) crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system with the space group P6, rarely seen among minerals.
Read More About Reederite-(Y) / Source
Reedmergnerite

Reedmergnerite is a borosilicate mineral named in honor of Frank S. Reed and John L. Mergner. It is approved by the International Mineralogical Association but was first described prior to the association’s formation, first published in 1955. Although it is approved, it got grandfathered, meaning the name reedmergnerite is still believed to refer to a valid species. Reedmergnerite has a synthetic potassium analogue.
Read More About Reedmergnerite / Source
Reidite
Reidite is a rare polymorph of ZrSiO4 created when zircon experiences high pressure and temperature. Reidite is denser than zircon and has the same crystal structure as scheelite. All natural occurrences of reidite are associated with meteorite impact events.
On Earth, reidite has been reported from ten impact structures: the Chesapeake Bay Crater in Virginia; Ries Crater in Germany; Xiuyan Crater in China; Woodleigh Crater in Western Australia; Rock Elm Crater in Wisconsin; Dhala Crater in India; Stac Fada in Scotland; Haughton in Canada; Steen River in Canada, and Rochechouart in France. Reidite has also been found in one lunar meteorite.
Read More About Reidite / Source
Reinerite
Reinerite is a rare arsenite (arsenate(III)) mineral with chemical formula Zn3(AsO3)2. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system.
Read More About Reinerite / Source
Renierite

Renierite is a rare copper zinc germanium bearing sulfide mineral with the chemical formula (Cu,Zn)11(Ge,As)2Fe4S16. It occurs at the Kipushi Mine, Democratic Republic of the Congo; and Namibia, among other places.
Renierite was named after Armand Renier (26 June 1876 – 9 October 1951), a Belgian geologist and director of the Belgian Geological Survey.
Read More About Renierite / Source
Rheniite

Rheniite is a very rare rhenium sulfide mineral with the chemical formula (ReS2). It forms metallic, silver grey platey crystals in the triclinic – pinacoidal class. It has a specific gravity of 7.5.
It was discovered at the Kudriavy Volcano, Iturup Island in the Kurile Islands, Russia and approved in 2004. It is found in active hot fumaroles on the volcano.
Rheniite is one of the first minerals of the element rhenium to be found. The other known approved rhenium mineral is the sulfide mineral tarkianite. Almost all commercially mined rhenium is retrieved as a by-product of molybdenum mining as rhenium occurs in amounts up to 0.2% in the mineral molybdenite. A discredited rhenium sulfide known as zappinite does not appear to be valid.
Rheniite has also been reported in the Pagoni Rachi Mo–Cu–Te–Ag–Au deposit in northeastern Greece where it occurs with molybdenite in quartz veins associated with an epithermal system in a dacite porphyry.
Read More About Rheniite / Source
Rhodium

Rhodium is a chemical element with the symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isotope: 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is usually found as a free metal or as an alloy with similar metals and rarely as a chemical compound in minerals such as bowieite and rhodplumsite. It is one of the rarest and most valuable precious metals.
Rhodium is found in platinum or nickel ores with the other members of the platinum group metals. It was discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston in one such ore, and named for the rose color of one of its chlorine compounds.
The element’s major use (consuming about 80% of world rhodium production) is as one of the catalysts in the three-way catalytic converters in automobiles. Because rhodium metal is inert against corrosion and most aggressive chemicals, and because of its rarity, rhodium is usually alloyed with platinum or palladium and applied in high-temperature and corrosion-resistive coatings. White gold is often plated with a thin rhodium layer to improve its appearance, while sterling silver is often rhodium-plated to resist tarnishing. Rhodium is sometimes used to cure silicones: a two-part silicone in which one part containing a silicon hydride and the other containing a vinyl-terminated silicone are mixed; one of these liquids contains a rhodium complex.Rhodium detectors are used in nuclear reactors to measure the neutron flux level. Other uses of rhodium include asymmetric hydrogenation used to form drug precursors and the processes for the production of acetic acid.
Read More About Rhodium / Source
Rhodochrosite

Rhodochrosite is a manganese carbonate mineral with chemical composition MnCO3. In its pure form (rare), it is typically a rose-red colour, but it can also be shades of pink to pale brown. It streaks white, and its Mohs hardness varies between 3.5 and 4.5. Its specific gravity is between 3.45 and 3.6. It crystallizes in the trigonal system, and cleaves with rhombohedral carbonate cleavage in three directions. Crystal twinning often is present. It is often confused with the manganese silicate, rhodonite, but is distinctly softer. Rhodochrosite is formed by the oxidation of manganese ore, and is found in South Africa, China, and the Americas. It is officially listed as one of the National symbols of Argentina.
Rhodochrosite forms a complete solid solution series with iron carbonate (siderite). Calcium (as well as magnesium and zinc, to a limited extent) frequently substitutes for manganese in the structure, leading to lighter shades of red and pink, depending on the degree of substitution. This is the reason for the pink color of rhodochrosite.
Read More About Rhodochrosite / Source
Rhodonite

Rhodonite is a manganese inosilicate, with the formula (Mn, Fe, Mg, Ca)SiO3, and member of the pyroxenoid group of minerals, crystallizing in the triclinic system. It commonly occurs as cleavable to compact masses with a rose-red color (its name comes from Ancient Greek ῥόδον (rhódon) ‘rose’), often tending to brown due to surface oxidation. The rose-red hue is caused by the manganese cation (Mn2+).Rhodonite crystals often have a thick tabular habit, but are rare. It has a perfect, prismatic cleavage, almost at right angles. The hardness is 5.5–6.5, and the specific gravity is 3.4–3.7; luster is vitreous, being less frequently pearly on cleavage surfaces. The manganese is often partly replaced by iron, magnesium, calcium, and sometimes zinc, which may sometimes be present in considerable amounts; a greyish-brown variety containing as much as 20% of calcium oxide is called bustamite; fowlerite is a zinciferous variety containing 7% of zinc oxide.
The inosilicate (chain silicate) structure of rhodonite has a repeat unit of five silica tetrahedra. The rare polymorph pyroxmangite, formed at different conditions of pressure and temperature, has the same chemical composition but a repeat unit of seven tetrahedra.
Rhodonite has also been worked as an ornamental stone. In the iron and manganese mines at Pajsberg near Filipstad and Långban in Värmland, Sweden, small brilliant and translucent crystals (pajsbergite) and cleavage masses occur. Fowlerite occurs as large, rough crystals, somewhat resembling pink feldspar, with franklinite and zinc ores in granular limestone at Franklin Furnace in New Jersey.
Rhodonite is the official gemstone of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Read More About Rhodonite / Source
Rhodplumsite
Rhodplumsite is a rare rhodium-lead sulfide mineral, chemical formula Rh3Pb2S2. It was originally discovered within a platinum nugget, in grains up to 40 μm in size. Its name originates from its composition; rhodium and lead (plumbum in Latin). Although this mineral contains large amounts of rhodium, it is not an economically viable ore of rhodium due to its rarity.
Read More About Rhodplumsite / Source
Rhomboclase
Rhomboclase is an acidic iron sulfate mineral with a formula reported as H5Fe3+O2(SO4)2·2(H2O) or HFe(SO4)2·4(H2O). It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and typically occurs as tabular crystals with a rhombic outline. It occurs as transparent colorless, blue, green, yellow or grey crystals with a vitreous to pearly luster.Rhomboclase forms within the oxidizing environment of pyrite rich ore deposits and is reported as a post mine mineral of arid regions.It was first described in 1888 for an occurrence in Slovakia and was named from Latin, rhombus, rhomb, and Greek klasis, to break, for its crystal form and perfect basal cleavage.
Read More About Rhomboclase / Source
Richterite

Richterite is a sodium calcium magnesium silicate mineral belonging to the amphibole group. If iron replaces the magnesium within the structure of the mineral, it is called ferrorichterite; if fluorine replaces the hydroxyl, it is called fluororichterite. Richterite crystals are long and prismatic, or prismatic to fibrous aggregate, or rock-bound crystals. Colors of richterite range from brown, grayish-brown, yellow, brownish- to rose-red, or pale to dark green. Richterite occurs in thermally metamorphosed limestones in contact metamorphic zones. It also occurs as a hydrothermal product in mafic igneous rocks, and in manganese-rich ore deposits. Localities include Mont-Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, and Wilberforce and Tory Hill, Ontario, Canada; Långban and Pajsberg, Sweden; West Kimberley, Western Australia; Sanka, Myanmar; and, in the US, at Iron Hill, Colorado; Leucite Hills, Wyoming; and Libby, Montana. The mineral was named in 1865 for the German mineralogist Hieronymous Theodor Richter (1824–1898).
Read More About Richterite / Source
Rickardite

Rickardite is a telluride mineral, a copper telluride (Cu7Te5) or Cu3-x (x = 0 to 0.36)Te2. It was first described for an occurrence in the Good Hope Mine, Vulcan district, Gunnison County, Colorado, US, and named for mining engineer Thomas Arthur Rickard (1864–1953). It is a low temperature hydrothermal mineral that occurs associated with vulcanite, native tellurium, cameronite, petzite, sylvanite, berthierite, pyrite, arsenopyrite and bornite.
Read More About Rickardite / Source
Riebeckite

Riebeckite is a sodium-rich member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals, chemical formula Na2(Fe2+3Fe3+2)Si8O22(OH)2. It forms a solid solution series with magnesioriebeckite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system, usually as long prismatic crystals showing a diamond-shaped cross section, but also in fibrous, bladed, acicular, columnar, and radiating forms. Its Mohs hardness is 5.0–6.0, and its specific gravity is 3.0–3.4. Cleavage is perfect, two directions in the shape of a diamond; fracture is uneven, splintery. It is often translucent to nearly opaque.
Read More About Riebeckite / Source
Ringwoodite

Ringwoodite is a high-pressure phase of Mg2SiO4 (magnesium silicate) formed at high temperatures and pressures of the Earth’s mantle between 525 and 660 km (326 and 410 mi) depth. It may also contain iron and hydrogen. It is polymorphous with the olivine phase forsterite (a magnesium iron silicate).
Ringwoodite is notable for being able to contain hydroxide ions (oxygen and hydrogen atoms bound together) within its structure. In this case two hydroxide ions usually take the place of a magnesium ion and two oxide ions.Combined with evidence of its occurrence deep in the Earth’s mantle, this suggests that there is from one to three times the world ocean’s equivalent of water in the mantle transition zone from 410 to 660 km deep.This mineral was first identified in the Tenham meteorite in 1969, and is inferred to be present in large quantities in the Earth’s mantle.
Olivine, wadsleyite, and ringwoodite are polymorphs found in the upper mantle of the earth. At depths greater than about 660 kilometres (410 mi), other minerals, including some with the perovskite structure, are stable. The properties of these minerals determine many of the properties of the mantle.
Ringwoodite was named after the Australian earth scientist Ted Ringwood (1930–1993), who studied polymorphic phase transitions in the common mantle minerals olivine and pyroxene at pressures equivalent to depths as great as about 600 km.
Read More About Ringwoodite / Source
Roaldite
Roaldite is a rare meteorite mineral containing iron, nickel and nitrogen. Its chemical formula is (Fe,Ni)4N.
It was first described in 1981 for an occurrence in the Youngedin meteorite, Avon, Western Australia. It was named after Roald Norbach Nielsen (born 1928), a Danish expert in electron microprobe. The mineral has also been reported from the Jerslev meteorite, Sjaelland, Denmark, and the Canyon Diablo meteorite of Meteor Crater in Arizona.
Read More About Roaldite / Source
Robertsite

Robertsite, Ca3(Mn3+)4[(OH)3| (PO4)2]2·3(H2O) (alternatively formulated Ca2(Mn3(PO4)3O2)(H2O)3), is a secondary phosphate mineral named for Willard Lincoln Roberts (1923–1987), mineralogist and professor at South Dakota School of Mines in Rapid City, South Dakota.
The type locality for Robertsite is the Tip Top mine, Custer County, South Dakota, US. Robertsite occurs at the Tip Top Mine as minute crystal aggregates and crusts found on quartz associated with triphylite. It is a dark reddish brown to black monoclinic mineral.
It occurs as a secondary mineral in pegmatite. It is also reported from the Khoa Rang Kai phosphate deposit, Chiang Mai, Thailand in a limestone guano deposit. It is associated with rockbridgeite, ferrisicklerite, leucophosphite, jahnsite, montgomeryite, collinsite and hureaulite in the type locality. In the guano deposit it occurs with carbonate-fluorapatite, calcite, dolomite, quartz and clay minerals. In the Omo Valley of Ethiopia it occurs with mitridatite associated with fossil fish in Pliocene/Pleistocene lake sediments.Recently, in an exploration conducted by the Italian La Venta Geographical Association, confirmed the existence of Robertsite in the Puerto Princesa Subterranean River National Park, located about 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of the city center of Puerto Princesa, Palawan, Philippines.
Mitridatite group:
Arseniosiderite-mitridatite series:Ca2(Fe3+)3[(O)2|(AsO4)3]·3H2O
to
Ca2(Fe3+)3[(O)2|(PO4)3]·3H2O
Arseniosiderite-robertsite series:Ca2(Fe3+)3[(O)2|(AsO4)3]·3H2O
to
Ca3(Mn3+)4[(OH)3|(PO4)2]2·3H2O
Read More About Robertsite / Source
Rodalquilarite

Rodalquilarite is a rare iron tellurite chloride mineral with formula H3Fe3+2(Te4+O3)4Cl or Fe2(TeO2OH)3(TeO3)Cl. Rodalquilarite crystallizes in the triclinic system and typically occurs as stout green prisms and encrustations.
Read More About Rodalquilarite / Source
Romanèchite

Romanèchite ((Ba,H2O)2(Mn4+,Mn3+)5O10) is the primary constituent of psilomelane, which is a mixture of minerals. Most psilomelane is not pure romanechite, so it is incorrect to consider them synonyms. Romanèchite is a valuable ore of manganese, which is used in steelmaking and sodium battery production. It has a monoclinic crystal structure, a hardness of 6 and a specific gravity of 4.7-5. Romanèchite’s structure consists of 2 × 3 tunnels formed by Mn oxide octahedra.It is associated with hematite, barite, pyrolusite, quartz and other manganese oxide minerals. It has been found in France, Germany, England, Brazil, India, and various parts of the United States, including Arizona, Virginia, Tennessee and Michigan, and sites throughout the Appalachian Valley and Ridge.
Read More About Romanèchite / Source
Romeite

Roméite is a calcium antimonate mineral with the chemical formula (Ca,Fe,Mn,Na)2(Sb,Ti)2O6(O,OH,F). It is a honey-yellow mineral crystallizing in the hexoctahedral crystal system. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5-6.0. It occurs in Algeria, Australia, Brazil, China, Europe, Japan, New Zealand, and the United States in metamorphic iron-manganese deposits and in hydrothermal antimony-bearing veins.
Its type locality is Prabornaz Mine, Saint-Marcel, Aosta Valley, Italy. It was named after Jean-Baptiste L. Romé de l’Isle. Brugger, et al. (1997) used infrared spectroscopy to measure water content in Roméite crystals.
Read More About Romeite / Source
Rosasite

Rosasite is a carbonate mineral with minor potential for use as a zinc and copper ore. Chemically, it is a copper zinc carbonate hydroxide with a copper to zinc ratio of 3:2, occurring in the secondary oxidation zone of copper-zinc deposits. It was originally discovered in 1908 in the Rosas mine in Sardinia, Italy, and is named after the location. Fibrous blue-green rosasite crystals are usually found in globular aggregates, often associated with red limonite and other colorful minerals. It is very similar to aurichalcite, but can be distinguished by its superior hardness.
Read More About Rosasite / Source
Roscoelite

Roscoelite is a green mineral from the mica group that contains vanadium.
The chemical formula is K(V3+, Al, Mg)2AlSi3O10(OH)2.
Crystals of roscoelite take on the monoclinic form, and are from the 2/m point group.
The appearance is semi transparent to translucent coloured olive brown to green brown. The lustre is pearly. The mineral shows pleochroism with X showing green-brown, and Y and Z axes showing olive-green colour. The mineral was named after Henry Enfield Roscoe who first produced vanadium metal.
Read More About Roscoelite / Source
Roselite

Roselite is a rare arsenate mineral with chemical formula: Ca2(Co,Mg)[AsO4]2·H2O. It was first described in 1825 for an occurrence in the Rappold mines of Schneeberg, Saxony, Germany and named by Armand Lévy after German mineralogist Gustav Rose. It occurs in cobalt bearing hydrothermal environments and was associated with veins of quartz and chalcedony in the type locality. It has also been reported from Italy, Morocco, Chile, British Columbia and several locations in Germany.The pleochroism of roselite depends on chemical composition with darker rose colored varieties being higher in cobalt content and lighter rose colored varieties are higher in calcium and magnesium content (Palache et al., 1960). This gives rise to two different pleochroism schemes, one for dark rose and one for light rose. Dark rose varieties have X: dark rose, Y: pale rose, Z: paler rose. Light rose varieties have X: pale rose, Y: paler rose, Z: palest rose.
Read More About Roselite / Source
Rosenbergite

Rosenbergite is a mineral with the chemical formula AlF3·3H2O. It is a trihydrate of aluminium fluoride.
It is colorless. Its crystals are tetragonal to dipyramidal. It is named after Philip E. Rosenberg, a United States geochemist. It is found in the Celtine Mine in Tuscany, Italy and Mount Erebus, Ross Island, Antarctica. It is not radioactive. Rosenbergite is rated 3–3.5 on the Mohs Scale.
Read More About Rosenbergite / Source
Rosickýite

Rosickyite is a rare native element mineral that is a polymorph of sulfur. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system and is a high temperature, high density polymorph. It occurs as soft, colorless to pale yellow crystals and efflorescences.It was first described in 1930 for an occurrence in Havirna, near Letovice, Moravia, Czech Republic. It was named for Vojtĕch Rosický (1880–1942), of Masaryk University, Brno.Rosickyite occurs as in Death Valley within an evaporite layer produced by a microbial community. The otherwise unstable polymorph was produced and stabilized within a cyanobacteria dominated layer.
Read More About Rosickýite / Source
Routhierite

Routhierite is a rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with formula Tl(Cu,Ag)(Hg,Zn)2(As,Sb)2S6.
It was first described in 1974 for an occurrence in the Jas Roux deposit in the French Alps. It was named after French geologist Pierre Routhier (1916–2008). It is also reported from the Northern Ural Mountains, Russia and the Thunder Bay district of Ontario, Canada.
Read More About Routhierite / Source
Rozenite

Rozenite is a hydrous iron sulfate mineral, Fe2+SO4•4(H2O).
It occurs as a secondary mineral, formed under low humidity at less than 21 °C (70 °F) as an alteration of copper-free melanterite, which is a post mine alteration product of pyrite or marcasite. It also occurs in lacustrine sediments and coal seams. Associated minerals include melanterite, epsomite, jarosite, gypsum, sulfur, pyrite, marcasite and limonite.It was first described in 1960 for an occurrence on Ornak Mountain, Western Tatra Mountains, Małopolskie, Poland. It was named for Polish mineralogist Zygmunt Rozen (1874–1936).The thermal expansion of rozenite was studied from −254 °C (−425.2 °F) to 17 °C (63 °F) using neutron diffraction. Rozenite exhibits negative linear thermal expansion, meaning that it expands in one direction upon cooling.
Read More About Rozenite / Source
Rubicline

Rubicline, also referred to as Rb-microcline, is the rubidium analogue of microcline, an important tectosilicate mineral. Its chemical formula is (Rb, K)[AlSi3O8] with an ideal composition of RbAlSi3O8. Chemical analysis by electron microprobe indicated the average weight of the crystal is 56.66% SiO2, 16.95% Al2O3, and 23.77% Rb2O, along with trace amounts of caesium oxide (Cs2O) and iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3).Rubicline was first discovered in 1998 in Elba, Italy, by a team from the University of Manitoba. It was the first mineral to have been discovered with rubidium as an essential constituent. It has also been found in Mozambique and the Kola Peninsula in Russia. Rubicline occurs as small, abundant, rounded grains found within veins of rubidian microcline. Pure rubicline with an ideal potassium-free composition has never been found in nature. Rubicline was synthesized in 2001 by placing powdered albite in a solvent of RbCl. This mixture was then placed in a silver tube containing H2O, heated to 400 °C and pressurized to 60 MPa.Unlike microcline, which can be yellow, red, or green, rubicline is colorless. It is also transparent, brittle, and has a vitreous luster. Rubicline has been classified as both triclinic and monoclinic. The crystal does not show twinning. Other minerals in this group include adularia, anorthoclase, buddingtonite, celsian, hyalophane, microcline, monalbite, orthoclase, and sanidine.Like all rubidium compounds, rubicline is mildly radioactive. Activity and dose rate of various amounts of rubicline are listed in the table below.
If held in hand for one hour.
Government estimate of average annual exposure (360 mRem)
Max permissible adult dose 50,000 mRem/yr (hands), 15,000 mRem/yr (eyes)
Lethal exposure 400,000 to 500,000 mRem
Read More About Rubicline / Source
Ruizite

Ruizite is a sorosilicate mineral with formula Ca2Mn2Si4O11(OH)4·2H2O. It was discovered at the Christmas mine in Christmas, Arizona, and described in 1977. The mineral is named for discoverer Joe Ana Ruiz.
Read More About Ruizite / Source
Russellite (mineral)

Russellite is a bismuth tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Bi2WO6. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. Russellite is yellow or yellow-green in color, with a Mohs hardness of 3+1⁄2.Russellite is named for the mineralogist Sir Arthur Russell, and the type locality is the Castle-an-Dinas Mine, near St Columb Major in Cornwall, where it was found in 1938 in wolframite.
It occurs as a secondary alteration of other bismuth bearing minerals in tin – tungsten
hydrothermal ore deposits, pegmatites and greisens. It typically occurs associated with native bismuth, bismuthinite, bismite, wolframite, ferberite, scheelite, ferritungstite, anthoinite, mpororoite, koechlinite, cassiterite, topaz, muscovite, tourmaline and quartz.
Read More About Russellite (mineral) / Source
Ruthenium

Ruthenium is a chemical element with the symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most other chemicals. Russian-born scientist of Baltic-German ancestry Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element in 1844 at Kazan State University and named ruthenium in honor of Russia. Ruthenium is usually found as a minor component of platinum ores; the annual production has risen from about 19 tonnes in 2009 to some 35.5 tonnes in 2017. Most ruthenium produced is used in wear-resistant electrical contacts and thick-film resistors. A minor application for ruthenium is in platinum alloys and as a chemistry catalyst. A new application of ruthenium is as the capping layer for extreme ultraviolet photomasks. Ruthenium is generally found in ores with the other platinum group metals in the Ural Mountains and in North and South America. Small but commercially important quantities are also found in pentlandite extracted from Sudbury, Ontario and in pyroxenite deposits in South Africa.
Read More About Ruthenium / Source
Rutherfordine

Rutherfordine is a mineral containing almost pure uranyl carbonate (UO2CO3). It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system in translucent lathlike, elongated, commonly radiating in fibrous, and in pulverulent, earthy to very fine-grained dense masses. It has a specific gravity of 5.7 and exhibits two directions of cleavage. It appears as brownish, brownish yellow, white, light brown orange, or light yellow fluorescent encrustations. It is also known as diderichite.
It was first described in 1906 for an occurrence in the Morogoro Region of Tanzania. It was named for Ernest Rutherford. It has been reported in the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Northern Territory of Australia and a variety of locations worldwide.It occurs as a secondary mineral as a weathering product of uraninite. In addition to uraninite it occurs associated with the rare minerals becquerelite, masuyite, schoepite, kasolite, curite, boltwoodite, vandendriesscheite, billietite, metatorbernite, fourmarierite, studtite and sklodowskite. It forms under acidic to neutral pH and is the only known mineral that contains only uranyl and carbonate.
Read More About Rutherfordine / Source
Rutile

Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite.
Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum.
Rutile derives its name from the Latin rutilus (‘red’), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner using specimens obtained in Horcajuelo de la Sierra, Madrid (Spain), which is consequently the type locality.
Read More About Rutile / Source
Rynersonite
Rynersonite (Ca(Ta,Nb)2O6) is an oxide mineral. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. It is dull, translucent mineral, fibrous in nature. Usually off-white to pale pink in color. It occurs in granitic pegmatites and was first described for an occurrence in San Diego County, California in 1978.Besides the San Diego, California area, Rynersonite is also found in Colorado and Kampala, Uganda.
Read More About Rynersonite / Source
Sabatierite
Sabatierite (Cu6TlSe4) is a mineral found in the Czech Republic. The composition of the mineral is more likely (Cu4TlSe3) that has been chemically and crystalographically characterized having tetragonal symmetry. It is named for the French mineralogist Germain Sabatier (born 1923).
Read More About Sabatierite / Source
Sabieite
Sabieite is a mineral with the chemical formula (NH4)Fe3+(SO4)2. Its type locality is Lone Creek Falls cave, Sabie, Pilgrim’s Rest District Ehlanzeni, Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. Its crystals are trigonal to trapezohedral. It is white and leaves a white streak. It is transparent and has an earthy luster. Sabieite is rated 2 on the Mohs Scale.
Read More About Sabieite / Source
Sabinaite

Sabinaite (Na4Zr2TiO4(CO3)4) is a rare carbonate mineral. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system as colorless to white prisms within cavities. It is more typically found as powdery coatings and masses. It has a specific gravity of 3.36.It has been found in vugs in a carbonatite sill on Montreal Island and within sodalite syenite in the alkali intrusion at Mont Saint-Hilaire in Quebec, Canada.
It was first described in 1980 for an occurrence in the Francon quarry, Montreal Island. It is named after Ann Sabina (1930–2015), a mineralogist working for the Geological Survey of Canada.
Read More About Sabinaite / Source
Sacrofanite
Sacrofanite is a rare silicate mineral that has the general formula of (Na,Ca)9(Si,Al)12O24(SO4,CO3,OH,Cl)4·n(H2O). It was approved as a mineral by the International Mineralogical Association in 1980. Its name comes from the Sacrofano Caldera in the Monti Sabatini from which it was discovered in Latium, Italy.
Read More About Sacrofanite / Source
Safflorite

Safflorite is a rare cobalt iron arsenide mineral with the chemical formula (Co,Fe)As2. Pure safflorite is CoAs2, but iron is virtually always present. Safflorite is a member of the three-way substitution series of arsenides known as the loellingite or loellingite group. More than fifty percent iron makes the mineral loellingite whereas more than fifty percent nickel and the mineral is rammelsbergite. A parallel series of antimonide minerals exist.
Safflorite along with the other minerals crystallize in the orthorhombic system forming opaque gray to white massive to radiating forms, Clinosafflorite has a monoclinic symmetry. It has a mohs hardness of 4.5 and a specific gravity of 6.9 to 7.3. Twinning is common and star shaped twins are frequently found.
It was first described in 1835 from the Schneeberg District, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany. Safflorite occurs with other arsenide minerals as an accessory in silver mining districts. It alters to the arsenate erythrite in the secondary environment.
Read More About Safflorite / Source
Salammoniac

Salammoniac, also sal ammoniac or salmiac, is a rare naturally occurring mineral composed of ammonium chloride, NH4Cl. It forms colorless, white, or yellow-brown crystals in the isometric-hexoctahedral class. It has very poor cleavage and is brittle to conchoidal fracture. It is quite soft, with a Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2, and it has a low specific gravity of 1.5. It is water-soluble. Sal ammoniac is also the archaic name for the chemical compound ammonium chloride.
Pliny, in Book XXXI of his Natural History, refers to a salt produced in the Roman province of Cyrenaica named hammoniacum, so called because of its proximity to the nearby Temple of Jupiter Amun (Greek Ἄμμων Ammon). However, the description Pliny gives of the salt does not conform to the properties of ammonium chloride. According to Herbert Hoover’s commentary in his English translation of Georgius Agricola’s De re metallica, it is likely to have been common sea salt. In any case, that salt ultimately gave ammonia and ammonium compounds their name.
The first attested reference to sal ammoniac as ammonium chloride is in the Pseudo-Geber work De inventione veritatis, where a preparation of sal ammoniac is given in the chapter De Salis armoniaci præparatione, salis armoniaci being a common name in the Middle Ages for sal ammoniac.It typically forms as encrustations formed by sublimation around volcanic vents and is found around volcanic fumaroles, guano deposits and burning coal seams. Associated minerals include sodium alum, native sulfur and other fumarole minerals. Notable occurrences include Tajikistan; Mount Vesuvius, Italy; and Parícutin, Michoacan, Mexico.
Read More About Salammoniac / Source
Saleeite

Saleeite is a secondary uranium mineral occurring in the oxidized zones of uranium deposits, or as disseminations in carnotite-bearing sandstones. Its chemical formula is Mg(UO2)2(PO4)2·10(H2O).
It was discovered in 1932 at Shinkolobwe, Katanga Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and is named for Belgian mineralogist Achille Salée (1883-1932), Professor at Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium. It was later determined that the Katanga mineral was meta-saleeite Mg(UO2)2(PO4)2·8(H2O) and the type locality was assigned to the Weißer Hirsch Mine, Neustädtel, Schneeberg District, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany.
Read More About Saleeite / Source
Saliotite
Saliotite is a rare colorless to pearl white phyllosilicate mineral in the smectite group with formula (Li,Na)Al3(AlSi3O10)(OH)5. It is an ordered 1:1 interstratification of cookeite and paragonite. It has perfect cleavage, a pearly luster and leaves a white streak. Its crystal structure is monoclinic, and it is a soft mineral with a hardness rated 2-3 on the Mohs scale.Saliotite was first described in 1994 for an occurrence in an outcrop of high grade schist north of Almeria, Andalusia, Spain. It was named for French geologist Pierre Saliot.
Read More About Saliotite / Source
Salzburgite
Salzburgite has a general empirical formula of Pb2Cu2Bi7S12 and an orthorhombic crystal structure. This mineral is very similar to paarite in that they both have nearly the same empirical formulas. They are both of the bismuthinite – aikinite series. Salzburgite was named after the region in which it was found, Salzburg, Austria.
Read More About Salzburgite / Source
Samarskite-(Y)

Samarskite is a radioactive rare earth mineral series which includes samarskite-(Y), with the chemical formula (YFe3+Fe2+U,Th,Ca)2(Nb,Ta)2O8 and samarskite-(Yb), with the chemical formula (YbFe3+)2(Nb,Ta)2O8. The formula for samarskite-(Y) is also given as (Y,Fe3+,U)(Nb,Ta)O4.Samarskite crystallizes in the orthorhombic – dipyramidal class as black to yellowish brown stubby prisms although it is typically found as anhedral masses. Specimens with a high uranium content are typically metamict and appear coated with a yellow brown earthy rind.
Samarskite occurs in rare earth bearing granite pegmatites with other rare minerals. It occurs in association with columbite, zircon, monazite, uraninite, aeschynite, magnetite, albite, topaz, beryl, garnet, muscovite and biotite.Samarskite was first described in 1847 for an occurrence in Miass, Ilmen Mountains, Southern Ural Mountains of Russia. The chemical element samarium was first isolated from a specimen of samarskite in 1879. Samarium was named after samarskite which was named for the Russian mine official, Colonel Vasili Samarsky-Bykhovets (1803–1870).Samarskite-(Yb) was first described in 2004 for an occurrence in the South Platte Pegmatite District, Jefferson County, Colorado.
Read More About Samarskite-(Y) / Source
Sampleite

Sampleite has a general formula of NaCaCu5(PO4)4Cl•5(H2O). It was first described in 1942 for an occurrence in Chuquicamata, Chile and was named after Mat Sample, a mine superintendent for the Chile Exploration Company.Sampleite is monoclinic. It belongs to the space group P21/n or P21/c. In a thin section it has a high surface relief and will have sharp boundaries with the surrounding medium. Sampleite is anisotropic and has visible pleochroism and birefringence.
It is characteristically found in earthy crusts in a highly sericitized rock and is present in highly oxidized conditions near the surface. When it occurs as micaceous rosettes and aggregates it can be associated with dendrites of manganese and iron oxides. Sampleite appears to be the most recent mineral deposited with the exception of gypsum.
Read More About Sampleite / Source
Samsonite (mineral)

Samsonite is a silver manganese antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula Ag4MnSb2S6. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with a typical slender radiating prismatic habit. It is metallic black to steel black with no cleavage and a brittle to conchoidal fracture. In thin fragments it appears reddish brown in transmitted light and also leaves a red streak. It is soft, Mohs hardness of 2.5, and has a specific gravity of 5.51.
It was first named in 1910 after an occurrence in the Samson Vein of the Sankt Andreasberg silver mines, Harz Mountains, Germany.
Read More About Samsonite (mineral) / Source
Samuelsonite
Samuelsonite is a complex mineral that is found near North Groton, Grafton County, New Hampshire, US. Additionally, it is most commonly found as a secondary mineral in granite pegmatite. Samuelsonite is named after Peter B. Samuelson, a prospector from Rumney, New Hampshire.
The mineral has a pale yellow color and has a hardness of 5 on Mohs scale. The crystal is generally yellow, flat, and with straited crystals and blue trolleites. Samuelsonite is monoclinic. There are three vectors of unequal length in this crystal system. The three vectors form a rectangular prism with a parallelogram at the base. Therefore, two of the vectors are perpendicular, while the third makes an angle that is not equal to 90°. Samuelsonite has biaxial birefringence (trirefringence), meaning when light passes through the optic axis it is split into two rays due to the difference in refractive index of the ray with parallel polarized light compared to the ray with perpendicular polarized light.
Read More About Samuelsonite / Source
Sanbornite

Sanbornite is a rare barium phyllosilicate mineral with formula BaSi2O5. Sanbornite is a colorless to white to pale green, platey orthorhombic mineral with Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 3.74.
It was first described from Incline, Mariposa County, California in 1932 and named for mineralogist Frank B. Sanborn (1862–1936).
Read More About Sanbornite / Source
Saneroite

Saneroite (Na2(Mn,Mn)10Si11VO34(OH)4) is a silicate mineral found in Italy. It is named after Edoardo Sanero, a professor at the University of Genova. It is a triclinic mineral with space group symmetry P1.
Read More About Saneroite / Source
Sanidine

Sanidine is the high temperature form of potassium feldspar with a general formula K(AlSi3O8). Sanidine is found most typically in felsic volcanic rocks such as obsidian, rhyolite and trachyte. Sanidine crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. Orthoclase is a monoclinic polymorph stable at lower temperatures. At yet lower temperatures, microcline, a triclinic polymorph of potassium feldspar, is stable.
Due to the high temperature and rapid quenching, sanidine can contain more sodium in its structure than the two polymorphs that equilibrated at lower temperatures. Sanidine and high albite constitute a solid solution series with intermediate compositions termed anorthoclase. Exsolution of an albite phase does occur; resulting cryptoperthite can best be observed in electron microprobe images.
Read More About Sanidine / Source
Santabarbaraite

Santabarbaraite is an amorphous ferric hydroxy phosphate mineral hydrate that was discovered in Tuscany, Italy during 2000. It also can be found in Victoria, Australia and Lake Baikal, Siberia.This phosphate mineral has a simplified formula Fe3+3(PO4)2(OH)3·5H2O, which is the same formula of another non-amorphous phosphate mineral called allanpringite. Santabarbaraite occurs as pseudomorphic masses after vivianite (Fe2+3(PO4)2·8H2O). In the process, monoclinic vivianite oxidizes to form the amorphous santabarbaraite. Pseudomorphism may be seen in Victoria, Australia, in Wannon Falls (originally a well-known locality for vivianite). It also may be seen at Lake Baikal, Siberia where the oxidized santabarbaraite may be seen as a rim surrounding vivianite due to exposure to air.
Read More About Santabarbaraite / Source
Santite
Santite (KB5O8·4H2O) is a hydrated borate mineral of potassium found in Tuscany, Italy. It is named for Georgi Santi (1746–1823), a former director of the Museum of Natural History, Italy.
Read More About Santite / Source
Saponite

Saponite is a trioctahedral mineral of the smectite group. Its chemical formula is Ca0.25(Mg,Fe)3((Si,Al)4O10)(OH)2·n(H2O). It is soluble in sulfuric acid. It was first described in 1840 by Svanberg. Varieties of saponite are griffithite, bowlingite and sobotkite.
It is soft, massive, and plastic, and exists in veins and cavities in serpentinite and basalt. The name is derived from the Greek sapo, soap. Other names include bowlingite; mountain soap; piotine; soapstone.
Read More About Saponite / Source
Sapphirine

Sapphirine is a rare mineral, a silicate of magnesium and aluminium with the chemical formula (Mg,Al)8(Al,Si)6O20 (with iron as a major impurity). Named for its sapphire-like colour, sapphirine is primarily of interest to researchers and collectors: well-formed crystals are treasured and occasionally cut into gemstones. Sapphirine has also been synthesized for experimental purposes via a hydrothermal process.
Read More About Sapphirine / Source
Sarabauite

Sarabauite (sar-a-bau’-ite) is a red monoclinic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula: CaSb10O10S6.
Read More About Sarabauite / Source
Sarcolite

Sarcolite is a mineral named due to its color. Its name originates from the Greek word sárx (σάρξ), meaning flesh and from the Greek word for stone, líthos (λίθος), for being a mineral. It was first described in 1959, but had been a valid species since 1807. It is grandfathered, meaning the name sarcolite still refers to a valid species till this day. Researchers were able to create lab-grown sarcolites with the same crystal structure and formula, although the lab grown ones show different, uniaxial (-) optical properties.
Read More About Sarcolite / Source
Sarkinite

Sarkinite, synonymous with chondrarsenite and polyarsenite, is a mineral with formula Mn2(AsO4)(OH). The mineral is named for the Greek word σάρκιυος, meaning made of flesh, for its red color and greasy luster. The mineral was first noted in Sweden in 1865 as chondrarsenite, though not identified as sarkinite until 1885.
Read More About Sarkinite / Source
Sassolite

Sassolite is a borate mineral, specifically the mineral form of boric acid. It is usually white to gray, and colourless in transmitted light. It can also take on a yellow colour from sulfur impurities, or brown from iron oxides.
Read More About Sassolite / Source
Satterlyite

Satterlyite is a hydroxyl bearing iron phosphate mineral. The mineral can be found in phosphatic shales and was first discovered in the Big Fish River area in Yukon Territory, Canada.
Satterlyite is part of the phosphate mineral group. Satterlyite is a transparent, light brown to light yellow mineral with a density of 3.68 g/cm3. The structure of satterlyite is made up of two pairs of face shared, distorted (Fe,Mg)O6 octahedra, linked together by sharing edges to form double chains along the [001] plain.
The first satterlyite mineral was discovered in the Big Fish River area in Yukon Territory, westernmost of Canada; by a geologist at Ontario Department of Mines in Canada, Jack Satterly, and the mineral was also named after him (Kolitsch, 2002).
Read More About Satterlyite / Source
Sauconite

Sauconite is a complex phyllosilicate mineral of the smectite clay group, formula Na0.3Zn3(SiAl)4O10(OH)2·4H2O. It forms soft earthy bluish white to red-brown monoclinic crystals typically massive to micaceous in habit. It has a Mohs hardness of 1 to 2 and a specific gravity of 2.45. Optically it is biaxial positive with refractive index values of nα = 1.550 – 1.580, nβ = 1.590 – 1.620 and nγ = 1.590 – 1.620.
It is found in vugs and seams in the oxidized zones of zinc and copper deposits. It occurs in association with hemimorphite, smithsonite, chrysocolla, coronadite and various iron oxides.
It was named for the Saucon Valley in Pennsylvania, where it was originally discovered in 1875.
Read More About Sauconite / Source
Sborgite
Sborgite is a sodium borate mineral with formula Na[B5O6(OH)4]·3H2O. The formula can be written as the oxide formulation, Na2O.5B2O3.10H2O. Sometimes called sodium pentaborate pentahydrate it contains the pentaborate anion, (B5O6(OH)4)−.
Sborgite is colorless with monoclinic crystals. It was named for Umberto Sborgi, (1883–1955), Professor of Chemistry, University of Milan, Italy. Sborgite occurs in Tuscany, Italy and the Furnace Creek district, Death Valley, California, US.
Read More About Sborgite / Source
Scapolite

The scapolites (Gr. σκάπος, rod, and λίθος, stone) are a group of rock-forming silicate minerals composed of aluminium, calcium, and sodium silicate with chlorine, carbonate and sulfate. The two endmembers are meionite (Ca4Al6Si6O24CO3) and marialite (Na4Al3Si9O24Cl). Silvialite (Ca,Na)4Al6Si6O24(SO4,CO3) is also a recognized member of the group.
Read More About Scapolite / Source
Schäferite
Schäferite is a rare vanadate mineral with chemical formula Ca2NaMg2[VO4]3. Schäferite is isometric, which means that it has three axes of equal length and 90° angles between the axes. Schäferite is isotropic, meaning that the velocity of light is the same no matter which direction the light passes through.It was named after Helmut Schäfer (born 1931) who discovered it in a quarry on the Bellerberg Volcano in Germany. It is found only in the Eifel Mountains volcanic area near Mayen, Laacher See district of Germany. It occurs within a xenolith in a leucite tephrite. It is the magnesium analogue of palenzonaite and is a member of the garnet structural group.
Read More About Schäferite / Source
Scheelite

Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula CaWO4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist K. Scheele (1742-1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors and are occasionally fashioned into gemstones when suitably free of flaws. Scheelite has been synthesized using the Czochralski process; the material produced may be used to imitate diamond, as a scintillator, or as a solid-state lasing medium. It was also used in radium paint in the same fashion as was zinc sulphide, and Thomas Edison invented a fluoroscope with a calcium tungstate-coated screen, making the images six times brighter than those with barium platinocyanide; the latter chemical allowed Röntgen to discover X-rays in early November 1895.
Read More About Scheelite / Source
Schizolite
Schizolite is a mineral with the formula NaCaMnSi3O8(OH) first described in 1901 after discovery in South Greenland by Winther. Its name comes from the Greek word ‘σϗιζω’ (sϗizo) after its perfect cleavage. It was dropped from the valid species status in 1955 as a variety of pectolite based on Schaller’s work. It’s a member of the Wollastonite group.Marshall Sussman, a mineral dealer, sold minerals that were believed to be bustamites from the Wessels mine in 2011. After the third of the stock was sold they realized the gem might be a new specimen, took it down from the market immediately, and waited for approval. It was approved by the International Mineralogical Association as a mineral in 2013, with the intended name sussmanite. However, it was decided that this name was too similar to another existing gem’s name, zussmanite so the name marshallsussmanite was chosen, after the famous mineral dealer Marshall Sussman. It is believed to be a pectolite variant which contains manganese in place of calcium. The name was reverted to Schizolite in 2018.
Read More About Schizolite / Source
Schmiederite

Schmiederite is a secondary mineral in the oxidized zone of selenium-bearing hydrothermal base metal deposits. Its chemical formula is Pb2Cu2(Se4+O3)(Se6+O4)(OH)4.It was first described in 1962 for an occurrence in the Cóndor mine, Los Llantenes district, Sierra de Cacheuta, La Rioja Province, Argentina (type locality). It was named for Oscar Schmieder (1891–1980), German geographer.
Read More About Schmiederite / Source
Schoepite

Schoepite, empirical formula (UO2)8O2(OH)12•12(H2O) is a rare alteration product of uraninite in hydrothermal uranium deposits. It may also form directly from ianthinite. The mineral presents as a transparent to translucent yellow, lemon yellow, brownish yellow, or amber orthorhombic tabular crystals. Although over 20 other crystal forms have been noted; rarely in microcrystalline aggregates. When exposed to air schoepite converts over a short time to the metaschoepite form (UO3 • nH2O, n < 2) within a few months of being exposed to ambient air.
The hardness is 2.5, density is 4.8 g/cm3, and it streaks yellow.
It was first described from specimens from Shinkolobwe mine in Belgian Congo in 1923, several additional localities are known.
Schoepite was named to honor Alfred Schoep (1881–1966), Professor of Mineralogy at the University of Ghent, Belgium.
Read More About Schoepite / Source
Tourmaline

Tourmaline ( TOOR-mə-lin, -leen) is a crystalline silicate mineral group in which boron is compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. This gemstone comes in a wide variety of colors.
The name is derived from the Sinhalese tōramalli (ටෝරමල්ලි), which refers to the carnelian gemstones.
Read More About Tourmaline / Source
Schreibersite

Schreibersite is generally a rare iron nickel phosphide mineral, (Fe,Ni)3P, though common in iron-nickel meteorites. It has been found on Disko Island in Greenland and Illinois.Another name used for the mineral is rhabdite. It forms tetragonal crystals with perfect 001 cleavage. Its color ranges from bronze to brass yellow to silver white. It has a density of 7.5 and a hardness of 6.5 – 7. It is opaque with a metallic luster and a dark gray streak. It was named after the Austrian scientist Carl Franz Anton Ritter von Schreibers (1775–1852), who was one of the first to describe it from iron meteorites.Schreibersite is reported from the Magura Meteorite, Arva-(present name – Orava), Slovak Republic; the Sikhote-Alin Meteorite in eastern Russia; the São Julião de Moreira Meteorite, Viana do Castelo, Portugal; the Gebel Kamil (meteorite) in Egypt; and numerous other locations including the Moon.In 2007, researchers reported that schreibersite and other meteoric phosphorus bearing minerals may be the ultimate source for the phosphorus that is so important for life on Earth. In 2013, researchers reported that they had successfully produced pyrophosphite, a possible precursor to pyrophosphate, the molecule associated with ATP, a co-enzyme central to energy metabolism in all life on Earth. Their experiment consisted of subjecting a sample of schreibersite to a warm, acidic environment typically found in association with volcanic activity, activity that was far more common on the primordial Earth. They hypothesized that their experiment might represent what they termed “chemical life”, a stage of evolution which may have led to the emergence of fully biological life as exists today.In 1986 researchers found lightning can create schreibersite and may have been the source of phosphorus for early life.
Read More About Schreibersite / Source
Schreyerite
Schreyerite (V2Ti3O9), is a vanadium, titanium oxide mineral found in the Lasamba Hill, Kwale district in Coast Province, Kenya. It is polymorphous with kyzylkumite.
The mineral occurs as exsolution lamellae and particles in rutile, coexisting with kyanite, sillimanite, and tourmaline in a highly metamorphosed gneiss. It was named after German mineralogist and petrologist Werner Schreyer, for his research on mineralogy of rock-forming minerals and petrology of metamorphic rocks both in nature and by experiment.
Read More About Schreyerite / Source
Schröckingerite

Schröckingerite is a radioactive yellow uranium-containing carbonate mineral, hydrated sodium calcium uranyl sulfate carbonate fluoride. Schröckingerite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system, occurring as globular clusters, and fluoresces yellow-green under ultraviolet light.
Schröckingerite was first described in 1783 from an occurrence in Jáchymov, Bohemia, Czech Republic, and named for its discoverer, Julius Freiherr Schröckinger von Neudenberg (1814–1882).
Read More About Schröckingerite / Source
Schwertmannite

Schwertmannite is an iron-oxyhydroxysulfate mineral with an ideal chemical formula of Fe8O8(OH)6(SO4) · n H2O or Fe3+16O16(OH,SO4)12–13·10-12H2O. It is an opaque tetragonal mineral typically occurring as brownish yellow encrustations. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 – 3.5 and a specific gravity of 3.77 – 3.99.It was first described for an occurrence in Finland in 1994 and named for Udo Schwertmann (born 1927) soil scientist, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany.Schwertmannite (with a distinct “pin cushion” morphology) commonly forms in iron-rich, acid sulfate waters in the pH-range of 2 – 4. The mineral was first recognised officially as a new mineral from a natural acid-sulfate spring occurrence at Pyhäsalmi, Finland. However, it is more commonly reported as an orange precipitate in streams and lakes affected by acid mine drainage. Schwertmannite is also known to be central to iron-sulfur geochemistry in acid sulfate soils associated with coastal lowlands.
Read More About Schwertmannite / Source
Scolecite

Scolecite is a tectosilicate mineral belonging to the zeolite group; it is a hydrated calcium silicate, CaAl2Si3O10·3H2O. Only minor amounts of sodium and traces of potassium substitute for calcium. There is an absence of barium, strontium, iron and magnesium. Scolecite is isostructural (having the same structure) with the sodium-calcium zeolite mesolite and the sodium zeolite natrolite, but it does not form a continuous chemical series with either of them. It was described in 1813, and named from the Greek word, σκώληξ (sko-lecks) = “worm” because of its reaction to the blowpipe flame.
Read More About Scolecite / Source
Scorodite

Scorodite is a common hydrated iron arsenate mineral, with the chemical formula FeAsO4·2H2O. It is found in hydrothermal deposits and as a secondary mineral in gossans worldwide. Scorodite weathers to limonite.
Scorodite was discovered in the Schwarzenberg, Saxony district, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany. Named from the Greek Scorodion, “garlicky”. When heated it smells of garlic, which gives it the name.
Read More About Scorodite / Source
Scorzalite

Scorzalite ((Fe2+,Mg)Al2(OH,PO4)2) is a dark blue phosphate mineral containing iron, magnesium, and aluminium phosphate. Scorzalite forms one endmember of a solid solution series with the lighter, more magnesium-rich lazulite.
Scorzalite crystallizes in the monoclinic system in a dipyramidal form. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5-6 and a specific gravity of 3.4. It is infusible and insoluble in water, and only slightly soluble in warm hydrochloric acid.
Read More About Scorzalite / Source
Scotlandite
Scotlandite is a sulfite mineral first discovered in a mine at Leadhills in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, an area known to mineralogists and geologists for its wide range of different mineral species found in the veins that lie deep in the mine shafts. This specific mineral is found in the Susanna vein of Leadhills, where the crystals are formed as chisel-shaped or bladed. Scotlandite was actually the first naturally occurring sulfite, which has the ideal chemical formula of PbSO3. The mineral has been approved by the Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names, IMA, to be named scotlandite for Scotland.
Read More About Scotlandite / Source
Scrutinyite
Scrutinyite is a rare oxide mineral and is the alpha crystalline form of lead dioxide (α-PbO2), plattnerite being the other, beta form. The mineral was first reported in 1988 and its name reflects the scrutiny and efforts required to identify it from a very limited amount of available sample material.
Read More About Scrutinyite / Source
Seamanite

Seamanite, named for discoverer Arthur E. Seaman, is a rare manganese boron phosphate mineral with formula Mn3[B(OH)4](PO4)(OH)2. The yellow to pink mineral occurs as small, needle-shaped crystals. It was first discovered in 1917 from a mine in Iron County, Michigan, United States and identified in 1930. As of 2012, seamanite is known from four sites in Michigan and South Australia.
Read More About Seamanite / Source
Searlesite

Searlesite is a sodium borosilicate mineral, with the chemical formula NaBSi2O5(OH)2. It was discovered in 1914 at Searles Lake, California, and was named to honor John W. Searles (16 November 1828 – 7 October 1897), California pioneer, who drilled the well that yielded the first known Searlesite.
Searlesite is usually found disseminated in fine-grained lacustrine strata and often associated with altering volcanic ash. It may be a minor component of borate deposits, but it is rarely found concentrated or in megascopic crystals and so has not been developed as an ore mineral of boron. It occurs interbedded with oil shales or marls (Green River Formation, US) and in boron-bearing evaporite deposits (California, US); rarely in vugs in phonolite (Point of Rocks, New Mexico).
Read More About Searlesite / Source
Seeligerite

Seeligerite is a rare complex lead chlorate iodate mineral with formula: Pb3Cl3(IO3)O. It is a yellow mineral crystallizing in the orthorhombic system. It has perfect to good cleavage in two directions and a quite high specific gravity of 6.83 due to the lead content. It is translucent to transparent with refractive indices of nα=2.120 nβ=2.320 nγ=2.320.It was first reported in 1971 from the Casucha Mine, Sierra Gorda, Antofagasta Region, Chile.
Read More About Seeligerite / Source
Segelerite
Segelerite is a complex phosphate mineral with formula CaMgFe3+OH(PO4)2·H2O. It occurs in pegmatites and forms striking green or chartreuse crystals. It was discovered in 1974 in the Black Hills of South Dakota by an amateur mineralogist from New York, Curt G. Segeler (1901–1989), after whom it is named.
It is closely related to overite which is virtually the same mineral except that the iron is replaced by aluminium. Another mineral in the same series is juonniite wherein the iron is also replaced, this time by scandium.
Read More About Segelerite / Source
Seifertite
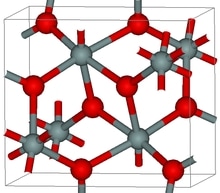
Seifertite is a silicate mineral with the formula SiO2 and is one of the densest polymorphs of silica. It has only been found in Martian and lunar meteorites, where it is presumably formed from either tridymite or cristobalite – other polymorphs of quartz – as a result of heating during the atmospheric re-entry and impact to the Earth, at an estimated minimal pressure of 35 GPa. It can also be produced in the laboratory by compressing cristobalite in a diamond anvil cell to pressures above 40 GPa. The mineral is named after Friedrich Seifert (born 1941), the founder of the Bayerisches Geoinstitut at University of Bayreuth, Germany, and is officially recognized by the International Mineralogical Association.Seifertite forms micrometre-sized crystalline lamellae embedded into a glassy SiO2 matrix. The lamellae are rather difficult to analyze, as they vitrify within seconds under laser or electron beams used for standard Raman spectroscopy or electron-beam microanalysis, even at much reduced beam intensities. Nevertheless, it was possible to verify that it is mainly composed of SiO2 with minor inclusions of Na2O (0.40 wt.%) and Al2O3 (1.14 wt.%). X-ray diffraction reveals that the mineral has scrutinyite (α-PbO2) type structure with an orthorhombic symmetry and Pbcn or Pb2n space group. Its lattice constants a = 4.097, b = 5.0462, c = 4.4946, Z = 4 correspond to the density of 4.294 g/cm3, which is among the highest for any forms of silica (for example, the density of quartz is 2.65 g/cm3). Only stishovite has a comparable density of about 4.287 g/cm3.
Read More About Seifertite / Source
Sekaninaite

Sekaninaite ((Fe+2,Mg)2Al4Si5O18) is a silicate mineral, the iron-rich analogue of cordierite.
It was first described in 1968 for an occurrence in Dolní Bory, Vysočina Region, Moravia, Czech Republic, and is now known also from Ireland, Japan, and Sweden. It was named after a Czech mineralogist, Josef Sekanina (1901–1986). In Brockley on Rathlin Island, Ireland sekaninaite occurs in bauxitic clay within the contact aureole of a diabase intrusive plug.
Read More About Sekaninaite / Source
Selenium

Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, and also has similarities to arsenic. It seldom occurs in its elemental state or as pure ore compounds in the Earth’s crust. Selenium – from Greek selḗnē (σελήνη ‘Moon’) – was discovered in 1817 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius, who noted the similarity of the new element to the previously discovered tellurium (named for the Earth).
Selenium is found in metal sulfide ores, where it partially replaces the sulfur. Commercially, selenium is produced as a byproduct in the refining of these ores, most often during production. Minerals that are pure selenide or selenate compounds are known but rare. The chief commercial uses for selenium today are glassmaking and pigments. Selenium is a semiconductor and is used in photocells. Applications in electronics, once important, have been mostly replaced with silicon semiconductor devices. Selenium is still used in a few types of DC power surge protectors and one type of fluorescent quantum dot.
Although trace amounts of selenium are necessary for cellular function in many animals, including humans, both elemental selenium and (especially) selenium salts are toxic in even small doses, causing selenosis. Selenium is listed as an ingredient in many multivitamins and other dietary supplements, as well as in infant formula, and is a component of the antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin reductase (which indirectly reduce certain oxidized molecules in animals and some plants) as well as in 3 deiodinase enzymes. Selenium requirements in plants differ by species, with some plants requiring relatively large amounts and others apparently not requiring any.
Read More About Selenium / Source
Seligmannite

Seligmanite is a rare mineral, with the chemical formula PbCuAsS3. Originally described from the Lengenbach Quarry, Valais Canton, Switzerland; it has also been found in the Raura district, Lima Region, Peru; at Tsumeb, Oshikoto Region, Namibia; and at the Sterling Mine, Sussex County, New Jersey, US.
Read More About Seligmannite / Source
Sellaite

Sellaite is a magnesium fluoride mineral with the formula MgF2. It crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system, typically as clear to white vitreous prisms. It may be fibrous and occur as radiating aggregates. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 2.97 to 3.15. Refractive index values are nω = 1.378 and nε = 1.390.
Read More About Sellaite / Source
Semseyite

Semseyite is a rarely occurring sulfosalt mineral and is part of the class of lead antimony sulfides. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system with the chemical composition Pb9Sb8S21. The mineral forms dark gray to black aggregates.
Read More About Semseyite / Source
Antimony trioxide

Antimony(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb2O3. It is the most important commercial compound of antimony. It is found in nature as the minerals valentinite and senarmontite. Like most polymeric oxides, Sb2O3 dissolves in aqueous solutions with hydrolysis. A mixed arsenic-antimony oxide occurs in nature as the very rare mineral stibioclaudetite.
Read More About Antimony trioxide / Source
Sengierite

Sengierite is a rare oxide and hydroxide mineral, chemically a copper and uranyl vanadate, belonging to the carnotite group. Its chemical formula is Cu2(OH)2[UO2|VO4]2·6H2O.Sengierite was first discovered at the Luiswishi Mine about 20 kilometres (12 mi) north of Lubumbashi in Katanga Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and was first described in 1949 by Johannes F. Vaes and Paul F. Kerr, the mineral was named after Edgar Sengier (1879–1963), a former Director of the Union Minière du Haut Katanga.
Read More About Sengierite / Source
Sepiolite

Sepiolite, also known in English by the German name meerschaum ( MEER-shawm, -shəm; German: [ˈmeːɐ̯ʃaʊm] (listen); meaning “sea foam”), is a soft white clay mineral, often used to make tobacco pipes (known as meerschaum pipes). A complex magnesium silicate, a typical chemical formula for which is Mg4Si6O15(OH)2·6H2O, it can be present in fibrous, fine-particulate, and solid forms.
The fibrous clay minerals have recently been shown to exist as a continuous polysomatic series where the endmembers are sepiolite and palygorskite. There is a continuous variation in chemical composition from sepiolite, the most magnesic and trioctahedral endmember, to palygorskite, the least magnesic, most Al- Fe- bearing, dioctahedral endmember.Originally named meerschaum by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1788, it was named sepiolite by Ernst Friedrich Glocker in 1847 for an occurrence in Bettolino, Baldissero Canavese, Torino Province, Piedmont, Italy. The name comes from Greek sepion (σήπιον), meaning “cuttlebone” (the porous internal shell of the cuttlefish), + lithos (λίθος), meaning stone, after a perceived resemblance of this mineral to cuttlebone. Because of its low relative density and its high porosity, it may float upon water, hence its German name. It is sometimes found floating on the Black Sea and rather suggestive of sea-foam, hence the German origin of the name as well as the French name for the same substance, écume de mer.
Read More About Sepiolite / Source
Serandite

Serandite is a mineral with formula Na(Mn2+,Ca)2Si3O8(OH). The mineral was discovered in Guinea in 1931 and named for J. M. Sérand. Serandite is generally red, brown, black or colorless. The correct name lacks an accent.
Read More About Serandite / Source
Serendibite

Serendibite is an extremely rare silicate mineral that was first discovered in 1902 in Sri Lanka by Dunil Palitha Gunasekera and named after Serendib, the old Arabic name for Sri Lanka.
The mineral is found in skarns associated with boron metasomatism of carbonate rocks where intruded by granite. Minerals occurring with serendibite include diopside, spinel, phlogopite, scapolite, calcite, tremolite, apatite, grandidierite, sinhalite, hyalophane, uvite, pargasite, clinozoisite, forsterite, warwickite and graphite.
Read More About Serendibite / Source
Serpentine subgroup

Serpentine subgroup (part of the kaolinite-serpentine group in the category of phyllosilicates) are greenish, brownish, or spotted minerals commonly found in serpentinite. They are used as a source of magnesium and asbestos, and as decorative stone. The name comes from the greenish colour and smooth or scaly appearance from the Latin serpentinus, meaning “serpent rock”.Serpentine subgroup is a set of common rock-forming hydrous magnesium iron phyllosilicate ((Mg,Fe)3Si2O5(OH)4) minerals, resulting from the metamorphism of the minerals that are contained in mafic to ultramafic rocks. They may contain minor amounts of other elements including chromium, manganese, cobalt or nickel. In mineralogy and gemology, serpentine may refer to any of the 20 varieties belonging to the serpentine subgroup. Owing to admixture, these varieties are not always easy to individualize, and distinctions are not usually made. There are three important mineral polymorphs of serpentine: antigorite, lizardite and chrysotile.
Serpentine minerals are polymorphous, meaning that they have the same chemical formulae, but the atoms are arranged into different structures, or crystal lattices. Chrysotile, which has a fibrous habit, is one polymorph of serpentine and is one of the more important asbestos minerals. Other polymorphs in the serpentine subgroup may have a platy habit. Antigorite and lizardite are the polymorphs with platy habit.
Many types of serpentine have been used for jewelry and hardstone carving, sometimes under the name “false jade” or “Teton jade”.
Read More About Serpentine subgroup / Source
Serpierite

Serpierite (Ca(Cu,Zn)4(SO4)2(OH)6·3H2O) is a rare, sky-blue coloured hydrated sulfate mineral, often found as a post-mining product. It is a member of the devilline group, which has members aldridgeite (Cd,Ca)(Cu,Zn)4(SO4)2(OH)6·3H2O, campigliaite Cu4Mn2+(SO4)2(OH)6·4H2O, devilline CaCu4(SO4)2(OH)6·3H2O, kobyashevite Cu5(SO4)2(OH)6·4H2O, lautenthalite PbCu4(SO4)2(OH)6·3H2O and an unnamed dimorph of devilline. It is the calcium analogue of aldridgeite and it is dimorphous with orthoserpierite CaCu4(SO4)2(OH)6·3H2O.It was discovered in 1881 and named by Alfred Des Cloizeaux in honour of Giovanni Battista Serpieri. Serpieri was an Italian revolutionary, engineer and mining entrepreneur who developed mines in the Lavrion area of Greece and founded the Montecatini Company. He was born in Italy in 1832 and died in Greece in 1897.
Read More About Serpierite / Source
Sewardite
Sewardite is a rare arsenate mineral with formula of CaFe3+2(AsO4)2(OH)2. Sewardite was discovered in 1982 and named for the mineralogist, Terry M. Seward (born 1940), a professor of geochemistry in Zürich, Switzerland.
Read More About Sewardite / Source
Shandite
Shandite is a sulfide mineral with chemical formula: Ni3Pb2S2. It was discovered in 1948 by the German mineralogist Paul Raumdohr who named it named after Scottish petrologist, Samuel James Shand (1882–1957). Ramdohr characterized shandite by its metallic luster and a brass-yellow color. It has a specific gravity of 8.92, and a Mohs hardness value of 4. Shandite is commonly found as an inclusion in other minerals such as Heazelwoodite Ni3S2 or serpentine.
Its crystal system is trigonal hexagonal scalenohedral with symbol 32/m. It belongs to the space group R3m. Shandite is an anisotropic mineral, which means it has different properties when being viewed from different directions. In cross-polarized light it appears as gray blue or yellow-brown colors. It also has very distinct relief, which means it stands out against its mounting medium and can be easily seen. It has an index of refraction of 1.54, which is the measure of the speed of light through the substance. In plane polarized light, shandite has a creamy white color and distinct pleochroism, which is the property that makes it appear to be different colors at different angles. It has strong birefringence, which is the decomposition of light into two rays, and appears dark blue and gray.
In subsequent decades several compounds with shandite type structure were synthesized by several chemists. The group of compounds M3A2Ch2 with shandite type crystal structures was subsequently called “shandites”. They include Co3Sn2S2 = Sn2Co3S2 = Co3/2SnS that became famous in recent years as layered half metal ferromagnet and topological semi metal including kagome layers of cobalt atoms.
Read More About Shandite / Source
Shattuckite

Shattuckite is a copper silicate hydroxide mineral with formula Cu5(SiO3)4(OH)2. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic – dipyramidal crystal system and usually occurs in a granular massive form and also as fibrous acicular crystals. It is closely allied to plancheite in structure and appearance.
Shattuckite is a relatively rare copper silicate mineral. It was first discovered in 1915 in the copper mines of Bisbee, Arizona, specifically the Shattuck Mine (hence the name). It is a secondary mineral that forms from the alteration of other secondary minerals. At the Shattuck Mine, it forms pseudomorphs after malachite. A pseudomorph is an atom by atom replacement of a crystal structure by another crystal structure, but with little alteration of the outward shape of the original crystal. It is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Shattuckite / Source
Shigaite

Shigaite is a mineral with formula NaAl3(Mn2+)6(SO4)2(OH)18·12H2O that typically occurs as small, hexagonal crystals or thin coatings. It is named for Shiga Prefecture, Japan, where it was discovered in 1985. The formula was significantly revised in 1996, identifying sodium as a previously unknown constituent.
Read More About Shigaite / Source
Shortite

Shortite is a sodium-calcium carbonate mineral, with the chemical formula Na2Ca2(CO3)3. It was discovered by J. J. Fahey in well cuttings from the Green River Formation, Sweetwater County, Wyoming, US, and was named to honor Maxwell N. Short (1889–1952), Professor of Mineralogy, University of Arizona.
Shortite is associated with commercial trona ores, and some care must be taken when beneficiating crude trona to avoid contamination with shortite.
Read More About Shortite / Source
Siderite

Siderite is a mineral composed of iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3). Its name comes from the Ancient Greek word σίδηρος (sídēros), meaning “iron”. A valuable iron ore, it consists of 48% iron and lacks sulfur and phosphorus. Zinc, magnesium, and manganese commonly substitute for the iron, resulting in the siderite-smithsonite, siderite-magnesite, and siderite-rhodochrosite solid solution series.Siderite has Mohs hardness of 3.75 to 4.25, a specific gravity of 3.96, a white streak and a vitreous lustre or pearly luster. Siderite is antiferromagnetic below its Néel temperature of 37 K (−236 °C) which can assist in its identification.It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system, and are rhombohedral in shape, typically with curved and striated faces. It also occurs in masses. Color ranges from yellow to dark brown or black, the latter being due to the presence of manganese.
Siderite is commonly found in hydrothermal veins, and is associated with barite, fluorite, galena, and others. It is also a common diagenetic mineral in shales and sandstones, where it sometimes forms concretions, which can encase three-dimensionally preserved fossils. In sedimentary rocks, siderite commonly forms at shallow burial depths and its elemental composition is often related to the depositional environment of the enclosing sediments. In addition, a number of recent studies have used the oxygen isotopic composition of sphaerosiderite (a type associated with soils) as a proxy for the isotopic composition of meteoric water shortly after deposition.
Read More About Siderite / Source
Siderophyllite

Siderophyllite is a rare member of the mica group of silicate minerals with formula KFe2+2Al(Al2Si2)O10(F,OH)2.
The mineral occurs in nepheline syenite pegmatites and granite and aplite greisens. It is associated with microcline and astrophyllite at Pikes Peak, Colorado. It is also found in the alkali pegmatites of Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec.It was first described in 1880 for an occurrence near Pikes Peak, Colorado. The name derives from the Greek sideros, iron, and phyllon, leaf, in reference to its iron rich composition and perfect basal cleavage.
Read More About Siderophyllite / Source
Siderotil
Siderotil is an iron(II) sulfate hydrate mineral with formula: FeSO4·5H2O which forms by the dehydration of melanterite. Copper commonly occurs substituting for iron in the structure. It typically occurs as fibrous or powdery encrustations, but may also occur as acicular triclinic crystals.It was first described in 1891 for an occurrence in the Idrija Mine, Idrija, Slovenia. Its name derives from the Greek sideros (iron) and tilos (fiber) in reference to its iron content and typical fibrous form. However, the material at the Idrija location may not be siderotil, but the mineral has been authenticated from a wide variety of worldwide locations.
Read More About Siderotil / Source
Siegenite

Siegenite (also called grimmite, or nickel cobalt sulfide) is a ternary transition metal dichalcogenide compound with the chemical formula (Ni,Co)3S4. It has been actively studied as a promising material system for electrodes in electrochemical energy applications due to its better conductivity, greater mechanical and thermal stability, and higher performance compared to metal oxides currently in use. Potential applications of this material system include supercapacitors, batteries, electrocatalysis, dye-sensitized solar cells, photocatalysis, glucose sensors, and microwave absorption.In synthetic chemistry, a range of chemical compositions with the formula NixCo3-xS4 (0 < x < 3) are often referred to as the siegenite system. However, according to the new IMA list of minerals (updated November 2022), the normal spinel NiCo2S4 is called grimmite, the inverse spinel CoNi2S4 is called siegenite, and the endmembers Ni2+(Ni3+)2S4 and Co2+(Co3+)2S4 are called polydymite and linnaeite, respectively. In 2020, NiCo2S4 (grimmite) is approved as a valid mineral species by the IMA.
Read More About Siegenite / Source
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive.
Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron.
Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth’s crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide (silica) or silicates. More than 90% of the Earth’s crust is composed of silicate minerals, making silicon the second most abundant element in the Earth’s crust (about 28% by mass), after oxygen.
Most silicon is used commercially without being separated, often with very little processing of the natural minerals. Such use includes industrial construction with clays, silica sand, and stone. Silicates are used in Portland cement for mortar and stucco, and mixed with silica sand and gravel to make concrete for walkways, foundations, and roads. They are also used in whiteware ceramics such as porcelain, and in traditional silicate-based soda-lime glass and many other specialty glasses. Silicon compounds such as silicon carbide are used as abrasives and components of high-strength ceramics. Silicon is the basis of the widely used synthetic polymers called silicones.
The late 20th century to early 21st century has been described as the Silicon Age (also known as the Digital Age or Information Age) because of the large impact that elemental silicon has on the modern world economy. The small portion of very highly purified elemental silicon used in semiconductor electronics (<10%) is essential to the transistors and integrated circuit chips used in most modern technology such as smartphones and other computers. In 2019, 32.4% of the semiconductor market segment was for networks and communications devices, and the semiconductors industry is projected to reach $726.73 billion by 2027.Silicon is an essential element in biology. Only traces are required by most animals, but some sea sponges and microorganisms, such as diatoms and radiolaria, secrete skeletal structures made of silica. Silica is deposited in many plant tissues.
Read More About Silicon / Source
Sillimanite

Sillimanite is an aluminosilicate mineral with the chemical formula Al2SiO5. Sillimanite is named after the American chemist Benjamin Silliman (1779–1864). It was first described in 1824 for an occurrence in Chester, Connecticut.
Read More About Sillimanite / Source
Silver

Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from Latin argentum ‘silver’, derived from the Proto-Indo-European h₂erǵ ‘shiny, white’) and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth’s crust in the pure, free elemental form (“native silver”), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining.
Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as “0.940 fine”. As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures.
Other than in currency and as an investment medium (coins and bullion), silver is used in solar panels, water filtration, jewellery, ornaments, high-value tableware and utensils (hence the term “silverware”), in electrical contacts and conductors, in specialized mirrors, window coatings, in catalysis of chemical reactions, as a colorant in stained glass, and in specialized confectionery. Its compounds are used in photographic and X-ray film. Dilute solutions of silver nitrate and other silver compounds are used as disinfectants and microbiocides (oligodynamic effect), added to bandages, wound-dressings, catheters, and other medical instruments.
Read More About Silver / Source
Simonellite
Simonellite (1,1-dimethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-7-isopropyl phenanthrene) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with a chemical formula C19H24. It is similar to retene.
Simonellite occurs naturally as an organic mineral derived from diterpenes present in conifer resins. It is named after its discoverer, Vittorio Simonelli (1860–1929), an Italian geologist. It forms colorless to white orthorhombic crystals. It occurs in Fognano, Tuscany, Italy.
Simonellite, together with cadalene, retene and ip-iHMN, is a biomarker of higher plants, which makes it useful for paleobotanic analysis of rock sediments.
Read More About Simonellite / Source
Simpsonite

Simpsonite has a general formula of Al4(Ta,Nb)3O13(OH). It occurs as euhedral to subhedral tabular to short and prismatic crystals, commonly in subparallel groups. Under the petrographic microscope it has a very high relief.
Discovered in 1938, it was named after Edward Sydney Simpson (1875–1939), government mineralogist and analyst of Western Australia. It is an accessory mineral in some tantalum-rich granite pegmatites. It occurs in association with tantalite, manganotantalite, microlite, tapiolite, beryl, spodumene, montebrasite, pollucite, petalite, eucryptite, tourmaline, muscovite and quartz. It is found in a few locations around the world, notably in the Onca and Paraiba mines of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil and at Tabba Tabba, Western Australia.
Read More About Simpsonite / Source
Sincosite

Sincosite is a green mineral discovered in 1922. It is named for Sincos, Daniel Alcides Carrión Province, Peru, where it was first discovered.
Read More About Sincosite / Source
Sinkankasite

Sinkankasite, mineral formula: H2MnAl(PO4)2(OH)·6H2O, was named after John Sinkankas (1915–2002), noted author and mineral collector, Scripps Institute of Oceanography. It is triclinic; as colorless, bladed to prismatic crystals up to 4 mm in length, often as divergent, radial aggregates and as pseudomorphs after triphlyte crystals; occurs in the Barker pegmatite (formerly Ferguson pegmatite), east of Keystone, South Dakota, and in the Palermo pegmatite, North Groton, New Hampshire.
Read More About Sinkankasite / Source
Sinoite
Sinoite is rare mineral with the chemical formula Si2N2O. It was first found in 1905 in chondrite meteorites and identified as a distinct mineral in 1965. Sinoite crystallizes upon meteorite impact as grains smaller than 0.2 mm surrounded by Fe-Ni alloys and the mineral enstatite. It is named after its SiNO composition and can be prepared in the laboratory as a silicon oxynitride ceramic.
The crystalline structure of silicon oxynitride is built by SiN3O tetrahedra connected through oxygen atoms along the c axis and through nitrogen atoms perpendicular to it. The strong covalent bonding of this structure results in high flexural strength and resistance to heating and oxidation up to temperatures of about 1600 °C.
Read More About Sinoite / Source
Skaergaardite
Skaergaardite is an intermetallic platinum group mineral with the general chemical formula PdCu. The mineral is named after its discovery location: the Skaergaard intrusion, Kangerdlugssuaq area, East Greenland. The mineral name was approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 2003. The mineral has also been reported in the Duluth intrusion in Minnesota and the Rum layered intrusion in Scotland.
Read More About Skaergaardite / Source
Sklodowskite

Sklodowskite is a uranium mineral with the chemical formula: Mg(UO2)2(HSiO4)2·5H2O. It is a secondary mineral which contains magnesium and is a bright yellow colour, its crystal habit is acicular, but can form in other shapes. It has a Mohs hardness of about 2–3.
It is named after the maiden name of Marie Skłodowska Curie. It is the magnesium analogue of the much more common uranium mineral Cuprosklodowskite, which contains copper instead.
It was discovered by Alfred Schoep (1881–1966) in 1924.
Read More About Sklodowskite / Source
Skutterudite

Skutterudite is a cobalt arsenide mineral containing variable amounts of nickel and iron substituting for cobalt with the ideal formula CoAs3. Some references give the arsenic a variable formula subscript of 2–3. High nickel varieties are referred to as nickel-skutterudite, previously chloanthite. It is a hydrothermal ore mineral found in moderate to high temperature veins with other Ni-Co minerals. Associated minerals are arsenopyrite, native silver, erythrite, annabergite, nickeline, cobaltite, silver sulfosalts, native bismuth, calcite, siderite, barite and quartz. It is mined as an ore of cobalt and nickel with a by-product of arsenic.
The crystal structure of this mineral has been found to be exhibited by several compounds with important technological uses.
The mineral has a bright metallic luster, and is tin white or light steel gray in color with a black streak. The specific gravity is 6.5 and the hardness is 5.5–6. Its crystal structure is isometric with cube and octahedron forms similar to that of pyrite. The arsenic content gives a garlic odor when heated or crushed.
Skutterudite was discovered in Skuterud Mines, Modum, Buskerud, Norway, in 1845. Smaltite is an alternative name for the mineral. Notable occurrences include Cobalt, Ontario, Skuterud, Norway, and Franklin, New Jersey, in the United States. The rare arsenide minerals are classified in Dana’s sulfide mineral group, even though it contains no sulfur.
Read More About Skutterudite / Source
Smaltite

Smaltite is a variety of the mineral skutterudite consisting of cobalt, iron, nickel, and arsenide. It has the chemical formula (Co,Fe,Ni)As2.
Smaltite crystallizes in the cubic system with the same hemihedral symmetry as pyrite; crystals have usually the form of cubes or cubo-octahedra, but are imperfectly developed and of somewhat rare occurrence. More often the mineral is found as compact or granular masses. The color is tin-white to steel-grey, with a metallic luster; the streak is greyish black. Hardness is 5.5 and the specific gravity is 6.5. The cobalt is partly replaced by iron and nickel, and as the latter increases in amount there is a passage to the isomorphous species chloanthite (NiAs2).Smaltite occurs in veins with ores of cobalt, nickel, copper and silver. The best known localities are Cobalt, Ontario and Schneeberg in Saxony, Germany. The name smaltite was given by F. S. Beudant in 1832 because the mineral was used in the preparation of smalt for producing a blue color in porcelain and glass.
Read More About Smaltite / Source
Smectite
A smectite (from ancient Greek σμηκτός smektos ‘lubricated’; σμηκτρίς smektris ‘walker’s earth’, ‘fuller’s earth’; rubbing earth; earth that has the property of cleaning) is a mineral mixtures of various swelling sheet silicates (phyllosilicates), which have a three-layer 2:1 (TOT) structure and belong to the clay minerals. Smectites mainly consist of montmorillonite, but can often contain secondary minerals such as quartz and calcite.
Read More About Smectite / Source
Smithsonite

Smithsonite, also known as zinc spar, is the mineral form of zinc carbonate (ZnCO3). Historically, smithsonite was identified with hemimorphite before it was realized that they were two different minerals. The two minerals are very similar in appearance and the term calamine has been used for both, leading to some confusion. The distinct mineral smithsonite was named in 1832 by François Sulpice Beudant in honor of English chemist and mineralogist James Smithson (c.1765–1829), who first identified the mineral in 1802.Smithsonite is a variably colored trigonal mineral which only rarely is found in well formed crystals. The typical habit is as earthy botryoidal masses. It has a Mohs hardness of 4.5 and a specific gravity of 4.4 to 4.5.
Smithsonite occurs as a secondary mineral in the weathering or oxidation zone of zinc-bearing ore deposits. It sometimes occurs as replacement bodies in carbonate rocks and as such may constitute zinc ore. It commonly occurs in association with hemimorphite, willemite, hydrozincite, cerussite, malachite, azurite, aurichalcite and anglesite. It forms two limited solid solution series, with substitution of manganese leading to rhodochrosite, and with iron, leading to siderite. A variety rich in cadmium, which gives it a bright yellow color, is sometimes called turkey fat ore.
Read More About Smithsonite / Source
Sodalite

Sodalite ( SOH-də-lyte) is a tectosilicate mineral with the formula Na8(Al6Si6O24)Cl2, with royal blue varieties widely used as an ornamental gemstone. Although massive sodalite samples are opaque, crystals are usually transparent to translucent. Sodalite is a member of the sodalite group with hauyne, nosean, lazurite and tugtupite.
First discovered by Europeans in 1811 in the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex in Greenland, sodalite did not become important as an ornamental stone until 1891 when vast deposits of fine material were discovered in Ontario, Canada.
Read More About Sodalite / Source
Soddyite

Soddyite is a mineral of uranium. It has yellow crystals and usually mixed with curite in oxidized uranium ores. It is named after the British radiochemist and physicist Frederick Soddy (1877–1956). Soddyite has been a valid species since 1922, following its discovery in the locality of the Shinkolobwe uranium mine in the Haut-Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
Read More About Soddyite / Source
Sonolite

Sonolite is a mineral with formula Mn9(SiO4)4(OH,F)2. The mineral was discovered in 1960 in the Sono mine in Kyoto Prefecture, Japan. In 1963, it was identified as a new mineral and named after the Sono mine.
Read More About Sonolite / Source
Sperrylite

Sperrylite is a platinum arsenide mineral with the chemical formula PtAs2 and is an opaque metallic tin white mineral which crystallizes in the isometric system with the pyrite group structure. It forms cubic, octahedral or pyritohedral crystals in addition to massive and reniform habits. It has a Mohs hardness of 6 – 7 and a very high specific gravity of 10.6.
It was discovered by Francis Louis Sperry, an American chemist, in 1889 at Sudbury.
The most important occurrence of sperrylite is in the nickel ore deposit of Sudbury Basin in Ontario, Canada. It also occurs in the layered igneous complex of the Bushveld region of South Africa and the Oktyabr’skoye copper-nickel deposit of the Eastern-Siberian Region, Russia.
Read More About Sperrylite / Source
Spertiniite

Spertiniite is a rare copper hydroxide mineral. Chemically, it is copper(II) hydroxide with the formula Cu(OH)2. It occurs as blue to blue-green tabular orthorhombic crystal aggregates in a secondary alkaline environment altering chalcocite. Associated minerals include chalcocite, atacamite, native copper, diopside, grossular, and vesuvianite.
Read More About Spertiniite / Source
Spessartine

Spessartine is a nesosilicate, manganese aluminium garnet species, Mn2+3Al2(SiO4)3. This mineral is sometimes mistakenly referred to as spessartite.Spessartine’s name is a derivative of Spessart in Bavaria, Germany, the type locality of the mineral. It occurs most often in granite pegmatite and allied rock types and in certain low-grade metamorphic phyllites. Sources include Australia, Myanmar, India, Afghanistan, Israel, Madagascar, Namibia, Nigeria, Mozambique, Tanzania and the United States. Spessartine of an orange-yellow has been called Mandarin garnet and is found in Madagascar. Violet-red spessartines are found in rhyolites in Colorado and Maine. In Madagascar, spessartines are exploited either in their bedrock or in alluvium. The orange garnets result from sodium-rich pegmatites. Spessartines are found in bedrock in the highlands in the Sahatany valley. Those in alluvium are generally found in southern Madagascar or in the Maevatanana region.Spessartine forms a solid solution series with the garnet species almandine. Well-formed crystals from this series, varying in color from very dark-red to bright yellow-orange, were found in Latinka, Rhodope Mountains, Kardzhali Province, Bulgaria. Spessartine, like the other garnets, always occurs as a blend with other species. Gems with high spessartine content tend toward a light orange hue, while almandine prevalence induces red or brownish hues.
Read More About Spessartine / Source
Sphalerite

Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula (Zn,Fe)S. It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in sedimentary exhalative, Mississippi-Valley type, and volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfides), calcite, dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite.German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word sphaleros, meaning “deceiving”, due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral.In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as zinc blende, black-jack, and ruby blende. Marmatite is an opaque black variety with a high iron content.
Read More About Sphalerite / Source
Spherocobaltite

Spherocobaltite or sphaerocobaltite is a cobalt carbonate mineral with chemical composition CoCO3. In its (rare) pure form, it is typically a rose-red color, but impure specimens can be shades of pink to pale brown. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system.
Read More About Spherocobaltite / Source
Spinel

Spinel is the magnesium/aluminium member of the larger spinel group of minerals. It has the formula MgAl2O4 in the cubic crystal system. Its name comes from the Latin word spinella, which means spine in reference to its pointed crystals.
Read More About Spinel / Source
Spodumene

Spodumene is a pyroxene mineral consisting of lithium aluminium inosilicate, LiAl(SiO3)2, and is a source of lithium. It occurs as colorless to yellowish, purplish, or lilac kunzite (see below), yellowish-green or emerald-green hiddenite, prismatic crystals, often of great size. Single crystals of 14.3 m (47 ft) in size are reported from the Black Hills of South Dakota, United States.The naturally-occurring low-temperature form α-spodumene is in the monoclinic system , and the high-temperature β-spodumene crystallizes in the tetragonal system. α-spodumene converts to β-spodumene at temperatures above 900 °C. Crystals are typically heavily striated parallel to the principal axis. Crystal faces are often etched and pitted with triangular markings.
Read More About Spodumene / Source
Spurrite

Spurrite is a white, yellow or light blue mineral with monoclinic crystals. Its chemical formula is Ca5(SiO4)2CO3.Spurrite is generally formed in contact metamorphism zones as mafic magmas are intruded into carbonate rocks. Spurrite’s space group is P 2/a. It is biaxial with a birefringence of 0.0390–0.0400, giving second order red interference colors when viewed under crossed polarizers in a petrographic microscope.The calcium is in six-fold coordination with the oxygen, the silicon is in a four-fold coordination with the oxygen and the carbon is in two-fold coordination. One unique characteristic of spurrite is that it actually abides by two twin laws. Polysynthetic twinning can occur along its (001) and another type of twinning can occur parallel to its optical axes.
Read More About Spurrite / Source
Stannite

Stannite is a mineral, a sulfide of copper, iron, and tin, in the category of thiostannates.
Read More About Stannite / Source
Stannoidite

Stannoidite is a sulfide mineral composed of five chemical elements: copper, iron, zinc, tin and sulfur. Its name originates from Latin stannum (tin) and Greek eides (or Latin oïda meaning “like”). The mineral is found in hydrothermal Cu-Sn deposits.Stannoidite was first described in 1969 for an occurrence in the Konjo mine, Okayama prefecture, Honshu Island, Japan.
Read More About Stannoidite / Source
Staurolite

Staurolite is a reddish brown to black, mostly opaque, nesosilicate mineral with a white streak. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, has a Mohs hardness of 7 to 7.5 and the chemical formula: Fe2+2Al9O6(SiO4)4(O,OH)2. Magnesium, zinc and manganese substitute in the iron site and trivalent iron can substitute for aluminium.
Read More About Staurolite / Source
Steacyite

Steacyite is a complex silicate mineral containing thorium and uranium; formula Kvariable(Ca,Na)2(Th,U)Si8O20. It forms small brown or yellow green crystals, often cruciform twinned crystals. It is radioactive. It was discovered at Mont-Saint-Hilaire, Quebec in 1982 and is named after Harold Robert Steacy (1923–2012), mineralogist.
Read More About Steacyite / Source
Stellerite

Stellerite is a rare mineral discovered by and named after Georg Wilhelm Steller, a German explorer and zoologist. The mineral has a general formula of Ca[Al2Si7O18]·7H2O. Like most rare minerals, there are few commercial uses for stellerite. Mineral collectors are lucky to find it in good enough crystal form. Zeolites, including stellerite, have been studied using a dehydration process to gauge the potential use of their phases as molecular sieves, sorbents, and catalysts.
Read More About Stellerite / Source
Stephanite

Stephanite is a silver antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula: Ag5SbS4. It is composed of 68.8% silver, and sometimes is of importance as an ore of this metal.
Read More About Stephanite / Source
Stercorite
Stercorite is the mineral form of microcosmic salt. The name comes from the Latin “stercus”, meaning dung, since the mineral was originally discovered among guano.
Read More About Stercorite / Source
Stibarsen

Stibarsen or allemontite is a natural form of arsenic antimonide (AsSb) or antimony arsenide (SbAs). The name stibarsen is derived from Latin stibium (antimony) and arsenic, whereas allemonite refers to the locality Allemont in France where the mineral was discovered. It is found in veins at Allemont, Isère, France; Valtellina, Italy; and the Comstock Lode, Nevada; and in a lithium pegmatites at Varuträsk, Sweden. Stibarsen is often mixed with pure arsenic or antimony, and the original description in 1941 proposed to use stibarsen for AsSb and allemontite for the mixtures. Since 1982, the International Mineralogical Association considers stibarsen as the correct mineral name.
Read More About Stibarsen / Source
Stibiconite
Stibiconite is an antimony oxide mineral with formula: Sb3O6(OH). Its name originates from Greek stíbi (στίβι), ‘antimony’ and kónis (κόνις), ‘powder’, alluding to its composition and habit. It is a member of the pyrochlore super group.
Read More About Stibiconite / Source
Stibiopalladinite

Stibiopalladinite is a mineral containing the chemical elements palladium and antimony. Its chemical formula is Pd5Sb2. It is a silvery white to steel grey opaque mineral crystallizing in the hexagonal crystal system.It was first described in 1929 for an occurrence in the Bushveld igneous complex of South Africa.
Read More About Stibiopalladinite / Source
Stibnite

Stibnite, sometimes called antimonite, is a sulfide mineral with the formula Sb2S3. This soft grey material crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. It is the most important source for the metalloid antimony. The name is derived from the Greek στίβι stibi through the Latin stibium as the former name for the mineral and the element antimony.
Read More About Stibnite / Source
Stichtite

Stichtite is a mineral, a carbonate of chromium and magnesium; formula Mg6Cr2CO3(OH)16·4H2O. Its colour ranges from pink through lilac to a rich purple colour. It is formed as an alteration product of chromite containing serpentine. It occurs in association with barbertonite (the hexagonal polymorph of Mg6Cr2CO3(OH)16·4H2O), chromite and antigorite.Discovered in 1910 on the west coast of Tasmania, Australia, it was first recognised by A.S. Wesley a former chief chemist with the Mount Lyell Mining and Railway Company, it was named after Robert Carl Sticht the manager of the mine.It is observed in combination with green serpentine at Stichtite Hill near the Dundas Extended Mine, Dundas – east of Zeehan, as well as on the southern shore of Macquarie Harbour. It is exhibited in the West Coast Pioneers Museum in Zeehan. The only commercial mine for stichtite serpentine is located on Stichtite Hill. Stichtite has also been reported from the Barberton District, Transvaal; Darwendale, Zimbabwe; near Bou Azzer, Morocco; Cunningsburgh, the Shetland Islands of Scotland; Langban, Varmland, Sweden; the Altai Mountains, Russia; Langmuir Township, Ontario and the Megantic, Quebec; Bahia, Brazil; and the Keonjhar district, Orissa, India.It is sometimes used as a gemstone.
Read More About Stichtite / Source
Stilbite

Stilbite is the name of a series of tectosilicate minerals of the zeolite group. Prior to 1997, stilbite was recognized as a mineral species, but a reclassification in 1997 by the International Mineralogical Association changed it to a series name, with the mineral species being named:
Stilbite-Ca
Stilbite-NaStilbite-Ca, by far the more common of the two, is a hydrous calcium sodium and aluminium silicate, NaCa4(Si27Al9)O72·28(H2O). In the case of stilbite-Na, sodium dominates over calcium. The species are visually indistinguishable, and the series name stilbite is still used whenever testing has not been performed.
Read More About Stilbite / Source
Stillwaterite
Stillwaterite is a palladium arsenide mineral which has a general formula of Pd8As3. Stillwaterite was first discovered in the Banded and Upper zones of the Stillwater igneous complex in Montana, United States, and has been reported in the Lac-des-Iles area of Ontario, Canada. Outside of North America, this rare mineral has been found in northern Finland.
Read More About Stillwaterite / Source
Stilpnomelane

Stilpnomelane is a phyllosilicate mineral. It has the chemical formula K(Fe2+,Mg,Fe3+)8(Si,Al)12(O,OH)27·n(H2O).Stilpnomelane occurs associated with banded iron formations. It is a metamorphic mineral associated with the blueschist and greenschist facies.It was first described in 1827 for an occurrence in Moravia in the Czech Republic. The name is derived from the Greek stilpnos for shining, and melanos for black.
Read More About Stilpnomelane / Source
Stishovite
Stishovite is an extremely hard, dense tetragonal form (polymorph) of silicon dioxide. It is very rare on the Earth’s surface; however, it may be a predominant form of silicon dioxide in the Earth, especially in the lower mantle.Stishovite was named after Sergey M. Stishov, a Russian high-pressure physicist who first synthesized the mineral in 1961. It was discovered in Meteor Crater in 1962 by Edward C. T. Chao.Unlike other silica polymorphs, the crystal structure of stishovite resembles that of rutile (TiO2). The silicon in stishovite adopts an octahedral coordination geometry, being bound to six oxides. Similarly, the oxides are three-connected, unlike low-pressure forms of SiO2. In most silicates, silicon is tetrahedral, being bound to four oxides. It was long considered the hardest known oxide (~30 GPa Vickers); however, boron suboxide has been discovered in 2002 to be much harder. At normal temperature and pressure, stishovite is metastable.
Stishovite can be separated from quartz by applying hydrogen fluoride (HF); unlike quartz, stishovite will not react.
Read More About Stishovite / Source
Stolzite

Stolzite is a mineral, a lead tungstate; with the formula PbWO4. It is similar to, and often associated with, wulfenite which is the same chemical formula except that the tungsten is replaced by molybdenum. Stolzite crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system and is dimorphous with the monoclinic form raspite.Lead tungstate crystals have the optical transparency of glass combined with much higher density (8.28 g/cm3 vs ~2.2 g/cm3 for fused silica). They are used as scintillators in particle physics because of their short radiation length (0.89 cm), low Molière radius (2.2 cm), quick scintillation response, and radiation hardness. Lead tungstate crystals are used in the Compact Muon Solenoid’s electromagnetic calorimeter.It was first described in 1820 by August Breithaupt, who called it Scheelbleispath and then by François Sulpice Beudant in 1832, who called it scheelitine. In 1845, Wilhelm Karl Ritter von Haidinger coined the name stolzite for an occurrence in Krusne Hory (Erzgebirge), Czech Republic, naming it after Joseph Alexi Stolz of Teplice in Bohemia. It occurs in oxidized hydrothermal tungsten-lead ore deposits typically in association with raspite, cerussite, anglesite, pyromorphite and mimetite.
Read More About Stolzite / Source
Strashimirite

Strashimirite (IMA symbol: Ssh) is a rare monoclinic mineral containing arsenic, copper, hydrogen, and oxygen. It has the chemical formula Cu8(AsO4)4(OH)4·5(H2O).This mineral was discovered in Zapachitsa (Zapacica) copper deposit, Svoge, Sofia Oblast, Bulgaria in 1960, by the Bulgarian mineralogist Jordanka Minceva-Stefanova. She named the mineral after Strashimir Dimitrov (1892-1960), Professor in Mineralogy and Petrography at Sofia University “St Kliment Ohridski”, Bulgaria. The International Mineralogical Association approved it as a new mineral in 1968.It occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation zone of copper arsenide deposits. It occurs associated with tyrolite, cornwallite, clinoclase, euchroite, olivenite, parnauite, goudeyite, arthurite, metazeunerite, chalcophyllite, cyanotrichite, scorodite, pharmacosiderite, brochantite,
azurite, malachite and chrysocolla.Although it remains quite rare, strashimirite has subsequently been identified in a number of locations including: Novoveska Huta in the Czech Republic; on the west flank of Cherbadung (Pizzo Cervandone), Binntal,
Valais, Switzerland; in Kamsdorf and Saalfeld, Thuringia, Germany; the Clara mine, near Oberwolfach, Black Forest, Germany; in the Richelsdorf Mountains, Hesse, Germany; Cap Garonne mine, near le Pradet, Var, and Triembach-au-Val, Haut-Rhin, France; Wheals Gorland and Unity, Gwennap, Cornwall, England; the Tynagh mine, near Loughrea, Co.
Galway, Ireland; the Majuba Hill mine, Antelope district, Pershing Co. Nevada, US; and the Centennial Eureka mine, Tintic district, Juab Co., Utah, US.
Read More About Strashimirite / Source
Strengite

Strengite is a relatively rare iron phosphate mineral with the formula: FePO4 · 2H2O. The mineral is named after the German mineralogist Johann August Streng (1830–1897). Lavender, pink or purple in hue, it is similar to variscite and is partially soluble, particularly in conditions where there is a low pH and low oxidation-reduction potential. The color comes from ferric ion (Fe3+ )
Read More About Strengite / Source
Stromeyerite

Stromeyerite is a sulfide mineral of copper and silver, with the chemical formula AgCuS. It forms opaque blue grey to dark blue orthorhombic crystals.
It was discovered in 1832 in Central Bohemia Region, Czech Republic, and named after the German chemist, Friedrich Stromeyer who performed the first analysis of the mineral.
Read More About Stromeyerite / Source
Strontianite

Strontianite (SrCO3) is an important raw material for the extraction of strontium. It is a rare carbonate mineral and one of only a few strontium minerals. It is a member of the aragonite group.
Aragonite group members: aragonite (CaCO3), witherite (BaCO3), strontianite (SrCO3), cerussite (PbCO3)
The ideal formula of strontianite is SrCO3, with molar mass 147.63 g, but calcium (Ca) can substitute for up to 27% of the strontium (Sr) cations, and barium (Ba) up to 3.3%.The mineral was named in 1791 for the locality, Strontian, Argyllshire, Scotland, where the element strontium had been discovered the previous year. Although good mineral specimens of strontianite are rare, strontium is a fairly common element, with abundance in the Earth’s crust of 370 parts per million by weight, 87 parts per million by moles, much more common than copper with only 60 parts per million by weight, 19 by moles.
Strontium is never found free in nature. The principal strontium ores are celestine SrSO4 and strontianite SrCO3. The main commercial process for strontium metal production is reduction of strontium oxide with aluminium.
Read More About Strontianite / Source
Struvite

Struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) is a phosphate mineral with formula: NH4MgPO4·6H2O. Struvite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as white to yellowish or brownish-white pyramidal crystals or in platy mica-like forms. It is a soft mineral with Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2 and has a low specific gravity of 1.7. It is sparingly soluble in neutral and alkaline conditions, but readily soluble in acid.
Struvite urinary stones and crystals form readily in the urine of animals and humans that are infected with ammonia-producing organisms. They are potentiated by alkaline urine and high magnesium excretion (high magnesium/plant-based diets). They also are potentiated by a specific urinary protein in domestic cats.
Read More About Struvite / Source
Studenitsite

Studenitsite is a rare borate mineral with chemical formula of NaCa2[B9O14(OH)4]·2H2O.
Studenitsite has a vitreous luster, a Mohs hardness of 6 and color of light-dirty yellow. It is a monoclinic mineral and belongs to the space group P2/c. The basic unit of the crystal structure[B9O14(OH)4]5-layers has a Miller Index of (001). Studenitsite has a low surface relief, which means the measure of the relative difference between the index of refraction of the mineral and surrounding medium is small. Birefringence is the difference between two principal indices of refraction of a uniaxial crystal. Studenitsite has a maximum birefringent value of δ = 0.032. Studenitsite has three indices of refraction. Their values are nα = 1.532, nβ = 1.538, nγ = 1.564. Indices of refraction are the ratio of the light’s speed in the mineral and the medium.Studenitsite is an extremely rare mineral that has only been found in the Piskaya deposit, Yarondolskii Basin, on the Ibar River, 280 km south of Belgrade, Serbia. The deposit is classified as a volcanogenic-sedimentary borate deposit with clay and carbonate minerals. It occurs associated with colemanite, howlite, ulexite and pentahydroborite. It is a rare but important mineral for understanding the volcanic settings in Western Serbia. It was named after the Studenica cloister near the discovery location.
Read More About Studenitsite / Source
Studtite

Studtite, chemical formula [(UO2)O2(H2O)2]·2(H2O) or UO4·4(H2O), is a secondary uranium mineral containing peroxide formed by the alpha-radiolysis of water during formation. It occurs as pale yellow to white needle-like crystals often in acicular, white sprays.
Studtite was originally described by Vaes in 1947 from specimens from Shinkolobwe, Katanga Copper Crescent, Katanga (Shaba), Democratic Republic of Congo, and has since been reported from several other localities. The mineral was named for Franz Edward Studt, an English prospector and geologist who was working for the Belgians.
When exposed to air studtite converts over a short time to the metastudtite UO4·2(H2O) form. Despite their apparent chemical simplicity, these two uranyl species are the only reported peroxide minerals.They may also be readily formed on the surface of nuclear waste under long-term storage and have been found on the surface of spent nuclear fuel stored at the Hanford, Washington nuclear site. It has also been reported that studtite has since formed on the corium lavas that were created during the course of the Chernobyl nuclear plant accident. Thus, there is considerable evidence that uranyl peroxides such as studtite and metastudtite will be important alteration phases of nuclear waste, possibly at the expense of other minerals, such as uranyl oxides and silicates, which have been more thoroughly studied and are better understood. The formation of these minerals may impact the long-term performance of deep geological repository sites such as Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository. Due to insufficient information about these minerals it is unknown if they will make radioactive wastes more or less stable, but the presence of studtite and metastudtite provides a pathway for mobilizing insoluble U(IV) from the corroding fuel surface into soluble uranyl species.
Read More About Studtite / Source
Sturmanite

Sturmanite is a rare sulfate mineral with the chemical formula Ca6Fe3+2(SO4)2.5(B(OH)4)(OH)12 · 25 H2O. It crystallises in the tetragonal system and it has a Moh’s hardness of 2.5. Sturmanite has a bright yellow to amber colour and falls in the ettringite group. It was named after Bozidar Darko Sturman (born 1937), Croatian-Canadian mineralogist and Curator Emeritus of Mineralogy, Royal Ontario Museum.
Read More About Sturmanite / Source
Stützite

Stützite or stuetzite is a silver telluride mineral with formula: Ag5−xTe3 (with x = 0.24 to 0.36) or Ag7Te4.It was first described in 1951 from a museum specimen from Sacarimb, Romania. It was named for Austrian mineralogist Xavier Stütz (1747–1806).It occurs with other sulfide and telluride minerals in hydrothermal ore occurrences. Associated minerals include sylvanite, hessite, altaite, petzite, empressite, native tellurium, native gold, galena, sphalerite, colusite, tennantite and pyrite.
Read More About Stützite / Source
Suanite
Suanite is a magnesium borate mineral with formula Mg2B2O5.
It was first described in 1953 by Japanese scientist Takeo Watanabe from the University of Tokyo.
His first contact with the mineral was during analysis of gold- and copper- bearing skarn minerals from the Hol Kol mine, located in North Korea obtained in 1939. Due to the small sample size available to him, he was only able to determine the unknown substance’s optical properties under a microscope. Watanabe was able to return to the site in 1943 and obtain further samples that permitted him to perform chemical analysis on the material.
Read More About Suanite / Source
Suessite
Suessite is a rare iron silicide mineral with chemical formula: Fe3Si. The mineral was named after Professor Hans E. Suess. It was discovered in 1982 during the chemical analysis of The North Haig olivine pigeonite achondrite (ureilite). It is a cream white color in reflected light, and ranges in size from 1 μm “blebs” to elongated grains that can reach up to 0.45 cm in length. This mineral belongs in the isometric crystal class. The isometric class has crystallographic axes that are all the same length and each of the three axes perpendicular to the other two. It is isotropic, has a structural type of DO3 and a crystal lattice of BiF3.
Read More About Suessite / Source
Sugilite

Sugilite ( SOO-gə-lyte, -jee-) is a relatively rare pink to purple cyclosilicate mineral with the complex chemical formula KNa2(Fe, Mn, Al)2Li3Si12O30. Sugilite crystallizes in the hexagonal system with prismatic crystals. The crystals are rarely found and the form is usually massive. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5–6.5 and a specific gravity of 2.75–2.80. It is mostly translucent.
Sugilite was first described in 1944 by the Japanese petrologist Ken-ichi Sugi (1901–1948) for an occurrence on Iwagi Islet, Japan, where it is found in an aegirine syenite intrusive stock. It is found in a similar environment at Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada. In the Wessels mine in Northern Cape Province of South Africa, sugilite is mined from a strata-bound manganese deposit. It is also reported from Liguria and Tuscany, Italy; New South Wales, Australia and Madhya Pradesh, India.Sugilite is commonly pronounced with a soft “g”, as in “ginger”. However, as with most minerals, its pronunciation is intended to be the same as the person it is named after; in this case, the Japanese name Sugi has a hard “g”, as in “geese”.The mineral is also referred to as lavulite, luvulite, and royal azel by gem and mineral collectors.
Read More About Sugilite / Source
Sulfur

Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature.
Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means “burning stone”. Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum. The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of sulfuric acid for sulfate and phosphate fertilizers, and other chemical processes. Sulfur is used in matches, insecticides, and fungicides. Many sulfur compounds are odoriferous, and the smells of odorized natural gas, skunk scent, grapefruit, and garlic are due to organosulfur compounds. Hydrogen sulfide gives the characteristic odor to rotting eggs and other biological processes.
Sulfur is an essential element for all life, but almost always in the form of organosulfur compounds or metal sulfides. Amino acids (two proteinogenic: cysteine and methionine, and many other non-coded: cystine, taurine, etc.) and two vitamins (biotin and thiamine) are organosulfur compounds crucial for life. Many cofactors also contain sulfur, including glutathione, and iron–sulfur proteins. Disulfides, S–S bonds, confer mechanical strength and insolubility of the (among others) protein keratin, found in outer skin, hair, and feathers. Sulfur is one of the core chemical elements needed for biochemical functioning and is an elemental macronutrient for all living organisms.
Read More About Sulfur / Source
Sursassite

Sursassite is a sorosilicate mineral. It was first discovered in 1926. It was first found in the Sursass (Oberhalbstein), a district of Graubünden, Switzerland. It is generally found in deposits of metamorphosed manganese.
Read More About Sursassite / Source
Susannite

Susannite is a lead sulfate carbonate hydroxide mineral. It has the formula Pb4SO4(CO3)2(OH)2. Susannite is the higher temperature phase of the two and forms above 80 °C when fluids oxidize the lead ore deposits. It is trimorphous with leadhillite and macphersonite.Susannite crystallizes in the trigonal system. It is quite soft with a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3.0 and a relatively high specific gravity of 6.57.
It was discovered in 1827 in the Susannah Mine, Leadhills in the county of Lanark, Scotland. In addition to the type locality in Scotland, it has also been reported from various locations in Germany, the Tiger Mine in Pinal County, Arizona, from Iporanga, Sao Paulo, Brazil, and the Tsumeb mine of Namibia.
Read More About Susannite / Source
Sussexite

Sussexite is a manganese borate mineral MnBO2(OH). Crystals are monoclinic prismatic and typically fibrous in occurrence. Colour is white, pink, yellowish white with a pearly lustre. It has a Mohs hardness of 3 and a specific gravity of 3.12.It is named after the Franklin Mining District in Sussex County, New Jersey, US where it was first discovered in 1868.
Sussexite also occurs in France, Italy, Namibia, North Korea, South Africa, Switzerland, and the US states of Michigan, New Jersey, Utah and Virginia.
Read More About Sussexite / Source
Svanbergite

Svanbergite is a colorless, yellow or reddish mineral with the chemical formula SrAl3(PO4)(SO4)(OH)6. It has rhombohedral crystals.It was first described for an occurrence in Varmland, Sweden in 1854 and named for Swedish chemist Lars Fredrik Svanberg (1805–1878).It occurs in high aluminium medium-grade metamorphic rocks; in bauxite deposits and from sulfate enriched argillic alteration ( high silica and clay) associated with hydrothermal systems often replacing apatite. It occurs with pyrophyllite, kyanite, andalusite, lazulite, augelite, alunite, kaolinite and quartz.
Read More About Svanbergite / Source
Sweetite
Sweetite has a general formula of Zn(OH)2. The name is given after a curator of mineral department of The British Museum, Jessie May Sweet (1901–1979). It occurs in an oxidized vein in limestone bedrock with galena, ashoverite, wülfingite, anglesite, cerussite, hydrocerussite, litharge, fluorite, palygorskite and calcite.Sweetite is tetragonal, which means crystallographically it contains one axis of unequal length and two axes of equal length. The angles between three of the axes are all 90°. It belongs to the space group 4/m. Some crystals show evidence of a basal plane and a few are tabular. In terms of its optical properties, sweetite has two indices of refraction, 1.635 along the ordinary ray and 1.628 along the extraordinary ray. The index of refraction is the velocity of light in vacuum divided by the velocity of light in medium. It also has the birefringence of 0.007. The birefringence means the decomposition of light into two rays when passing through a mineral. Sweetite is 1.64 – 1.65 in relief, which is medium to high in intensity and means a measure of the relative difference between the index of refraction of a mineral and its surrounding medium.Sweetite is mostly found from a limestone quarry 200–300 m northwest of Milltown, near Ashover, Derbyshire, England.
Read More About Sweetite / Source
Switzerite

Switzerite is a mineral with the chemical formula of (Mn)3(PO4)2·7H2O. The mineral was named after George Switzer, former Curator of Minerals at the US National Museum.The mineral is monoclinic prismatic, meaning that it has one mirror plane, one 2-fold rotation axis which is perpendicular to the mirror plane and a center of symmetry. Switzerite is a part of the monoclinic space group P 21/a. For its optical properties, Switzerite is classified as anisotropic, has a low surface relief and birefringence of δ = 0.020.Switzerite was first discovered in the 1960s and is a relatively uncommon mineral found in a few localities in Europe, North America, and Australia. This mineral is found in phosphate mines, along with other phosphate minerals. Alone, Switzerite does not have a huge significance due to its rarity and extremely small size. This mineral is found with other phosphate minerals thus, the importance of Switzerite is that it is used, along with the other phosphate minerals, for agricultural purposes. It is unstable and immediately dehydrates into metaswitzerite on exposure to the atmosphere.
Read More About Switzerite / Source
Sylvanite

Sylvanite or silver gold telluride, chemical formula (Ag,Au)Te2, is the most common telluride of gold.
Read More About Sylvanite / Source
Sylvite

Sylvite, or sylvine, is potassium chloride (KCl) in natural mineral form. It forms crystals in the isometric system very similar to normal rock salt, halite (NaCl). The two are, in fact, isomorphous. Sylvite is colorless to white with shades of yellow and red due to inclusions. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a specific gravity of 1.99. It has a refractive index of 1.4903. Sylvite has a salty taste with a distinct bitterness.
Sylvite is one of the last evaporite minerals to precipitate out of solution. As such, it is only found in very dry saline areas. Its principal use is as a potassium fertilizer.
Sylvite is found in many evaporite deposits worldwide. Massive bedded deposits occur in New Mexico and western Texas, and in Utah in the US, but the largest world source is in Saskatchewan, Canada. The vast deposits in Saskatchewan, Canada were formed by the evaporation of a Devonian seaway. Sylvite is the official mineral of Saskatchewan.
Sylvite was first described in 1832 at Mount Vesuvius near Napoli in Italy and named for the Dutch chemist, François Sylvius de le Boe (1614–1672).Sylvite, along with quartz, fluorite and halite, is used for spectroscopic prisms and lenses.
Read More About Sylvite / Source
Synchysite-(Ce)

Synchysite-(Ce) is a carbonate mineral and an end member of the synchysite group. The general chemical formula is Ca(Ce,La)(CO3)2F.
Read More About Synchysite-(Ce) / Source
Syngenite

Syngenite is an uncommon potassium calcium sulfate mineral with formula K2Ca(SO4)2·H2O. It forms as prismatic monoclinic crystals and as encrustations.
Read More About Syngenite / Source
Szenicsite

Szenicsite is a copper hydroxy molybdate mineral, named after husband and wife Terry and Marissa Szenics, American mineral collectors who found the first specimens. When it was first discovered in Atacama, Chile, it was thought to be lindgrenite. The occurrence appeared in an isolated area, which was about one cubic meter in size. The mineral occurred in cavities of copper bearing powellite and matrix rich molybdenite. These cavities were filled with a material resembling clay. Outside of the zone the szenicsite crystals grew, copper levels seemed to decrease, and the mineralization changed to lindgrenite. Moving further from the zone, the minerals growing seemed to be lacking copper, and consisted of powellite blebs in the ore. Szenicsite was approved by the IMA in 1993.
Read More About Szenicsite / Source
Taaffeite

Taaffeite (; BeMgAl4O8) is a mineral, named after its discoverer Richard Taaffe (1898–1967) who found the first sample, a cut and polished gem, in October 1945 in a jeweler’s shop in Dublin, Ireland. As such, it is the only gemstone to have been initially identified from a faceted stone. Most pieces of the gem, prior to Taaffe, had been misidentified as spinel. For many years afterwards, it was known only in a few samples, and it is still one of the rarest gemstone minerals in the world.Since 2002, the International Mineralogical Association-approved name for taaffeite as a mineral is magnesiotaaffeite-2N’2S.
Read More About Taaffeite / Source
Tachyhydrite
Tachyhydrite is an unstable mineral, a hydrous chloride of calcium and magnesium with formula: CaMg2Cl6·12H2O. It is a rare component of marine evaporite salt deposits. Upon exposure to moist air it rapidly deliquesces and dissolves.
It forms a colorless to yellow trigonal crystal with a vitreous luster. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 2 and has a low specific gravity of 1.66. It has good cleavage in three directions and typically occurs in crystalline masses.
It was first described in 1856 for an occurrence in Stassfurt, Saxony, Germany. Its name is from the Greek for quick water, in reference to its ready deliquescence.According to a patent filed years ago by a Halliburton researcher, high strength hydrochloric acid treatment of magnesium containing carbonates creates tachyhydrite, which will seal the rock pores and inhibit oil flow unless washed with a light acid or water before and after the treatment.
Read More About Tachyhydrite / Source
Taenite

Taenite is a mineral found naturally on Earth mostly in iron meteorites. It is an alloy of iron and nickel, with a chemical formula of Fe,Ni and nickel proportions of 20% up to 65%.
The name is derived from the Greek ταινία for “band, ribbon”. Taenite is a major constituent of iron meteorites. In octahedrites it is found in bands interleaving with kamacite forming Widmanstätten patterns, whereas in ataxites it is the dominant constituent. In octahedrites a fine intermixture with kamacite can occur, which is called plessite.
Taenite is one of four known Fe-Ni meteorite minerals: The others are kamacite, tetrataenite, and antitaenite.
Read More About Taenite / Source
Taikanite
Taikanite is a silicate mineral. It was named after the Taikan Range, Russia, its type locality.
Read More About Taikanite / Source
Talc

Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant. It is an ingredient in ceramics, paints, and roofing material. It is a main ingredient in many cosmetics. It occurs as foliated to fibrous masses, and in an exceptionally rare crystal form. It has a perfect basal cleavage and an uneven flat fracture, and it is foliated with a two-dimensional platy form.
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 1 as the hardness of talc, the softest mineral. When scraped on a streak plate, talc produces a white streak; though this indicator is of little importance, because most silicate minerals produce a white streak. Talc is translucent to opaque, with colors ranging from whitish grey to green with a vitreous and pearly luster. Talc is not soluble in water, and is slightly soluble in dilute mineral acids.Soapstone is a metamorphic rock composed predominantly of talc.
Talmessite

Talmessite is a hydrated calcium magnesium arsenate, often with significant amounts of cobalt or nickel. It was named in 1960 for the type locality, the Talmessi mine, Anarak district, Iran. It forms a series with β-Roselite, where cobalt replaces some of the magnesium, and with gaitite, where zinc replaces the magnesium. All these minerals are members of the fairfieldite group. Talmessite is dimorphic with wendwilsonite (which is not a member of this group).
Read More About Talmessite / Source
Talnakhite

Talnakhite is a mineral of chalcopyrite group with formula: Cu9(Fe, Ni)8S16. It was named after the Talnakh ore deposit, near Norilsk in Western Siberia, Russia where it was discovered as reported in 1963 by I. Budko and E. Kulagov. It was officially named “talnakhite” in 1968. Despite the initial announcement it turned out to be not a face centered high-temperature polymorph of chalcopyrite, but to have composition Cu18(Fe, Ni)18S32. At 80 °C (176 °F) to 100 °C (212 °F) it decomposes to tetragonal cubanite plus bornite.
Read More About Talnakhite / Source
Tamarugite

Tamarugite (NaAl(SO4)2·6H2O) is a colorless monoclinic sulfate mineral.Deposits containing tamarugite are geographically dispersed with occurrences of the mineral on all seven continents (Antarctica, Oceania, North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa). also in the Ghoroghchi area in Iran. The mineral’s name comes from the Tamarugal Pampa locality in Chile. It is also known as lapparentite.
Read More About Tamarugite / Source
Tangeite

Tangeite, also known as calciovolborthite, is a calcium, copper vanadate mineral with formula: CaCu(VO4)(OH). It occurs as a secondary mineral that can be found in sandstone and also in the oxidized zones of vanadium bearing deposits.
It was named in 1925 by Aleksandr Evgenievich Fersman for its discovery locality in the Tange Gorge, Ferghana Valley, Alai Mountains, Kyrgyzstan.
Read More About Tangeite / Source
Tantalite

The mineral group tantalite [(Fe, Mn)Ta2O6] is the primary source of the chemical element tantalum, a corrosion (heat and acid) resistant metal. It is chemically similar to columbite, and the two are often grouped together as a semi-singular mineral called coltan or “columbite-tantalite” in many mineral guides. However, tantalite has a much greater specific gravity than columbite (8.0+ compared to columbite’s 5.2). Iron-rich tantalite is the mineral tantalite-(Fe) or ferrotantalite and manganese-rich is tantalite-(Mn) or manganotantalite.
Tantalite is also very close to tapiolite. Those minerals have the same chemical composition, but different crystal symmetry: orthorhombic for tantalite and tetragonal for tapiolite.Tantalite is black to brown in both color and streak. Manganese-rich tantalites can be brown and translucent.
Read More About Tantalite / Source
Tantite
Tantite is a rare tantalum oxide mineral with formula: Ta2O5. Tantite forms transparent microscopic colorless triclinic – pedial crystals with an adamantine luster. It has a Mohs hardness of 7 and a high specific gravity of 8.45. Chemical analyses show minor inclusion (1.3%) of niobium oxide.
It was first described in 1983 for an occurrence in a pegmatite in the Kola peninsula, Russia. It has also been reported from a pegmatite complex in Florence County, Wisconsin. Associated mineral species include elbaite, lepidolite, spodumene, columbite-tantalite, wodginite, and microlite.
Read More About Tantite / Source
Tapiolite

Tapiolite [(Fe, Mn)(Nb, Ta)2O6] is a black mineral series that is an ore of niobium and tantalum. The tapiolite group includes tapiolite-(Fe) or ferrotapiolite and tapiolite-(Mn) or manganotapiolite. Tapiolite-(Fe) is by far the more common of the two.The minerals have a submetallic luster and a high specific gravity with tapiolite-Fe having a higher specific gravity (7.90) versus 7.72 for tapiolite-Mn.The mineral was named in 1863 after the forest god Tapio of Finnish mythology, and the original tapiolite material came from Sukula, Tammela, Tavastia Proper, Finland.Tapiolite is very close to columbite and tantalite. Those minerals have the same chemical composition, but different crystal symmetry orthorhombic for tantalite or columbite and tetragonal for tapiolite.
Read More About Tapiolite / Source
Taranakite

Taranakite is a hydrated alkali iron-aluminium phosphate mineral with chemical formula (K,Na)3(Al,Fe3+)5(PO4)2(HPO4)6·18 H2O. It forms from the reaction of clay minerals or aluminous rocks with solutions enriched in phosphate derived from bat or bird guano or, less commonly, from bones or other organic matter. Taranakite is most commonly found in humid, bat inhabited caves near the boundary of guano layers with the cave surface. It is also found in perennially wet coastal locations that have been occupied by bird colonies. The type location, and its namesake, the Sugar Loaf Islands off Taranaki, New Zealand, is an example of a coastal occurrence.
Taranakite forms small white, pale yellow, or gray crystals, which are typically found in pulverulent nodular aggregates, or crusts. Taranakite crystallizes in the hexagonal system, and is noted as having the longest crystallographic axis of any known mineral: the c-axis of the taranakite unit cell is 9.505 nanometers long.
Read More About Taranakite / Source
Tarapacaite
Tarapacáite is the mineral form of potassium chromate with the chemical formula K2CrO4. It forms bright yellow crystals and was discovered in 1878. It is named for the former Tarapacá Province, Peru; nowadays belonging to Chile. The boundaries between Peru, Bolivia and Chile were vague in the Atacama Desert before the War of the Pacific (1879–1883). Its type locality is Oficina Maria Elena, Maria Elena, Tocopilla Province, Antofagasta Region, Chile. It is unlikely to occur anywhere except in highly arid conditions as it is easily soluble in water.
Read More About Tarapacaite / Source
Tarbuttite

Tarbuttite is a rare phosphate mineral with formula Zn2(PO4)(OH). It was discovered in 1907 in what is now Zambia and named for Percy Coventry Tarbutt.
Read More About Tarbuttite / Source
Tausonite

Tausonite is the rare naturally occurring mineral form of strontium titanate: chemical formula: SrTiO3. It occurs as red to orange brown cubic crystals and crystal masses.
It is a member of the perovskite group.
It was first described in 1982 for an occurrence in a syenite intrusive in Tausonite Hill, Murun Massif, Olyokma-Chara Plateau, Sakha Republic, Yakutia, geologically part of the Aldan Shield, Eastern-Siberian Region, Russia. It was named for Russian geochemist Lev Vladimirovich Tauson (1917–1989). It has also been reported from a fenite dike associated with a carbonatite complex in Sarambi, Concepción Department, Paraguay. and in high pressure metamorphic rocks along the Kotaki River area of Honshu Island, Japan.
Read More About Tausonite / Source
Teallite

Teallite is a sulfide mineral of tin and lead with chemical formula: PbSnS2. It occurs in hydrothermal veins and is sometimes mined as an ore of tin. Teallite forms soft silvery grey mica-like plates and crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. The Mohs hardness is 1.5 to 2 and the specific gravity is 6.4.
Teallite was first described in 1904 from its type locality in Santa Rosa, Antequera, Bolivia. It was named for the British geologist Jethro Justinian Harris Teall (1849–1924).
Read More About Teallite / Source
Tellurite
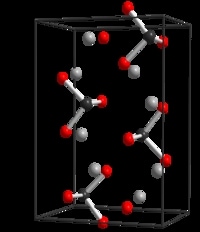
The tellurite ion is TeO2−3. A tellurite (compound), for example sodium tellurite, is a compound that contains this ion. They are typically colorless or white salts, which in some ways are comparable to sulfite. A mineral with the formula TeO2 is called tellurite.
Read More About Tellurite / Source
Tellurium

Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth’s crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.Tellurium-bearing compounds were first discovered in 1782 in a gold mine in Kleinschlatten, Transylvania (now Zlatna, Romania) by Austrian mineralogist Franz-Joseph Müller von Reichenstein, although it was Martin Heinrich Klaproth who named the new element in 1798 after the Latin tellus ‘earth’. Gold telluride minerals are the most notable natural gold compounds. However, they are not a commercially significant source of tellurium itself, which is normally extracted as a by-product of copper and lead production.
Commercially, the primary use of tellurium is CdTe solar panels and thermoelectric devices. A more traditional application in copper (tellurium copper) and steel alloys, where tellurium improves machinability also consumes a considerable portion of tellurium production. Tellurium is considered a technology-critical element.Tellurium has no biological function, although fungi can use it in place of sulfur and selenium in amino acids such as tellurocysteine and telluromethionine. In humans, tellurium is partly metabolized into dimethyl telluride, (CH3)2Te, a gas with a garlic-like odor exhaled in the breath of victims of tellurium exposure or poisoning.
Read More About Tellurium / Source
Tellurobismuthite

Tellurobismuthite, or tellurbismuth, is a telluride mineral: bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3). It crystallizes in the trigonal system. There are natural cleavage planes in the (0001) direction as the crystal is effectively lamellar (layered) in that plane. The Mohs hardness is 1.5 – 2 and the specific gravity is 7.815. It is a dull grey color, which exhibits a splendent luster on fresh cleavage planes.
Read More About Tellurobismuthite / Source
Temagamite
Temagamite is a bright white palladium mercury telluride mineral with a hardness of 2+1⁄2 on the Mohs scale. Its chemical formula is Pd3HgTe3. It was discovered at the Temagami Mine on Temagami Island, Lake Temagami in 1973, and it represents a rare mineral in the Temagami Greenstone Belt.
It occurs as microscopic inclusions within massive chalcopyrite at Temagami in association with other rare tellurides: merenskyite, stützite, hessite and an unnamed Pd-Hg-Ag telluride. In addition to the discovery locality, it has been reported from the Stillwater igneous complex in Montana and the New Rambler copper–nickel mine in the Medicine Bow Mountains of Wyoming.
Read More About Temagamite / Source
Tennantite

Tennantite is a copper arsenic sulfosalt mineral with an ideal formula Cu12As4S13. Due to variable substitution of the copper by iron and zinc the formula is Cu6[Cu4(Fe,Zn)2]As4S13. It is gray-black, steel-gray, iron-gray or black in color. A closely related mineral, tetrahedrite (Cu12Sb4S13) has antimony substituting for arsenic and the two form a solid solution series. The two have very similar properties and is often difficult to distinguish between tennantite and tetrahedrite. Iron, zinc, and silver substitute up to about 15% for the copper site.The mineral was first described for an occurrence in Cornwall, England in 1819, where it occurs as small crystals of cubic or dodecahedral form, and was named after the English chemist Smithson Tennant (1761–1815).
It is found in hydrothermal veins and contact metamorphic deposits in association with other Cu–Pb–Zn–Ag sulfides and sulfosalts, pyrite, calcite, dolomite, siderite, barite, fluorite and quartz.The arsenic component of tennantite causes the metal smelted from the ore to be harder than that of pure copper, because it is a copper-arsenic alloy. In the later 20th century, it was found that arsenical coppers had been more widely used in antiquity than had been previously realised, and it has been proposed that discoveries made by smelting ores like tennantite were significant steps in the progress towards the Bronze Age.
Read More About Tennantite / Source
Tenorite

Tenorite is a copper oxide mineral with the chemical formula CuO.
Read More About Tenorite / Source
Tephroite

Tephroite is the manganese endmember of the olivine group of nesosilicate minerals with the formula Mn2SiO4. A solid solution series exists between tephroite and its analogues, the group endmembers fayalite and forsterite. Divalent iron or magnesium may readily replace manganese in the olivine crystal structure.
It was first described for an occurrence at the Sterling Hill Mine and Franklin, New Jersey, United States. It occurs in iron-manganese ore deposits and their related skarns. It also occurs in metamorphosed manganese-rich sediments. It occurs in association with: zincite, willemite, franklinite, rhodonite, jacobsite, diopside, gageite, bustamite, manganocalcite, glaucochroite, calcite, banalsite and alleghanyite. It can also be found in England and Sweden.
Tephroite has a hardness of 6 and a specific gravity of approximately 4.1, which is heavy for non-metallic minerals. Its name comes from the Greek tephros, “ash gray”, for its color. It can also be found olive-green, greenish-blue, pink, or brown. Other names for tephroite include mangan olivine and mangan peridot.
Read More About Tephroite / Source
Terlinguaite

Terlinguaite is the naturally occurring mineral with formula Hg2ClO. It is formed by the weathering of other mercury-containing minerals. It was discovered in 1900 in the Terlingua District of Brewster County, Texas, for which it is named. Its color is yellow, greenish yellow, brown, or olive green.
Read More About Terlinguaite / Source
Teruggite
Teruggite is a mineral with the chemical formula Ca4MgAs2B12O22(OH)12·12H2O. It is colorless. Its crystals are monoclinic prismatic. It is transparent. It is not radioactive. It has vitreous luster. Teruggite is rated 2.5 on the Mohs Scale of hardness.
Read More About Teruggite / Source
Tetradymite

Tetradymite is a mineral consisting of bismuth, tellurium and sulfide, Bi2Te2S, also known as telluric bismuth. If sulfur is absent the mineral is tellurobismuthite and the formula is then Bi2Te3. Traces of selenium are usually present.
Crystals are rhombohedral, but are rarely distinctly developed; they are twinned together in groups of four; hence the name of the mineral, from the Greek for fourfold. There is a perfect cleavage parallel to the basal plane and the mineral usually occurs in foliated masses of irregular outline. The color is steel-gray, and the luster metallic and brilliant. The mineral is very soft (H = 1.5 – 2) and marks paper. The specific gravity is 7.2 to 7.9.The type locality is Zupkov (Zsubko; Schubkau), Stredoslovenský Kraj, Slovak Republic where it was reported in 1831. It was first found, in 1815, at Telemark in Norway. It often occurs in high temperature hydrothermal quartz veins associated with native gold and in contact metamorphic deposits.
Read More About Tetradymite / Source
Tetrahedrite

Tetrahedrite is a copper antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula: (Cu,Fe)12Sb4S13. It is the antimony endmember of the continuous solid solution series with arsenic-bearing tennantite. Pure endmembers of the series are seldom if ever seen in nature. Of the two, the antimony rich phase is more common. Other elements also substitute in the structure, most notably iron and zinc, along with less common silver, mercury and lead. Bismuth also substitutes for the antimony site and bismuthian tetrahedrite or annivite is a recognized variety. The related, silver dominant, mineral species freibergite, although rare, is notable in that it can contain up to 18% silver.
Read More About Tetrahedrite / Source
Tetrataenite

Tetrataenite is a native metal alloy composed of chemically-ordered L10-type FeNi, recognized as a mineral in 1980. The mineral is named after its tetragonal crystal structure and its relation to the iron-nickel alloy, taenite. It is one of the mineral phases found in meteoric iron.
Read More About Tetrataenite / Source
Thaumasite

Thaumasite is a calcium silicate mineral, containing Si atoms in unusual octahedral configuration, with chemical formula Ca3Si(OH)6(CO3)(SO4)·12H2O, also sometimes more simply written as CaSiO3·CaCO3·CaSO4·15H2O.
It occurs as colorless to white prismatic hexagonal crystals, typically as acicular radiating groups. It also occurs as fibrous masses. Its Mohs hardness is 3.5 and it has a specific gravity of 1.88 to 1.90. Optically it is uniaxial negative with indices of refraction of nω = 1.507 and nε = 1.468.
It occurs as a hydrothermal alteration mineral in sulfide ore deposits and geothermal alteration of basalt and tuff. It occurs with zeolites, apophyllite, analcime, calcite, gypsum and pyrite.Thaumasite can also be formed in man-made concrete structures at the detriment of calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H, with dashes denoting the non-stoichiometry of this hydrated cement phase acting as the “glue” in hardened cement paste) during cement alteration, especially when sulfate attack develops. The reaction consuming the silicates of the “cement glue” can lead to harmful decohesion and softening (more rarely to expansion and cracking) of concrete. Unlike conventional sulfate attack, in which the calcium hydroxide (portlandite) and calcium aluminate hydrates react with sulfates to form gypsum and ettringite (an expansive phase) respectively, in the case of the thaumasite form of sulfate attack (TSA) the calcium silicate hydrates ensuring the cohesion in the hardened cement paste are also destroyed. As a consequence, even concrete containing sulfate-resisting Portland cement may be affected.It was first described in 1878 in Sweden and named from the Greek, “thaumazein”, to be surprised, in reference to its unusual composition with carbonate, sulfate and hydroxysilicate anions.The silicate structure of thaumasite is unusual due to the presence of non-tetrahedral silicon in its crystal lattice. Indeed, an atypic octahedral configuration is observed for Si present in thaumasite in the form of hexahydroxysilicate: [Si(OH)6]2−, a species exhibiting a geometry similar to that of the hexafluorosilicate [SiF6]2−.
Read More About Thaumasite / Source
Thénardite

Thénardite is an anhydrous sodium sulfate mineral, Na2SO4 which occurs in arid evaporite environments, specifically lakes and playas. It also occurs in dry caves and old mine workings as an efflorescence and as a crusty sublimate deposit around fumaroles. It occurs in volcanic caves on Mount Etna, Italy. It was first described in 1825 for an occurrence in the Espartinas Saltworks, Ciempozuelos, Madrid, Spain and was named for the French chemist, Louis Jacques Thénard (1777–1826).Thénardite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and often forms yellowish, reddish to gray white prismatic crystals although usually in massive crust deposits. Thénardite is fluorescent, white in shortwave and yellow-green in longwave UV radiation.
In humid conditions, thenardite progressively absorbs water and converts to the deca-hydrated mineral mirabilite, Na2SO4 · 10 H2O.
Read More About Thénardite / Source
Thermonatrite

Thermonatrite is a naturally occurring evaporite mineral form of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3·H2O.It was first described in 1845. Its name is from the Greek θερμός thermos, “heat”, plus natron, because it may be a dehydration product of natron.Typical occurrence is in dry saline lake beds and as soil encrustations. It has been reported from volcanic fumaroles and in association with carbonatite-related veins. Common associated minerals include trona, natron and halite.
Read More About Thermonatrite / Source
Thiospinel
The thiospinel group is a group of sulfide minerals with a general formula AB2X4 where A is nominally a +2 metal, B is a +3 metal and X is -2 sulfide or similar anion (selenide or telluride). Thio refers to sulfur and spinel indicates their isometric spinel-like structure.As the chalcogens S, Se and Te are less electronegative than oxygen, the bonding in these materials is generally more covalent than in the oxospinels. Some are (magnetic) semiconductors but others display, at times complicated, metallic behavior, often coupled with equally complicated magnetic properties. The assignment of oxidation states is also not always as straightforward as in the more ionic oxocompounds, as is shown in the case of carrollite.
Group members include:
Cadmoindite – CdIn2S4
Carrollite – CuCo2S4
Fletcherite – Cu(Ni,Co)2S4
Greigite – Fe2+Fe3+2S4
Indite – FeIn2S4
Kalininite – ZnCr2S4
Linnaeite – Co2+Co3+2S4
Polydymite – Ni2+Ni3+2S4
Siegenite – (Ni,Co)3S4
Tyrrellite – Cu(Co,Ni)2Se4
Violarite – Fe2+Ni3+2S4
Read More About Thiospinel / Source
Thomasclarkite-(Y)

Thomasclarkite-(Y) is a rare mineral which was known as UK-93 until 1997, when it was renamed in honour of Thomas H. Clark (1893–1996), McGill University professor. The mineral is one of many rare-earth element minerals from Mont Saint-Hilaire. The only reported occurrence is in an alkalic pegmatite dike in an intrusive gabbro-nepheline syenite.
Read More About Thomasclarkite-(Y) / Source
Thomsenolite

Thomsenolite is a mineral with formula: NaCaAlF6·H2O. It is an alteration product of cryolite.It was discovered in 1868 in Ivigtut, Greenland and named for Hans Peter Jorgen Julius Thomsen (1826–1909).
Read More About Thomsenolite / Source
Thomsonite

Thomsonite is the name of a series of tecto-silicate minerals of the zeolite group. Prior to 1997, thomsonite was recognized as a mineral species, but a reclassification in 1997 by the International Mineralogical Association changed it to a series name, with the mineral species being named thomsonite-Ca and thomsonite-Sr. Thomsonite-Ca, by far the more common of the two, is a hydrous sodium, calcium and aluminium silicate, NaCa2Al5Si5O20·6H2O. Strontium can substitute for the calcium and the appropriate species name depends on the dominant element. The species are visually indistinguishable and the series name thomsonite is used whenever testing has not been performed. Globally, thomsonite is one of the rarer zeolites.
Thomsonite was first identified in material from Scotland in 1820. It is named for the Scottish chemist Thomas Thomson. The crystal system of thomsonite is orthorhombic. The Mohs hardness is 5 to 5.5. It is transparent to translucent and has a density of 2.3 to 2.4. It may be colorless, white, beige, or somewhat green, yellow, or red. The crystals tend to be long thin blades that typically form radial aggregates, and sometimes fans and tufts. The aggregates are variable and may be spikey in appearance, dense and ball-like, or form worm-like growths. Tight acicular radiating clusters and sphericules are common forms.
Thomsonite occurs with other zeolites in the amygdaloidal cavities of basaltic volcanic rocks, and occasionally in granitic pegmatites. Examples have been found in Faroe Islands (var. Faroelite), Scotland, Arkansas, Colorado, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, Oregon, Ontario, Nova Scotia, India, and Russia.Nodules of massive thomsonite that display an attractive banded coloring are found along the shore of Lake Superior. Most of these thomsonite nodules and their derived pebbles are less than 0.6 cm (1/4 inch). Those enclosed in basalt are extremely difficult to remove without breaking them. Consequently, a very large percentage of those used as gemstones are from pebbles collected from beaches.
Read More About Thomsonite / Source
Thorianite

Thorianite is a rare thorium oxide mineral, ThO2. It was originally described by Ananda Coomaraswamy in 1904 as uraninite, but recognized as a new species by Wyndham R. Dunstan. It was so named by Dunstan on account of its high percentage of thorium; it also contains the oxides of uranium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium and neodymium. Helium is present, and the mineral is slightly less radioactive than pitchblende, but is harder to shield due to its high energy gamma rays. It is common in the alluvial gem-gravels of Sri Lanka, where it occurs mostly as water worn, small, heavy, black, cubic crystals. The largest crystals are usually near 1.5 cm. Larger crystals, up to 6 cm (2.4 in), have been reported from Madagascar.
Read More About Thorianite / Source
Thorite

Thorite, (Th,U)SiO4, is a rare nesosilicate of thorium that crystallizes in the tetragonal system and is isomorphous with zircon and hafnon. It is the most common mineral of thorium and is nearly always strongly radioactive. It was named in 1829 to reflect its thorium content. Thorite was discovered in 1828 on the island of Løvøya, Norway, by the vicar and mineralogist, Hans Morten Thrane Esmark, who sent the first specimens of this black mineral to his father, Jens Esmark, who was a professor of mineralogy and geology.
Read More About Thorite / Source
Thortveitite

Thortveitite is a rare mineral consisting of scandium yttrium silicate (Sc,Y)2Si2O7. It is the primary source of scandium. Occurrence is in granitic pegmatites. It was named after Olaus Thortveit, a Norwegian engineer. It is grayish-green, black or gray in color.A transparent gem quality example was found in 2004, and reported in “The Journal of Gemmology”.
Read More About Thortveitite / Source
Tiemannite

Tiemannite is a mineral, mercury selenide, formula HgSe. It occurs in hydrothermal veins associated with other selenides, or other mercury minerals such as cinnabar, and often with calcite. Discovered in 1855 in Germany, it is named after Johann Carl Wilhelm Tiemann (1848–1899).
Read More About Tiemannite / Source
Tienshanite

Tienshanite, named for the Tian Shan Range in Mongolia, is a rare borosilicate mineral, though rock-forming in some parts of its original locality at the Dara-i-Pioz Glacier in Tajikistan. Its formula is extremely complex: KNa3(Na,K,[])6(Ca,Y,RE)2Ba6(Mn2+,Fe2+,Zn,Ti)6(Ti,Nb)6Si36B12O114[O5.5(OH,F)3.5]F2.
Read More About Tienshanite / Source
Tin

Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from Latin stannum) and atomic number 50. A silvery-coloured metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, the so-called “tin cry” can be heard as a result of twinning in tin crystals; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, zinc, and mercury in its solid state.
Pure tin after solidifying presents a mirror-like appearance similar to most metals. In most tin alloys (e.g. pewter) the metal solidifies with a dull grey colour.
Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, SnO2. Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th-most abundant element on Earth and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the largest number of stable isotopes in the periodic table, due to its magic number of protons.
It has two main allotropes: at room temperature, the stable allotrope is β-tin, a silvery-white, malleable metal; at low temperatures it is less dense grey α-tin, which has the diamond cubic structure. Metallic tin does not easily oxidize in air and water.
The first tin alloy used on a large scale was bronze, made of 1⁄8 tin and 7⁄8 copper, from as early as 3000 BC. After 600 BC, pure metallic tin was produced. Pewter, which is an alloy of 85–90% tin with the remainder commonly consisting of copper, antimony, bismuth, and sometimes lead and silver, has been used for flatware since the Bronze Age. In modern times, tin is used in many alloys, most notably tin-lead soft solders, which are typically 60% or more tin, and in the manufacture of transparent, electrically conducting films of indium tin oxide in optoelectronic applications. Another large application is corrosion-resistant tin plating of steel. Because of the low toxicity of inorganic tin, tin-plated steel is widely used for food packaging as tin cans. Some organotin compounds can be extremely toxic.
Tinaksite

Tinaksite (chemical formula K2Na(Ca,Mn2+)2TiO[Si7O18(OH)]) is a mineral found in northern Russia. Tinaksite can be grayish-white, yellowish, orange, or brown, and it is often found in charoite. Its name is derived from its composition: titanium (Ti), sodium (Na) potassium (K) and silicon (Si). The International Mineralogical Association first recognized tinaksite as a mineral in 1965.
Read More About Tinaksite / Source
Tincalconite

Tincalconite is a hydrous sodium borate mineral closely related to borax, and is a secondary mineral that forms as a dehydration product of borax. Its formula is Na2B4O7·5H2O or Na2[B4O5(OH)4]·3H2O.
Tincalconite typically occurs as a fine grained white powder. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system and has been found as primary euhedral di-rhombohedral, pseudo-octahedral crystals. It is also found pseudomorphically replacing borax crystals. It has a specific gravity of 1.88 and a Mohs hardness of 2. Refractive index values are nω=1.460 and nε=1.470.
While most tincalconite is created by man through exposing borax to dry air, there are natural occurrences of tincalconite, as in Searles Lake, California where it was first described in 1878. In addition to several California and Nevada locations it is reported from Argentina, Italy, Turkey and Ukraine.
The name comes from “tincal”, Sanskrit for borax, and Greek, “konis”, meaning powder, for its composition and typical powdery nature.
Read More About Tincalconite / Source
Titanite

Titanite, or sphene (from the Greek sphenos (σφηνώ), meaning wedge), is a calcium titanium nesosilicate mineral, CaTiSiO5. Trace impurities of iron and aluminium are typically present. Also commonly present are rare earth metals including cerium and yttrium; calcium may be partly replaced by thorium.
Read More About Titanite / Source
Titanium

Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine.
Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth’s crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and titanium trichloride (TiCl3), which is used as a catalyst in the production of polypropylene.Titanium can be alloyed with iron, aluminium, vanadium, and molybdenum, among other elements, to produce strong, lightweight alloys for aerospace (jet engines, missiles, and spacecraft), military, industrial processes (chemicals and petrochemicals, desalination plants, pulp, and paper), automotive, agriculture (farming), medical prostheses, orthopedic implants, dental and endodontic instruments and files, dental implants, sporting goods, jewelry, mobile phones, and other applications.The two most useful properties of the metal are corrosion resistance and strength-to-density ratio, the highest of any metallic element. In its unalloyed condition, titanium is as strong as some steels, but less dense. There are two allotropic forms and five naturally occurring isotopes of this element, 46Ti through 50Ti, with 48Ti being the most abundant (73.8%).
Read More About Titanium / Source
Titanowodginite

Titanowodginite is a mineral with the chemical formula MnTiTa2O8. Titanowodginite has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 and a vitreous luster. It is an iridescent dark brown to black crystal that commonly forms in a matrix of smoky quartz or white beryl in a complex zoned pegmatite.It was first described in 1992 for an occurrence in the Tanco Mine located in southern Manitoba, Canada. It was named because it is a titanium bearing member of the wodginite group.
Read More About Titanowodginite / Source
Tobermorite

Tobermorite is a calcium silicate hydrate mineral with chemical formula:
Ca5Si6O16(OH)2·4H2O or
Ca5Si6(O,OH)18·5H2O.
Two structural varieties are distinguished: tobermorite-11 Å and tobermorite-14 Å.
Tobermorite occurs in hydrated cement paste and can be found in nature as an alteration mineral in metamorphosed limestone and in skarn. It has been reported to occur in the Maqarin Area of north Jordan and in the Crestmore Quarry near Crestmore Heights, Riverside County, California.
Tobermorite was first described in 1880 for an occurrence in Scotland, on the Isle of Mull, around the locality of Tobermory.
Read More About Tobermorite / Source
Todorokite

Todorokite is a rare complex hydrous manganese oxide mineral with the chemical formula (Na,Ca,K,Ba,Sr)1-x(Mn,Mg,Al)6O12·3-4H2O. It was named in 1934 for the type locality, the Todoroki mine, Hokkaido, Japan. It belongs to the prismatic class 2/m of the monoclinic crystal system, but the angle β between the a and c axes is close to 90°, making it seem orthorhombic. It is a brown to black mineral which occurs in massive or tuberose forms. It is quite soft with a Mohs hardness of 1.5, and a specific gravity of 3.49 – 3.82. It is a component of deep ocean basin manganese nodules.
Read More About Todorokite / Source
Tokyoite

Tokyoite is a rare barium manganese vanadate mineral with the chemical formula: Ba2(Mn3+,Fe3+)OH(VO4)2. It is the manganese analogue of the iron rich gamagarite and the barium analogue of the lead vanadate, brackebuschite.It occurs in low-grade metamorphosed sedimentary manganese ore deposits associated with hyalophane, braunite and tamaite.It was first reported for an occurrence in the Shiromaru Mine, Okutama, Tama district, Tokyo Prefecture, Kantō region, Honshu Island, Japan and approved by the IMA in 2003. It has been found in two mines in Italy and one in Japan, for which it was named.
Read More About Tokyoite / Source
Tongbaite
Tongbaite is a rare mineral that has the chemical formula Cr3C2, or chromium carbide.
It was first described in 1983 for an occurrence in Liu village, Tongbai County (桐柏县), Henan Province, China and named for the locality. It occurs in an ultramafic rock deposit. It has also been found in the Tibet Autonomous Region and the Isovsky District, in the Urals of Russia.
Read More About Tongbaite / Source
Topaz

Topaz is a silicate mineral of aluminium and fluorine with the chemical formula Al2SiO4(F,OH)2. It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can make it pale blue or golden brown to yellow orange. Topaz is often treated with heat or radiation to make it a deep blue, reddish-orange, pale green, pink, or purple.
Although it is often associated with golden yellow and blue, it comes in a variety of colors, including colorless. The rarest are natural pinks, reds, and delicate golden oranges, sometimes with pink hues.Topaz is a nesosilicate mineral. It is one of the hardest naturally occurring minerals and has a relatively low index of refraction. It occurs in many places in the world.
Read More About Topaz / Source
Torbernite

Torbernite is a radioactive, hydrated green copper uranyl phosphate mineral, found in granites and other uranium-bearing deposits as a secondary mineral. Its name derives from the Swedish chemist Torbern Bergman (1735–1784), It is also known as chalcolite. Torbernite is isostructural with the related uranium mineral, autunite.The chemical formula of torbernite is similar to that of autunite in which a Cu2+ cation replaces a Ca2+. The number of water hydration molecules can vary between 12 and 8, giving rise to the variety of metatorbernite when torbernite spontaneously dehydrates. Their respective chemical compositions are the following:
Torbernite
Cu(UO2)2(PO4)2 · 12 H2OMetatorbernite
Cu(UO2)2(PO4)2 · 8 H2OTorbernite’s most common alternative names are copper uranite and cupro-uranite.
Read More About Torbernite / Source
Tranquillityite
Tranquillityite is silicate mineral with formula (Fe2+)8Ti3Zr2 Si3O24. It is mostly composed of iron, oxygen, silicon, zirconium and titanium with smaller fractions of yttrium and calcium. It is named after the Mare Tranquillitatis (Sea of Tranquility), the place on the Moon where the rock samples were found during the 1969 Apollo 11 mission. It was the last mineral brought from the Moon which was thought to be unique, with no counterpart on Earth, until it was discovered in Australia in 2011.
Read More About Tranquillityite / Source
Tremolite

Tremolite is a member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals with composition: Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2. Tremolite forms by metamorphism of sediments rich in dolomite and quartz. Tremolite forms a series with actinolite and ferro-actinolite. Pure magnesium tremolite is creamy white, but the color grades to dark green with increasing iron content. It has a hardness on Mohs scale of 5 to 6. Nephrite, one of the two minerals of the gemstone jade, is a green variety of tremolite.
The fibrous form of tremolite is one of the six recognised types of asbestos. This material is toxic, and inhaling the fibers can lead to asbestosis, lung cancer and both pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma. Fibrous tremolite is sometimes found as a contaminant in vermiculite, chrysotile (itself a type of asbestos) and talc.
Read More About Tremolite / Source
Trevorite

Trevorite is a rare nickel iron oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. It has the chemical formula NiFe3+2O4. It is a black mineral with the typical spinel properties of crystallising in the cubic system, black streaked, infusible and insoluble in most acids.
There is at least partial solid solution between trevorite and magnetite, with many magnetites from ultramafic rocks containing at least trace amounts of Ni. Fe2+ and Mg2+ may substitute for Ni in trevorite.
Read More About Trevorite / Source
Tridymite

Tridymite is a high-temperature polymorph of silica and usually occurs as minute tabular white or colorless pseudo-hexagonal crystals, or scales, in cavities in felsic volcanic rocks. Its chemical formula is SiO2. Tridymite was first described in 1868 and the type location is in Hidalgo, Mexico. The name is from the Greek tridymos for triplet as tridymite commonly occurs as twinned crystal trillings (compound crystals comprising three twinned crystal components).
Read More About Tridymite / Source
Triphylite

Triphylite is a lithium iron(II) phosphate mineral with the chemical formula LiFePO4. It is a member of the triphylite group and forms a complete solid solution series with the lithium manganese(II) phosphate, lithiophilite. Triphylite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. It rarely forms prismatic crystals and is more frequently found in hypidiomorphic rock. It is bluish- to greenish-gray in color, but upon alteration becomes brown to black.
Read More About Triphylite / Source
Triplite

Triplite is a rare phosphate mineral with formula: (Mn, Fe)2PO4(F, OH). It occurs in phosphate-rich granitic pegmatites typically as irregular brown opaque masses. Triplite was first described in 1813 for an occurrence in Chanteloube, Limousin, France. The name is from the Greek triplos for triple, in reference to the three cleavage directions. In color and appearance, it is very similar to rhodocrosite, another manganese bearing mineral. Chemically, it is also quite similar to triploidite the difference being that triplite is fluorine dominant while triploidite is hydroxide dominant.
Read More About Triplite / Source
Triploidite

Triploidite is an uncommon manganese iron phosphate mineral with formula: (Mn, Fe)2PO4OH. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system and typically occurs as elongated and striated slender prisms which may be columnar to fibrous. Its crystals may be pinkish to yellowish brown or red-orange.It was first described in 1878 for an occurrence in the Branchville Quarry, Branchville, Fairfield County, Connecticut. The name is derived from its resemblance to triplite.It typically occurs as a hydrothermal alteration product of primary phosphate minerals in granite pegmatites. It occurs with triplite, lithiophilite, triphylite, eosphorite, dickinsonite and rhodochrosite.It forms a solid solution series with the iron rich wolfeite.
Read More About Triploidite / Source
Tripuhyite

Tripuhyite is an iron antimonate mineral with composition FeSbO4.
Read More About Tripuhyite / Source
Troilite

Troilite is a rare iron sulfide mineral with the simple formula of FeS. It is the iron-rich endmember of the pyrrhotite group. Pyrrhotite has the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2) which is iron deficient. As troilite lacks the iron deficiency which gives pyrrhotite its characteristic magnetism, troilite is non-magnetic.Troilite can be found as a native mineral on Earth but is more abundant in meteorites, in particular, those originating from the Moon and Mars. It is among the minerals found in samples of the meteorite that struck Russia in Chelyabinsk on February 15th, 2013. Uniform presence of troilite on the Moon and possibly on Mars has been confirmed by the Apollo, Viking and Phobos space probes. The relative intensities of isotopes of sulfur are rather constant in meteorites as compared to the Earth minerals, and therefore troilite from Canyon Diablo meteorite is chosen as the international sulfur isotope ratio standard, the Canyon Diablo Troilite (CDT).
Read More About Troilite / Source
Trona

Trona (trisodium hydrogendicarbonate dihydrate, also sodium sesquicarbonate dihydrate, Na2CO3•2NaHCO3•3H2O) is a non-marine evaporite mineral. It is mined as the primary source of sodium carbonate in the United States, where it has replaced the Solvay process used in most of the rest of the world for sodium carbonate production.
Read More About Trona / Source
Tschermakite

The endmember hornblende tschermakite (☐Ca2(Mg3Al2)(Si6Al2)O22(OH)2) is a calcium rich monoclinic amphibole mineral. It is frequently synthesized along with its ternary solid solution series members tremolite and cummingtonite so that the thermodynamic properties of its assemblage can be applied to solving other solid solution series from a variety of amphibole minerals.
Read More About Tschermakite / Source
Tschermigite

Tschermigite is a mineral form of ammonium alum, formula NH4Al(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is found in burning coal seams, bituminous shale and fumaroles. Because of its extreme water solubility it is unlikely to persist except in the dryest of conditions. Discovered in 1852 at Cermiky, also known as Tschermig in Bohemia. It is colorless and named for where it was discovered.
Read More About Tschermigite / Source
Tsumcorite

Tsumcorite is a rare hydrated lead arsenate mineral that was discovered in 1971, and reported by Geier, Kautz and Muller. It was named after the TSUMeb CORporation mine at Tsumeb, in Namibia, in recognition of the Corporation’s support for mineralogical investigations of the orebody at its Mineral Research Laboratory.
Read More About Tsumcorite / Source
Tsumebite

Tsumebite is a rare phosphate mineral named in 1912 after the locality where it was first found, the Tsumeb mine in Namibia, well known to mineral collectors for the wide range of minerals found there. Tsumebite is a compound phosphate and sulfate of lead and copper, with hydroxyl, formula Pb2Cu(PO4)(SO4)(OH). There is a similar mineral called arsentsumebite, where the phosphate group PO4 is replaced by the arsenate group AsO4, giving the formula Pb2Cu(AsO4)(SO4)(OH). Both minerals are members of the brackebuschite group.
Read More About Tsumebite / Source
Tugtupite

Tugtupite is a beryllium aluminium tectosilicate. It also contains sodium and chlorine and has the formula Na4AlBeSi4O12Cl. Tugtupite is a member of the silica-deficient feldspathoid mineral group. It occurs in high alkali intrusive igneous rocks.
Tugtupite is tenebrescent, sharing much of its crystal structure with sodalite, and the two minerals are occasionally found together in the same sample.
Tugtupite occurs as vitreous, transparent to translucent masses of tetragonal crystals and is commonly found in white, pink, to crimson, and even blue and green. It has a Mohs hardness of 4 and a specific gravity of 2.36. It fluoresces crimson under ultraviolet radiation.
It was first found in 1962 at Tugtup agtakôrfia Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of southwest Greenland. It has also been found at Mont-Saint-Hilaire in Quebec and in the Lovozero Massif of the Kola Peninsula in Russia
The name is derived from the Greenlandic Inuit word for reindeer (tuttu), and means “reindeer blood.”The U.S. Geological Survey reports that in Nepal, tugtupite (as well as jasper and nephrite) were found extensively in most of the rivers from the Bardia to the Dang.It is used as a gemstone.
Read More About Tugtupite / Source
Tungsten

Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternate name.
The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements, melting at 3,422 °C (6,192 °F; 3,695 K). It also has the highest boiling point, at 5,930 °C (10,706 °F; 6,203 K). Its density is 19.30 grams per cubic centimetre (0.697 lb/cu in), comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work into metal. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw.Tungsten occurs in many alloys, which have numerous applications, including incandescent light bulb filaments, X-ray tubes, electrodes in gas tungsten arc welding, superalloys, and radiation shielding. Tungsten’s hardness and high density make it suitable for military applications in penetrating projectiles. Tungsten compounds are often used as industrial catalysts.
Tungsten is the only metal in the third transition series that is known to occur in biomolecules, being found in a few species of bacteria and archaea. However, tungsten interferes with molybdenum and copper metabolism and is somewhat toxic to most forms of animal life.
Read More About Tungsten / Source
Tungstite

Tungstite is a hydrous tungsten oxide mineral with formula: WO3·H2O. It is a secondary mineral formed by the weathering of other tungsten containing minerals. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system in translucent yellow to yellow green masses. It is clay-like with Mohs hardness of 2.5 and a specific gravity of 5.5.
It was first described in 1868 for an occurrence near Trumbull, Connecticut at the Hubbard Tungsten Mine at Long Hill.
Read More About Tungstite / Source
Tuperssuatsiaite

Tuperssuatsiaite is a rare clay mineral found in Greenland, Namibia and Brazil. It is a hydrated phyllosilicate (sheet silicate) of sodium and iron.
Read More About Tuperssuatsiaite / Source
Turquoise

Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrous phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula CuAl6(PO4)4(OH)8·4H2O. It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone for millennia due to its unique hue.
Like most other opaque gems, turquoise has been devalued by the introduction of treatments, imitations, and synthetics into the market. The robin egg blue or sky blue color of the Persian turquoise mined near the modern city of Nishapur, Iran, has been used as a guiding reference for evaluating turquoise quality.
Read More About Turquoise / Source
Tusionite

Tusionite is a rare colorless to transparent to translucent yellow brown trigonal borate mineral with chemical formula: MnSn(BO3)2. The mineral is composed of 18.86% manganese, 40.76% tin, 7.42% boron, and 32.96% oxygen. It is a late stage hydrothermal mineral and occurs rarely in granite pegmatites in miarolitic cavities.
Tusionite was named for the location where the mineral was first discovered and described in 1983 in the Tusion River Valley in the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan. Tusionite has also been reported from Recice in the Czech Republic and in pegmatites at Thomas Mountain, Riverside County, California.
Read More About Tusionite / Source
Tyrolite

Tyrolite is a hydrous calcium copper arsenate carbonate mineral with the formula CaCu5(AsO4)2CO3(OH)4⋅6H2O. Tyrolite forms glassy, blue to green orthorhombic radial crystals and botryoidal masses. It has a Mohs hardness of 1.5–2.0 and a specific gravity of 3.1–3.2. It is translucent with refractive indices of nα = 1.694, nβ = 1.726, and nγ = 1.730.
It is a secondary mineral formed by the weathering of associated copper and arsenic minerals. It was first described in 1845 for an occurrence in Schwaz, Tyrol, Austria.
Read More About Tyrolite / Source
Tyrrellite
Tyrrellite is a selenide mineral that has a chemical formula of Cu(Co,Ni)2Se4. It has been found in the Goldfields District in northern Saskatchewan, as well as in the Petrovice deposit, Czech Republic. It is named after the Canadian geologist Joseph Burr Tyrrell. Joseph Tyrrell was one of the first geologists from the Geological Survey of Canada to do research in the Goldfields District.
Read More About Tyrrellite / Source
Tyuyamunite

Tyuyamunite (pronounced tuh-YOO-ya-moon-ite) is a very rare uranium mineral with formula Ca(UO2)2V2O8·(5-8)H2O. It is a member of the carnotite group. It is a bright, canary-yellow color because of its high uranium content. Also, because of tyuyamunite’s high uranium content, it is radioactive. It was named by Konstantin Avtonomovich Nenadkevich, in 1912, after its type locality, Tyuya-Muyun, Fergana Valley, Kyrgyzstan.
Read More About Tyuyamunite / Source
Actinolite

Actinolite is an amphibole silicate mineral with the chemical formula Ca2(Mg4.5-2.5Fe2+0.5-2.5)Si8O22(OH)2.
Read More About Actinolite / Source
Uchucchacuaite

Uchucchacuaite (AgMnPb3Sb5S12) is a rare sulfosalt mineral found in hydrothermal deposits.
It was first described in 1984 for an occurrence in the Uchucchacua Mine, Oyon Province, Lima Department, Peru and named for the mine. It has also been reported from mines in Hokkaido, Japan. It occurs with alabandite, galena, benavidesite, sphalerite, pyrite, pyrrhotite and arsenopyrite in the Peru deposit.
Read More About Uchucchacuaite / Source
Uklonskovite
Uklonskovite (Na Mg(S O4)F) is a colorless monoclinic mineral found in Chile, Italy and Uzbekistan. It is named after Alexandr Sergeievich Uklonskii (b. 1888), mineralogist, Academy of Sciences, Uzbekistan. Its type locality is Kushkanatau salt deposit, Lower Amu Darya River, Karakalpakstan Respublikasi, Uzbekistan.
Read More About Uklonskovite / Source
Ulexite

Ulexite (NaCaB5O6(OH)6·5H2O, hydrated sodium calcium borate hydroxide), sometimes known as TV rock or television stone, is a mineral occurring in silky white rounded crystalline masses or in parallel fibers. The natural fibers of ulexite conduct light along their long axes, by internal reflection. Ulexite was named for the German chemist Georg Ludwig Ulex (1811–1883) who first discovered it.Ulexite is a structurally complex mineral, with a basic structure containing chains of sodium, water and hydroxide octahedra. The chains are linked together by calcium, water, hydroxide and oxygen polyhedra and massive boron units. The boron units have a formula of [B5O6(OH)6]3– and a charge of −3. They are composed of three borate tetrahedra and two borate triangular groups.
Ulexite is found in evaporite deposits and the precipitated ulexite commonly forms a “cotton ball” tuft of acicular crystals. Ulexite is frequently found associated with colemanite, borax, meyerhofferite, hydroboracite, probertite, glauberite, trona, mirabilite, calcite, gypsum and halite. It is found principally in California and Nevada, US; Tarapacá Region in Chile, and Kazakhstan. Ulexite is also found in a vein-like bedding habit composed of closely packed fibrous crystals.
Ulexite is also known as TV rock due to its unusual optical characteristics. The fibers of ulexite act as optical fibers, transmitting light along their lengths by internal reflection. When a piece of ulexite is cut with flat polished faces perpendicular to the orientation of the fibers, a good-quality specimen will display an image of whatever surface is adjacent to its other side.
The fiber-optic effect is the result of the polarization of light into slow and fast rays within each fiber, the internal reflection of the slow ray and the refraction of the fast ray into the slow ray of an adjacent fiber. An interesting consequence is the generation of three cones, two of which are polarized, when a laser beam obliquely illuminates the fibers. These cones can be seen when viewing a light source through the mineral.Ulexite decomposes/dissolves in hot water.
Read More About Ulexite / Source
Ullmannite

Ullmannite is a nickel antimony sulfide mineral with formula: NiSbS. Considerable substitution occurs with cobalt and iron in the nickel site along with bismuth and arsenic in the antimony site. A solid solution series exists with the high cobalt willyamite.
Read More About Ullmannite / Source
Ulrichite

Ulrichite is a rare green uranium phosphate mineral (CaCu(UO2)[PO4]2·4H2O). It crystallizes as monoclinic prisms which occur as apple green acicular radiating clusters. It is radioactive and exhibits strong yellow fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.Ulrichite was first described in 1988 for samples from the Lake Boga granite quarry, Lake Boga, Victoria, Australia. It was named for George H. F. Ulrich (1830–1900), a 19th-century government geologist and mines department inspector. The type locality at Lake Boga is the only reported occurrence and the type specimen is located at the Museum Victoria, Melbourne, Australia, as #M38576.It is of secondary origin in granite pegmatites where it is found in miarolitic cavities. It occurs associated with turquoise, chalcosiderite, cyrilovite, torbernite, libethenite, sampleite, saleeite and fluorapatite.
Read More About Ulrichite / Source
Ulvöspinel

Ulvöspinel or ulvite is an iron titanium oxide mineral with formula: Fe2TiO4 or TiFe2+2O4. It forms brown to black metallic isometric crystals with a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6. It belongs to the spinel group of minerals, as does magnetite, Fe3O4.
Ulvöspinel forms as solid solutions with magnetite at high temperatures and reducing conditions, and grains crystallized from some basalt-gabbro magmas are rich in the ulvöspinel component. The ulvöspinel component tends to oxidize to magnetite plus ilmenite during subsolidus cooling of the host rocks, and the ilmenite so produced may form apparent exsolution (trellis type) laminae in magnetite. The texture was once interpreted as indicating solid solution between ilmenite and magnetite, until the oxidation reaction and resultant textures were reproduced in laboratory experiments first described by Buddington and Lindsley (1964, Journal of Petrology 5, p. 310-357). The results are important to plate tectonics because magnetite is an important recorder of rock magnetism.
Ulvöspinel was first described by Fredrik Mogensen (1904-1978) from a dolerite layered intrusion in the Ulvö Islands, Ångermanland, Sweden in 1943. The locality is an iron, titanium and vanadium mining area that has been active since the 17th century. It is common in titaniferous magnetite iron ore deposits. It also occurs in kimberlites, in some reduced iron-bearing basalts and is common in lunar basalts.
Read More About Ulvöspinel / Source
Umangite

Umangite is a copper selenide mineral, Cu3Se2, discovered in 1891. It occurs only in small grains or fine granular aggregates with other copper minerals of the sulfide group. It has a hardness of 3. It is blue-black to red-violet in color with a black streak. It has a metallic luster.
Umangite is named after the locality of Sierra de Umango, La Rioja province in Argentina. It also occurs at other localities including the Harz Mountains in Germany, and at Skrickerum, Sweden.
Read More About Umangite / Source
Umbite

Umbite (chemical formula K2(Zr,Ti)Si3O9·H2O) is a potassium zirconosilicate mineral found in northern Russia. Named after Lake Umb (Lake Umbozero), its type locality is Vuonnemiok River Valley, Khibiny Massif, Kola Peninsula, Murmanskaja Oblast’, Northern Region, Russia.
Read More About Umbite / Source
Umohoite

Umohoite is a rare oxide and hydroxide mineral. The name of this mineral reflects its composition: uranyl (U), molybdate (Mo) and water (H2O). Its chemical formula is (UO2)MoO4·2H2O.Umohoide’s type location is in Marysvale, the mineral was first described by Paul F. Kerr and G. P. Brophy in 1953.
Read More About Umohoite / Source
Upalite
Upalite (Al(UO2)3(PO4)2O(OH)·7H2O) is a mineral found in the Democratic Republic of Congo. It is named after uranium, phosphorus and aluminium. Its type locality is Kobokobo pegmatite, Mwenga, Sud-Kivu, Democratic Republic of Congo.
Read More About Upalite / Source
Uraninite

Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the uranium causes the mineral to contain oxides of lead and trace amounts of helium. It may also contain thorium and rare-earth elements.
Read More About Uraninite / Source
Uranocircite

Uranocircite or Uranocircite-II is a uranium mineral with the chemical formula: Ba(UO2)2(PO4)2·10H2O. Uranocircite-I was discredited (the IMA-CMNMC published ‘The New IMA List of Minerals’, September 2012). It is a phosphate mineral which contains barium and is a green to yellow colour. It has a Mohs hardness of about 2.
Uranocircite was named after the Greek for “falcon” because it was discovered in Falkenstein, Germany. Uranocircite contains about 45% uranium in it and is mainly mined in Bergen in Saxony, Germany.
Read More About Uranocircite / Source
Uranophane

Uranophane (Ca(UO2)2(SiO3OH)2·5H2O), also known as uranotile, is a rare calcium uranium silicate hydrate mineral that forms from the oxidation of other uranium-bearing minerals. It has a yellow color and is radioactive.
Alice Mary Weeks, and Mary E. Thompson of the United States Geological Survey, identified uranophane in 1953.Classic samples have been produced at Madawaska Mine near Bancroft, Ontario.
Read More About Uranophane / Source
Uranopilite
Uranopilite is a minor ore of uranium with the chemistry (UO2)6SO4(OH)6O2·14H2O or, hydrated uranyl sulfate hydroxide.
As with many uranyl minerals, it is fluorescent and radioactive. It is straw yellow in normal light. Uranopilite fluoresces a bright green under ultraviolet light. Uranopilite contains clusters of six uranyl pentagonal bipyramids that share equatorial edges and vertices, with the clusters cross-linked to form chains by sharing vertices with sulfate tetrahedra. In uranopilite, the chains are linked directly by hydrogen bonds, as well as to interstitial H2O groups.
Uranopilite is associated with other uranyl minerals such as zippeite and johannite and, like them, is usually found as an efflorescent crust in uranium mines.
Notable occurrences include:
Wheal Owles, Cornwall, England
San Juan County, Utah, US
Northwest Territories, Canada
Bohemian region of Europe
Read More About Uranopilite / Source
Urea

Urea, also called carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two amino groups (–NH2) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. Urea is Neo-Latin, from French urée, from Ancient Greek οὖρον (oûron) ‘urine’, itself from Proto-Indo-European *h₂worsom.
It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic (LD50 is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules (NH3) with a carbon dioxide (CO2) molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry.
In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler discovered that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials, which was an important conceptual milestone in chemistry. This showed for the first time that a substance previously known only as a byproduct of life could be synthesized in the laboratory without biological starting materials, thereby contradicting the widely held doctrine of vitalism, which stated that only living organisms could produce the chemicals of life.
Uricite
Uricite is a rare organic mineral form of uric acid, C5H4N4O3. It is a soft yellowish white mineral which crystallizes in the monoclinic system.
Read More About Uricite / Source
Urusovite
Urusovite is a rare copper aluminium arsenate mineral with formula: CuAlAsO5. It is a monoclinic-prismatic light green mineral.
Its type locality and only reported occurrence is in the Novaya fumarole, Second scoria cone, North Breach, Great Fissure eruption, Tolbachik volcano, Kamchatka Oblast’, Far-Eastern Region, Russia. It was named after Vadim Sergeevich Urusov, crystal chemist of Moscow State University. It was approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 1998.
Read More About Urusovite / Source
Ussingite

Ussingite is a silicate mineral with formula Na2AlSi3O8(OH).It was named for Niels Viggo Ussing (1864–1911), Copenhagen, Denmark.
Read More About Ussingite / Source
Utahite

Utahite is an extremely rare secondary copper zinc tellurate mineral found as a product of oxidation. Its chemical formula is Cu5Zn3(Te6+O4)4(OH)8•7H2O.
It was first described in 1997 for an occurrence in the Centennial Eureka mine, one mile southeast of Eureka, Tintic District, Juab County, Utah, US (type locality). The discovery site was a mine dump of a hydrothermal ore deposit where it occurs with cesbronite and quartz. It has also been reported from the Empire Mine in the Tombstone District of Cochise County, Arizona.
Read More About Utahite / Source
Uvarovite

Uvarovite is a chromium-bearing garnet group species with the formula: Ca3Cr2(SiO4)3. It was discovered in 1832 by Germain Henri Hess who named it after Count Sergei Semenovitch Uvarov (1765–1855), a Russian statesman and amateur mineral collector. It is classified in the ugrandite group alongside the other calcium-bearing garnets andradite and grossular.Uvarovite is the rarest of the common members of the garnet group, and is the only consistently green garnet species, with an emerald-green color. It occurs as well-formed fine-sized crystals.
Read More About Uvarovite / Source
Uytenbogaardtite

The mineral uytenbogaardtite, Ag3AuS2, is a soft, greyish white sulfide mineral, occurring in hydrothermal Au-Ag-quartz veins. It occurs as tiny crystals, visible only with a microscope. It has a metallic luster and a hardness on the Mohs scale of 2 (gypsum).
It forms, together with petzite (Ag3AuTe2) and fischesserite (Ag3AuSe2) the uytenbogaardtite group. The type locality is Tambang Sawah, Bengkulu district, Sumatra island, Indonesia.
Common impurities in the uytenbogaardtite are copper, selenium, and tellurium.
It is named after the Dutch mineralogist Willem Uytenbogaardt (1918–2012), Professor of Geology, Technical University, Delft, The Netherlands, prominent ore microscopist.
Read More About Uytenbogaardtite / Source
Vaesite

Vaesite (NiS2) is a mineral found together with cattierite in the Democratic Republic of Congo. It is named after Johannes F. Vaes, a Belgian mineralologist. It is part of the pyrite group.
Read More About Vaesite / Source
Valentinite

Valentinite is an antimony oxide mineral with formula Sb2O3. Valentinite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and typically forms as radiating clusters of euhedral crystals or as fibrous masses. It is colorless to white with occasional shades or tints of yellow and red. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3 and a specific gravity of 5.76. Valentinite occurs as a weathering product of stibnite and other antimony minerals. It is dimorphous with the isometric antimony oxide senarmontite.
Read More About Valentinite / Source
Valleriite

Valleriite is an uncommon sulfide mineral (hydroxysulfide) of iron and copper with formula: 4(Fe,Cu)S·3(Mg,Al)(OH)2 or (Fe2+,Cu)4(Mg,Al)3S4(OH,O)6. It is an opaque, soft, bronze-yellow to brown mineral which occurs as nodules or encrustations.
Read More About Valleriite / Source
Vanadinite

Vanadinite is a mineral belonging to the apatite group of phosphates, with the chemical formula Pb5(VO4)3Cl. It is one of the main industrial ores of the metal vanadium and a minor source of lead. A dense, brittle mineral, it is usually found in the form of red hexagonal crystals. It is an uncommon mineral, formed by the oxidation of lead ore deposits such as galena. First discovered in 1801 in Mexico, vanadinite deposits have since been unearthed in South America, Europe, Africa, and North America.
Read More About Vanadinite / Source
Vanadiocarpholite
Vanadiocarpholite (Mn+2V+3AlSi2O6(OH)4) is straw yellow to brown silicate mineral. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. It is the vanadium rich variety of carpholite (Mn+2Al2Si2O6(OH)4).
Read More About Vanadiocarpholite / Source
Vanadium

Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer (passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation.
Spanish-Mexican scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called “brown lead”. Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it “vanadium” after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors found in vanadium compounds. Del Rio’s lead mineral was ultimately named vanadinite for its vanadium content. In 1867 Henry Enfield Roscoe obtained the pure element.
Vanadium occurs naturally in about 65 minerals and fossil fuel deposits. It is produced in China and Russia from steel smelter slag. Other countries produce it either from magnetite directly, flue dust of heavy oil, or as a byproduct of uranium mining. It is mainly used to produce specialty steel alloys such as high-speed tool steels, and some aluminium alloys. The most important industrial vanadium compound, vanadium pentoxide, is used as a catalyst for the production of sulfuric acid. The vanadium redox battery for energy storage may be an important application in the future.
Large amounts of vanadium ions are found in a few organisms, possibly as a toxin. The oxide and some other salts of vanadium have moderate toxicity. Particularly in the ocean, vanadium is used by some life forms as an active center of enzymes, such as the vanadium bromoperoxidase of some ocean algae.
Read More About Vanadium / Source
Vandenbrandeite

Vandenbrandeite is a mineral named after a belgian geologist, Pierre Van den Brande, who discovered an ore deposit. It was named in 1932, and has been a valid mineral ever since then.
Read More About Vandenbrandeite / Source
Vantasselite

Vantasselite is a rare aluminium phosphate mineral with formula: Al4(PO4)3(OH)3 •9H2O. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and has a white color, a hardness of 2 to 2.5, a white streak and a pearly luster.It occurs in a quartzite quarry north of Bihain, Belgium It was first described in 1987 and named after Belgian mineralogist René Van Tassel.
Read More About Vantasselite / Source
Vanuralite

Vanuralite is a mineral of uranium with chemical formula: Al(UO2)2(VO4)2(OH)·11(H2O). It has yellow crystals and a Mohs hardness of 2. The name comes from the composition of the mineral.
Read More About Vanuralite / Source
Variscite

Variscite is a hydrated aluminium phosphate mineral (AlPO4 · 2H2O). It is a relatively rare phosphate mineral. It is sometimes confused with turquoise; however, variscite is usually greener in color. The green color results from the presence of small amounts of trivalent chromium (Cr3+).
Read More About Variscite / Source
Vaterite
Vaterite is a mineral, a polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It was named after the German mineralogist Heinrich Vater. It is also known as mu-calcium carbonate (μ-CaCO3). Vaterite belongs to the hexagonal crystal system, whereas calcite is trigonal and aragonite is orthorhombic.
Vaterite, like aragonite, is a metastable phase of calcium carbonate at ambient conditions at the surface of the earth. As it is less stable than either calcite or aragonite, vaterite has a higher solubility than either of these phases. Therefore, once vaterite is exposed to water, it converts to calcite (at low temperature) or aragonite (at high temperature: ~60 °C). At 37 °C for example a solution-mediated transition from vaterite to calcite occurs, where the vaterite dissolves and subsequently precipitates as calcite assisted by an Ostwald ripening process.However, vaterite does occur naturally in mineral springs, organic tissue, gallstones, urinary calculi and plants. In those circumstances, some impurities (metal ions or organic matter) may stabilize the vaterite and prevent its transformation into calcite or aragonite. Vaterite is usually colorless.
Vaterite can be produced as the first mineral deposits repairing natural or experimentally-induced shell damage in some aragonite-shelled mollusks (e.g. gastropods). Subsequent shell deposition occurs as aragonite. In 2018, vaterite was identified as a constituent of a deposit formed on the leaves of Saxifraga at Cambridge University Botanic Garden.Vaterite has a JCPDS number of 13-192.
Read More About Vaterite / Source
Vauquelinite

Vauquelinite is a complex mineral with the formula CuPb2(CrO4)(PO4)(OH) making it a combined chromate and phosphate of copper and lead. It forms a series with the arsenate mineral fornacite.It was first described in 1818 in the Beryozovskoye deposit, Urals, Russia, and named for Louis Vauquelin (1763–1829), a French chemist. It occurs in oxidized hydrothermal ore deposits and is associated with crocoite, pyromorphite, mimetite, cerussite, beudantite and duftite at the type locality in Russia.
Read More About Vauquelinite / Source
Vauxite

Vauxite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Fe2+Al2(PO4)2(OH)2·6(H2O). It belongs to the laueite – paravauxite group, paravauxite subgroup, although Mindat puts it as a member of the vantasselite Al4(PO4)3(OH)3·9H2O group. There is no similarity in structure between vauxite and paravauxite Fe2+Al2(PO4)2(OH)2·8H2O or metavauxite Fe3+Al2(PO4)2(OH)2·8H2O, even though they are closely similar chemically and all minerals occur together as secondary minerals. Vauxite was named in 1922 for George Vaux Junior (1863–1927), an American attorney and mineral collector.
Read More About Vauxite / Source
Veatchite

Veatchite is an unusual strontium borate, with the chemical formula Sr2B11O16(OH)5·H2O. There are two known polytypes, veatchite-A and veatchite-p.Veatchite was discovered in 1938, at the Sterling Borax mine in Tick Canyon, Los Angeles County, California. Veatchite is named to honor John Veatch, the first person to detect boron in the mineral waters of California.
Read More About Veatchite / Source
Vermiculite

Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently, and commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the weathering or hydrothermal alteration of biotite or phlogopite.
Large commercial vermiculite mines currently exist in the United States, Russia, South Africa, China, and Brazil.
Read More About Vermiculite / Source
Vesuvianite

Vesuvianite, also known as idocrase, is a green, brown, yellow, or blue silicate mineral. Vesuvianite occurs as tetragonal crystals in skarn deposits and limestones that have been subjected to contact metamorphism. It was first discovered within included blocks or adjacent to lavas on Mount Vesuvius, hence its name. Attractive-looking crystals are sometimes cut as gemstones. Localities which have yielded fine crystallized specimens include Mount Vesuvius and the Ala Valley near Turin, Piedmont.The specific gravity is 3.4 and the Mohs hardness is 6+1⁄2. The name “vesuvianite” was given by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1795, because fine crystals of the mineral are found at Vesuvius; these are brown in color and occur in the ejected limestone blocks of Monte Somma. Several other names were applied to this species, one of which, “idocrase” by René Just Haüy in 1796, is now in common use.A sky bluish variety known as cyprine has been reported from Franklin, New Jersey and other locations; the blue is due to impurities of copper in a complex calcium aluminum sorosilicate. Californite is a name sometimes used for jade-like vesuvianite, also known as California jade, American jade or Vesuvianite jade. Xanthite is a manganese rich variety. Wiluite is an optically positive variety from Wilui, Siberia. Idocrase is an older synonym sometimes used for gemstone-quality vesuvianite.
Read More About Vesuvianite / Source
Villiaumite

Villiaumite is a rare halide mineral composed of sodium fluoride, NaF. It is very soluble in water and some specimens fluoresce under long and short wave ultraviolet light. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and is usually red, pink, or orange in color. It is toxic to humans.The red color is due to a broad absorption peaking at 512 nm. It is a result of radiation damage to the crystal.
Read More About Villiaumite / Source
Violarite
Violarite (Fe2+Ni23+S4) is a supergene sulfide mineral associated with the weathering and oxidation of primary pentlandite nickel sulfide ore minerals.
Violarite crystallises in the isometric system, with a hardness of 4.5 to 5.5 and a specific gravity of about 4, is dark violet grey to copper-red, often with verdigris and patina from associated copper and arsenic sulfides, and is typically in amorphous to massive infill of lower saprolite ultramafic lithologies.
Violarite has a characteristic violet colour, hence the name from the Latin ‘violaris’ alluding to its colour especially when viewed in polished section under a microscope.
Read More About Violarite / Source
Vishnevite

Vishnevite, or sulfatic cancrinite, is a mineral of the cancrinite group with the chemical formula (Na, Ca, K)6(Si, Al)12O24[(SO4),(CO3), Cl2]2-4·nH2O. It has hexagonal crystals.
Read More About Vishnevite / Source
Vivianite

Vivianite (Fe2+Fe2+2(PO4)2·8H2O) is a hydrated iron phosphate mineral found in a number of geological environments. Small amounts of manganese Mn2+, magnesium Mg2+, and calcium Ca2+ may substitute for iron Fe2+ in the structure. Pure vivianite is colorless, but the mineral oxidizes very easily, changing the color, and it is usually found as deep blue to deep bluish green prismatic to flattened crystals.Vivianite crystals are often found inside fossil shells, such as those of bivalves and gastropods, or attached to fossil bone.
It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1817, the year of his death, after either John Henry Vivian (1785–1855), a Welsh-Cornish politician, mine owner and mineralogist living in Truro, Cornwall, England, or after Jeffrey G. Vivian, an English mineralogist. Vivianite was discovered at Wheal Kind, in St Agnes, Cornwall.
Read More About Vivianite / Source
Vladimirite

Vladimirite is a rare calcium arsenate mineral with a formula of Ca5(HAsO4)2(AsO4)2·5H2O. It is named after the Vladimirovskoye deposit in Russia, where it was discovered in the 1950s.
Vladimirite is monoclinic-prismatic, which means crystallographically, it contains three axes of unequal length and the angles between two of the axes are 90 degrees, and one is less than 90 degrees. It belongs to the space group P21/c. The mineral also has an orthorhombic polytype. In terms of its optical properties, vladimirite is anisotropic which means the velocity of light varies depending on direction through the mineral. Relief is a diagnostic characteristic of a mineral in plane polarized light that refers to the various ways different minerals “stand out”. Vladimirite’s calculated relief is 1.65-1.661, which is moderate. It is colorless in plane polarized light, and it is weakly pleochroic. Pleochroism is the variety of colors under plane polarized light displayed by crystals at various angles.
Read More About Vladimirite / Source
Vlasovite

Vlasovite is a rare inosilicate (chain silicate) mineral with sodium and zirconium, with the chemical formula Na2ZrSi4O11.
It was discovered in 1961 at Vavnbed Mountain in the Lovozero Massif, in the Northern Region of Russia. The researchers who first identified it, R P Tikhonenkova and M E Kazakova, named it for Kuzma Aleksevich Vlasov (1905–1964), a Russian mineralogist and geochemist who studied the Lovozero massif, and who was the founder of the Institute of Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Crystal Chemistry of Rare Elements, Moscow, Russia.
Read More About Vlasovite / Source
Volborthite

Volborthite is a mineral containing copper and vanadium, with the formula Cu3V2O7(OH)2·2H2O. Found originally in 1838 in the Urals, it was first named knaufite but was later changed to volborthite for Alexander von Volborth (1800–1876), a Russian paleontologist.Tangeite (synonym: calciovolborthite), CaCuVO4(OH), is closely related.
Read More About Volborthite / Source
Vuagnatite
Vuagnatite is a member of the adelite-descloizite group which was named after Prof. Dr. Marc Bernard Vuagnat. Its type locality is in Turkey, at Bögürtlencik Tepe. It was approved in 1975 by the IMA.
Read More About Vuagnatite / Source
Vulcanite
Vulcanite is a rare copper telluride mineral. The mineral has a metallic luster, and has a green or bronze-yellow tint. It has a hardness between 1 and 2 on the Mohs scale (between talc and gypsum). Its crystal structure is orthorhombic.
Vulcanite is named for the place where it was discovered in 1961, the Mammoth Good Hope Mine in Vulcan (ghost town and district), Gunnison County, Colorado. Small deposits have also been discovered in Japan, Russia, Saudi Arabia, and Norway. It occurs with native tellurium, rickardite, petzite, and sylvanite.
Read More About Vulcanite / Source
Wadsleyite

Wadsleyite is an orthorhombic mineral with the formula β-(Mg,Fe)2SiO4. It was first found in nature in the Peace River meteorite from Alberta, Canada. It is formed by a phase transformation from olivine (α-(Mg,Fe)2SiO4) under increasing pressure and eventually transforms into spinel-structured ringwoodite (γ-(Mg,Fe)2SiO4) as pressure increases further. The structure can take up a limited amount of other bivalent cations instead of magnesium, but contrary to the α and γ structures, a β structure with the sum formula Fe2SiO4 is not thermodynamically stable. Its cell parameters are approximately a = 5.7 Å, b = 11.71 Å and c = 8.24 Å.
Wadsleyite is found to be stable in the upper part of the Transition Zone of the Earth’s mantle between 410–520 kilometres (250–320 mi) in depth. Because of oxygen atoms not bound to silicon in the Si2O7 groups of wadsleyite, it leaves some oxygen atoms insufficiently bonded. Thus, these oxygens are hydrated easily, allowing for high concentrations of hydrogen atoms in the mineral. Hydrous wadsleyite is considered a potential site for water storage in the Earth’s mantle due to the low electrostatic potential of the under bonded oxygen atoms. Although wadsleyite does not contain H in its chemical formula, it may contain more than 3 percent by weight H2O, and may coexist with a hydrous melt at transition zone pressure-temperature conditions. The solubility of water and the density of wadsleyite depend on the temperature and pressure in the Earth. Even though their maximum water storage capabilities might be reduced to about 0.5-1 wt% along the normal geotherm, the Transition Zone which holds up to 60 vol% wadsleyite could still be a major water reservoir in the Earth’s interior. Furthermore, the transformation resulting in wadsleyite is thought to occur also in the shock event when a meteorite impacts the Earth or another planet at very high velocity.
Wadsleyite was first identified by Ringwood and Major in 1966 and was confirmed to be a stable phase by Akimoto and Sato in 1968. The phase was originally known as β-Mg2SiO4 or “beta-phase”. Wadsleyite was named for mineralogist Arthur David Wadsley (1918–1969).
Read More About Wadsleyite / Source
Wagnerite

Wagnerite is a mineral, a combined phosphate and fluoride of iron and magnesium, with the formula (Mg,Fe2+)2PO4F. It occurs in pegmatite associated with other phosphate minerals. It is named after Franz Michael von Wagner (1768–1851), a German mining official in Munich.
Read More About Wagnerite / Source
Wairakite

Wairakite is a zeolite mineral with an analcime structure but containing a calcium ion. The chemical composition is Ca8(Al16Si32O96)•16H2O. It is named for the location of its discovery in Wairakei, North Island, New Zealand, by Alfred Steiner in 1955. The first finds were in hydrothermally altered rhyolitic tuffs, ignimbrites and volcaniclastic rocks. The mineral has since been found in metamorphic rocks and in geothermal areas. It was most likely first successfully synthesized in a laboratory in 1970.
Read More About Wairakite / Source
Wakabayashilite

Wakabayashilite is a rare arsenic, antimony sulfide mineral with formula [(As,Sb)6S9][As4S5].
Read More About Wakabayashilite / Source
Wakefieldite

Wakefieldite ((La,Ce,Nd,Y)VO4) is an uncommon rare-earth element vanadate mineral. There are four main types described of wakefieldite- wakefieldite-(La), wakefieldite-(Ce), wakefieldite-(Nd), and wakefieldite-(Y), depending upon the dominant rare-earth metal ion present. Wakefieldite has a Mohs hardness ranging from 4 to 5. Wakefieldite forms crystals of tetragonal structure. In terms of crystal structure, it is the vanadate analog of the rare-earth phosphate mineral xenotime. Unlike xenotime, it is more favorable for wakefieldite to contain the lighter rare-earth elements over the heavier ones. Due to the lanthanide contraction, the heavier rare earths have smaller ionic radii than the lighter ones. When the phosphate anion is replaced by the larger vanadate anion, the tetragonal crystal system preferentially accommodates the larger light rare-earth elements.Wakefieldite was first described for an occurrence in the Evans Lou mine, St. Pierre de Wakefield, Quebec, Canada and later designated Wakefieldite-(Y).
Read More About Wakefieldite / Source
Walfordite

Walfordite is a very rare tellurite mineral that was discovered in Chile in 1999. The mineral is described as orange with orange-yellow streak, and is determined to have a chemical formula of Fe3+,Te6+Te4+3O8 with minor titanium and magnesium substitution resulting in an approximate empirical formula of (Fe3+,Te6+,Ti4+,Mg)(Te4+)3O8.
Read More About Walfordite / Source
Wardite

Wardite is a hydrous sodium aluminium phosphate hydroxide mineral with formula: NaAl3(PO4)2(OH)4·2(H2O). Wardite is of interest for its rare crystallography. It crystallizes in the tetragonal trapezohedral class and is one of only a few minerals in that class. Wardite forms vitreous green to bluish green to white to colorless crystals, masses, and fibrous encrustations. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 and a specific gravity of 2.81–2.87.
Read More About Wardite / Source
Warikahnite

Warikahnite is a rare zinc arsenate mineral of the triclinic crystal system with Hermann- Mauguin notation 1, belonging to the space group P1. It occurs in the Tsumeb mine in Namibia on corroded tennantite in the second oxidation zone under hydrothermal conditions in a dolomite-hosted polymetallic ore deposit. It is associated with adamite, stranskiite, koritnigite, claudetite, tsumcorite, and ludlockite. The origin of discovery was in a dolosmite ore formation within an oxidized hydrothermal zone, in the E9 pillar, 31st level of the Tsumeb Mine in Namibia, Southwest Africa. It has also been found at Lavrion, Greece and Plaka, Greece as microscopic white needles.
Read More About Warikahnite / Source
Warwickite

Warwickite is an iron magnesium titanium borate mineral with the chemical formula (MgFe)3Ti(O, BO3)2 or Mg(Ti,Fe3+, Al)(BO3)O. It occurs as brown to black prismatic orthorhombic crystals which are vitreous and transparent. It has a Mohs hardness of 3 to 4 and a specific gravity of 3.36.
Read More About Warwickite / Source
Wassonite
Wassonite is an extremely rare titanium sulfide mineral with chemical formula TiS. Its discovery was announced in a 2011 NASA press release as a single small grain within an enstatite chondrite meteorite called “Yamato 691”, which was found during a 1969 Japanese expedition to Antarctica. This grain represents the first observation in nature of the synthetic compound titanium(II) sulfide.
The mineral was named after John T. Wasson, a professor at the University of California, Los Angeles and was approved by the International Mineralogical Association.
Read More About Wassonite / Source
Water (mineral)

Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H2O. It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, and it is the main constituent of Earth’s hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. “Water” is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure.
Because Earth’s environment is relatively close to water’s triple point, water exists on earth as a solid, liquid, and gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor.
Water covers about 71% of the Earth’s surface, with seas and oceans making up most of the water volume on earth (about 96.5%). Small portions of water occur as groundwater (1.7%), in the glaciers and the ice caps of Antarctica and Greenland (1.7%), and in the air as vapor, clouds (consisting of ice and liquid water suspended in air), and precipitation (0.001%). Water moves continually through the water cycle of evaporation, transpiration (evapotranspiration), condensation, precipitation, and runoff, usually reaching the sea.
Water plays an important role in the world economy. Approximately 70% of the freshwater used by humans goes to agriculture. Fishing in salt and fresh water bodies has been, and continues to be, a major source of food for many parts of the world, providing 6.5% of global protein. Much of the long-distance trade of commodities (such as oil, natural gas, and manufactured products) is transported by boats through seas, rivers, lakes, and canals. Large quantities of water, ice, and steam are used for cooling and heating, in industry and homes. Water is an excellent solvent for a wide variety of substances both mineral and organic; as such it is widely used in industrial processes, and in cooking and washing. Water, ice and snow are also central to many sports and other forms of entertainment, such as swimming, pleasure boating, boat racing, surfing, sport fishing, diving, ice skating and skiing.
Read More About Water (mineral) / Source
Wattersite

Wattersite is a rare mercury chromate mineral with the formula Hg+14Hg+2Cr+6O6. It occurs in association with native mercury and cinnabar in a hydrothermally altered serpentinite. It was first described from Clear Creek claim, San Benito County, California, USA in 1961. It was named to honor Californian mineral collector Lucius “Lu” Watters.
Read More About Wattersite / Source
Wavellite

Wavellite is an aluminium basic phosphate mineral with formula Al3(PO4)2(OH, F)3·5H2O. Distinct crystals are rare, and it normally occurs as translucent green radial or spherical clusters.
Read More About Wavellite / Source
Weddellite

Weddellite (CaC2O4·2H2O) is a mineral form of calcium oxalate named for occurrences of millimeter-sized crystals found in bottom sediments of the Weddell Sea, off Antarctica. Occasionally, weddellite partially dehydrates to whewellite, forming excellent pseudomorphs of grainy whewellite after weddellite’s short tetragonal dipyramids. It was first described in 1936 but only named in 1942.
Read More About Weddellite / Source
Weeksite

Weeksite is a naturally occurring uranium silicate mineral with the chemical formula: K2(UO2)2Si6O15•4(H2O), potassium uranyl silicate. Weeksite has a Mohs hardness of 1-2. It was named for USGS mineralogist Alice Mary Dowse Weeks (1909–1988).
Read More About Weeksite / Source
Weilite

Weilite (CaHAsO4) is a rare arsenate mineral. It is a translucent white triclinic mineral with a waxy luster.It was first described in 1963 for occurrences in Gabe Gottes Mine, Haut-Rhin, Alsace, France; Wittichen, Schenkenzell, Black Forest, Baden-Württemberg, Germany; and the Schneeberg District, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany. It is named after French mineralogist René Weil of the University of Strasbourg. It occurs in the oxidized zone of arsenic-bearing hydrothermal veins. It occurs as an alteration product of pharmacolite and haidingerite.
Read More About Weilite / Source
Weissite
Weissite is a telluride mineral, a copper telluride. Its chemical formula is Cu2−xTe. Weissite has hexagonal crystal structure. Its specific gravity is 6 and its Mohs hardness is 3. Occurrence is in Gunnison County, Colorado, Arizona and New Mexico in the United States. It is also reported from Kalgoorlie, Western Australia and Dalarna and Värmland, Sweden.Weissite occurs in hydrothermal deposits associated with pyrite, native tellurium, sylvanite, petzite, rickardite, native sulfur, native gold, calaverite and krennerite.It was first described in 1927 for an occurrence in the Good Hope Mine in the Vulcan District of Gunnison County, Colorado. It was named for mine owner Louis Weiss.
Read More About Weissite / Source
Weloganite

Weloganite is a rare carbonate mineral with formula: Na2(Sr,Ca)3Zr(CO3)6·3H2O. It was discovered by Canadian government mineralogist Ann P. Sabina in 1967 and named for Canadian geologist Sir William Edmond Logan (1798–1875). It was first discovered in Francon Quarry, Montreal, Quebec, Canada and has only been reported from a few localities worldwide.
Read More About Weloganite / Source
Whewellite

Whewellite is a mineral, hydrated calcium oxalate, formula Ca C2O4·H2O. Because of its organic content it is thought to have an indirect biological origin; this hypothesis is supported by its presence in coal and sedimentary nodules. However, it has also been found in hydrothermal deposits where a biological source appears improbable. For this reason, it may be classed as a true mineral.
Whewellite, or at least crystalline calcium oxalate, does also arise from biological sources. Small crystals or flakes of it are sometimes found on the surfaces of some cacti, and kidney stones frequently have the same composition.
Whewellite was named after William Whewell (1794–1866), an English polymath, naturalist and scientist, professor of moral philosophy at Cambridge and inventor of the system of crystallographic indexing.
Read More About Whewellite / Source
Whiteite

Whitlockite

Whitlockite is a mineral, an unusual form of calcium phosphate. Its formula is Ca9(MgFe)(PO4)6PO3OH. It is a relatively rare mineral but is found in granitic pegmatites, phosphate rock deposits, guano caves and in chondrite meteorites. It was first described in 1941 and named for Herbert Percy Whitlock (1868–1948), American mineralogist and curator at the American Museum of Natural History in New York City.With regards to periodontal dentistry, magnesium whitlockite comprises one component of many of the inorganic content of calculus. It is found primarily in subgingival calculus (as opposed to supragingival calculus). It is also found more in posterior as opposed to anterior regions of the oral cavity.
Read More About Whitlockite / Source
Willemite

Willemite is a zinc silicate mineral (Zn2SiO4) and a minor ore of zinc. It is highly fluorescent (green) under shortwave ultraviolet light. It occurs in a variety of colors in daylight, in fibrous masses and apple-green gemmy masses. Troostite is a variant in which part of the zinc is partly replaced by manganese, it occurs in solid brown masses.
It was discovered in 1829 in the Belgian Vieille-Montagne mine. Armand Lévy was shown samples by a student at the university where he was teaching. Lévy named it after William I of the Netherlands
(it is occasionally spelled villemite).
The troostite variety is named after Dutch-American mineralogist Gerard Troost.
Read More About Willemite / Source
Wiluite

Wiluite is a dark green, brownish, or black blocky silicate mineral with the chemical formula Ca19(Al,Mg,Fe,Ti)13(B,Al,[ ])5Si18O68(O,OH)10. It has a Mohs hardness of 6 and a specific gravity of 3.36. It has a vitreous lustre, poor cleavage and an irregular brittle fracture. It crystallizes in the tetragonal system and occurs as well-formed crystals with good external form. It is isostructural with the vesuvianite group and is associated with wollastonite and olive-green grossulars (viluites) in a serpentinized skarn.
The minerals that wiluite and viluite refer to have often been confused, and may refer to grossular, or wiluite.
It was discovered in the 1990s and named for the Wilui River region, Sakha Republic (Yakutia), Russia.
Viluite was introduced as a mineral name twice. Von Leonhard used it for a mineral that was considered the same as vesuvianite. However, that material was recently shown to be rich in boron and thus different from vesuvianite. In 1998 that material was named Wiluite. The other author to introduce viluite was Severgin, who used it in reference to what is widely known as grossular, a member of the garnet group.
Read More About Wiluite / Source
Witherite

Witherite is a barium carbonate mineral, BaCO3, in the aragonite group. Witherite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system and virtually always is twinned. The mineral is colorless, milky-white, grey, pale-yellow, green, to pale-brown. The specific gravity is 4.3, which is high for a translucent mineral. It fluoresces light blue under both long- and short-wave UV light, and is phosphorescent under short-wave UV light.Witherite forms in low-temperature hydrothermal environments. It is commonly associated with fluorite, celestine, galena, barite, calcite, and aragonite. Witherite occurrences include: Cave-in-Rock, Illinois, US; Pigeon Roost Mine, Glenwood, Arkansas, US; Settlingstones Mine Northumberland; Alston Moor, Cumbria; Anglezarke, Lancashire and Burnhope, County Durham, England; Thunder Bay area, Ontario, Canada, Germany, and Poland (Tarnowskie Góry and Tajno at Suwałki Region).
Witherite was named after William Withering (1741–1799) an English physician and naturalist who in 1784 published his research on the new mineral. He could show that barite and the new mineral were two different minerals.
Read More About Witherite / Source
Wodginite

Wodginite is a manganese, tin, tantalum oxide mineral with the chemical formula Mn2+(Sn,Ta)Ta2O8. It may also include significant amounts of niobium.
Read More About Wodginite / Source
Wolframite

Wolframite is an iron, manganese, and tungstate mineral with a chemical formula of (Fe,Mn)WO4 that is the intermediate mineral between ferberite (Fe2+ rich) and hübnerite (Mn2+ rich). Along with scheelite, the wolframite series are the most important tungsten ore minerals. Wolframite is found in quartz veins and pegmatites associated with granitic intrusives. Associated minerals include cassiterite, scheelite, bismuth, quartz, pyrite, galena, sphalerite, and arsenopyrite.
This mineral was historically found in Europe in Bohemia, Saxony, and in the UK in Devon and Cornwall. China reportedly has the world’s largest supply of tungsten ore with about 60%. Other producers are Spain, Canada, Portugal, Russia, Australia, Thailand, South Korea, Rwanda, Bolivia, the United States, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Read More About Wolframite / Source
Wollastonite

Wollastonite is a calcium inosilicate mineral (CaSiO3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or dolomite is subjected to high temperature and pressure, which sometimes occurs in the presence of silica-bearing fluids as in skarns or in contact with metamorphic rocks. Associated minerals include garnets, vesuvianite, diopside, tremolite, epidote, plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene and calcite. It is named after the English chemist and mineralogist William Hyde Wollaston (1766–1828).
Despite its chemical similarity to the compositional spectrum of the pyroxene group of minerals—where magnesium (Mg) and iron (Fe) substitution for calcium ends with diopside and hedenbergite respectively—it is structurally very different, with a third SiO4−4 tetrahedron in the linked chain (as opposed to two in the pyroxenes).
Read More About Wollastonite / Source
Woodhouseite

Woodhouseite belongs to the beudantite group AB3(XO4)(SO4)(OH)6 where A = Ba, Ca, Pb or Sr, B = Al or Fe and X = S, As or P. Minerals in this group are isostructural with each other and also with minerals in the crandallite and alunite groups. They crystallise in the rhombohedral system with space group R3m and crystals are usually either tabular {0001} or pseudo-cubic to pseudo-cuboctahedral.
Woodhouseite was named after Professor Charles Douglas Woodhouse (1888–1975), an American mineralogist and mineral collector from the University of California, Santa Barbara, US, and one-time General Manager of Champion Sillimanite, Inc.
Read More About Woodhouseite / Source
Wöhlerite

Wöhlerite, also known as wöehlerite is a member of the amphibole supergroup, and the wöhlerite subgroup within it. It was named after German chemist Friedrich Wöhler. It was first described by Scheerer in 1843, but the crystal structure was later solved by Mellino & Merlino in 1979. Once approved, it was grandfathered by the IMA.
Read More About Wöhlerite / Source
Wulfenite

Wulfenite is a lead molybdate mineral with the formula PbMoO4. It can be most often found as thin tabular crystals with a bright orange-red to yellow-orange color, sometimes brown, although the color can be highly variable. In its yellow form it is sometimes called “yellow lead ore”.
It crystallizes in the tetragonal system, often occurring as stubby, pyramidal or tabular crystals. It also occurs as earthy, granular masses. It is found in many localities, associated with lead ores as a secondary mineral associated with the oxidized zone of lead deposits. It is also a secondary ore of molybdenum, and is sought by collectors.
Read More About Wulfenite / Source
Wurtzite

Wurtzite is a zinc and iron sulfide mineral with the chemical formula (Zn,Fe)S, a less frequently encountered structural polymorph form of sphalerite. The iron content is variable up to eight percent. It is trimorphous with matraite and sphalerite.It occurs in hydrothermal deposits associated with sphalerite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, barite and marcasite. It also occurs in low-temperature clay-ironstone concretions.It was first described in 1861 for an occurrence in the San José Mine, Oruro City, Cercado Province, Oruro Department, Bolivia, and named for French chemist Charles-Adolphe Wurtz. It has widespread distribution. In Europe it is reported from Příbram, Czech Republic; Hesse, Germany; and Liskeard, Cornwall, England. In the US it is reported from Litchfield County, Connecticut; Butte, Silver Bow County, Montana; at Frisco, Beaver County, Utah; and from the Joplin district, Jasper County, Missouri.
Read More About Wurtzite / Source
Wüstite

Wüstite (FeO) is a mineral form of iron(II) oxide found with meteorites and native iron. It has a grey colour with a greenish tint in reflected light. Wüstite crystallizes in the isometric-hexoctahedral crystal system in opaque to translucent metallic grains. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 to 5.5 and a specific gravity of 5.88. Wüstite is a typical example of a non-stoichiometric compound.
Wüstite was named after Fritz Wüst (1860–1938), a German metallurgist and founding director of the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut für Eisenforschung (presently Max Planck Institute for Iron Research GmbH).In addition to its type locality in Germany, it has been reported from Disko Island, Greenland; the Jharia coalfield, Jharkhand, India; and as inclusions in diamonds in a number of kimberlite pipes. It also is reported from deep sea manganese nodules.
Its presence indicates a highly reducing environment.
Read More About Wüstite / Source
Wyartite
Wyartite CaU5+(UO2)2(CO3)O4(OH)·7H2O is a uranium bearing mineral named after Jean Wyart (1902–1992), mineralogist at the Sorbonne, Paris. It has greenish-black, black, or violet-black, translucent to opaque orthorhombic crystals. A hardness of 3 – 4 Mohs. Its other names are Ianthinite (of Bignand), Wyartit and Wyartita. It belongs to the uranium carbonate group of minerals. It is found next to rutherfordine in Shinkolobwe, Shaba, Zaire.Determination of the structure of wyartite provided the first evidence for a pentavalent uranium mineral. Like all uranium minerals it is radioactive.
Read More About Wyartite / Source
Xanthiosite

Xanthiosite is an arsenate mineral first discovered in Germany in 1858; it may also be found in Greece. It is not radioactive.
Read More About Xanthiosite / Source
Xanthoconite

Xanthoconite is a sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula Ag3AsS3.
Read More About Xanthoconite / Source
Xanthoxenite
Xanthoxenite is a rare calcium iron(III) phosphate mineral with formula: Ca4Fe3+2(PO4)4(OH)2·3H2O. It occurs as earthy pale to brownish yellow incrustations and lath shaped crystals. It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system. It occurs as an alteration product of triphylite in pegmatites. It occurs associated with apatite, whitlockite, childrenite–eosphorite, laueite, strunzite, stewartite, mitridatite, amblygonite and siderite.It has been found in Australia, Brazil, Portugal, Spain, Ukraine, and the United States. It was first described in 1920 for an occurrence in North Groton, Grafton County, New Hampshire.
Read More About Xanthoxenite / Source
Xenophyllite
Xenophyllite is a rare phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Na4Fe7(PO4)6.
Xenophyllite was described for an occurrence in the Augustinovka meteorite, Dnepropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine. It was approved by the IMA in 2006.
Read More About Xenophyllite / Source
Xenotime

Xenotime is a rare-earth phosphate mineral, the major component of which is yttrium orthophosphate (YPO4). It forms a solid solution series with chernovite-(Y) (YAsO4) and therefore may contain trace impurities of arsenic, as well as silicon dioxide and calcium. The rare-earth elements dysprosium, erbium, terbium and ytterbium, as well as metal elements such as thorium and uranium (all replacing yttrium) are the expressive secondary components of xenotime. Due to uranium and thorium impurities, some xenotime specimens may be weakly to strongly radioactive. Lithiophyllite, monazite and purpurite are sometimes grouped with xenotime in the informal “anhydrous phosphates” group. Xenotime is used chiefly as a source of yttrium and heavy lanthanide metals (dysprosium, ytterbium, erbium and gadolinium). Occasionally, gemstones are also cut from the finest xenotime crystals.
Read More About Xenotime / Source
Xiangjiangite
Xiangjiangite is a phosphate mineral discovered near and named for the Xiang Jiang River in China. It was approved by the IMA in 1978, and was named after its locality.
Read More About Xiangjiangite / Source
Xieite
Xieite is an iron chromium oxide mineral with formula Fe2+Cr2O4. It is a member of the spinel group and a high pressure polymorph of chromite.It was discovered in samples taken from the Suizhou meteorite which fell in 1986 in the Zengdu District of China.
Read More About Xieite / Source
Xifengite
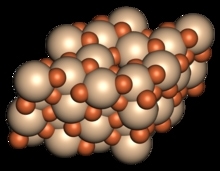
Xifengite (Fe5Si3) is a rare metallic iron silicide mineral. The crystal system of xifengite is hexagonal. It has a specific gravity of 6.45 and a Mohs hardness of 5.5. It occurs as steel gray inclusions within other meteorite derived nickel iron mineral phases.
It was first described in 1984 and named for the eastern passageway, Xifengkou, of the Great Wall of China. The type locality is the Yanshan meteorite of the Hebei Province, China. It has also been reported from dredgings along the East Pacific Rise.
The other known natural iron silicide minerals are gupeiite (Fe3Si), hapkeite (Fe2Si), linzhiite (FeSi2), luobusaite (Fe0.84Si2), naquite (FeSi), suessite ((Fe,Ni)3Si), and zangboite (TiFeSi2).
Read More About Xifengite / Source
Xilingolite
Xilingolite is a lead sulfide mineral with formula Pb3Bi2S6. It has a hardness of 3, a metallic luster, and usually exhibits a lead-grey color. It is a dimorph of lillianite, exhibiting increased Pb-Bi order and decreased symmetry.Its crystal system is monoclinic, with three axes of unequal length two of which are at an oblique angle to each other while the third axis is perpendicular to the plane formed by the other two. Xilingolite is opaque, meaning that its internal structure does not allow for light to be transmitted through it. The mineral also exhibits white to blue-tinted-white pleochroism under reflected light.
Read More About Xilingolite / Source
Ximengite
Ximengite is a phosphate mineral discovered in and named for the Ximeng tin-mining district in China.
Read More About Ximengite / Source
Xingzhongite
Xingzhongite is an opaque, metallic mineral named for its location of discovery in China.
Read More About Xingzhongite / Source
Xitieshanite
Xitieshanite is a hydrous iron sulfate–chloride mineral with chemical formula: Fe3+(SO4)Cl·6(H2O).
It was discovered in 1983 and named for the discovery location of Xitieshan lead/zinc ore deposit in the Qinghai Province, China. It was approved by the IMA in the year of its discovery. The mineral has also been reported in 2005 from acid mine drainage from a coal mine in Green Valley, Vigo County, Indiana.
Read More About Xitieshanite / Source
Xocolatlite

Xocolatlite is a sulfate mineral named for its chocolatey appearance. Discovered in the La Bambolla gold mine of Moctezuma, Sonora, Mexico, Xocolatlite’s name is derived from the Nahuatl word xocolatl (literally “bitter water”; a root word of “chocolate”), a drink made from cocoa, water, and chili.
Read More About Xocolatlite / Source
Xocomecatlite

Xocomecatlite is a rare tellurate mineral with formula: Cu3(TeO4)(OH)4. It is an orthorhombic mineral which occurs as aggregates or spherules of green needlelike crystals.
It was first described in 1975 for an occurrence in the Oriental mine near Moctezuma, Sonora, Mexico. It has also been reported from the Centennial Eureka mine in the Tintic District, Juab County, Utah and the Emerald mine of the Tombstone District, Cochise County, Arizona in the United States. The name is derived from xocomecatl, the Nahuatl word for “bunches of grapes”, and alludes to the mineral’s appearance as a set of green spherules. It occurs in the oxidized zone of gold-tellurium veins in altered rhyolite. It occurs associated with other rare tellurate minerals: parakhinite, dugganite, tlapallite, mcalpineite, leisingite, jensenite; the sulfate – phosphate minerals: hinsdalite–svanbergite; and the oxide goethite.
Read More About Xocomecatlite / Source
Xonotlite

Xonotlite, or eakleite, is a mineral of general formula Ca6Si6O17(OH)2 named by the German mineralogist Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg in 1866. The name originates from its discovery locality, Tetela de Xonotla, Puebla, Mexico. Although it was discovered in 1866, it was first described in 1959. It is approved by the IMA, but it is a grandfathered species, meaning the name supposedly represents a valid species til this day.
Read More About Xonotlite / Source
Ye'elimite

Ye’elimite is the naturally occurring form of anhydrous calcium sulfoaluminate, Ca4(AlO2)6SO4. It gets its name from Har Ye’elim in Israel in the Hatrurim Basin west of the Dead Sea where it was first found in nature by Shulamit Gross, an Israeli mineralogist and geologist who studied the Hatrurim Formation.The mineral is cubic, with 16 formula units per unit cell, and a cell dimension of 1.8392 nm, and is readily detected and quantified in mixtures by powder x-ray diffraction.
Read More About Ye'elimite / Source
Yingjiangite

Yingjiangite is a mineral named after its type locality in the Yingjiang county in 1990. It is a member of the phosphuranylite group, although the species was doubted by two geologists. It is easily confused with phosphuranylite, though the two geologists (José Moacyr Vianna Coutinho and Daniel Atencio) claim that the mineral might be identical to it, even though yingjiangite was approved in 1989-1990 by the IMA.
Read More About Yingjiangite / Source
Yoshiokaite
Yoshiokaite, a mineral formed as shocked crystal fragments in devitrified glass, was discovered in lunar regolith breccia collected from a trench by the Apollo 14 crew in 1971. Although there have been other minerals (armalcolite and tranquillityite) that have been originally discovered on the moon, yoshiokaite is the first new mineral with origin related to lunar highlands. Yoshiokaite is considered to be a member of the feldspathoid group.
Yoshiokaite was named after mineralogist, Takashi Yoshioka, who synthesized a metastable phase solid solution between
CaAl
2
Si
2
O
8
{displaystyle {ce {CaAl2Si2O8}}}
and
CaAl
2
O
4
{displaystyle {ce {CaAl2O4}}}
with a nepheline-like structure and formula. Yoshioka’s research on the synthetic phase helped understand the probable origins of the mineral. Yoshiokaite was approved as a mineral in 1989 by the Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names of the International Mineralogical Association.
Read More About Yoshiokaite / Source
Yttrialite

Yttrialite or Yttrialite-(Y) is a rare yttrium thorium sorosilicate mineral with formula: (Y,Th)2Si2O7. It forms green to orange yellow masses with conchoidal fracture. It crystallizes in the monoclinic-prismatic crystal system. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 to 5.5 and a specific gravity of 4.58. It is highly radioactive due to the thorium content.
It is found associated with gadolinite. It was first described in 1889 for an occurrence in the Rode Ranch pegmatite on Baringer Hill, Llano County, Texas. It has also been reported from the Suishouyama pegmatite on Honshū, Japan, and from occurrences in Norway and Sweden.
Read More About Yttrialite / Source
Yttrogummite
Yttrogummite is an yttrium-bearing variety of gummite mineral. It is a rare earth mineral containing relatively large amounts of the yttrium earths. It is an alteration product of yttrian uraninite.It was first described by Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld, who discovered it in Arendal, Norway in 1870s.
Read More About Yttrogummite / Source
Oxyyttropyrochlore-(Y)

Oxyyttropyrochlore-(Y), also referred to as “obruchevite” or “yttropyrochlore-(Y)”, is a potential (not yet accepted) zero-valent-dominant mineral of the pyrochlore group. Its formula can be written as (Y,◻)2Nb2O2O.
The name “yttropyrochlore-(Y)” for this compound was used by Kalita (1957), and Ercit et al. (2003), but it has become obsolete and the mineral status is not yet clear. The yttropyrochlore-(Y) as mentioned by Tindle & Breaks (1998) is in fact “oxyyttropyrochlore-(Y)”.
Read More About Oxyyttropyrochlore-(Y) / Source
Yugawaralite

Yugawaralite is a clear or pinkish mineral of the Zeolite group. It was first described by Sakurai and Hayashi (1952) near a waterfall by some hot springs near Yugawara.
Read More About Yugawaralite / Source
Yuksporite

Yuksporite is a rare inosilicate mineral with double width, unbranched chains, and the complicated chemical formula K4(Ca,Na)14Sr2Mn(Ti,Nb)4(O,OH)4(Si6O17)2(Si2O7)3(H2O,OH)3.
It contains the relatively rare elements strontium, titanium and niobium, as well as the commoner metallic elements potassium, calcium, sodium and manganese. As with all silicates, it contains groups of linked silicon and oxygen atoms, as well as some associated water molecules.
Yuksporite is a member of the umbite group that has just two known members, umbite, K2ZrSi>3O9·H2O, and yuksporite. It was first reported in 1922, from nepheline syenite occurrences in the Kola Peninsula, Russia, and named by Alexander Fersman for the locality, near Mount Yukspor.
Read More About Yuksporite / Source
Zabuyelite

Zabuyelite is the natural mineral form of lithium carbonate, with a formula Li2CO3. It was discovered in 1987 at Lake Zabuye, Tibet, after which it is named. It forms colorless vitreous monoclinic crystals.
It occurs as inclusions within halite in lithium rich evaporites and as solid phase in fluid inclusions in the mineral spodumene. Associated minerals include halite, gaylussite and northupite in the Tibet locality.In addition to the Tibetan salt lake it has been reported from Bikita and Kamativi
in Zimbabwe, from Kings Mountain, Cleveland County, North Carolina, US and the Tanco pegmatite, Bernic Lake, Manitoba, Canada.
Read More About Zabuyelite / Source
Zaccagnaite
Zaccagnaite is a mineral, with a formula Zn4Al2CO3(OH)12·3H2O. It occurs as white hexagonal crystals associated with calcite in cavites in Carrara marble of the Italian Alps and is thought to have formed by hydrothermal alteration of sphalerite in an aluminium rich environment. It is named after Domenico Zaccagna (1851–1940), an Italian mineral collector.
Read More About Zaccagnaite / Source
Zaherite

Zaherite is a mineral, a complex sulfate of aluminium, formula Al12(OH)26(SO4)5·20H2O. It was discovered in the Salt range, Punjab, Pakistan by M. A. Zaher of the Bangladesh Geological Survey after whom it is named in 1977. This mineral would be extremely soluble in water and unlikely to persist anywhere except in the most arid of environments. It spontaneously, and reversibly dehydrates around room temperature. Its color is white to blue-green.
Read More About Zaherite / Source
Zaïrite

Zaïrite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Bi(Fe3+,Al)3[(OH)6|(PO4)2]. The name was given from where it was locally discovered in Eta-Etu, Kivu, Congo (Zaïre) in 1975.
Read More About Zaïrite / Source
Zakharovite

Zakharovite is a mineral, a silicate of sodium and manganese; formula Na4Mn5Si10O24(OH)6·6H2O. It has a yellow colour with a pearly lustre. Discovered in 1982 in the Kola peninsula of Northern Russia, it is named after Evgeny Evgenevich Zakharov (1902–1980), the director of the Moscow Institute of Geological Exploration.
Read More About Zakharovite / Source
Zanazziite

Zanazziite is a complex hydrated phosphate mineral from the roscherite group. It is a magnesium beryllium phosphate mineral. Zanazziite arises as barrel-shaped crystals and can reach up to 4 mm. It grows alongside quartz minerals. It is found in the crevices of Lavra da Ilha pegmatite, near Taquaral, in northeastern Minas Gerais, Brazil. Zanazziite is named after Pier F. Zanazzi. Zanazziite has an ideal chemical formula of Ca2Mg5Be4(PO4)6(OH)4·6H2O.
Read More About Zanazziite / Source
Zaratite

Zaratite is a bright emerald green nickel carbonate mineral with formula Ni3CO3(OH)4·4H2O. Zaratite crystallizes in the isometric crystal system as massive to mammillary encrustations and vein fillings. It has a specific gravity of 2.6 and a Mohs hardness of 3 to 3.5. It has no cleavage and is brittle to conchoidal fracture. The luster is vitreous to greasy.
It is a rare secondary mineral formed by hydration or alteration of the primary nickel and iron bearing minerals, chromite, pentlandite, pyrrhotite, and millerite, during the serpentinization of ultramafic rocks. Hellyerite, NiCO3·6H2O, is a related mineral.
It was found originally in Galicia, Spain in 1851, and named after Spanish diplomat and dramatist Antonio Gil y Zárate (1793–1861).
Read More About Zaratite / Source
Zavaritskite

Zavaritskite is a rare mineral of the halide class, bismuth oxyhalide with the chemical formula (BiO)F. It is named after the Soviet geologist and petrographer, academician of the USSR Academy of Sciences Alexander Nikolaevich Zavaritsky. It was discovered in 1962 by Soviet scientists. Zavaritskite is part of matlockite group of minerals.
Read More About Zavaritskite / Source
Zektzerite

The mineral zektzerite is a member of the tuhualite group and was first found in 1966 by Seattle mineralogist Benjamin Bartlett “Bart” Cannon. It was discovered in the Willow creek basin below Silver Star mountain in miarolitic cavities within the alkaline arfvedsonite granite phase of the Golden Horn batholith, Okanogan County, Washington. It is named for Jack Zektzer (born 1936), mathematician and mineral collector of Seattle, Washington.The mineral was misidentified as alkali beryl (morganite) at that time. Subsequently, in September, 1975, additional specimens of the mineral were found in a “float boulder” (a glacial erratic, or dropstone) on the north side of Kangaroo Ridge at an approximate elevation of 6,500 feet (2,000 m); it was recognized that the material was not beryl.
Read More About Zektzerite / Source
Zellerite

Zellerite is a uranium mineral, named after its discoverer, geologist Howard Davis Zeller. It has a type locality of the Lucky MC uranium mine in Wyoming, USA. It was approved by the IMA in 1965, but was first published a year after its approval.
Read More About Zellerite / Source
Zemannite

Zemannite is a very rare oxide mineral with the chemical formula Mg0.5ZnFe3+[TeO3]3·4.5H2O. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system and forms small prismatic brown crystals. Because of the rarity and small crystal size, zemannite has no applications and serves as a collector’s item.
Read More About Zemannite / Source
Zeolite
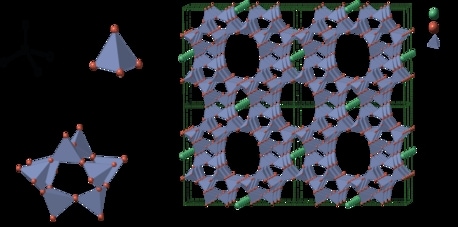
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula Mn+1/n(AlO2)−(SiO2)x・yH2O where Mn+1/n is either a metal ion or H+. These positive ions can be exchanged for others in a contacting electrolyte solution. H+ exchanged zeolites are particularly useful as solid acid catalysts.The term zeolite was originally coined in 1756 by Swedish mineralogist Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who observed that rapidly heating a material, believed to have been stilbite, produced large amounts of steam from water that had been adsorbed by the material. Based on this, he called the material zeolite, from the Greek ζέω (zéō), meaning “to boil” and λίθος (líthos), meaning “stone”.Zeolites occur naturally but are also produced industrially on a large scale. As of December 2018, 253 unique zeolite frameworks have been identified, and over 40 naturally occurring zeolite frameworks are known. Every new zeolite structure that is obtained is examined by the International Zeolite Association Structure Commission (IZA-SC) and receives a three letter designation.
Read More About Zeolite / Source
Zeunerite

Zeunerite is a green copper uranium arsenate mineral with formula Cu(UO2)2(AsO4)2•(10-16)H2O. It is a member of the autunite group. The associated mineral metazeunerite is a dehydration product of zeunerite.
Zeunerite occurs as a secondary mineral in the oxidized weathering zone of hydrothermal uranium ore deposits which contain arsenic. Olivenite, mansfieldite, scorodite, azurite and malachite are found in association with zeunerite.It was first described in 1872 for an occurrence in the Schneeberg District, Erzgebirge, Saxony, Germany. It was named for Gustav Anton Zeuner (1828–1907).
Read More About Zeunerite / Source
Zhanghengite

Zhanghengite is a mineral consisting of 80% copper and zinc, 10% iron with the balance made up of chromium and aluminium. Its color is golden yellow. It was discovered in 1986 during the analysis of the Bo Xian meteorite and is named after Zhang Heng, an ancient Chinese astronomer.
Read More About Zhanghengite / Source
Zhangpeishanite
Zhangpeishanite is a mineral named after Zhang Peishan (Chinese: 张培善), a Chinese mineralogist at the Institute of Geology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in recognition of his contributions to studying the mineralogy Bayan Obo deposit, where the mineral is mined. The Bayan Obo deposit is also known for being a world class deposit. The mineral got approved by the IMA in 2006 but was published two years after its approval. The mineral consists of barium chloride fluoride.
Read More About Zhangpeishanite / Source
Zharchikhite
Zharchikhite is a halide mineral, a hydroxyl fluoride of aluminium; formula AlF(OH)2. It forms colourless, transparent crystals. Discovered in 1968, it is named after its original locality, the Zharchinskoya Deposit, which is in Buryatia, Russia.
Read More About Zharchikhite / Source
Ziesite
Ziesite is a copper vanadate mineral with formula: β-Cu2V2O7. It was discovered in 1980 as monoclinic crystals occurring as volcanic sublimates around fumaroles in the crater of the Izalco Volcano, El Salvador. It is named after Emanuel George Zies (1883–1981), an American geochemist who studied Izalco in the 1930s.
Closely related is blossite, also a copper vanadate with formula of α-Cu2V2O7. It forms orthorhombic crystals. Blossite was also first described for specimens from the Izalco volcano.
Ziesite and blossite are polymorphs, different crystal structure for the same chemical composition and are quite similar in physical properties.
Associated minerals include stoiberite, shcherbinaite, bannermanite, fingerite, mcbirneyite, blossite, chalcocyanite and chalcanthite.
Read More About Ziesite / Source
Zimbabweite

Zimbabweite is a mineral; formula (Na,K)2PbAs4(Nb,Ta,Ti)4O18. It is generally classed as an arsenite but is notable for also containing niobium and tantalum. A yellow brown mineral with orthorhombic crystal habit and a hardness of 5. It was discovered in 1986 in kaolinized pegmatite, i.e. weathered to clay, in Zimbabwe.
Read More About Zimbabweite / Source
Zincite

Zincite is the mineral form of zinc oxide (ZnO). Its crystal form is rare in nature; a notable exception to this is at the Franklin and Sterling Hill Mines in New Jersey, an area also famed for its many fluorescent minerals. It has a hexagonal crystal structure and a color that depends on the presence of impurities. The zincite found at the Franklin Furnace is red-colored, mostly due to iron and manganese dopants, and associated with willemite and franklinite.
Zincite crystals can be grown artificially, and synthetic zincite crystals are available as a by-product of zinc smelting. Synthetic crystals can be colorless or can range in color from dark red, orange, or yellow to light green.
Both natural and synthetic zincite crystals are significant for their early use as semiconductor crystal detectors in the early development of crystal radios before the advent of vacuum tubes. As an early radio detector it was used in conjunction with another mineral, galena, and this device was known as the cat’s-whisker detector.
Read More About Zincite / Source
Zinclipscombite

Zinclipscombite is a dark-green to brown zinc iron phosphate mineral with the formula Zn(Fe3+)2(PO4)2(OH)2. It occurs as fibrous spheres and exhibits tetragonal crystal structure.In the classification of non-silicate minerals zinclipscombite is in the lipscombite group, which also includes lipscombite.
Read More About Zinclipscombite / Source
Zincmelanterite
Zincmelanterite is a mineral, a sulfate of zinc, copper and iron with the chemical formula (Zn,Cu,Fe)SO4·7H2O. It is a soft monoclinic yellow green mineral with Mohs hardness of 2 and a specific gravity of 2.02.
It was discovered in 1920 in the Vulcan mining district of Gunnison County, Colorado, United States, and is named for its zinc content and its resemblance to melanterite.
Read More About Zincmelanterite / Source
Zincobotryogen
Zincobotryogen is a hydrous sulfate mineral with the chemical formula (Zn,Mg,Mn)Fe3+(SO4)2(OH)·7H2O. It forms bright orange red monoclinic prismatic crystals that exhibit a vitreous to greasy luster. Its specific gravity is 2.201 and it has a Mohs hardness of 2.5.
It is a rare secondary mineral which forms in arid climates by alteration of other zinc minerals. It was named for its zinc content and it relationship to botryogen. It has been reported from the Xitieshan Mine, Qinghai, Northwest Region, China; Rammelsberg mine, near Goslar, Harz Mountains, Germany; the Bisbee district of Arizona and various mines in Colorado.
Read More About Zincobotryogen / Source
Zincochromite

Zincochromite is a zinc chromium oxide mineral with the formula ZnCr2O4. It is the zinc analogue of chromite, hence the name. It was first described in 1987 as an occurrence in a uranium deposit near Lake Onega, Russia. It has also been reported from Dolo Hill, New South Wales, Australia, and from the Tarkwa Mine in the Ashanti gold belt of Ghana.
Read More About Zincochromite / Source
Zincolivenite

Zincolivenite is a copper zinc arsenate mineral with formula CuZn(AsO4)(OH) that is a member of the olivenite group. Its colors range from green to blue, and its name comes from its composition of zinc and olivenite.It was first described from St Constantine, Lavrion District Mines, Laurium, Attica, Greece. It was approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 2006.
Read More About Zincolivenite / Source
Zinkenite

Zinkenite is a steel-gray metallic sulfosalt mineral composed of lead antimony sulfide Pb9Sb22S42. Zinkenite occurs as acicular needle-like crystals.It was first described in 1826 for an occurrence in the Harz Mountains, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany and named after its discoverer, German mineralogist and mining geologist, Johann Karl Ludwig Zinken (1790–1862).
Read More About Zinkenite / Source
Zinnwaldite

Zinnwaldite, KLiFeAl(AlSi3)O10(OH,F)2, potassium lithium iron aluminium silicate hydroxide fluoride is a silicate mineral in the mica group. The IMA status is as a series between siderophyllite (KFe2Al(Al2Si2)O10(F,OH)2) and polylithionite (KLi2AlSi4O10(F,OH)2) and not considered a valid mineral species.
Read More About Zinnwaldite / Source
Zippeite

Zippeite is a hydrous potassium uranium sulfate mineral with formula: K4(UO2)6(SO4)3(OH)10·4(H2O). It forms yellow to reddish brown monoclinic-prismatic crystals with perfect cleavage. The typical form is as encrustations and pulverulent earthy masses. It forms as efflorescent encrustations in underground uranium mines. It has a Mohs hardness of 2 and a specific gravity of 3.66. It is strongly fluorescent yellow under ultraviolet light and is moderately radioactive.
Read More About Zippeite / Source
Zircon

Zircon is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is ZrSiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the range of substitution in zircon is (Zr1–y, REEy)(SiO4)1–x(OH)4x–y. Zircon precipitates from silicate melts and has relatively high concentrations of high field strength incompatible elements. For example, hafnium is almost always present in quantities ranging from 1 to 4%. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural color of zircon varies between colorless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue, and green.
The name derives from the Persian zargun, meaning “gold-hued”. This word is changed into “jargoon”, a term applied to light-colored zircons. The English word “zircon” is derived from Zirkon, which is the German adaptation of this word. Yellow, orange, and red zircon is also known as “hyacinth”, from the flower hyacinthus, whose name is of Ancient Greek origin.
Read More About Zircon / Source
Zirkelite
Zirkelite is an oxide mineral with the chemical formula (Ca,Th,Ce)Zr(Ti,Nb)2O7. It occurs as well-formed fine sized isometric crystals. It is a black, brown or yellow mineral with a hardness of 5.5 and a specific gravity of 4.7.
Read More About Zirkelite / Source
Znucalite
Znucalite or CaZn11(UO2)(CO3)3(OH)20·4(H2O) is a rare, radioactive, white to pale cream colored uranium-containing carbonate mineral, hydrated calcium zinc uranyl carbonate hydroxide. Znucalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system, often forming aggregates or crusts, and is found as a rare secondary species in carbonate-hosted (meaning it is mined from carbonate containing formations such as limestone) polymetallic veins, and nearby oxidizing uranium veins; on dump material and coating mine walls, apparently of post-mine origin. It fluoresces yellow-green under UV light.It was first described in 1989, after being discovered in Lill Mine, Černojamské deposit (Black pits deposit) in the Czech Republic. It was named in 1990 by Petr Ondruš, František Veselovský, and R. Rybka for its constituent elements.
Read More About Znucalite / Source
Zoisite

Zoisite, first known as saualpite, after its type locality, is a calcium aluminum hydroxy sorosilicate belonging to the epidote group of minerals. Its chemical formula is Ca2Al3(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH).
Zoisite occurs as prismatic, orthorhombic (2/m 2/m 2/m) crystals or in massive form, being found in metamorphic and pegmatitic rock. Zoisite may be blue to violet, green, brown, pink, yellow, gray, or colorless. Blue crystals are known under the name tanzanite. It has a vitreous luster and a conchoidal to uneven fracture. When euhedral, zoisite crystals are striated parallel to the principal axis (c-axis). Also parallel to the principal axis is one direction of perfect cleavage. The mineral is between 6 and 7 on the Mohs hardness scale, and its specific gravity ranges from 3.10 to 3.38, depending on the variety. It streaks white and is said to be brittle. Clinozoisite is a more common monoclinic polymorph of Ca2Al3(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH).
Transparent material is fashioned into gemstones while translucent-to-opaque material is usually carved.
The mineral was described by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1805. He named it after the Carniolan naturalist Sigmund Zois, who sent him its specimens from Saualpe in Carinthia. Zois realized that this was an unknown mineral when it was brought to him by a mineral dealer, presumed to be Simon Prešern, in 1797.Sources of zoisite include Tanzania (tanzanite), Kenya (anyolite), Norway (thulite), Switzerland, Austria, India, Pakistan, and the U.S. state of Washington.
Read More About Zoisite / Source
Zorite

Zorite is a silicate mineral with the chemical formula of Na2Ti(Si,Al)3O9·nH2O. It is named because of its pink color, after the Russian word “zoria” which refers to the rosy hue of the sky at dawn. It is primarily found in Mount Karnasurta, Lovozero Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia. The Lovozero Massif is an area with an igneous mountain range, home to various types of minerals such as eudialyte, loparite, and natrosilitite.
Crystallographically, zorite belongs in the orthorhombic group, which has 3 axes, a, b, and c that are of unequal lengths (a≠b≠c) that form 90° with each other. It also belongs in the point group 2/m2/m2/m. The state of aggregation for zorite is acicular. Zorite has perfect cleavage along the planes {010} and {001}, while having poor cleavage along the plane {110}. Zorite is anisotropic, which means that the velocity of light is not the same in all directions. It belongs in the biaxial group, because it is an orthorhombic mineral. Under plane polarized light, zorite displays different colors depending on the angle that the light hits the mineral. This quality is called pleochroism and zorite is rose along the x-axis, colorless along the y-axis, and bluish along the z-axis. The index of refraction of zorite is 1.59, which is the velocity of light through vacuum over the velocity of light through zorite. Zorite is studied to better understand silicate structures.
In 2003, zorite was looked into to analyze the symmetry and topology of a family of three minerals found in Russia, Nenadkevichite, Labuntsovite, and Zorite. Zorite was also studied to comprehend how silicate structures change when an element is replaced, for example when the sodium is replaced with potassium, caesium and phosphorus. Furthermore, because of its rarity, zorite is one of the collectors’ items coveted for its scarcity, as well as it being a valuable source to understanding silicate topology.
Read More About Zorite / Source
Zunyite

Zunyite is a sorosilicate mineral, Al13Si5O20(OH,F)18Cl, composed of aluminium, silicon, hydrogen, chlorine, oxygen, and fluorine.
Read More About Zunyite / Source
Zussmanite
Zussmanite is a hydrated iron-rich silicate mineral with the chemical formula K(Fe2+,Mg,Mn)13[AlSi17O42](OH)14. It occurs as pale green crystals with perfect cleavage.
Read More About Zussmanite / Source
Zykaite

Zykaite or zýkaite is a grey-white mineral consisting of arsenic, hydrogen, iron, sulfur and oxygen with formula: Fe3+4(AsO4)3(SO4)(OH)·15(H2O). This dull mineral is very soft with a Mohs hardness of only 2 and a specific gravity of 2.5. It is translucent and crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system.Its common associates include limonite, gypsum, scorodite, quartz and arsenopyrite. It is found in the Czech Republic, Poland and Germany.Zykaite was first described in 1978 for an occurrence in the Safary mine, Kutná Hora, Bohemia, Czech Republic and named in honour of Vaclav Zyka (born 1926), a Czech geochemist.
Read More About Zykaite / Source


