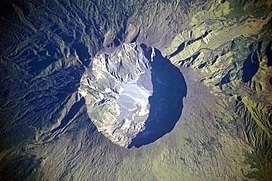
Mount Tambora
Mount Tambora, or Tomboro, is an active stratovolcano in West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Located on Sumbawa in the Lesser Sunda Islands, it was formed by the active subduction zones beneath it. Before 1815, its elevation reached more than 4,300 metres (14,100 feet) high, making it one of the tallest peaks in the Indonesian archipelago.
Tambora violently erupted in a series of eruptions beginning 5 April, 1815, culminating in the largest eruption in recorded human history and the largest of the Holocene (10,000 years ago to present). The magma chamber under Tambora had been drained by previous eruptions and underwent several centuries of dormancy as it refilled. Volcanic activity reached a peak that year, culminating in an explosive eruption. The explosion was heard on Sumatra island, more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 miles) away. Heavy volcanic ash rains were observed as far away as Borneo, Sulawesi, Java, and Maluku islands, and the maximum elevation of Tambora was reduced from about 4,300 metres (14,100 ft) to 2,850 metres (9,350 feet). Although estimates vary, the death toll was at least 71,000 people. The eruption contributed to global climate anomalies in the following years, while 1816 became known as the “year without a summer” because of the impact on North American and European weather. In the Northern Hemisphere, crops failed and livestock died, resulting in the worst famine of the century.

