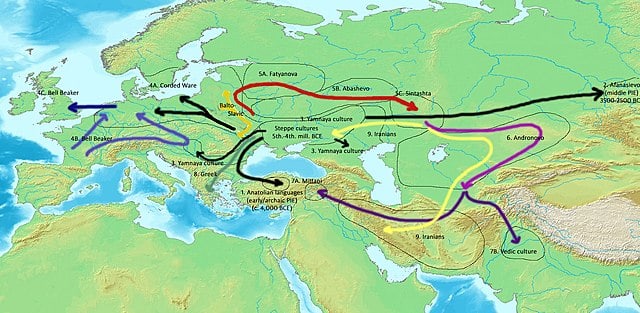
kurgan Culture
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory or Kurgan model) or Steppe theory is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and parts of Asia. It postulates that the people of a Kurgan culture in the Pontic steppe north of the Black Sea were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). The term is derived from the Russian kurgan (курга́н), meaning tumulus or burial mound. The Steppe theory was first formulated by Otto Schrader (1883) and V. Gordon Childe (1926), then systematized in the 1950s by Marija Gimbutas, who used the term to group various cultures, including the Yamnaya (or Pit Grave), culture and its predecessors. David Anthony instead uses the core Yamnaya culture and its relationship with other cultures as a point of reference.
Gimbutas defined the Kurgan culture as composed of four successive periods, with the earliest (Kurgan I) including the Samara and Seroglazovo cultures of the Dnieper–Volga region in the Copper Age (early 4th millennium BC). The people of these cultures were nomadic pastoralists, who, according to the model, by the early 3rd millennium BC had expanded throughout the Pontic–Caspian steppe and into Eastern Europe.
Read More About kurgan Culture
