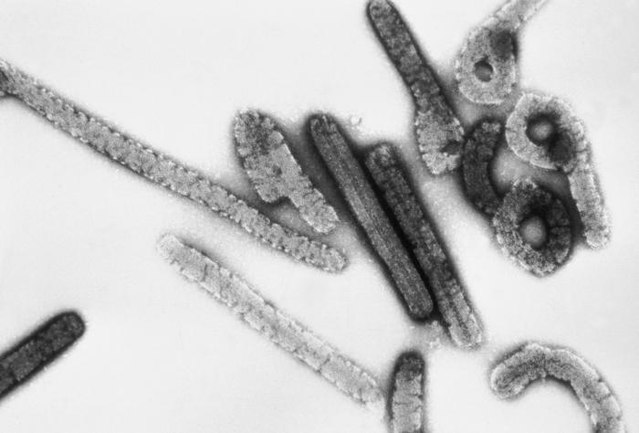
Marburg virus
Marburg virus is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the Filoviridae family of viruses and a member of the species Marburg marburgvirus, genus Marburgvirus. Marburg virus (MARV) causes Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. The virus is considered to be extremely dangerous. The World Health Organization (WHO) rates it as a Risk Group 4 Pathogen (requiring biosafety level 4-equivalent containment). In the United States, the NIH/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ranks it as a Category A Priority Pathogen and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists it as a Category A Bioterrorism Agent. It is also listed as a biological agent for export control by the Australia Group.The virus can be transmitted by exposure to one species of fruit bats or it can be transmitted between people via body fluids through unprotected sex and broken skin. The disease can cause bleeding (haemorrhage), fever, and other symptoms similar to Ebola. However, Marburg virus is not the same as Ebola, although similar. Actual treatment of the virus after infection is not possible, but early, professional treatment of symptoms like dehydration considerably increases survival chances.In 2009, expanded clinical trials of an Ebola and Marburg vaccine began in Kampala, Uganda.
